Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Membrane Transport — Vocabulary Flashcards
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of vocabulary cards covering cell theory, cell shapes, membrane structure, membrane transport, organelles, and cytoskeletal components based on the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Cell Theory
All living organisms are made of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of structure and function; all cells arise from existing cells.
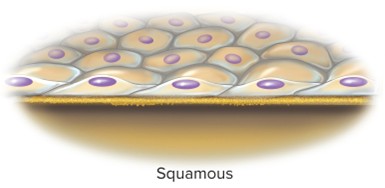
Squamous
Thin, flaky, or scaly cell shape that lines the esophagus and alveoli of the lungs and the epidermis.
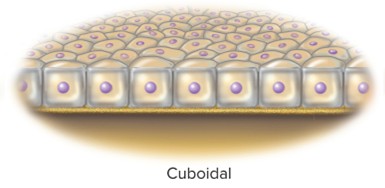
Cuboidal
Cube-like cell shape; appears squash-shaped, as seen in liver cells.
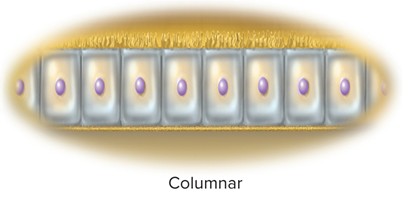
Columnar
Tall, column-like cells; inner lining of stomach and intestines.
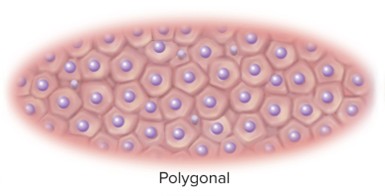
Polygonal
Irregularly angular cells with four or more sides; densely packed in glands.
Stellate
Star-shaped cell type, such as certain nerve cells.
Spheroid (ovoid)
Round to oval cells, such as white blood cells (WBCs).
Discoidal
Disc-shaped cells, such as red blood cells (RBCs).
Fusiform
Thick in the middle and tapered at the ends; seen in some smooth muscle cells and axons.
Fibrous
Threadlike cells, such as skeletal muscle fibers and certain axons.
Limit on cell size
Reasons:
cells may rupture if overly large (overfilled water ballon)
large cells cannot support themselves
If a cell is too large, molecules can’t diffuse fast enough to support metabolism and life
Organs composed of many small cells instead of fewer large ones
Major components of a cell
• Plasma (cell) membrane:
• Defines cell boundaries
• Made of proteins and lipids
• Composition can vary between regions of the cell (basal, lateral, apical surfaces)
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
Fluid outside cells
• ECF includes any fluid outside of cells
• ECF among the cells tissue (interstitial) fluid
E.g.: blood plasma, lymph, and cerebrospinal fluid
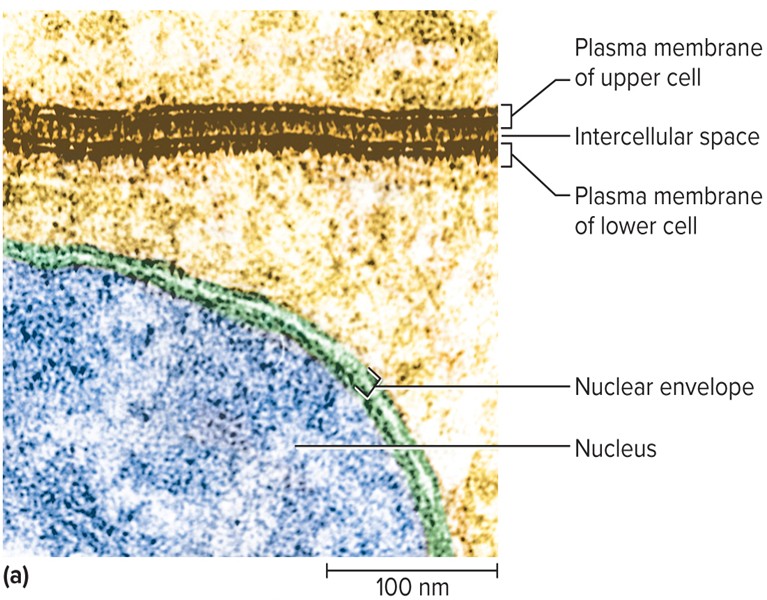
Plasma membrane
• defines the boundaries of the cell
• Governs the interactions with other cells
• Controls the passage of material into and out of the cell
Phospholipids
- 75% of membrane lipids
Amphipathic molecules arranged in a bilayer
- Hydrophilic phosphate heads face water on each side of membrane
- Hydrophobic tails—are directed toward the center, avoiding water
