FA lec two The knee, foot and ankle
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Which bones form the knee joint?
femur, tibia, patella
What type of joint is the knee?
Hinge-type condylar synovial
The medial meniscus of the knee is:
A) Circular and unattached to the capsule
B) Semicircular and attached to the capsule and MCL
C) Nearly a complete ring
D) Loosely attached to the tibia
B) Semicircular and attached to the capsule and MCL
Which ligament resists excessive abduction of the tibia on the femur?
A) Lateral collateral ligament
B) Posterior cruciate ligament
C) Medial collateral ligament
D) Anterior cruciate ligament
C) Medial collateral ligament
Which structure prevents anterior translation of the tibia on the femur?
A) Medial collateral ligament
B) Anterior cruciate ligament
C) Posterior cruciate ligament
D) Lateral collateral ligament
B) Anterior cruciate ligament
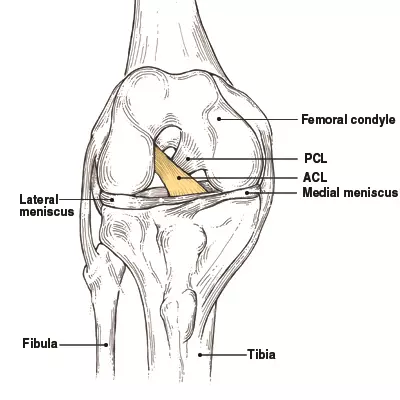
Which tibial plateau has a larger surface area and why?
A) Lateral plateau, because it supports more weight.
B) Medial plateau, because it helps distribute the weight more effectively.
C) Lateral plateau, because it is more mobile.
D) Medial plateau, because it is less prone to injury.
B) Medial plateau, because it helps distribute the weight more effectively.
What type of cartilage covers the menisci in the knee joint?
A) Hyaline cartilage
B) Elastic cartilage
C) Fibrocartilaginous rings
D) Articular cartilage
C) Fibrocartilaginous rings
What is the primary function of the menisci in the knee joint?
A) Enhancing blood flow
B) Shock absorption and load distribution
C) Preventing bone growth
D) Reducing muscle fatigue
B) Shock absorption and load distribution
Which meniscus is more prone to injury and why?
A) Lateral meniscus, because it is less mobile.
B) Medial meniscus, because it is less mobile and more firmly attached to the tibial plateau.
C) Lateral meniscus, because it is more mobile.
D) Medial meniscus, because it is more mobile.
B) Medial meniscus, because it is less mobile and more firmly attached to the tibial plateau.
How does the lateral meniscus differ from the medial meniscus in terms of mobility and shape?
A) The lateral meniscus is less mobile and nearly a complete ring.
B) The medial meniscus is more mobile and semicircular.
C) The lateral meniscus is more mobile and nearly a complete ring.
D) The medial meniscus is more mobile and nearly a complete ring.
C) The lateral meniscus is more mobile and nearly a complete ring.
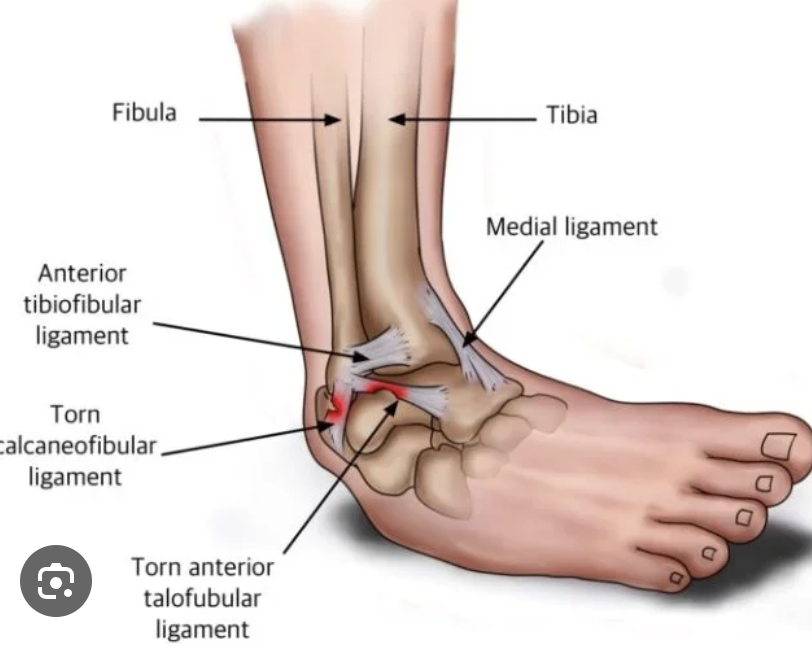
Which ligament is most commonly injured in an ankle sprain?
anterior talofibular ligament (inversion ankle sprains)
What does the absence of the dorsalis pedis pulse suggest?
