microbio- Enterobacteriaceae
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
rods
what is the shape of family Enterobacteriaceae?
negative; positive
bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae are oxidase _____ and catalase _____
yes, they have perithrichous flagella
are family Enterobacteriaceae motile bacteria?
peritrichous
family Enterobacteriaceae have ________ flagella
Macconkey, nonenriched, BG agar, Levine agar, ASAP, XLD
on what type of cultural media can family Enterobacteriaceae grow?
both- they are facultatively anaerobic
do family Enterobacteriaceae grow with or without oxygen?
Escherichia coli
Salmonella
Yersinia
Proteus
Enterobacter
Klebsiella
what 6 genera do we study in family Enterobacteriaceae?
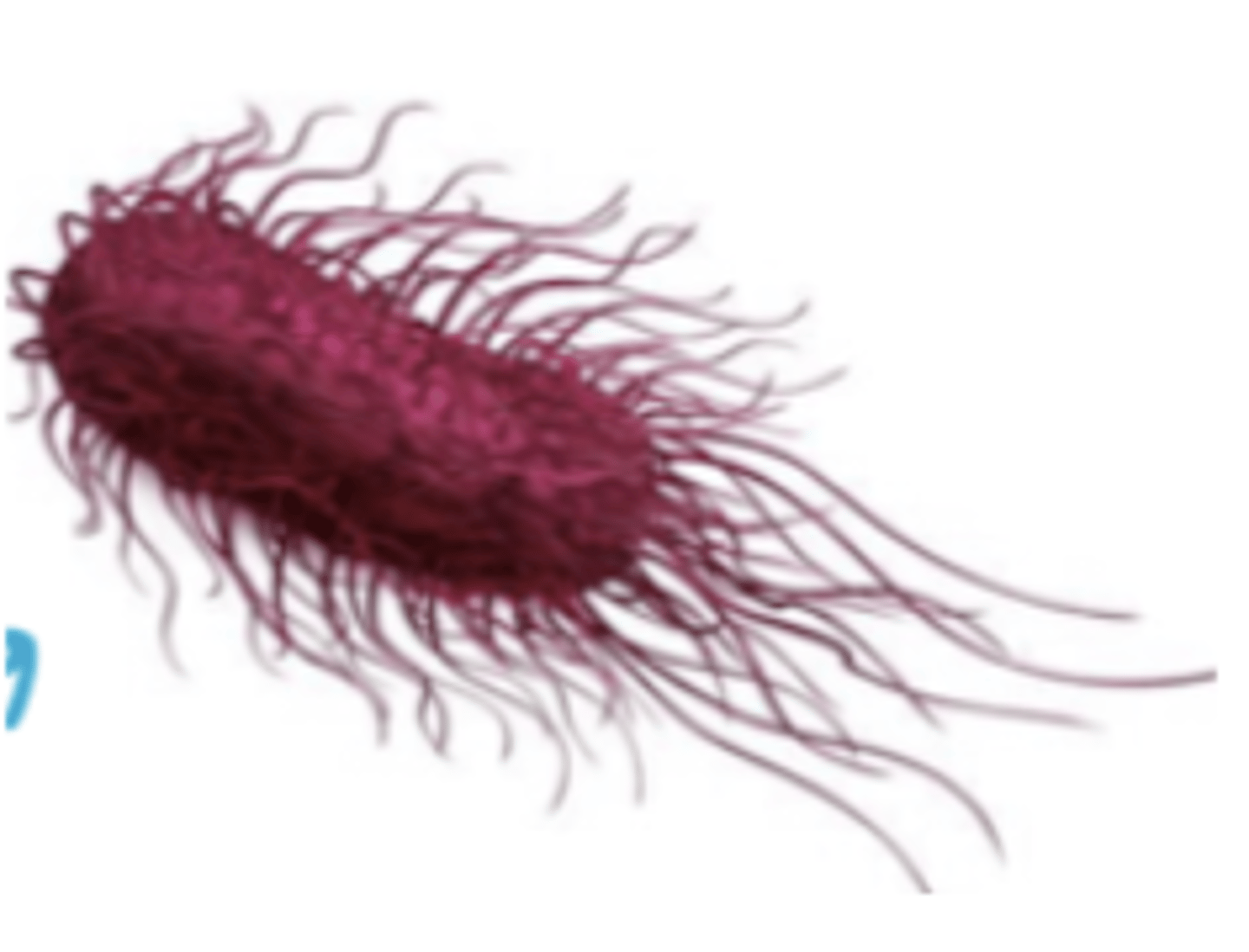
rod; peritrichous flagella
family Enterobacteriaceae look like this. what shape and type of flagella do they have?
Enteropathogenic (EPEC)
Enterotoxigenic (ETEC)
Enteroinvasive (EIEC)
Enterohemorrhagic (EHEC)
Enteroaggregative (EAST1)
Attaching and effacing (AEEC)
what are the 6 stains of E. coli?
it adheres to the enterocytes and eliminates microvilli
how does enteropathogenic E. coli work?
no, they eliminate the microvilli without producing toxins
do enteropathogenic E. coli produce enterotoxins to harm the enterocytes?
watery diarrhea
what type of diarrhea is associated with enteropathogenic E. coli?
E. coli
it is lactose +
which enterobacteria produces these colonies on macconkey agar?
