AP- Biology - Enzymes
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
chemical reaction
A process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals.

reactants
compounds that enter into a chemical reaction
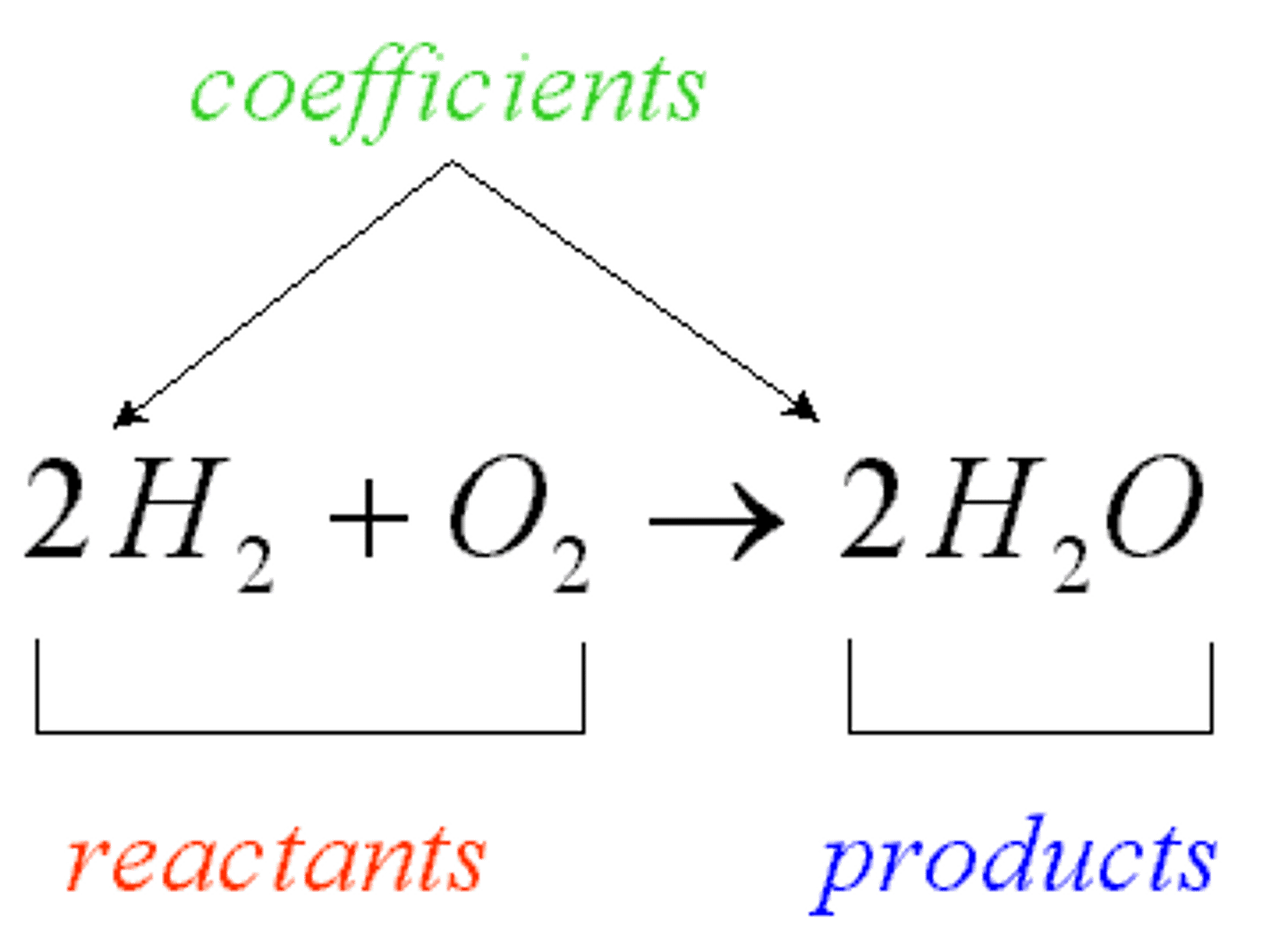
product
compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
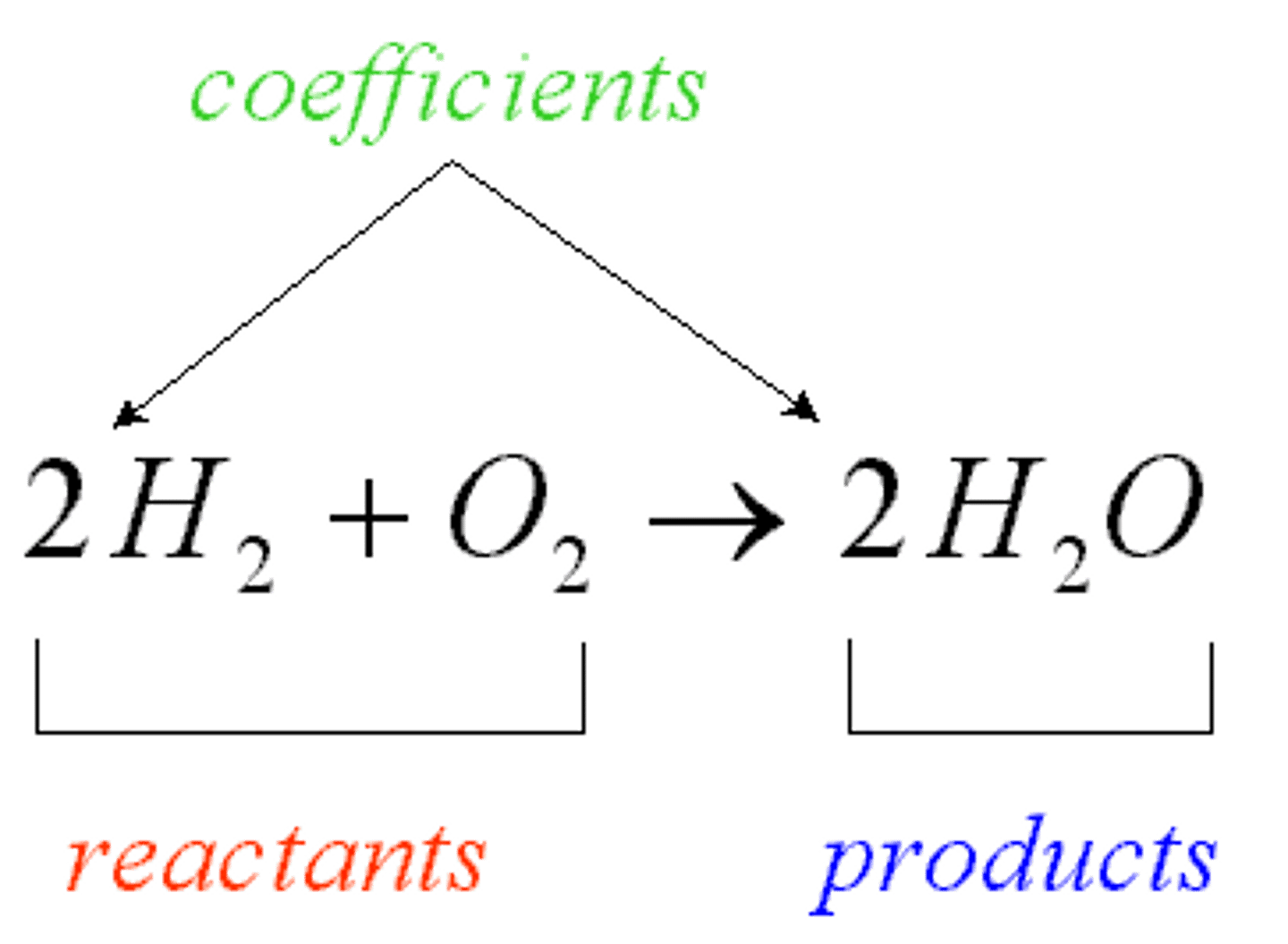
enzyme
biological catalysts usually globular that speed up the rate of chemical reactions
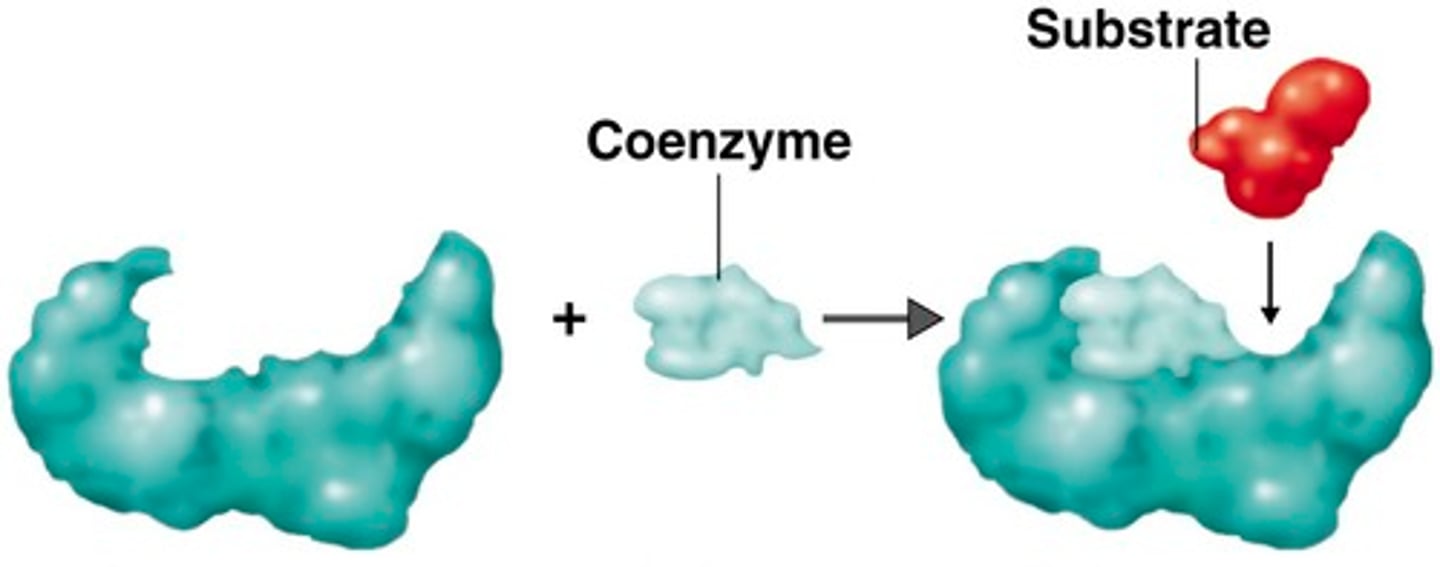
coenzyme
A non protein organic molecule serving to modify the active site of an enzyme before the reaction is allowed to occur. Most vitamins function important metabolic reactions in this role.
Competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
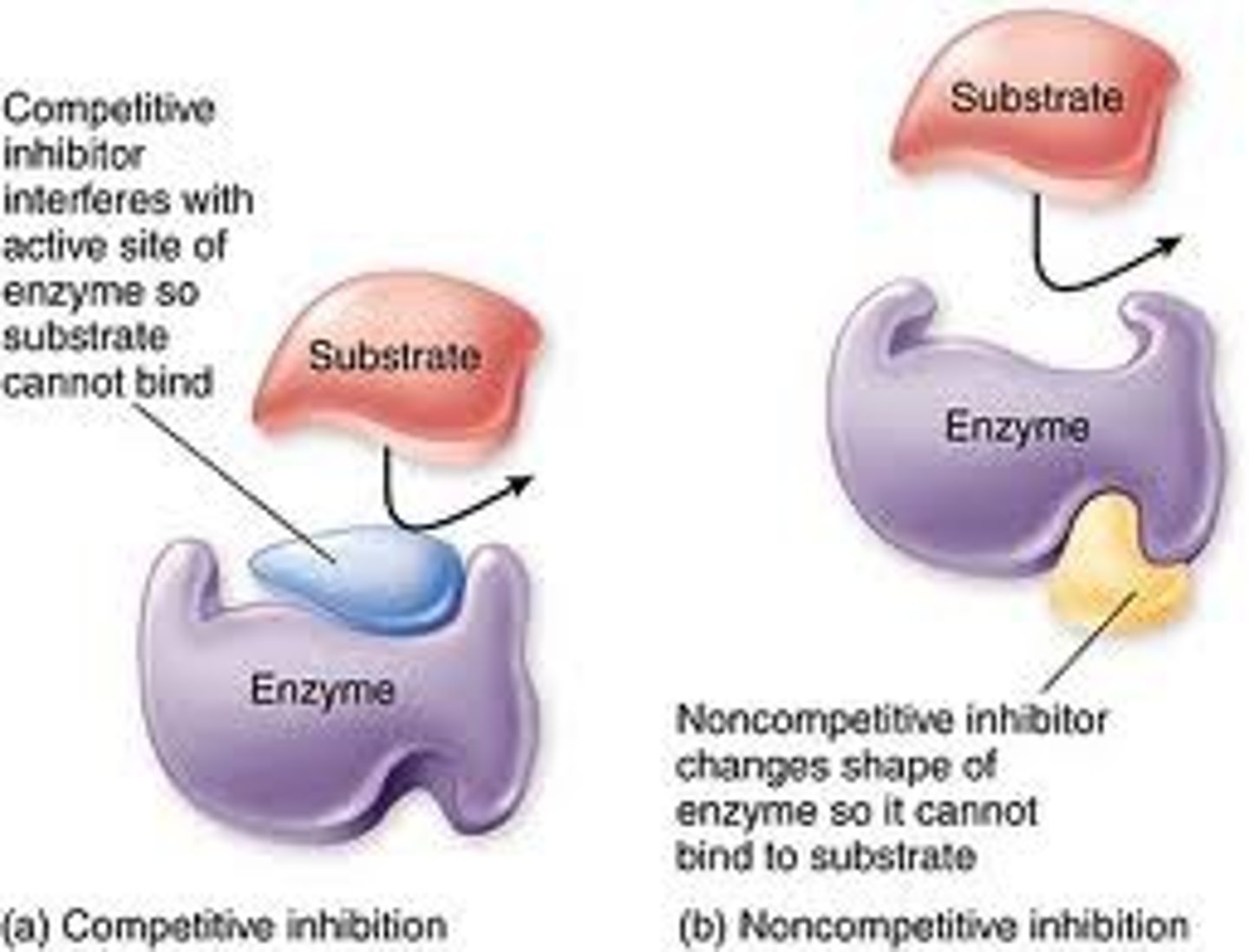
Noncompetitive inhibitor
a chemical that binds to an enzyme but not in the active site. This chemical will change