Appendages: Eyelids and Conjunctiva
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
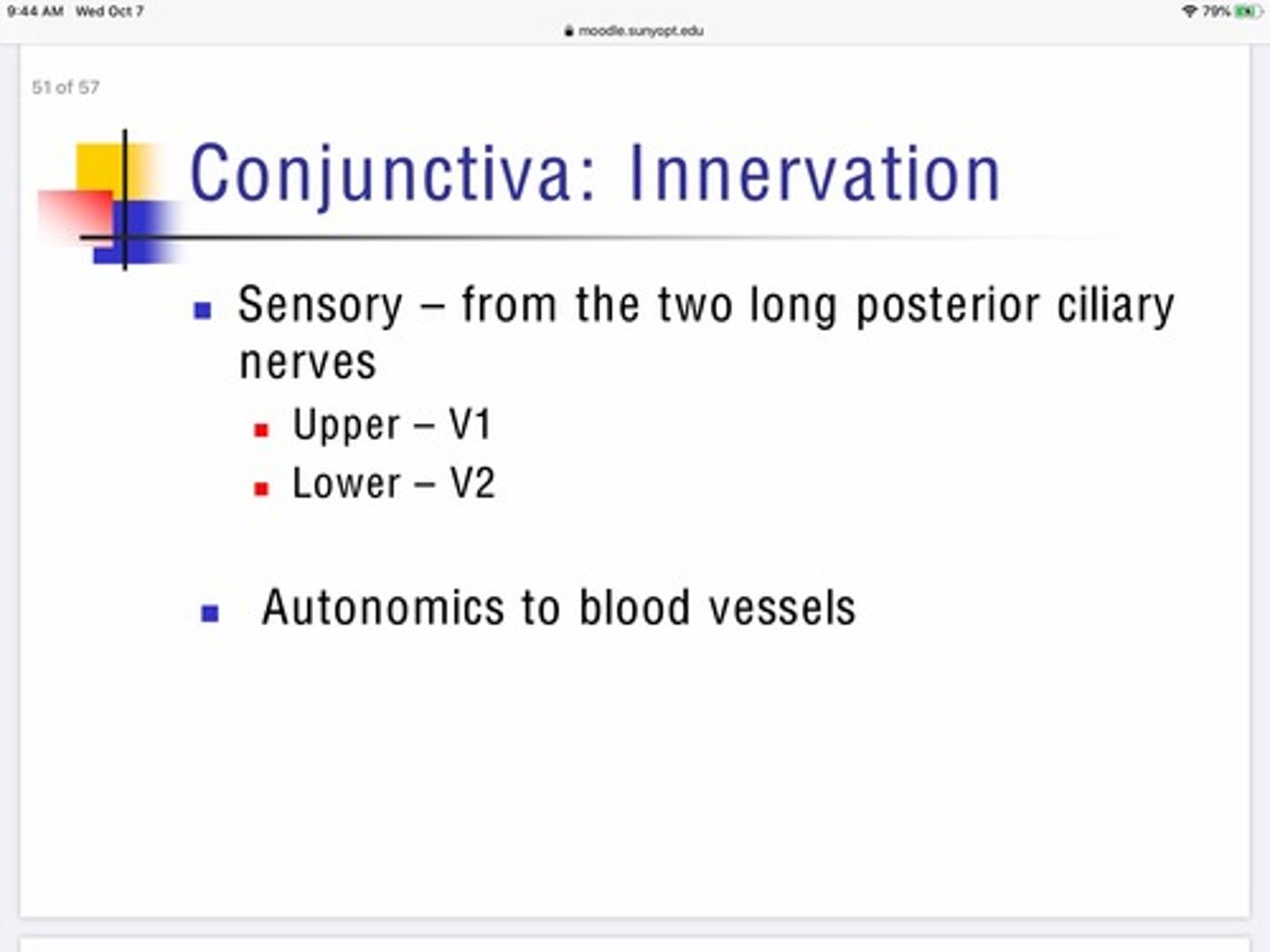
What muscle is responsible for elevating the eyebrow?
Frontalis muscle
Which ligament acts as a hammock for the eye?
Suspensory (lockwood) ligaments
What does the orbital portion of the orbicularis muscle do?
Closes eyes
Voluntary blinks
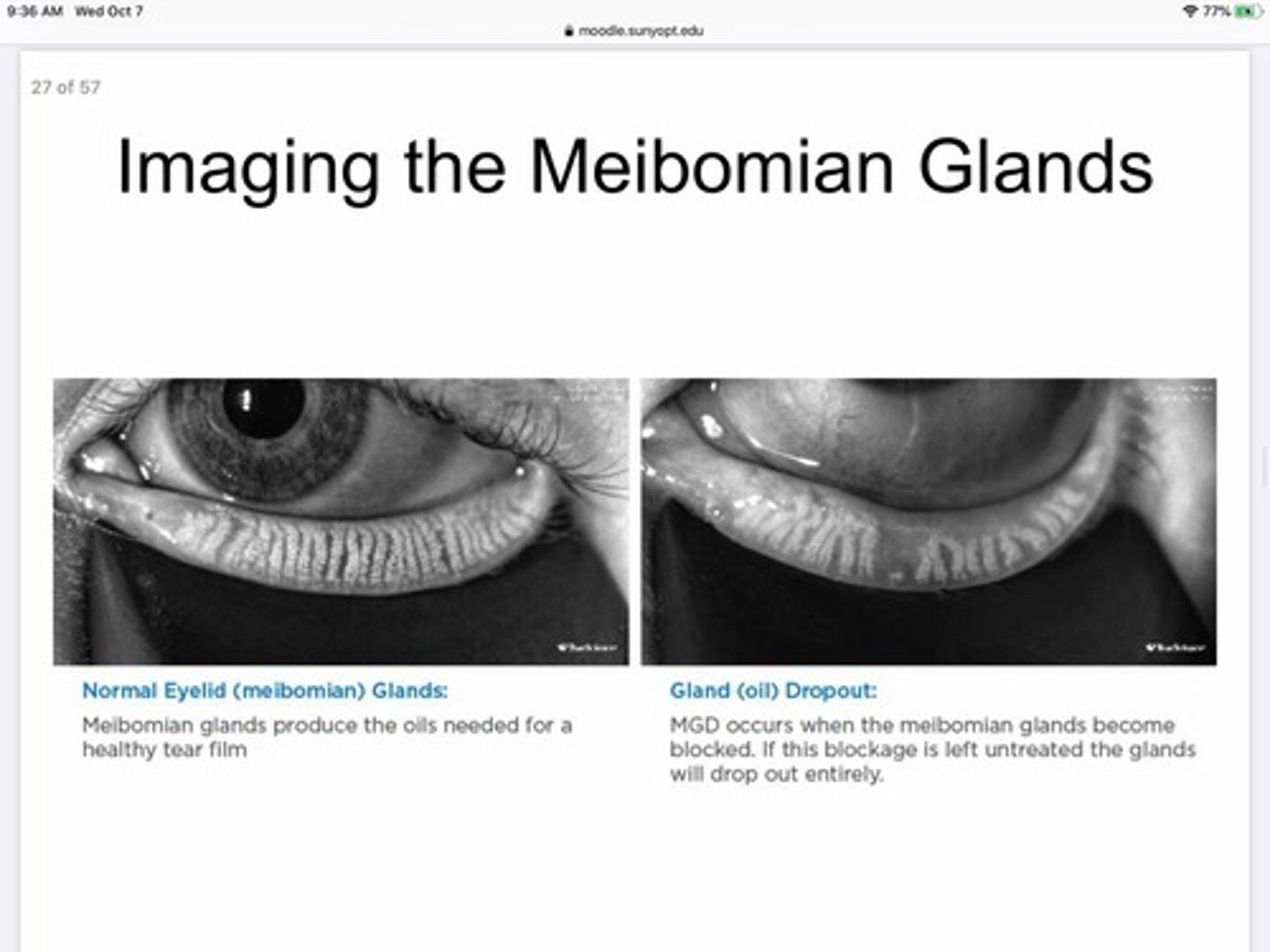
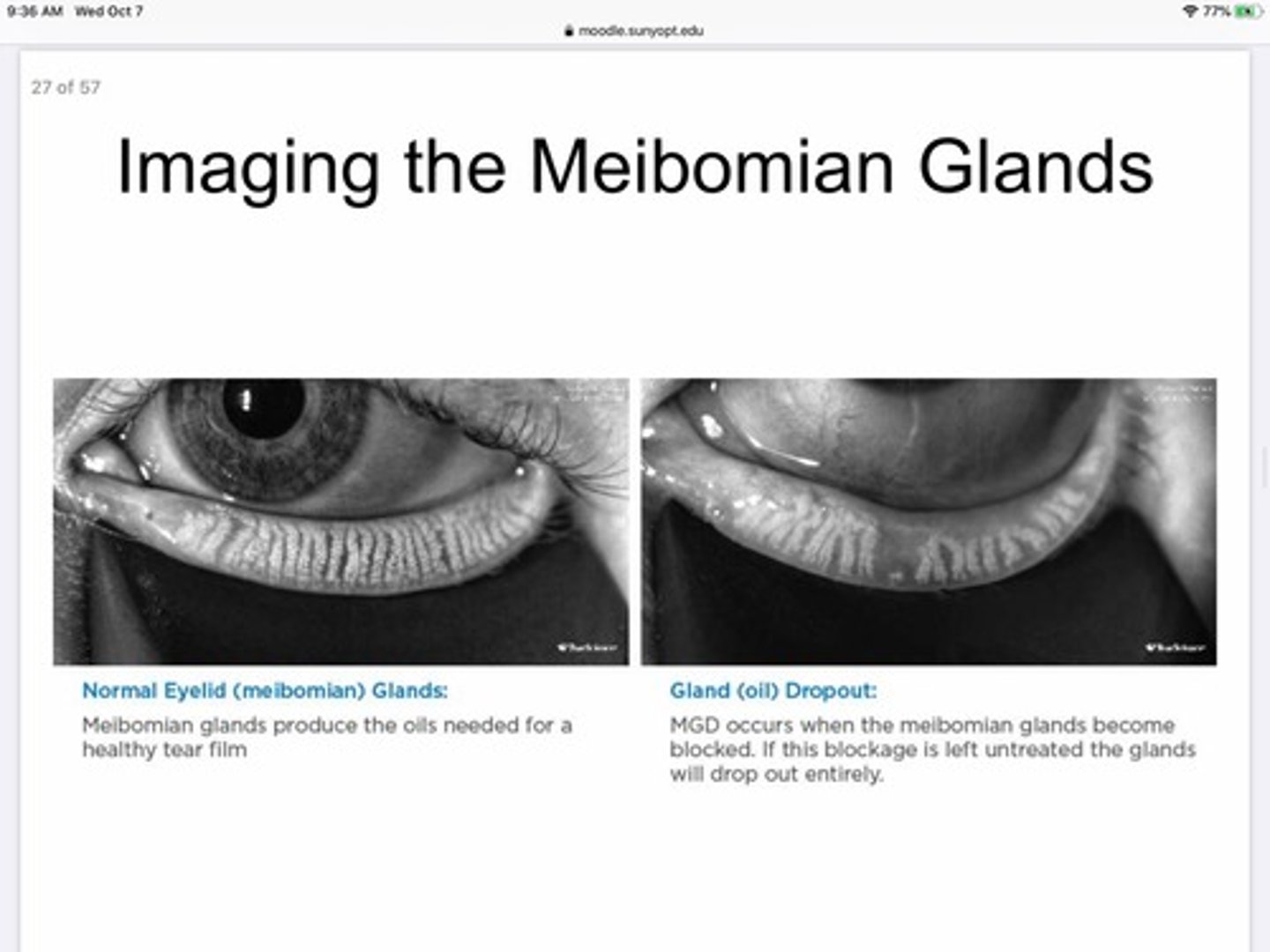
What happens to MBG if they stay clogged for to long?
They will 'drop out'
What is anastomoses?
where vessels unite or interconnect - can be arterial or venous or both
What vein is responsible for the flow of deoxygenated blood away from the lateral portion of the eyelid?
Jugular vein
The lacrimal glands secrete into the..
Fornix portion of the conjunctiva
Why is it important that the bulbar conjunctiva is loosely attached to the eye?
So it can swell and stretch for immune responses and not need/cause the palpebral portion to stretch
What muscle is responsible for depressing the medial portion of the eyebrow (anger)?
Procerus Muscle
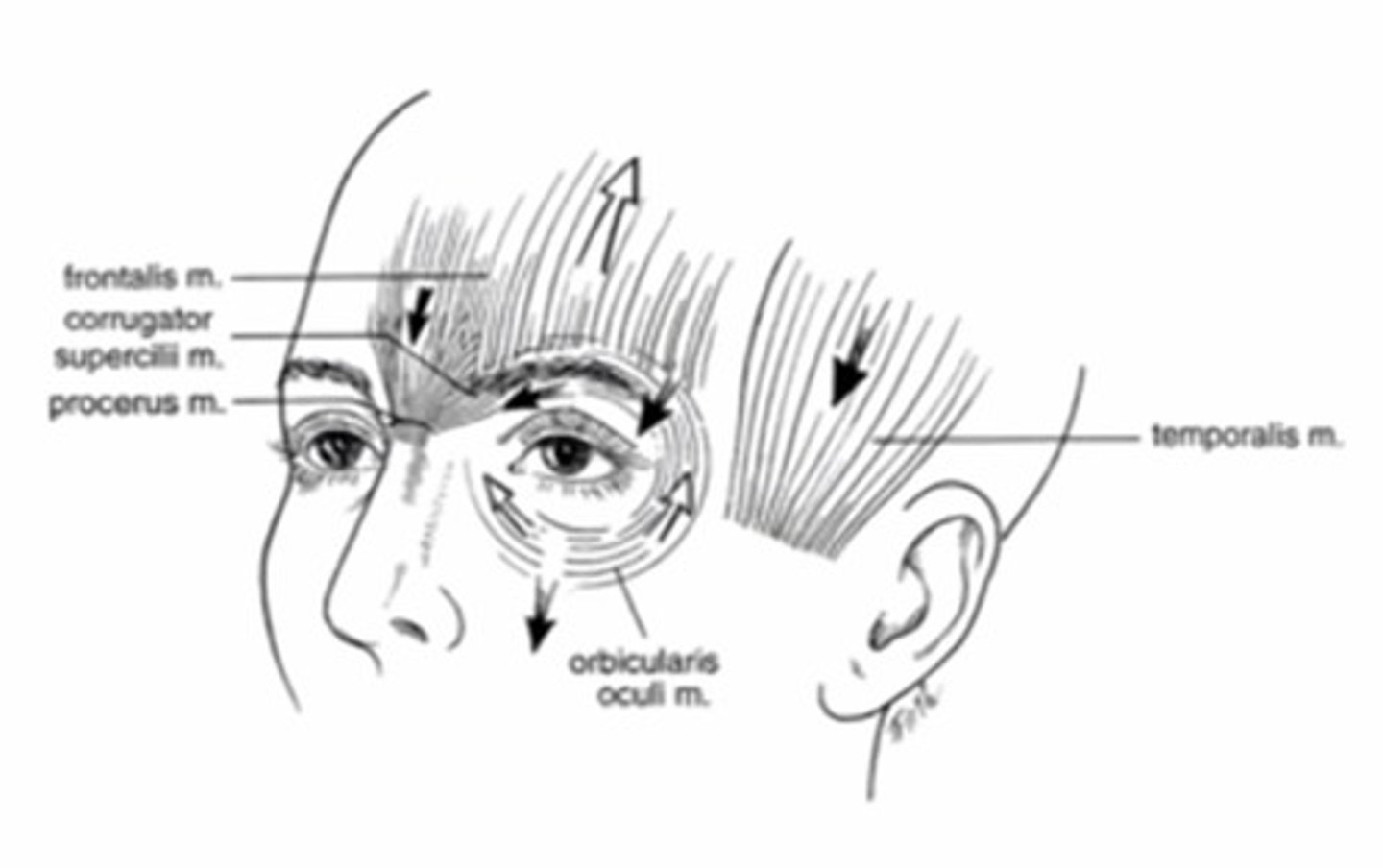
What muscle is responsible for lowering the eyebrows and closing the lids?
Orbicularis oculi - orbital portion
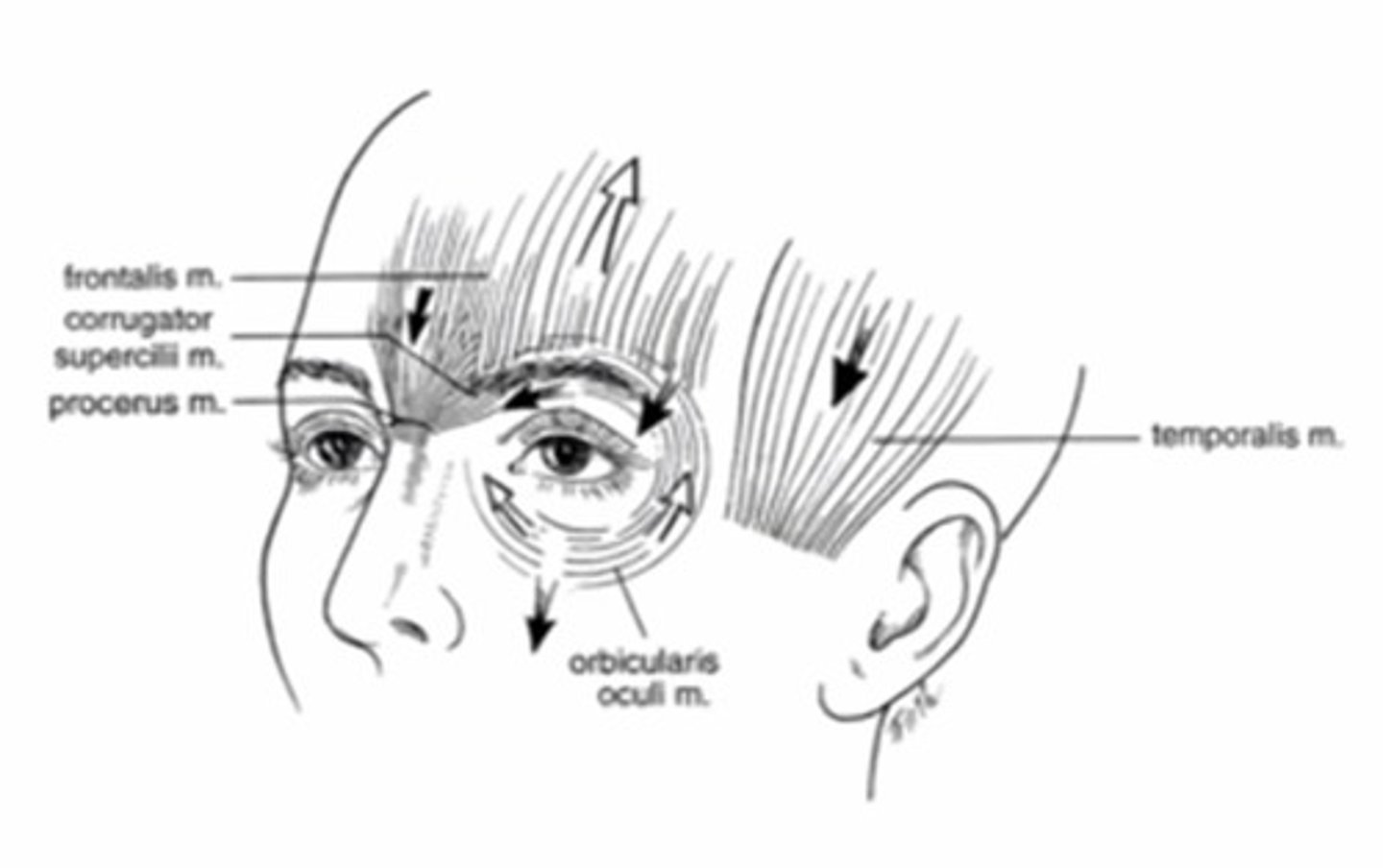
What muscle is responsible for pulling the eyebrows together (frowning)?
Corrugator supercilli
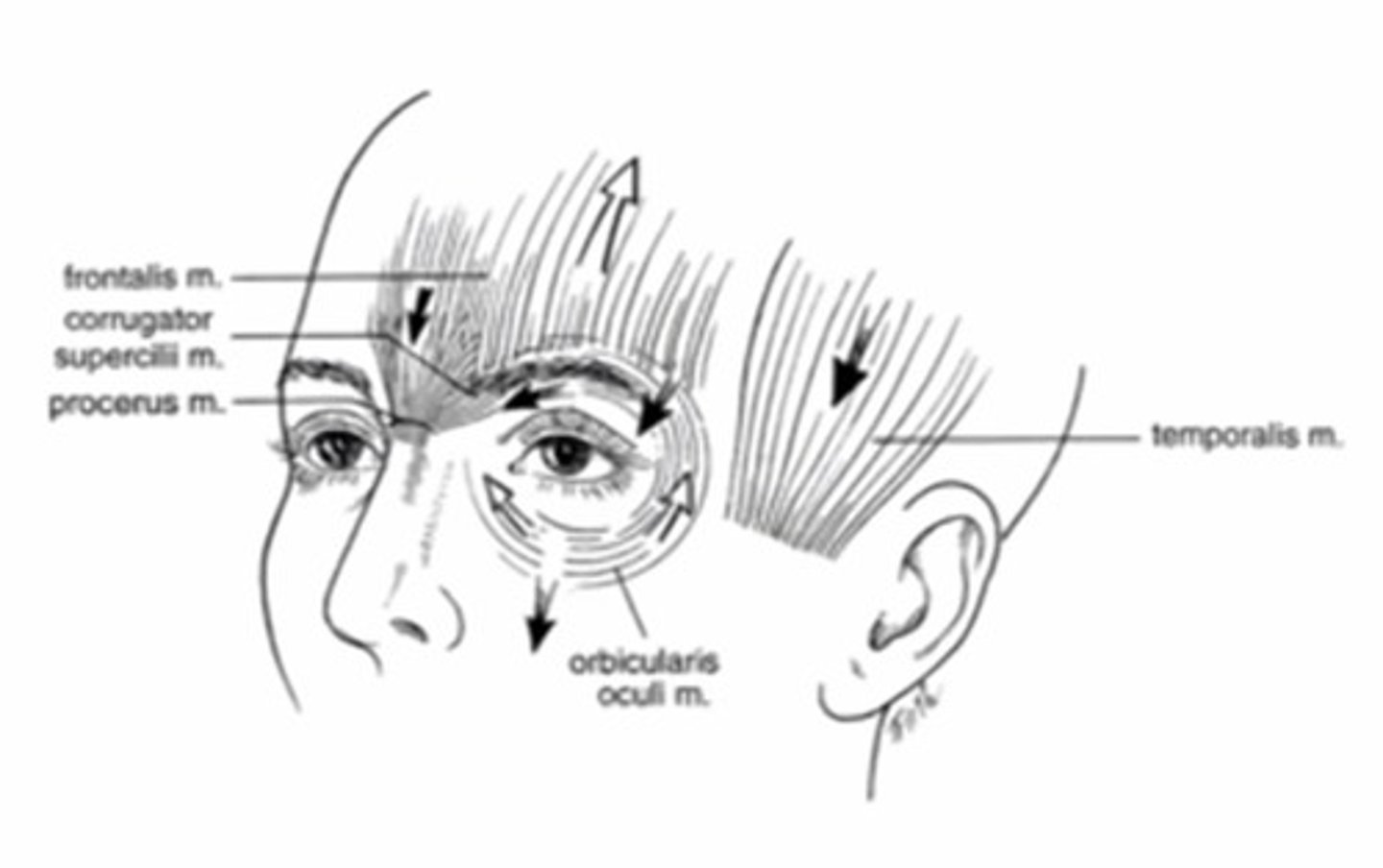
What is another name for eyelids?
palpebrae
What are the functions of the eyelids?
1. Protect eye from injury, and excessive light
2. Spread tears
What is the palpebral fissure?
open space between eyelids
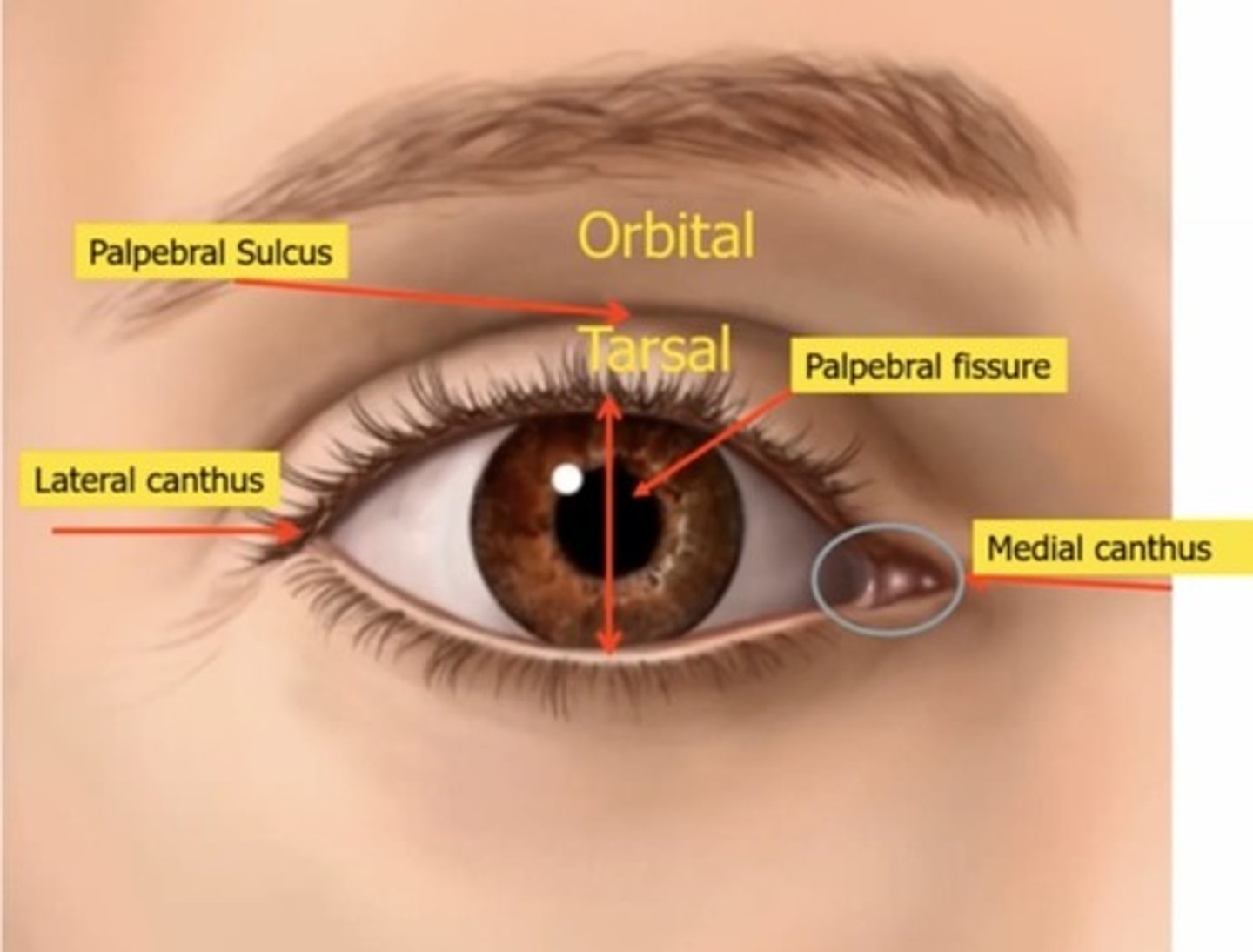
What is the average palpebral fissure length? (In mm)
9-10mm
What is the purpose of the lacrimal lake in the medial canthus?
Collects and Holds tears so they will go out via the punctum
What is the tenons capsule?
