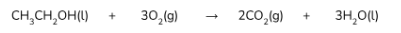Organic Chemistry (until ester naming)
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
General formula for Alkanes
CnH2n+2
1 Carbon
Meth
2 Carbons
Eth
3 Carbons
Prop
4 Carbons
But
5 Carbons
Pent
6 Carbons
Hex
7 Carbons
Hept
8 Carbons
Oct
9 Carbons
Non
10 Carbons
Dec
With 4 valence electrons, what are the 4 possibilities for each carbon atom?
➢ 4 single C–C bonds
➢ 2 single C–C bonds and 1 double C=C bond
➢ 1 single C–C bond and 1 triple C≡C bond
➢ 2 double C=C bonds
What is the definition of fossil fuels?
Fuels (including crude oil and natural gas) formed by natural resources such as buried dead organisms, due to heat and pressure acting on these organisms and anaerobic decomposition of these organisms.
What is the definition of crude oil?
A liquid mixture of different hydrocarbons of different molecular weights (that is found in geologic formations beneath Earth’s surface)
What is the definition of Natural Gas?
A naturally occurring hydrocarbon gas mixture, primarily consisting methane (impurities include carbon dioxide). It is typically found above the crude oil layer.
What is the definition of fractional distillation?
A separation technique that is used to separate a liquid mixture comprising of components with different boiling points.
Answer Format: Predict whether CH4 or C8H18 would have a higher boiling point.
C₈H₁₈ would have a higher boiling point than CH₄.
Boiling points increase with increasing Mr due to the larger electron clouds present.
This leads to stronger and more extensive intermolecular forces of attraction,
and more energy is needed to overcome these intermolecular forces of attraction for larger alkanes.
How does fractional distillation separate crude oil into the various components?
At the bottom of the fractionating column, crude oil is heated into vapour.
The vapour is pumped into a fractionating column where it is cool at the top but hot at the bottom.
As the hot vapour rises, it cools down. The smaller hydrocarbons (i.e. the hydrocarbons with lower boiling points) are collected at the top of the fractionating column (as gases) while the larger hydrocarbons (i.e. the hydrocarbons with higher boiling points) are collected at the bottom of the column.
#Smaller hydrocarbon molecules with lower boiling point due to weaker intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules collect at the top of the fractionating column.
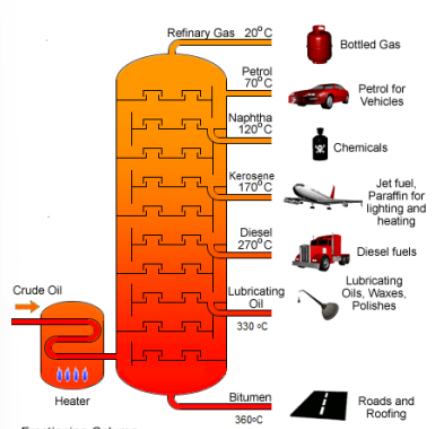
Boiling Points in Fractional Distillation (Top → Bottom)
Refinery Gas
Petrol
Naphtha
Kerosene
Diesel
Lubricating Oil
Bitumen
What is the definition of cracking?
The breaking down of long-chain (or bigger) hydrocarbons into smaller molecules.
Usually done under high temperature.
What is the definition of catalytic cracking?
When a catalyst (Al2O3, SiO2) is used to speed up the cracking process
Why is cracking important?
1. to produce petrol (long-chain hydrocarbons are less flammable).
2. to produce short-chain alkenes (which can be used to manufacture other compounds, e.g.
plastics).
3. to produce hydrogen (source of clean fuel) e.g. Toyota fuel cell cars
Eg. of Cracking
C₁₂H₂₆ → C₄H₈ + C₂H₆ + 3C₂H₄
Due to Principle of conservation of mass, Total C and H atoms in reactants must be equal to Total C and H atoms in products.
What is the definition of fossil fuels?
Non-renewable energy sources, which are energy sources that are finite.
Name some biofuels.
