H1 European Exploration and Impact on Indians
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Who inhabited Georgia before its official founding?
American Indians
How long did American Indians occupy the region that became Georgia?
Over 12,000 years
What is the purpose of this standard?
To recognize the long-standing occupation of American Indians in Georgia
How were American Indian cultures impacted by European exploration and settlement?
Their cultures were negatively impacted as Europeans sought control of the region
What is the significance of February 12, 1733, in relation to Georgia?
It is the official founding date of Georgia
What were the characteristics of American Indians living in Georgia at the time of European contact?
Mississippian culture, complex chiefdom society, large towns near rivers, earthen mounds, wattle and daub shelters, trade network, horticulture and agriculture.
What were the three prehistoric American Indian cultures that lived in southeastern North America before 800 CE?
Paleo, Archaic, Woodland.
When did the Mississippian American Indians rise to dominance?
Around 800 CE.
How did the Mississippian American Indians organize themselves?
Into a structured hierarchical society with elites and commoners.
What were the characteristics of the towns built by the Mississippian American Indians?
Large towns near rivers with central plazas, residential zones, and defense structures.
What were the earthen mounds in the Mississippian towns used for?
Religious and social activities, some served as cemeteries.
What were the shelters used by the Mississippian American Indians?
One-room wattle and daub shelters made of interwoven sticks and mud or clay.
What was the trade network like for the Mississippian American Indians?
Widespread trade network connecting towns, trading raw materials and finished goods like shell beads, pottery, and stone tools.
What type of cultivation did the early Mississippians practice?
Horticulture (garden cultivation).
What type of agriculture did the Mississippians eventually move into?
Large scale agriculture.
What were the dominant crops of the Mississippians?
Maize (corn), squash, sunflowers, pumpkins, and beans.
How did the Mississippians plant their crops?
Fields were intermixed with a variety of crops. (Three Sisters; corn, squash, beans)
What is chert?
Sedimentary rock used to make knives.
Who were the commoners in the Mississippian culture?
The work force.
Who were the elites in the Mississippian culture?
The power holders.
What is horticulture?
Garden cultivation; important to the Mississippian culture.
What is maize?
Another term for corn.
Who were the Mississippian Indians?
The last major prehistoric Native American culture in Georgia; known for being large-scale farmers and mound builders who traded throughout North America.
What is the Okefenokee Swamp?
The largest swamp in North America; home to many Native Americans and a location for Spanish missions.
What is wattle and daub?
Walls built of interwoven sticks and covered with mud or clay; used by early American Indian cultures and European settlers.
What did the tall corn stalks provide for ground level crops?
A shield against damaging sun rays.
What was tobacco planted for?
Ritual usage.
What evidence indicates that the Mississippians hunted?
Bone evidence and the use of bows and arrows and chert knives.
What animals did the Mississippians hunt?
Deer, rabbit, muskrat, beaver, raccoon, and turkey.
What other animals were part of the Mississippians' diet?
Turtle and fish.
What seasonal fruits did the Mississippians gather?
Plums, grapes, blackberries, and raspberries.
What did the Mississippians improve on?
Stone tools of previous cultures for hunting, farming, and human conflict.
What happened to the Mississippians after interacting with the Spanish?
Many succumbed to disease and the group eventually reorganized into the historic tribes of the Creek and the Cherokee.
What were the reasons for European exploration and settlement of North America?
Economic competition and desire for political and economic dominance.
What were the interests of the Spanish and British in the Southeastern area?
Spanish: God, Gold, and Glory. British: Mercantilism and creating permanent colonies.
What was France primarily interested in?
Developing a fur trade in Louisiana, the Ohio Valley, and Canada.
Who explored Georgia's coastline in search of a French colony?
Jean Ribault.
Where did Jean Ribault choose to establish a French colony?
South Carolina.
Who eventually moved from South Carolina to Georgia seeking religious freedom?
Protestants.
