PMI Exam 2 Concepts
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Speech/Resonance Assessment, Instrumental Procedures, Surgical Management in Cleft Lip/Palate, Speech Therapy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What does assessment look like for birth to 3, 3-4, annually, and after puberty to 18?
Birth to 3: SLP, Craniofacial team
3-4: More involved SLP assessment
Annually: depends on severity
After puberty to 18: every 2 years be assessed
Why shouldn’t we wait too long to evaluate and treat VPI?
lots of brain development at 3-4
critical time for learning
less mislearnings
What is the order of a speech/resonance assessment?
1) Diagnostic interview
2) Perceptual assessment goals
3) Instrumental assessment
What are language screenings used for?
identify risk of language delay
formal vs informal screening
Perceptual assessment order:
single sounds
syllables
counting
sentence
conversational speech
Why is single word perceptual assessment not advised?
Coarticulation is used more
Perceptual assessment: single sounds
How to test for: hypernasality, nasal emission, hyponasality/cul-de-sac resonance?
hypernasality: child prolongs a vowel
nasal emission: child prolongs /s/
hyponasality/cul-de-sac resonance: child prolongs /m/
Perceptual assessment: syllables
How to test for: hypernasality, nasal emission, hyponasality/cul-de-sac resonance, speech sound production?
hypernasality: repeat syllables of voiced consonants - ba
nasal emission: repeat syllables of voiceless consonants - pa, sa
hyponasality/cul-de-sac resonance: repeat syllables with nasal sounds - na, ma
speech sound production: helps assess obligatory vs compensatory error
Perceptual assessment: counting
How to test for: hypernasality and nasal emission, hyponasality?
hypernasality/nasal emission: count 60-69 - taxes VP port
hyponasality: count 90-99 - /n/ in connected speech
What should your tests/passages include to assess nasality?
Each sentence should have phonemes with the same placement
How do you elicit spontaneous conversational speech in perceptual assessment?
Verbal sequencing
What do you do if the client is shy during the conversation part of the perceptual assessment?
Use parent/sibling
What should be evaluated for speech sound production, nasal emission, resonance, and phonation?
Speech sound production: artic
Nasal Emission
Resonance: hypo vs hyper
Phonation: voicing, volume
When evaluating speech production, what errors could be present?
Placement, phonological, developmental
With structural anomalies, determine the presence of obligatory distortions and compensatory errors?
Obligatory: VPI, cleft palate
Compensatory: glottal stop, pharyngeal fricative
When assessing nasal emission, what should be learned?
Type
Inaudible: large gap
Audible: medium gap
Nasal rustle: small gap
Weak/omitted consonants
Short utterance length: 60-70 in 1 breath
Nasal grimace
How to determine differential diagnosis of nasal rustle?
Abnormal structure vs abnormal function
structure: small VP gap
function: posterior nasal fricative
What is the most important to determine in resonance evaluations?
Type of resonance or severity
What are the rating scales for resonance?
7 point scale
6 point scale: normal, mild, mild-mod, mod, mod-severe, severe
4 point scale: normal, mild, moderate, severe
2 point scale: normal, abnormal
Why are resonance rating scales unreliable?
Everyone hears things differently; rating severity DOES NOT matter
What are supplemental evaluation procedures for visual detection?
dental mirror: not reliable; if fogs up then some nasal emission
air paddle: if paper flutters then nasal emission; only works well with a lot of nasal emission
see-scape: if ball moves then nasal emission, can see feedback
What are supplemental evaluation procedures for tactile detection?
Feeling sides of nose (need lots of nasal emission to feel)
What are supplemental evaluation procedures for auditory detection?
cul-de-sac test (hold sides of nose shut) - tests hypernasality
stephoscope
straw
listening tube
What recommendations should be given for VPI and VP mislearning after assessment?