Fascial sheath, envelope of elastic connective tissue
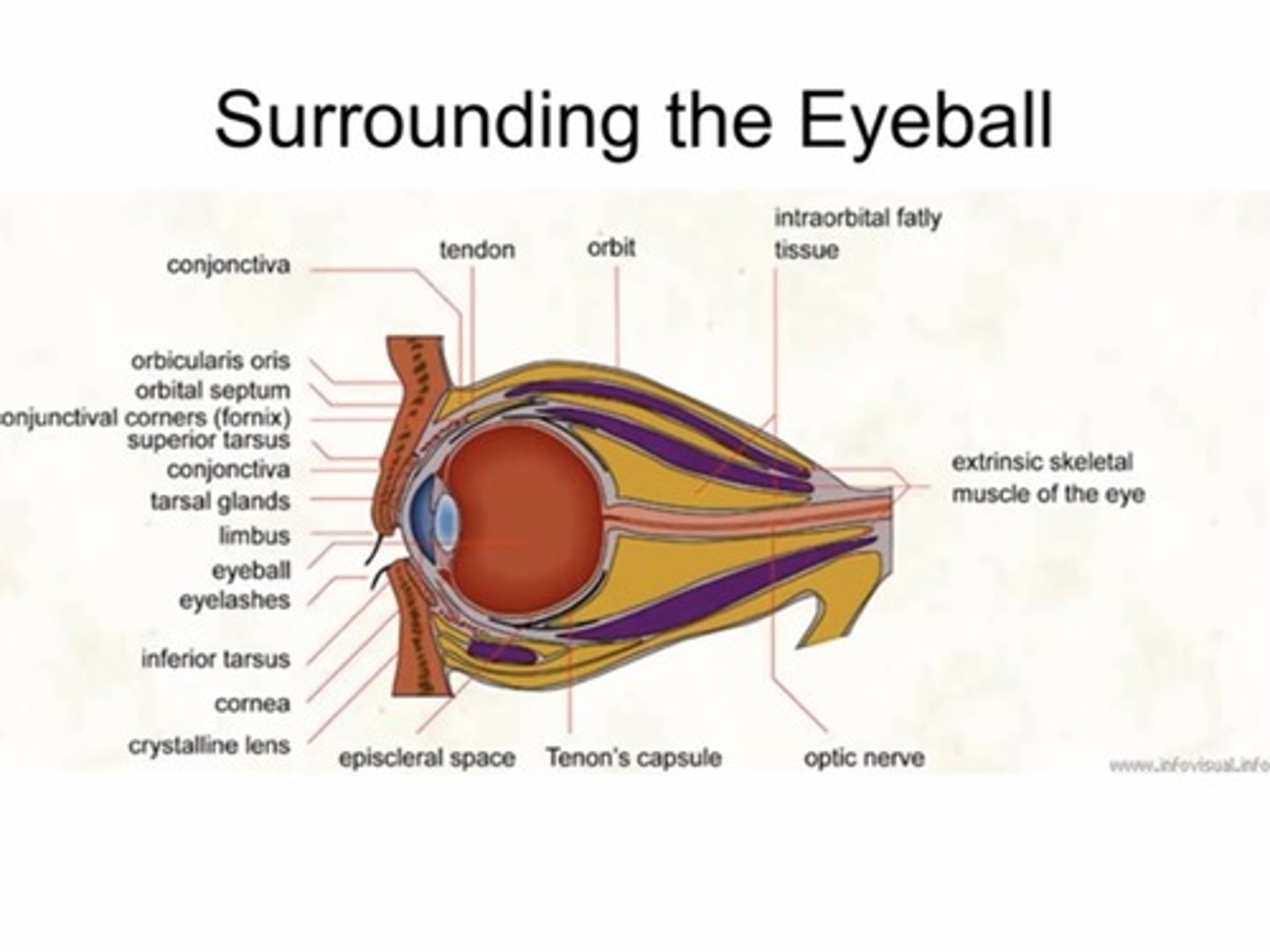
Where does tenons capsule begin and end?
Fuses with the optic nerve sheath posteriorly and intermuscular septum anteriorly (3mm behind the limbus)
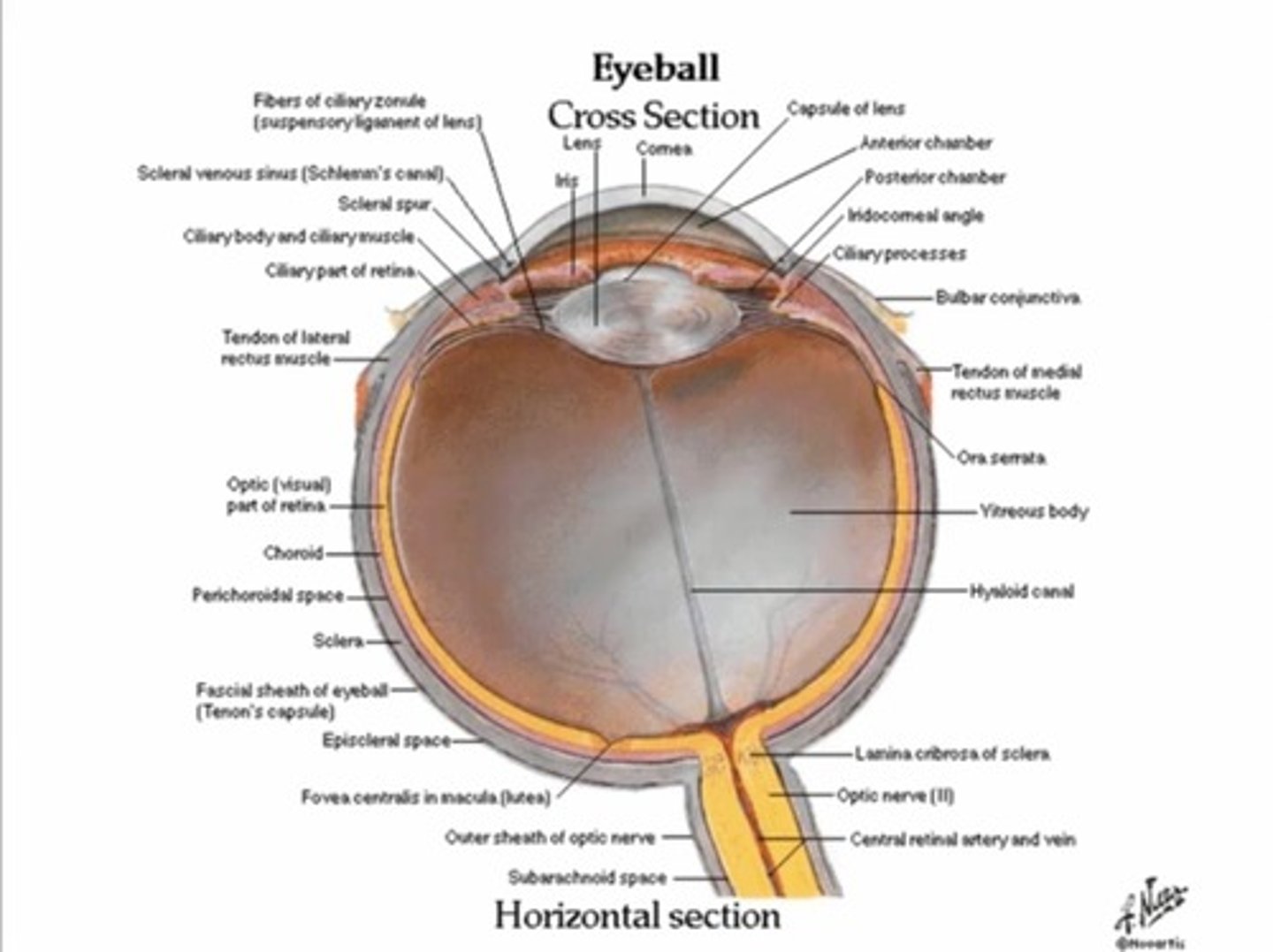
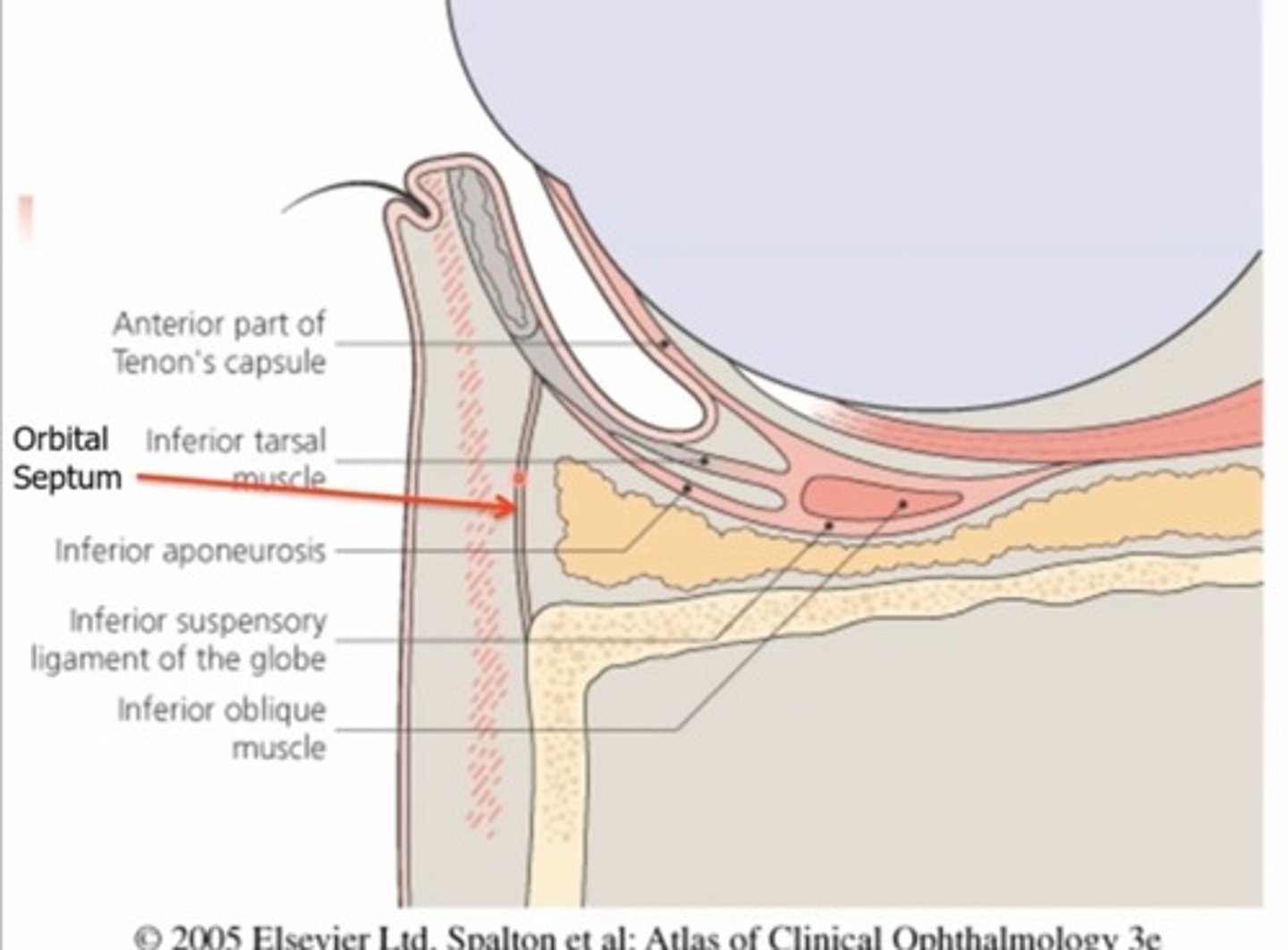
What structure protects the eye from infections in the skin around the eye?
Orbital septum, acts as a barrier between lid and fat pads around eyes
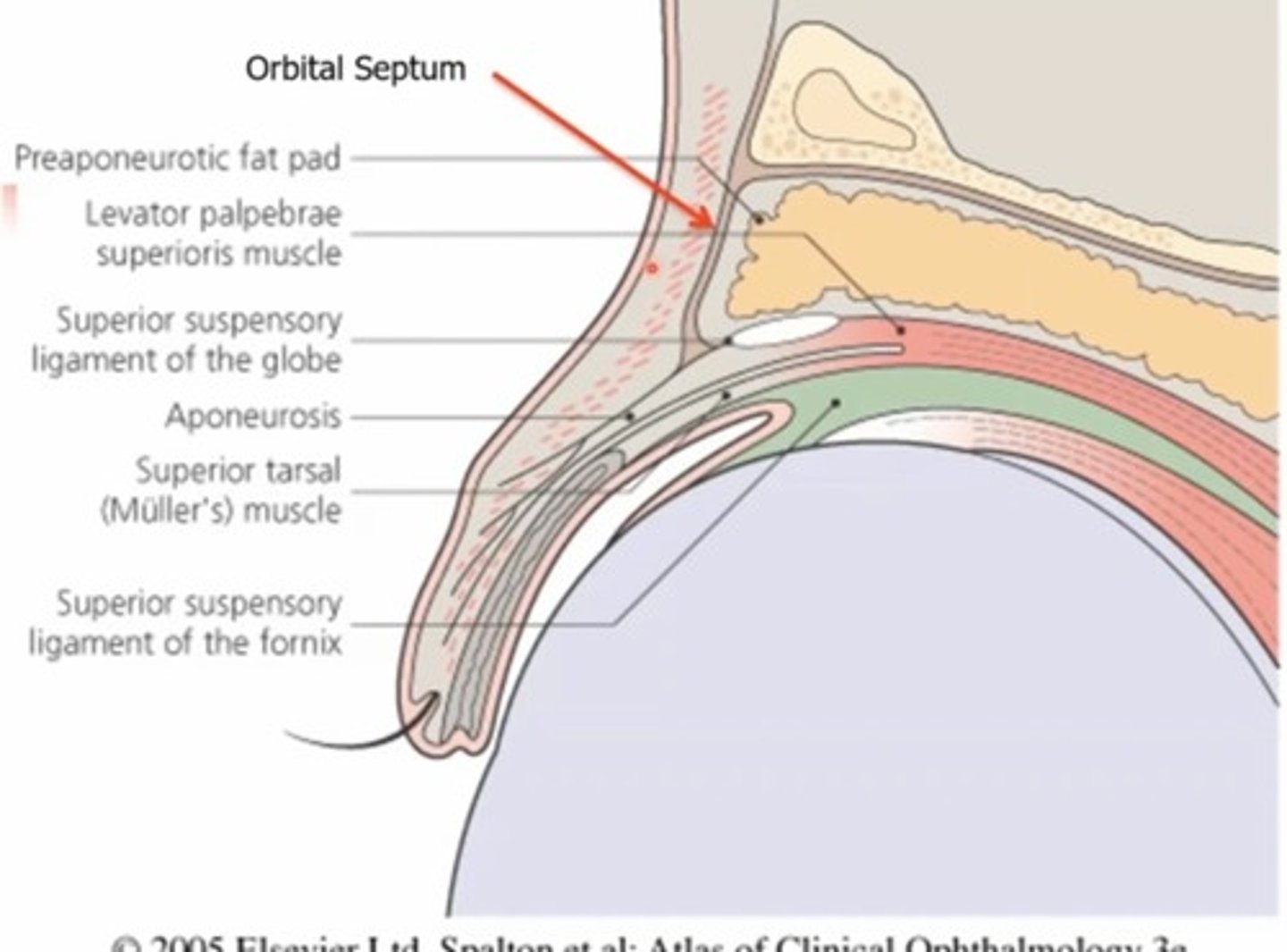
What is another name for tenons capsule?
Fascia bulbi
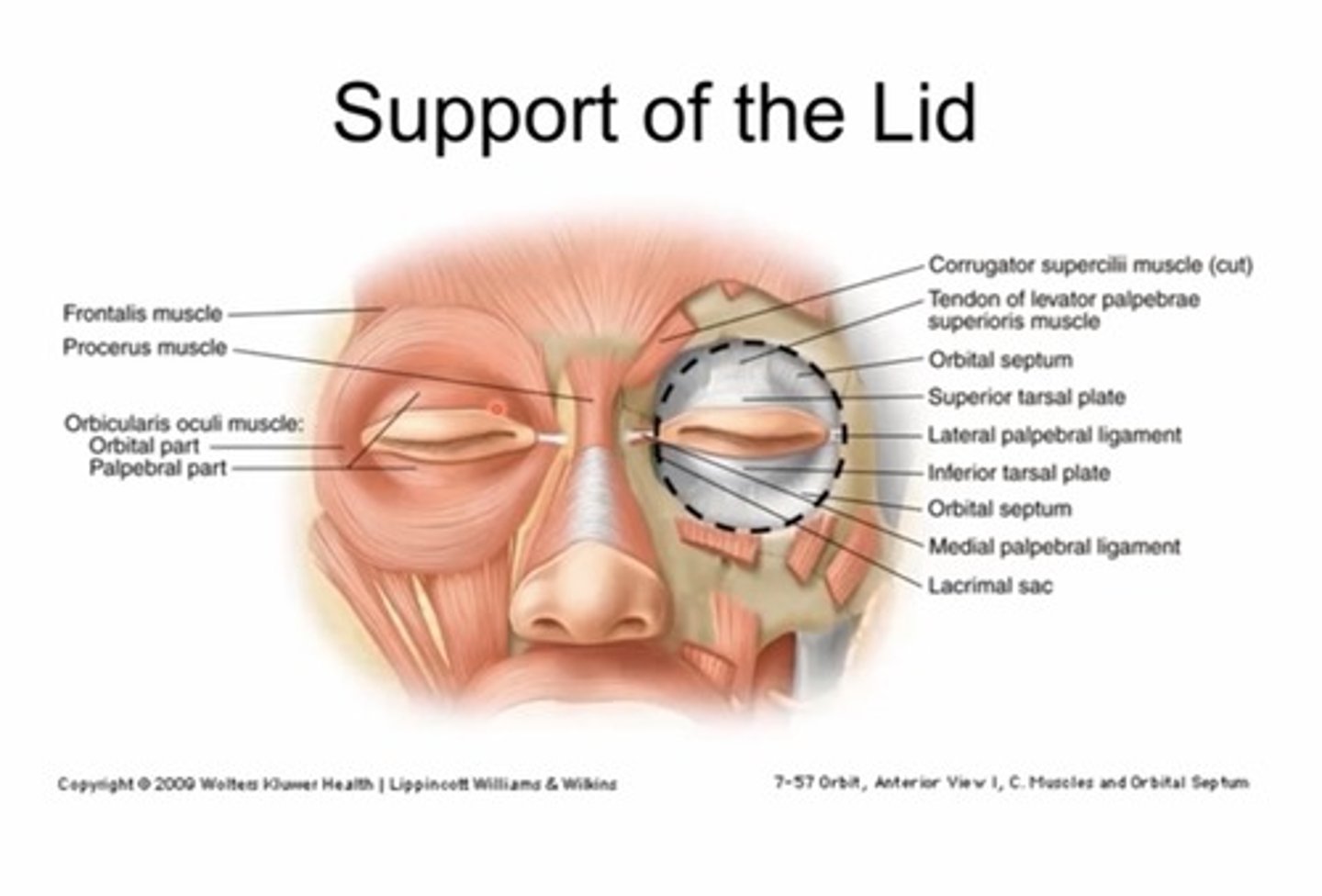
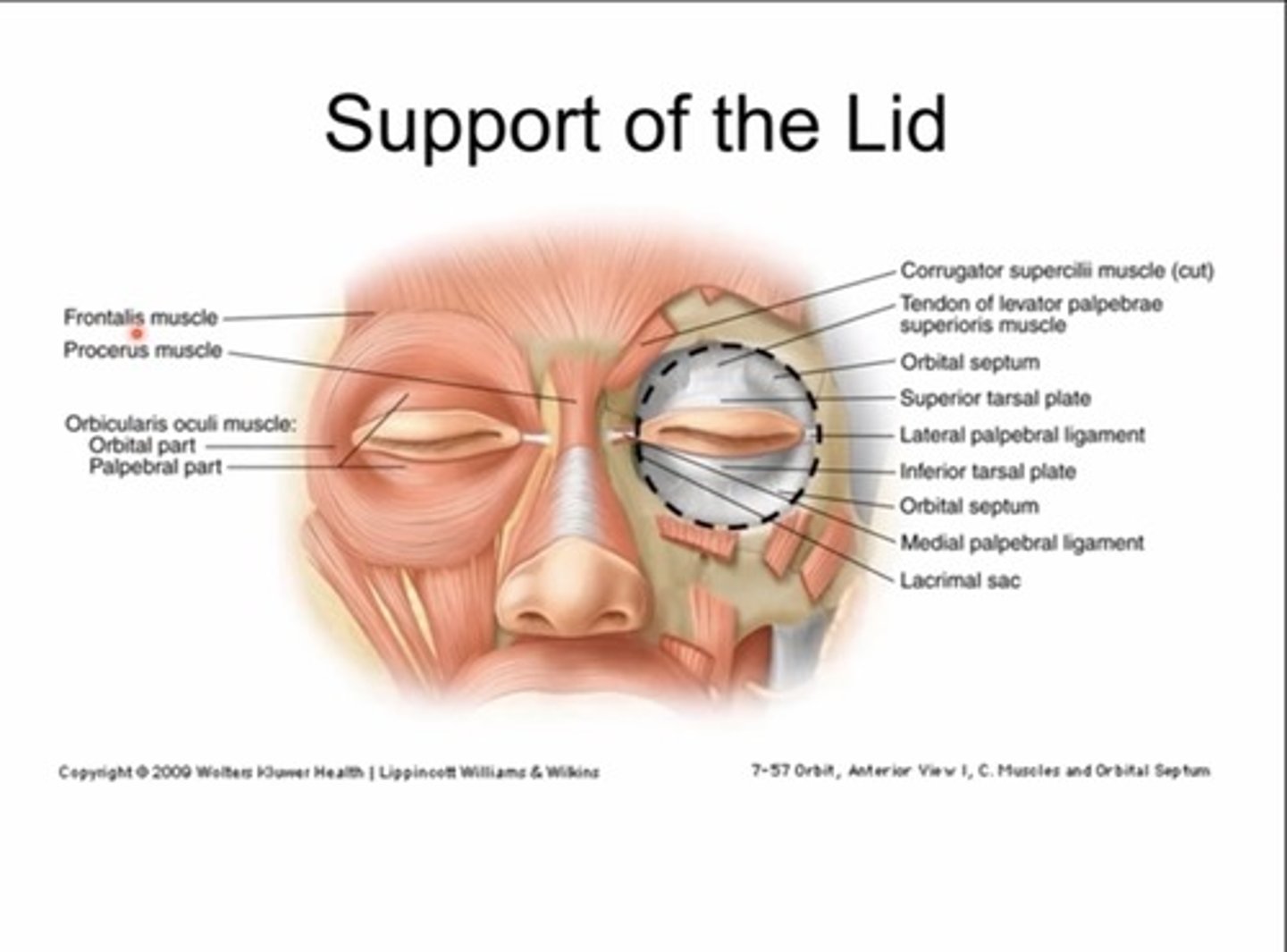
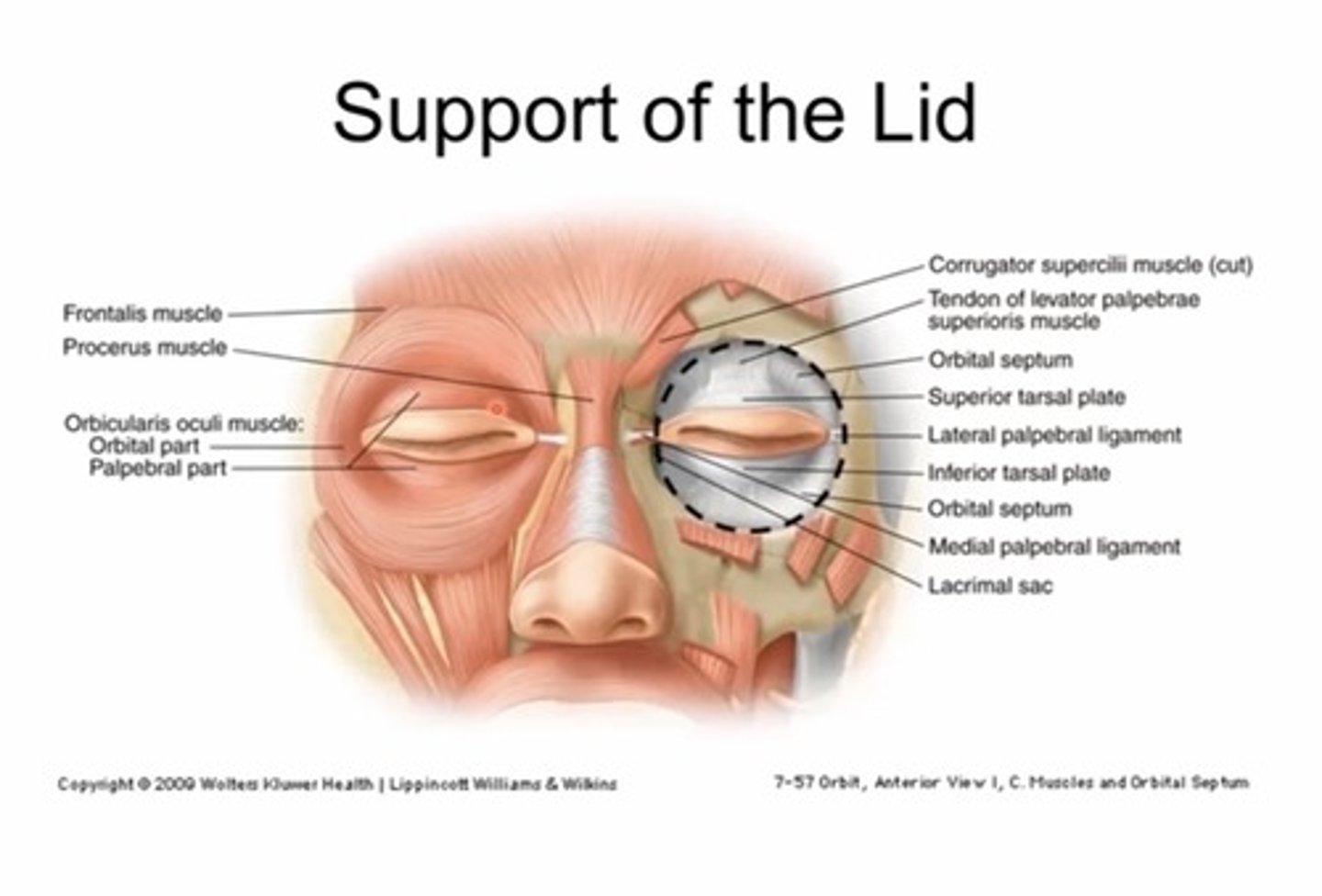
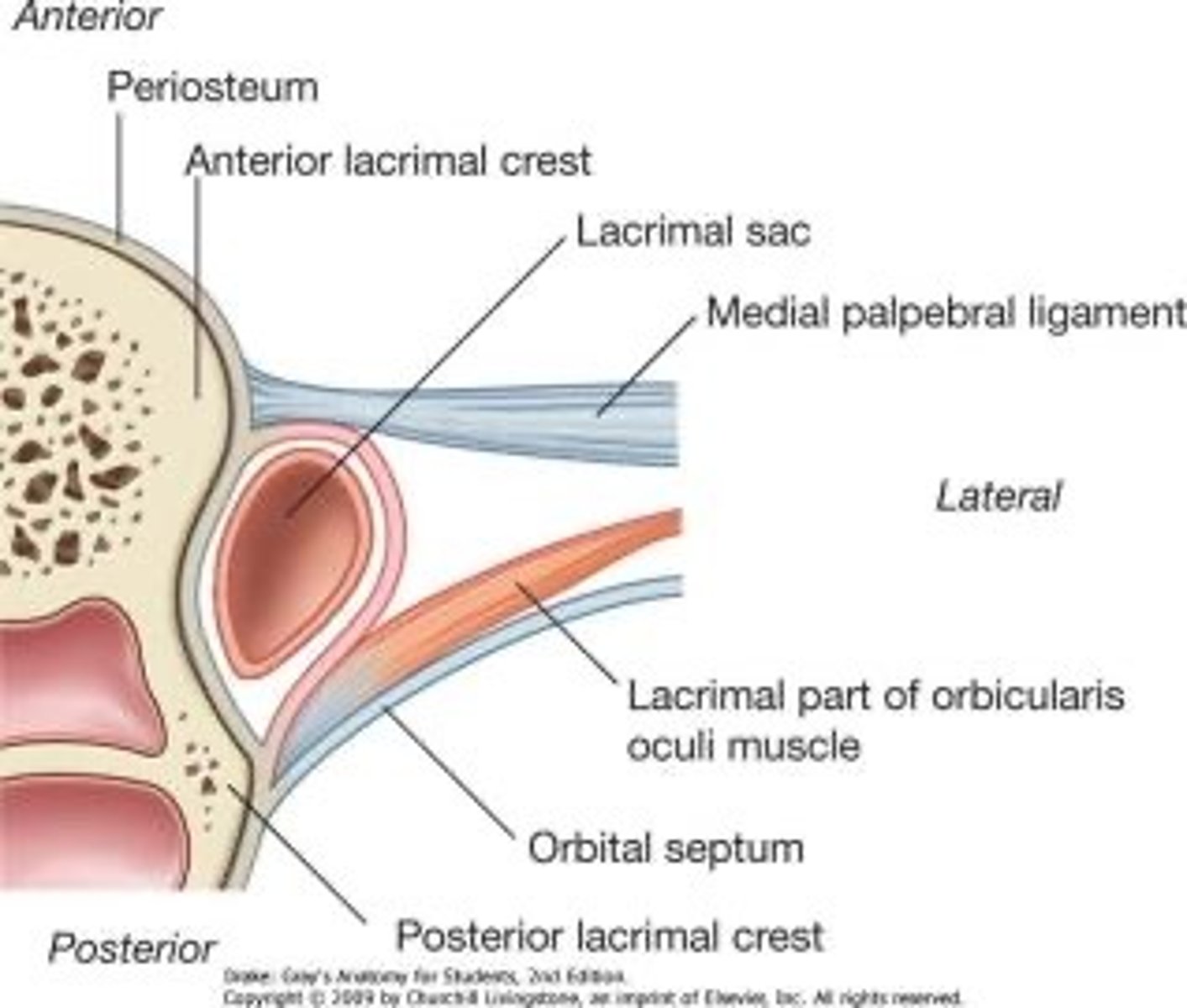
What is the orbital septum?
