[L1] Electric Potential
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
work
this is defined as the product of displacement (d) and a parallel applied force (f)
work
this is only done by a force on an object if that same force cause to move in the direction of the force
cause to move in the direction of the force
work is only done by a force on an object if that same force ____
(f*costheta)*d
the formula for work
work is positive
if force has a component in the direction of displacement, then work is ____
work is negative
if force has a component opposite to direction of displacement, then work is ____
no work
if force component is perpendicular to direction of displacement, then work is ____
energy
the ability to do work
potential energy (U)
it is defined as the ability to do work by virtue of position or condition
position or condition
potential energy is defined as the ability to do work by virtue of ____
kinetic energy (K)
it is defined as the ability to do work by virtue of motion (velocity)
motion (velocity)
kinetic energy is defined as the ability to do work by virtue of ____
field
a region of influence surrounding an object
consider the forces exerted on the ball. the force (F) does ____ work
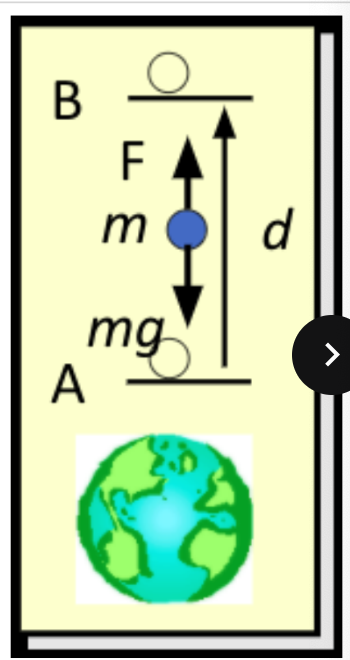
negative
consider the forces exerted on the ball. the force (mg) does ____ work
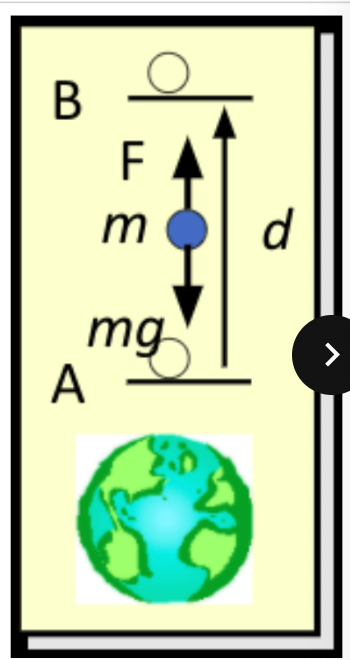
decreases (since the field can do positive work if m is released)
the potential energy at b relative to a ____ because the field can do positive work if m is released
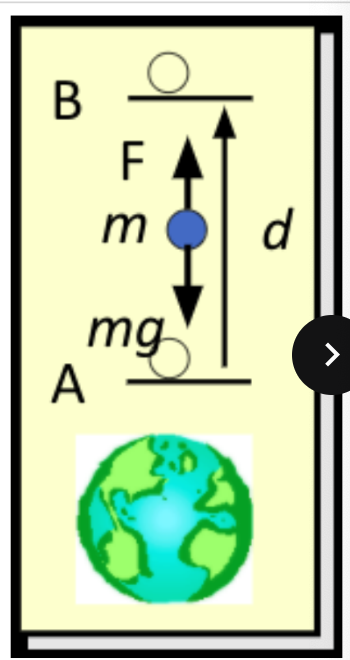
increases
the potential energy at a relative to b ____ because the field would need outside force to move m
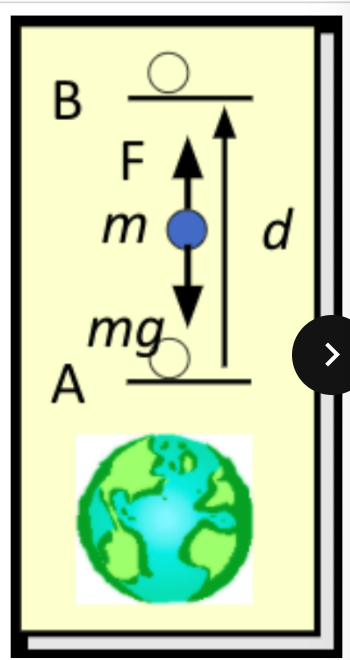
work done
____ is equal to the change in the object's potential energy
potential energy
work done is equal to the change in the object's _____
positive, negative
electric field is always from ____ surface to ____ surface
negative work
consider the work done by the electric field to move the positive charge q from A to B, a vertical height r. the electric field does ____ work
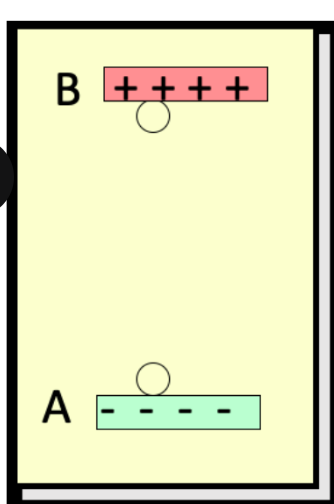
increases
consider the work done by the electric field to move the positive charge q from A to B, a vertical height r. the electric field ____ in potential energy