the shape of the enzyme (reversible)

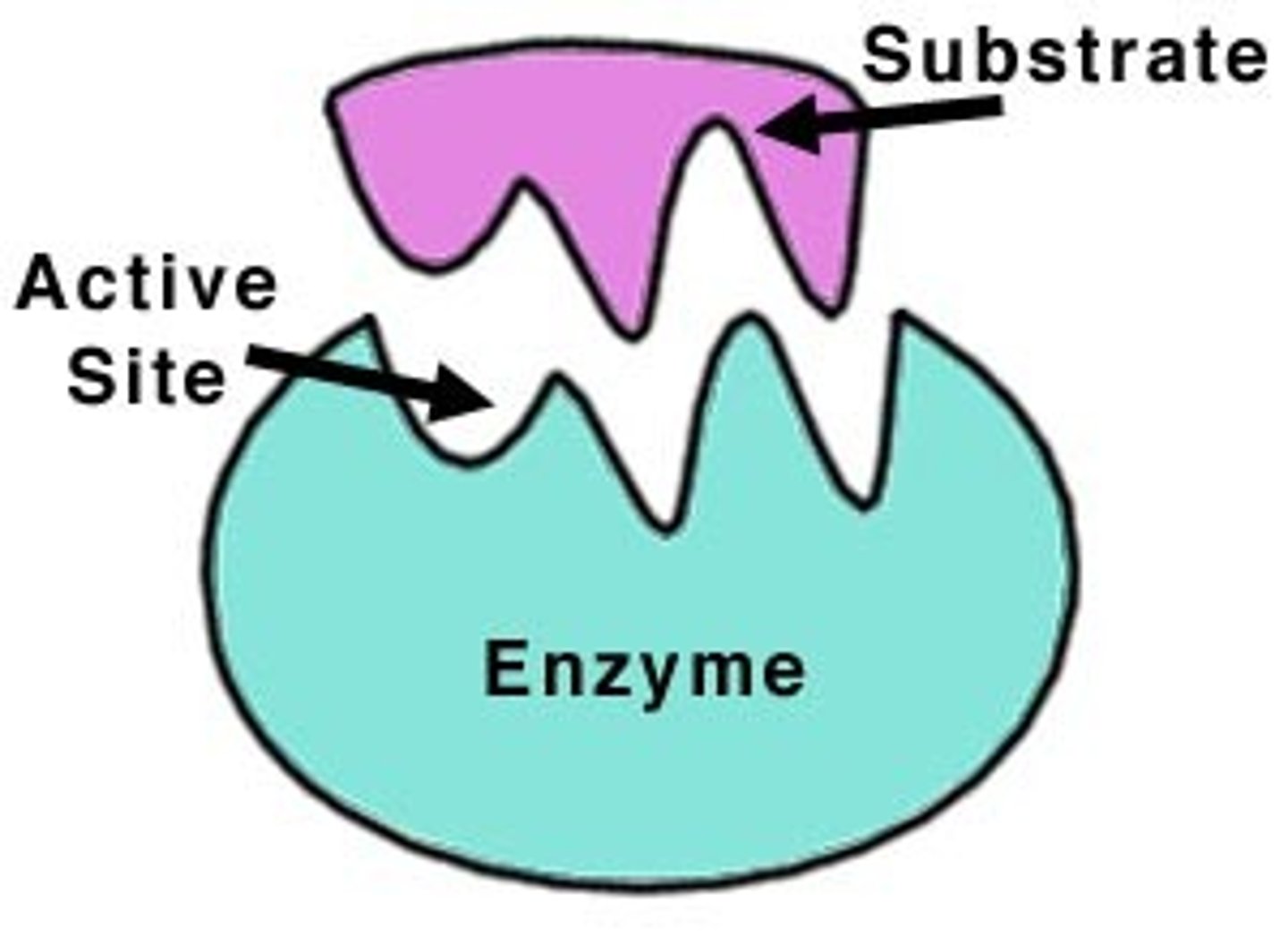
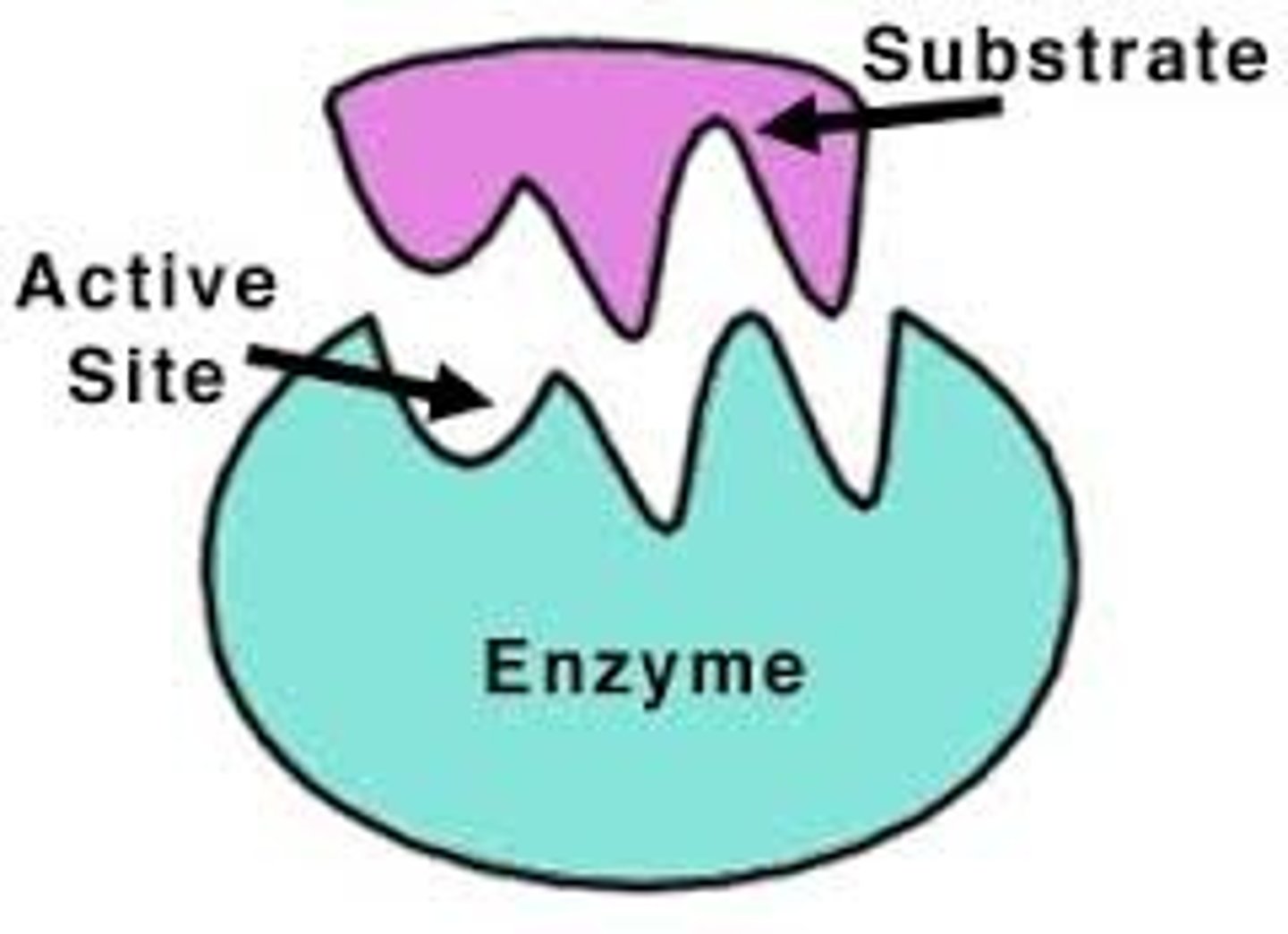
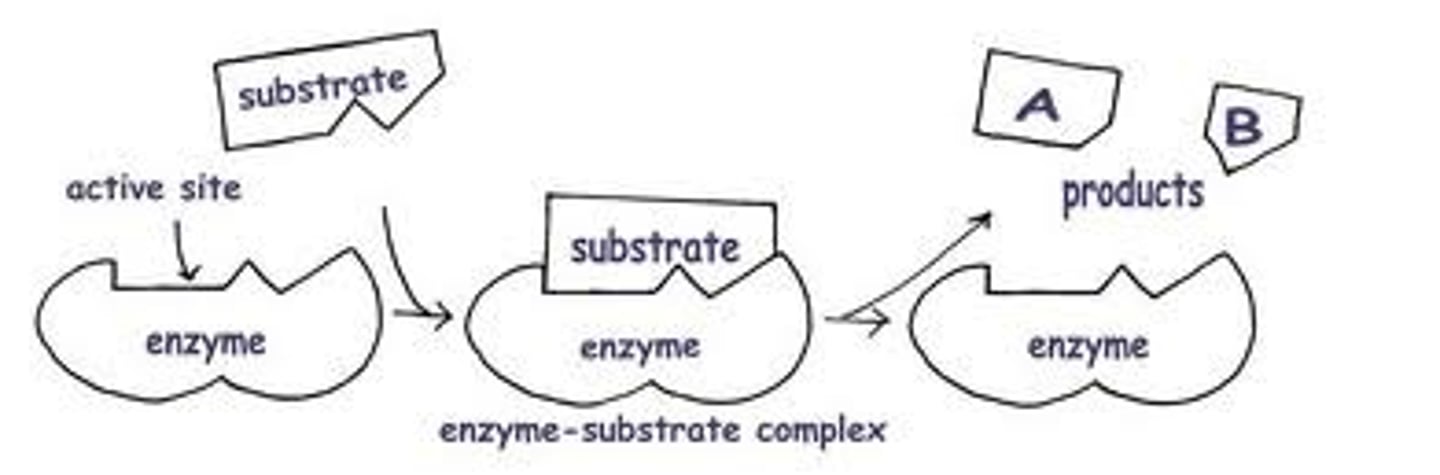
substrate
the substance an enzyme catalyzes, changes.