Membraneous, fibrous sheets (collagen) - has superior and inferior portion
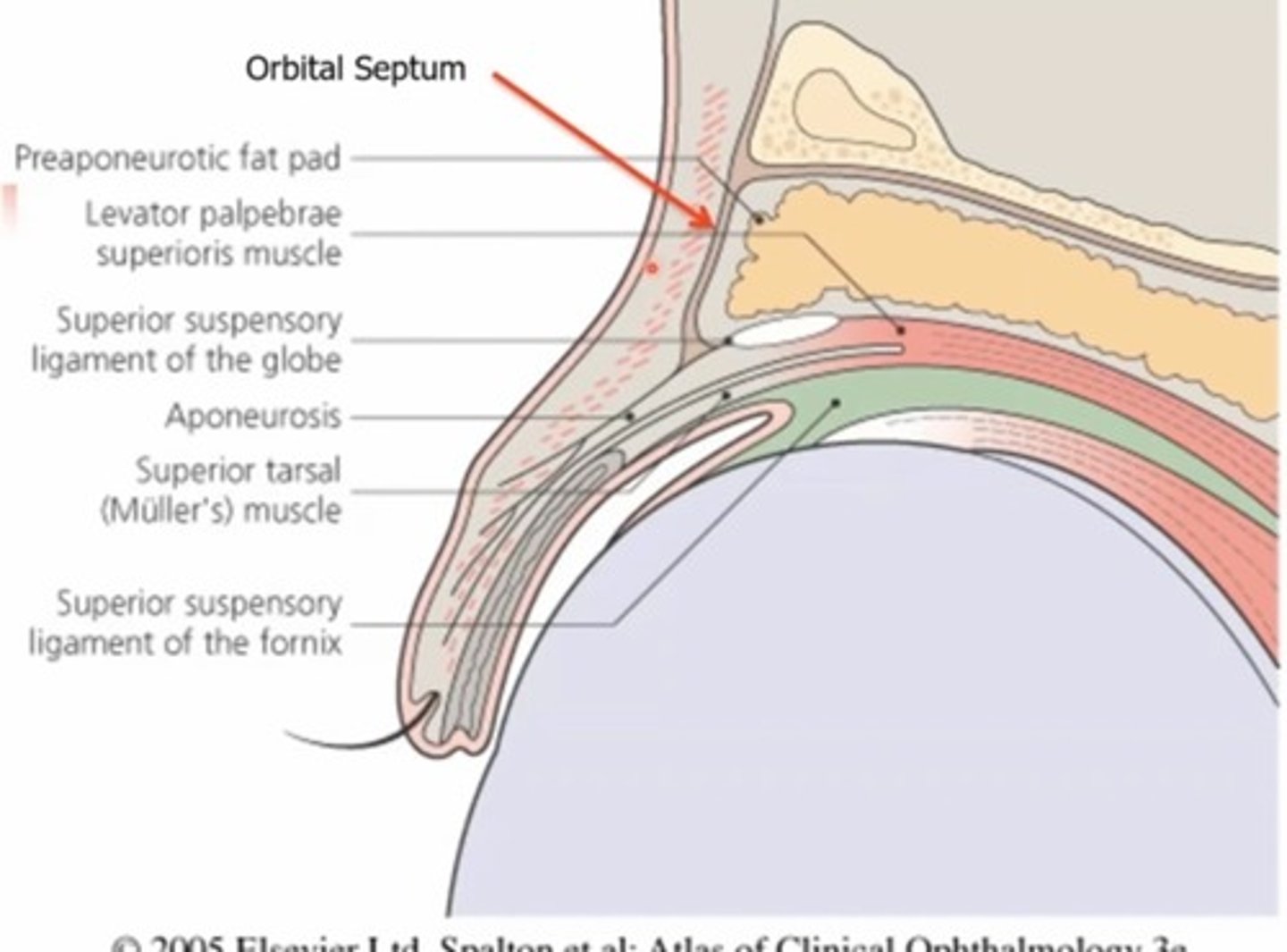
The superior septum extends from the orbital rim to.....
The tendon of the levator
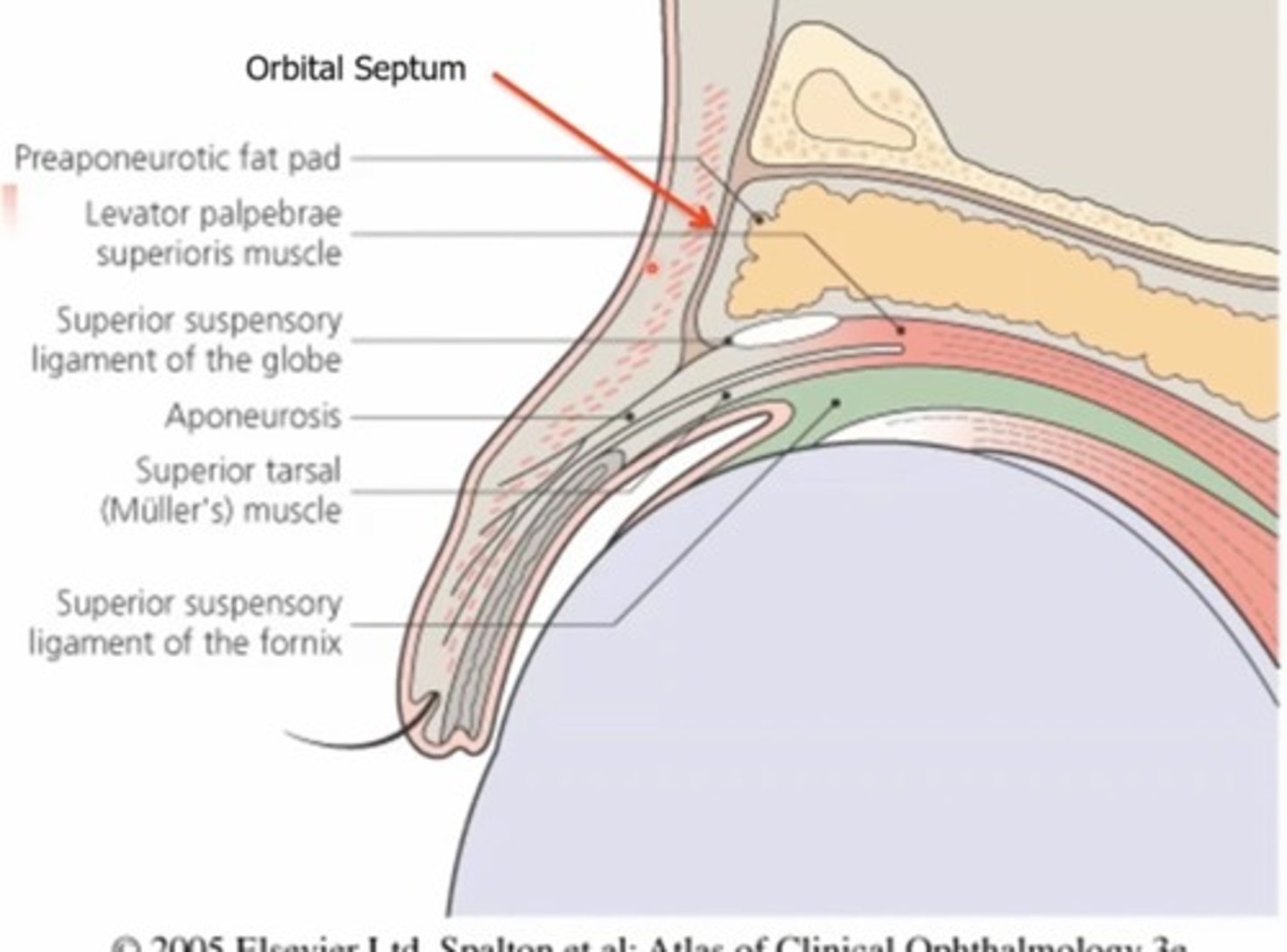
The inferior orbital septum extends from the orbital rim to the...
Inferior tarsal plate
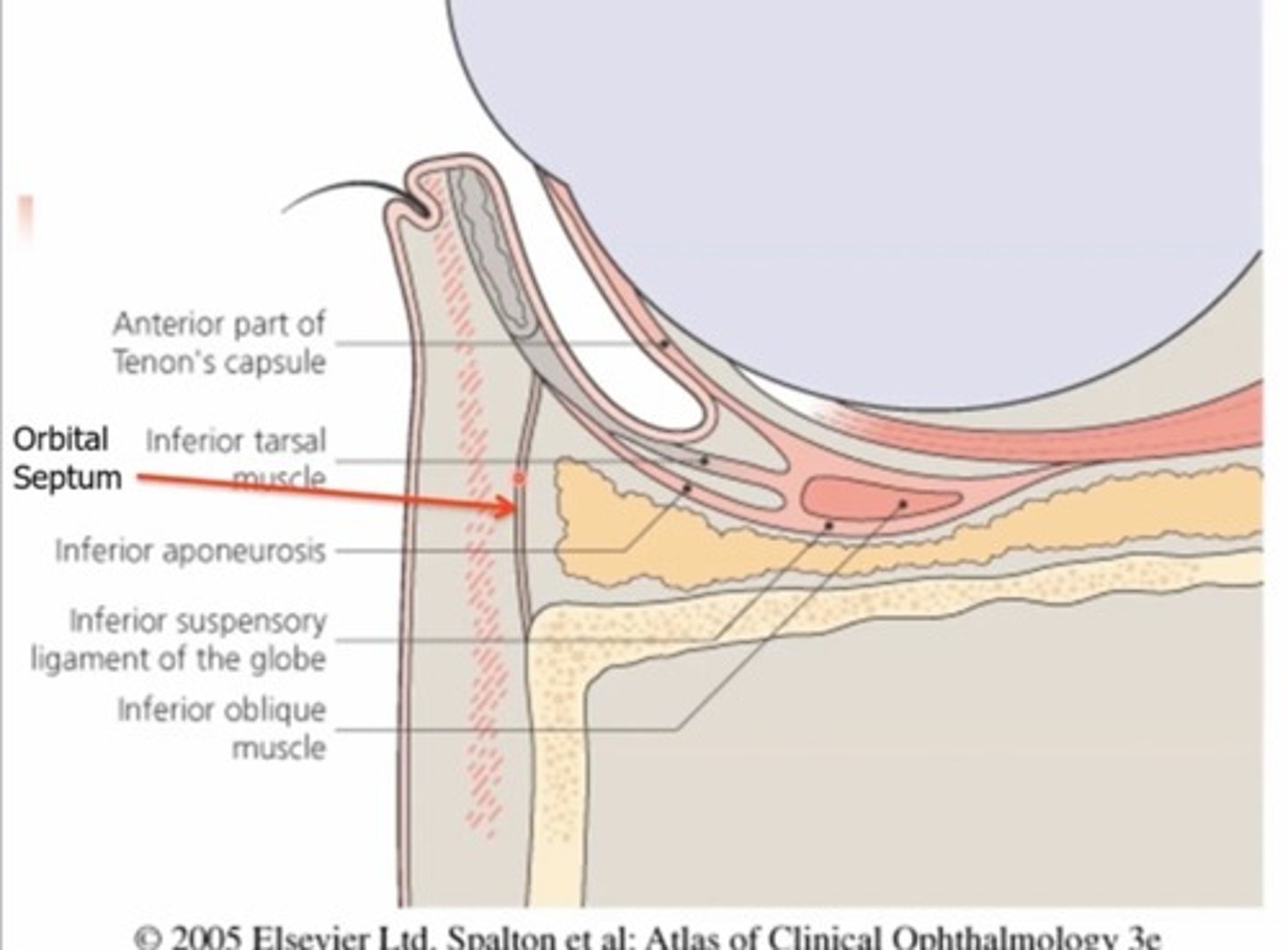
What are the functions of the tenons capsule?
1. Protective covering
2.Attachment site for EOMs
What is the function of the tarsal plates?
Maintain firmness and shape of lids
What are tarsal plates?
Dense, fibrous connective tissue
Found in the top and bottom lid
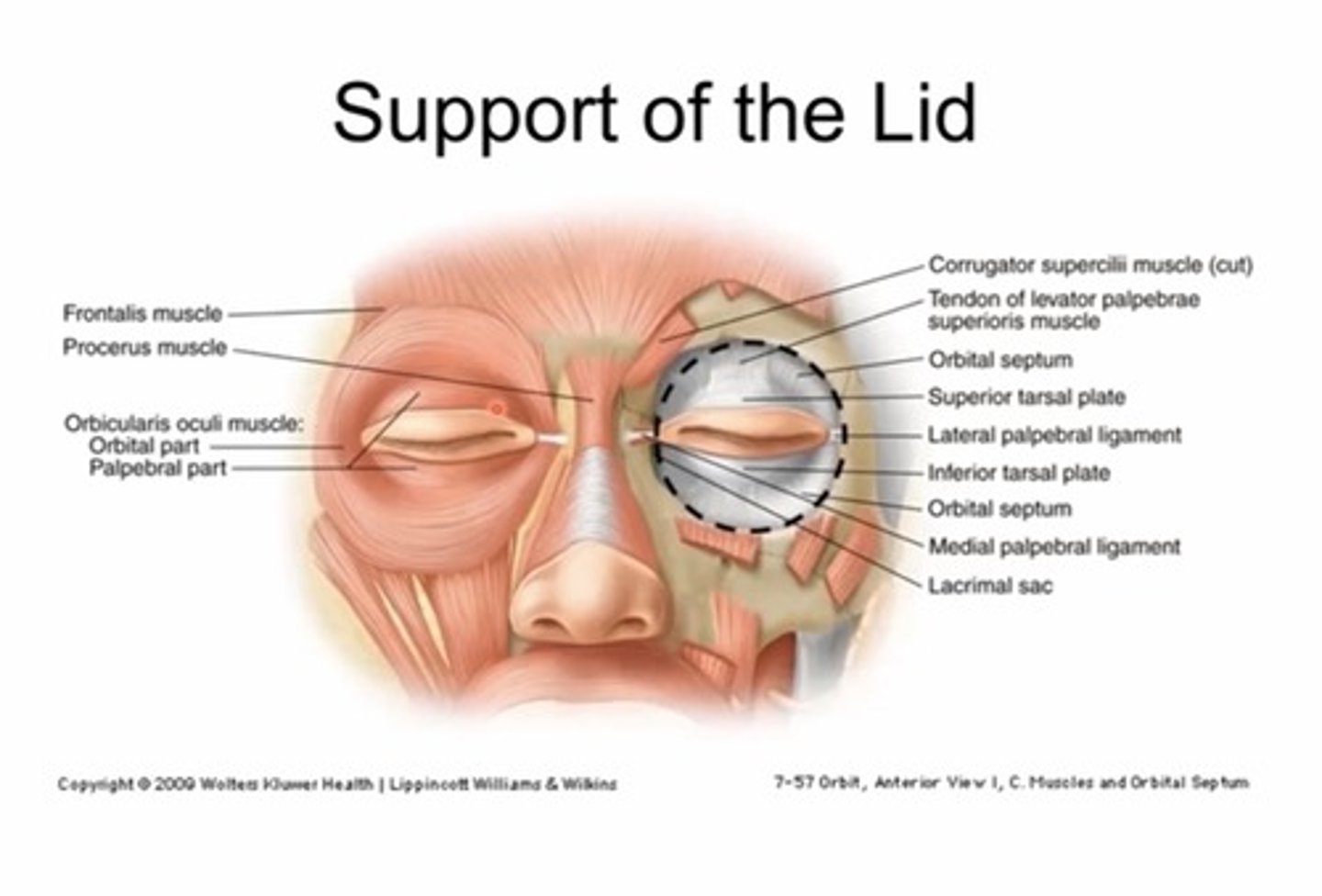
Which tarsal plate is bigger?
The superior tarsal plate is 10-11mm in height, the inferior TP is 5mm in height
That's why its easier to flip a top lid
What are the two portions of the lids?
Anterior and posterior lamella
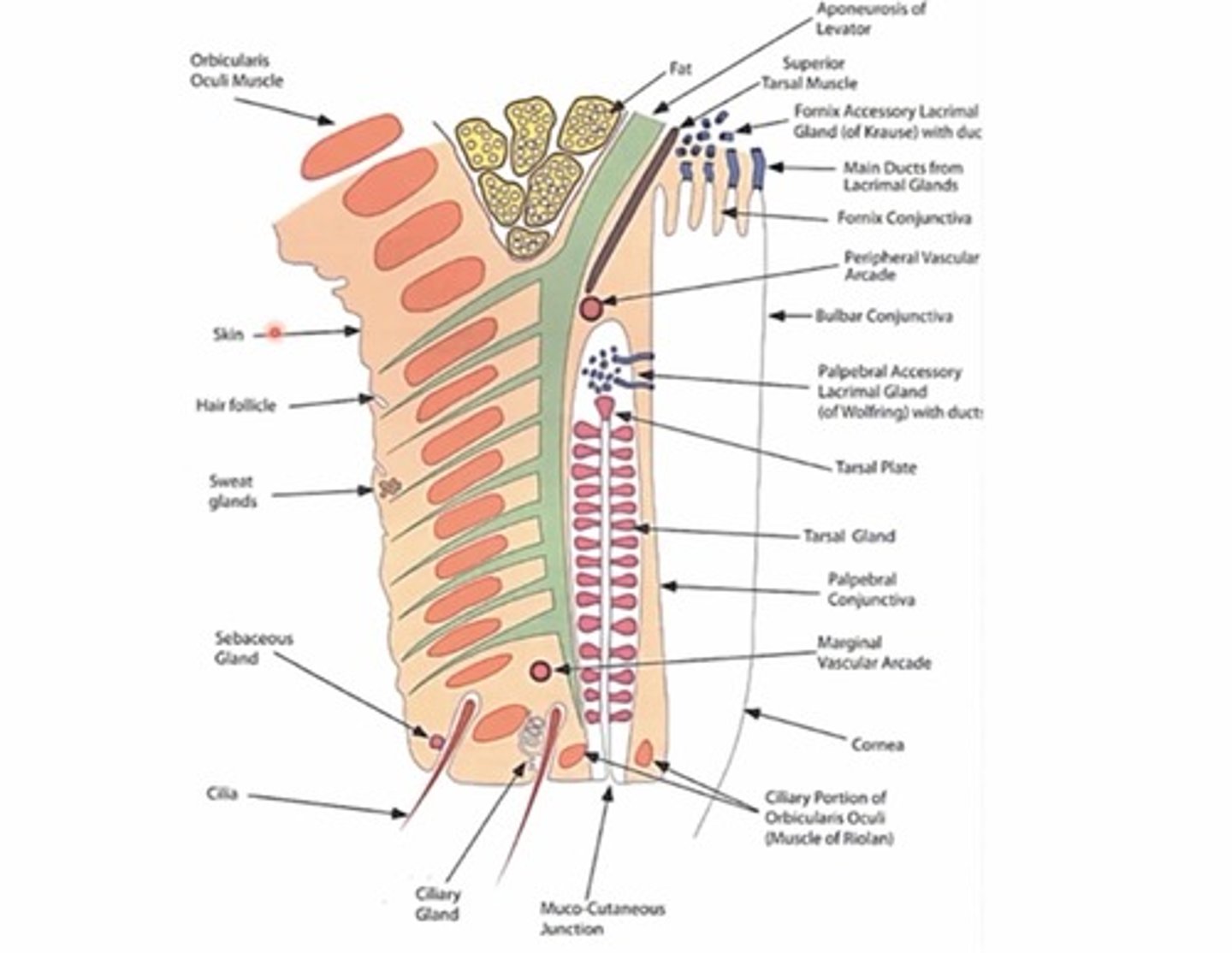
What's the nickname for the border between the anterior and posterior lamella?
The 'gray line'
What structures comprise the anterior lamella?
Eyelid skin
Orbicularis muscle
Lashes
Ciliary, sebaceous, and sweat glands
Levator aponeurosis
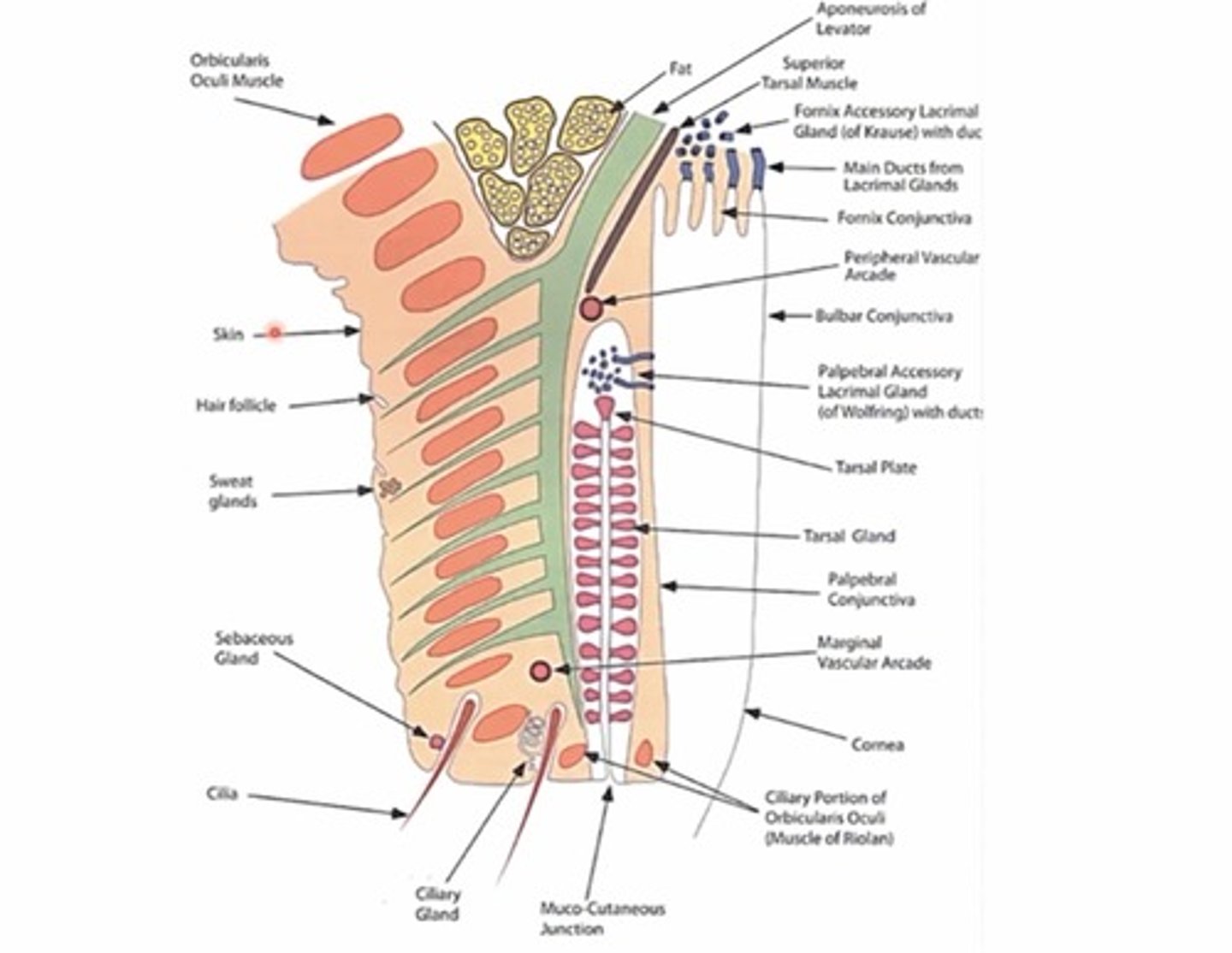
What structures comprise the posterior lamella?
Tarsal plates and glands (Meibomian glands - found inside tarsal plates)
Palpebral conjunctiva (back of lid)
Lacrimal glands
Muller muscle (tarsal muscle)
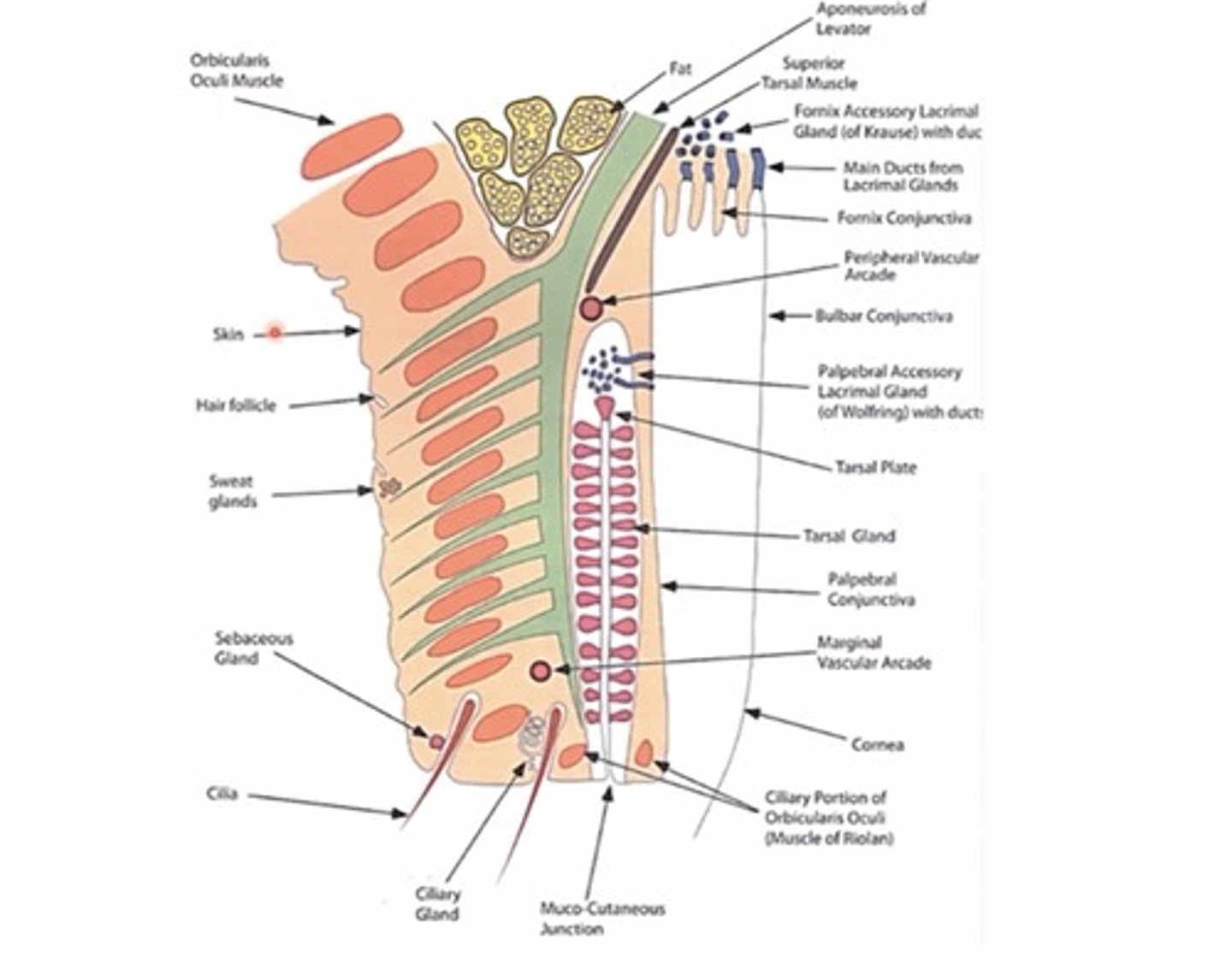
What is the muco-cutaneous junction?
