Med Term Module 2 Study Set
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Portage learning medical terminology module 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Homeostasis
a state of equilibrium that’s maintained in the body’s internal environment to support and sustain life. All of the individual parts contribute to maintaining homeostasis.
Anatomical terminology
terms that are used to describe specific locations, positions, or directions of the human body. ana: apart, tome: to cut
organization of the body smallest to largest
atom, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
tissue
a grouping of similar cells that work together to perform a specialized function
what are the 4 tissues
epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous
what does epithelial form
it forms the outer surfaces of the body and lines body cavities, as well as the tubes that lead to the exterior or the body
functions of epithelial tissue
protection, sensation, secretion, absorption, excretion, and diffusion
function of connective tissue
builds the support for the body’s organs and muscle sheaths and also connects muscles to bones and bones to joints.
what is the most abundant tissue type
connective tissue
3 types of muscle tissue
cardiac, smooth, skeletal
skeletal muscle
used by the body for movement and posture. voluntary control
smooth muscle
found in organs such as esophagus, stomach, intestines, and bladder. involuntary control
cardiac muscle
found in the heart. involuntary control
nervous tissue
functions to communicate throughout the body, nerve cells are excitable and can conduct electricity. nervous tissue coordinated and controls the functions of the body.
Organs
the different tissue types combine to form these structures in the body that perform specific purposes.
organ examples
