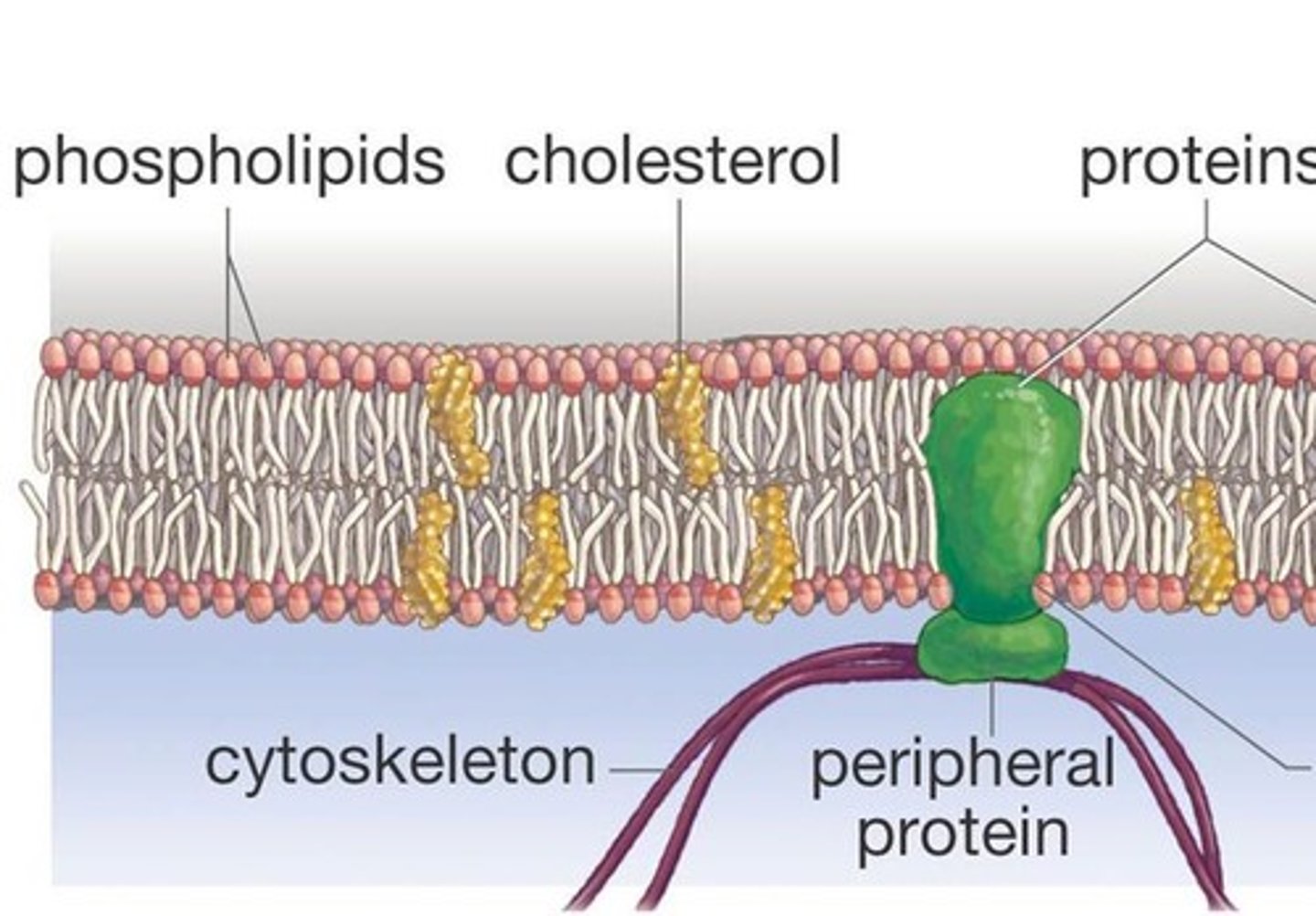
b) Fluid Mosaic Model
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Plasma Membrane Structure