This is the point where the keratin from the anterior lamella ends and mucus starts (b/w front and back lid)
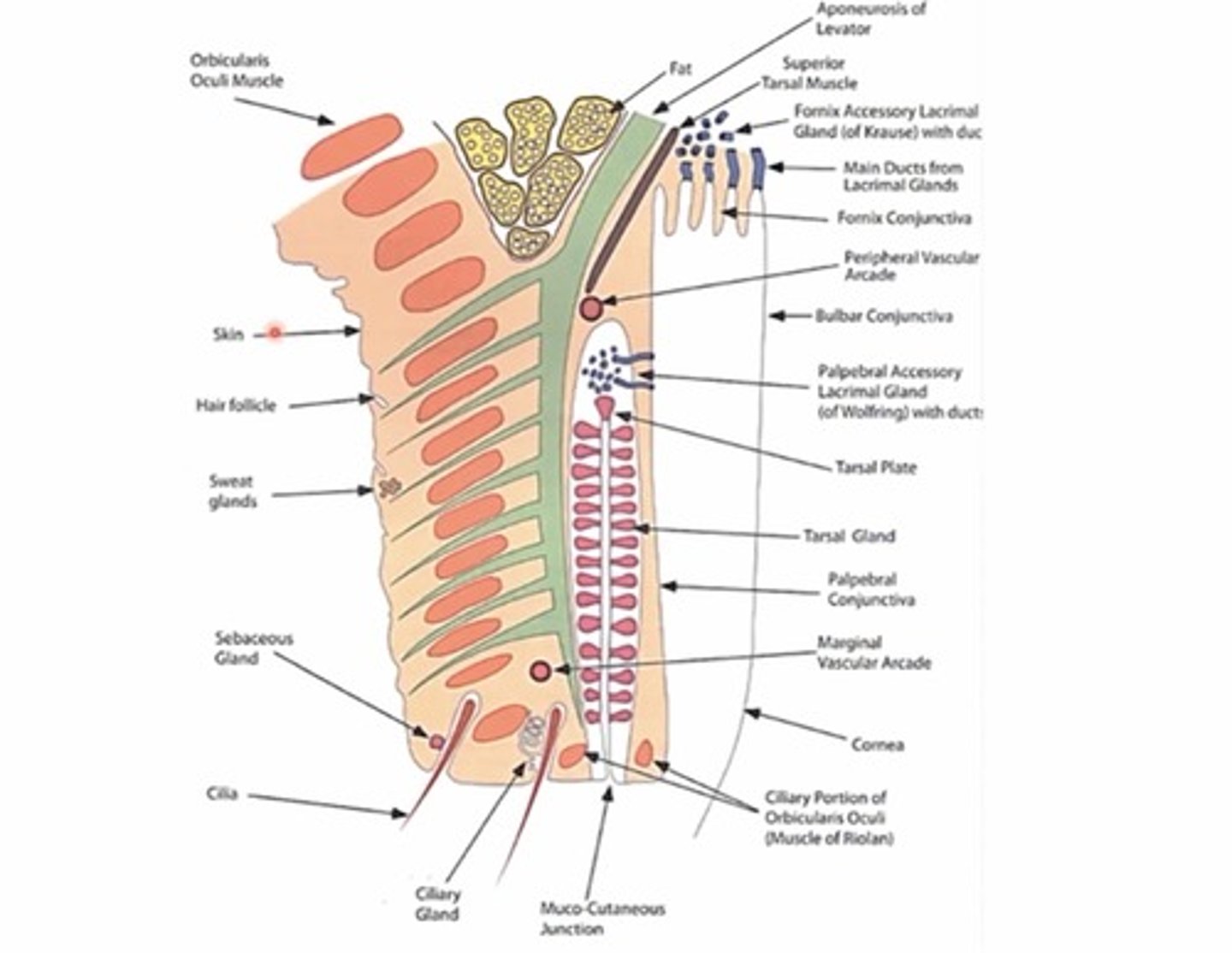
What are the parts of the orbicularis oculi muscle?
1. Orbital portion
2. Palpebral portion
3. Ciliary portion
4. Lacrimal portion
CLOP
What type of muscle is the orbicularis oculi muscle?
Sphincter muscle
What does the palpebral portion of the orbicularis muscle do?
Involuntary blinks
Blinking action 'milks' tarsal plate glands
Keeps lids tight to eyes so they dont droop
What does the ciliary portion of the orbicularis muscle do?
Surrounds the openings of the meibomian glands and it's contraction/relaxation regulations the MBG excretions onto the ocular surface
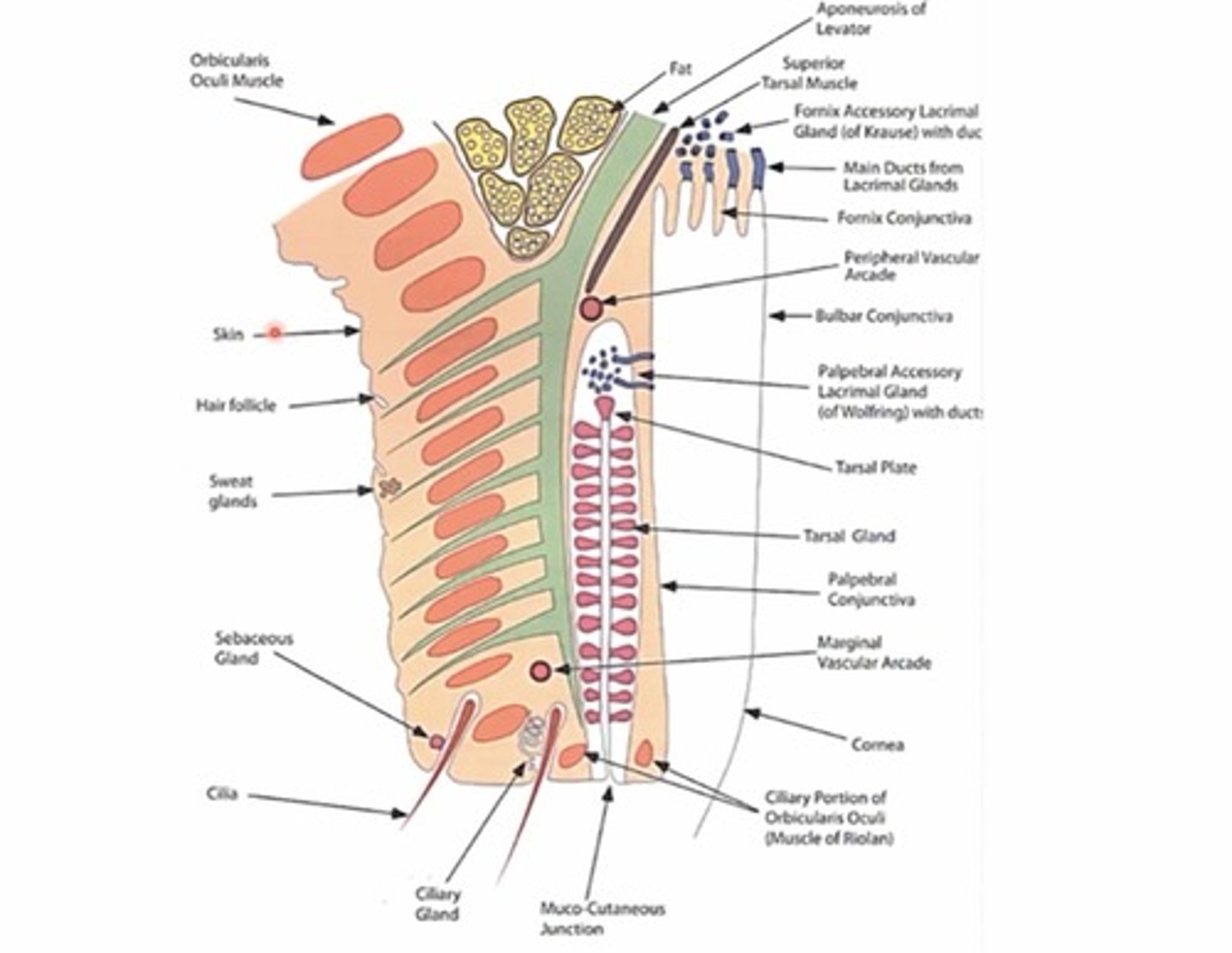
What is another name for the ciliary portion of the orbicularis muscle?
Muscle of Riolan
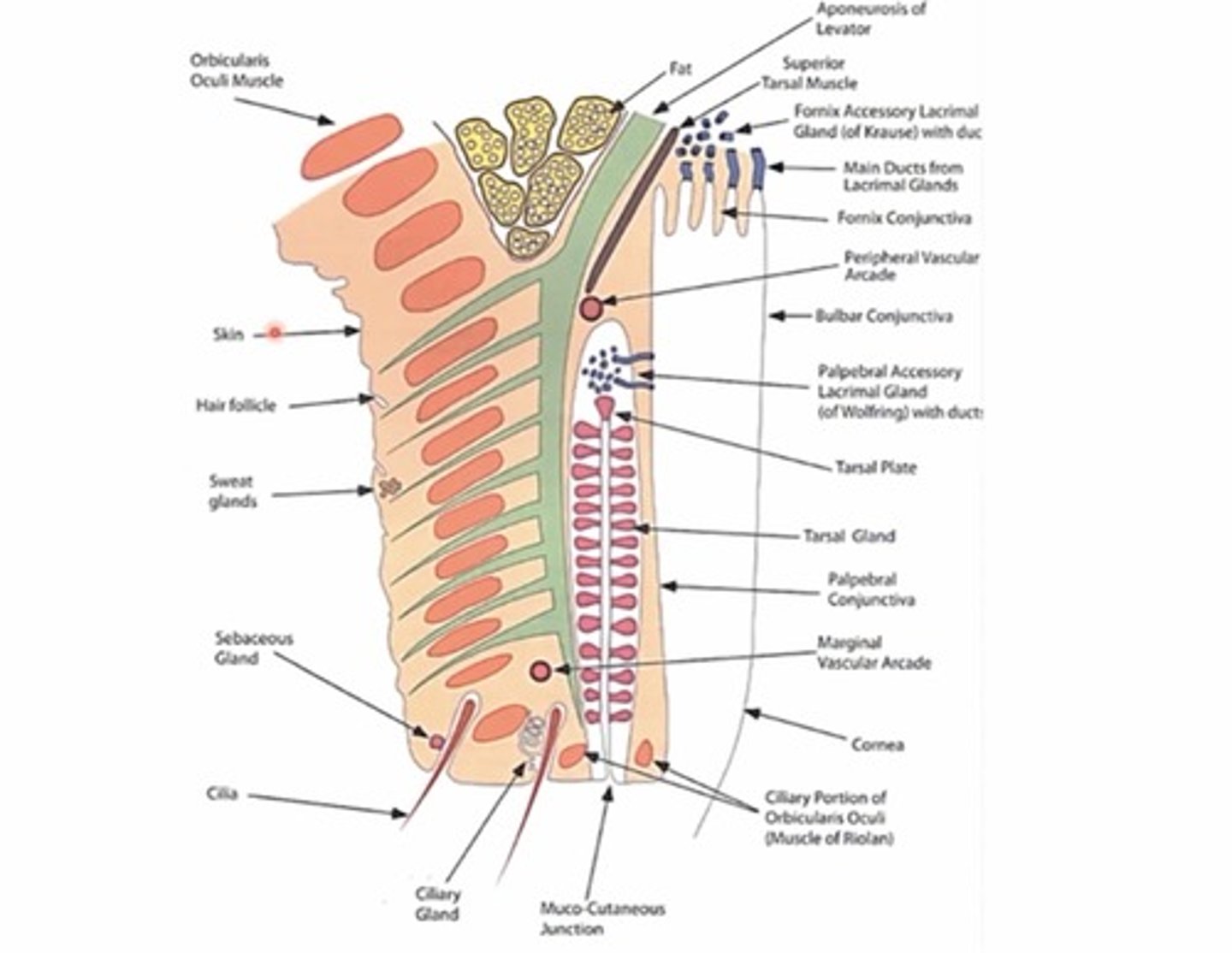
What is another name for the lacrimal portion of the orbicularis muscle?
Horners muscle
What is the aponeurosis of levator muscle?
Tendon in the lid that extends from the levator muscle

What separates the sections of the palpebral portion of the orbicularis in the lids?
The aponeurosis of levator muscle
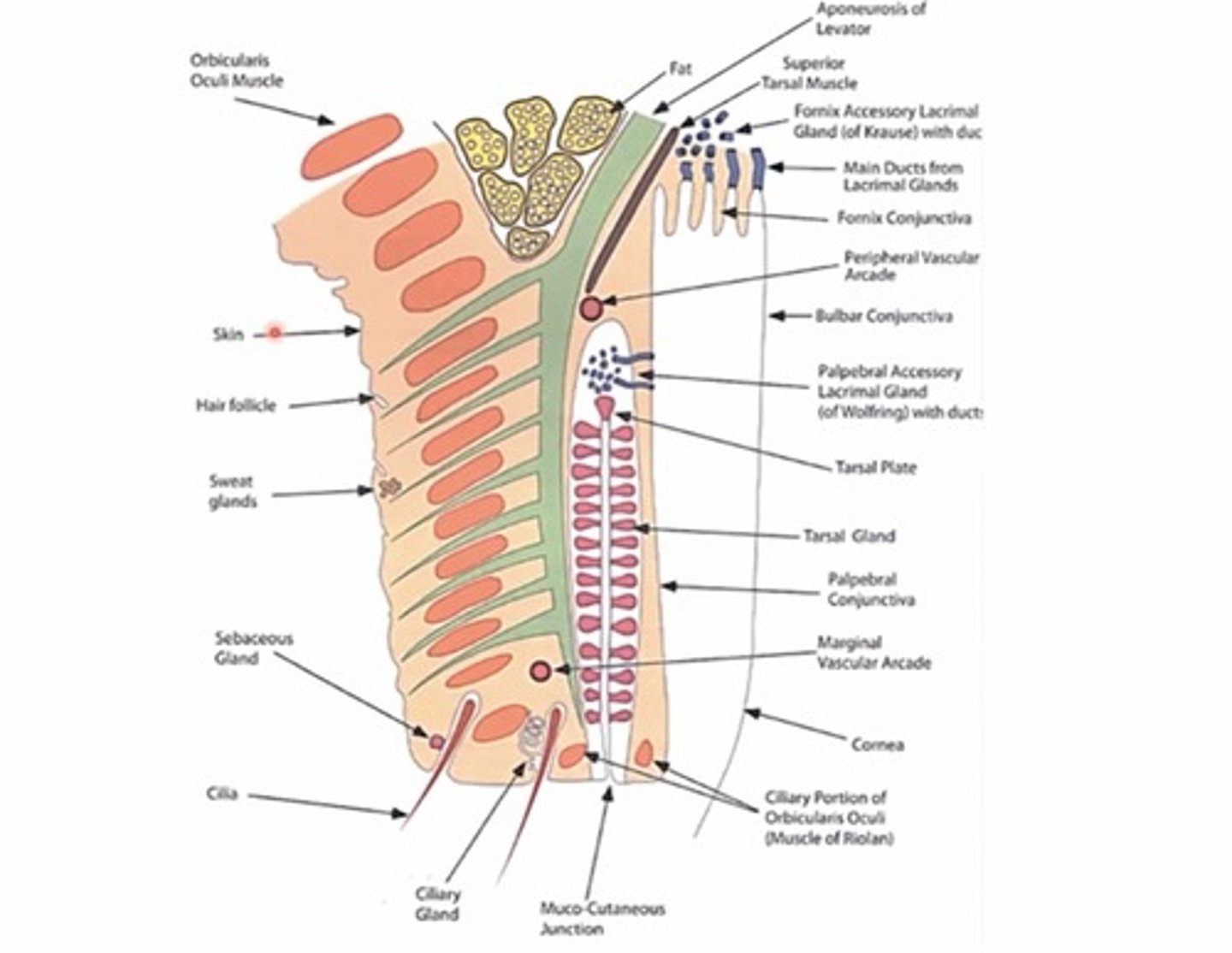
Where does the tarsal muscle originate from?
The levator muscle
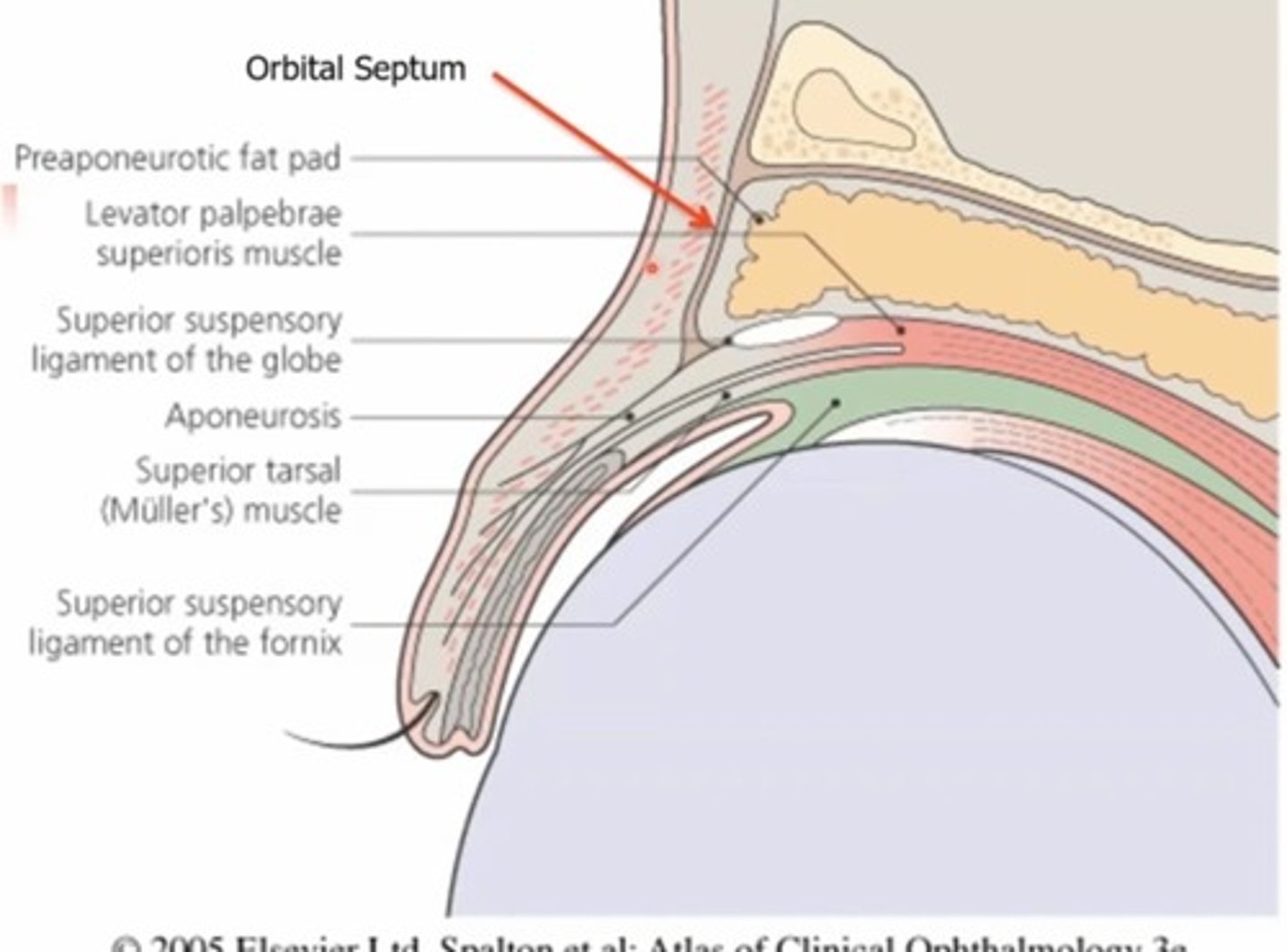
What nervous system innervates the tarsal muscle?
The sympathetic nervous system (muller muscle)
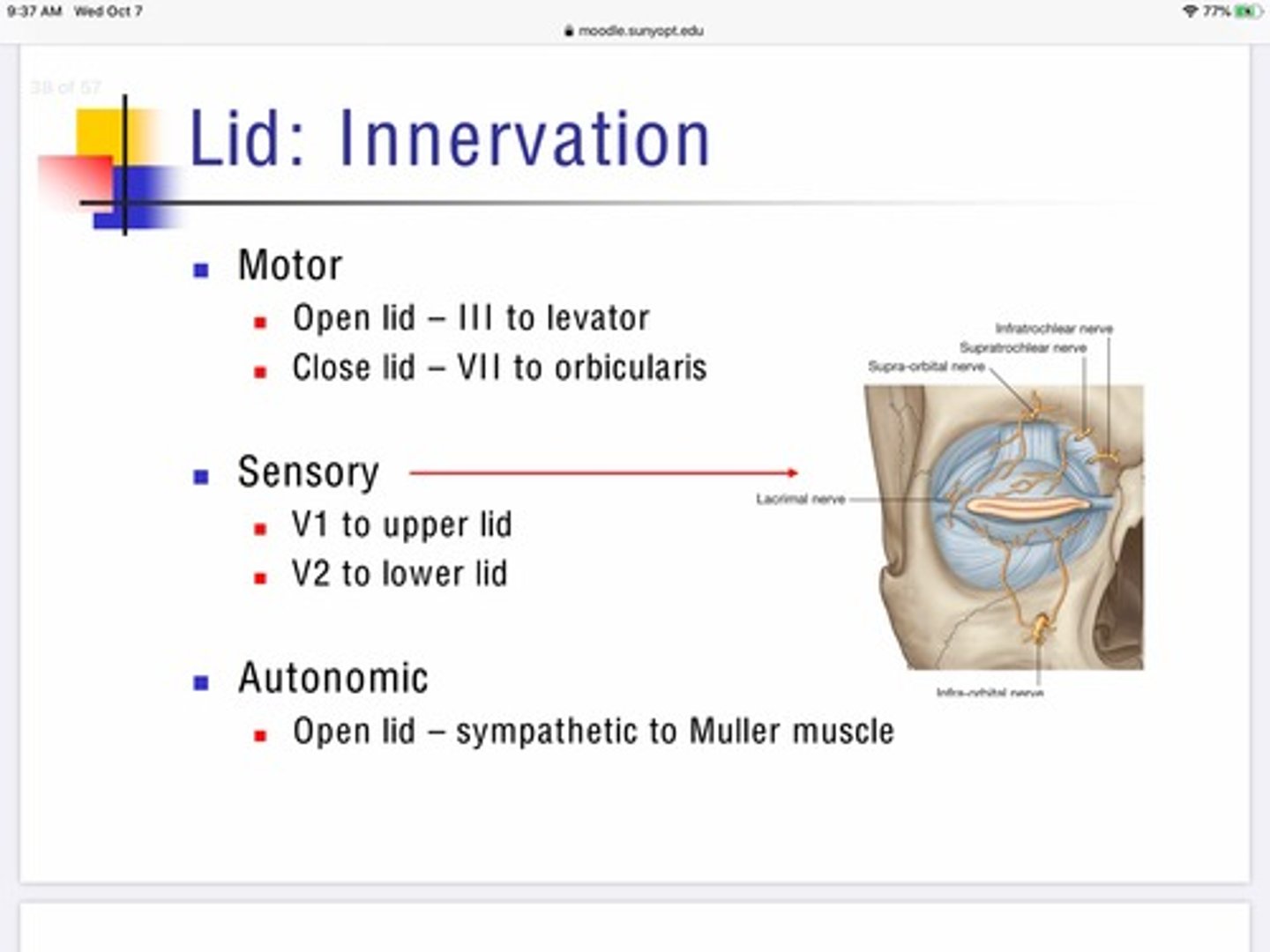
Orbicularis and levator are _______ of each other
Antagonists (work in opposition)
What glands are present in our lash line? What do they produce?
Ciliary glands - serous fluid
Sebaceous glands - oils
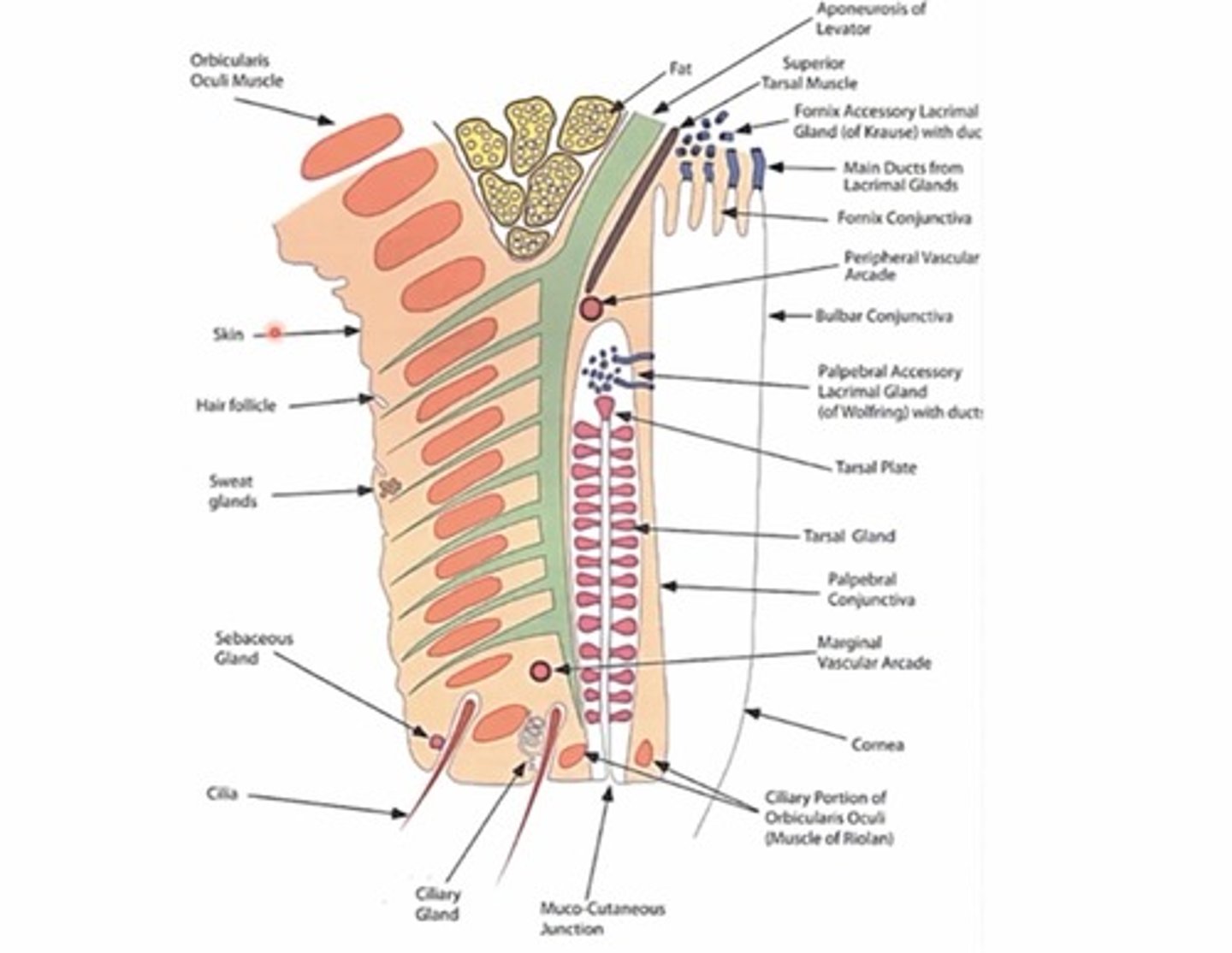
How many tarsal glands (meibomian glands) are in top and bottom lids on average?
30-40 in UL
20-30 in LL
What are the two types of lacrimal glands found in the posterior lamella?
