biodiversity exam 3
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
angiosperms
flowering plants; produce seeds enclosed in fruit. Most diverse plant group. divived between two clades -eudicots and -monocots
Eudicots
major group of angiosperms; have two seed leaves (Cotyledons), net-like veins, and flower pedals in 4 or 5
monocots
one sed leaf(cotyledon), parallel leaf vein(bundles of vascular tissues), fibrous roots, and flower pedals in muliples of 3

Monocot or Eudicot?
Monocot-Becasue flower parts in multiples of 3 (6 petals), parallel leaf veins - common in monocot
and 1 cotyledon
this is a lily flower
pollen
male gametophyte; carries sperm cells to the female ovule
fruit
matrure ovary of a flower, proects and aids in seed disperal
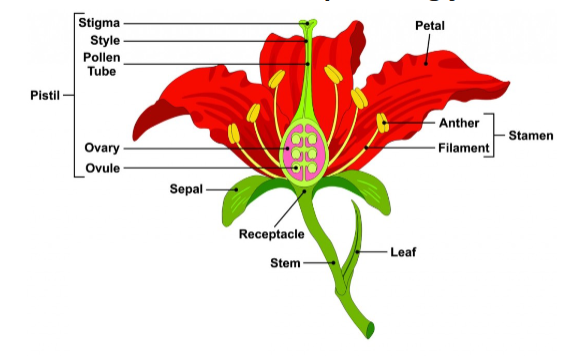
flower anatomy
Sepals (protect bud), Petals (attract pollinators), Stamens (male—anther + filament), Carpels/Pistil (female—stigma, style, ovary).
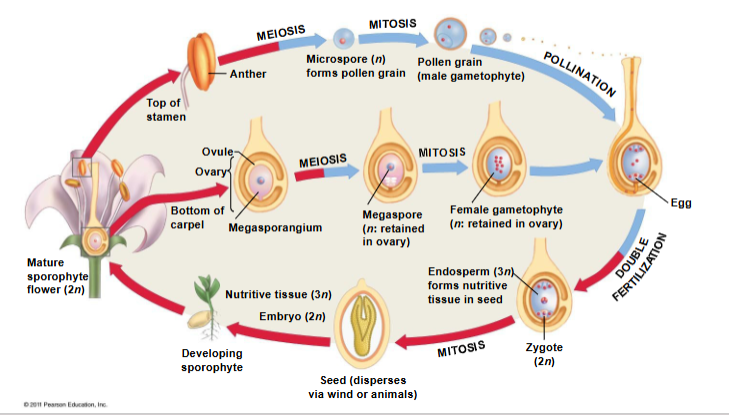
flower reproduction
Pollination: Transfer of pollen to stigma.
Fertilization: Sperm fertilizes egg to form zygote.
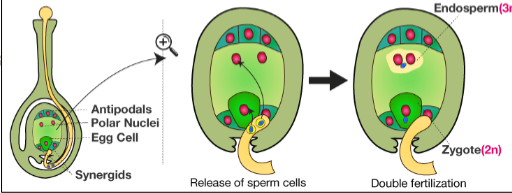
Double Fertilization: One sperm → egg (zygote), other sperm → central cell (endosperm = nutrition for embryo).
Fungi anatomy
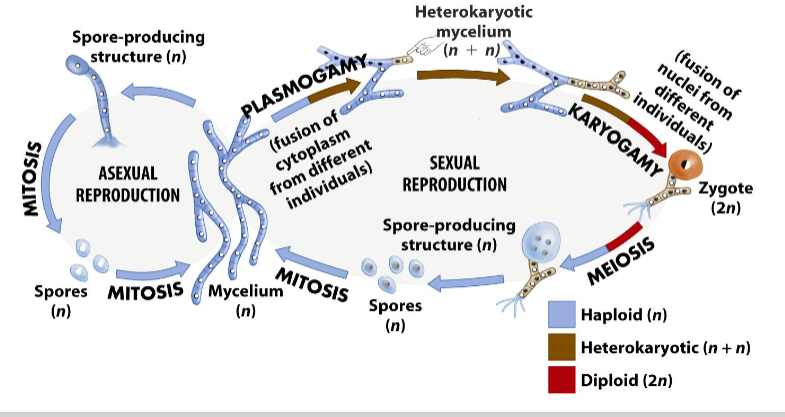
Made of hyphae (threadlike filaments) forming a mycelium.