What were the goals of Spanish conquistadores in North America?
Converting American Indians to Christianity, acquiring gold, and seeking personal fortune and fame.
What did the Spanish prioritize over self-sustaining colonies?
Their search for gold.
What was England's goal in creating colonies in North America?
To support the economic policy of mercantilism.
What is mercantilism?
An economic policy where a country seeks to export more than it imports.
What did the British colonies produce for the 'mother country'?
Raw materials.
What were the raw materials used for?
Production into finished products.
Where were the finished products shipped back to?
The colonies for purchase by the colonists.
Which European nations were involved in economic competition in North America?
French, Dutch, Spanish, and English.
What were the three G's that motivated the Spanish in exploration in North America?
God, Gold, and Glory.
What did the Spanish desire to do with the American Indians?
Convert them to Christianity.
What did the Spanish hope to fill their treasury with?
Gold.
What were the primary interests of France in North America?
Developing a fur trade.
What areas of North America was France primarily interested in?
Louisiana, the Ohio Valley, and Canada.
What is mercantilism?
English economic policy focused on exporting more than importing.
What are missions?
Churches set up by the Spanish to convert Native Americans to Christianity.
What were the English reasons for creating colonies?
Desire for religious freedom and new life (social mobility)
What was the impact of Spanish contact on American Indians?
Dramatic decline in American Indian culture and population.
Who was Hernando DeSoto?
First known European explorer in Georgia.
What did DeSoto do to the American Indians?
Starved and killed a large number of them.
Why did DeSoto move from Florida to southwest Georgia?
In search of gold.
What false information did the American Indians provide DeSoto?
Vast stores of gold further north.
What did DeSoto's men's journals give insight into?
Mississippian chiefdom culture.
What did DeSoto introduce to North America?
Pigs.
What diseases did DeSoto's expedition spread?
Smallpox, measles, and influenza.
What happened to DeSoto during his expedition?
He died near the Mississippi River and was buried in the river.