Fornix lacrimal gland of Krause
Palpebral Lacrimal gland of wolfring
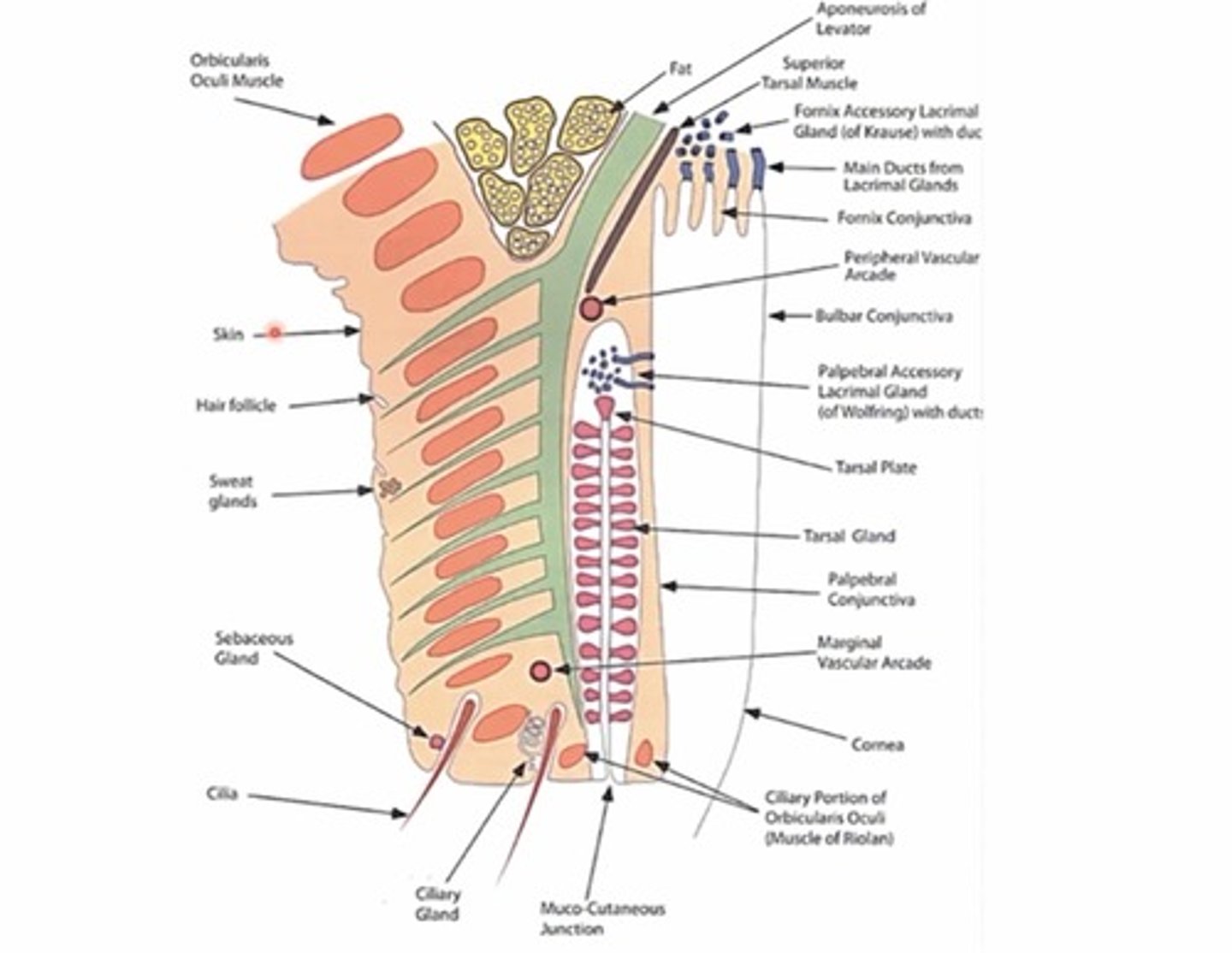
Where are lacrimal glands of Krause located?
Found in fornix portion of the conjunctiva
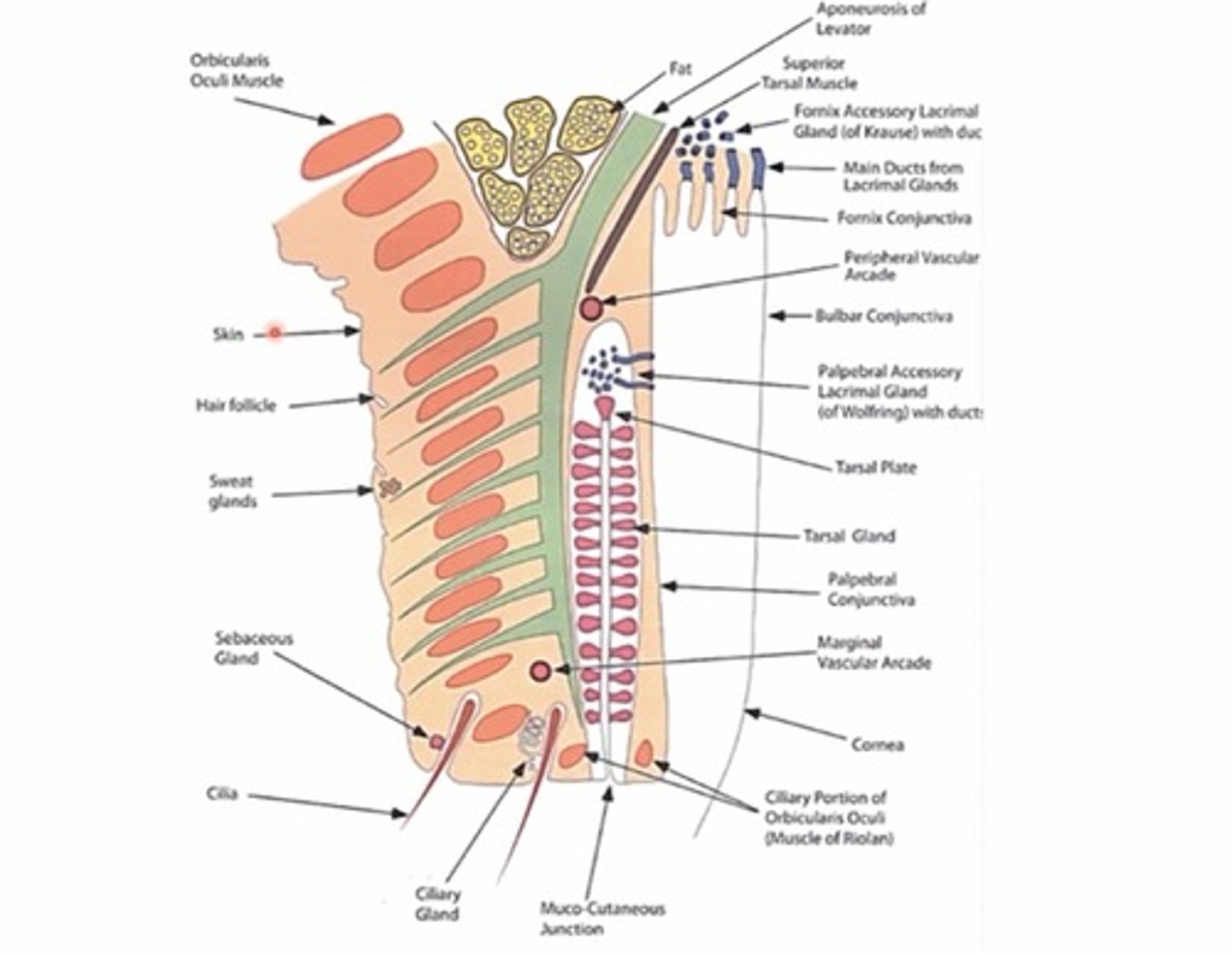
Where are lacrimal glands of wolfring located?
In the superior portion of the tarsal plates (closer to the fornix)
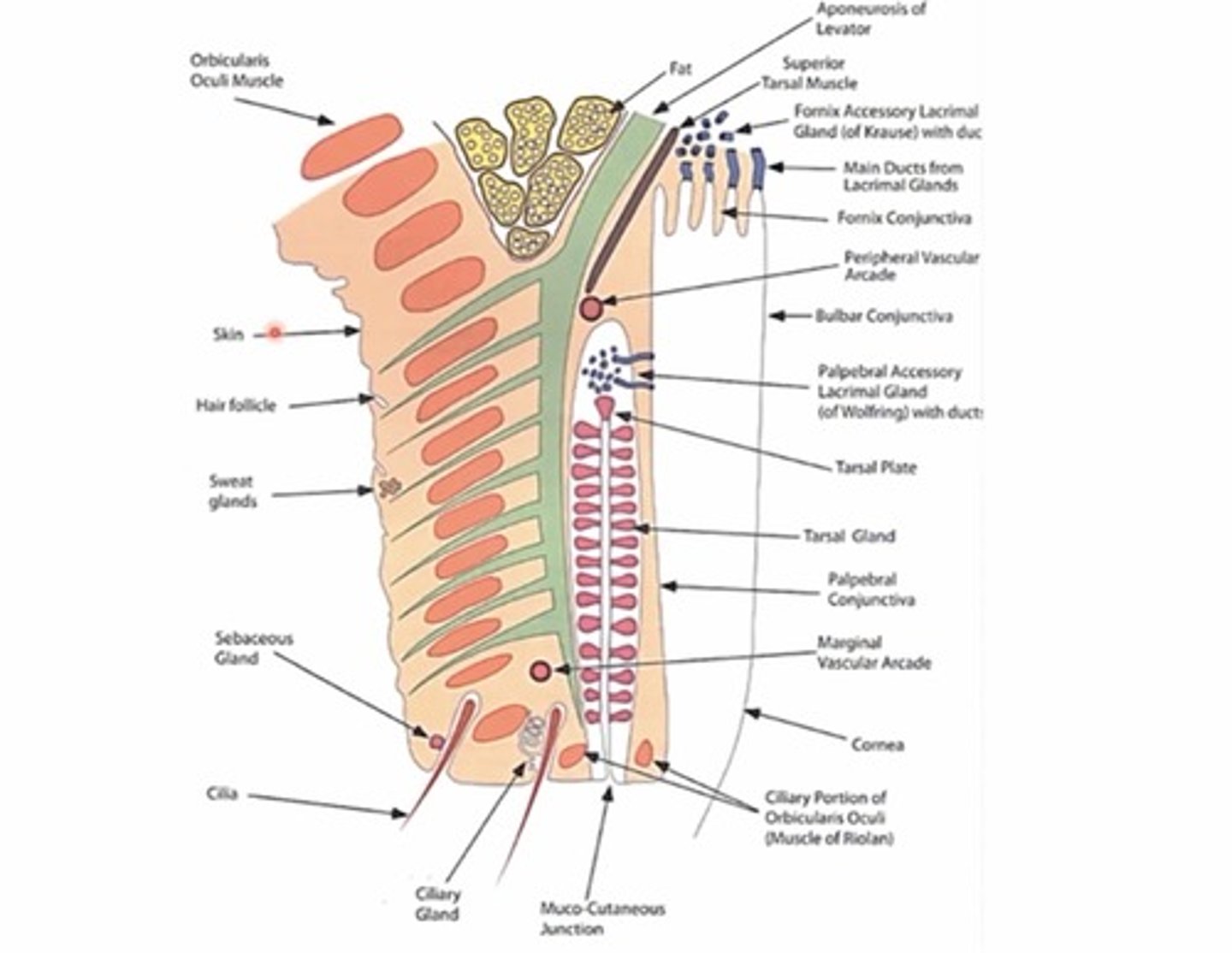
What is the function of the lacrimal glands in the posterior lamella?
create and Secrete serous fluid (aqueous portion of tear film)
What type of light can be used during imaging to visualize the meibomian glands?
Infrared light
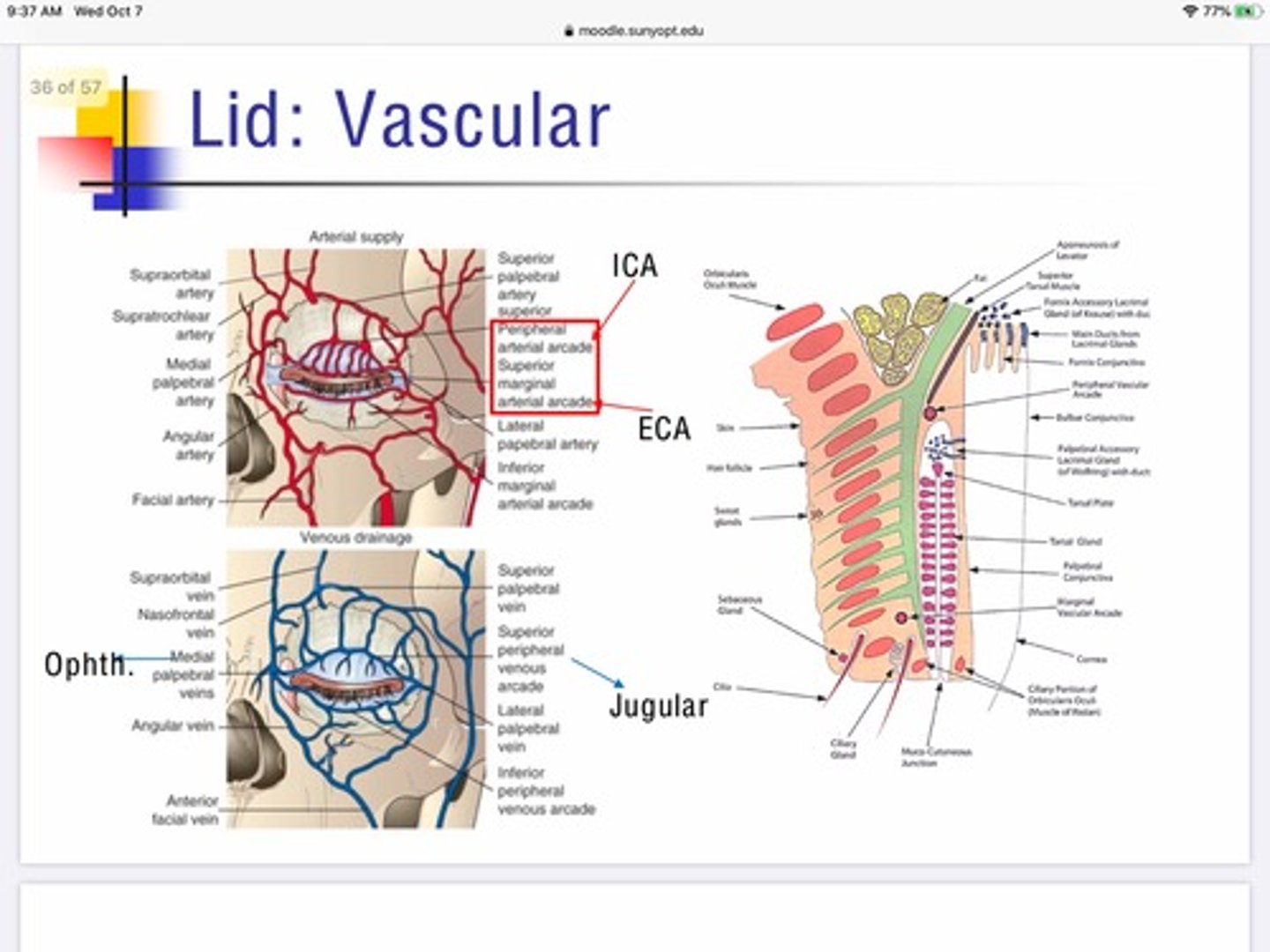
What artery supplies oxygenated blood flow for the peripheral arcade of the lid?
Internal carotid
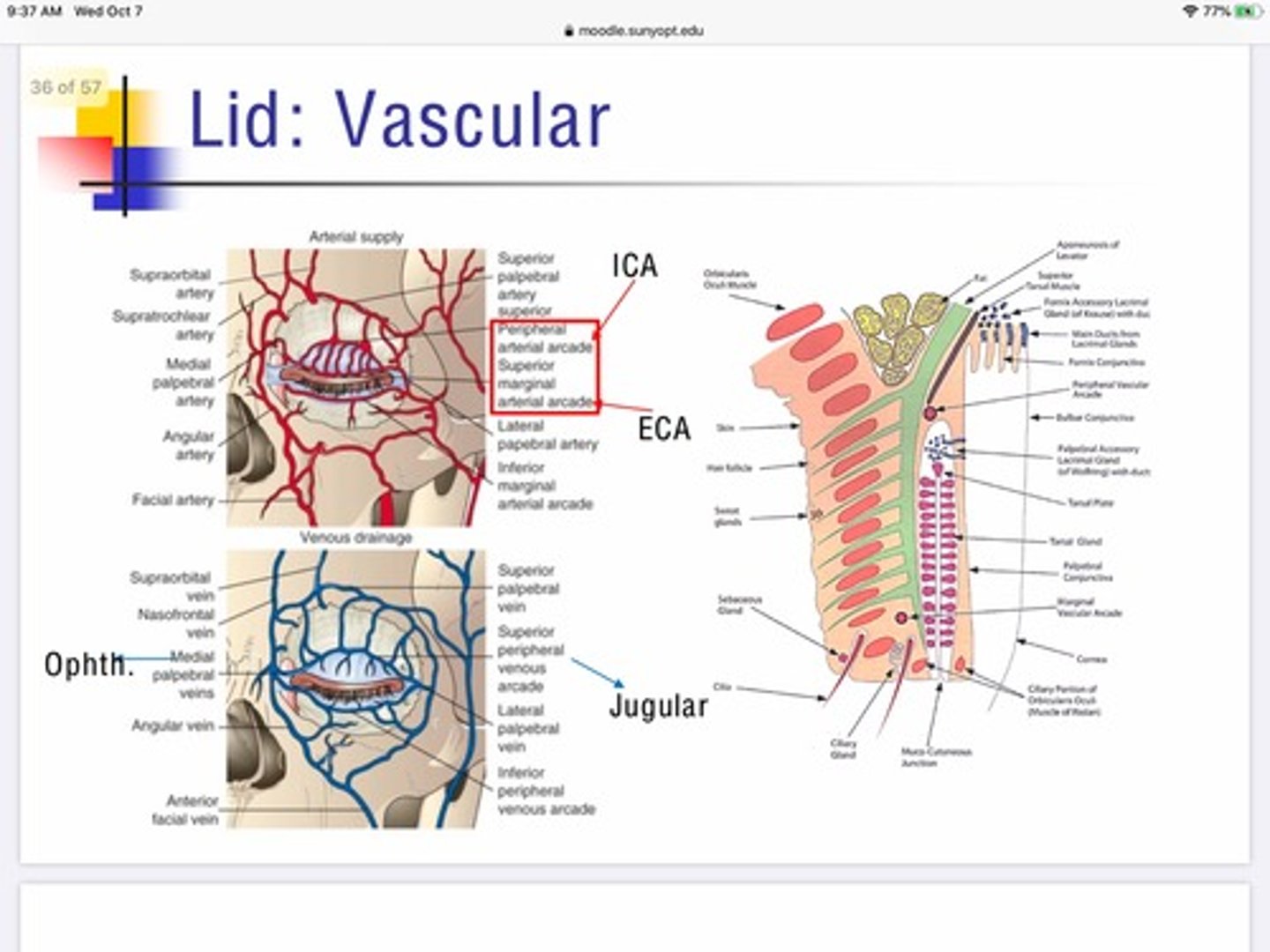
What artery supplies oxygenated blood flow for the marginal arcade of the lid?
External carotid
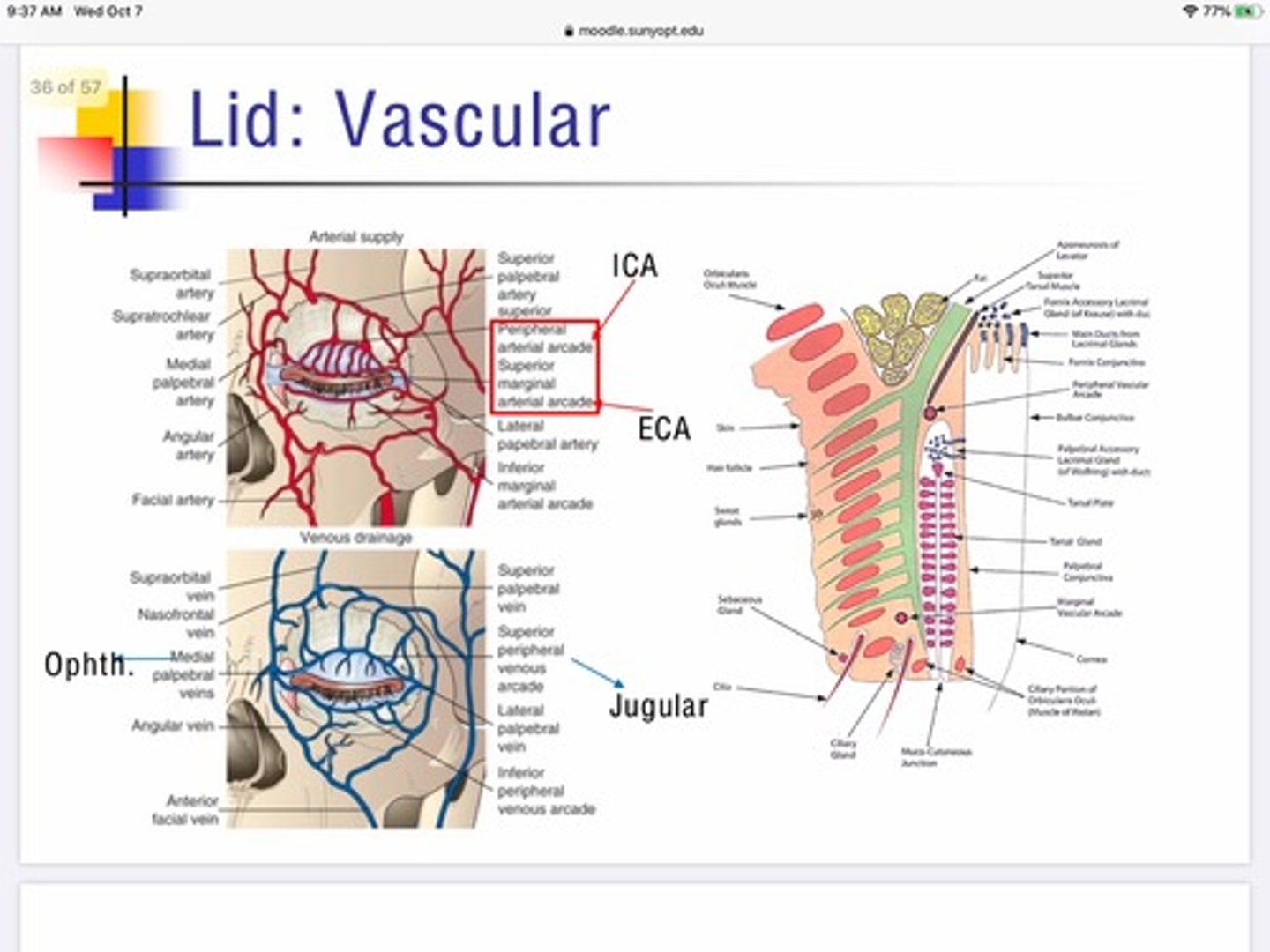
What vein is responsible for the flow of deoxygenated blood away from the medial portion of the eyelid?
Superior/inferior ophthalmic veins —-> leads to cavernous sinus
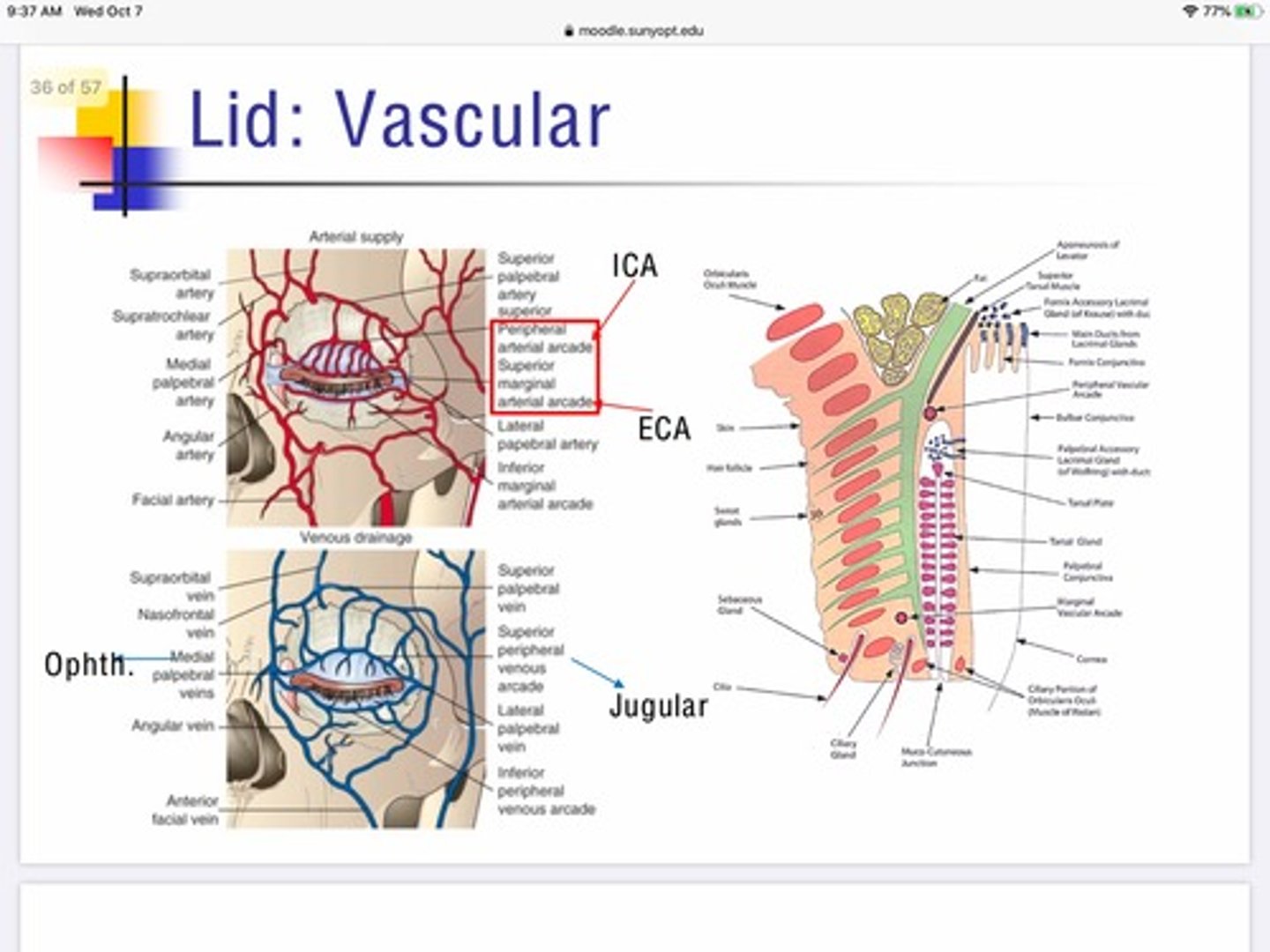
What's special about the artery innervation in the lids?