- Drift laterally, keeping membrane fluid
Cholesterol
About 20% of membrane lipids
Found near membrane surfaces among phospholipids
Holds phospholipids still, stiffening the membrane
Glycolipids
About 5% of membrane lipid
Phospholipids with short carbohydrate chains on extracellular face
Contribute to glycocalyx—carbohydrate coating on cell surface
Transmembrane proteins
pass completely through membrane/phospholipid bilayer
• Hydrophilic regions contact the water on both sides (cytoplasm/extracellular fluid)
• Hydrophobic regions pass through lipids of the membrane
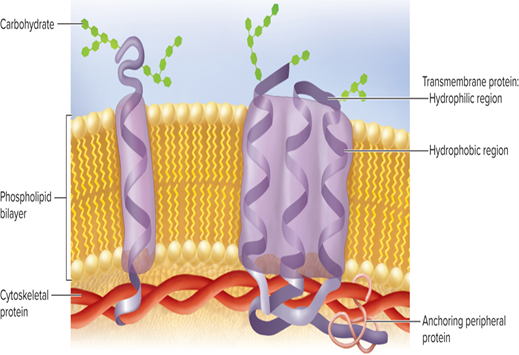
Peripheral proteins
Adhere to either the inner OR outer face of the membrane
Those on inner face are usually tethered to a transmembrane protein AND the cytoskeleton
Receptors
Bind chemical signals to trigger internal changes
• Specific for a particular messenger
• Can activate second messengers inside the cell
Enzymes (membrane enzymes)
catalyze (speed up) reactions including digestion of molecules
production of second messengers,
breakdown hormones and other signaling molecules whose job is complete
Channel proteins
Proteins that create passages for hydrophilic solutes and water to pass through the membrane.
Leak channels
Channels that are always open, allowing continuous passage of ions or materials.
Gated channels
open and close under different circumstances allowing solutes through sometimes
Ligand-gated channels
Channels that open in response to chemical messengers (ligands).
Voltage-gated channels
respond to electrical potential (voltage) across plasma membrane
Mechanically gated channels
respond to physical stress on cell (e.g.: stretch, pressure)
Carriers
Transmembrane proteins that bind to glucose, electrolytes and other solutes and CARRY them to the other side of the membrane
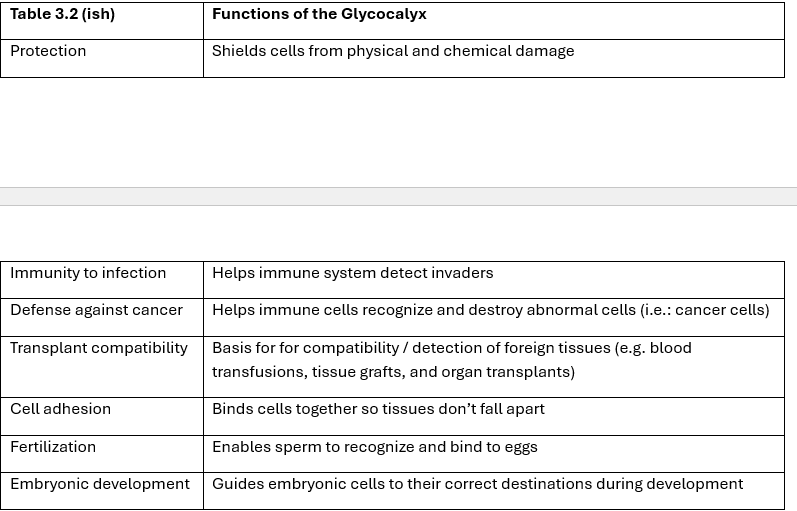
Cell identity markers
Glycoproteins contribute to the glycocalyx, acting like an ID tag, enabling the immune system to identify cells belonging to the body / foreign invaders
Glycocalyx
Carbohydrate coating on the cell surface formed by glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)
Mechanically link cell to another cell and to extracellular material
Second Messenger system
Epi (1st messenger) -> receptor -> G protein -> Adenylate cyclase
ATP to cAMP (2nd messenger) -> kinases -> + phosphate groups -> cell changes
Functions of Glycocalyx
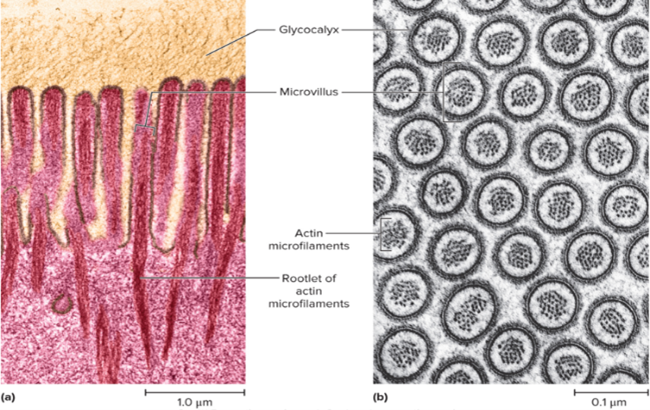
Microvilli
Extensions (1–2 μm) of the plasma membrane that increase surface area.