Bioethanol
Biodiesel
Biogas
Advantages of biofuel
• Carbon neutral, renewable and sustainable if crops and trees are replanted
• Reduces greenhouse emissions and pollution
• Biofuel production could provide money for less developed countries as they have the space to grow the crops required
• Provides jobs in the agriculture and energy sectors
Disadvantages of biofuel
• Many developed countries don't have the space to be able to produce enough plants to make biofuels because the land is needed for food production
• For bioethanol to be burnt in a car engine, some engine modification is needed, although (most) modern petrol engines can use petrol containing up to ten per cent ethanol without needing any modifications
• Although biofuels are in theory themselves carbon neutral, this does not take into account the carbon dioxide emissions associated with growing, harvesting and transporting the crops, or producing the ethanol from them
What is the definition of saturated and unsaturated compounds?
Saturated compounds have only single (C – C) bonds between their atoms.
Unsaturated compounds have double or triple bonds (π bonds) between their atoms.
What is the definition of a functional group?
an atom or group of atoms common to a series of organic compounds that determines the chemical properties of the series
What is the definition of a homologous series?
a series compounds with the same functional group and same general formula.
What are some similarities of those in the same homologous series?
Can be represented by a general molecular formula
Differ in formula by a constant –CH2– unit
Exhibit similar chemical properties but different physical properties
General formula for Alkenes
CnH2n
General formula for Halogenoalkanes
CnH2n+1X,
where X is –Cl, –Br or –I
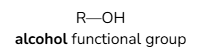
General formula for alcohols
CnH2n+1OH
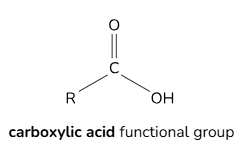
General formula for carboxylic acids
CnH2n+1COOH
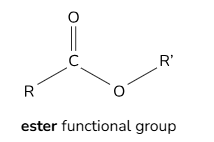
General formula for esters
RCOOR’
Functional groups of alkanes
None
Functional groups of Alkenes
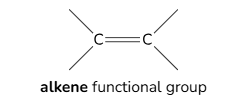
Functional groups of Halogenoalkanes
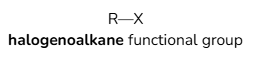
Functional groups of alcohols
Functional groups of carboxylic acids
Functional groups for esters
What is the definition of a structural formula?
the sequence in which the atoms are bonded to each other, for an unambiguous structure
e.g.
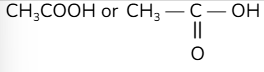
What is the definition of displayed formula/full structural formula?
the relative placing of all atoms and number of bonds between the atoms in the molecule. All bonds would have to be shown clearly.
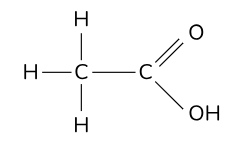
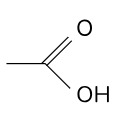
What is the definition of a skeletal formula?
derived from the structural formula. When writing the skeletal formula, the H and C atoms are removed, leaving just the C – C bonds in the skeleton and the associated functional groups
What are the types of organic reactions?
Addition (2 to 1)
Substitution (becomes conjoined with Br, etc)
Elimination (1 to 2)
Condensation (forms water or other small molecules)
What is the definition of addition?
Reaction where two reagents react to form a single product.
What is the definition of substitution?
Reaction where one atom or a group of atoms is substituted by another atom, group of atoms, or ion.
What is the definition of elimination?
Reaction involving the removal (elimination) of an atom or group of atoms from a single reactant molecule.
What is the definition of condensation?
Reaction involving two or more reactants to yield a product, with the formation of water or some other small molecule
What is the definition of isomer?
compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formula.
What are the type of constitutional/structural isomerism?
same molecular formula
different structural formula
There are:
chain
positional
functional group
What is chain isomerism?
Different arrangement of carbon chain
e.g. Butane and 2-methylpropane
What is positional isomerism?
Different positions of the same functional group on a carbon chain
e.g. Propan-1-ol and Propan-2-ol
What is functional group isomerism?
Different functional groups present
e.g. ethanoic acid and methyl methanoate
#Carboxylic acids and esters are functional group isomers.
Common Lab Techniques for Organic Reactions
Heating under reflux → to minimize loss of reactants due to vapourisation
Distillation → used when product is more volatile than reactants + components have different boiling points
Extraction using Separatory funnel → used when two solvents are immiscible
Recrystallisation → used when compounds in a particular solvent have different solubilities
How are branched chain alkanes formed?
Branched chain alkanes are formed when one (or many) of the H atoms of the straight chain alkanes is/ are replaced with one (or many) alkyl groups.