heart, liver, kidneys, brain, skin, uterus, lungs
systems
the body is organized into these that support the body as a whole. they are groups of different organs functioning together for a common purpose.
integumentary system
protective membrane, temp reg, and sensory receptor
skeletal system
framework and movement: shape, support, protection, and storage for minerals. movement possible through joints
muscular system
framework and movement: produces movement and heat, maintains posture
nervous system
transmits impulses, responds to change, responsible for communication, and exercises control over all parts of the body.
endocrine system
the glands of this system prod hormones, chem messengers, that control various parts of the body
cardiovascular system
transports O2 and CO2, delivers nutrients and hormones and removes waste
blood and the lymphatic system
transports O2, CO2, chemicals and cells that protect the body from foreign substances; stimulates immune response, protects the body, and transports proteins and fluids
respiratory system
furnishes O2 for individual tissues’ cells and removes their CO2
digestive system
absorption adn elimination
urinary system
produces, transports, and eliminates urine; kidneys help maintain levels/balances in the body
reproductie system
responsible for sexual characteristics
anatomical position
standing upright, head facing forward, arms extended by the side of the body with palms oriented to the front
sagittal plane
divides the body or structure vertically into right and left sections
midsagittal plane
divides the body or structure into equal right and left halves at the midline.
transverse/horizontal plane
divides the body or structure into superior and inferior sections
coronal/frontal plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior sections. it’s at a right angle to the midsagittal plane