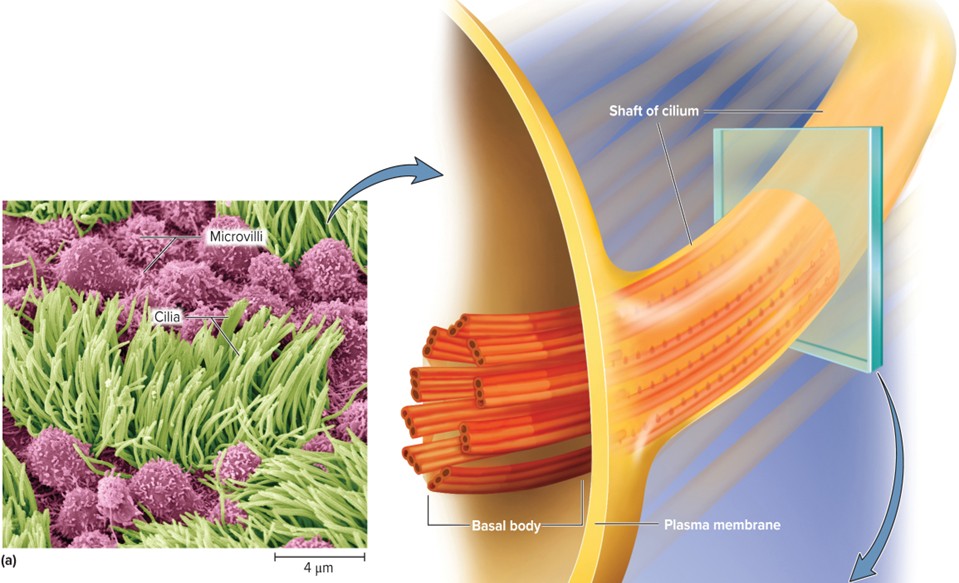
Cilia
Hair-like projections (7–10 μm)
• Single, nonmotile primary cilium found on nearly every cell; serves as “antenna” for monitoring nearby conditions
• Helps with balance in inner ear; light detection in retina
• Multiple nonmotile cilia found on sensory cells of nose
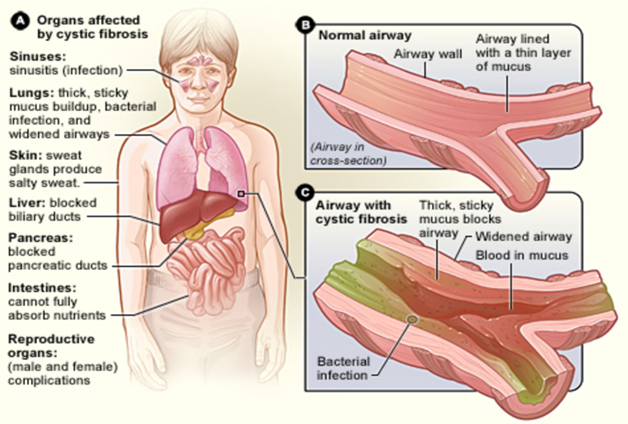
Cystic fibrosis
Hereditary disease in which chloride pumps exist but are not properly inserted into the plasma membrane.
Flagellum
Whiplike tail (sperm) that moves in an undulating, snake-like fashion; longer than a cilium.
