Ochem - Ch. 23: Metabolism and Energy Production
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chem 106
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
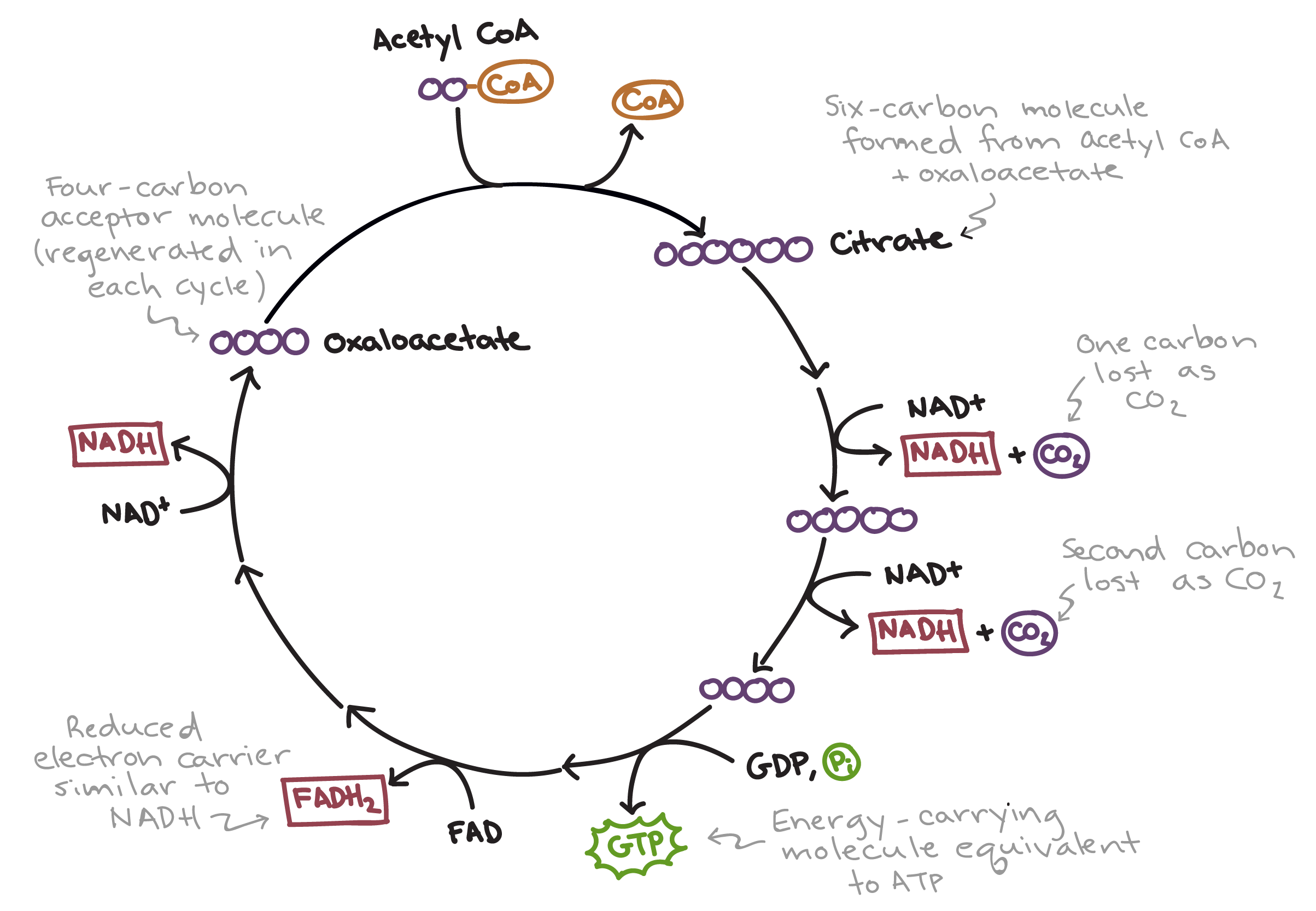
What happens in the Citric Acid Cycle?
Acetyl CoA is oxidized to CO₂, generating NADH, FADH₂, and GTP (or ATP).
What is the role of NADH and FADH₂?
They donate electrons to the ETC to produce ATP.