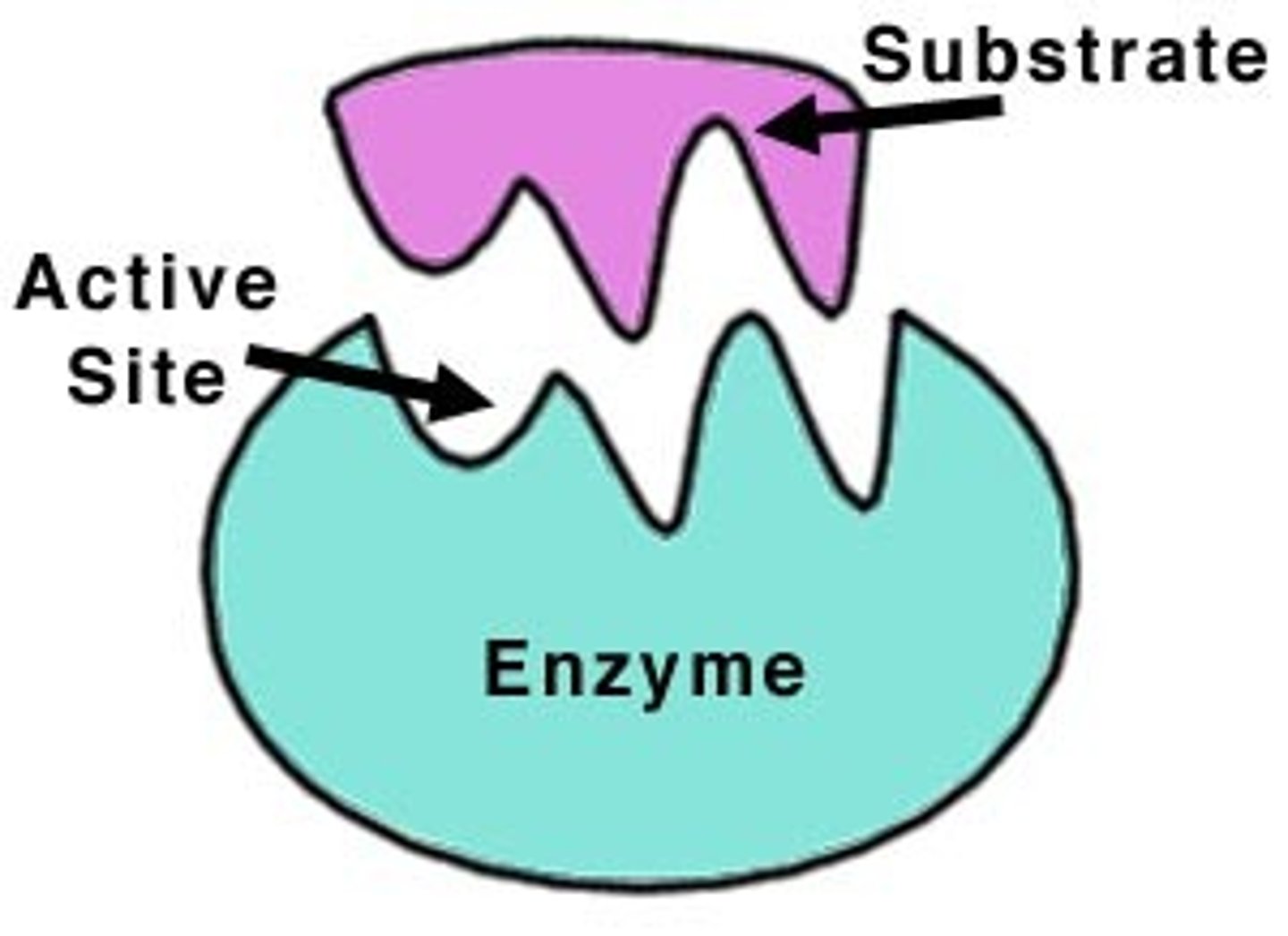
active site
the location on the enzyme where the substrate binds and goes through a chemical reaction.
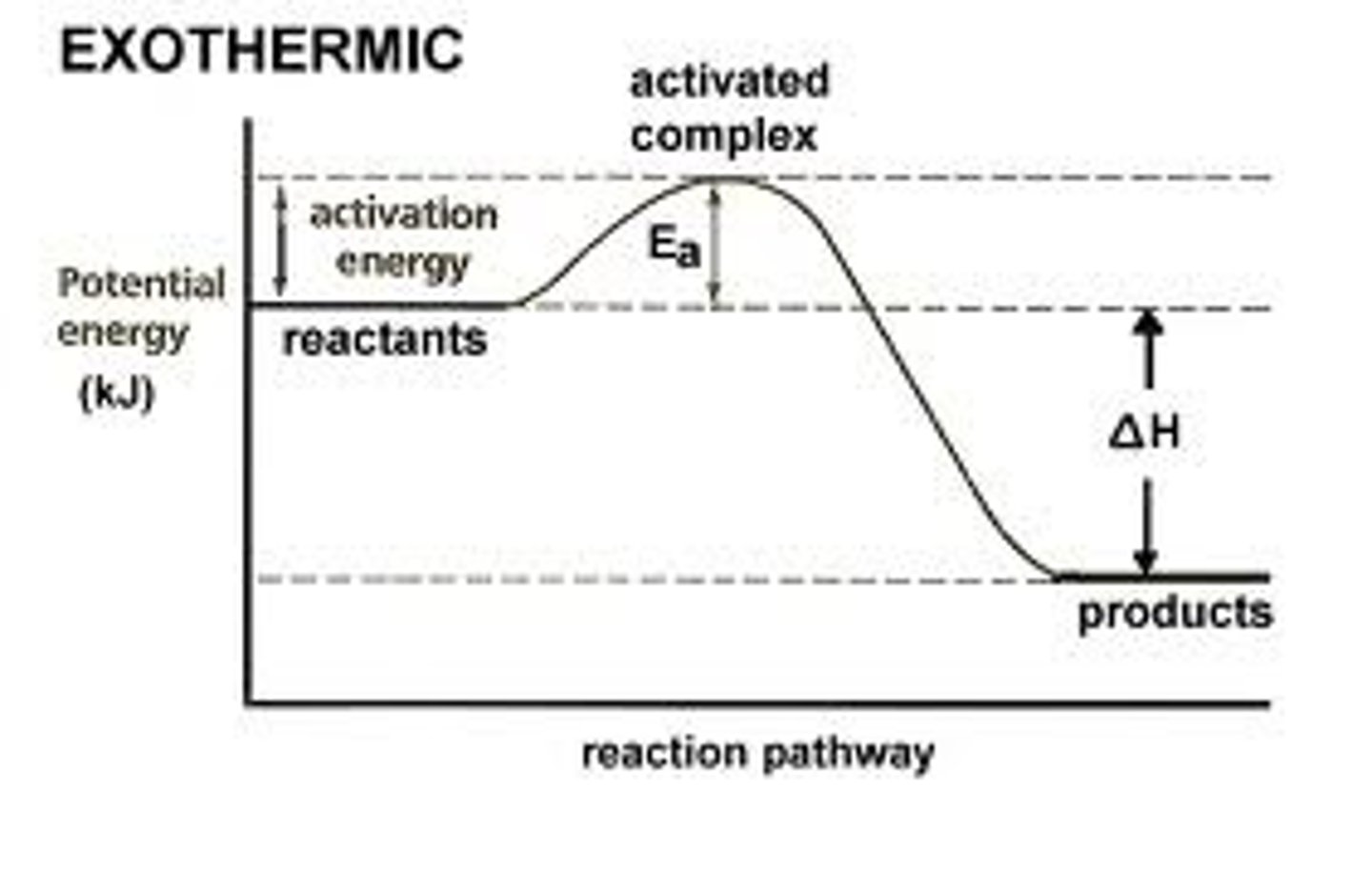
exothermic reaction
a chemical reaction where energy is given off, so that the products have less energy than the reactants.