A) Normal vascular function
B) Vascular insufficiency resulting from arterial disease
C) Increased blood flow to the foot
D) Venous insufficiency
B) Vascular insufficiency resulting from arterial disease
Why is palpating the dorsalis pedis pulse clinically significant?
A) It helps assess venous return from the foot.
B) It helps assess arterial blood flow to the foot.
C) It measures the strength of the foot muscles.
D) It detects nerve function in the foot.
B) It helps assess arterial blood flow to the foot.
Which condition can be indicated by an absent dorsalis pedis pulse?
A) Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
B) Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
C) Plantar fasciitis
D) Achilles tendinitis
A) Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
Which artery is palpated lateral to the EHL tendons on the dorsum of the foot?
A) Posterior tibial artery
B) Dorsalis pedis artery
C) Popliteal artery
D) Femoral artery
B) Dorsalis pedis artery
Which nerve injury leads to foot drop?
A) Tibial nerve
B) Common fibular nerve
C) Saphenous nerve
D) Femoral nerve
B) Common fibular nerve
The “unhappy triad” of knee injuries includes damage to the:
A) MCL, lateral meniscus, and PCL
B) MCL, medial meniscus, and ACL
C) LCL, lateral meniscus, and ACL
D) MCL, medial meniscus, and PCL
MCL, medial meniscus, and ACL
Which ligament in the foot is known as the “spring ligament”?
A) Long plantar ligament
B) Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
C) Short plantar ligament
D) Deltoid ligament
B) Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
In full knee extension, what mechanism increases stability?
A) Medial rotation of tibia
B) Lateral rotation of tibia
C) Flexion of knee
D) Abduction of tibia
B) Lateral rotation of tibia
in the last 20 degrees of extension “locks” the knee
Which arch of the foot is supported by the spring ligament?
A) Lateral longitudinal
B) Transverse
C) Medial longitudinal
D) None of the above
C) Medial longitudinal
The “drawer sign” test is used to check the integrity of what structure?
Cruciate ligaments
A Pott fracture-dislocation of the ankle is caused by:
A) Forceful inversion
B) Forceful eversion
C) Direct blow to fibula
D) Overuse injury
What indicates a positive anterior drawer sign?
Excessive forward movement of the tibia
A Pott fracture-dislocation of the ankle is caused by:
A) Forceful inversion
B) Forceful eversion
C) Direct blow to fibula
D) Overuse injury
B) Forceful eversion
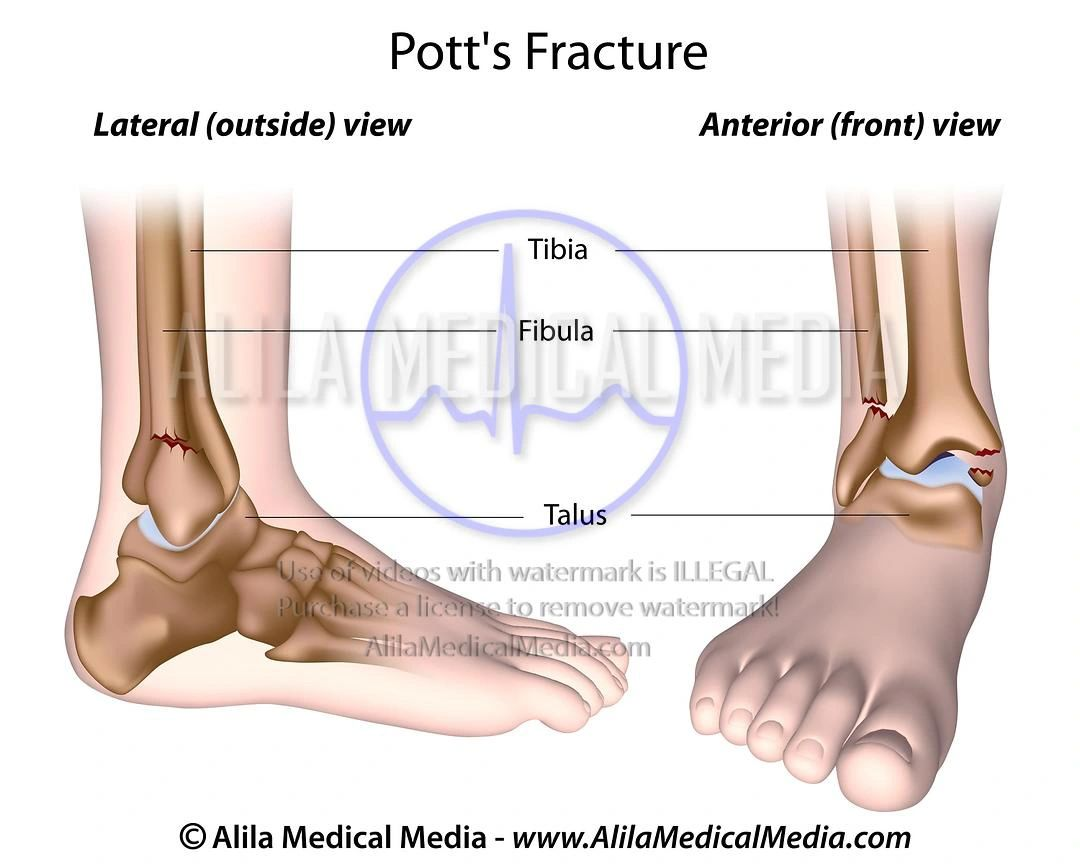
Which ligament is involved in a Pott fracture-dislocation when the foot is forcefully everted?