How are alkyl groups different from alkanes?
Alkyl groups, with general formula -CnH2n+1, are named by replacing -ane with -yl.
Alkyl general formula
-CnH2n+1
ANSWER:
Using structure, why do alkanes have low melting and boiling points?
Due to their simple molecular structures, low amount of energy is required to overcome the weak van der Waals’ forces of attraction between molecules.
ANSWER: How does boiling point change across alkanes?
Boiling points of alkanes increase with increasing Mr due to the larger electron cloud size.
There is greater distortion of electron cloud and stronger, more extensive intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules,
which requires more energy to be overcome.
ANSWER: Do straight chain alkanes or branched chain alkanes have a higher boiling point?
Branched chain alkanes have a lower boiling point.
This is because they have decreased surface area of contact,
which leads to lower extensiveness of weak intermolecular forces of attraction,
that requires less energy to overcome.
What is viscosity?
A measure of a fluid’s resistance to a change in shape or to flow.
ANSWER: How does viscosity change through alkanes?
Viscosity increases as the size of electron cloud increases with Mr
because the intermolecular forces of attraction between stronger and more extensive
which causes the liquid to flow less readily
ANSWER: What reactions can alkanes undergo?
Combustion
a. exothermic → used as fuel
b. complete = CO2 and H2O as products
c. incomplete = CO and H2O as products
Substitution (Halogenation)
a.
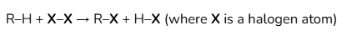
b. can use Cl, Br, I and F
ANSWER: Substitution of Alkanes (halogenation)
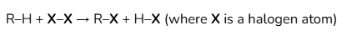
When substitution with (limited) Cl under UV light → decolourisation of greenish-yellow Cl2 + steamy acidic HCl gas fumes formed
When further substitution with (excess) Cl under UV light → multiple substituted products
When substitution with (limited) Br under UV light → decolourisation of reddish-brown Br2 + steamy acidic HCl gas fumes formed
What is the definition of a cycloalkane?
Cycloalkanes are saturated alkanes with a ring structure and the general formula CnH2n.
(shows functional group isomerism with alkenes)
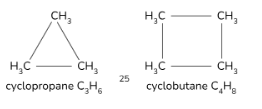
Cycloalkane general formula
CnH2n
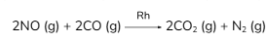
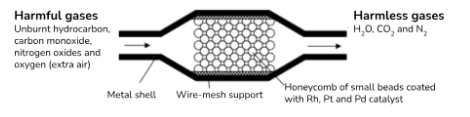
What is a catalytic converter?
exhaust system of motor vehicles converts harmful (CO, NO2, unburnt hydrocarbons) into harmless (H2O, CO2, N2) in presence of suitable catalyst
Lead poisons/deactivates catalyst so cars with it must be run on unleaded petrol
NOx is reduced to N2 by excess CO with Rh (rhodium) as catalyst
Unburnt hydrocarbons and CO are oxidised to CO2 and H2O with Pt and Pd as catalysts
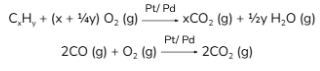
What is a parent chain of an alkene?
longest continuous chain that contains all functional groups
numbered starting from end closest to double bond
alkenes with 4 or more carbon atoms exhibit constitutional isomerism
ANSWER:
Using structure, why do alkenes have low melting and boiling points?
Due to their simple molecular structures, low amount of energy is required to overcome the weak van der Waals’ forces of attraction between molecules.
ANSWER: How does boiling point change across alkenes?
Boiling points of alkenes increase with increasing Mr due to the larger electron cloud size.
There is greater distortion of electron cloud and stronger, more extensive intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules,
which requires more energy to be overcome.
ANSWER: Do straight chain alkenes or branched chain alkanes have a higher boiling point?
Branched chain alkenes have a lower boiling point.
This is because they have decreased surface area of contact,
which leads to lower extensiveness of weak intermolecular forces of attraction,
that requires less energy to overcome.
ANSWER: What reactions can alkenes undergo?
Combustion
a. Burn with sootier flame compared to alkanes because they have a higher percentage by mass of C
b. complete = CO2 and H2O as products
c. incomplete = CO and H2O as products
Addition
a. of hydrogen to produce alkanes (hydrogenation)
b. of halogens
c. of steam (hydration)
d. of hydrogen halide (hydrohalogenation)
Oxidation
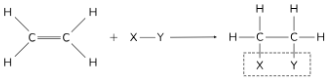
ANSWER: Addition for Alkenes to produce Alkanes (hydrogenation)
Reagents: H2
Reaction Conditions: Ni Catalyst, HTP
Reagents: H2
Reaction Conditions: Pd or Pt Catalyst, RTP
ANSWER: Oxidation Test for Alkenes
Reagents: KMnO4 in dilute H2SO4
Conditions: High heat
Observations: Purple KMnO4 is decolourised
ANSWER: Addition for alkenes of halogens in CCl4 or water to add OH
Reagents: Br2, RTP, in the dark
Observations: decolourisation of orange-red bromine (organic) or orange bromine (aq)
Reagents: Cl2, RTP, in the dark
Observations: decolourisation of pale yellow chlorine
How to distinguish alkenes with alkanes and alcohols
Addition of halogens (bromine) between alkenes WITH alkanes, alcohols
(alkene decolourise bromine while alkanes and alcohols don’t)
ANSWER: Addition for alkenes of steam (hydration) to produce alcohols
Reagents: Steam, Concentrated H3PO4 as catalyst, HTP
Observations: Alcohols formed
ANSWER: Addition for alkenes of hydrogen halide (hydrohalogenation) to produce halogenoalkanes
Reagents: Dry HX (g) or HX in inert organic, RTP
Observations: Halogenoalkanes produced
Alkenes are synthesised by elimination reacts of ..
alcohols in high heat using concentrated H3PO4 as catalyst
What is catalytic cracking?
the use of a catalyst, such as Al2O3 and SiO2, to speed up regular cracking processes
What is polymerisation?
the process whereby small molecular units join together to make very long molecules (macromolecules) called polymers
Alkenes undergo .. polymerisation.
addition
When does addition polymerisation occur?
when monomer units join together without losing any molecules or atoms
How is a polymer represented?
by a repeat unit within square brackets, e.g. [–CH2CH2–]n
What is present within alcohols?
intermolecular forces of attraction
hydrogen bonds between molecules
What is the hydrogen bond between alcohol molecules?
the electrostatic forces of attraction between a H atom covalently bonded to an O (electronegative) atom and a lone pair of electrons on another electronegative atom from another molecule
ANSWER: Why is the boiling point of alcohol higher than hydrocarbons of same Mr?
Due to -OH group that allows for hydrogen bonding between molecules
ANSWER: How does boiling point change across alkanes?
Boiling points of alkanes increase with increasing Mr due to the larger electron cloud size.
There is greater distortion of electron cloud and stronger, more extensive intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules,
which requires more energy to be overcome.
ANSWER: Do straight chain alcohols or branched chain alcohols have a higher boiling point?
Branched chain alcohols have a lower boiling point.
This is because they have decreased surface area of contact,
which leads to lower extensiveness of weak intermolecular forces of attraction,
that requires less energy to overcome.
Alcohols with 3 or more carbon atoms exhibit …
constitutional isomerism
ANSWER: What reactions can alcohols undergo?
Combustion
a. complete = CO2 and H2O as products
b. incomplete = CO and H2O as productsAcid-metal displacement
Oxidation
Condensation
Addition of steam
ANSWER: Alcohols acid-metal displacement
with reactive metals to form ionic salts and hydrogen gas
occurs at RTP
effervescence of H2 that extinguishes a lighted splint with a pop sound
anion forms on the carbon bonded on -OH group

Alcohols do not react with..
bases or carbonates
ANSWER: Oxidation of Alcohols to form carboxylic acids
Reagents: KMnO4 (aq), dilute H2SO4, heat under reflux
Observation: Purple KMnO4 is decolourised
Reagents: K2Cr2O7, dilute H2SO4, heat under reflux
Observation: Orange K2Cr2O7 turns green

What is a primary alcohol?
alcohols where the carbon atom bonded to the -OH group is bonded to two or three hydrogen atoms
Alcohols react with carboxylic acids in condensation reaction to form..
esters
What is fermentation?
Chemical process where microorganisms like yeast convert carbohydrates (e.g., sugars or starch) into ethanol and carbon dioxide
ANSWER: Burning alcohol in excess oxygen