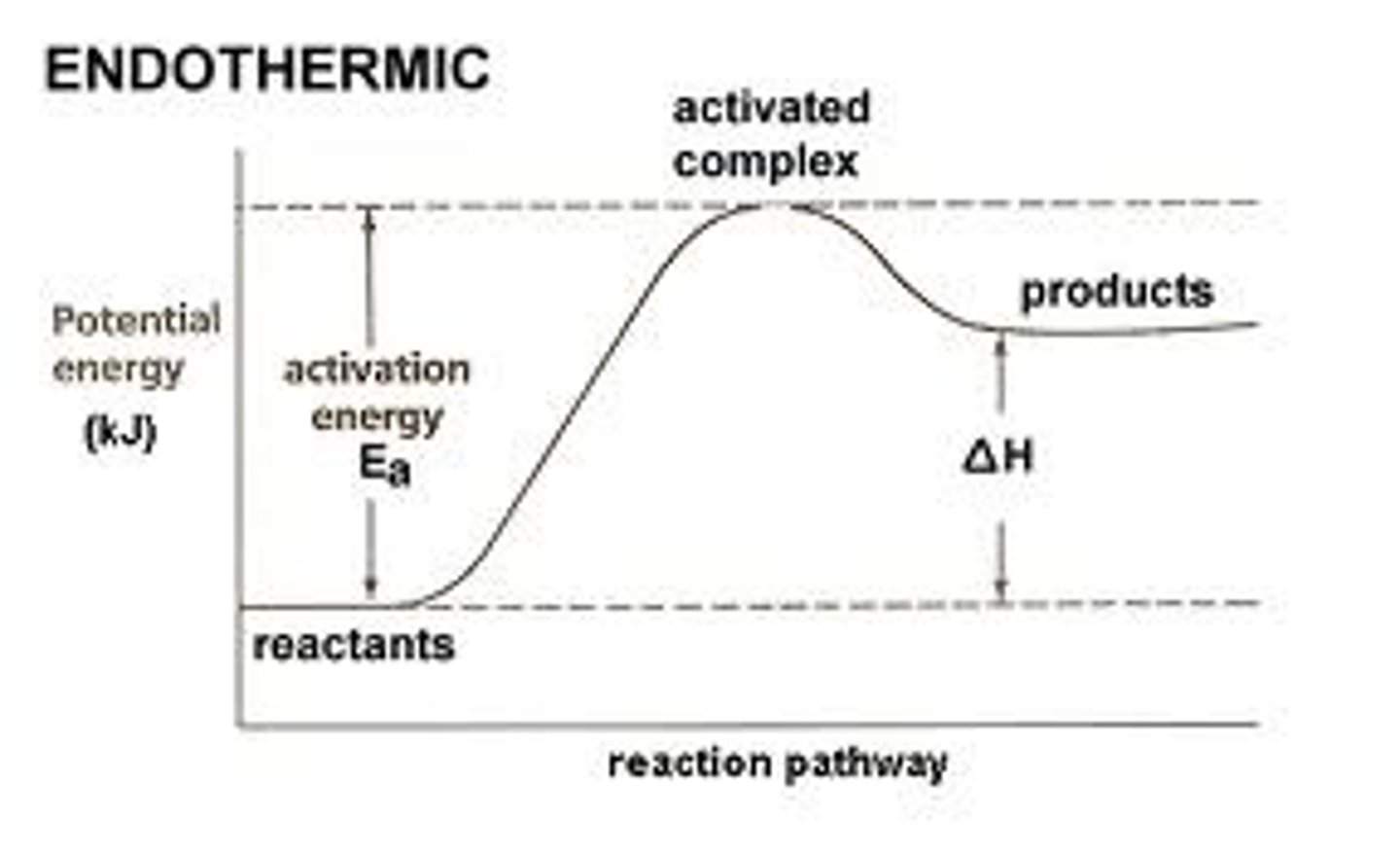
endothermic reaction
a chemical reaction where energy is taken in, so that the products have more energy than the reactants.
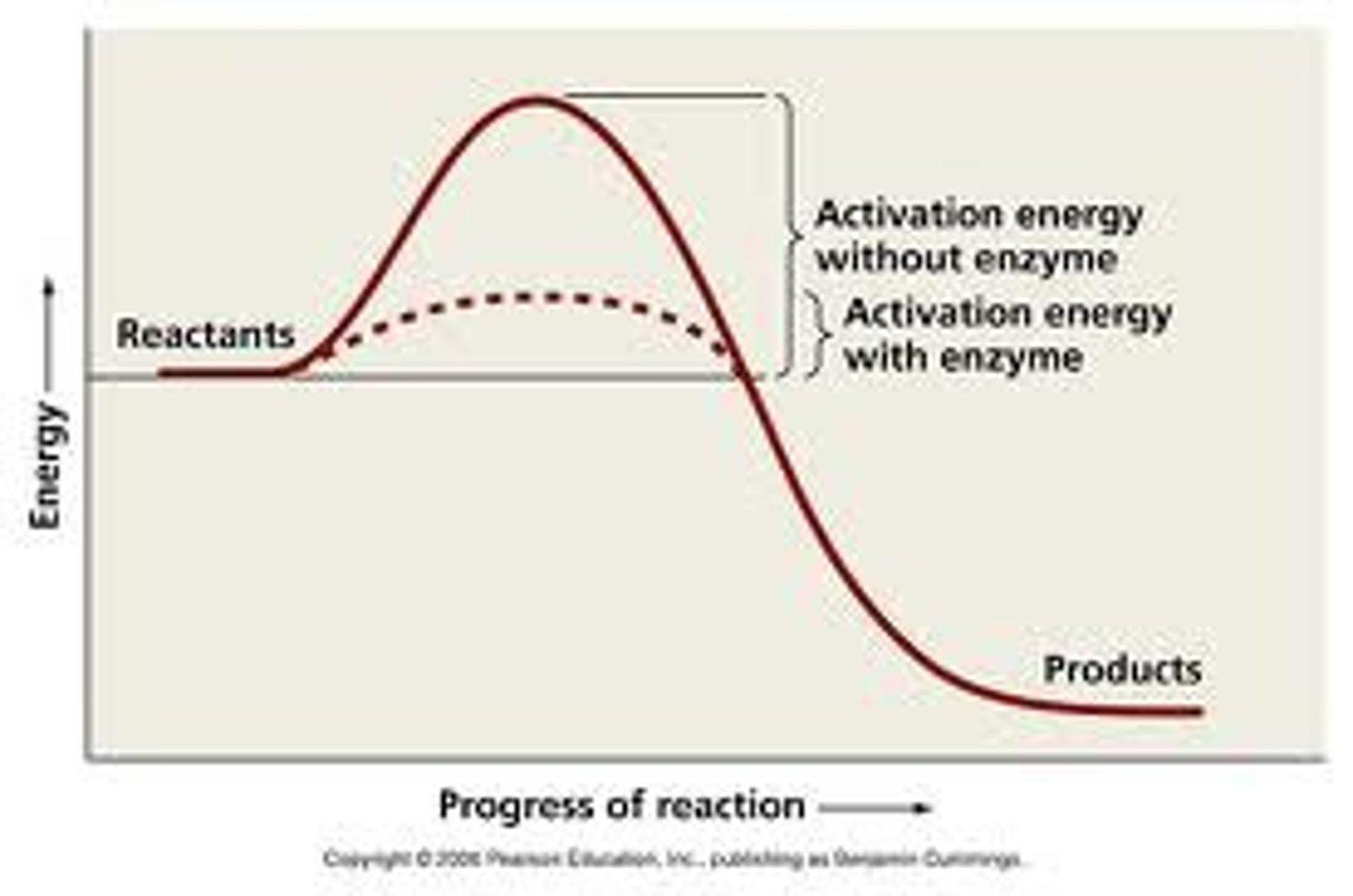
activation energy
Eₐ is the abbreviation used for the energy required to start a reaction.