A) Lateral collateral ligament
B) Medial (deltoid) ligament
C) Anterior cruciate ligament
D) Posterior cruciate ligament
B) Medial (deltoid) ligament
What movement occurs at the subtalar joint?
A) Flexion and extension
B) Inversion and eversion
C) Abduction
D) Adduction
What movement occurs at the subtalar joint
B) Inversion and eversion
What is the most common cause of plantar fasciitis?
B) Overuse and inappropriate footwear
Which nerve roots are tested by the calcaneal tendon jerk?
A) L3-L4
B) L5
C) S1-S2
D) S3-S4
C) S1-S2
What is pes planus?
Flat feet; can be flexible or rigid depending on weight-bearing
During a sports-related knee injury, a football player presents with a valgus force to the lateral aspect of the knee. On examination, there is excessive anterior translation of the tibia, and medial joint line tenderness. Which structures are most likely injured?
Valgus force stretches the MCL, which is attached to the medial meniscus; the ACL is commonly injured together—this is the "unhappy triad".
A patient with a history of chronic ankle sprains now has instability during inversion of the foot. On physical exam, which ligament is most likely incompetent?
A) Deltoid ligament
B) Anterior talofibular ligament
C) Long plantar ligament
D) Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
B) Anterior talofibular ligament.
The anterior talofibular ligament is the most commonly injured ligament in inversion ankle sprains.
In the last 20 degrees of knee extension, the knee "locks" due to:
A) Medial rotation of the tibia
B) Lateral rotation of the tibia
C) Flexion of the femur
D) Abduction of the tibia
B) Lateral rotation of the tibia
A patient experiences foot drop and cannot dorsiflex or evert the foot. Which gait adaptation is most likely to be observed?
A) Antalgic gait
B) Waddling gait
C) Steppage gait
D) Trendelenburg gait
Steppage gait is a compensation for foot drop, with exaggerated hip/knee flexion to clear the foot.
In a patient with suspected Pott fracture-dislocation, which mechanism of injury is most consistent?
A) Hyperextension of the ankle
B) Forced inversion of a plantarflexed foot
C) Forced eversion of the foot
D) Direct blow to the lateral malleolus
C) Forced eversion of the foot. (fracturing the medial malleolus and fibula)
runner has pain on the plantar surface of the foot and heel. Examination reveals tenderness at the insertion of the plantar fascia. Which condition is most likely?
A) Plantar fasciitis
B) Calcaneal bursitis
C) Pes planus
D) Hallux valgus
A) Plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis causes pain at the plantar fascia, especially at the heel after overuse.
Which nerve supplies the majority of the intrinsic plantar muscles of the foot, except for abductor hallucis, FDB, FHB, and first two lumbricals?
lateral plantar nerve
only abductor hallucis, FDB. FHB and the first two lumbricals is innervated by medial plantar nerve
A patient presents with a rigid flat foot that does not change with or without weight-bearing. Which structure is most likely degenerated or absent?
A) Plantar aponeurosis
B) Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
C) Long plantar ligament
D) Plantar calcaneocuboid ligament
B) Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring ligament) is essential for medial longitudinal arch integrity; its degeneration leads to rigid pes planus.
What is the primary dynamic stabilizer of the patellofemoral joint in the transverse plane?
A) Patellar tendon
B) Medial and lateral patellar retinacula
C) Popliteus muscle
D) Quadriceps femoris
B) Medial and lateral patellar retinacula (expansions of VM & VL) stabilize the patella transversely.