Exchange and Transport in Animals
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Where is oxygen exchanged in the body and why?
Alveoli in lungs
Needed for respiration
Where is carbon dioxide exchanged in the body and why?
Alveoli in lungs
Waste product of metabolism
Where is water exchanged in the body and why?
Nephrons in kidney
Needed for cells to function properly
Where are dissolved food molecules exchanged in the body and why?
Small intestine
Needed for respiration
Where are mineral ions exchanged in the body and why?
Small intestine
Needed for cells to function properly
Where is urea exchanged in the body and why?
Nephrons in kidney
Waste product of metabolism
Why do more complex organisms not rely solely on diffusion?
As an organism gets bigger, their surface area to volume ratio gets smaller
They need to have specialised exchange surfaces and transport systems
What happens in the lungs when you breathe?
Oxygen diffuses out of the air and into the blood
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood and into the air
How is the lung adapted for efficient gas exhange?
It contains millions of tiny alveoli (air sacks), creating a large surface area for diffusion of gases
How are alveoli adapted for efficient gas exchange?
One-cell thick- minimises diffusion distance
Good blood supply- this maintains a high concentration gradient
Large surface area
Moist lining- allows gasses to dissolve then diffuse
Good ventilation- good supply of air
What factors effect the rate of diffusion?
Increase in surface area
A shorter distance for diffusion
Maintenance of a high concentration gradient
What is Fick’s Law?
An equation used to calculate the rate of diffusion:
Rate of diffusion ∝ (Surface area x conc difference)/Membrane thickness
For the rate of diffusion to be as high as possible, the surface area and concentration difference need to be as big as possible and the thickness of the membrane has to be as low as possible
What is blood made of mainly?
Plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets
What is plasma and what does it do?
The liquid part of the blood
It carries blood cells through the blood vessels
It contains many dissolved substances, such as carbon dioxide and glucose
What are white blood cells like and what do they do?
Larger than red blood cells
They have a nucleus
They are part of the immune system and attack pathogens in the body
Some white blood cells (phagocytes) will ingest pathogens to destroy them
Other white blood cells (lymphocytes) produce chemical antibodies that attack pathogens and destroy them
What are platelets and what do they do?
Fragments of larger cells
They have no nucleus
They cause blood to clot when a blood vessel has been damaged
The clot blocks the wound and prevents pathogens getting into the blood
How are red blood cells adapted for their fuction?
They contain haemoglobin which can carry 4 oxygen molecules
Has a biconcave shape increasing surface area so more oxygen can be carried
Has no nucleus- more space to carry oxygen
What are the three types of blood vessels?
Arteries, veins and capillaries
How are veins structured and what is their function?
Carries blood to the heart
Thin, smooth muscle walls
Large lumen
They contain valves
This stops blood flowing backwards, so that it is returned to the heart
Large space to allow blood to flow easily back to the heart at low pressures
Blood is squeezed back to the heart by action of skeletal muscle
How are capillaries structured and what is their function?
Connects arteries and veins through cells
Substances are exchanged between the body cells and blood in capillaries
They are one blood cell wide
Walls are only one cell thick- short diffusion distance
Tiny vessel with narrow lumen
Waste products like carbon dioxide and other cells products like hormones move out of the body cells and into the blood
Substances need by cells such as oxygen and glucose move from the blood in the capillary into the body cells
What makes up the circulatory system?
The heart and blood vessels
What does the heart do?
Pumps blood around the body
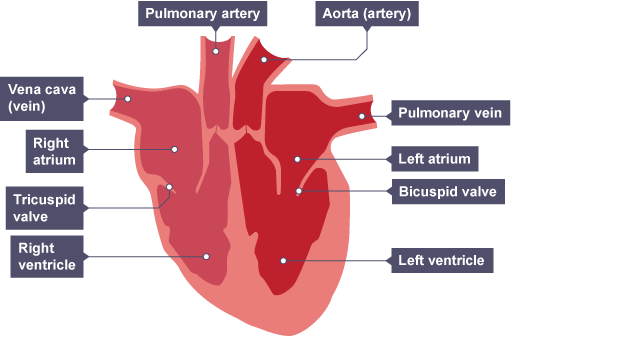
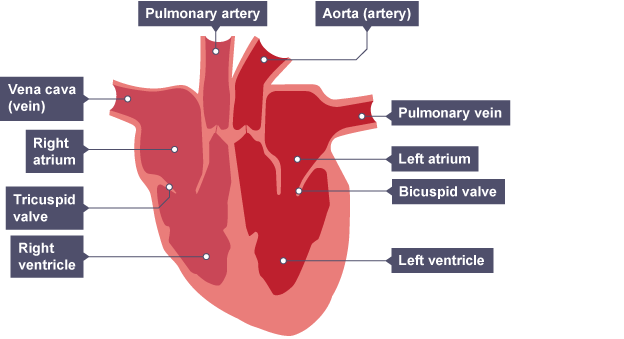
How does the heart function on the right side?