What did DeSoto's failed expedition lead to?
Increased exploration and colonization efforts by the French and Spanish.
What was the most successful Spanish colonization attempt?
The 'Mission Period' from 1568-1684.
What did Spain build during the 'Mission Period'?
Several missions (churches) on the barrier islands and mainland.
What were the Spanish missions?
Churches established by Spain.
When did the 'Mission Period' take place?
From 1568-1684.
What were the barrier islands?
Islands along the southeast coastline.
What did DeSoto's journey credit with introducing to North America?
Pigs and devastating diseases.
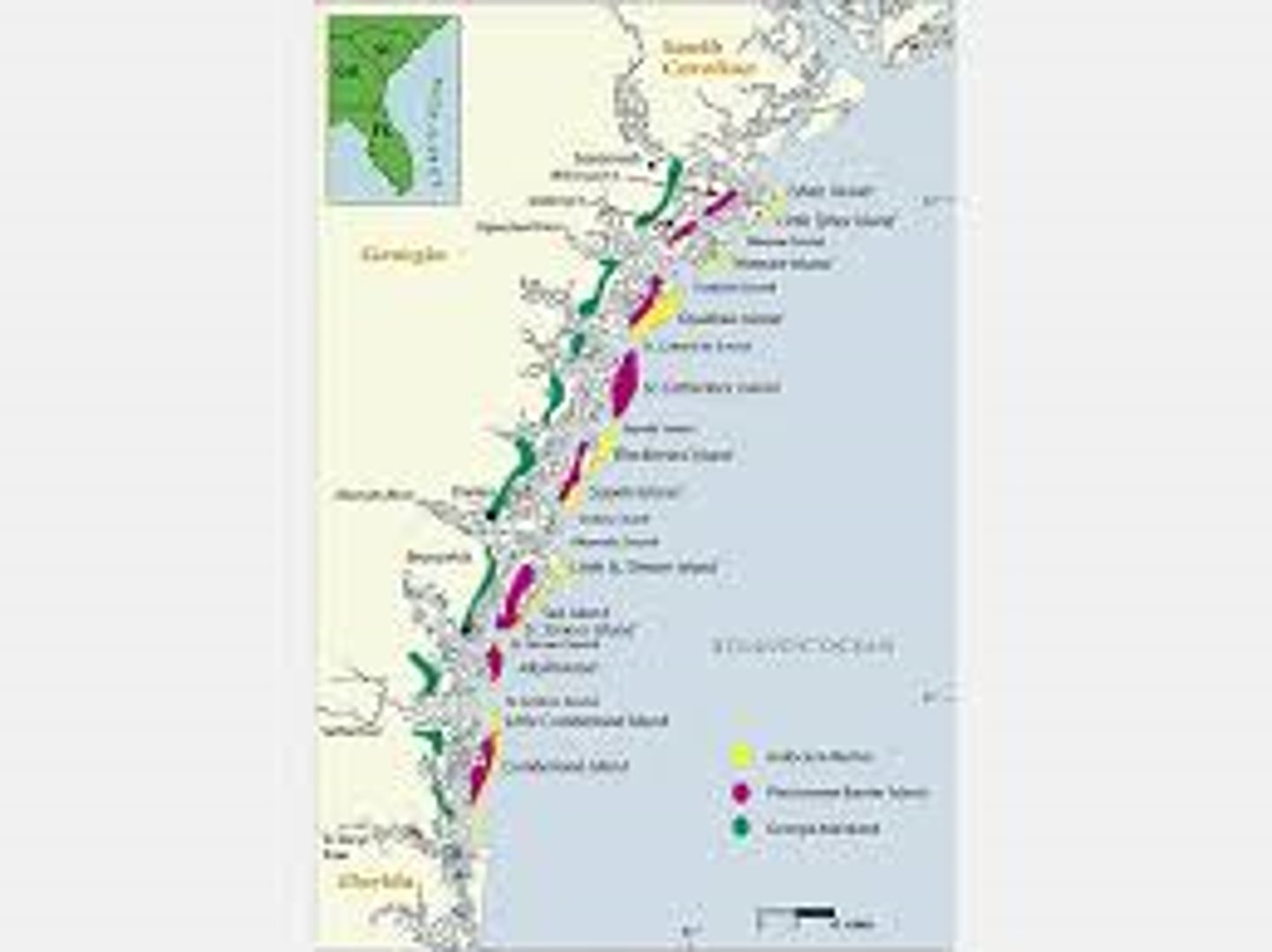
What were the missions on Cumberland Island, St. Catherine's Island, and near the Okefenokee Swamp?
Spanish missions built on these islands and near the swamp.
Where were the mainland missions located?
The mainland missions were located as far inland as Valdosta and Lumber City.
Why were the Spanish missions located near Mississippian towns?
To convert the American Indians to Christianity and encourage them to embrace Spanish political and economic systems.
What was the primary goal of the priests and friars in the missions?
The primary goal was to convert the American Indians to Christianity (Catholicism).
What requirement did unmarried American Indian males have to fulfill?
They were required to work in Saint Augustine for several months out of the year to show allegiance to the Spanish.
What impact did the close contact with the Spanish have on the American Indians?
It brought disease and death to the American Indians and caused considerable change to their own culture.
When did the Spanish mission system start to crumble?
By the mid-1600's.
What was the cause of the decline of the coastal missions?
British influence from the South Carolina colony and raids by American Indians.
When were the coastal missions abandoned by the Spanish?
By the 1680's.
What event in 1684 led to the end of the Spanish mission period in Georgia?
A pirate raid that pushed the remaining missionaries into Florida.
What are barrier islands?
Several islands off Georgia's coast inhabited by Native Americans and where the Spanish built missions.
Who was Hernando De Soto?
A Spanish Conquistador who led an expedition through the Southeastern United States and is credited as being the first European in Georgia.