The lid serves as a site of anastomoses between the internal and external carotid via interactions of the vascular network of the peripheral and marginal lid
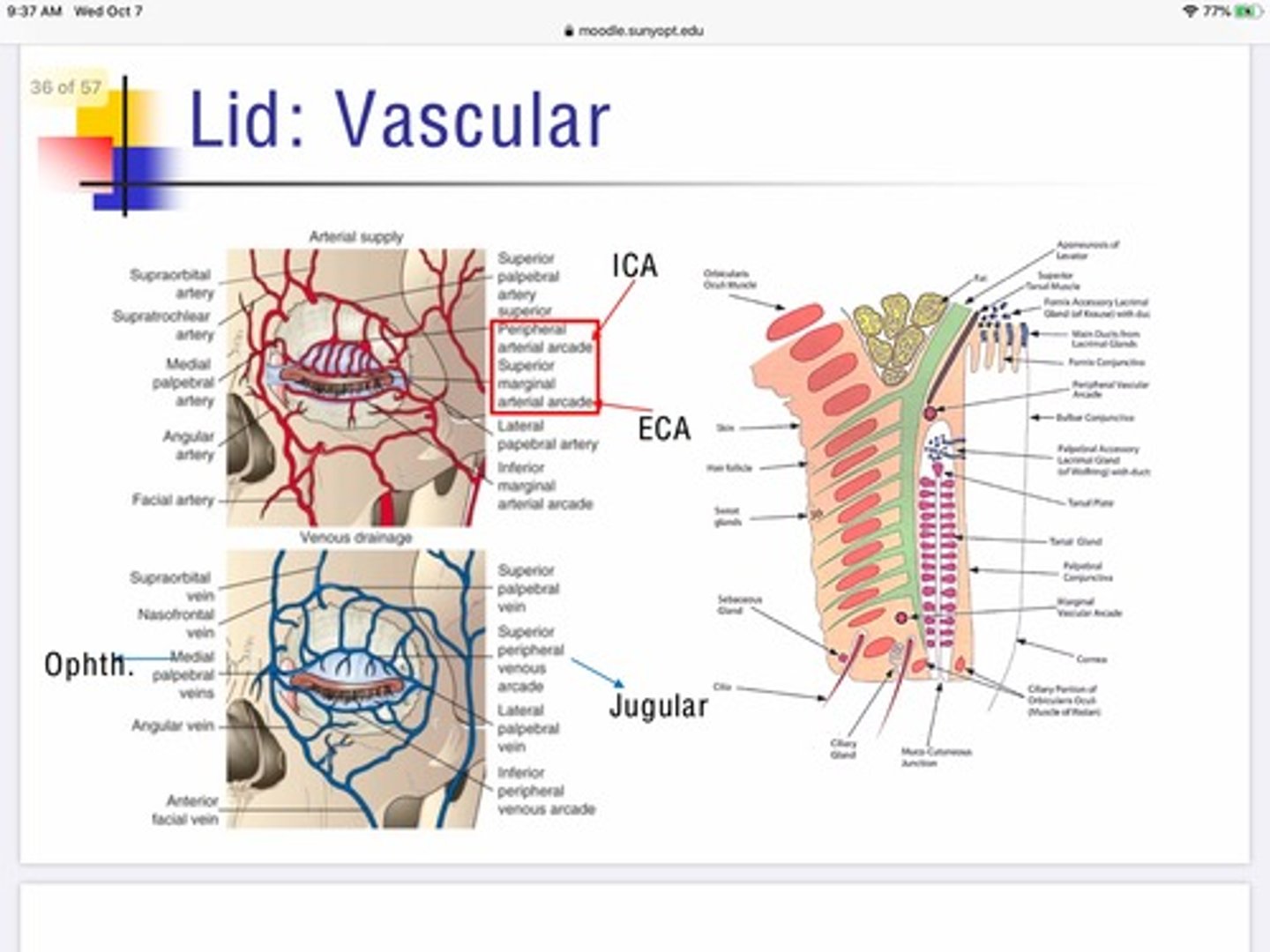
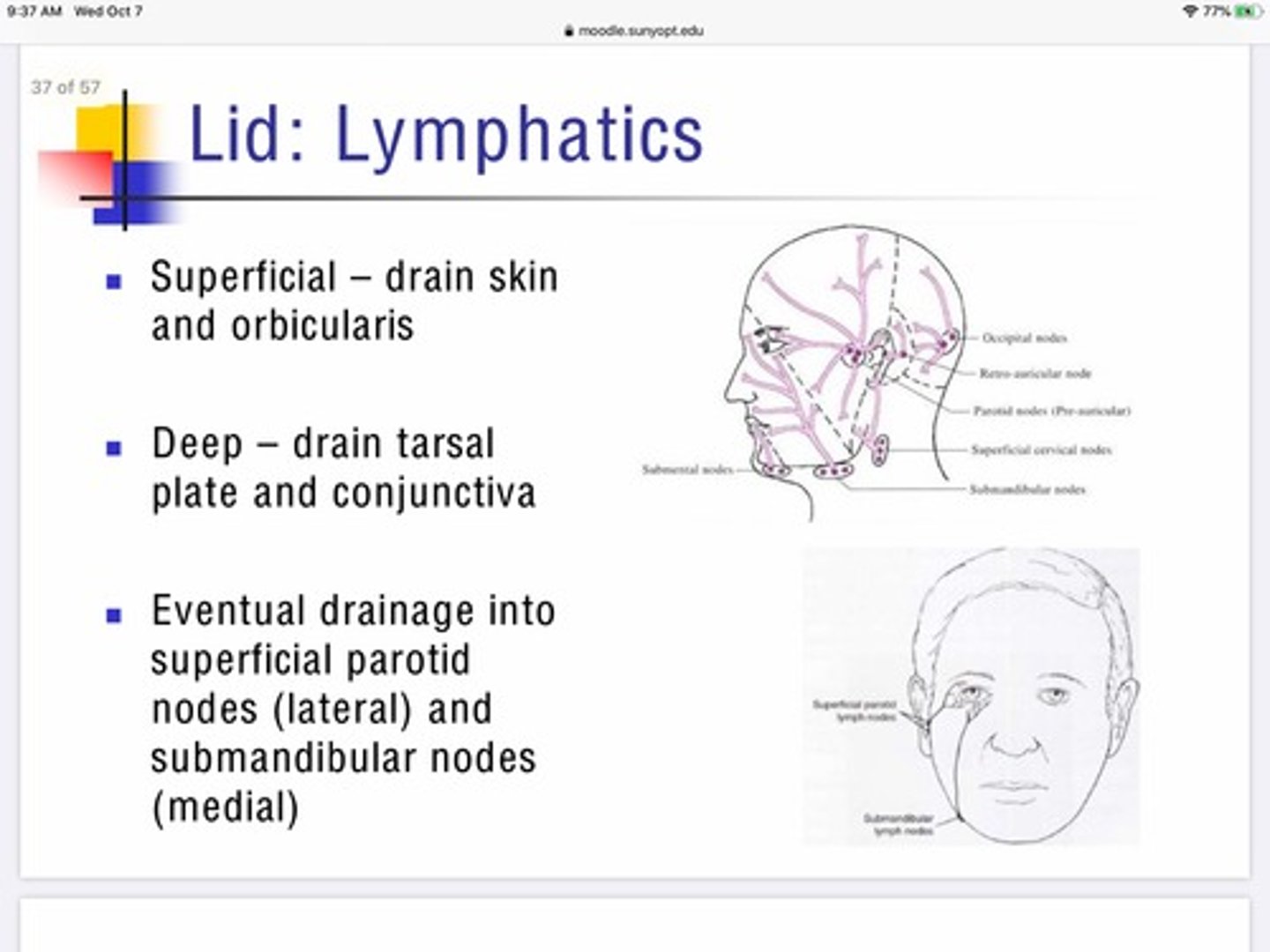
Describe the role of the superficial lymphatic system in maintaining the eyelids?
The superficial lymphatic system of the eyelid drains from the skin, and orbicularis
Basically handles the lymphatic drainage for the anterior portion of the lids
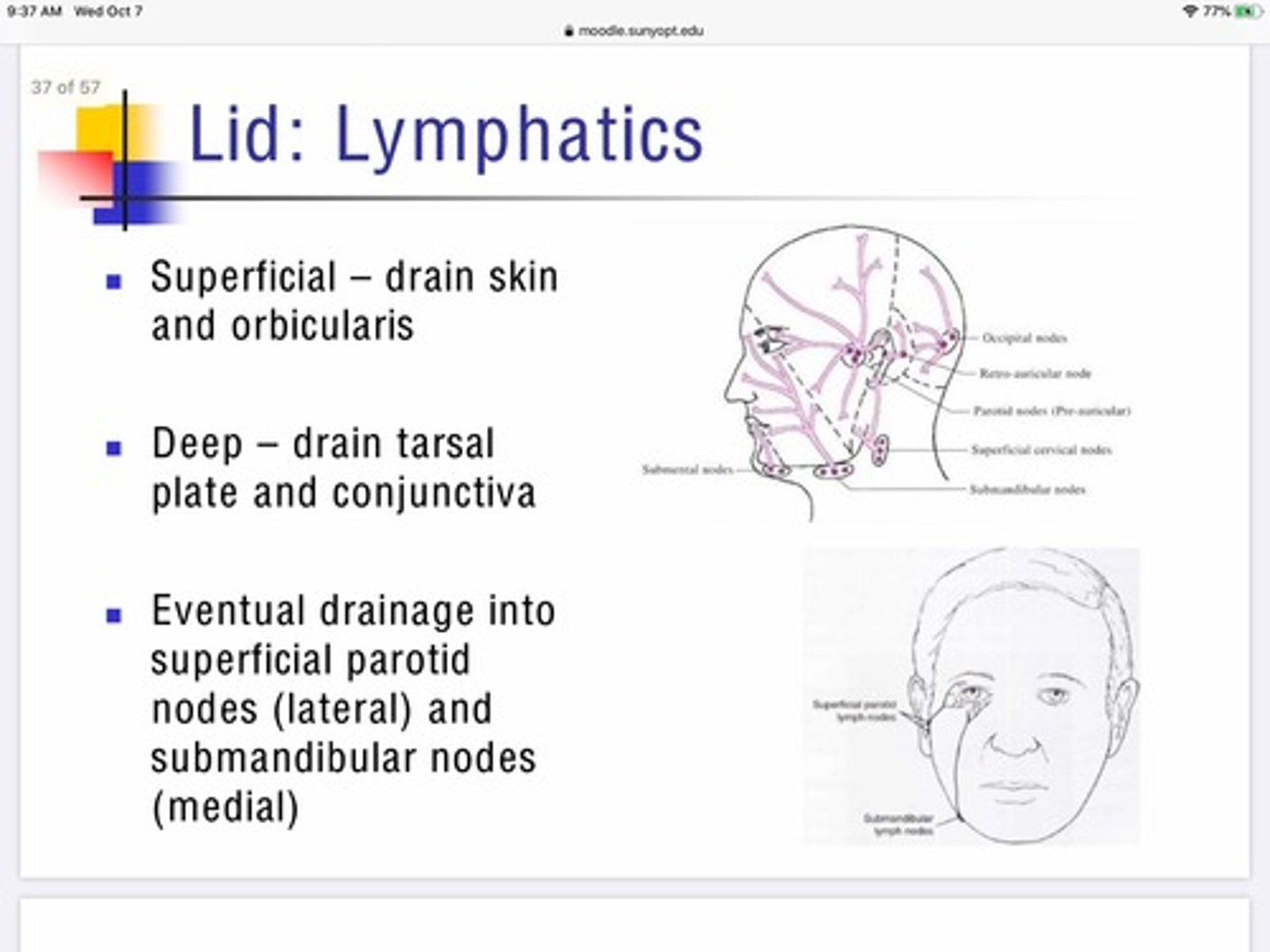
Describe the role of deep lymphatics in maintaining the eyelids?
The deep lymphatic system of the eyelids drain the tarsal plates and conjunctiva
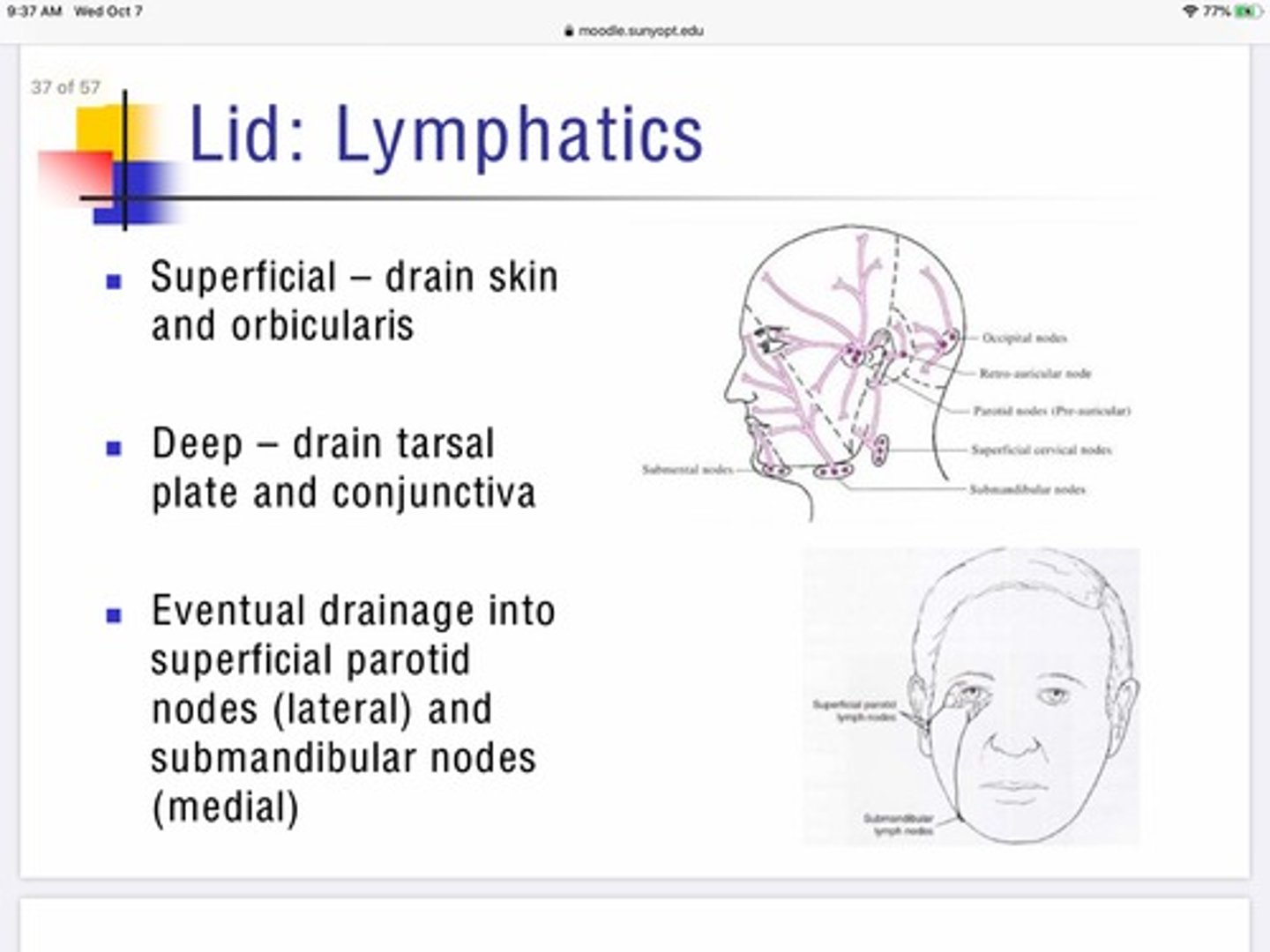
After the lymphatic systems of the eye lid collect their fluids where do they drain?
Lateral portion - drain into superficial parotid nodes
Medial portion - drain into submandibular nodes
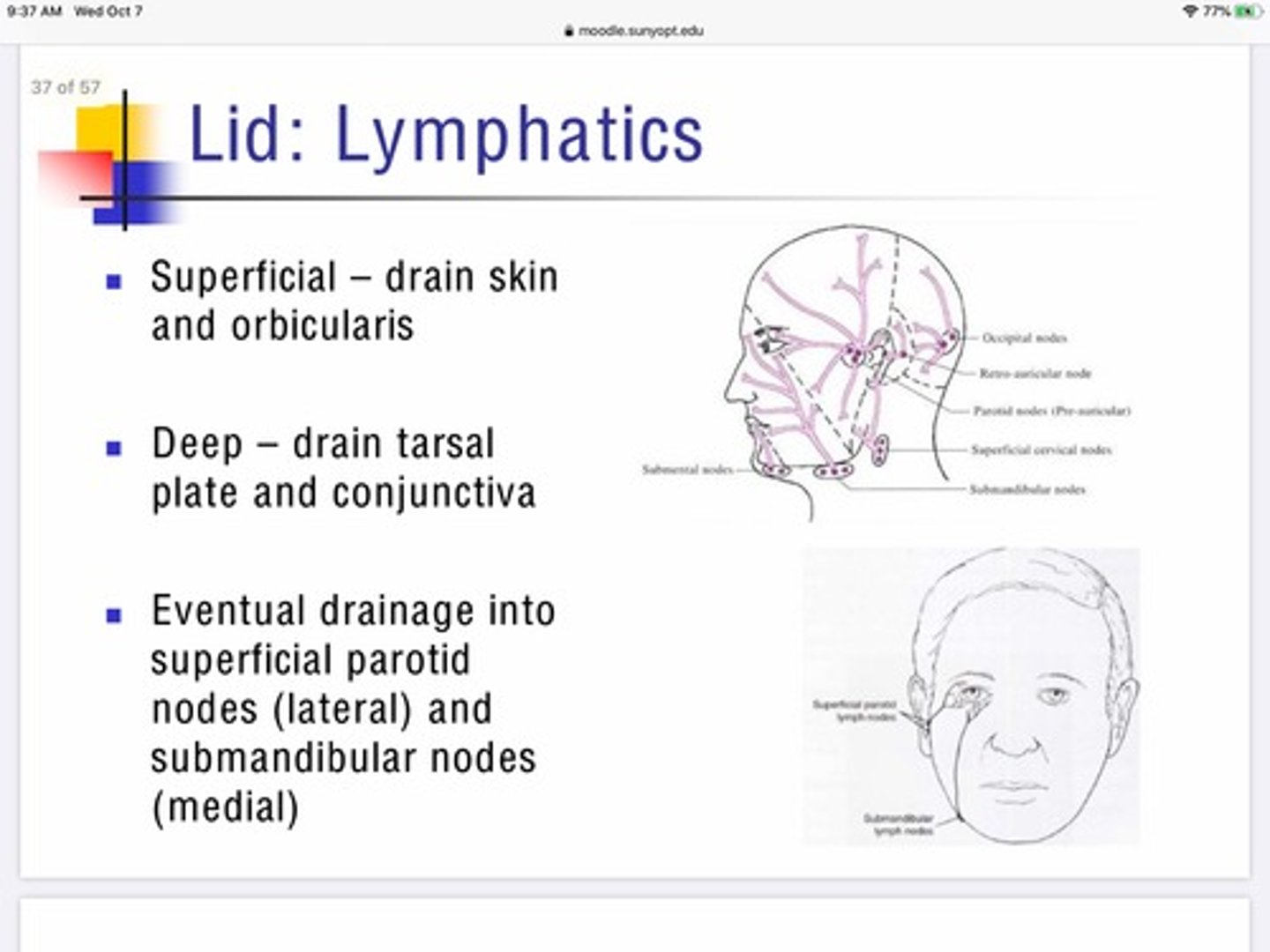
Can eye infections cause swelling of the lymph nodes in the head?
Yes, if the infection is viral we would expect swelling near the nodes under the jaw and in front of the ears
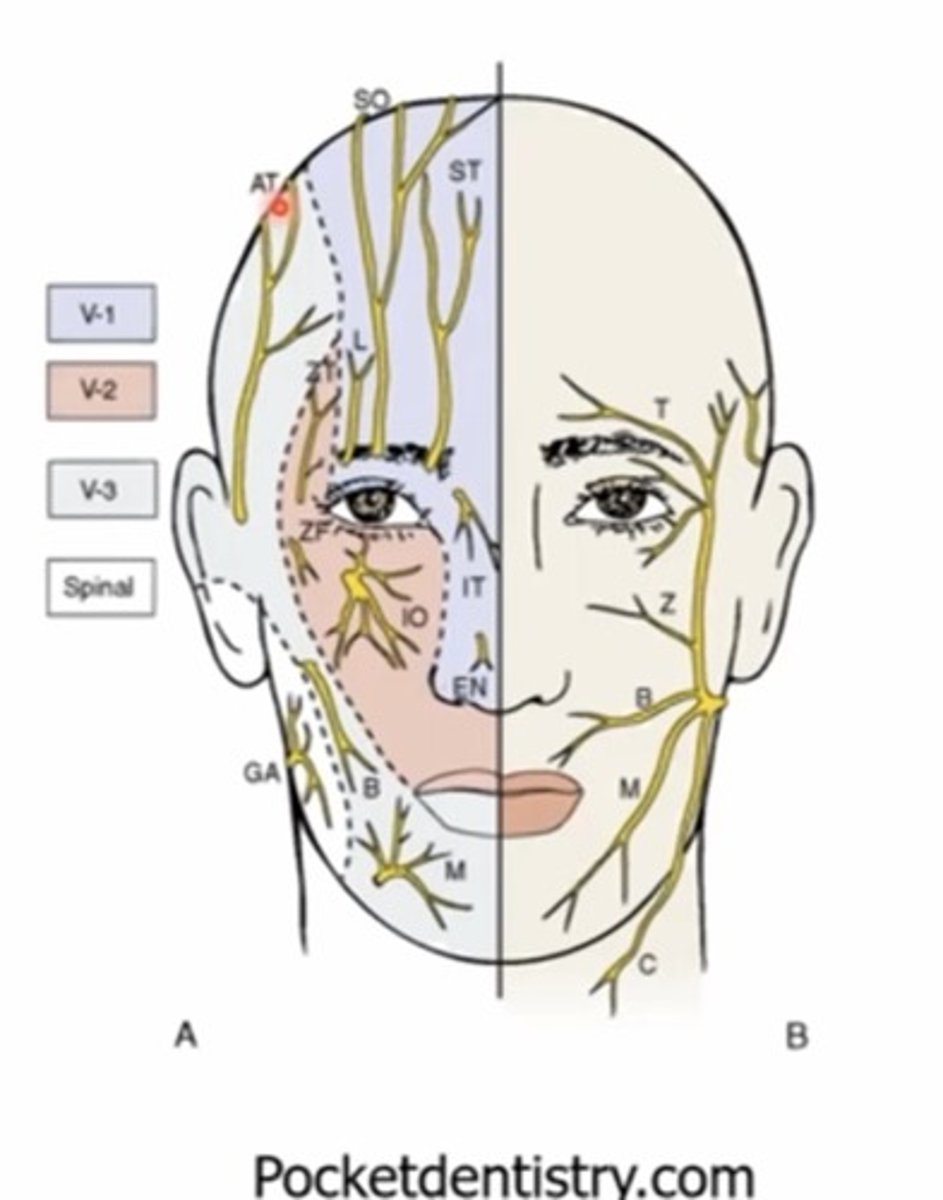
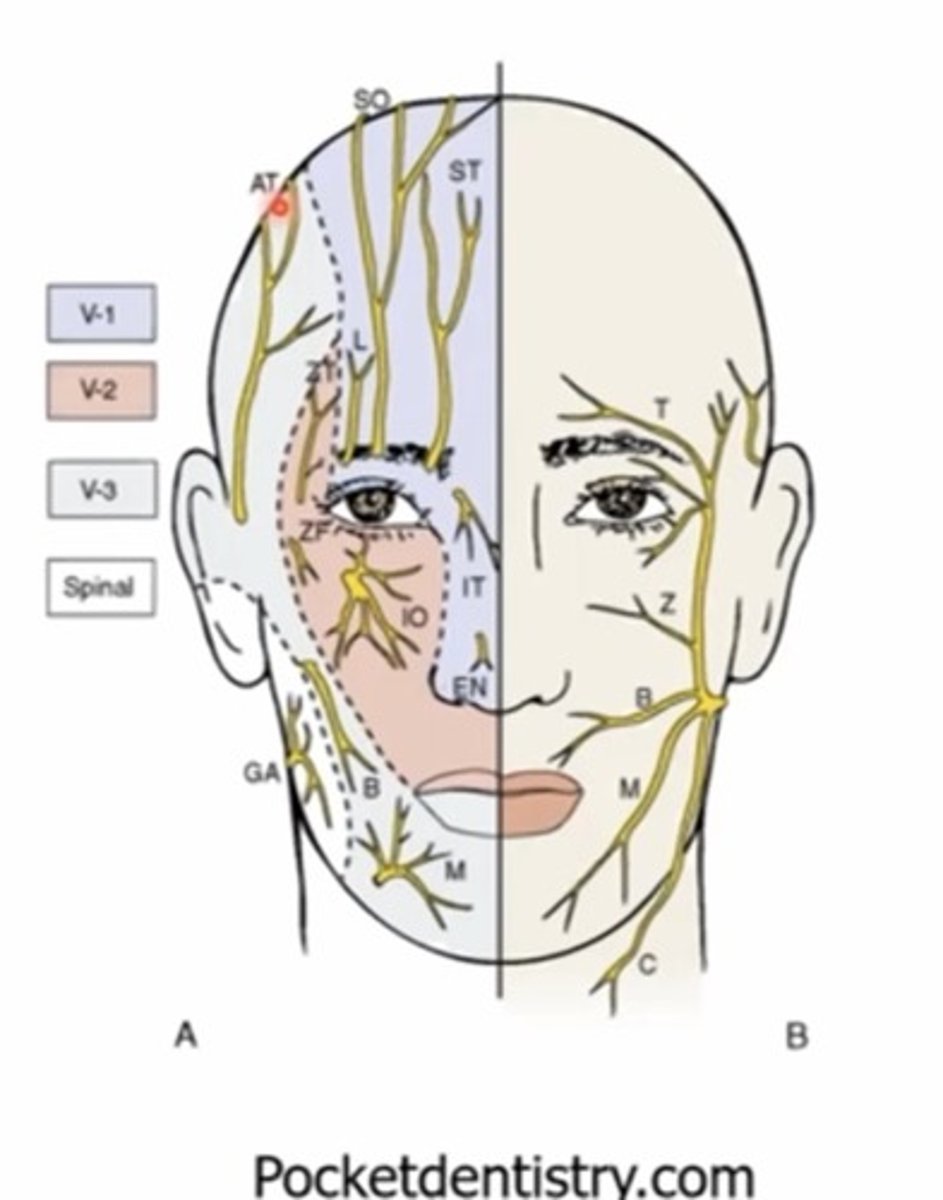
What nerve supplies the MAJORITY of sensation in and around the eye?
Trigeminal nerve - V
What is the motor innervation for the levator and orbicularis muscle? What do the muscles do?
Levator - lifts lid - III
Orbicularis - closes lids - VII
What is the sensory innervation for the lids?
V1 - upper lid
V2 - lower lid
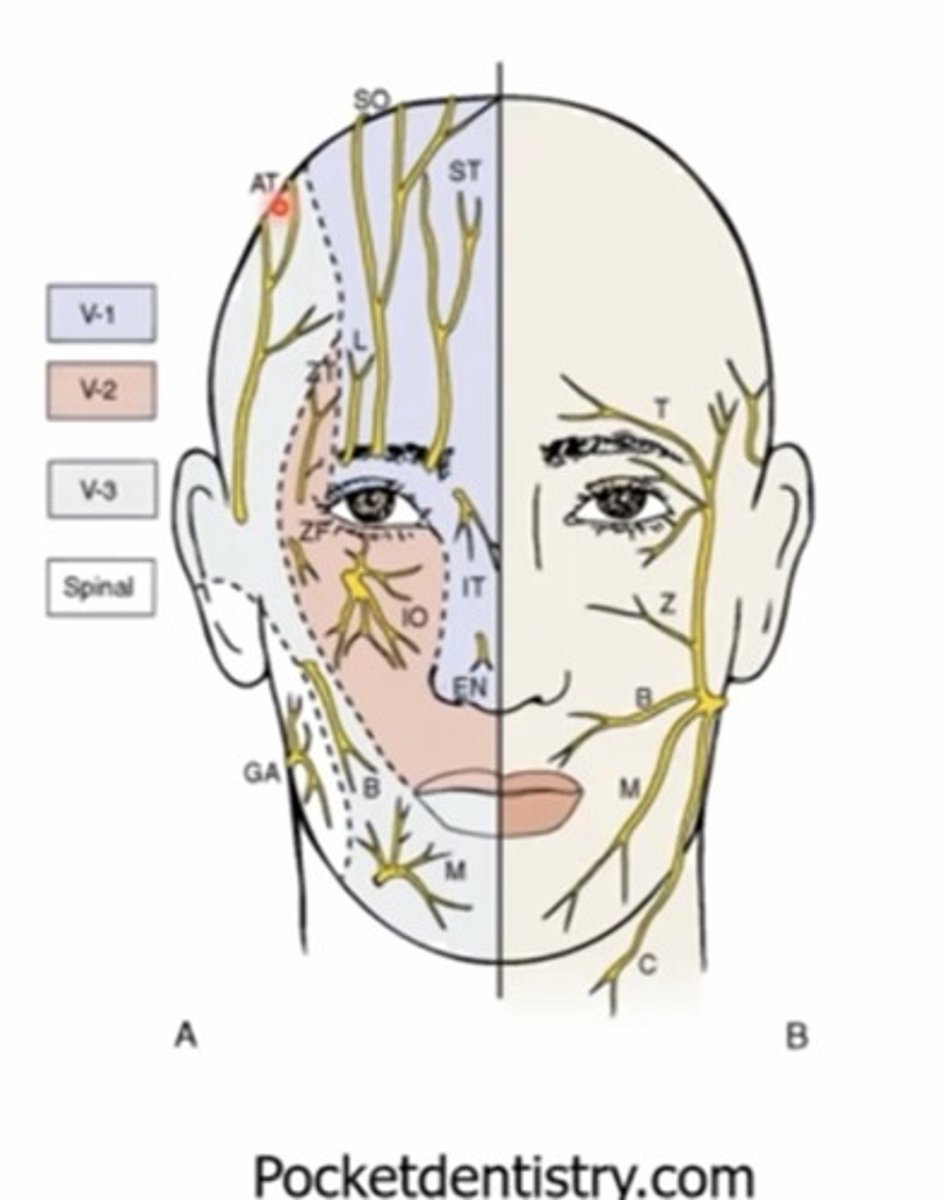
How many divisions does the trigeminal nerve have?
V1 and V2 - sensory only
V3 - motor and sensory
What muscle of the eye is innervated by the autonomic nervous system for its motor function.?
Muller muscle is innervated by the sympathetic system
What is the conjunctiva?