VPI+resonance disorders
surgery/prosthesis
speech therapy (as needed) after correction for compensatory productions
VP mislearning
speech therapy
What are the best supplemental evaluation procedures?
straw or tubes
SLPs diagnoses the ___ and ___ of speech/resonance disorder?
type and cause
What should always be done as part of a speech or resonance eval?
Examination of oral cavity (oral mech exam)
What does a examination of the oral cavity evaluate and not evaluate?
Evaluate
oral structures, oral function
view well below area of closure
Not Evaluate
VP structure, VP function
What tools are used for an intraoral exam?
gloves
flashlight
dental mirror
tongue blades
sanitizing wipes
hand sanitizer
How should one position a patient for an oral exam?
get the right position
for toddlers/infants:
place in parent’s lap facing parent
have child lay back so head is over parents knees
sit across from parent
close child’s nose if necessary
How does crying help during an oral exam?
Can see inside mouth
What does our oral motor assessment consist of?
Patient says /ae/
Sticks out their tongue and try touching chin with tongue during phonation
Use palatal palpation
Use dental mirror/blade to see in mouth and all the parts of mouth
What are signs of oral-motor dysfunction?
drooling
open-mouth posture/dropped jaw
anterior tongue position
history of feeding problems
difficulty executing oral-motor movements
Why should we palpate the palate?
To find submucous cleft
Only felt if cleft extends all the way to the bone of the hard palate
Speech therapy should began after ____ ______ are resolved?
structural abnormalities
What are the types of instrumental measures?
Indirect (does not visualize VP structures)
nasometry
aerodynamics
Direct (visualizes VP structures)
videofluoroscopy
nasopharyngoscopy
What does nasometry provide?
Evaluation of resonance and VP function
Provides biofeedback during treatment
Hand-held separator
Shows scores on nasogram
What equipment is involved in nasometry?
Nasal microphone, oral microphone, nasometer interface box, computer
What is the difference between the old and new version of the equipment in nasometry?
Old: headset
New: hand-held separator
What standardized passages are used for nasometry in adults?
Zoo, Rainbow, Nasal
What standardized passages are used for nasometry in kids?
MacKay-Kummer Simplified Nasometric Assessment Procedures revised (SNAP-R)
What score is compared to normative data for the passage?
nasalance
What is the display of speech signals created from nasometry?
nasogram; data points of what child said
What does high vs low scores mean in nasalance?
High means -> hypernasal/audible nasal emission
Low means -> hyponasal
What are the expected results of nasalance?
Normal: less than 20%
Mild Hypernasal/nasal emission: 30-40%
Clear hypernasality: greater than 40%
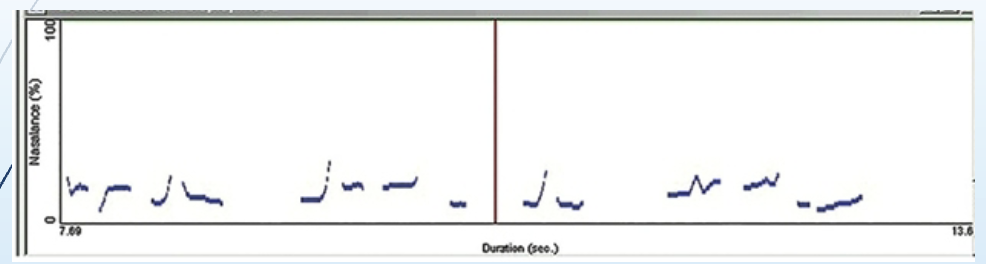
Is this nasogram normal, nasal emission, or hypernasality?
normal

Is this nasogram normal, nasal emission, or hypernasality?
hypernasality
What does hypernasal speech look like on a nasogram?
High solid and dotted lines
What does hyponasal speech look like on a nasogram?
Low solid and dotted lines
What does videofluoroscopy (VSS) show?
Confirm presence of VP opening and size
Differentiate cause of VP dysfunction
Shows view of entire PPW
What are the most common views of VSS?
lateral, frontal/anterior-posterior (AP), base
What does a lateral view of videofluoroscopy show?