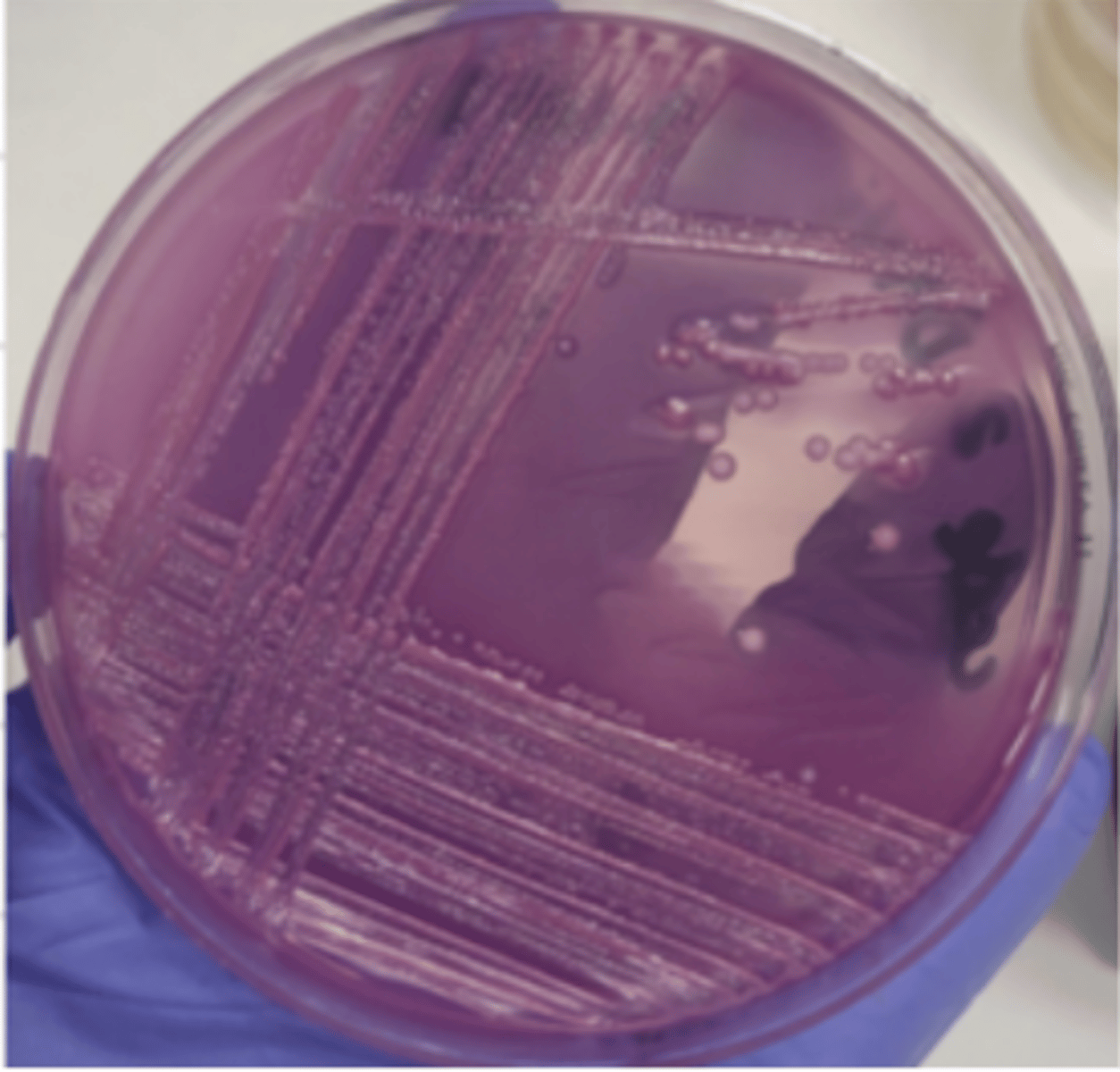
E. coli
which enterobacteria has lactose, which produces pink colonies on Macconkey agar?
E. coli
on BC agar, which genus of the family Enterobacteriaceae produces these yellow colonies?
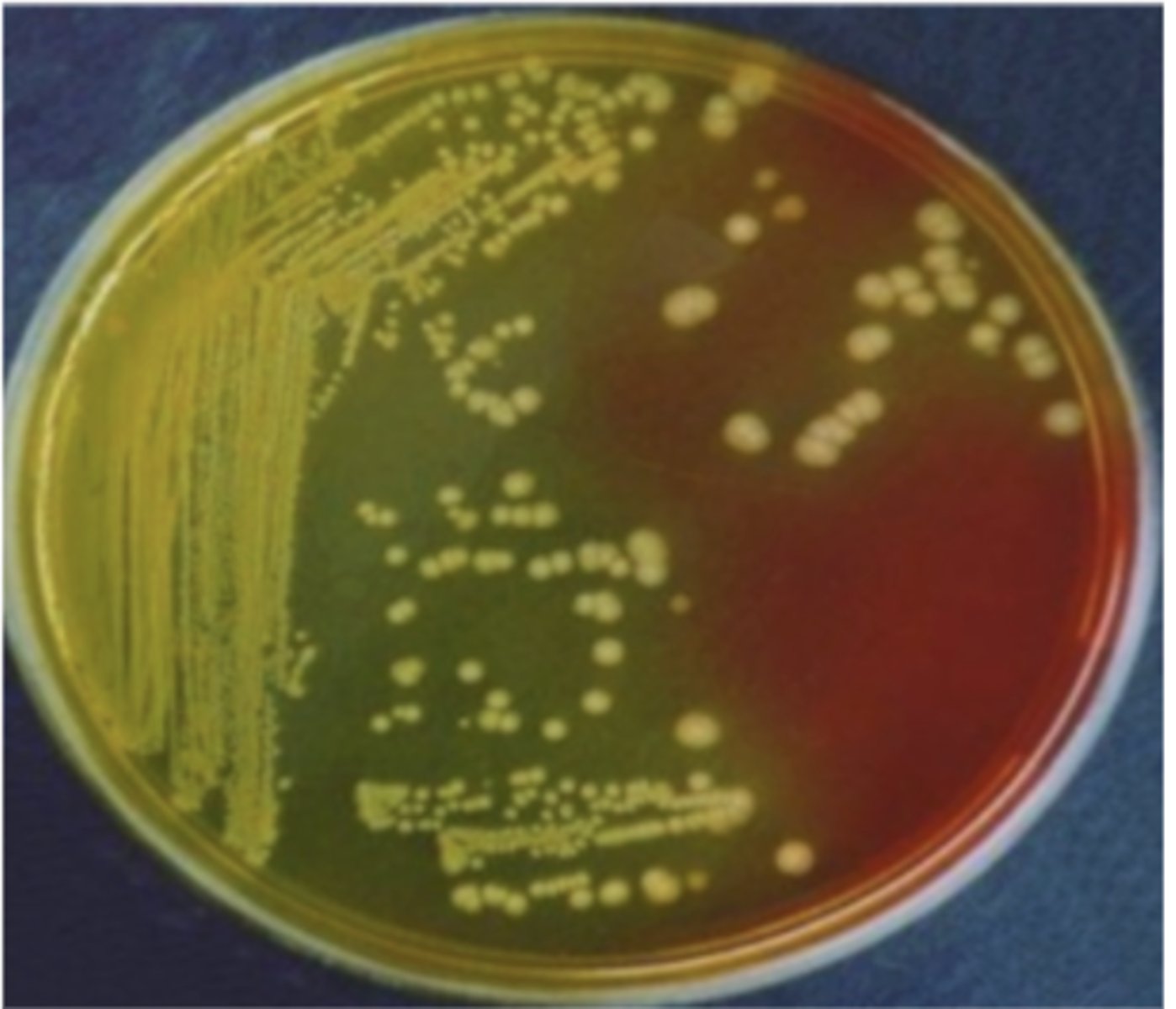
E. coli
which genus of the family Enterobacteriaceae produces metallic colonies on levine agar?