Transparent, highly vascular mucous membrane that lines the ocular surface and internal side of the lids
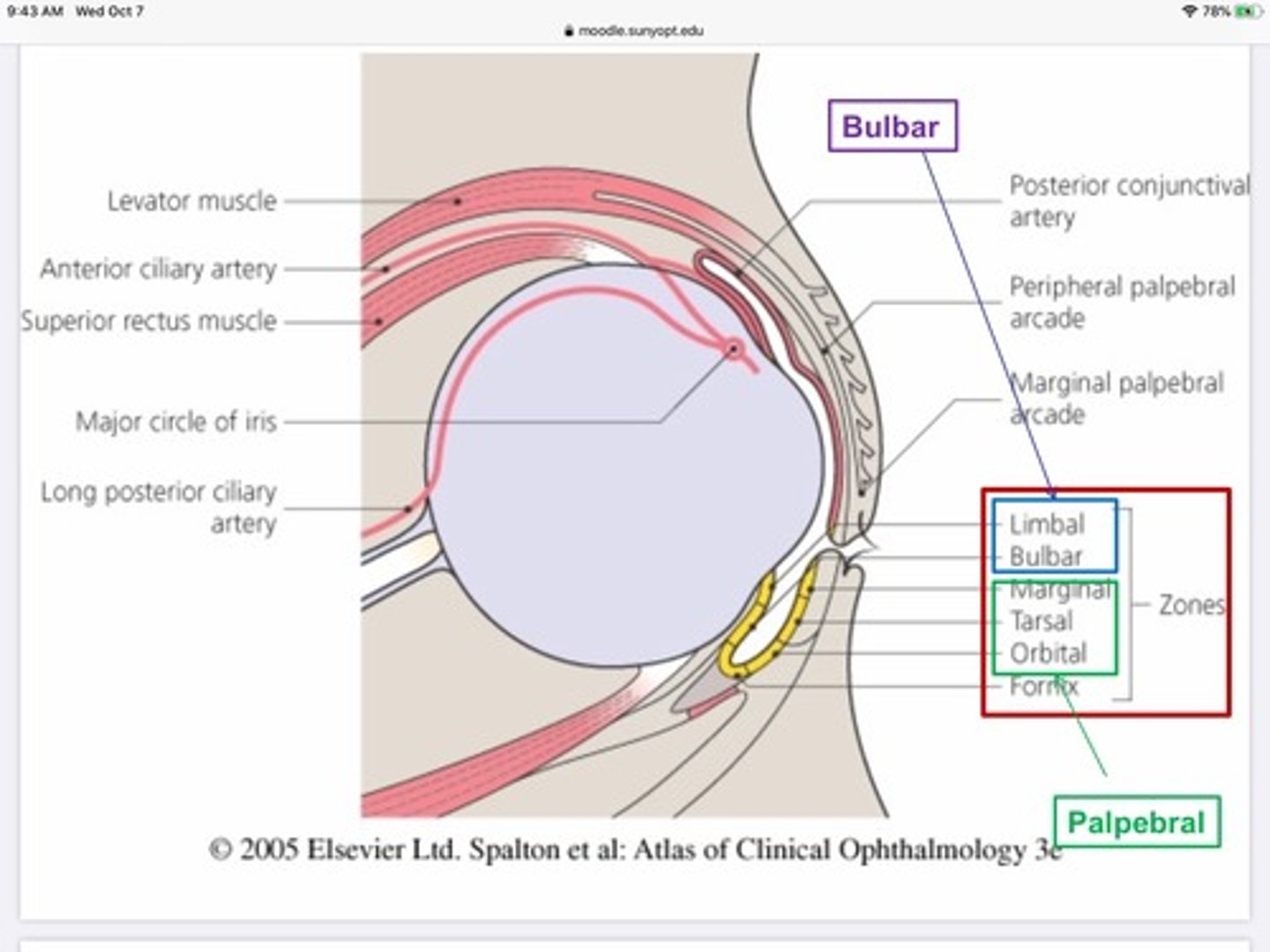
What are the functions of the conjunctiva?
Promote Smooth movement of the eye against the back surface of the lids
Produces part of the tear film (goblet cells)
Immune defense
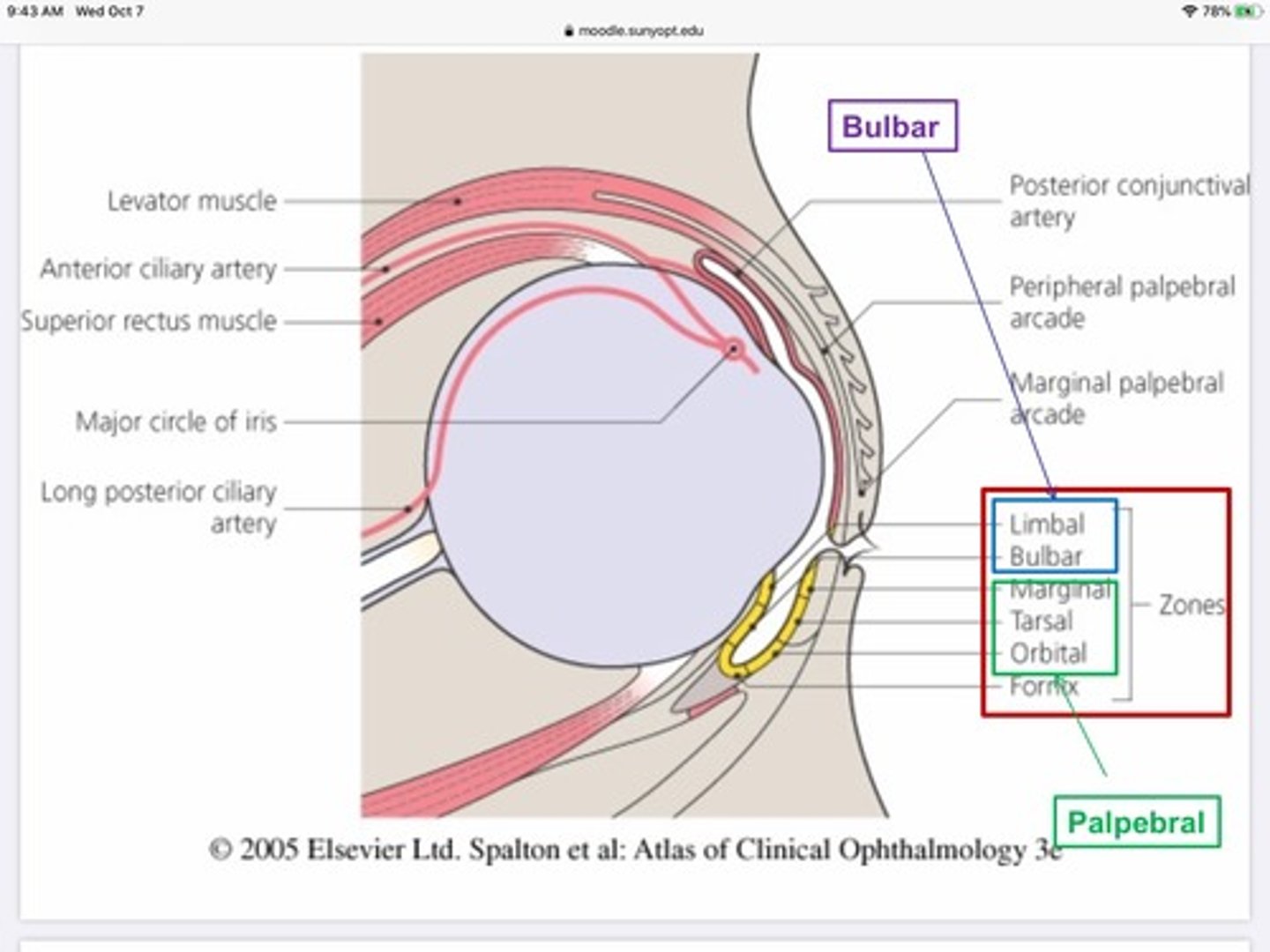
What are the three divisions of the conjunctiva?
Bulbar - on eye ball
Fornix - crease where conj. Folds back to reach lid
Palpebral - back of lid
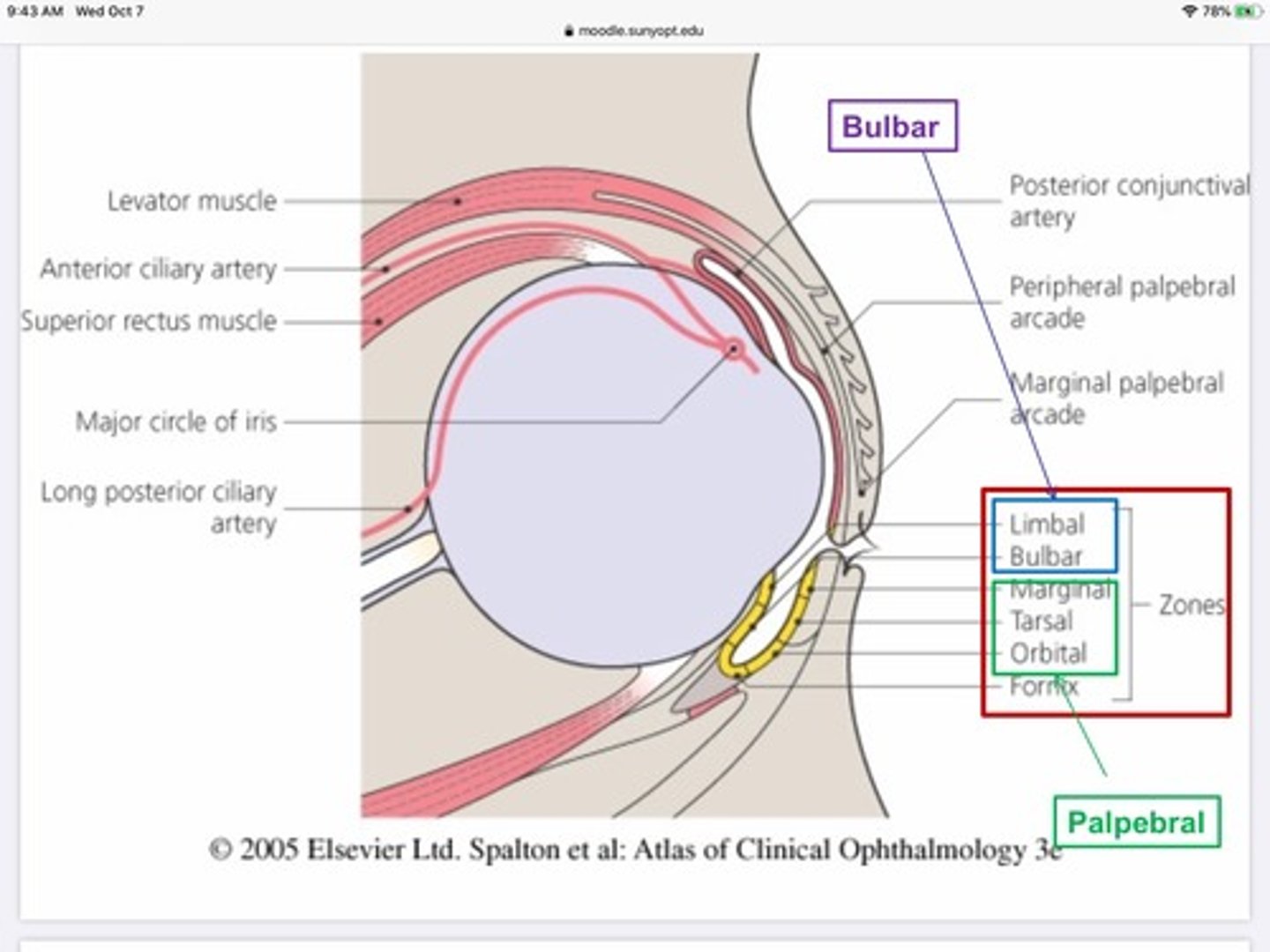
Compared to the other portions of the conjunctiva, the palpebral portion is...
Bound very tightly, rarely swells
What determines the amount of drop a patient can hold in their eye at one time?
The depth of the conjunctival sac
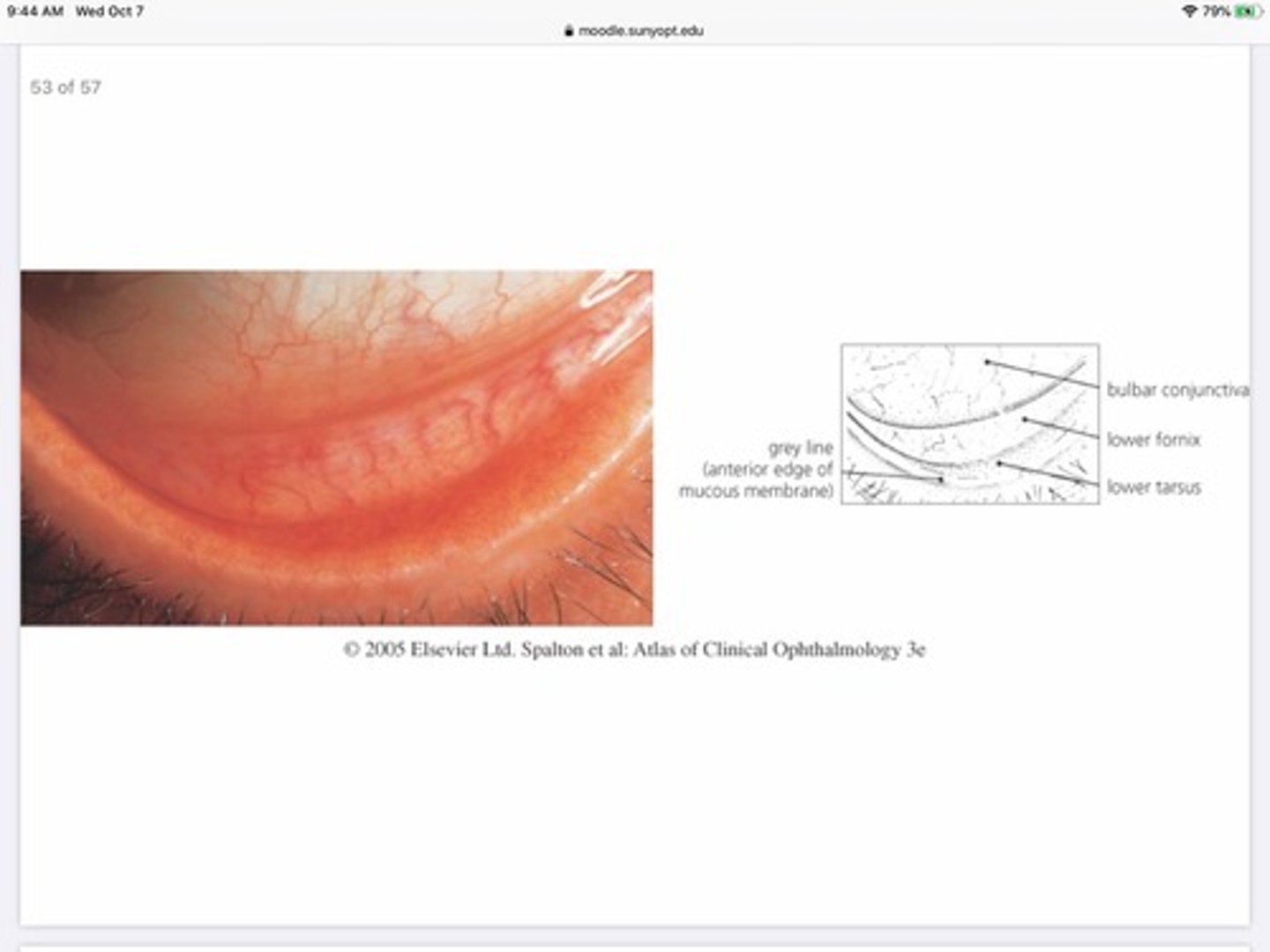
The conjunctiva meets skin at which landmark?
Much-cutaneous junction
What are the layers of the conjunctiva?
1. Non keratinized epithelium - 2-5 layers
2. Stroma
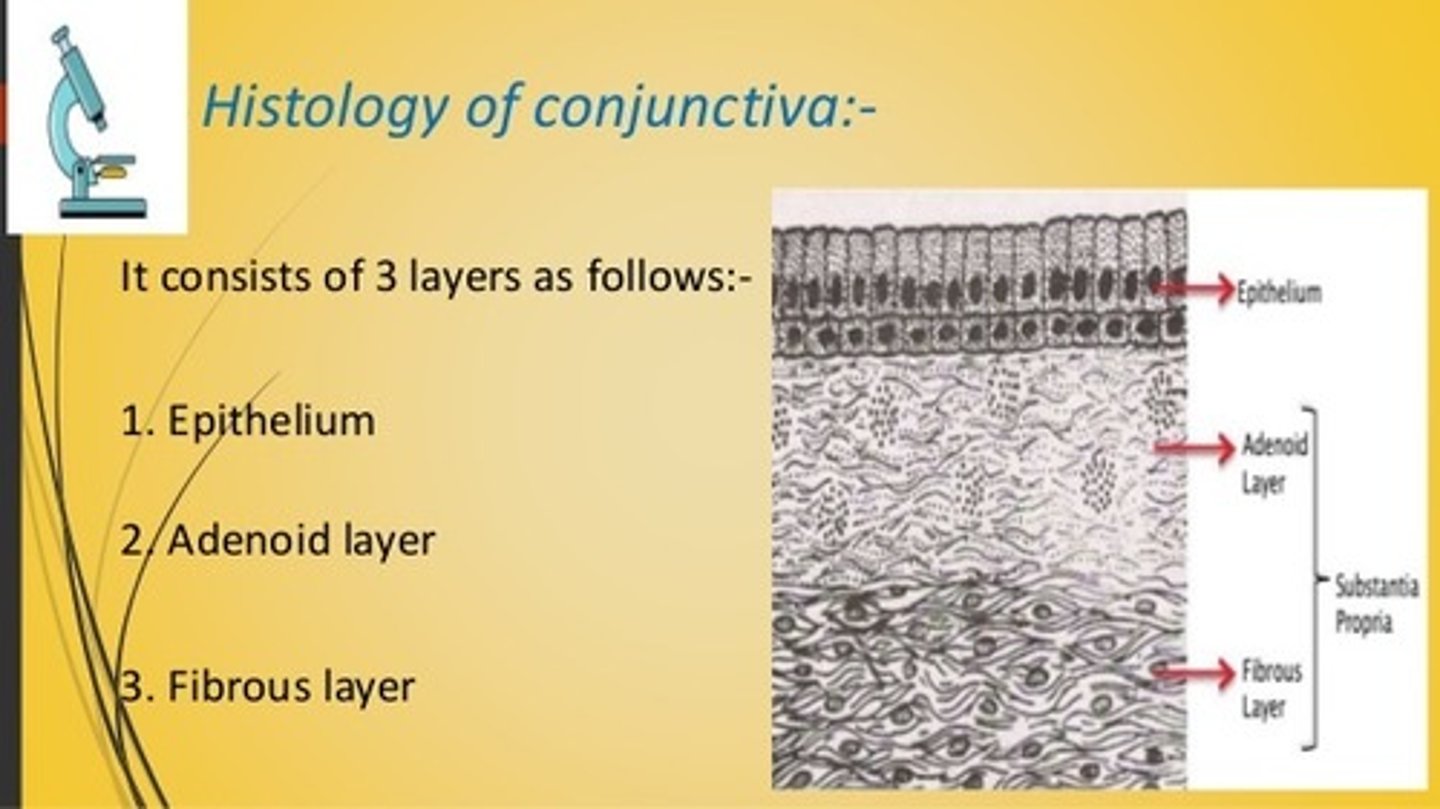
What are the 2 layers of the stroma in the conjunctiva?
Adenoid layer - top layer - 'glandular' - contains lymph vessels, fenestrated capillaries, veins, and arterioles
Deep fibrous layer - bottom layer - connective tissue, collagen
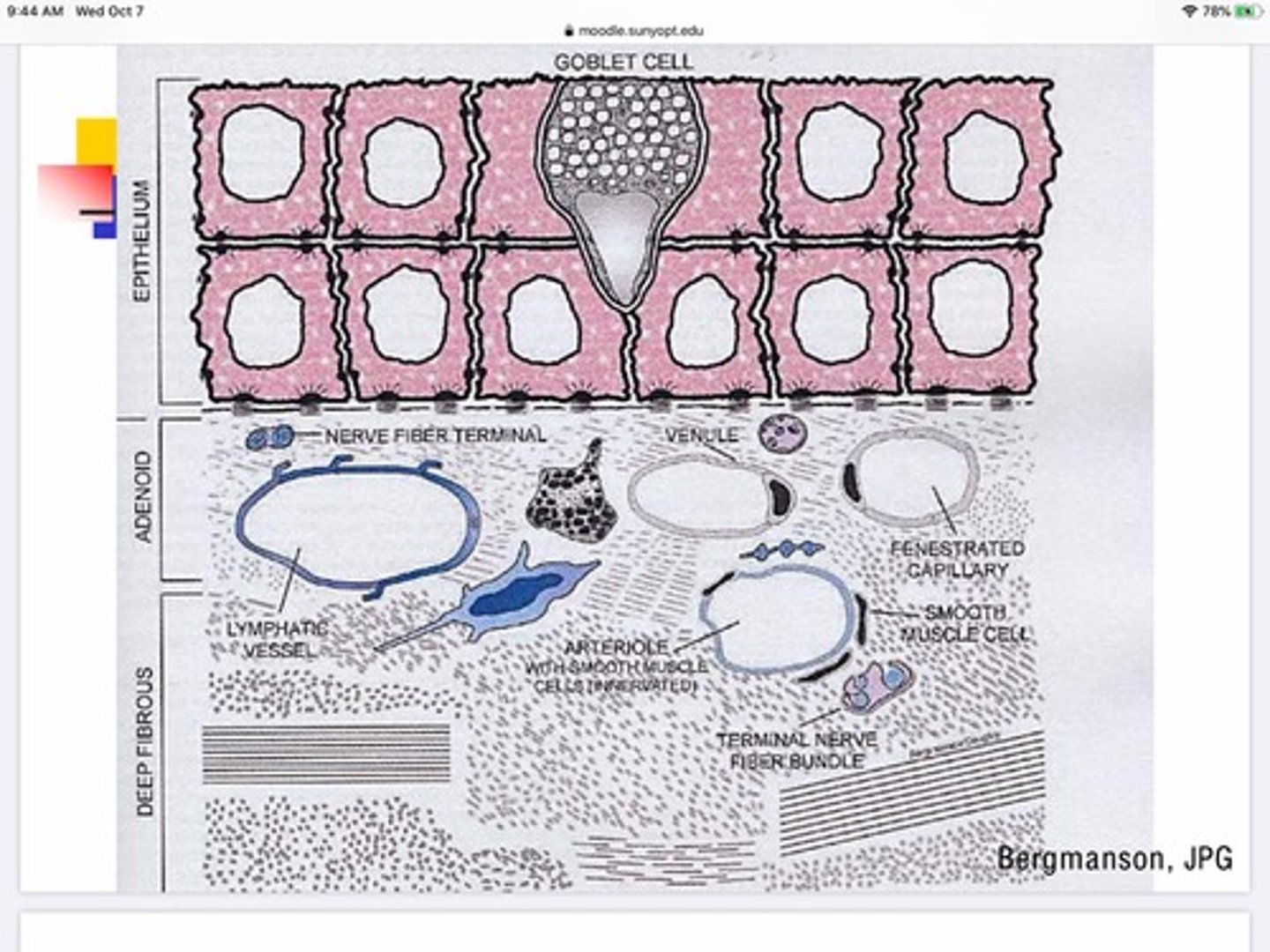
Where do goblet cells exist in the conjunctiva's layers?
Epithelium
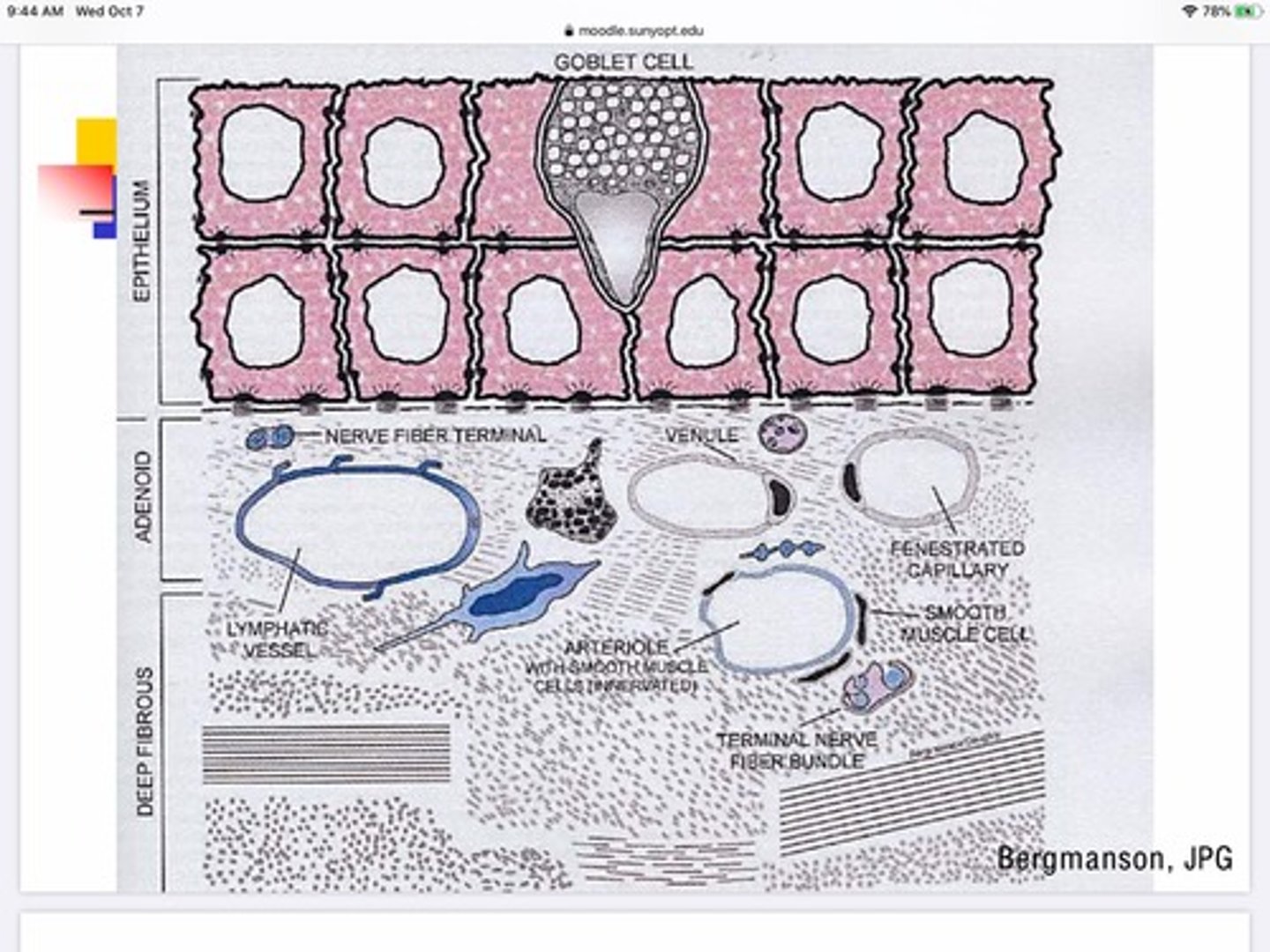
What do goblet cells do?
Secrete mucus for the tear film
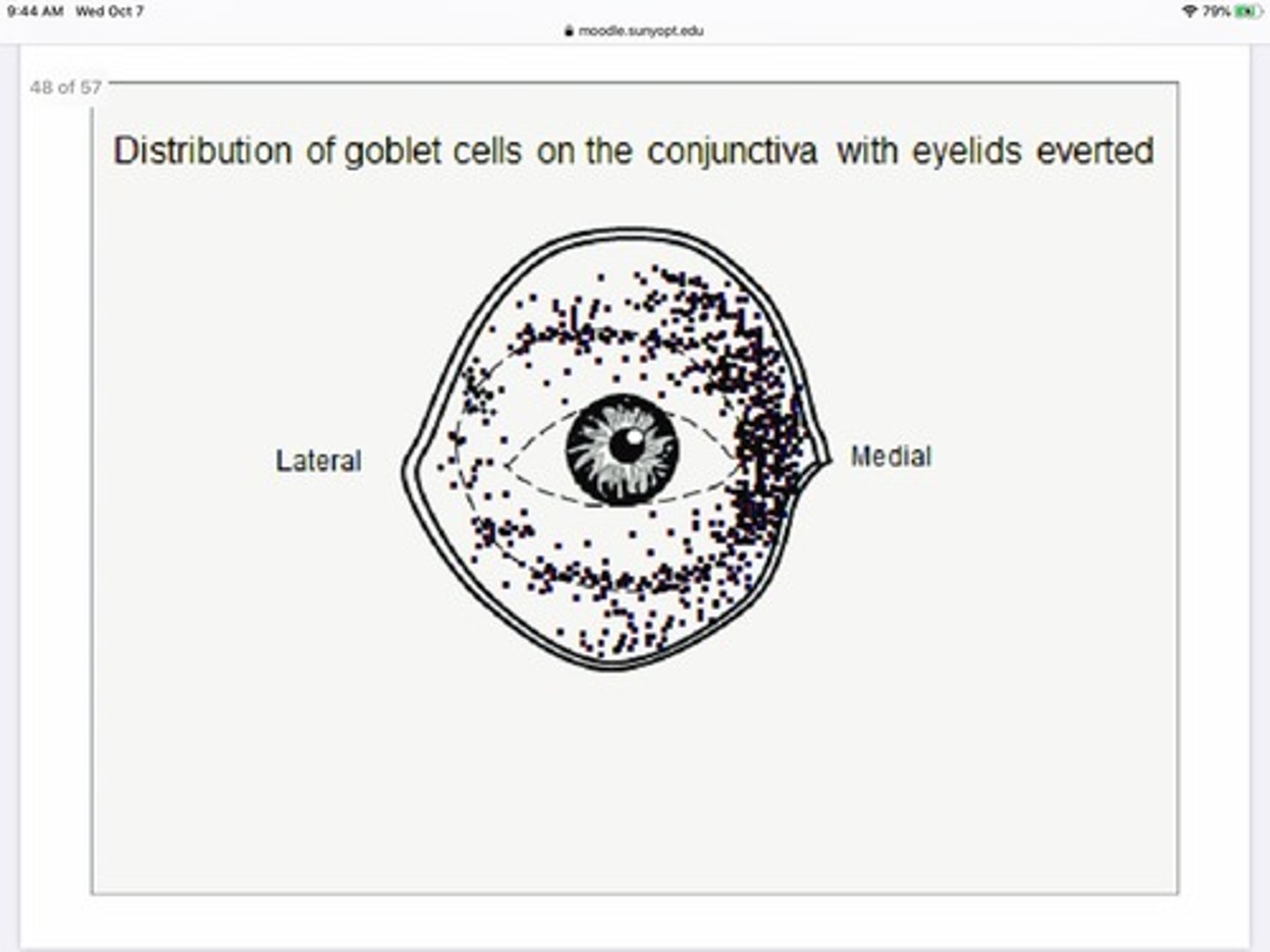
Where in the eye is there the greatest concentration of goblet cells?