Phospholipid Bilayer
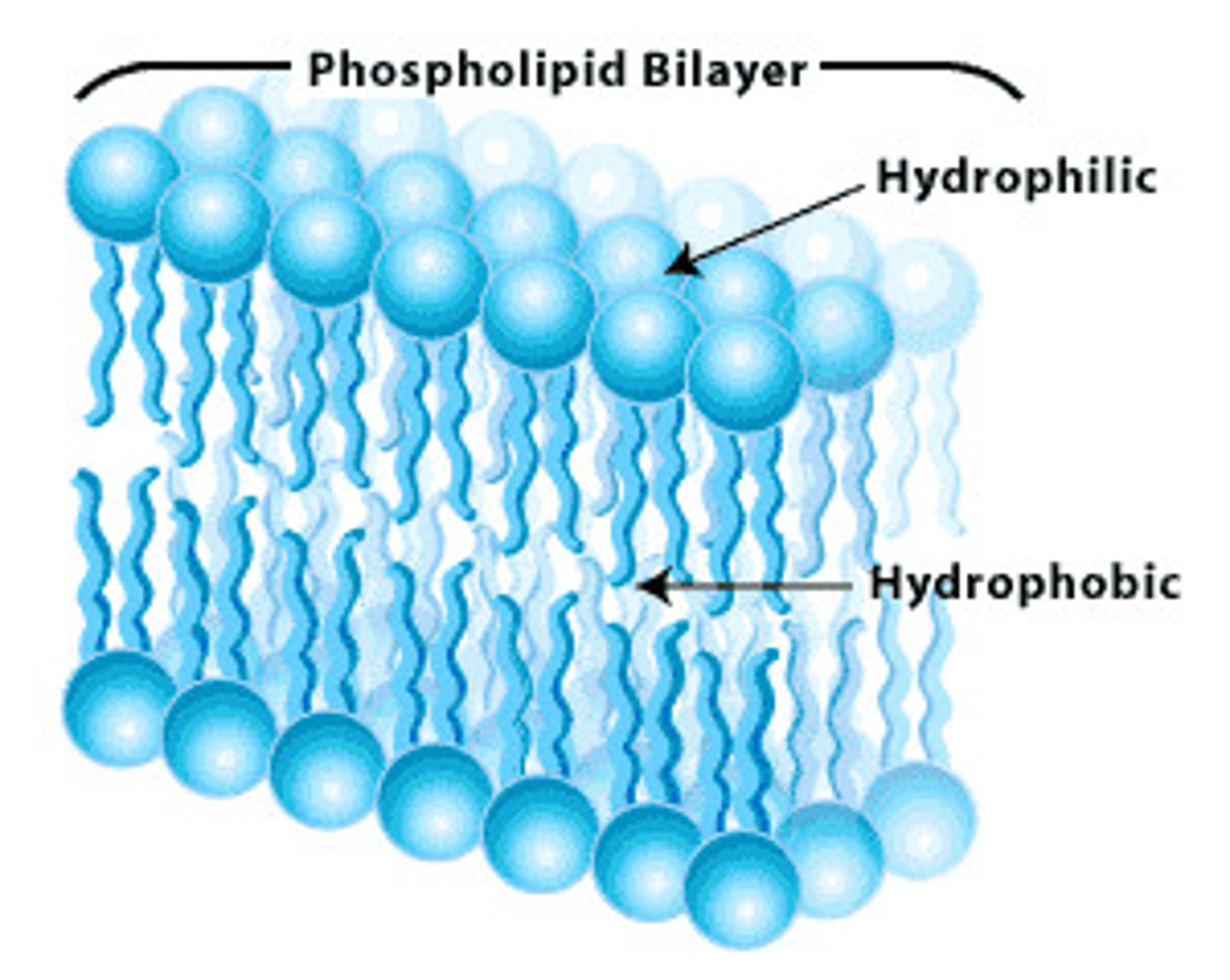
Why do phospholipids arrange themselves in a bilayer at the cell surface?
