3.7.2 Financial ratio analysis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is liquidity?
Liquidity is concerned with ability of a business to be able to pay its way - to settle liabilities e.g. monthly payroll, amounts due to suppliers & taxes collected on behalf of government etc
What is a liquidity ratio?
Assesses whether a business has sufficient cash or equivalent current assets to be able to pay its debts as they fall due
Where does the data to calculate liquidity ratios come from?
All the financial info you need is contained within the statement of financial position (AKA balance sheet)
What is the statement of financial position (balance sheet)?
Snapshot of business' assets (what it owns or is owed) and its liabilities (what it owes) on a particular day
What is an income statement?
Measures business performance over a given period of time, usually one year
Compares income of business against cost of goods or services & expenses incurred in earning that revenue
What is cash flow statement?
It shows how the business has generated and disposed of cash & liquid funds during period under review
How do we calculate liquidity ratios?
Compare the ratio of current assets and current liabilities
Current assets -> include cash, inventories, trade receivables (or trade debtors - amounts owed by customers)
Current liabilities -> amounts owed to suppliers, bank overdraft balances (money owed to bank)
How do we calculate current ratio? (classic liquidity ratio)
CURRENT ASSETS / CURRENT LIABILITIES
e.g. 2:1

Evaluating current ratio :
A ratio of 1.5 - 2 would suggest acceptable liquidity & efficient management of working capital
Low ratio (e.g. well below 1) indicates possible liquidity problems
High ratio suggets too much working capital tied up in inventories or debtors
However when evaluating current ratios dont forget :
Industry or market matters - they have diff requirements for holding inventories, or approaches to trade debt and credit
How does current ratio compare with competitors?
The trend is more important - sudden deterioration in current ratio is a good indicator of liquidity problems
What is Gearing?
Gearing measures the proportion of a business' capital (finance) provided by debt
What is the capital structure of a business?
It represents the finance provided to it to enable it to operate over the long term
Two parts to capital structure -> equity and debt
Equity finance -> amounts invested by owners of business (shareholders) e.g. share capital, retained profit
Debt finance -> finance provided to business by external parties e.g. bank loans, other long-term loans
What factors influence the mix of equity and debt in a financial structure?
Reasons for higher equity :
Where there is greater business risk (e.g. a startup)
where more flexibility required (e.g. dont have to pay dividends)
Reasons for higher debt :
where interest rates are very low = debt is cheap to finance
where profits & cash flows are strong - debt can be repaid easily
What are key benefits to calculating the gearing ratio?
A useful measure of financial health of a business
focuses on level of debt in financial structure
high gearing ratio can mean higher risk of business failure (but not always)
What is the formula for calculating the gearing ratio (%) ?
Gearing ratio

Is having a higher gearing a bad thing?
It depends
a gearing ratio of 50%+ is normally said to be high
gearing ratio of less than 20% normally said to be low
level of acceptable gearing depends on business & industry
What are the benefits of high gearing?
Less capital required to be invested by shareholders
debt can be a relatively cheap source of finance compared with dividends
easy to pay interest if profits and cash flows are strong
What are the benefits of low gearing?
less risk of defaulting on debts
shareholders rather than debt providers "call the shots"
business has capacity to add debt if required
What are Efficiency ratios?
They analyse how effectively a business is managing its assets
Three most commonly used ones :
Inventory turnover = measures how often each year a business sells and replaces inventory
Payables days = measures average length of time taken by a business to pay amounts it owes
Receivables days = measures average length of time taken by customers to pay amounts owed
What are inventories (or stocks)?
The raw materials, work in progress & finished goods held by a business to enable production & meet customer demand
How to calculate the Inventory turnover?
INVENTORY TURNOVER = COST OF SALES / INVENTORIES
Answer expressed as '“times” (a year)
What sectors will typically have a low inventory turnover and which will have high?
Engineering, construction & industrial distribution will have low inventory turnover
Whereas in retailing, fast food, restaurants & motor vehicle production has much higher inventory turnover
This needs to be borne in mind when comparing inventory turnover ratios of diff businesses
What should we remember when evaluating results of inventory turnover calculations?
Inventory turnover varies from industry to industry
Holding more inventory may improve customer service & allow business to meet demand
Seasonal fluctuations in demand during year may not be reflected in calculations
Inventory turnover is not relevant to most service businesses
How can a business improve (increase) its inventory turnover?
One or more of following might be an option :
Sell off or dispose of slow moving or obsolete inventory
Introduce lean production techniques to reduce amounts of inventory held
Rationalise product range made or sold
Negotiate sale or return arrangements with suppliers - so inventory can be returned if it doesn’t sell
What are Payables and Receivable days ratios concerned with?
How quickly payments are made (to creditors) and received (from customers) & they use similar formulae :
Both ratios expressed as “days”
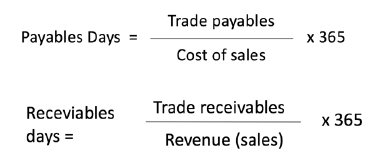
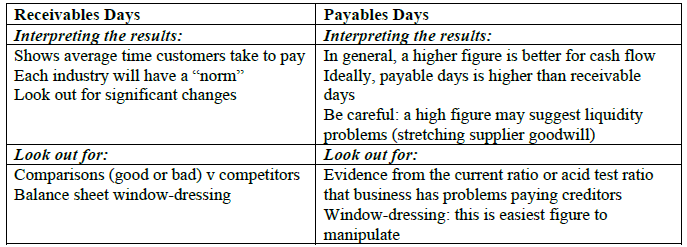
Evaluating Receivables & Payables days :
Evaluations :
What is Return on capital employed (ROCE) ?
A measure of relative profitability
Tells us what returns (profits) the business has made on resources available to it
How is ROCE particularly useful as a ratio?
It helps :
Evaluate overall performance of business
Provide a target return for individual projects
Benchmark performance with competitors
What information do you need to calculate ROCE?
Amount of profit earned in a particular period (usually a year) → get from income statement
To calculate capital employed → need info from balance sheet (statement of financial position)
What is the formula used to calculate ROCE (%) ?
ROCE (%)
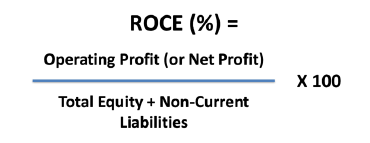
Evaluating ROCE :
ROCE will vary between industries → particularly important measure in capital intensive industries with significant amounts of capital employed
ROCE is based on a snapshot of a busines's’ balance sheet
Comparisons over time & with key competitors are most useful