sucrase
An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose

Catalase
an enzyme found in most aerobic organisms that breaks down H2O2 to water and oxygen

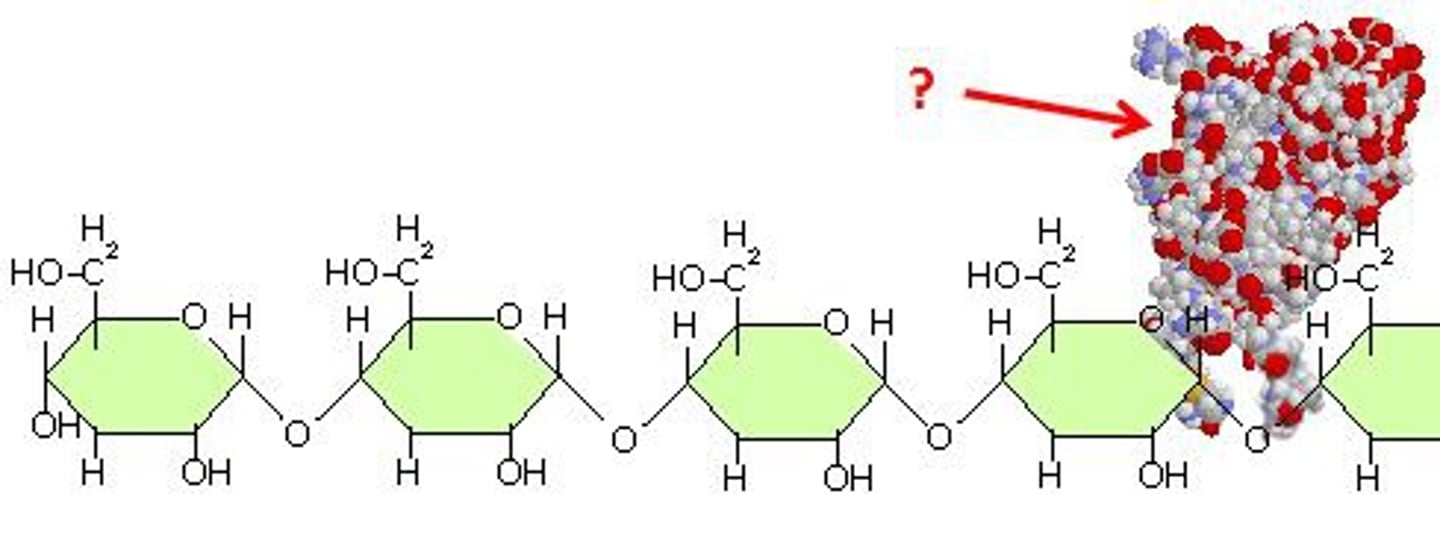
amylase
Enzyme that can break the bonds of starch to form the carbohydrate monomer, glucose.
lipase
Enzyme that can break the bonds of lipids to form the monomer, fatty acids.
protease
Enzyme that can break the polypeptide bonds of proteins to form the monomer, amino acids.
nuclease
Enzyme that can break the bonds of nucleic acids to form monomer, nucleotides
activated complex
the structure that is made up of the substrate bonded to the active site of the enzyme.
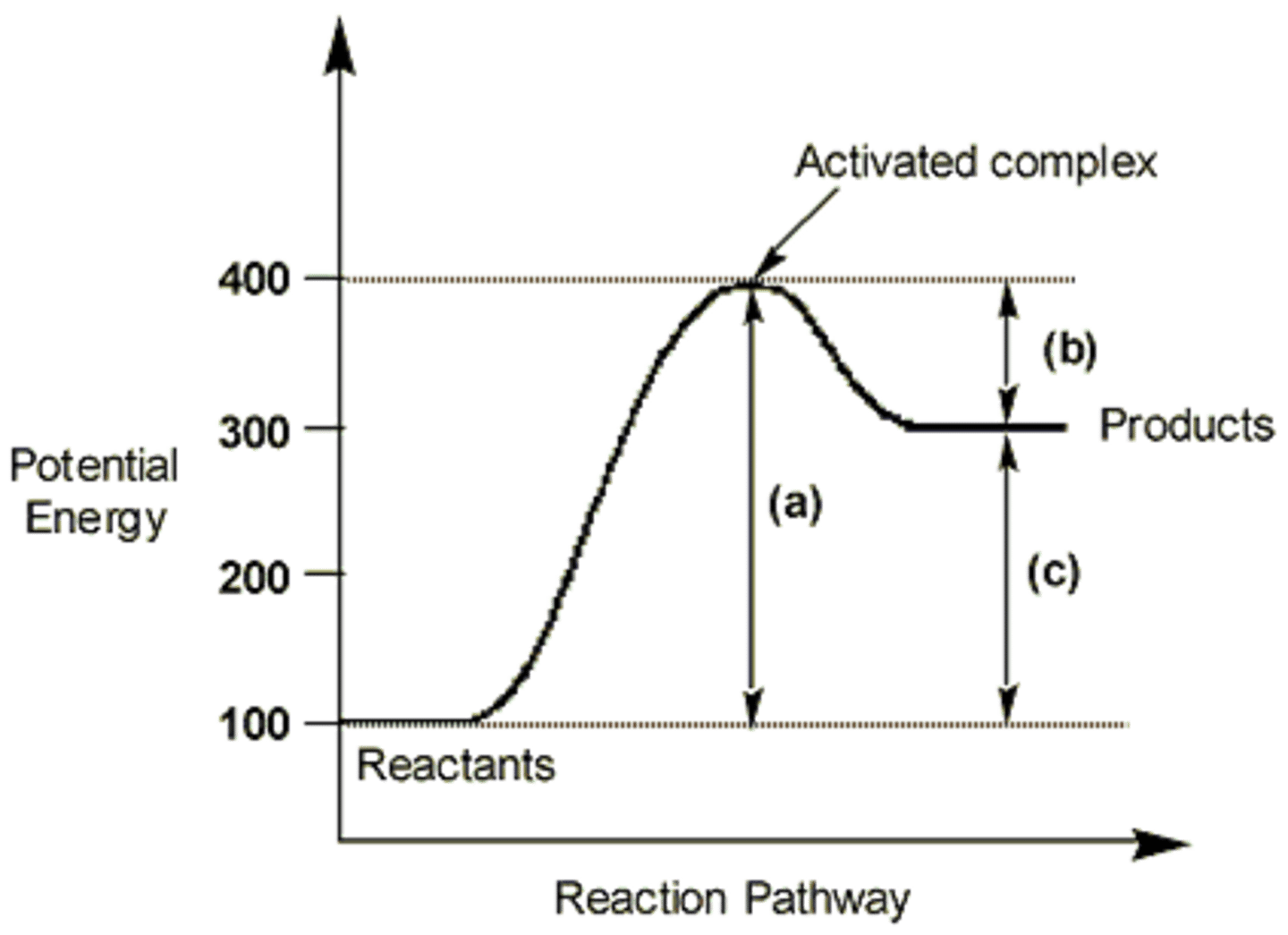
lock and key hypothesis
The substrate fits the active site of the enzyme like a key fits in a lock. There is no change to the shape of the enzyme or substrate.
induced fit hypothesis
The active site of the enzyme is flexible and conforms to fit the substrate like a glove fits on a hand.

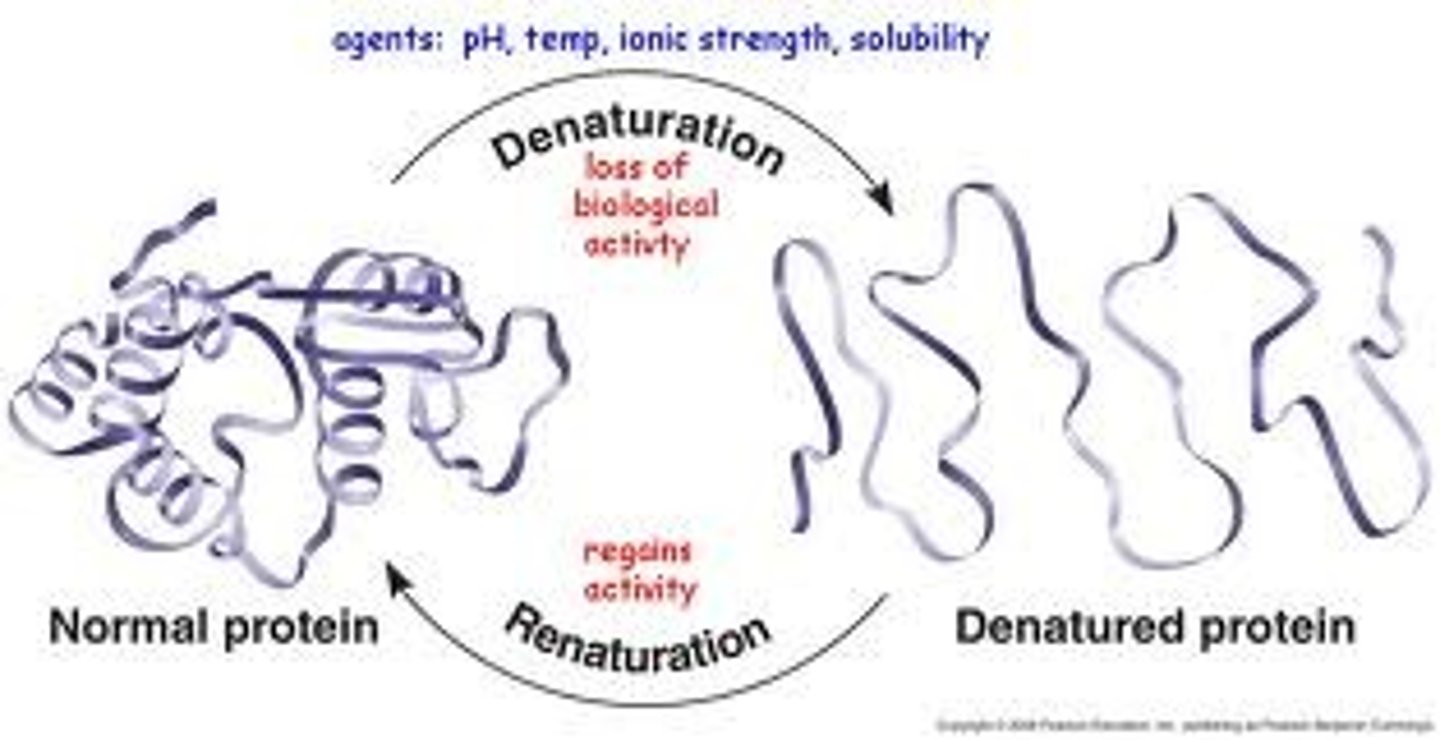
Denature
Characteristic of proteins; a change in shape that stops the protein from functioning.