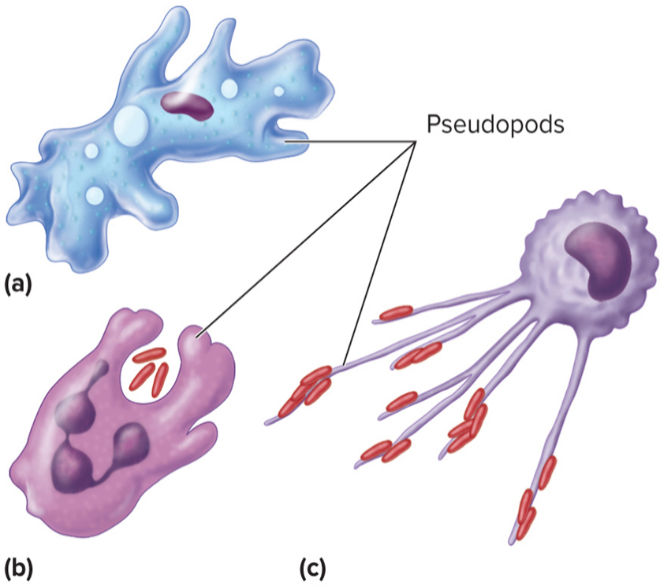
Pseudopods
Cytoplasm-filled extensions of the cell
used by white blood cells to crawl and engulf particles
platelets use them to adhere and form plugs.
Membrane transport
Movement of substances across the plasma membrane; selective permeability.
Selective permeability
Membrane property that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
preventing (barrier) others from passing between the cytoplasm and ECF
Passive transport
Movement of substances across the membrane without energy input (no ATP).
Active transport
Movement of substances against their gradient requiring energy (ATP).
Carrier-mediated transport
Transport via membrane carriers that bind and move solutes across the membrane.
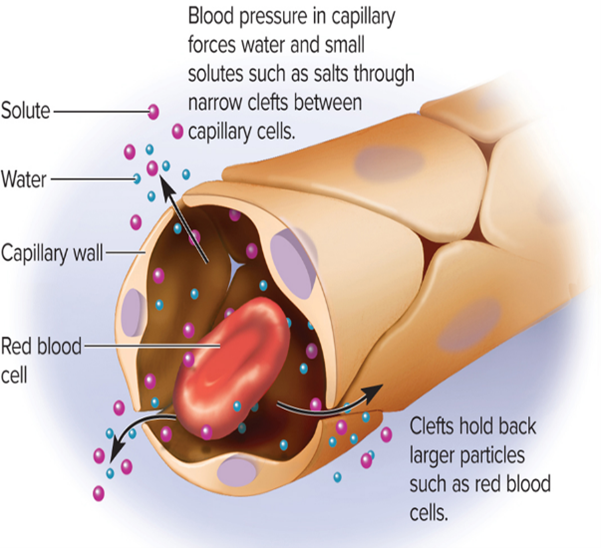
Filtration
• particles are driven through membrane by physical pressure
• Example: Blood capillaries – BP forces fluid through gaps in capillary wall.
Simple diffusion * KNOW FOR EXAM
Factors affecting diffusion rate and how they are affected:
-Temperature: ↑ temp., ↑ motion of particles, ↑ diffusion rate
-Molecular weight: small molecules move faster, ↑ diffusion rate
-Concentration gradient: ↑ difference (“steepness”), ↑ diffusion rate
-Membrane surface area: ↑ surface area, ↑ diffusion rate
-Membrane permeability:↑ permeability, ↑ diffusion rate
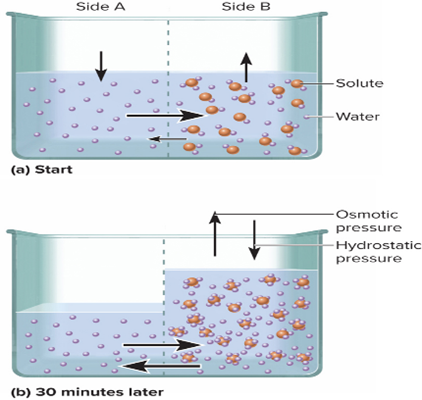
Osmosis
Net flow of water through a selectively permeable membrane
• Water moves from an area of higher water (lower solute) concentration to an area of lower water (higher solute) concentration
• Crucial consideration for IV fluids
Osmotic pressure
Hydrostatic pressure required to stop osmosis; reflects solute concentration.