The hydrophilic heads orientate themselves towards water and the hydrophobic tails orientate themselves away from water.
There is water outside the cell (extracellular fluid) and inside the cell (cytoplasm/intracellular fluid)
Why is it called the fluid mosaic model?
It if fluid because the membrane is constantly moving and very flexible
The proteins/glycoproteins in it give a mosaic appearance
What does intrinsic protein mean?
- They are transmembrane proteins that are embedded through a membrane.
- They have amino acids with hydrophobic R-groups on their external surfaces, which interact with the hydrophobic core of the membrane, keeping them in place.

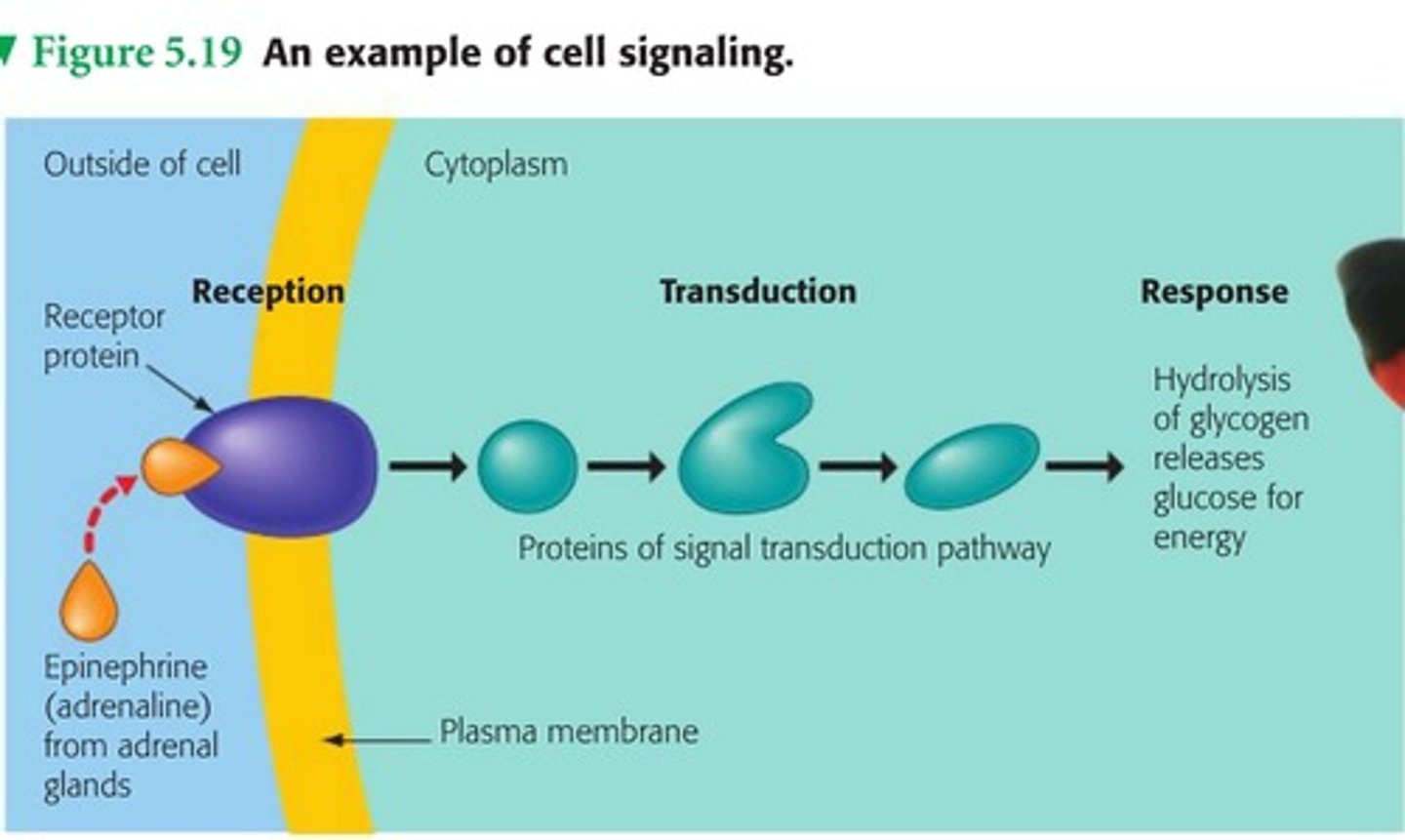
Glycoprotein Roles
- Cell recognition/identification
- Cell signalling
- Act as antigens
- Act as receptors. These receptors are complementary and specific.