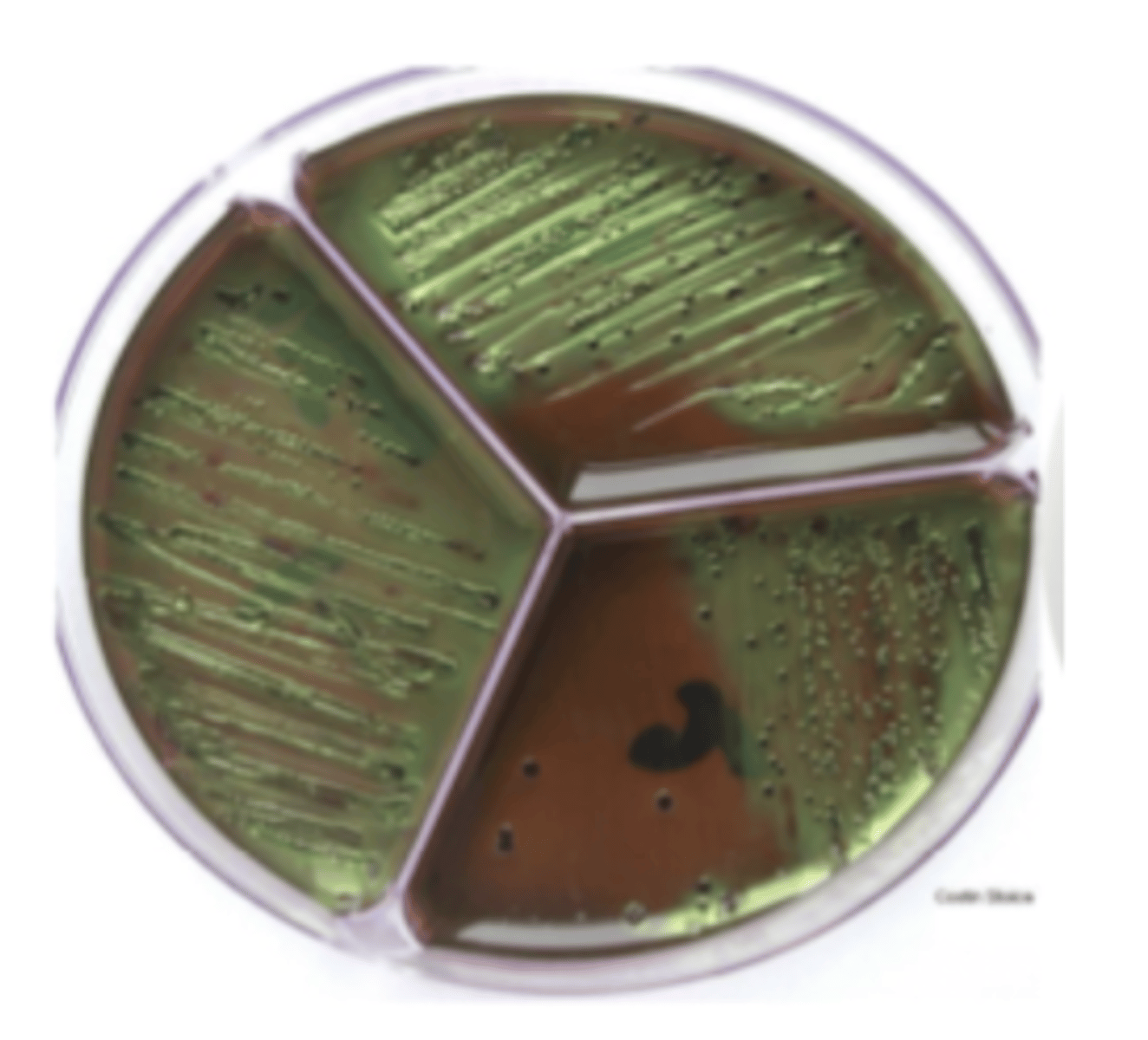
mastitis
reproductive infections
septicemia
what extraintestinal infections can E. coli occasionally produce?
+
is E. coli indole + or -?
A (+)
which indole result does E. coli produce?
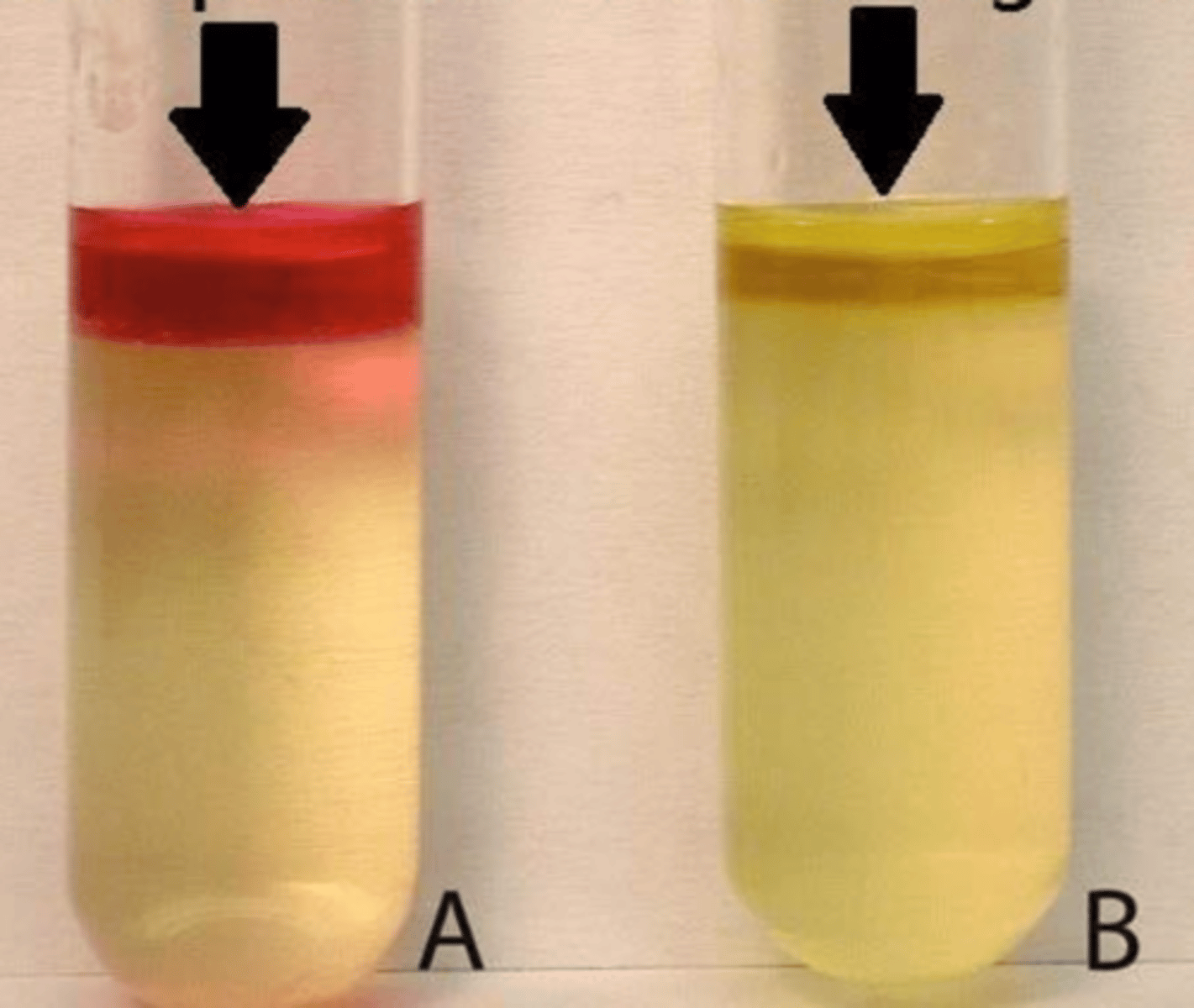

B (-)
which indole result does Salmonella produce?

it has enterotoxins that affect the function of enterocytes in neonatal and weaned piglets, calves, and lambs
how does Enterotoxic E. coli work pathogenically?
Enterotoxic E. coli (ETEC)
what strains of E. coli does this describe: it's enterotoxins affect the function of enterocytes in neonatal and weaned piglets, calves, and lambs
it invades the enterocyte and multiplies inside of it
how does enteroinvasive E. coli work pathogenically?
enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
which E. coli strain invades the enterocyte and multiplies within it?
enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
which E. coli strain has verotoxins/shiga toxins?
it has verotoxins/shiga toxins that destroys enterocytes and causes septicemia
how does enterohemorrhagic E. coli work?
ruminants
the main reservoir species of enterohemorrhagic E. coli is _________
enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
what E. coli strain most commonly produces septicemia?
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
what type of E. coli produces bloody diarrhea?
bloody diarrhea
what type of diarrhea does enterohemorrhagic E. coli cause?
it produces an aggregation of E. coli, eliminates microvilli, and produces enterotoxins
how does enteroaggregative E. coli work pathogenically?
yes
does enteroaggregative E. coli produce enterotoxins?
watery mucoid diarrhea, sometimes with traces of blood
what type of diarrhea does enteroaggregative E. coli cause?
it adheres to enterocytes and causes elongation of their microvilli
how does attaching and effacing E. coli work?
enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC)
enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
which strain of E. coli produce watery diarrhea?
because it can cause septicemia
this is most common with enterohemorrhagic E. coli
why can E. coli cause pulmonary fibrosis? which strain is most likely to cause this?
Attaching and effacing E. coli (AEEC)
which E. coli strain causes elongation of the microvilli on enterocytes?
E. coli
because it ferments both lactose and glucose
which genus of family Enterobacteriaceae produces this result in a TSI test?

lactose and glucose
what carbohydrates does E. coli ferment?
Salmonella Typhimurium
Salmonella Enteriditis
what are the 2 serotypes in the genus Salmonella?
fecal-oral route, usually feces with Salmonella contaminates food/water that is then ingested
how does salmonella enter the body?
it attaches to enterocytes and penetrates them, and then replicate in their vesicles and become engulfed by macrophages
after the entrance of Salmonella via ingestion, what does it do?
yes
can Salmonella produce septicemia?
Salmonella
which genus of family Enterobacteriaceae commonly causes subclinical infections, where the bacteria remains latent in the lymph nodes, but can be activated by stress?
stress; acute fatal septicemia
if Salmonella becomes latent in the lymph nodes of its host, it can be triggered by _____ and cause ______
yes, it has LPS, an endotoxin that causes a local inflammatory response, leading to damage to intestinal epithelial cells
does Salmonella have toxins?
diarrhea
food poisoning
septicemia
abortion
what are the clinical signs of Salmonella?
Salmonella
which bacteria belonging to family Enterobacteriaceae produces pink colonies on brilliant green (BG) agar?
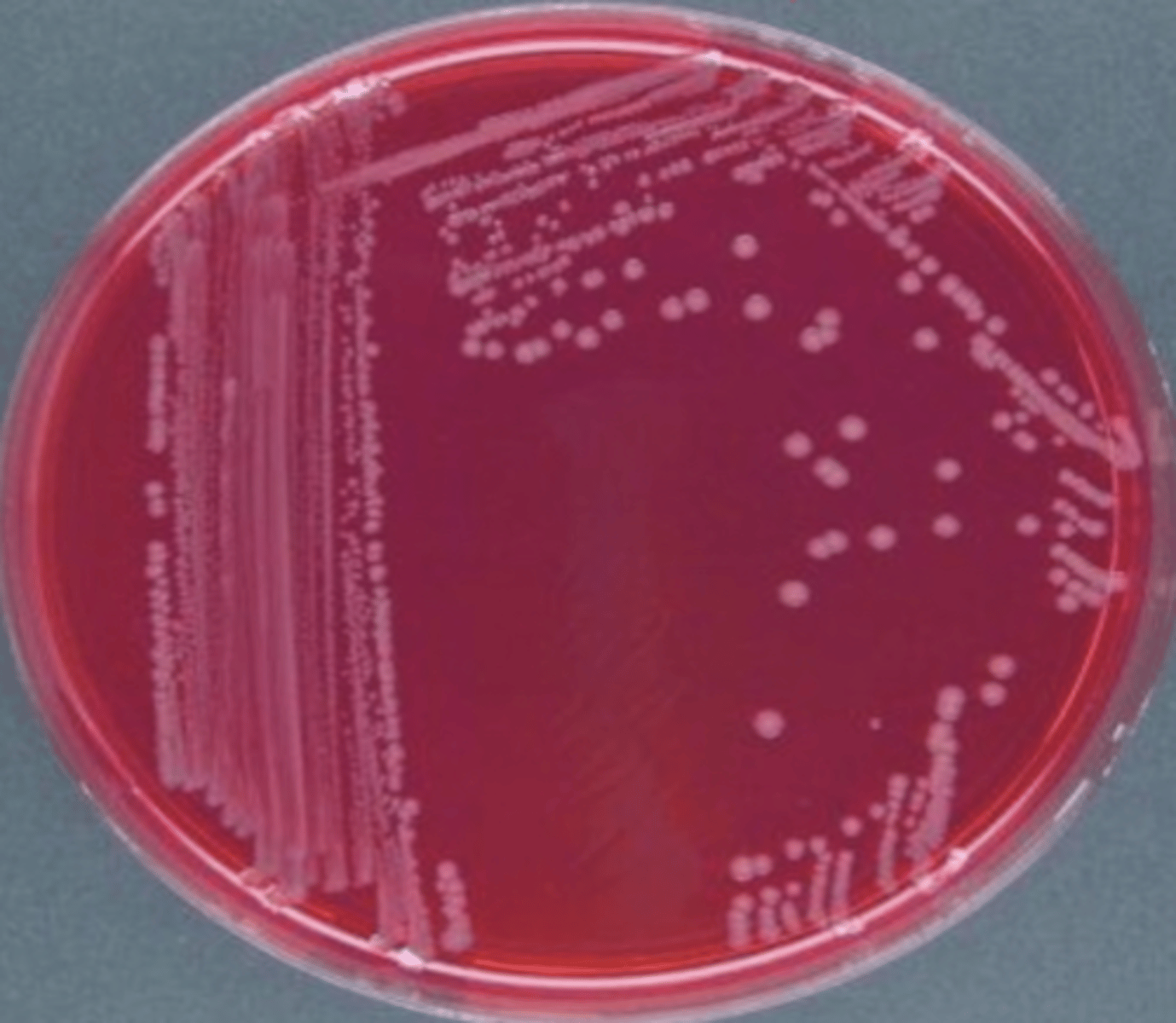
yellow
which type of reaction does Salmonella produce on Macconkey agar?

Salmonella- it is lactose -
which enterobacteria causes this result on Macconkey agar?
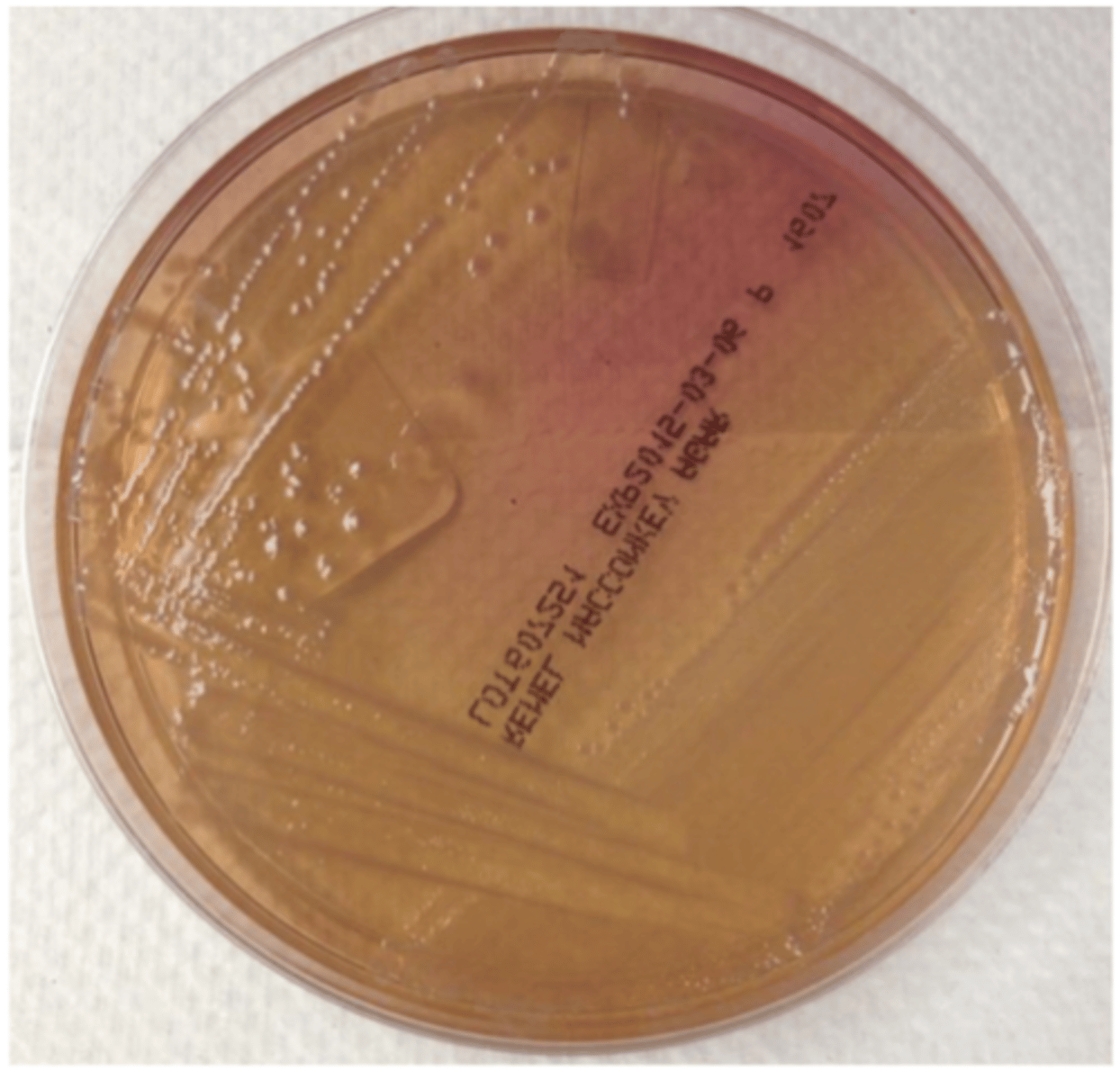
yes
can all bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae grow on macconkey agar?
-; produces a yellow macconkey
is Salmonella lactose + or -? what reaction does this produce on macconkey agar?
+; produces a pink macconkey
is E. coli lactose + or -? what reaction does this produce on macconkey agar?
Salmonella
which Enterobaceriaceae produces black colonies on XLD agar?

Salmonella
the purple colonies on this ASAP agar plate are what bacteria?
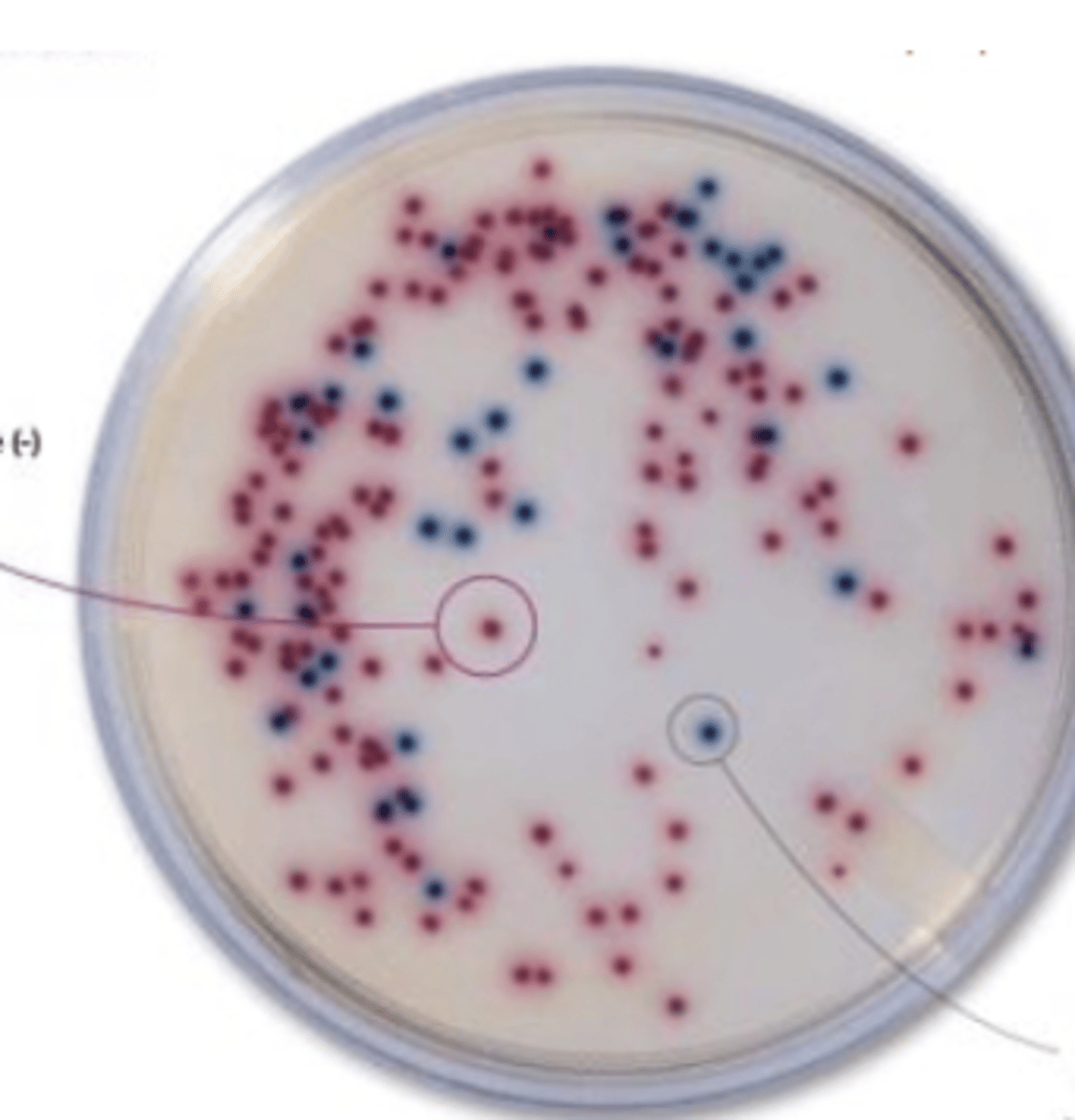
-
is Salmonella indole + or -?
the left 2 tubes- black
because it produces H2S and ferments glucose
which TSI test does Salmonella produce? why?