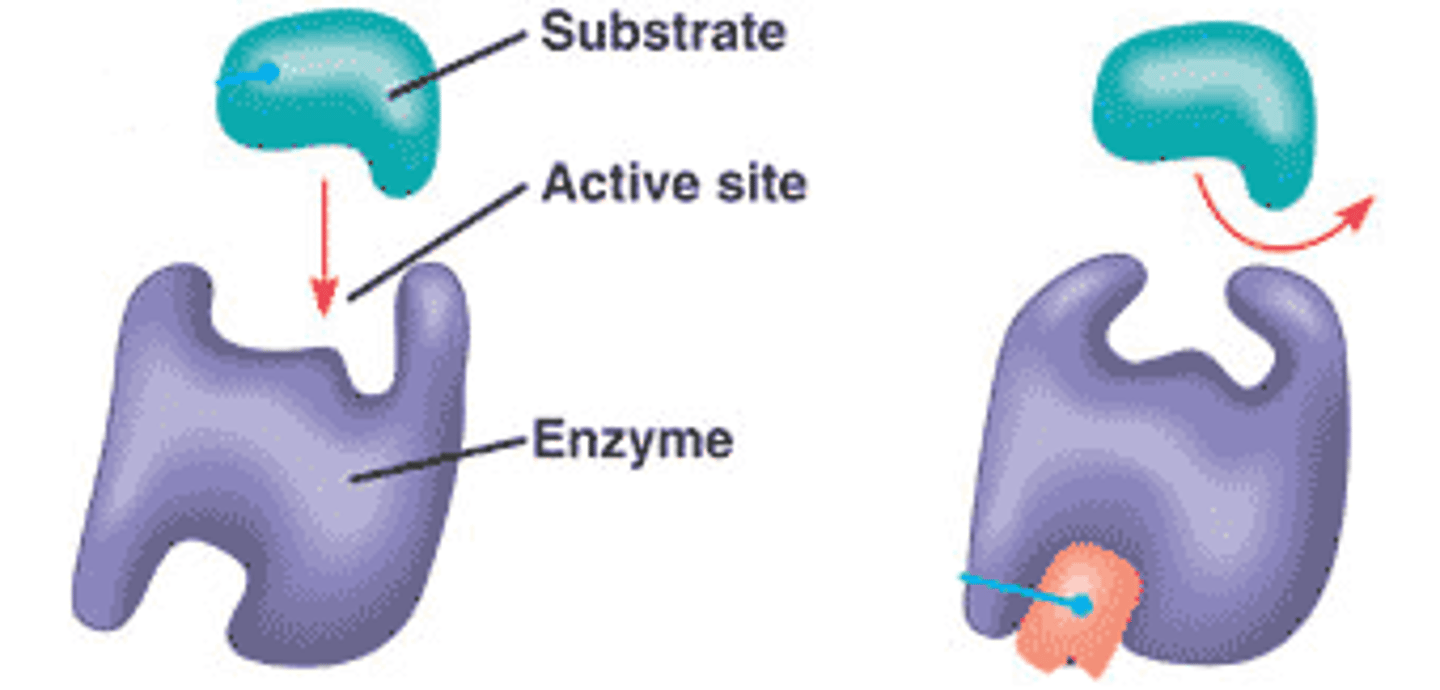
Allosteric
__________ regulation of enzyme occurs when a molecule binds to an enzyme changing the protein's shape
Catalyst
______ an agent that speeds up a chemical reaction without itself being permanently altered
G
An exergonic reaction releases free energy. The abbreviation for free energy is: Named after the American Scientist Josiah Gibbs
Transition State
The less stable state that occurs and is usually a high-energy state between reactants and products in a chemical reaction
Inducing Strain
The enzyme cause bonds in the substrate to stretch
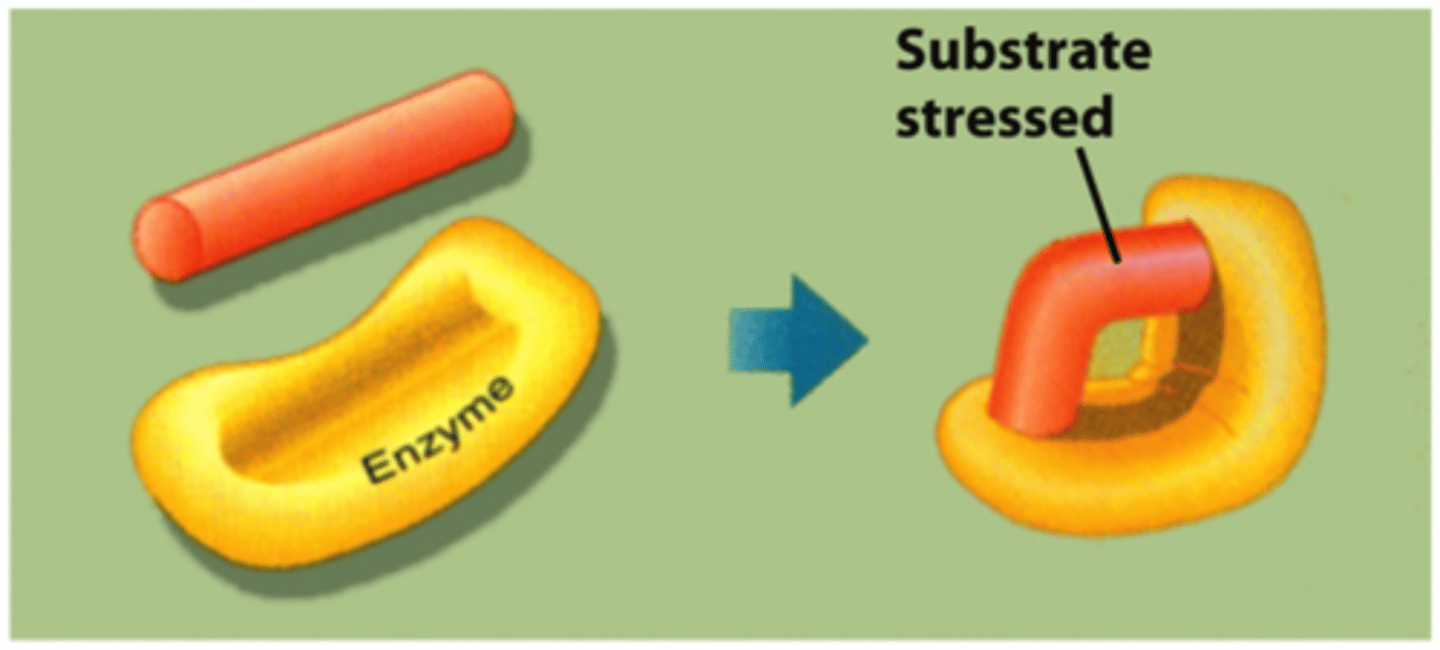
Substrate orientation
When Enzyme bring together specific atoms into a correct position that are otherwise rotating and tumbling so that bonds can form
Side chain (R group)
the part of the enzyme that can add H+ ions to or from substrate destabilizing covalent bonds
Metal
__________ ions such as Copper, Zinc iron bind to certain enzymes to initiated chemical reactions.
Heme
Organic molecules with iron an iron cofactor (A Prosthetic Group) that are permanently bond to enzyme responsible Oxygen transport
Irreversible Inhibition
When an enzyme inhibitor that covalently binds to the amino acid side chain at the active site of an enzyme it is called _______________

Reversible Inhibition
When an enzyme inhibitor binds is similar to the substate and non-covalently bind to the active site and there slows down the enzyme
Protein Kinases
enzymes that reversibly activate or inactivate other proteins by adding phosphate groups to (phosphorylating) them
Activator
A non-covalent binding regulator that can cause an enzyme to change shape and expose and expose an otherwise unexposed active site in allosteric regulation
Shape
in Biology the prefix allo means "different" and stereos means "__________"
Hydrogen
The specificity and activity of an enzyme depends on it 3D structure and this in turn depends on ______________ bonds
hydrophobic
Changes in H+ ions (acidity) concentration can alter how _____________ some regions of protein are.