Cell walls of chitin. Absorb nutrients externally (heterotrophs).
Fungi reproductive cycle
Can reproduce sexually (via spores from meiosis) or asexually (by budding or spore production).
Often alternate between haploid, dikaryotic, and diploid stages.
What is the ecological role of fungi?
Decomposers (recycle nutrients), mutualists, and pathogens.
Critical for nutrient cycling and plant health.
what are the major groups of fungi?
Basidiomycota: Club fungi—mushrooms, puffballs. Produce spores on basidia.
Ascomycota: Sac fungi—yeast, molds, morels. Produce spores in asci.
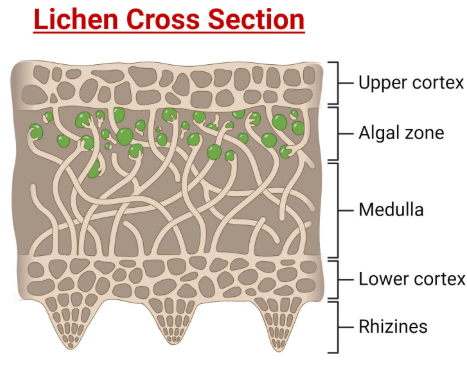
Lichens
Symbiosis between fungus (structure) and alga or cyanobacterium (photosynthesis).
Important colonizers of bare rock and nutrient-poor environments.
mycorrhizal associations
Ectomycorrhizae: Fungus forms sheath around roots; exchange nutrients with plant.
Endomycorrhizae (Arbuscular): Fungal hyphae penetrate root cells.
Function: Help plants absorb water/minerals; fungus gains carbohydrates.
ECTOmycorrhizal
Fungus forms sheath around roots; exchange nutrients with plant.
OUTSIDE OF CELL
ENDOmycorrhizal
: Fungal hyphae penetrate root cells.
INSIDE OF CELL
Parasitic Fungi
feed on living organism, sometimes causing disease
White - nose syndrome
Fungal disease affecting bats, caused by Pseudogymnoascus destructans; disrupts hibernation and causes high mortality.
What are the stages of animal development?
Zygote → Cleavage → Blastula → Gastrula → Organogenesis.
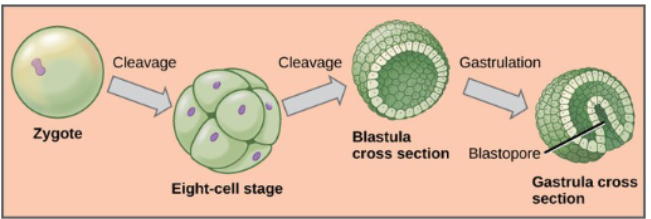
Animal development - evolution of tissues
No true tissues: Sponges (Porifera).
Diploblastic: Two layers (ectoderm & endoderm) — Cnidaria.
Triploblastic: Three layers (adds mesoderm) — all other animals.
what is double fertilization?
One sperm fertilizes egg → zygote; other fertilizes central cell → endosperm (nutritive tissue).
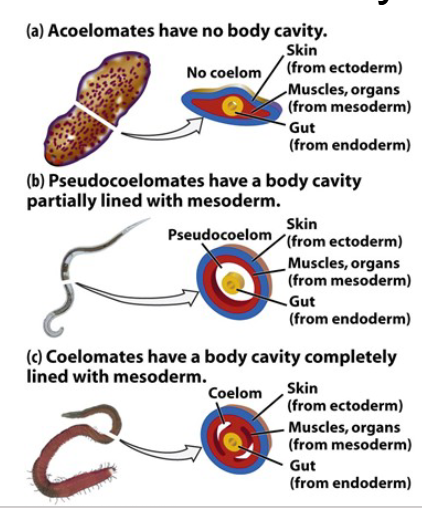
Evolution of body cavities
Coelom-body cavity
Acoelomate: No body cavity (flatworms).
Pseudocoelomate: Cavity not fully lined with mesoderm (nematodes).
Coelomate: True coelom fully lined by mesoderm (earthworms, humans).
evolution of symmetry
Asymmetrical: No symmetry (sponges).
Radial: Symmetry around central axis (jellyfish).
Bilateral: Two mirrored sides; allows cephalization (most animals).
Porifera
Sponges
Unique Traits: No true tissues/organs; filter feeders; sessile adults.
Anatomy: Pores, spongocoel (central cavity), choanocytes (feeding cells).
Ecological Role: Filter water; habitat for microorganisms; reef structure.

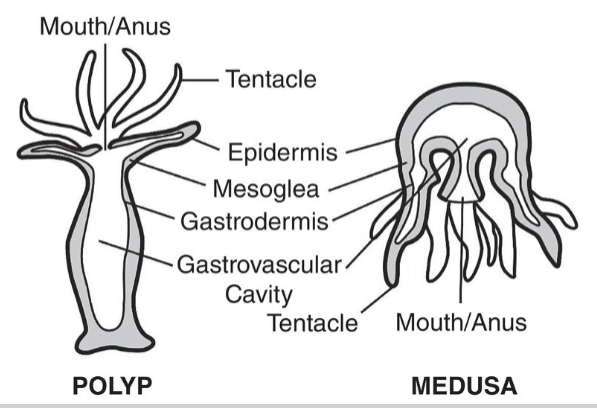
Cnidaria
Unique Traits: Stinging cells (nematocysts), radial symmetry.
Anatomy: Two layers (epidermis, gastrodermis), gastrovascular cavity.
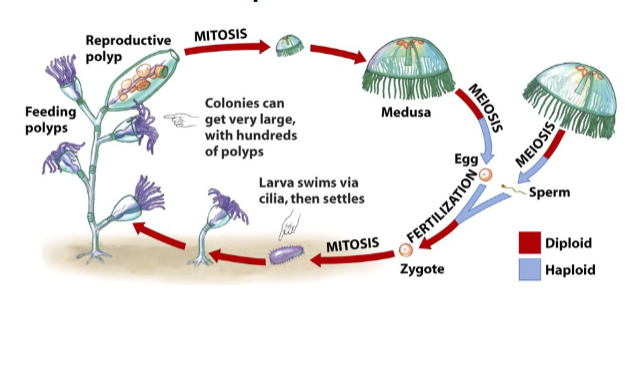
Reproduction: Alternates between polyp (sessile) and medusa (free-swimming) forms.
Diversity: Corals (build reefs), anemones (sessile), Portuguese man-of-war (colonial), jellyfish (medusa).
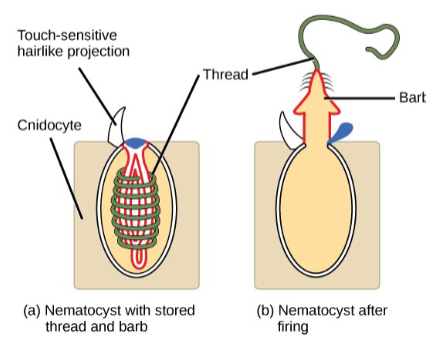
what is a nematocyst
Cnidocyte with nematocyst is
the defining characteristic of the
group.
These cells sting and grab prey.
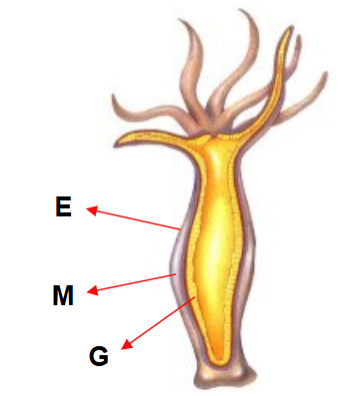
Cnidaria - anatomy
Epidermis (E) : outer layer of the
organism.
Mesoglea (M) : extracellular matrix that
functions as hydrostatic skeleton.
Gastrodermis (G) : inner layer of the
organism.
what is extracellular digestion
enzymes break down food particles and cells of the gastrodermis absorb the nutrients. Digestion in the gastrovascular cavity(only one opening)
characteristic of jellyfish
cnidaria reproduction cycle
Flatworms (Platyhelminthes)
Traits: Acoelomate, bilateral, simple organs, no circulatory system.
Ecology: Free-living (planarians) or parasitic (tapeworms, flukes).
Nematodes (Roundworms
Traits: Pseudocoelomate, complete digestive tract, tough cuticle.
Ecology: Soil decomposers, parasites (e.g., hookworms, C. elegans model organism).
Fungi reproductive cycle
Flower Morphology
flower reproductive cycle