yes, all bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae ferments glucose
does Salmonella ferment glucose?
Salmonella- it both ferments glucose and produces H2S
which genus in family Enterobacteriaceae produces this TSI result?

Y. pestis
Y. pseudotuberculosis
Y. enterocolitica
what 3 species do we study in the genus Yersinia?
flea and rat bites, sometimes cat bites and scratches
how is Yersinia pestis transmitted?
bubonic plague
pneumonic plague
which well-known diseases are caused by Yersinia pestis?
Yersinia pestis
what bacteria causes bubonic plague and pneumonic plague?
Yersinia- it only ferments glucose
what bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae produces this result with a TSI test?
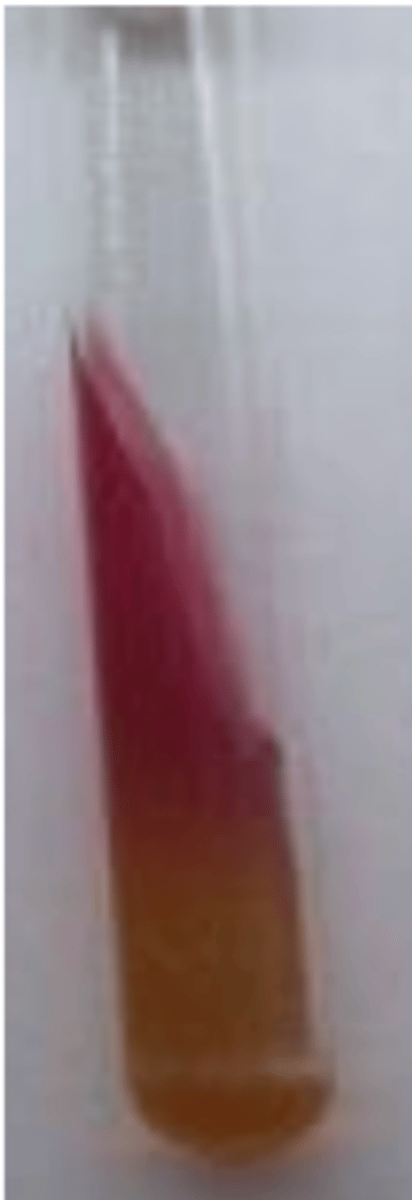

Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
(acute necrotizing enteritis is a type of pseudotuberculosis)
which enterobacteria causes acute necrotizing enteritis in wild rodents, lagomorphs, and birds?
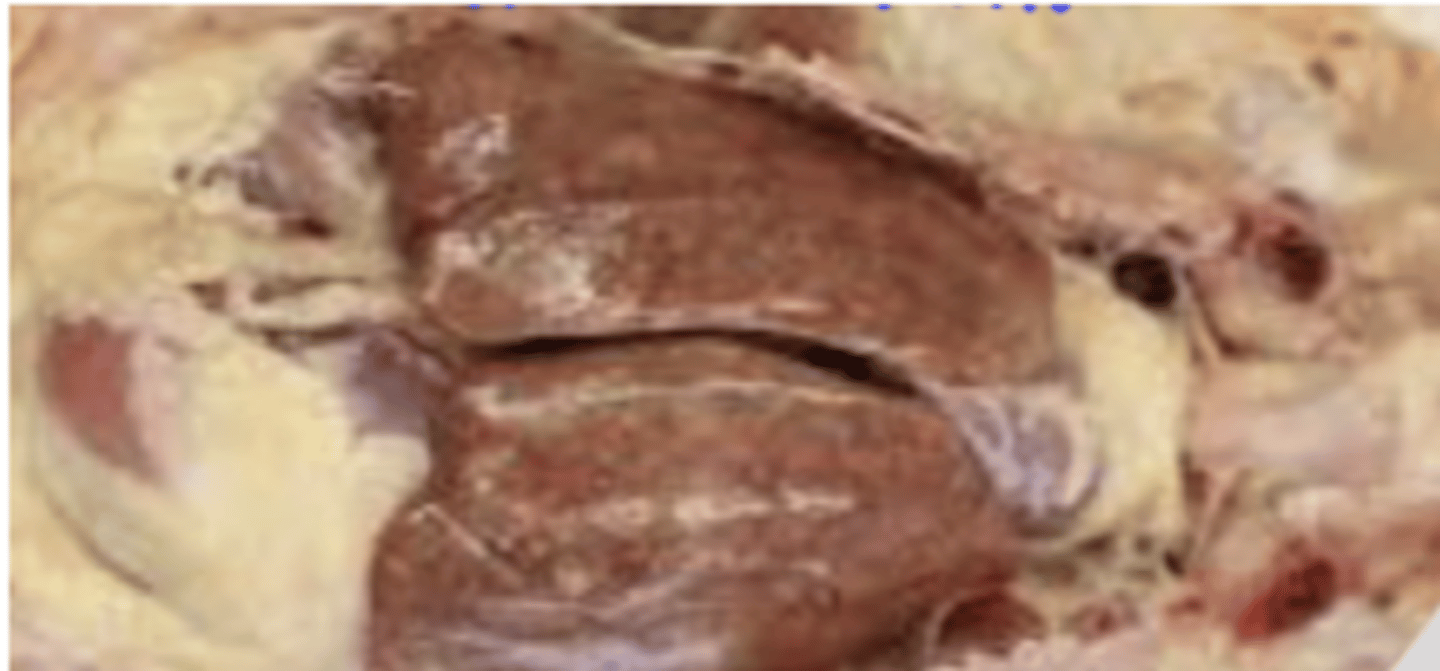
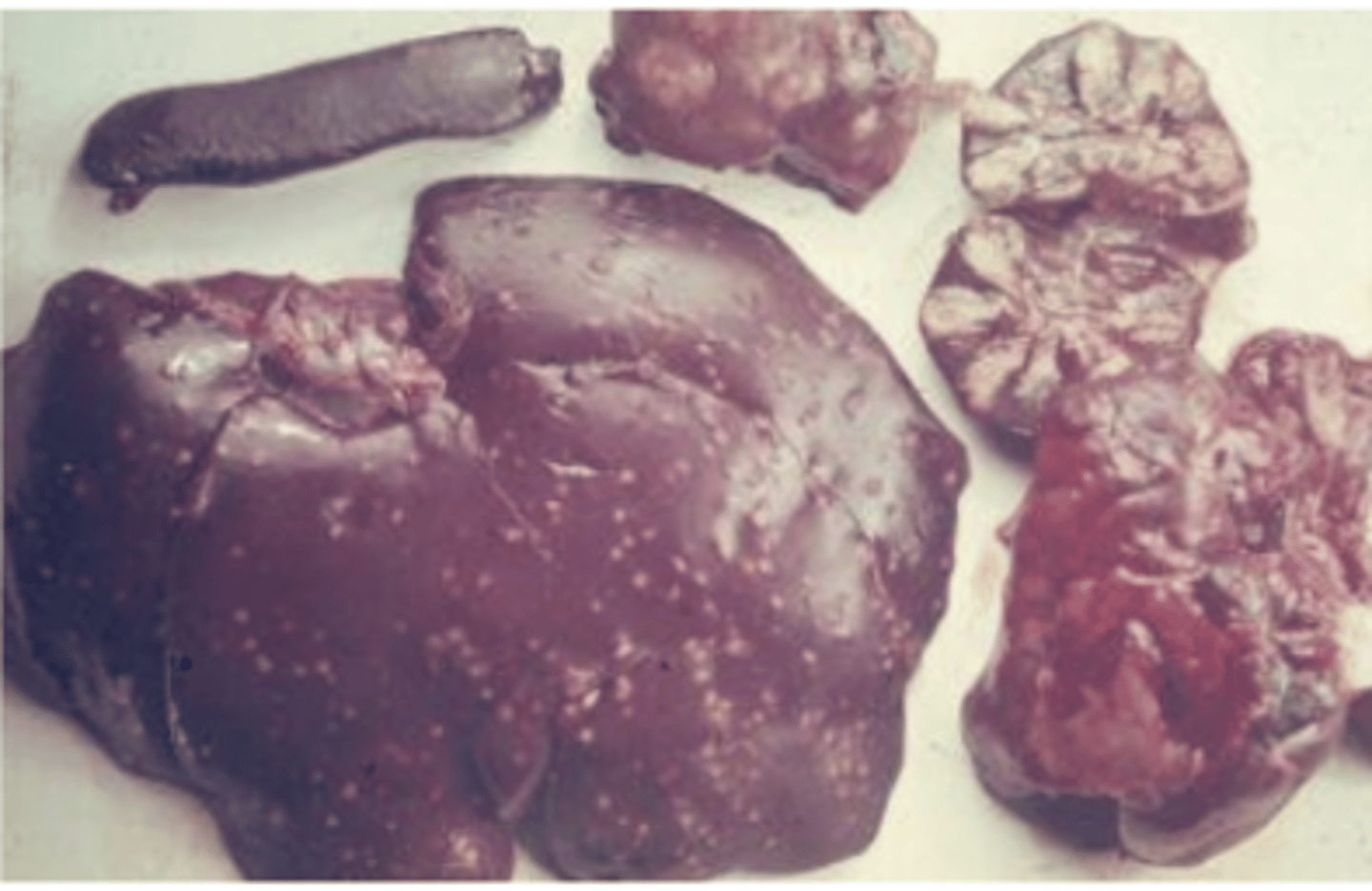
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
what enterobacteria causes these granulomas?

ingestion
how is Yersinia pseudotuberculosis transmitted?
ingestion
how is Yersinia enterocolitica transmitted?
Yersinia pestis
which enterobacteria is transmitted by flea, rat, and cat bites and scratches?
acute necrotizing enteritis/pseudotuberculosis
wild rodents, lagomorphs, and birds
what is the clinical disease of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and which animals does it more commonly effect?
no
does Yersinia ferment lactose?
Y. enterocolitis
what Yersinia species causes a latent infection, with ability to become acute gastroenteritis?
Y. pestis
which is the most invasive species of Yersinia?
it has an antiphagocytic protein capsule and a plasminogen activator that helps systemic spread
what factors make Yersinia pestis so invasive?
it can do both, it is facultatively intracellular
does the bacteria Yersinia replicate inside or outside of cells?
mesenteric lymph nodes
Yersinia is engulfed by macrophages and transported to ________
P. mirabilis
P. vulgaris
what are the 2 important species of the genus Proteus?
false- these species rarely cause enteric disease in domestic animals, they are normal microbiota of the animal's GI tract and can sometimes, but rarely, cause localized infection
true or false: Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Klebsiella pneumoniae are all enterobacteria that are a common cause of enteric disease in domestic animals
Enterobacter
Proteus
Klebsiella
which bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae are opportunistic pathogens- normally living in the GI tract of animals, but certain situations can cause overgrowth, which will lead to a localized infection?
coliform mastitis in cows and sows
what clinical disease can be caused by Enterobacter aerogenes?
Enterobacter aerogenes
which bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae can cause coliform mastitis in cows and sows when conditions cause its overgrowth?
Proteus mirabilis and vulgaris
what bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae has the potential to cause UTIs in dogs and horses and otitis externa in dogs?
Proteus mirabilis/vulgaris
which enterobacteria can cause otitis externa in dogs?
intercurrent infection
tissue devitalization
inherent vulnerability of certain organs
what factors predispose an animal for clinical disease by Enterobacter, Proteus, or Klebsiella?
a capsular material that inhibits phagocytosis
adhesins that allow attachment (especially in the urinary tract)
LPS- causes inflammatory response, which leads to pyrexia, endothelial damage, and microthrombosis
what are the pathogenic factors that Proteus
Enterobacter and
Klebsiella have?
urinary tract
Proteus, Enterobacter, and Klebsiella have adhesins that allow attachment to host cells, especially in what part of the body?