gives work back
consider the work done by the electric field to move the positive charge q from A to B, a vertical height r. if released, the field ____
positive work
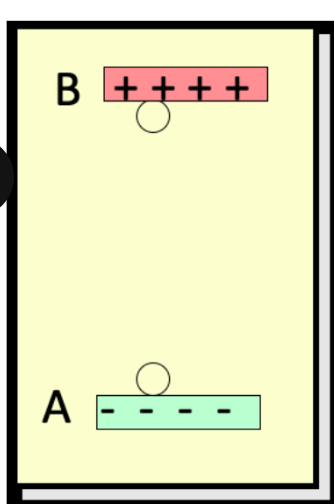
consider work done by the electric field to move the positive charge q from B to A, a vertical height r. the electric field does ____ work
decreases
consider work done by the electric field to move the positive charge q from B to A, a vertical height r. the potential energy ____
nothing happened
consider work done by the electric field to move the positive charge q from B to A, a vertical height r. if released, ____
positive work
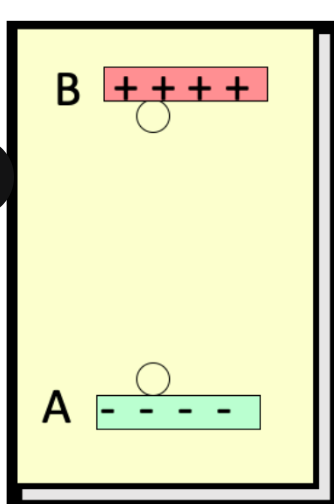
when positive charge moves in the direction of the electric field, the field does ____ work on the charge
decreases
when positive charge moves in the direction of the electric field, the potential energy ____
negative
when positive charge moves opposite the direction of the electric field, the field does ____ work on the charge
increases
when positive charge moves opposite the direction of the electric field, the potential energy ____
positive work
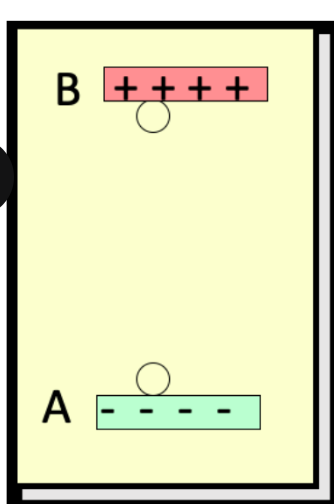
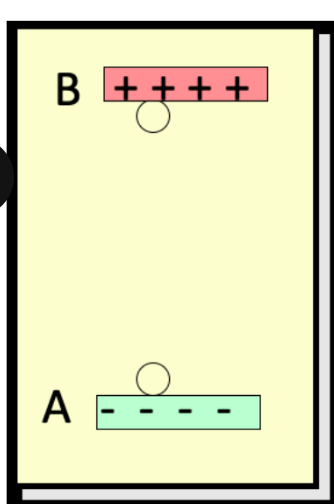
consider work done by the electric field to move the negative charge q from A to B, a vertical height r. the electric field does ____ work on -q
decreased
consider work done by the electric field to move the negative charge q from A to B, a vertical height r. the potential energy is ____
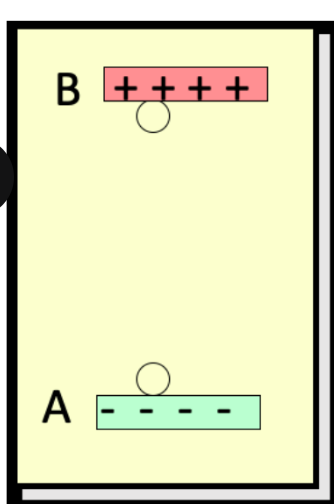
consider work done by the electric field to move the negative charge q from A to B, a vertical height r. if released from b, nothing happens
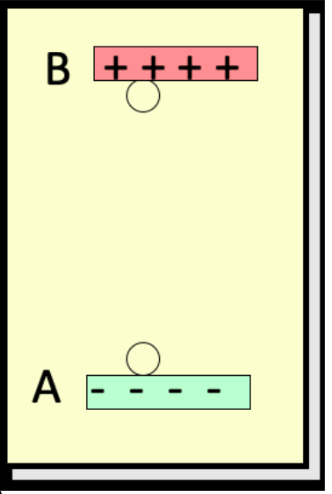
negative work
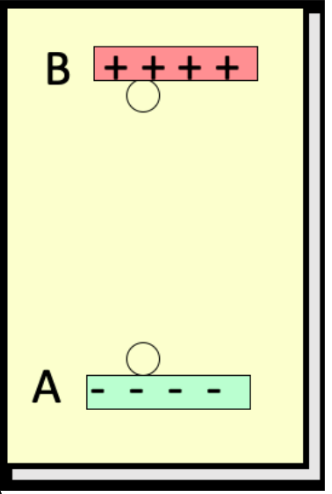
consider work done by the electric field to move the negative charge q from B to A, a vertical height r. the electric field does ____ work on -q
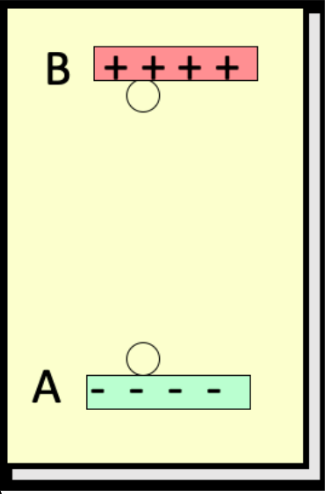
increased
consider work done by the electric field to move the negative charge q from B to A, a vertical height r. the potential energy is ____
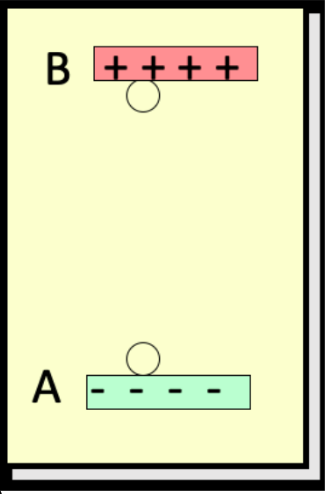
gives work back
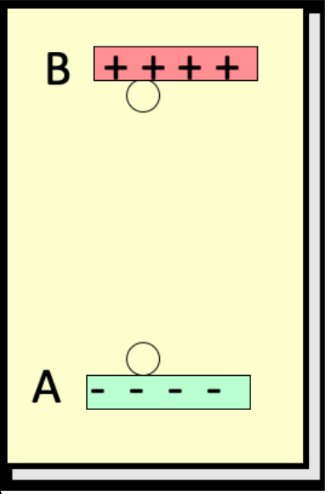
consider work done by the electric field to move the negative charge q from B to A, a vertical height r. if released from a, the field _____