Note that the right side will be on the left in a diagram
The right side contains deoxygenated blood
The vena cava brings oxygenated blood from the body to the heart
The blood flows through the right atrium and down into the right ventricle
The tricuspid valve stops blood flowing backwards
the right ventricle contracts, forcefully pumping blood out of the pulmonary artery which carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
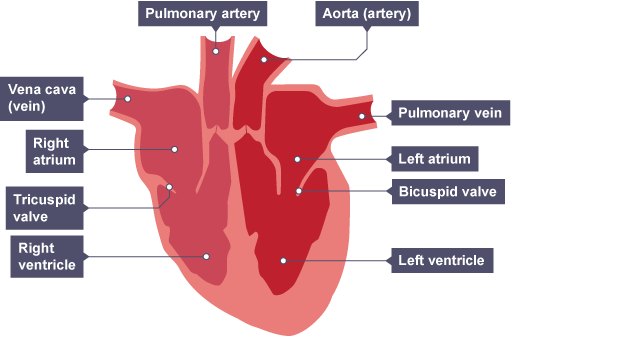
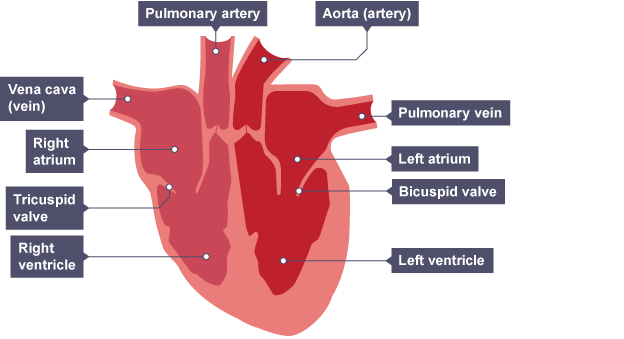
How does the heart function on left side?
Note that the left side will be on the right in a diagram
The left side contains oxygenated blood
The pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
The blood flows through the left atrium and down into the left ventricle
The bicuspid valve stops blood flowing backwards
the left ventricle contracts, forcefully pumping blood out of the heart through the aorta which carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body
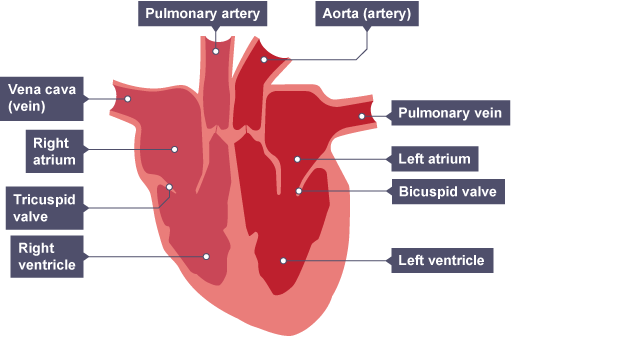
What do arteries do?
They take blood away from the heart
What is the part of the heart called that separates the right and left side?
The septum
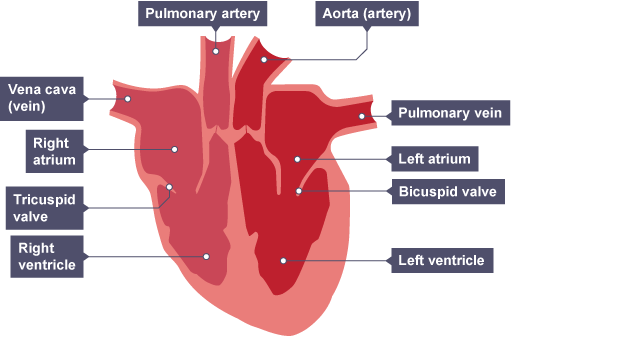
How does blood circulate around the body?
Blood enters the atria
The atria contract forcing blood into the ventricles
The ventricles contract, forcing blood into the arteries
Blood flows through the arteries to the organs and returns to the heart through veins
What is cellular respiration?
A process that releases energy from glucose for use in cellular activities
What is aerobic respiration?
Takes place mostly in mitochondria
Exothermic because it releases energy
Main source of energy for cells
Requires oxygen
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + water
What is energy from respiration used for in animals?
Metabolic processes to build larger molecules from smaller ones such as proteins from amino acids
To enable muscle contraction
To maintain steady body temperature in cold surroundings
What is energy from respiration used for in plants?
Used to build larger molecules from smaller ones e.g sugars, nitrates and other nutrients into amino acids, which are then used to make proteins
When does anaerobic respiration take place?
When there is not enough oxygen or aerobic respiration is not possible
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration?
Glucose → Lactic acid
How does anaerobic respiration work?
It is the incomplete breakdown of glucose to release energy
Does not use oxygen
Can supply energy to muscles when there is not enough oxygen for aerobic respiration
In muscle cells it produces lactic acid
Blood flowing through muscles then removes lactic acid
19 times less energy is released than aerobic respiration
What does lactic acid do to muscles?
It causes pain and muscle fatigue, and inhibits the ability for muscles to contract
What is anaerobic respiration like in plant and fungal cells?
It produces ethanol
Involves the breakdown of glucose
No oxygen is used
Less energy is released per glucose molecule than anaerobic respiration in animals
What are the advantages of anaerobic respiration?
It can release energy for the muscles to contract when then heart and lungs cannot deliver oxygen fast enough for aerobic respiration
Respiration can continue in organisms that have no, or very limited, oxygen supply
What are the disadvantages of anaerobic respiration?
Releases less energy than aerobic respiration
Lactic acid is not removed from the body, it builds up in muscles and must be removed after exercise
Lactic acid can build up in muscle cells, causing cramps and soreness
How to calculate rate of respiration?
rate = change/time
What is the equation for cardiac output?
Cardiac output= stroke volume x heart rate
What is pulse measured as?
Beats per minute (bpm)
What does a faster heart rate cause?
Blood being pumped around the body faster
Blood takes oxygen and glucose to the cells faster and removes carbon dioxide faster
What is the structure of the arteries and what is their function?
Carries blood away from the heart
Has small lumen
Thick walls
Thick layer of muscle and elastic fibers
Arteries stretch as high pressure blood is pumped through it before returning to it’s original shape- this is felt as a pulse