Increases as amount of nonpermeating solute rises
• Nonpermeating solutes cannot pass through membrane
• Example: proteins
Hydrostatic pressure
fluid pressure on the membrane, opposing filtration.
Reverse osmosis
Forcing water through a membrane by applying pressure to override osmotic pressure.
Osmolarity
Total solute concentration of a solution.
• Includes all solutes that cannot cross the membrane
• E.g.: Blood plasma, tissue fluid, and intracellular fluid are all about 300 milliosmoles per liter (mOsm/L)
Tonicity
How a solution affect’s a cell’s water movement, volume, and pressure.
Isotonic solution
Same solute concentration inside & outside the cell
• No net water movement -> cell stays the same size
• E.g.: 0.9% NaCl (normal saline)
Hypotonic solution
Lower osmolarity than the cell; water enters the cell and it may swell.
Hypertonic solution
Higher osmolarity than the cell; water leaves the cell and it may shrink (Crenation).
Carrier-mediated transport
• proteins (carriers) in cell membrane carry solutes into or out of cell (or organelle)
Carriers exhibit specificity for their specific solutes
• Solute (ligand) binds to receptor site on carrier protein
• Solute is released unchanged on other side of membrane
• Carriers also exhibit saturation
• Transport rate increases with solute concentration, but only to a point called the transport maximum
Uniport
Moves one solute at a time
• E.g.: Calcium pump
Symport
Moves 2+ solutes in the same direction at the same time.
• Secondary Active Transport
• E.g.: Sodium-glucose symporter (SGLT)
Antiport
Moves 2+ solutes in opposite directions at the same time
• Secondary Active Transport
E.g.: Sodium-potassium pump, sodium-calcium exchanger
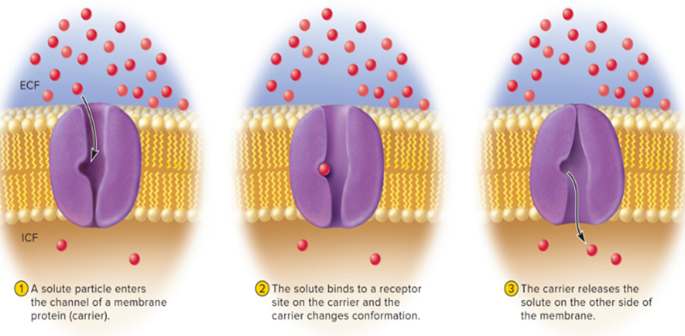
Facilitated diffusion
carrier moves solute DOWN its concentration gradient
• No ATP needed
• Solute attaches to binding site on carrier, carrier changes shape, then releases solute on other side of membrane
Primary active transport
carrier moves solute through a membrane UP its concentration gradient
Active transport powered directly by ATP (e.g., Na+/K+ pump).
Sodium-potassium pump
Sodium and potassium ions are pumped against their gradients; maintains Na+ outside and K+ inside the cell.