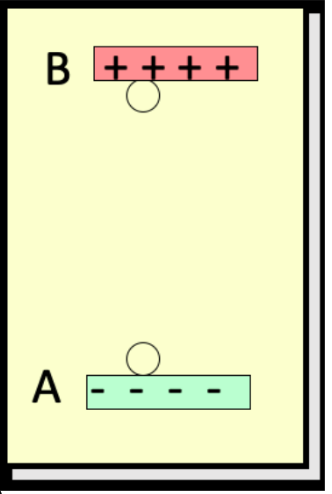
more work/energy is needed
how can you compare the amount of work or potential energy needed to move 1C of charge to that of 10C in an electric field
electric potential energy, u, of a charged particle at a point in an electric field region
____ is equal to the work done by the electric field to bring that point to a point of infinite distance
electric potential energy
this is the energy of a charge object due to its position in an electric field
only the endpoints
the work done by the electric force fo this path (epe of two-point charges) depends on ____
the path taken, distances ra and rb (distance between the two points)
the work done on charge qo by the electric field of charge q does not depend on ____, but only on ____
ra an rb (point charges), details of the path
the work done by q0 on the electric field e produced by q depends only on ____ and ____, not on the ____
positive
the potential energy is ____ if the charges q and q0 have the same sign
negative
the potential energy is ____ if the charges q and q0 have opposite signs
approaches positive infinity
if q and q0 have the same sign, as r approaches 0, u ____
approaches 0
if q and q0 have the same sign, as r approaches infinity, u ____
approaches negative infinity
if q and q0 have opposite signs, as r approaches 0, u ____
approaches 0
if q and q0 have opposite signs, as r approaches infinity, u ____
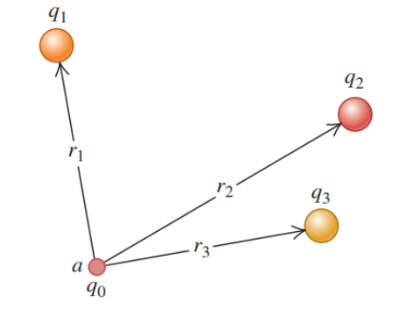
distances (r1, r2, r3)
the potential energy associated with a charge q0 at point a depends on other charges, q1, q2, and q3, and on their ____
fields due to the individual charges
the total electric field at each point is the vector sum of the _____
contributions from the individual charges
the total work done on q0 during any displacement is the sum of the ____
electric potential
the potential energy per unit charge associated with a test charge at that point
potential energy, unit charge
electric potential is the ____ per ____ associated with a test charge at that point
scalar
potential energy and charge are both ____ quantities, so potential is anlso ____
potential at point a, potential at point b
we call va and vb the ____ and ____ respectively
work done per unit charge
the ____ by the electric force when a charged object moves from a to b is equal to the potential at a minus the potential at b
potential at a minus the potential at b
the work done per unit charge by the electric force when a charged object moves from a to b is equal to the ____
vab, the potential (in v)
____ of a with respect to b, equals the work done (in j) done by the electric force when a unit (1 c) charge moves from a to b
a to b
vab, the potential (in v) of a with respect to b, equals the work done (in j) done by the electric force when a unit (1 c) charge moves from ____
b to a
vab, the potential (in v) of a with respect to b, equals the work (in j) that must be done to move a unit (1c) slowly from ____ against the electric force
vab, the potential (in v)
____ of a with respect to b, equals the work (in j) that must be done to move a unit (1c) slowly from b to a against the electric force
a potential of one volt
____ at a given point means that a charge of one coulomb placed at that point will experience a potential energy of one joule
a charge of one coulomb
a potential of one volt at a given point means that ____ placed at that point will experience a potential energy of one joule
potential energy of one joule
a potential of one volt at a given point means that a charge of one coulomb placed at that point will experience a ____
potential energy, unit charge
electric potential is the ____ per ____
voltage
also known as electric potential difference
electric potential difference
also known as voltage
voltage or electric potential difference
this is the difference of potential between two points
increases
in a positive point charge, voltage ____ as you move inward
decreases
in a positive point charge, voltage ____ as you move outward
decreases
in a negative point charge, voltage ____ as you move inward
increases
in a negative point charge, voltage ____ as you move outward
equipotential surface
it is a three-dimensional surface on which the electric potential (v) is the same at every point
electric potential (v)
an equipotential surface is a three-dimensional surface on which the ____ is the same at every point
mutually perpendicular
field lines and equipotential surfaces are always _____


it moves against the direction of electric field. if it doesn’t, the electric field does work on it (positive or negative)
work is only done on charge when ____