3.1 - Display Types
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
LCD Advantages
Lightweight
Relatively low power
Relatively inexpensive
LCD Disadvantages
Black levels are a challenge
Requires separate backlight
Florescent, LED, etc.
Lights are difficult to replace
LCD Technologies
TN (Twisted Nematic)
VA (Vertical Alignment)
IPS (In Plain Switching)
TN (Twisted Nematic) LCD
The original LCD technology.
Advantages: Fast response times.
Disadvantages: Poor viewing angles - color shifts.
IPS (In Plain Switching)
Advantages: Excellent color representation.
Disadvantages: Can be more expensive to produce than TN.
VA (Vertical Alignment)
A good compromise between TN and IPS.
Advantages: Good color representation.
Disadvantages: Often slower response times than TN.
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode)
Organic compound emits light when receiving an electric current.
No backlight - the organic compound provides the light.
Lighter and thinner
Flexible and mobile - no glass needed
Tablets, phones, smart watches.
Very accurate color representation.
Tends to be a bit higher cost than LCD.
Mini LED
Same backlight technology as a conventional LED-backlit LCD.
But much smaller LEDs.
Each LED can be enabled or disabled.
And the color and intensity can be different.
Much better control over dark screen areas.
Deeper blacks, better color representation.
Touchscreen
Merge laptop and tablet input.
Digitizer responds to touch
No keyboard required
But often still available
Many options for input
Use the best one for the job.
Digitizer
Use a pen-like device as an input.
Stylus input
Useful for graphical input
Used commonly on laptop / tablets
Or hybrid devices.
Backlight and inverter
LCD displays need a backlight
Florescent lamp or LED lights
Some laptops have inverters
Turn DC into AC
Verify backlight
Look closely
Use a flashlight
May need to replace the LCD inverter or display.
Choose carefully
Display Attributes
Not all displays are created equal
Various specifications, options, and settings.
Requirements can vary.
Web browsing
Video and photo editing
Information displays
Phones
Evaluate all technical details
Choose the best display for the requirement.
Pixel Denisty
Measure how many pixels are in an inch.
Or pixels per centimeter
Apply a physical measurement to the display.
A higher pixel density looks better.
Higher clarity and sharpness
Consider how the image will be viewed.
Displays, printers (dots per inch).
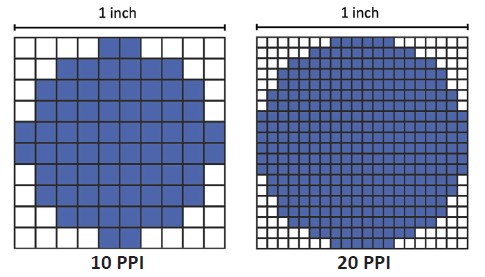
Pixel Density Comparison
Number of pixels / Number of inches
Pixels per (divided by) inch.
27 inch (diagonal) 4K display
3,840 horizontal pixels / 24 inches wide (not diagonal).
160 pixels per inch.
65 inch (diagonal) 4K television
3,840 horizontal pixels / 57 inches wide.
67 pixels per inch.
Refresh Rates
We are viewing many images shown consecutively.
A still “frame” or image.
Usually measured in hertz (Hz)
Number of cycles per second - frames per second (FPS)
Frame rates may vary
Movies: 24 fps
Television: 30 fps
Video games: 60 fps and higher
Higher refresh rates are useful for rapidly moving content.
Video games, sporting events, video production.
Maximum refresh rate is determined by the video adapter/processor and the display device.
The connection between the two is important.
HDMI 2.1 supports K at 144 Hz
DisplayPort 2.1 supports dual 4K at 144 Hz
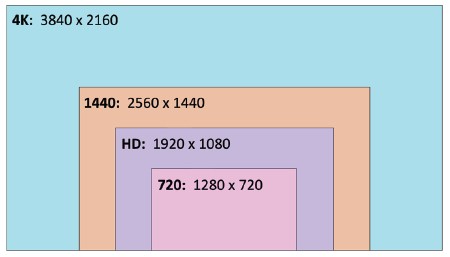
Screen Resolution
The number of pixels - width x height
More pixels means more detailed display output.
perceived sharpness, a clearer view.
Many standards
Resolutions can vary widely - 16:9 aspect ratio is common.
Color Gamut
The range of colors available on a display or output device.
This is less than the capabilities of the human eye.
Considerations in a display
Color representation
Range of colors
Standards of color
sRGB: Standard Red Green Blue
Adobe RGB
ITU (International Telecommunication Union) - Standards for HDTV
Color Coverage
A display may be compared with an existing color gamut standard.
Part of the display specification.
Gamut compatibility can vary.
High percentages tend to be more expensive.
OLED displays provide a wide color gamut.
Best-in-class color gamut support.