directional terms
describe the location of a body part in relation to another body part
cavities
are hollow spaces that contain organs. they are enclosed with membranes that are specific to the this that they cover
2 posterior cavities
cranial and spinal cavities
2 anterior cavities
thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity
cranial cavity
contains the brain. the brain is protected by the meninges and the skull.
spinal cavity
contains the spinal cord. protected by the vertebrae and covered by the meninges
thoracic cavity
contains the heart, lungs, esophagus, trachea, aorta, and thymus gland. protected by the ribs and separated from the abdominopelvic cavity by the diaphragm
divisions of the thoracic cavity
mediastinum and pleural cavities
mediastinum
central region of the thoracic cavity, contains the heart, trachea, esophagus, aorta, and thymus gland
pleural cavities
located lateral to the mediastinum on either side. each contains a lung and is covered by the pleura
divisions of the abdominopelvic cavity
abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
abdominal cavity
contains the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, small intestine, and most of large intestine. covered by the peritoneum
pelvic cavity
contains the bladder, ureters, urethra, and rest of large intestine. in girls, vagina, uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. in boys, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, bulbourethral gland, and vas deferens. covered by the peritoneum
9 abdominal regions
right hypochondriac, right lumbar, right iliac, epigastric, umbilical, hypogastric, left hypochondriac, left lumbar, and left iliac regions
4 abdominal quardants
right upper, right lower, left upper, and left lower quadrants
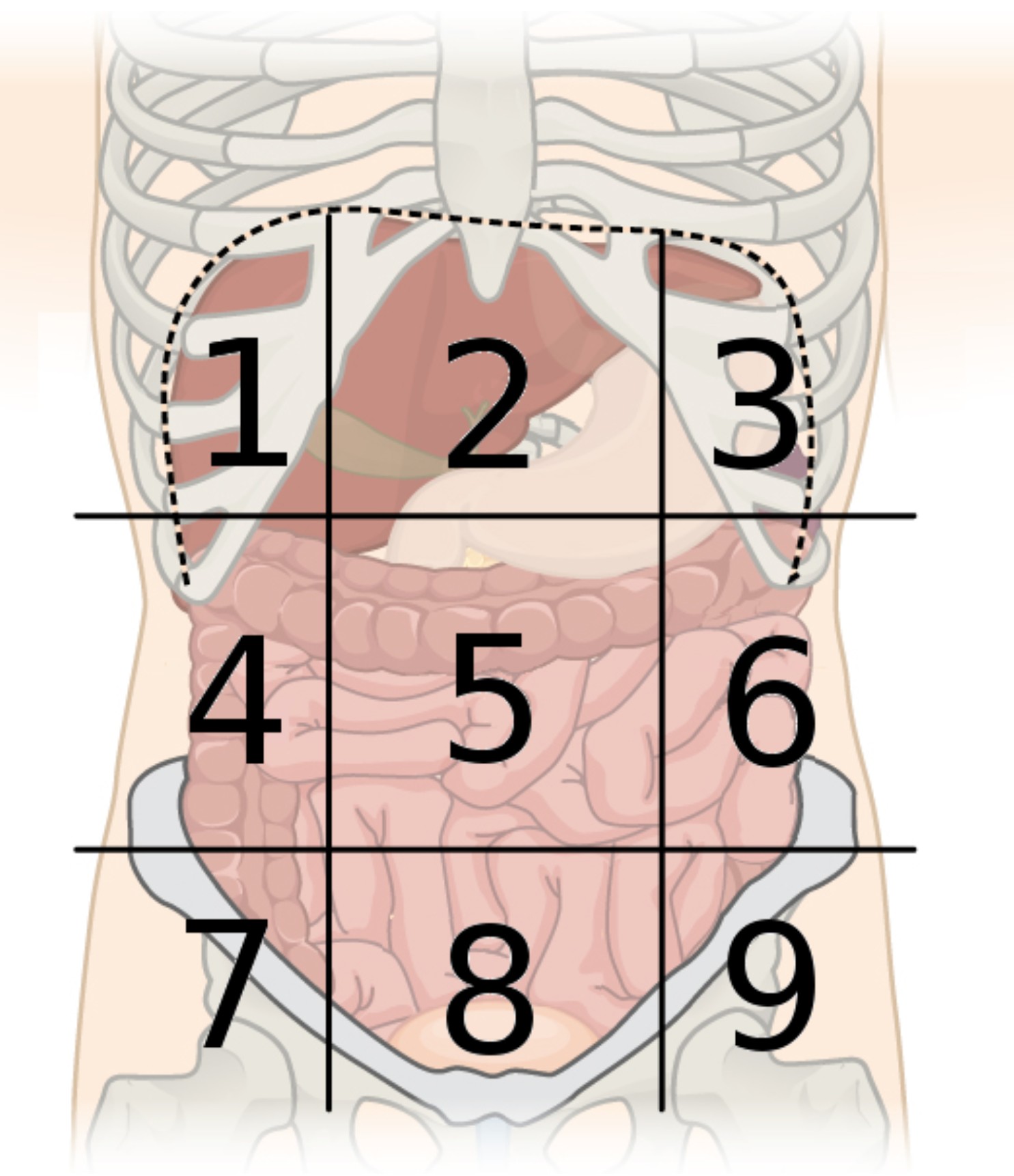