- Cell adhesion
Examples of Cell Signalling with Glycoproteins:
- Receptors for neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine at nerve cell synapses. The binding of the neurotransmitters triggers or prevent an impulse in the next neurones.
- Receptors for peptide hormones, including insulin and glucagon, which affect the uptake and storage of glucose by cells.
- Some drugs act by binding to cell receptors. They can reduce a cell's response.
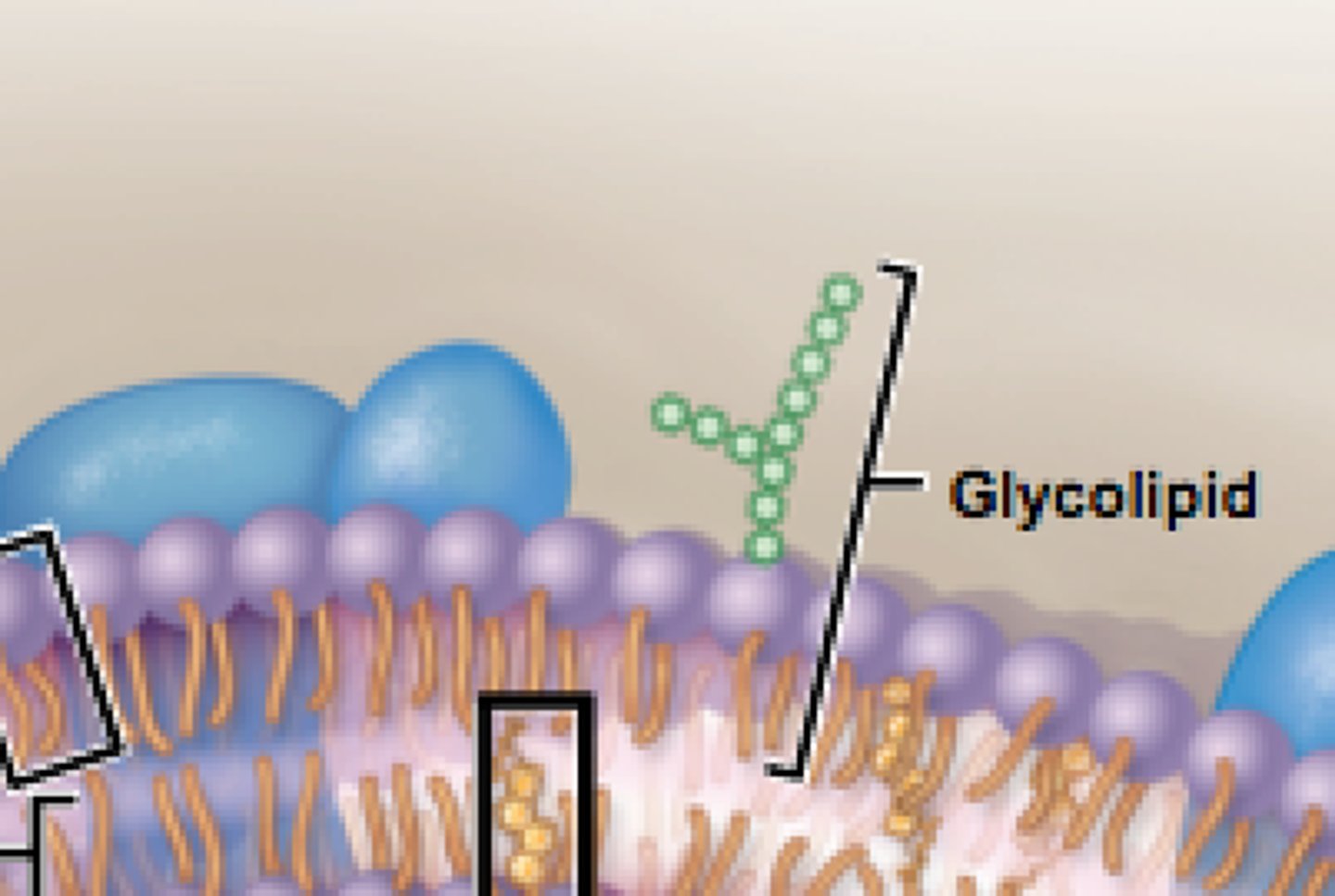
Glycolipid
- Cell recognition/identification
- Cell signalling
- Act as antigens
- Act as receptors. These receptors are complementary and specific.