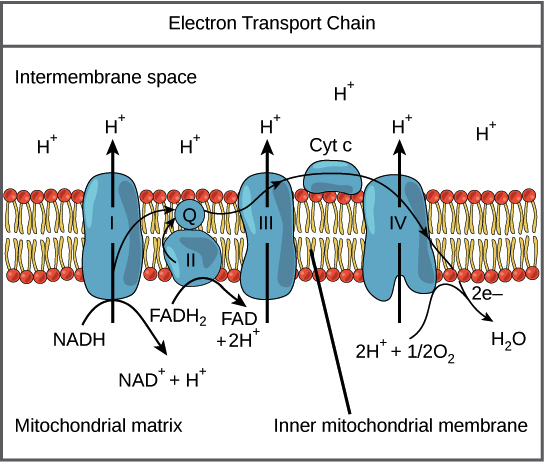
What is the ETC?
A series of proteins in the mitochondria that transfer electrons and pump protons to create a gradient for ATP synthesis.
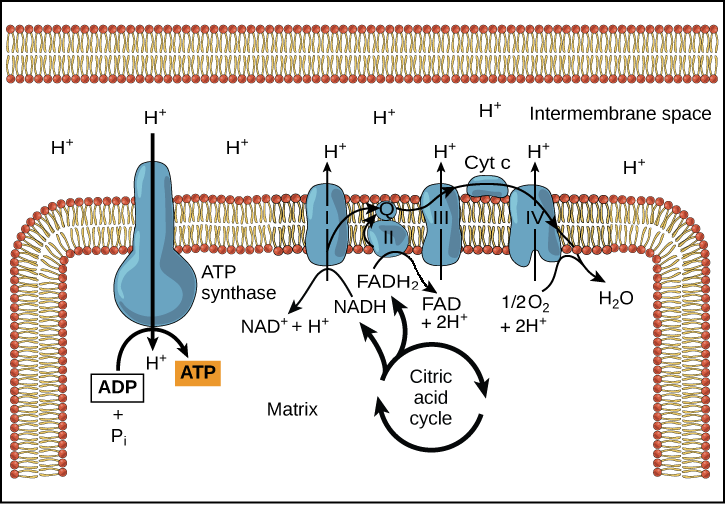
How is ATP produced by oxidative phosphorylation?
ATP synthase uses the proton gradient generated by the ETC to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi.
How many ATP are formed from NADH and FADH₂?
NADH → ~2.5 ATP; FADH₂ → ~1.5 ATP.
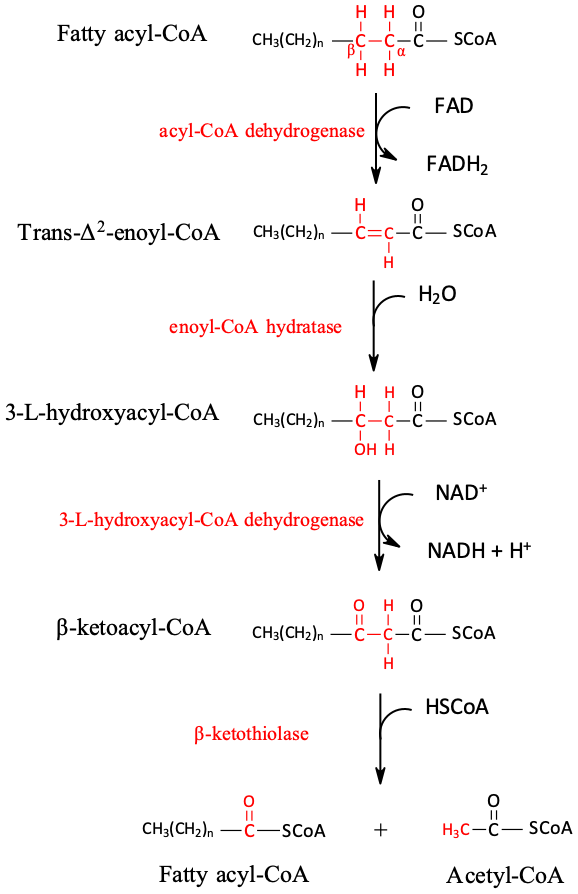
What is fatty acid oxidation (β-oxidation)?
The breakdown of fatty acids into acetyl CoA units, producing NADH and FADH₂.
How do you calculate the number of β-oxidation cycles?
(Number of carbons ÷ 2) - 1 = cycles. Ex, C16 → 7 cycles → 8 acetyl CoA.