region 1
right hypochondriac region
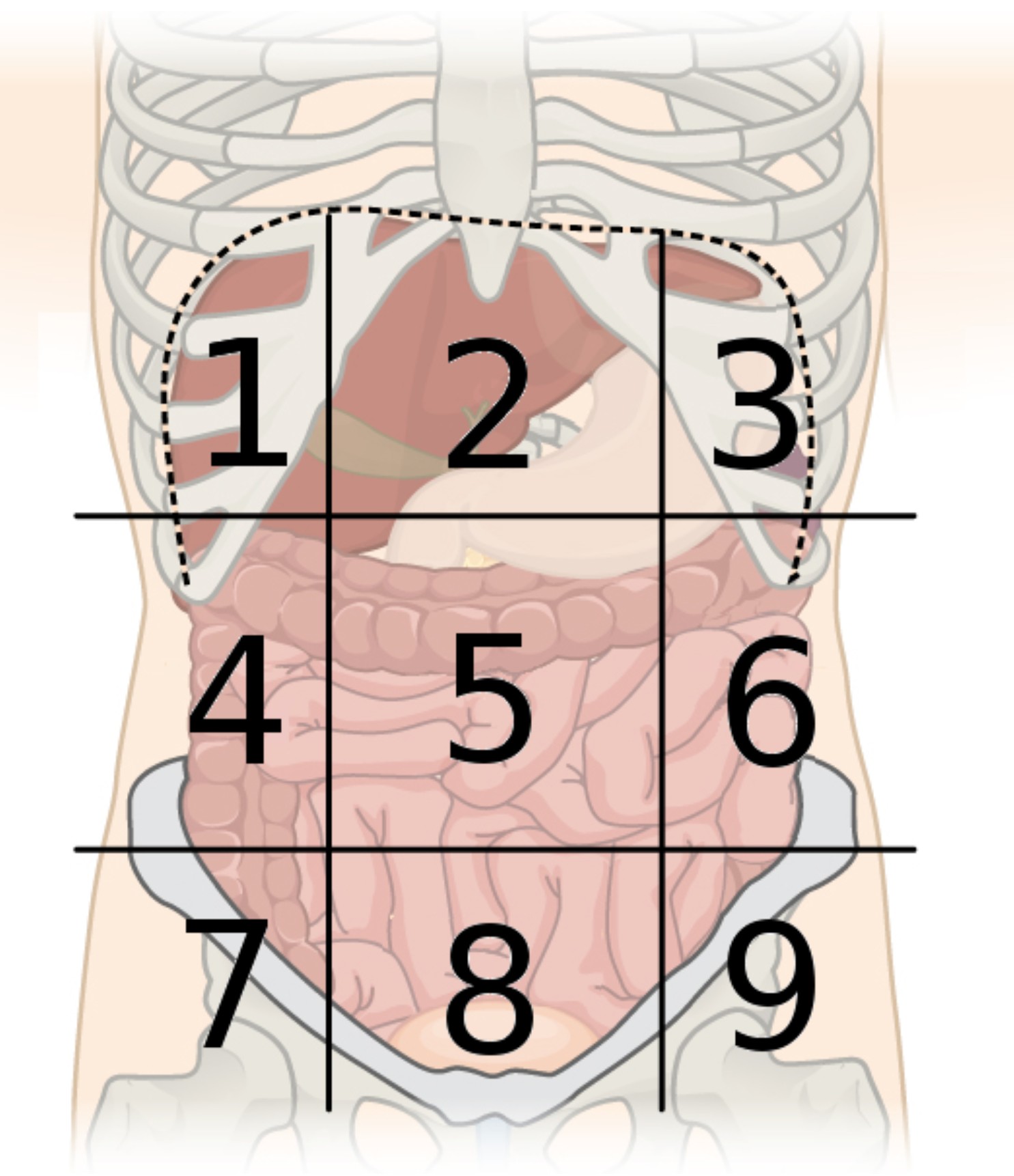
region 2
epigastric region
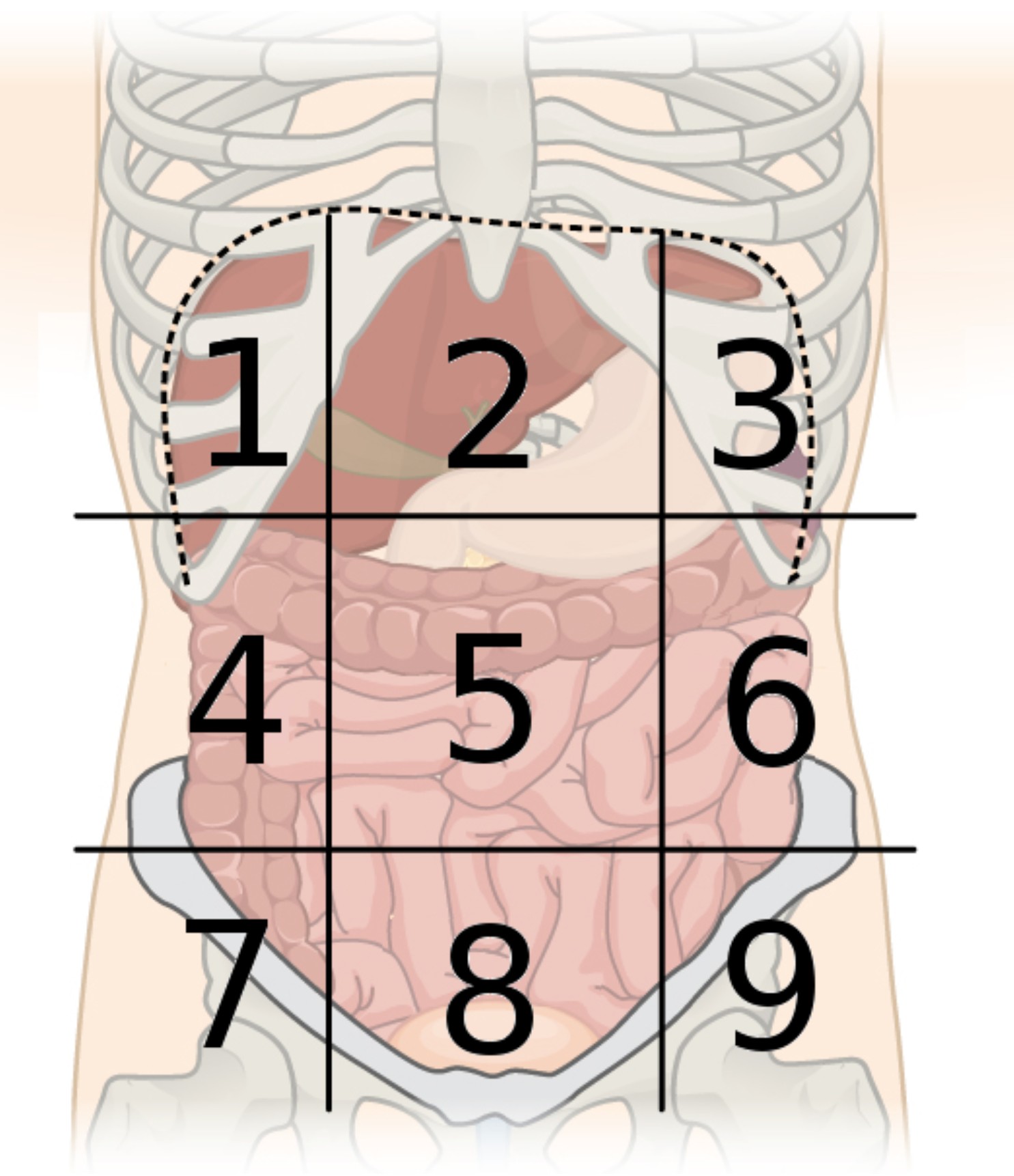
region 3
left hypochondriac region
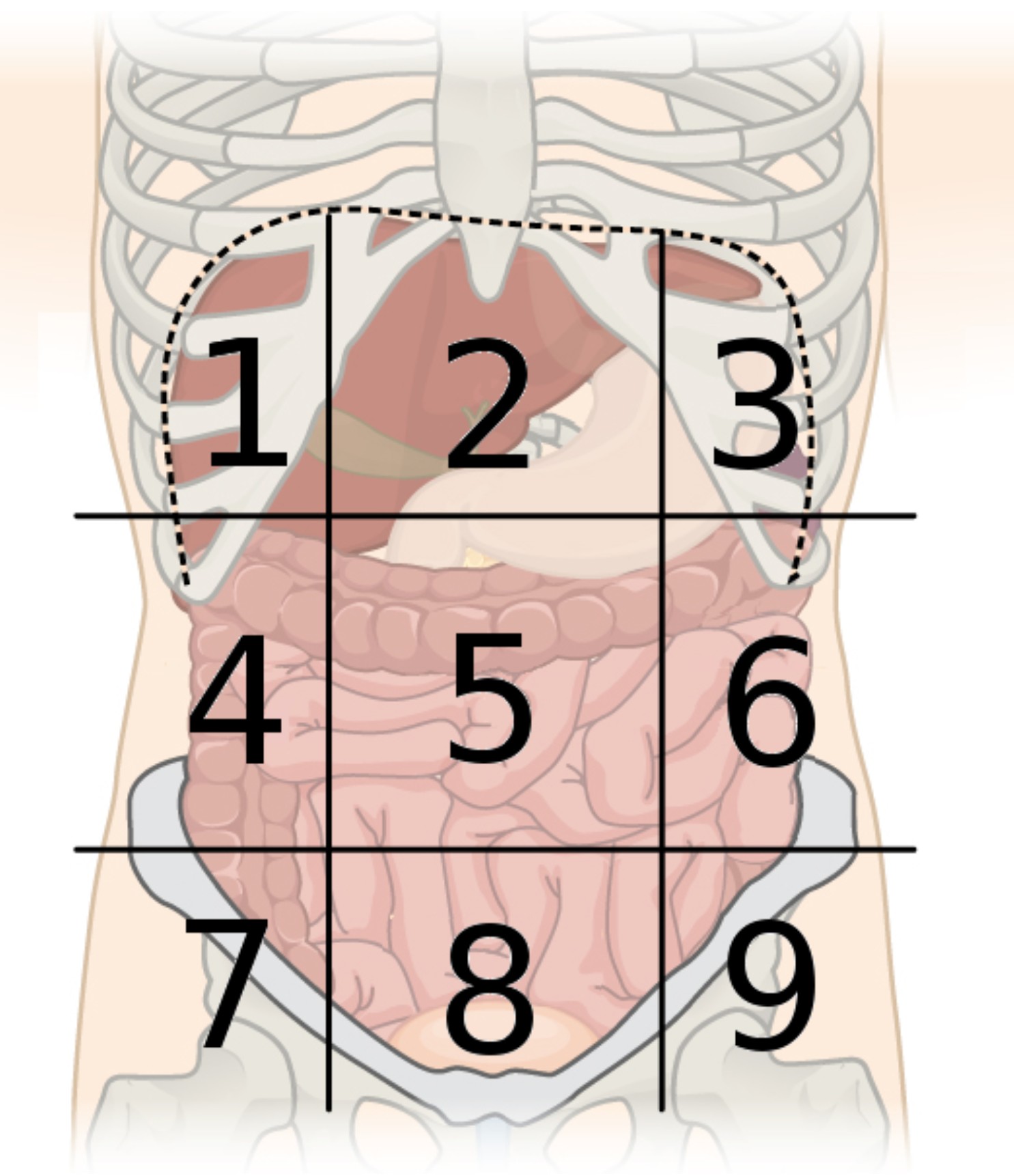
region 4
right lumbar region
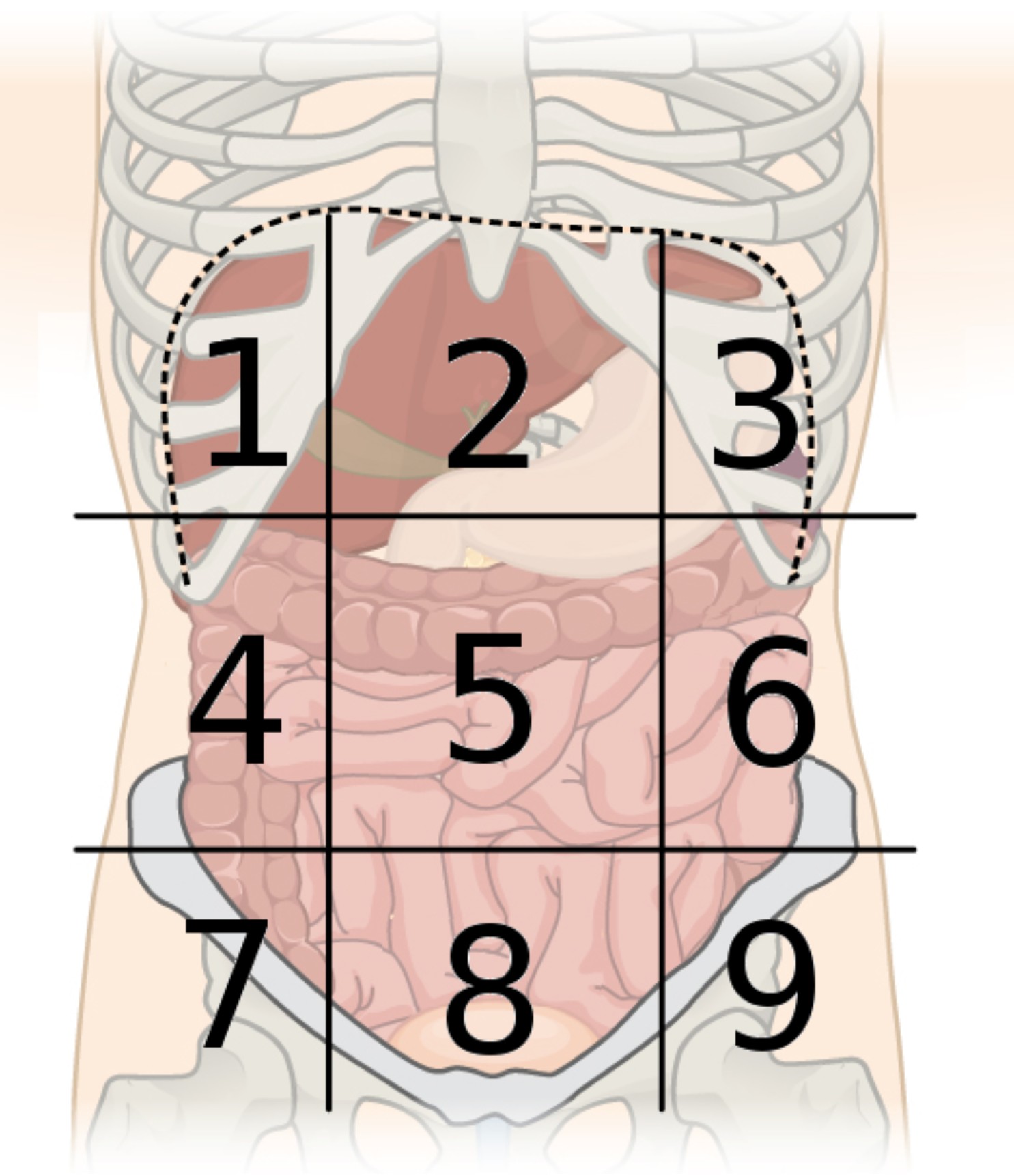
region 5
umbilical region
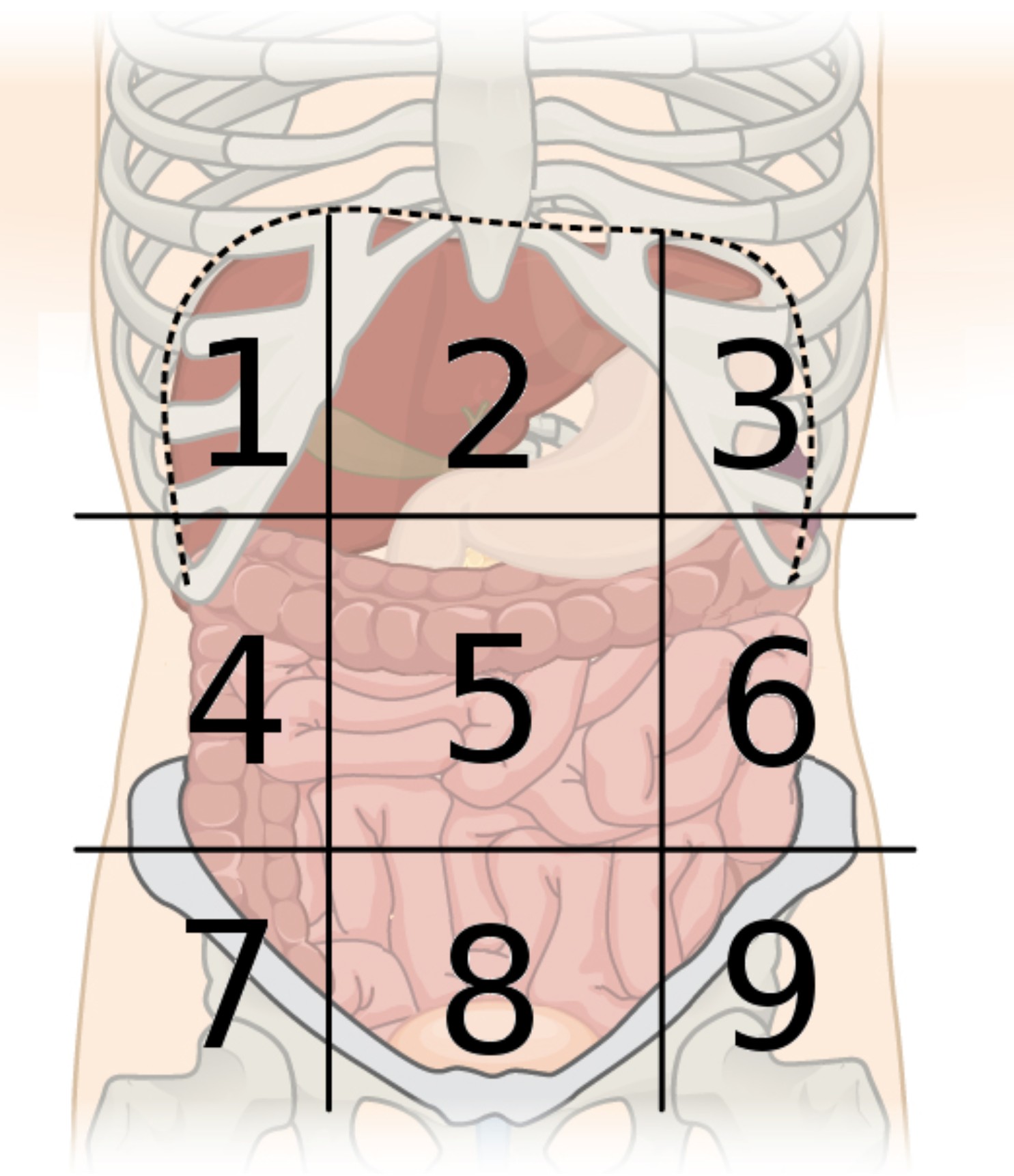
region 6
left lumbar region
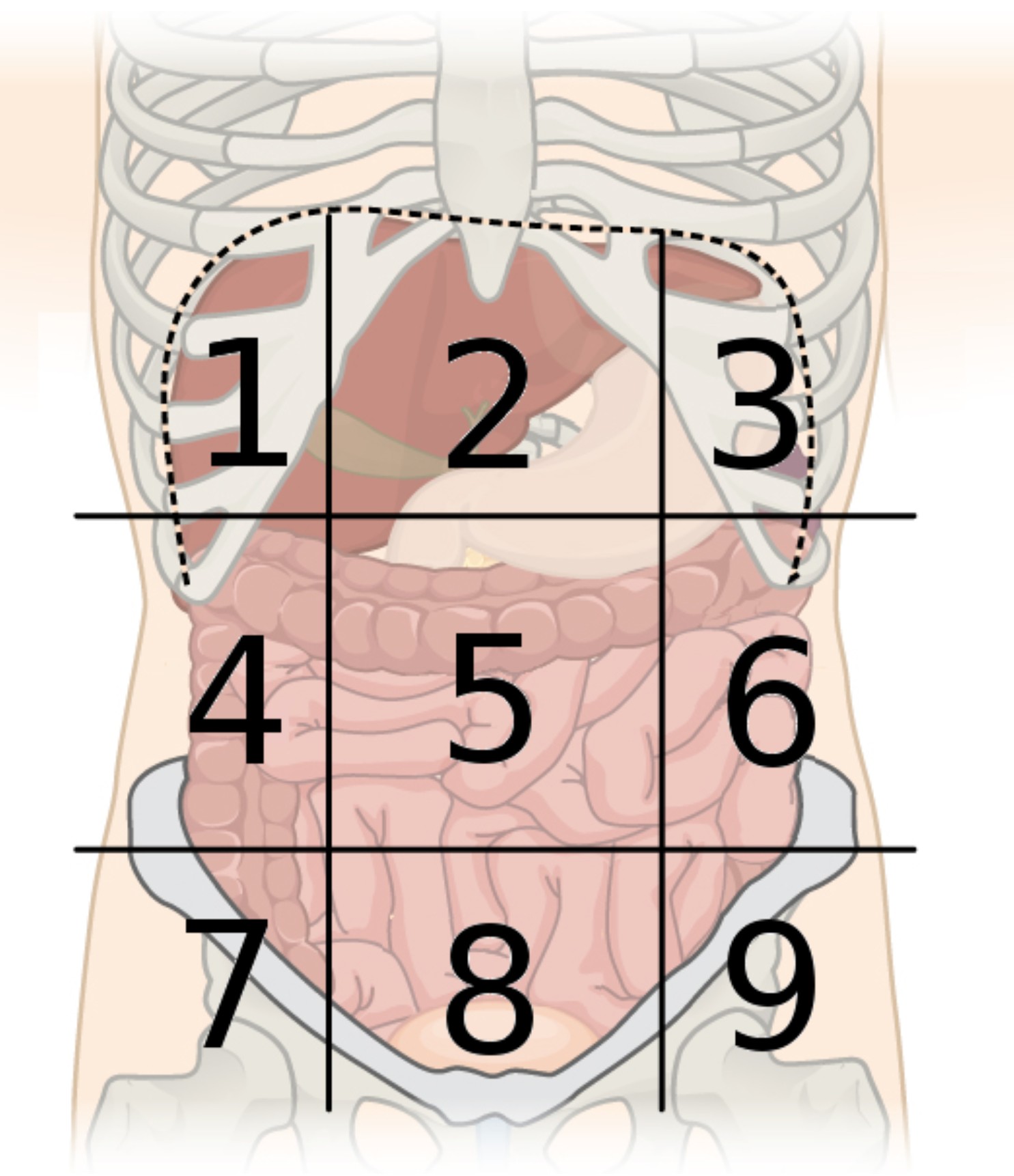
region 7
right iliac region
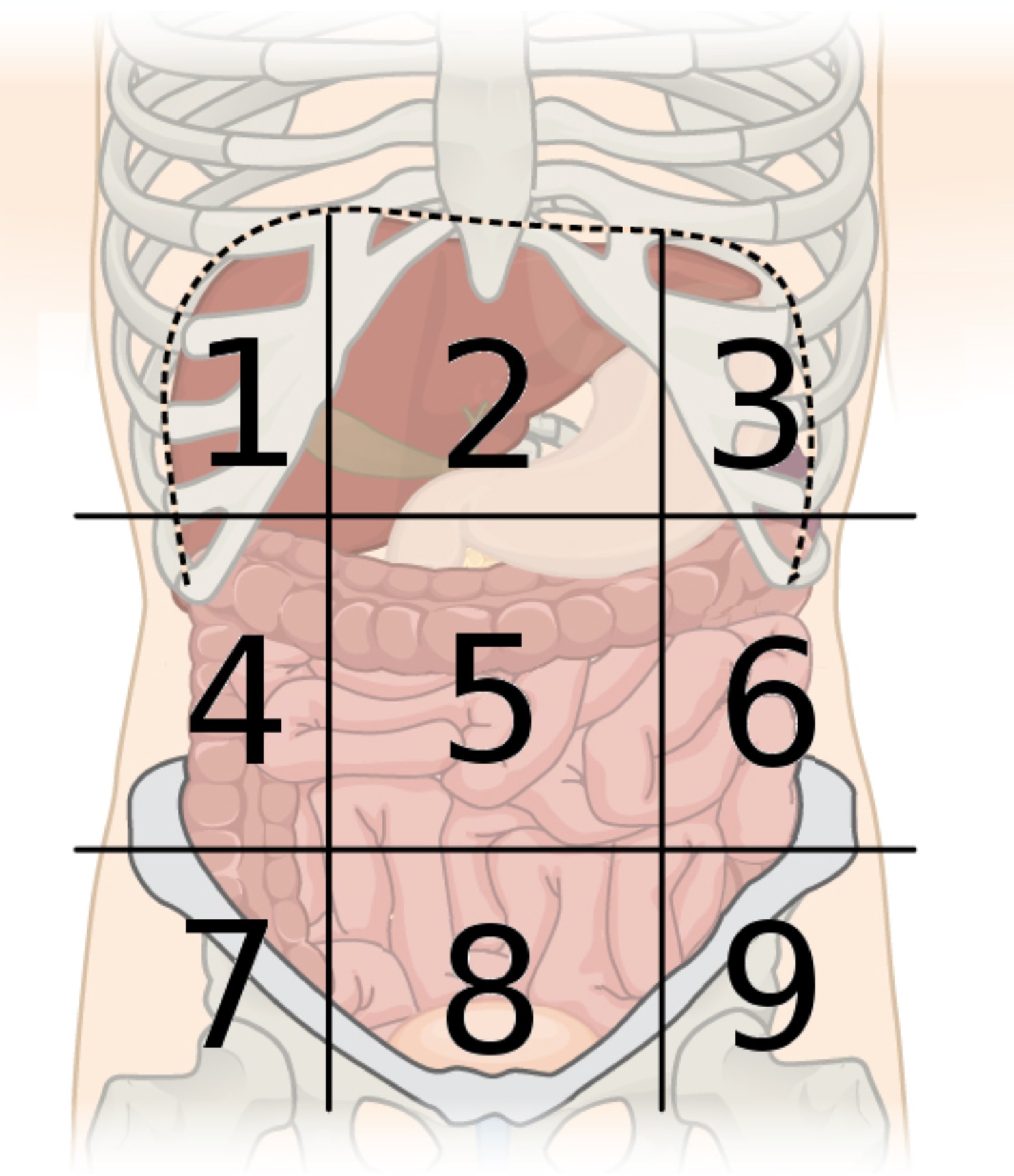
region 8
hypogastric region
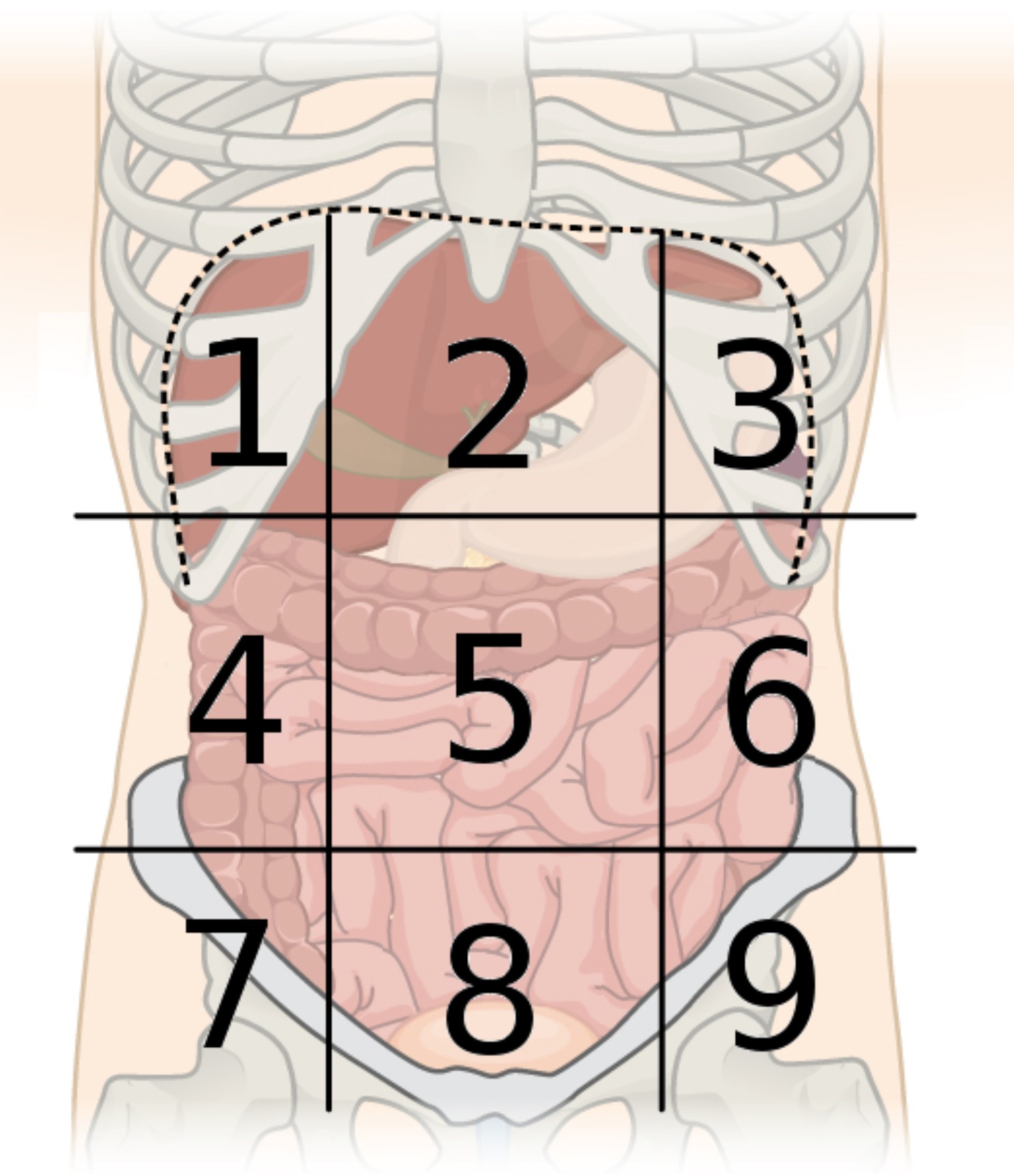
region 9
left iliac region
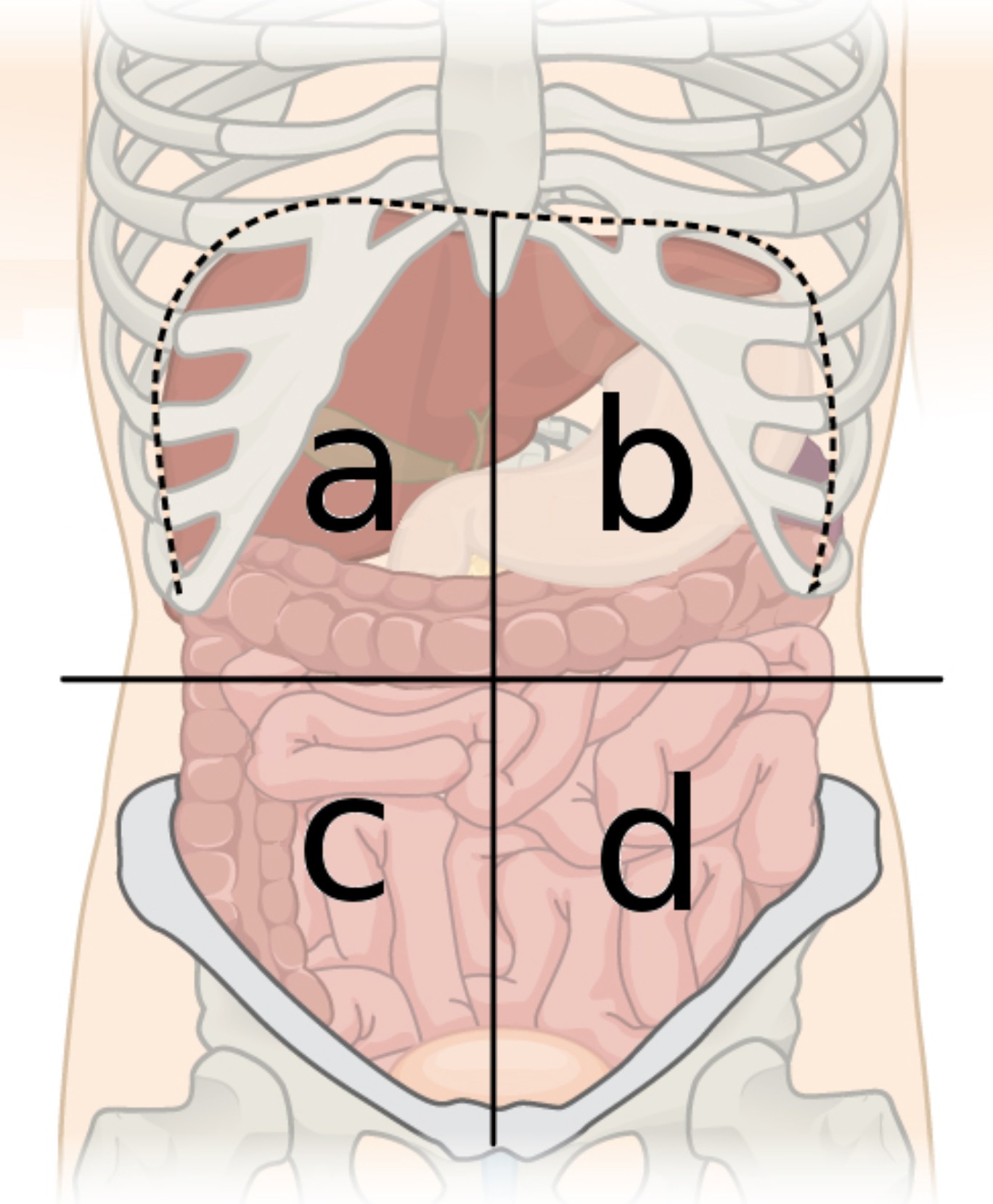
a
right upper quadrant (RUQ)
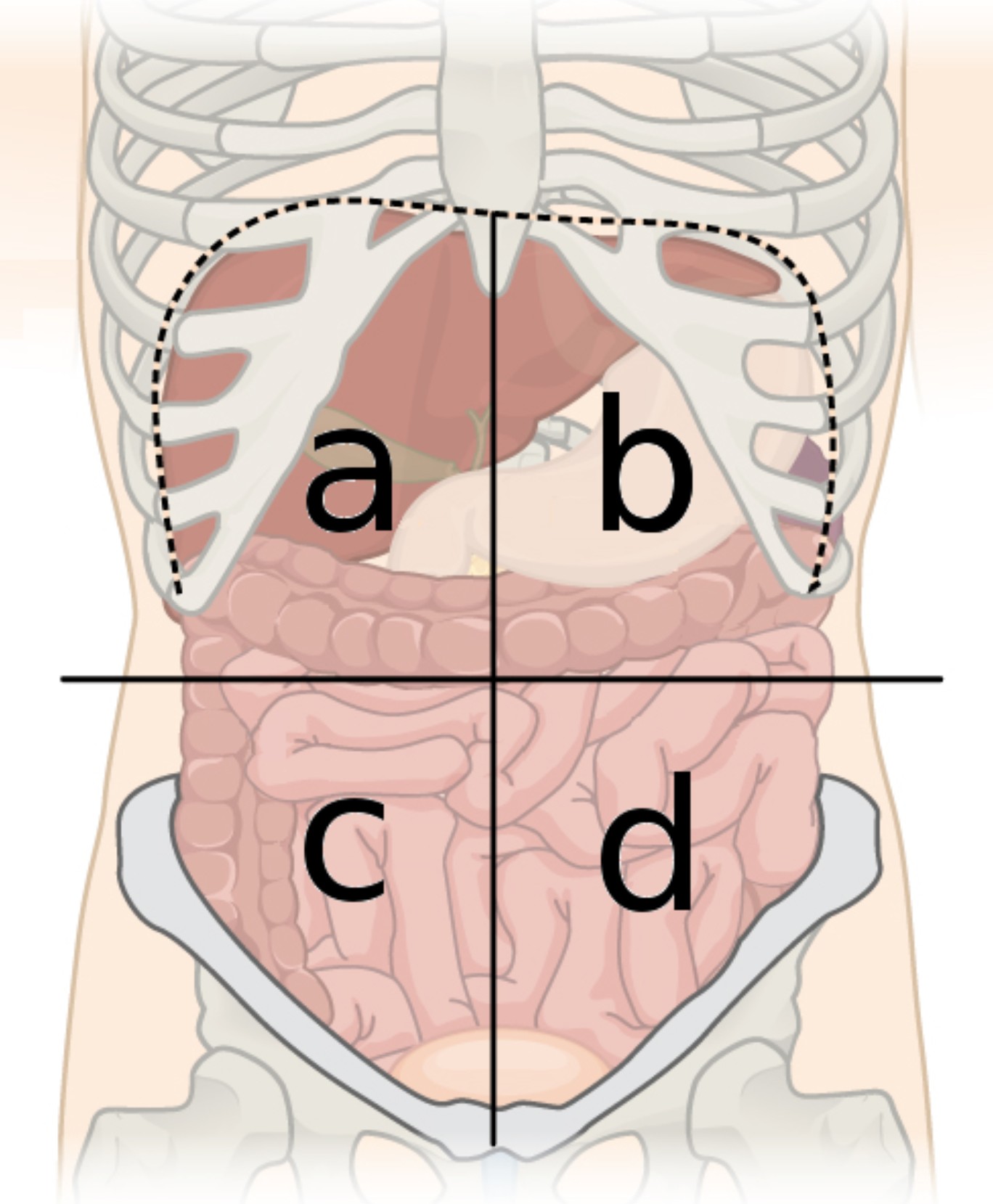
b
left upper quadrant (LUQ)
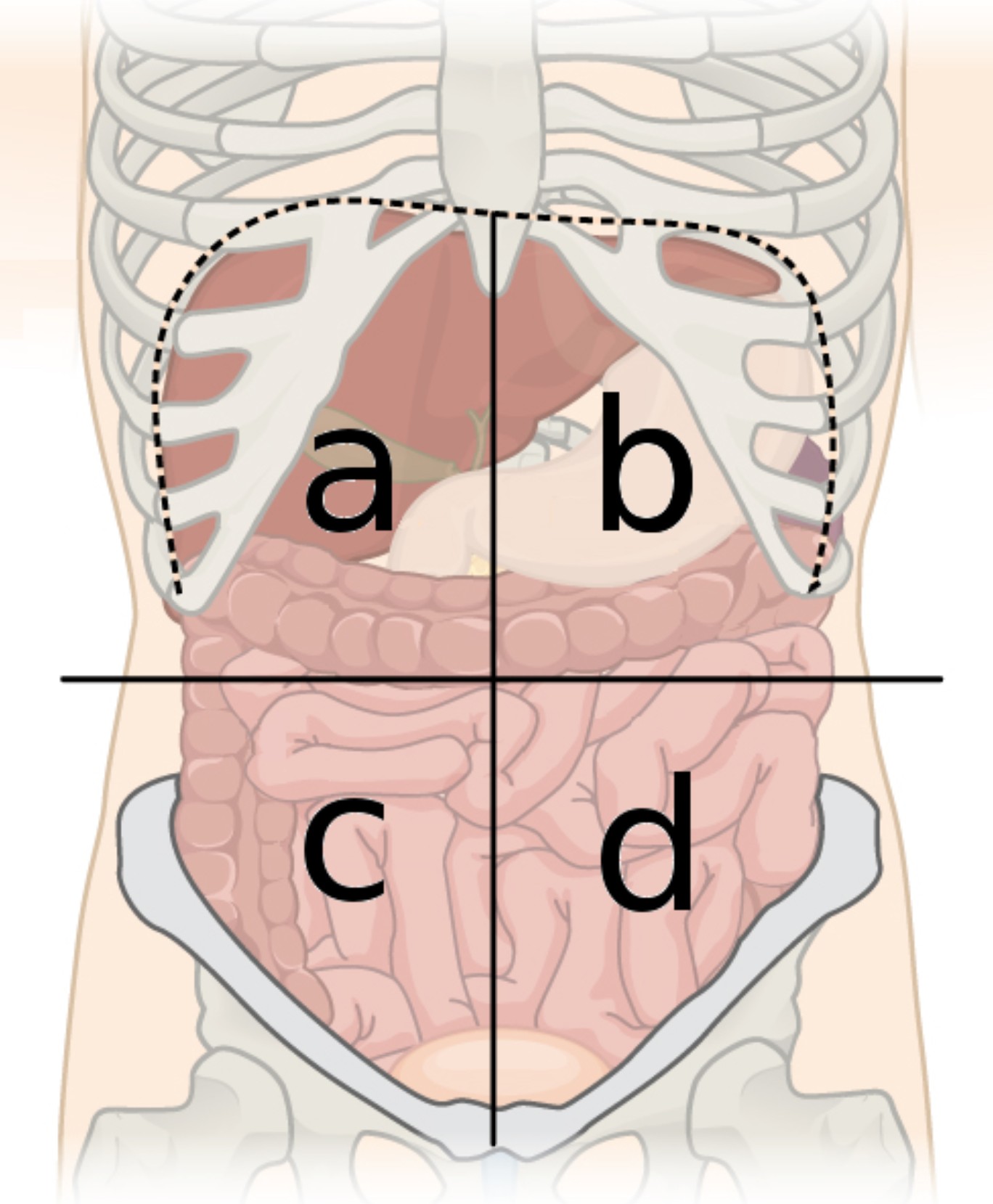
c
right lower quadrant (RLQ)
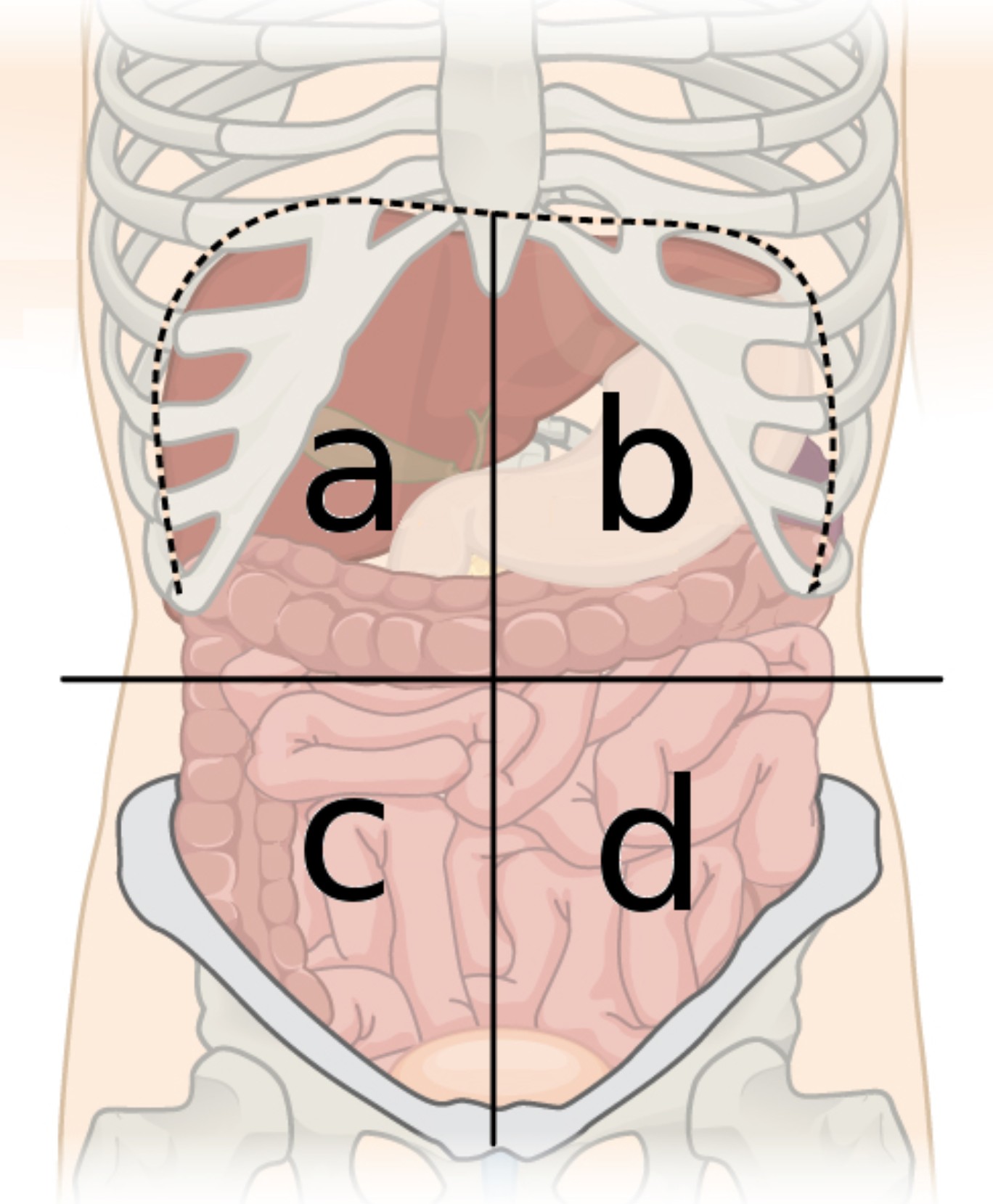
d
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
right upper quadrant contains
majority of the liver, the right kidney, portion of LI, small portion of pancreas, gallbladder, and section of SI
right lower quadrant contains
portions of LI and SI, right ureter, appendix, right ovary and fallopian tube
left upper quadrant contains
small portion of liver, spleen, left kidney, stomach, majority of pancreas, portions of SI and LI
left lower quadrant contains
portions of SI and LI, left ureter, and left ovary and fallopian tube
prone
body positioned horizontally face down, with back oriented superiorly
supine
body positioned horizontally face up, with back oriented inferiorly
lithotomy position
supine position in which buttocks are at the end of the exam table, the hips and knees are flexed, and the feet are supported by stirrups. often used in gynecological exams and surgeries
fowler position/ semi-recumbent position
supine position, however, the head of the bed is elevated 45*