Lay down on side/sit up; shows velum and PPW in left/right plane
What does a frontal (AP) view of videofluoroscopy show?
Lay down flat/sit up; shows LPW at rest and during speech
What does a base view of videofluoroscopy show?
Lay in sphinx position; shows perimeter of VP port
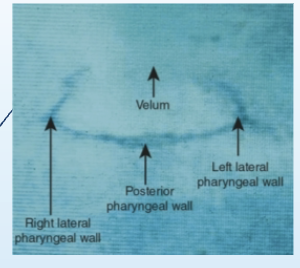
Is this image a lateral, frontal (AP), or base view?
Base view
Who interprets videofluoroscopy?
Radiologist and SLP
How do videofluoroscopy and nasopharyngoscopy differ?
Videofluoroscopy: uses barium and radiation so used less often, shows entire view of PPW including velum contracts the PPW during speech
Nasopharyngoscopy: camera down throat, great view of all structures, no radiation, very expensive and requires cooperation
What can be seen in nasopharyngoscopy?
Can see the size, location, probable cause of VPI
VP gap in midline = defect in velum
Nasal surface of velum can show submucous cleft
Nasal surface of hard palate can show size + extent of oronasal fistula
What equipment does nasopharyngoscopy use?
Flexible fiberoptic endoscope. Size of scope ranges from 2.2 mm to almost 5 mm in diameter
Eyepiece with a lever for moving the tip of the scope
Specially designed camera that attaches to the eye piece
External microphone
How is the scope passed during nasopharyngoscopy?
inserted through largest nostril
scope guided up and over inferior turbinate through middle meatus (biggest)
once scope in nasopharynx, turn down with lever so that it is perpendicular to the opening
can be rotated slightly from one side to the other to see both sides of port
What malformations can be interpreted from nasopharyngoscopy?
submucous cleft
oronasal fistula
irregular adenoids
tonsillar hypertrophy
lateral gaps due to bow tie closure
narrow coronal gap
large gap
large VP opening with a Passavant’s ridge
vocal nodules
What is the timeline of when each surgical procedure occurs?
Cleft palate repairs: 9-12 months (10 months)
Cleft lip repairs: 10-12 weeks (3 months)
VPI surgery: 3-5 years, aren’t speaking much before then
Alveolar grafts: age 6-11
Oronasal fistula: as needed when school age, age 6-7
Orthognathic surgery: 14-16 GIRLS, 16-18 BOYS
What are the types of dental appliance prosthetics?
Fixed bridge, dentures, overlay dentures, dental implants
What are the types of Obturators and what are they used for?
Palatal, Palatal lift, Speech bulb obturator
For feeding + speech
What does not work for speech therapy?
Oral-motor exercises
What is the goal of speech therapy?
Normal speech and resonance
What members of the medical team make up the cleft palate team?
Plastic surgeon
SLP
Orthodontist
At least one other specialist
What members of the medical team make up the Craniofacial Team?
Craniofacial surgeon
Orthodontist
Mental health professional
SLP
What does each cleft palate team require?
Team Coordinator
What are the types of teams?
Multidisciplinary
Interdisciplinary
Transdisciplinary
What is type of team has members care for patients independently with limited communication?
Multidisciplinary
What type of team has members work together to coordinate plan of care for the patient?
Interdisciplinary
What type of team has members work cooperatively and truly understand each other’s disciplines?
Transdisciplinary
When is speech therapy appropriate?
Ideally after VPI surgery
Before if goal is to limit nasal emission
Compensatory errors
Placement errors that are mislearned
Biofeedback
When is speech therapy not appropriate?
Obligatory distortions (placement normal, anatomy not)
What surgery is for VPI?
Pharyngoplasty
What surgery is for cleft palate repair?
Palatoplasty
What surgery is for cleft lip repair?
Cheilorraphy