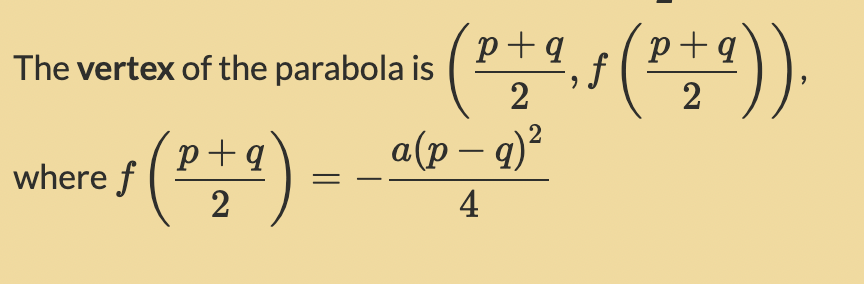Maths important things 2.6 - test week 1
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Standard form
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
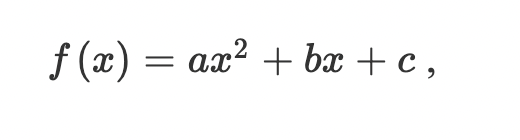
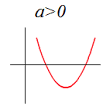
Standard form: If a>0, the parabola opens…
…upwards; its vertex is the minimum turning point and the curve is concave up.
Standard form: If a<0, the parabola opens…
…downwards; the vertex is the maximum turning point and the curve is concave down.
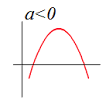
Standard form: y-intercept of the parabola
(0,c)
Standard form: The vertex of the parabola is…
(-b/2a, f(-b/2a))
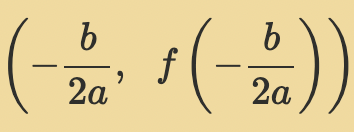
The axis of symmetry of the parabola is the vertical line…
-b/2a
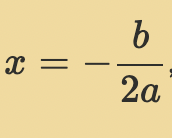
Vertex form
f(x) = a(x-h)2 + k
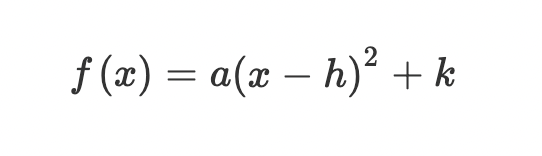
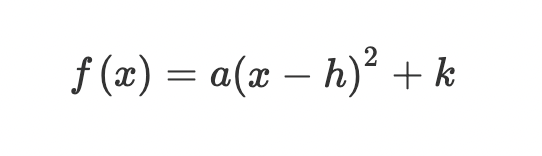
Vertex form: The vertex of the parabola is the point…
(h,k)
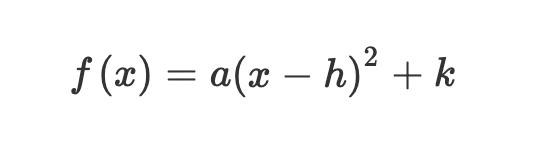
Vertex form: If a>0, the parabola is…
concave up
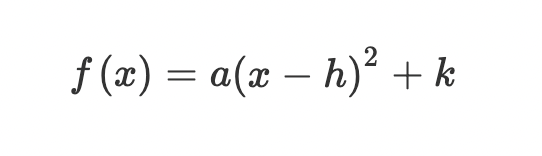
Vertex form: If a<0, the parabola is…
concave down
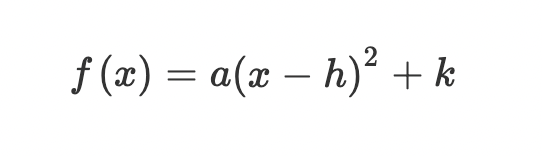
Vertex form: The axis of symmetry has equation…
x = h
Vertex form: The y-intercept is…
(0, ah2 + k)
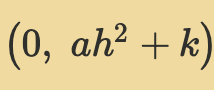
Factorised form
f(x) = a(x-p)(x-q)
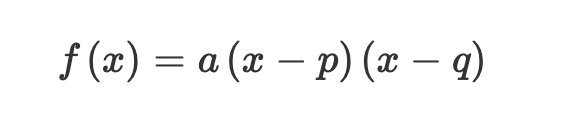
Factorised form: The x-intercepts of the parabola are…
(p, 0) and (q, 0)
Factorised form: The y-intercepts of the parabola are…
(0, apq)
Factorised form: The axis of symmetry has equation…
x = p+q/2
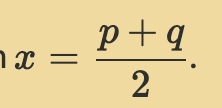
Factorised form: The vertex of the parabola is…
(p+q/2, f(p+q/2)), where f(p+q/2) = −a(p−q)²/4