- Cell adhesion
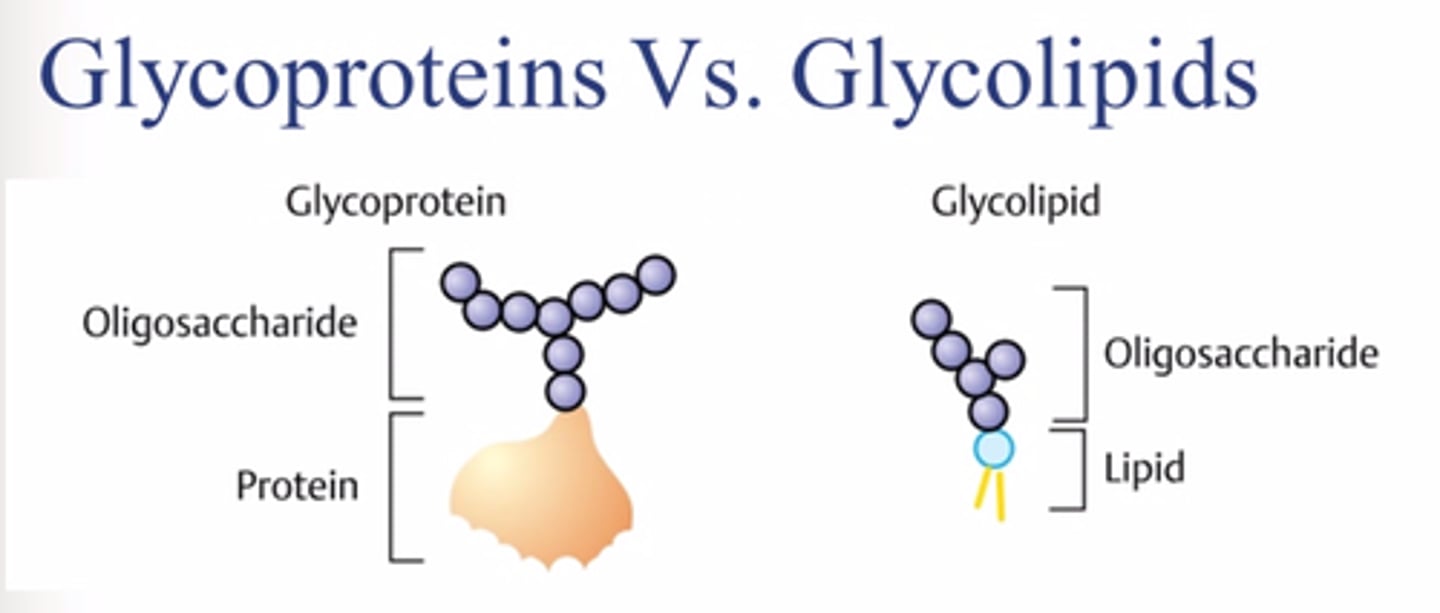
Difference between glycoprotein and glycolipid
Glycoprotein is a protein attached to a carbohydrate, whereas a glycolipid is a protein attached to a lipid
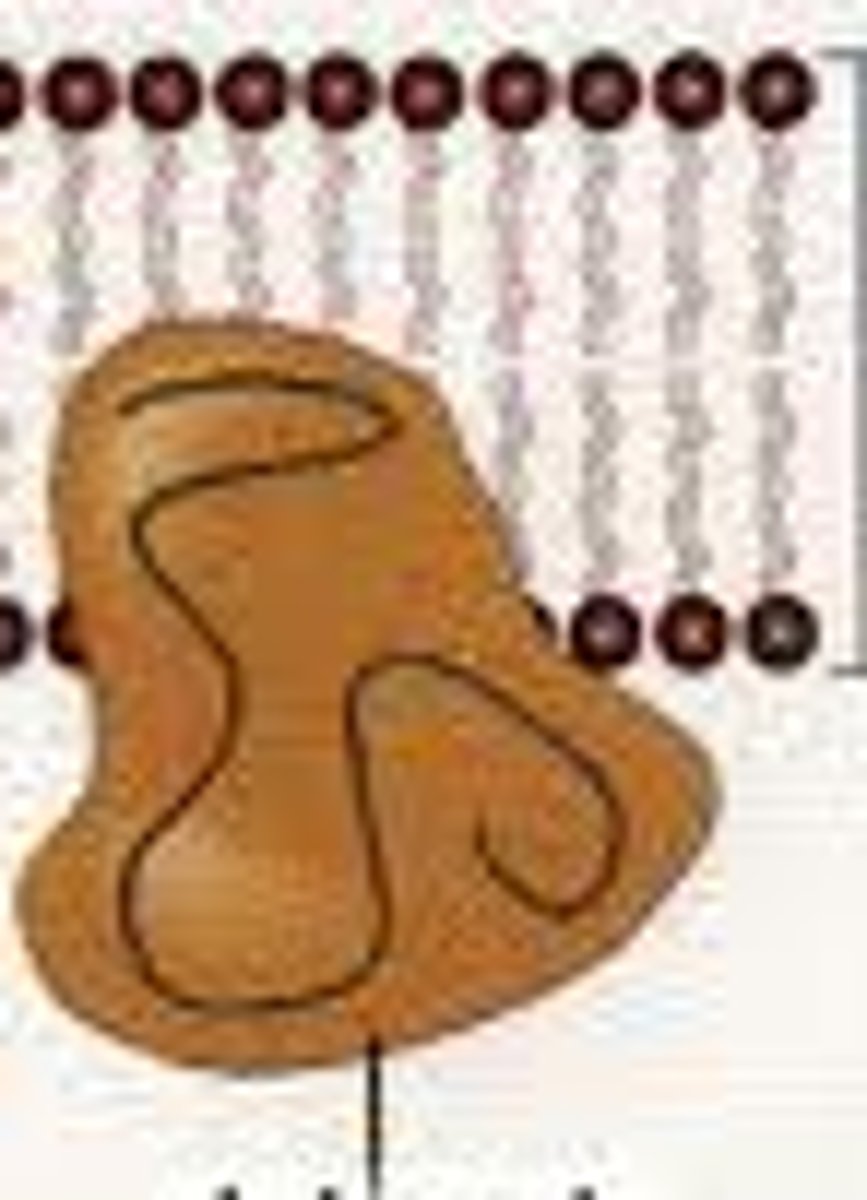
What does extrinsic protein mean?
- They are present in one side of the bilayer
- They have hydrophilic R-groups on their outer surfaces and interact with the polar heads of the phospholipids or with intrinisc proteins
- They can be present in either layer and some move between layers

Examples of extrinsic proteins
- Carrier proteins
- Channel proteins
What do carrier proteins transport?
Large and polar substances
What do channel proteins transport?
Polar substances
Cholesterol in biological membranes
It is found between the tails of the phospholipid and regulates fluidity. The more cholesterol, the less fluid the membrane.