Medially
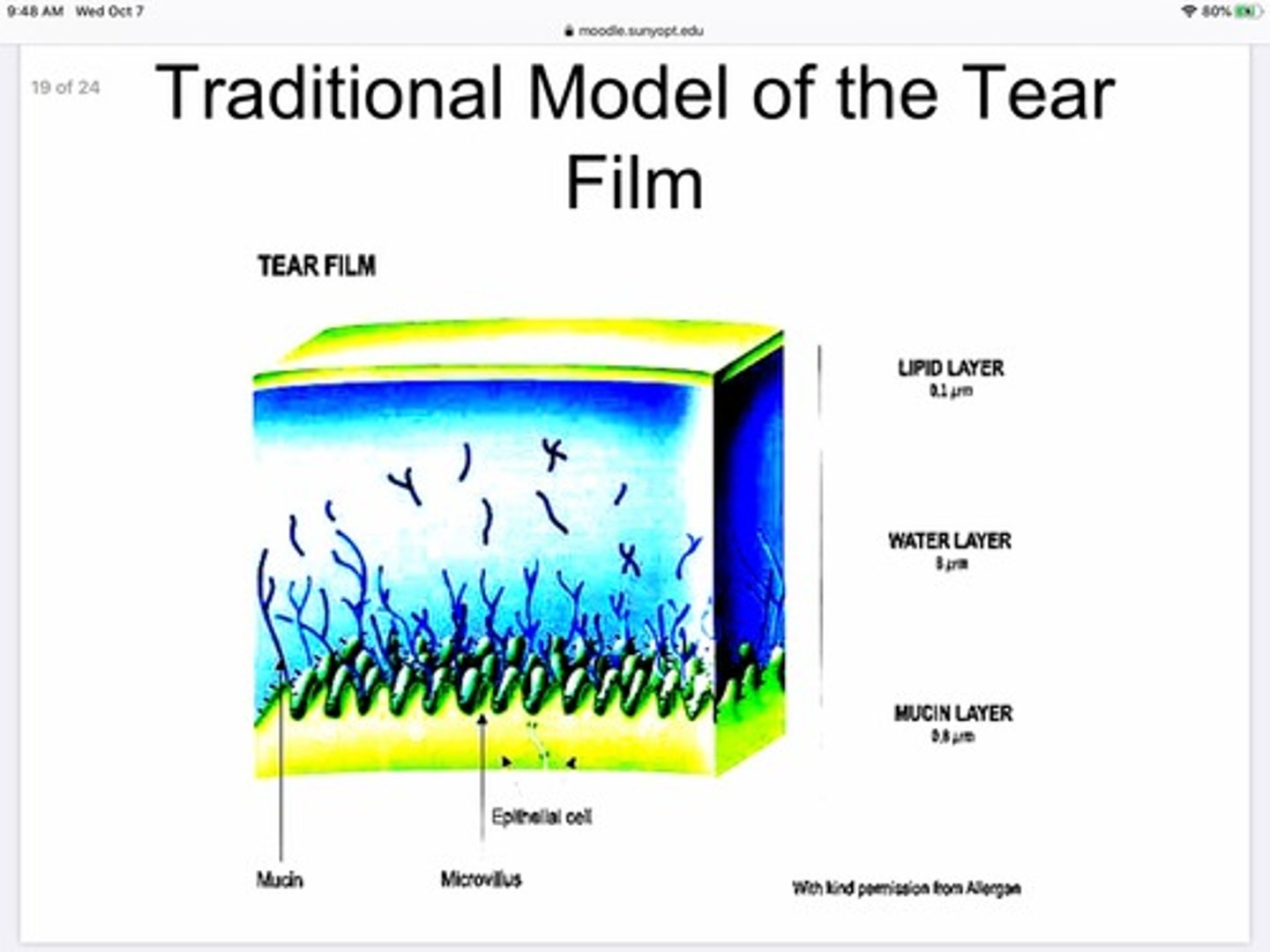
What are the layers of the tear film based on the 'traditional model of the tear film'
Aqueous layer
Lipid layer
Mucus layer
What glands secrete for the aqueous layer of the tear film?
Lacrimal glands and accessory lacrimal glands
What glands are responsible for producing the lipid layer of the tear film?
MBG glands, and glands of Zeiss
The outside and inside of the eyelids are divided into two regions:
Marginal
Peripheral
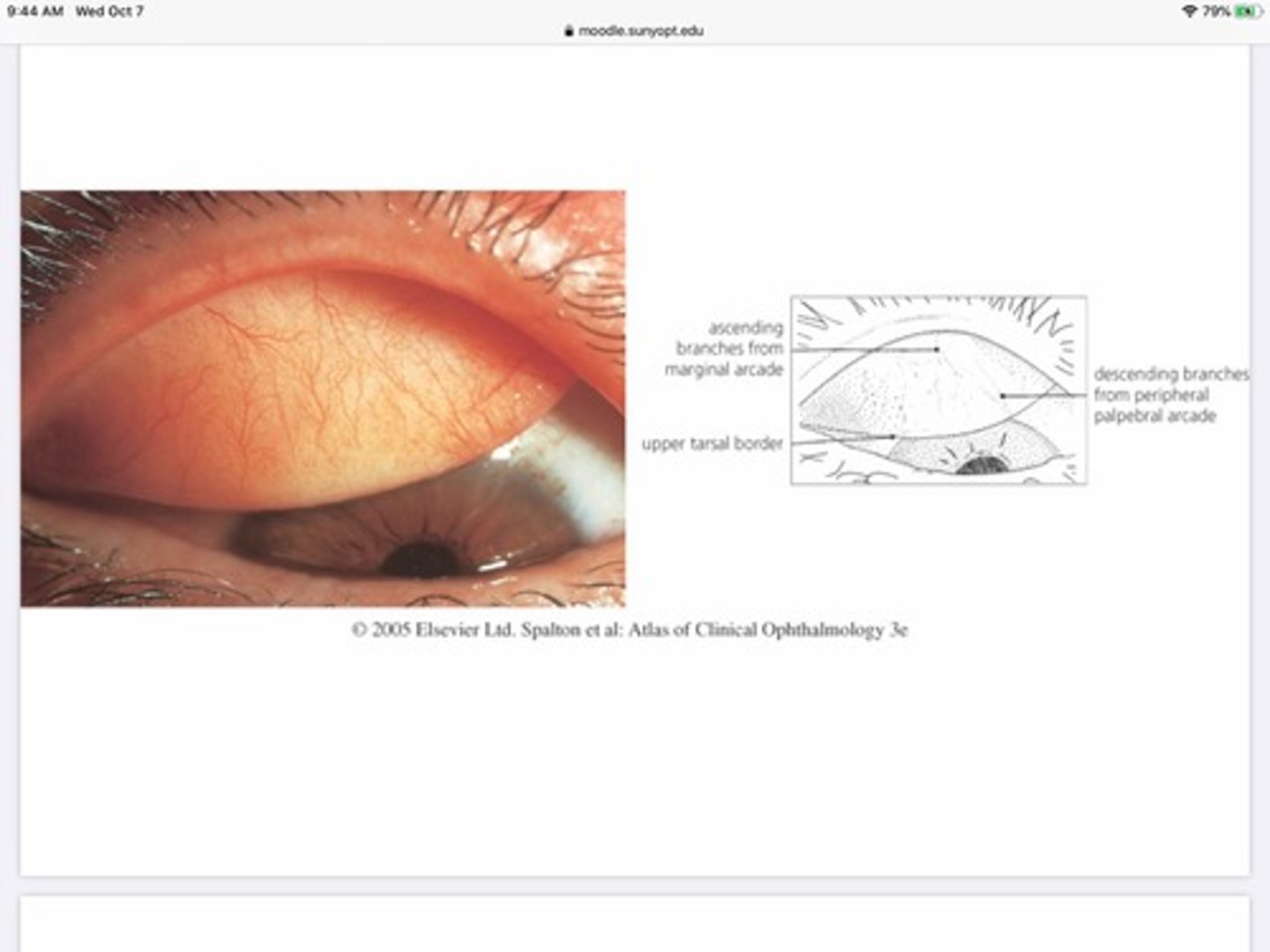
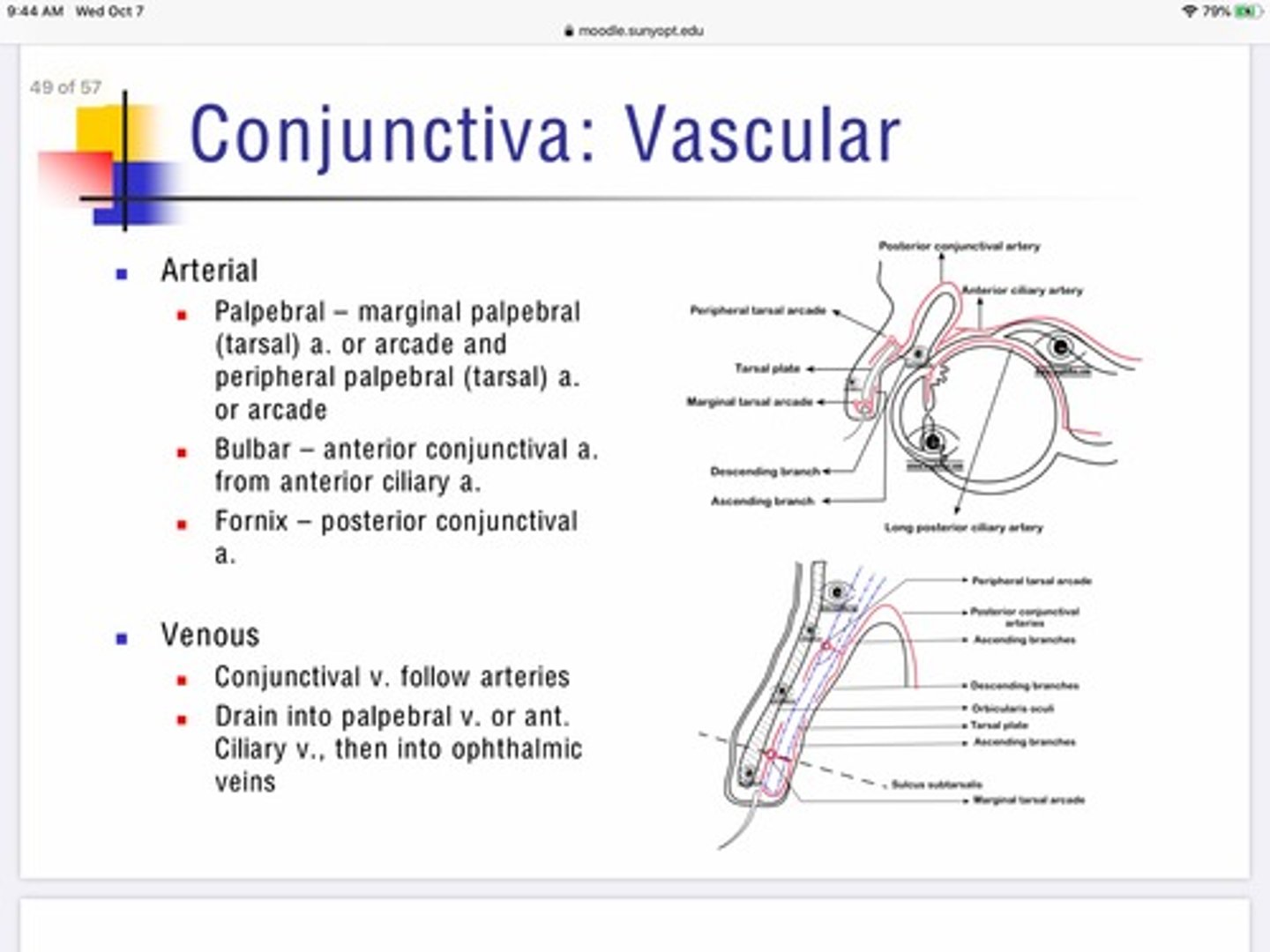
Which arteries provide blood to the palpebral portion of the conjunctiva?
Marginal palpebral artery
Peripheral palpebral artery
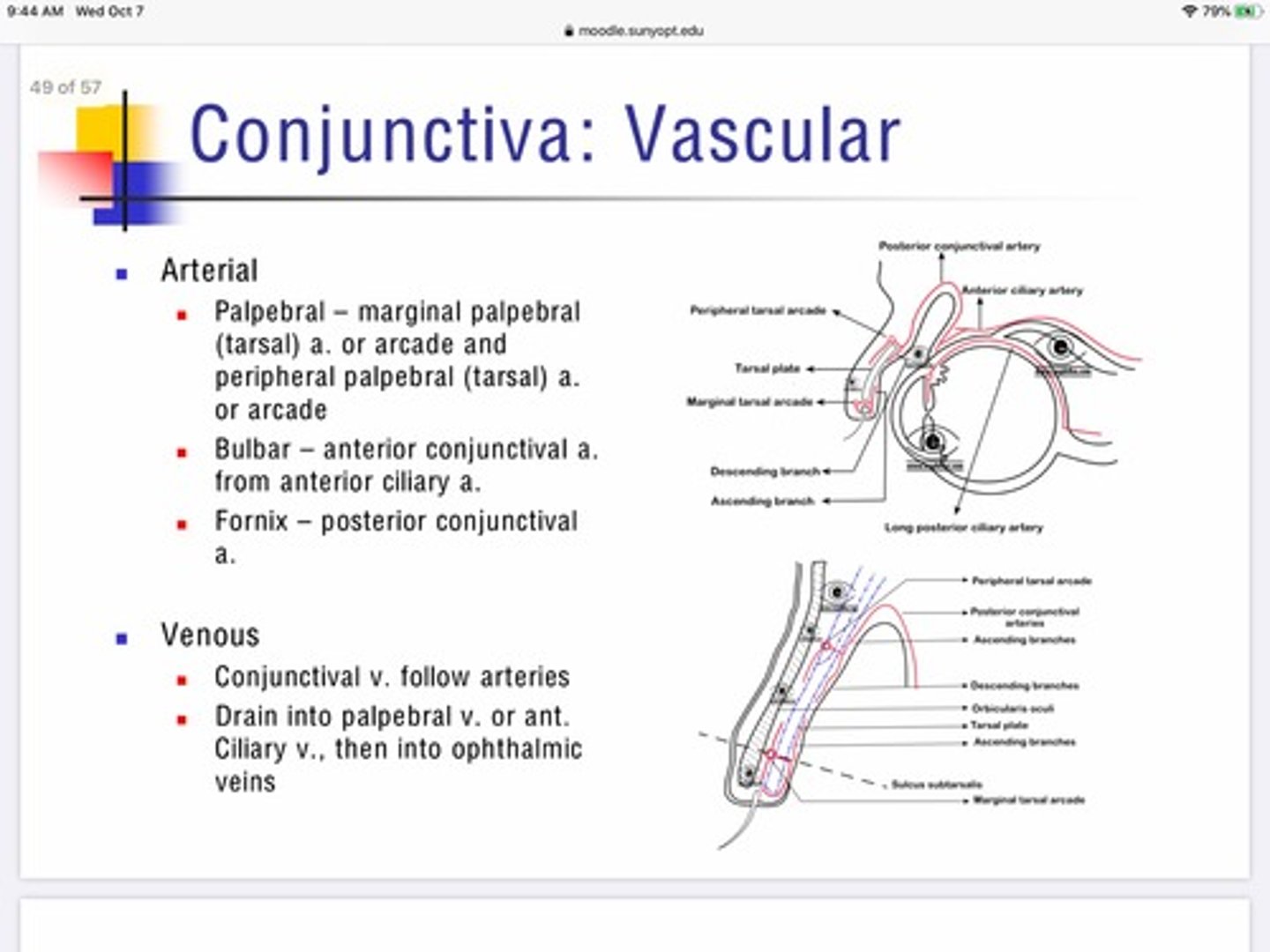
Which arteries provide blood to the bulbar portion of the conjunctiva?
Anterior conjunctival artery which is a branch from the anterior ciliary artery

Which arteries provide blood to the fornix portion of the conjunctiva?
Posterior conjunctival artery
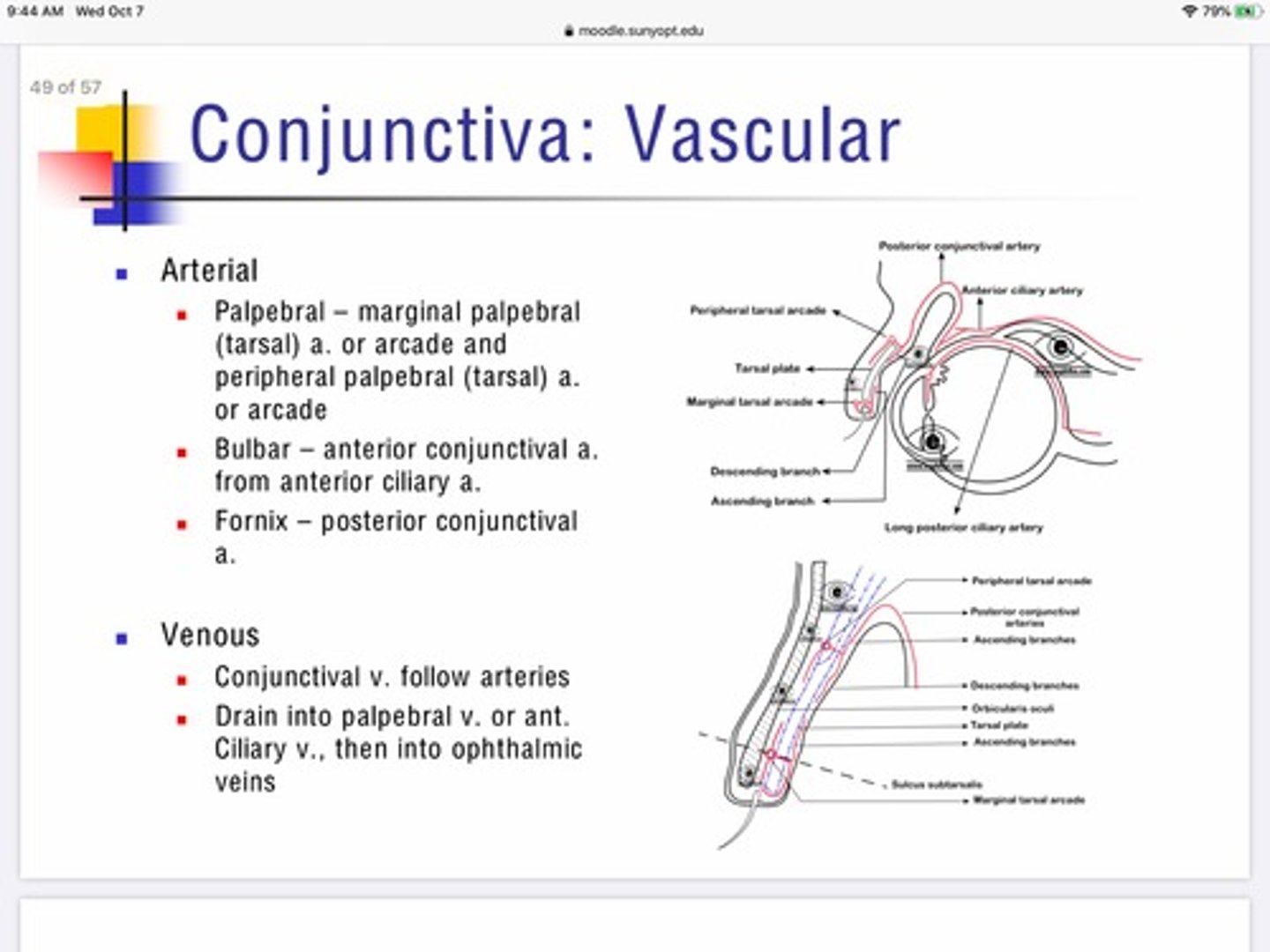
Describe the venous innervation of the conjunctiva?
Conjunctiva is unique that the veins pair with the arteries for entry/exit
Everything drains into palpebral vein or anterior ciliary vein —-> ophthalmic veins. —> cavernous sinus
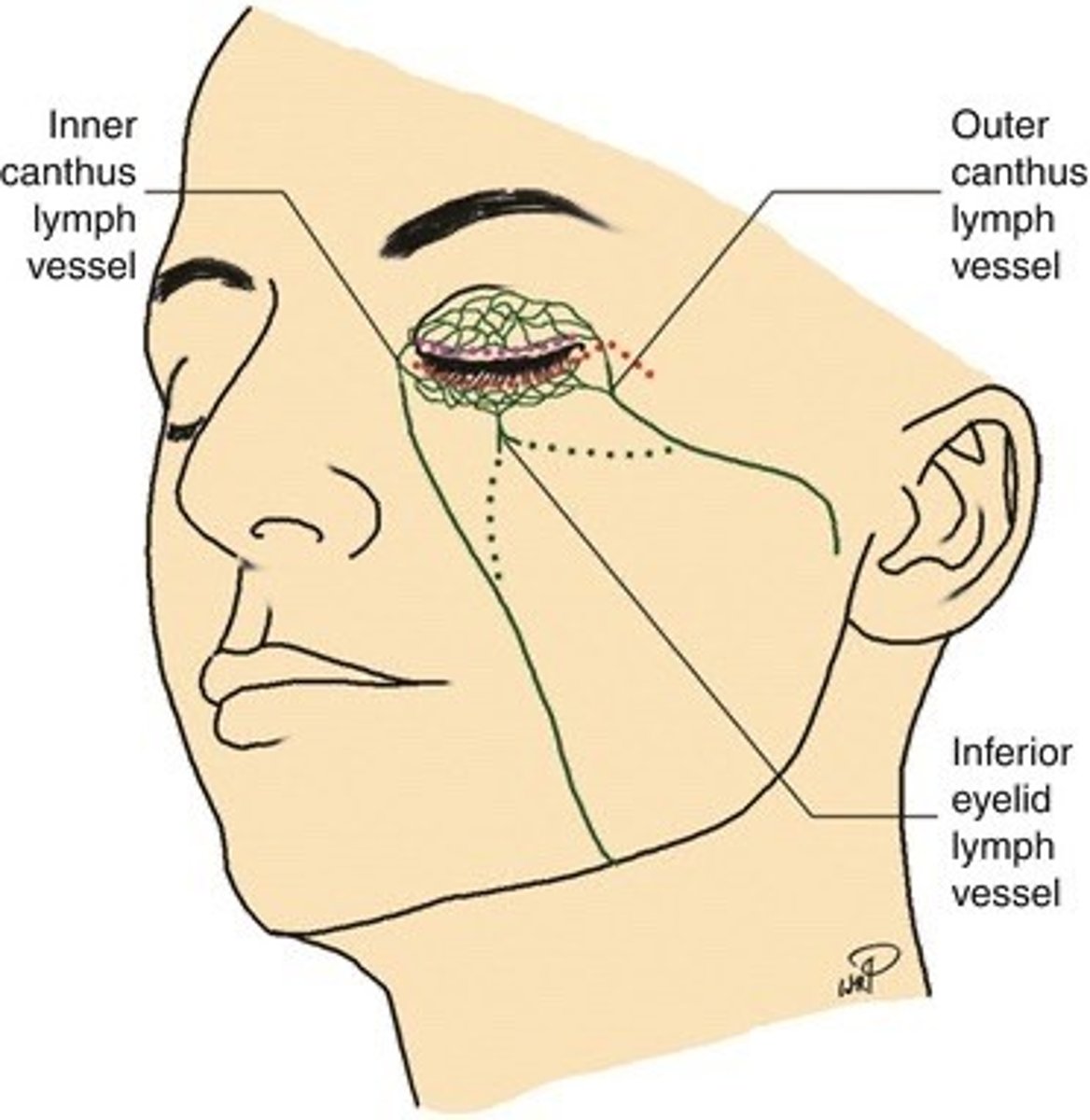
The outer canthus of the eye drains to the
Parotid node (pre-auricular)
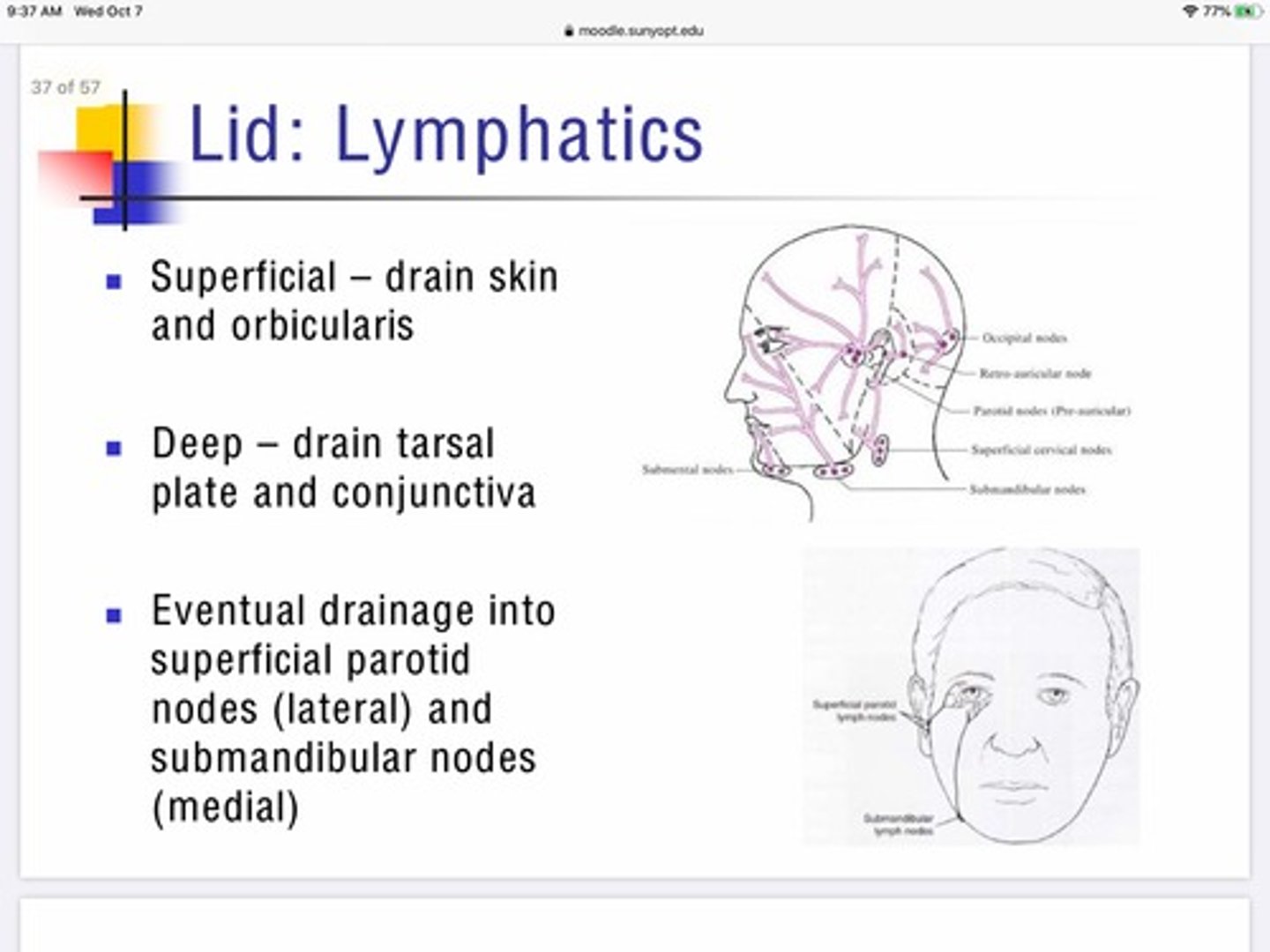
The inner canthus of the eye drains to the
Sub-mandibular node
How is the conjunctiva innervated by nerves?
Sensory - from 2 long posterior ciliary nerves
Upper conj - V1
Lower conj - V2
How does the autonomic nervous system innervated the conjunctiva?
Blood vessels, maintains vasomotor tone