Functions of the Sodium-potassium pump
• Maintains Na+ gradient, allowing for secondary active transport
• Regulates solute concentration and thus osmosis and cell volume
• Maintains negatively charged resting membrane potential
Produces heat
Secondary active transport
Carrier moves solute through membrane
• Uses ATP indirectly
• E.g.: Sodium-glucose transporter (SGLT)
• Moves glucose into cell, up its concentration gradient, while simultaneously carrying sodium down its gradient
Vesicular transport
Moving stuff through the membrane using vesicles
• Stuff moved: Large particles, fluid droplets, or numerous molecules at once
• Vesicles = little “bubbles” of membrane that carry things
Endocytosis
brings material INTO cell
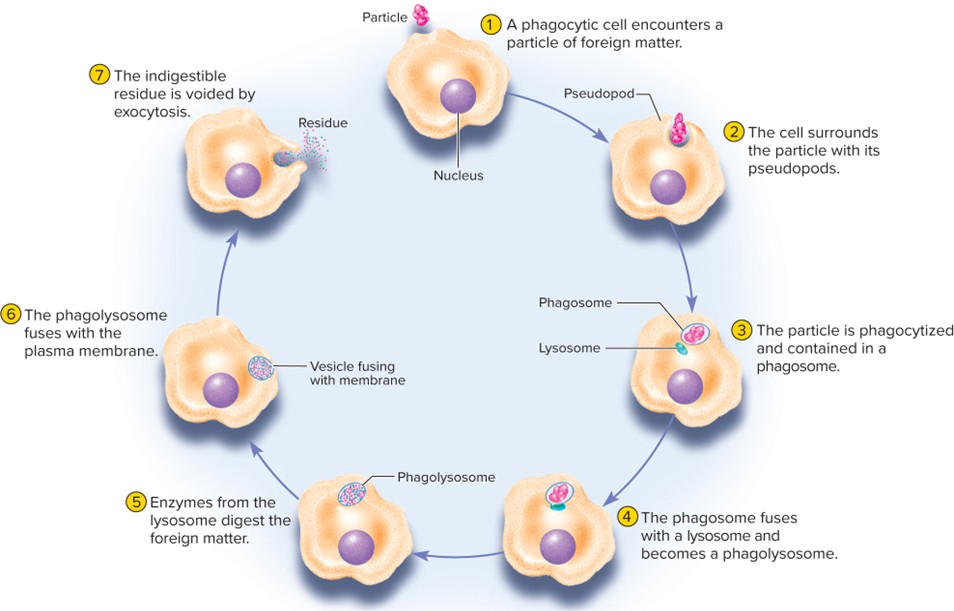
Phagocytosis (“Cell eating”)
Cell engulfs large particles (e.g.; bacteria, debris)
• Pseudopods (extensions) wrap around large particles -> internalize it into a vesicle = phagosome -> fuses with a lysosome -> phagolysosome -> break down/digested -> Eliminated through Exocytosis
Pinocytosis (“cell drinking”)
Cell takes in droplets of ECF containing useful molecules in the cell
Receptor-mediated endocytosis (“Picky”)
Cells internalize specific molecules (ligands)
• E.g.: liver cell absorbing cholesterol from the blood by binding LDL particles to receptors on its membrane
• Entry of viruses/toxins
Transcytosis
• Transport of material across the cell by capturing it on one side and releasing it on the other
• E.g.: movement of molecules across capillary walls
Exocytosis
Moves material OUT of the cell
• Vesicle fuses with membrane, releasing contents outside
• Also replaces any plasma membrane lost during endocytosis
Cytosol
is a clear, viscous, watery colloid within the cell
• Contains enzymes, other proteins, amino acids, ATP, electrolytes, dissolved gases, metabolic wastes
Cytoskeleton
is a network of protein filaments and cylinders
Functions:
• Structural support, determines cell shape, organizes cell contents
• Directs movement of materials within cell and contributes to movements of the cell as a whole
• Composed of microfilaments, intermediate fibers, microtubules
Microfilaments
Thin (about 6 nm) Actin filaments; support, movement, and cell surface changes.
Intermediate filaments
8–10 nm filaments; provide mechanical support and integrity.
Microtubules
25 nm hollow tubes; tubulin-based; form the mitotic spindle, move organelles, and shape the cell.
Nucleus
Largest organelle; control center housing genetic material and regulating gene expression.
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane surrounding the nucleus; barrier between nucleus and cytoplasm.
Nucleoplasm
Gel-like fluid inside the nucleus that suspends components and supports replication/transcription.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Flattened sacs studded with ribosomes; synthesizes phospholipids and proteins.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Tubular ER without ribosomes; makes lipids and steroids; detoxifies substances.
Golgi Complex
Stack of flattened sacs; packages, modifies proteins, and synthesizes carbohydrates.
Lysosomes
Membrane-bound packages of enzymes; sites of autophagy and autolysis.
Peroxisomes
Organelle like lysosomes but with different enzymes; detoxifies harmful substances and fatty acids.
Mitochondria
Double-membrane-bound organelle; powerhouse producing ATP via cellular respiration.
Proteasomes
Hollow, cylindrical organelles that degrade damaged or unneeded proteins.
Ribosomes
Tiny particles that synthesize proteins by linking amino acids.
Centrosome
Region near the nucleus serving as the organizing center for microtubules during cell division.
Centriole
Paired short cylinders (9 triplets) that organize the formation of cilia and flagella.
Basal bodies
9 triplet microtubules arranged as a cylinder; anchor cilia and flagella to the cell.
Inclusions
Non-membrane-bound substances stored in the cell; not essential for survival.