pH
After looking at the graph the enzyme activity of the the three different enzymes is being regulated by what variable

Temperature
After looking at the shape of graph the enzyme activity of this enzymes is being regulated by what variable:
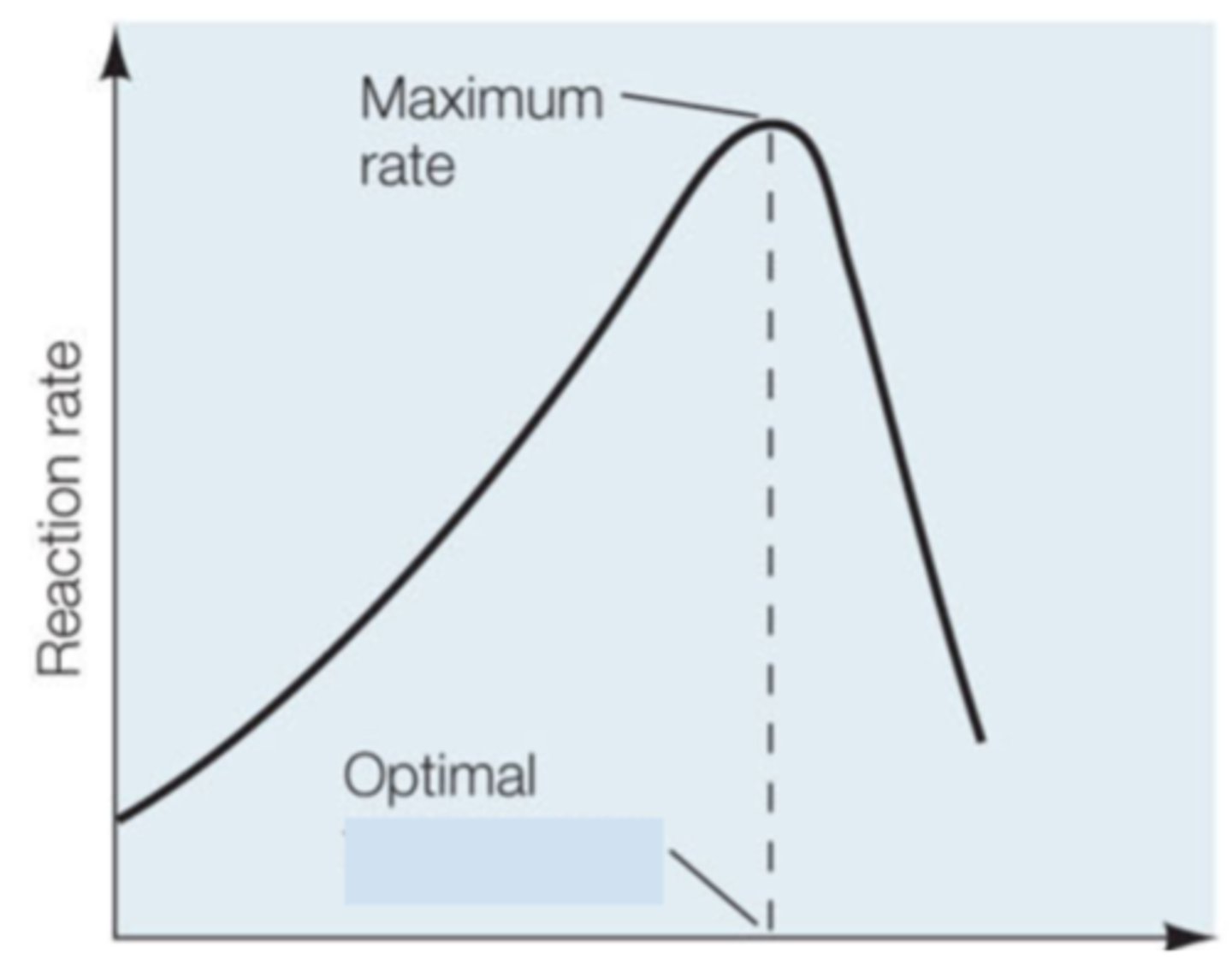
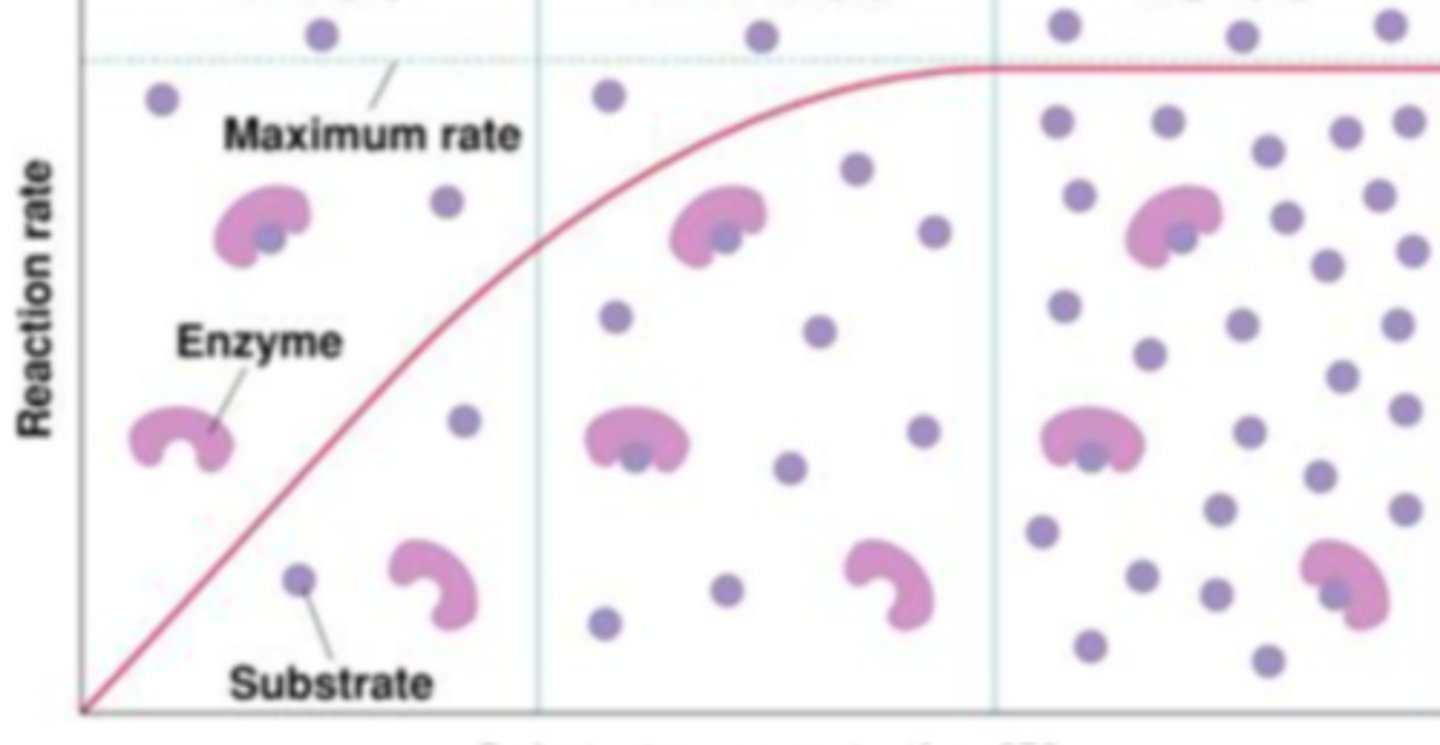
Substrate Concentration
After looking at the shape of graph the enzyme activity of this enzymes is being regulated by what variable: