Embryology – From Gametogenesis to Early Organogenesis
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key embryology terms from fertilization through early organogenesis, implantation, germ layers, neurulation, pharyngeal structures, brain divisions, skull development, and germ-layer derivatives.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms

Fertilization
Fusion of a sperm and an ovum in the ampulla of the fallopian tube to form a diploid (2n, 23 pairs) zygote.
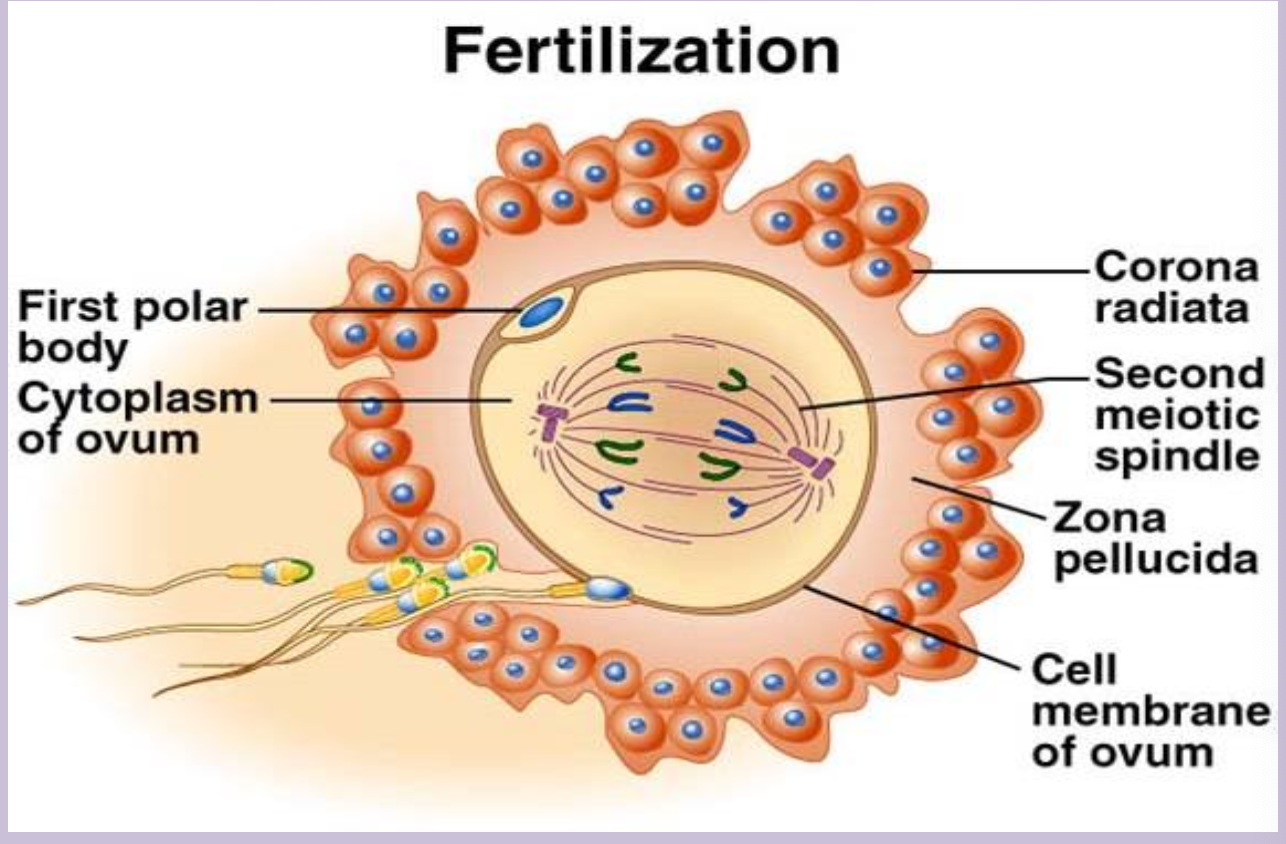
Ampulla of the uterine tube
Dilated region of the fallopian tube where fertilization normally occurs.
Zygote
Single-celled embryo created after fertilization that has the full diploid (2n) chromosome complement.
Pronuclei
Male and female haploid nuclei that come together and lose their membranes, and intermingle before the first mitotic division of the zygote. Fertilization ends as this occurs.
Diploid number
Total of 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) restored at fertilization.
Results of Fertilization
Restoration of diploid number of chromosomes w/ both mom and dad chromosomes
determination of sex
initiation of cleavage…oocyte degenerates 24 hrs after ovulation if no fertilzation
Corpus luteum
Degeneration prevented by B-HCG
Develops from the ruptured follicle after ovulation.
Produces progesterone until 4th month, and then the placenta takes over
Post-Fertilization
pronuclei replicate their DNA, after DNA synthesis chromosomes organize on their spindles to prepare for mitotic division
23 M and F double chromosomes split longitudinally at centromere and sister chromatids move to opposite pole and provide each sister with normal diploid number
Zona pellucida
Glycoprotein shell surrounding the oocyte and early embryo that prevents premature implantation and polyspermy.
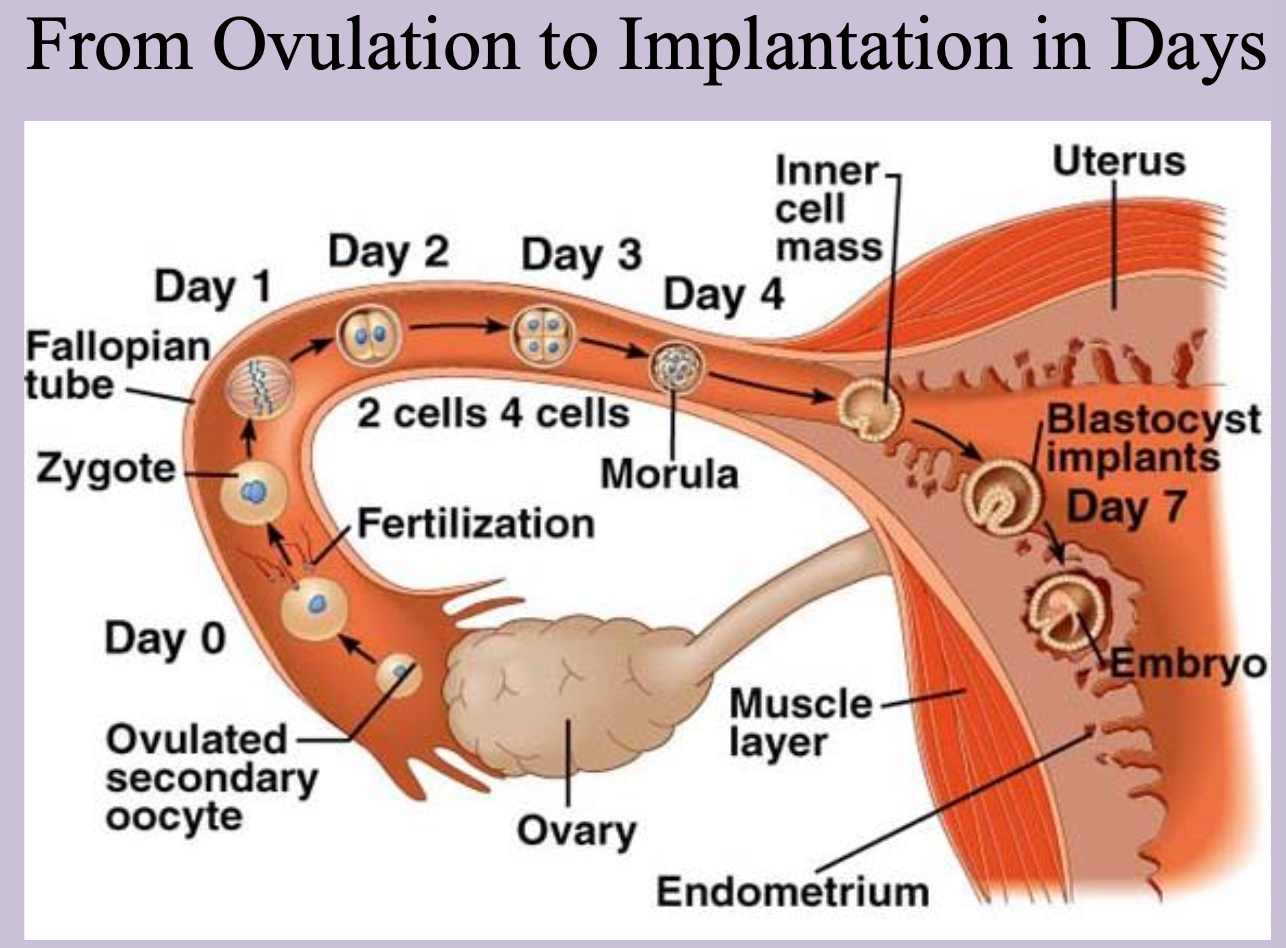
Cleavage
Rapid mitotic divisions of the 2 cell zygote producing smaller cells called blastomeres while the total size stays the same.
Surrounded by zona pellucida
Takes 1-3 days
Blastomere
Individual cell produced during cleavage of the early embryo.
Morula
Solid ball of about 16 blastomeres (day ~3) that reaches the uterine cavity; composed of inner (embryo proper) and outer cell masses (extraembryonic membranes - trophoblast and future placenta)
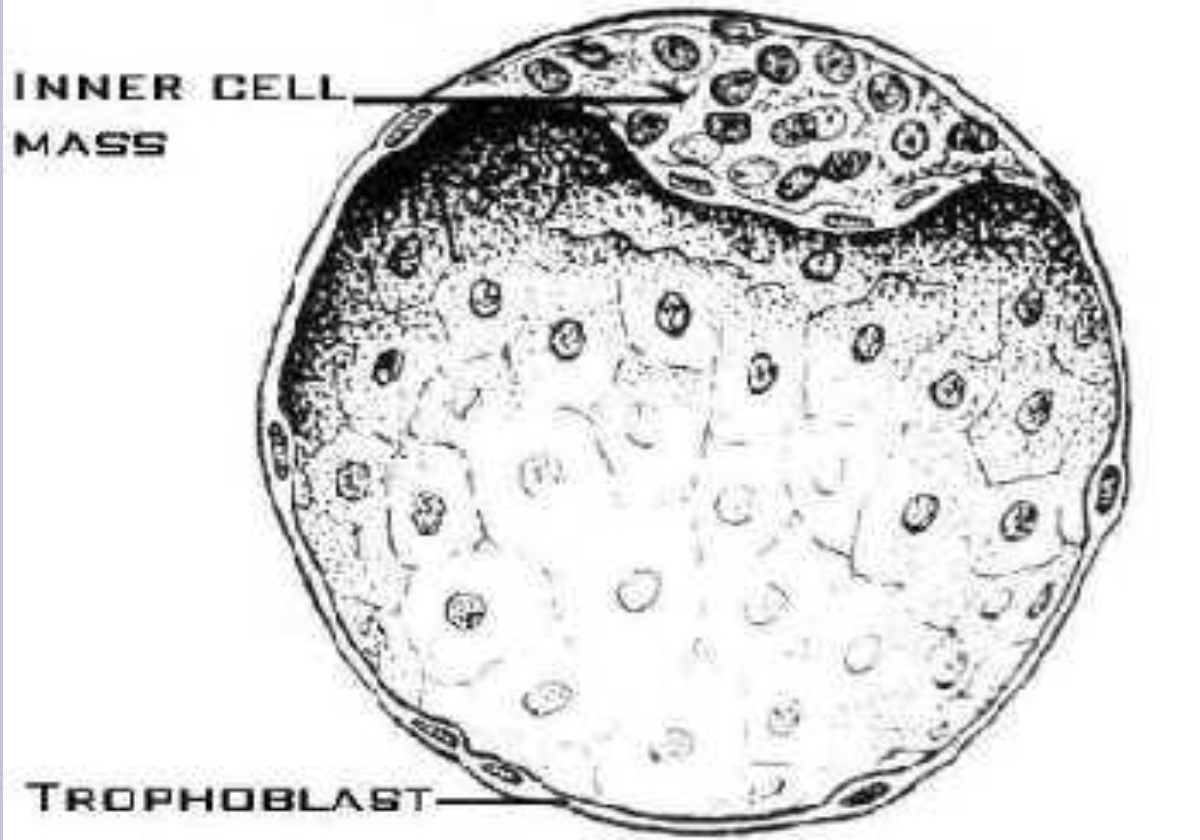
Inner cell mass (embryoblast)
Central cells of the morula that form the embryo proper.
Outer cell mass
Peripheral cells of the morula that become the trophoblast and extra-embryonic membranes.
Blastocyst
Stage formed when fluid creates the blastocele within the morula; consists of embryoblast, trophoblast, and cavity.
Zona pellucida disappears as blastocyst enlarges
Blastocele
Fluid-filled cavity inside the blastocyst.
Implantation
Attachment and penetration of the blastocyst through the epithelial layer into the endometrium (begins ~day 6.)
Trophoblast
Outer layer of the blastocyst that contributes to the placenta; differentiates into syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast.
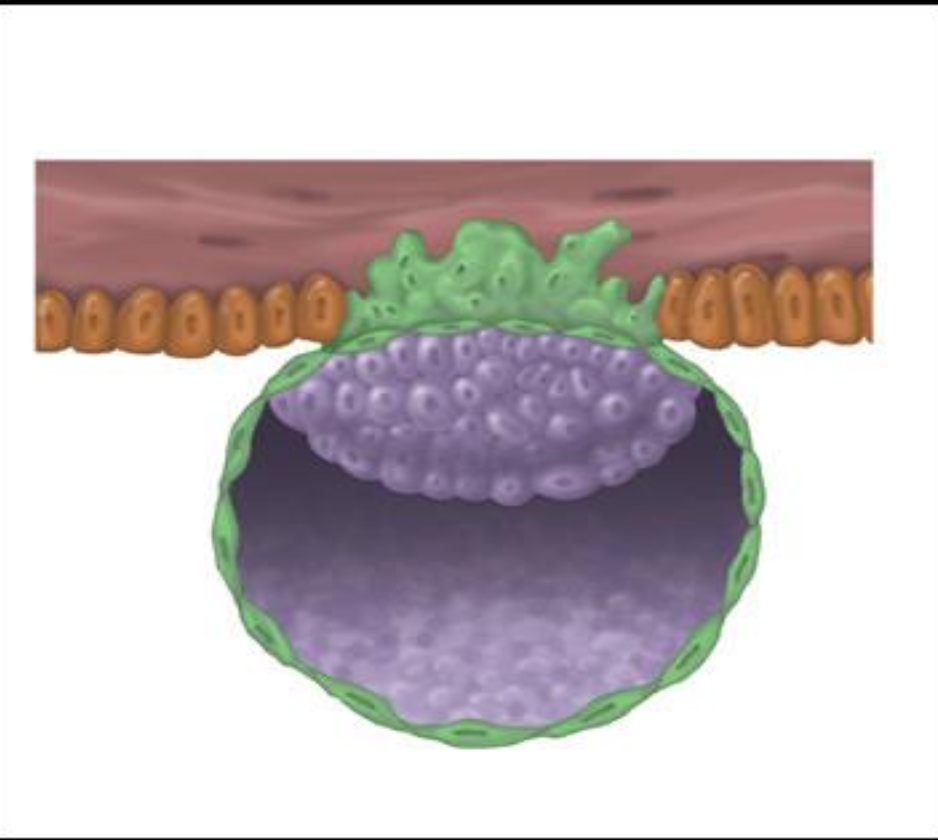
Syncytiotrophoblast
Multinucleated outer trophoblastic layer that invades the endometrium and secretes hCG.
Cytotrophoblast
Inner, mononuclear trophoblastic layer retaining distinct cell boundaries.
How is Implantation Accomplished?
-normally occurs posterior or anterior wall of endometrium
Erosion accompanied by substances released by layer of trophoblast over the embryoblast pole which allows it to invade and embed into the endometrial stroma between the surface openings of uterine glands
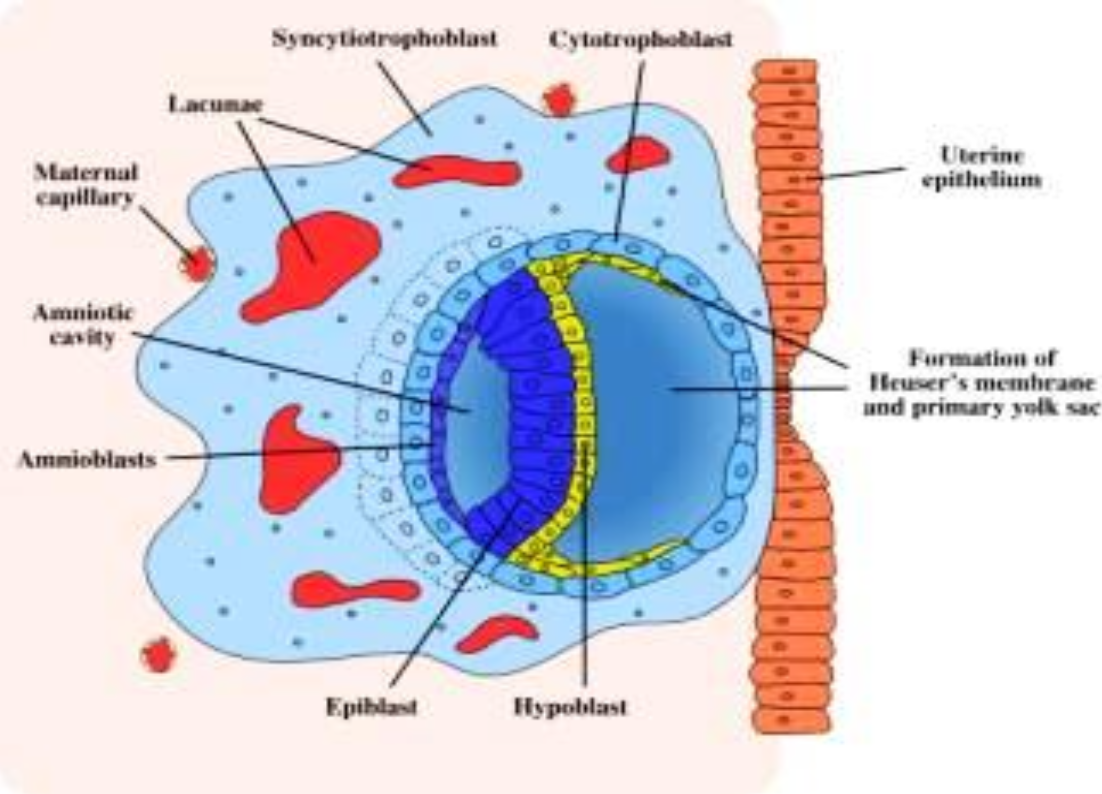
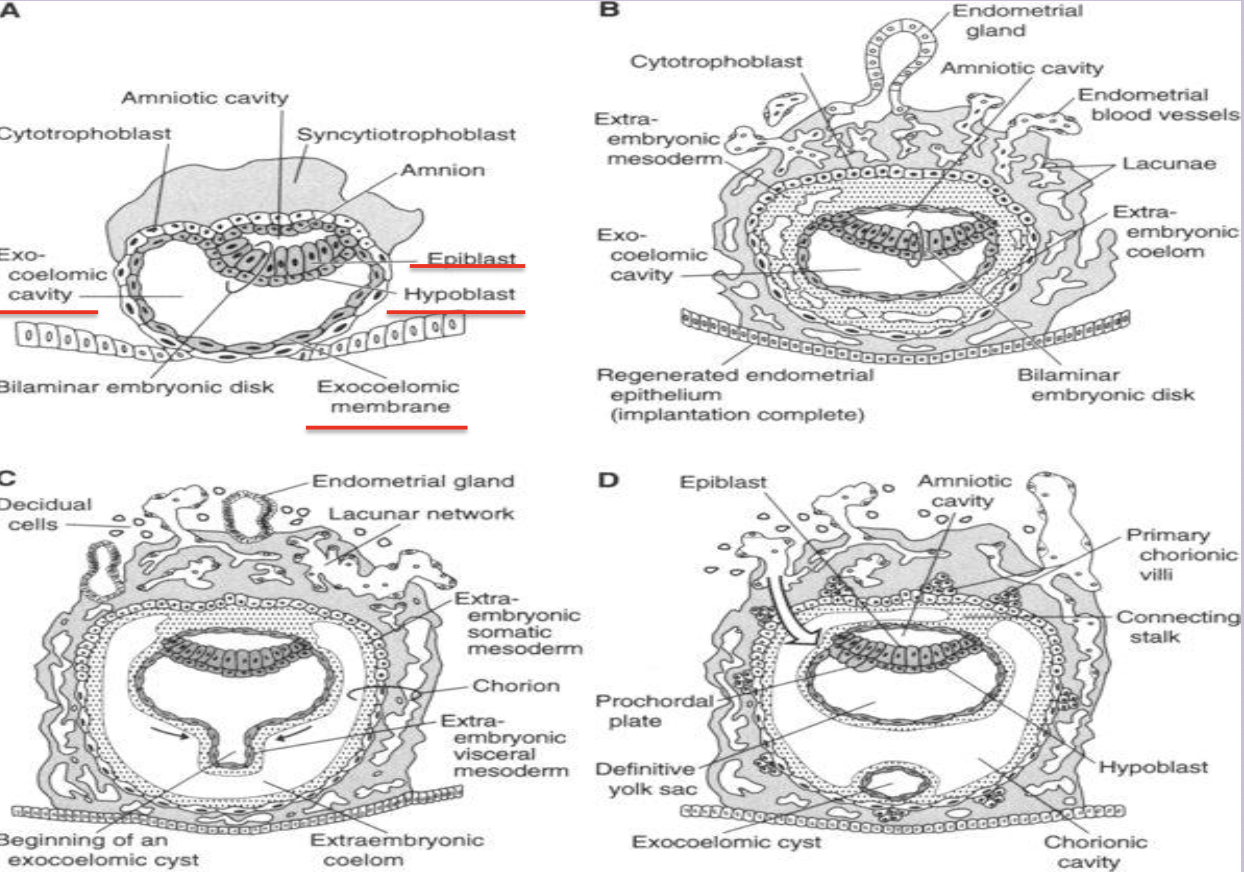
Bilaminar Embryoblast
Embryoblast —> inner cell mass results in flattened disc with 2 layers
Epiblast—>ectoderm
Hypoblast—> endoderm
Amnio forms as amniotic cavity enlarges and needs epithelial roof. Amnion comes from cytotrophoblasts
2nd Week of Life - Bilaminar and Early Trilaminar Period
Embedded balstocyst receives food from
Early Uteroplacental Circulation
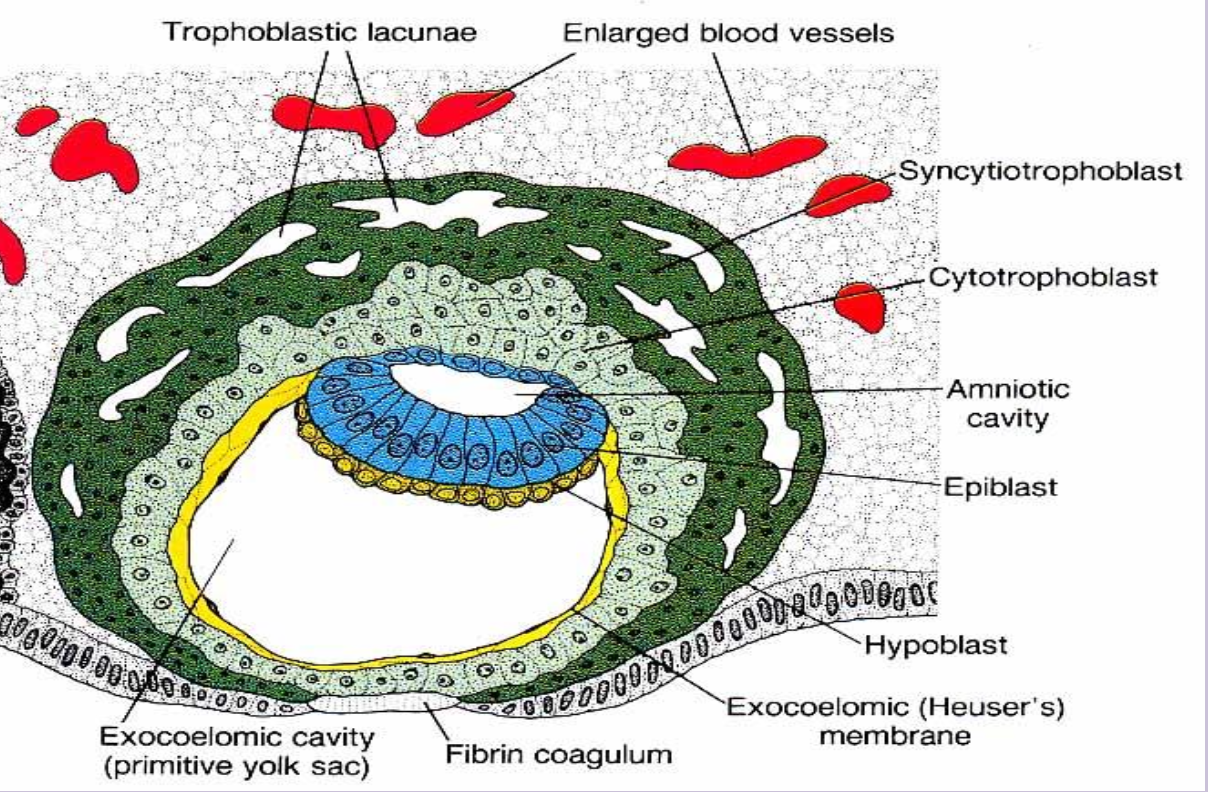
Syncytiotrophoblast invades into endometrium, and erode walls of dilated maternal vessels and lacunae fill with maternal blood and establish early placental circulation
Decidua
Endometrial stromal cells enlarge around conceptus, increase in number, and accumulate glycogen and lipids
Day 9-10 Changes
Cytotrophoblast flatten to creat a thin membrane that lines inner surface of cytotrophoblast
—> This membrane and hypoblast cells form lining of Primitive Yolk Sac
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Hormone from syncytiotrophoblast that maintains the corpus luteum of pregnancy.
Corpus luteum
Post-ovulation structure in the ovary that secretes progesterone; maintained by hCG if pregnancy occurs.
Amniotic cavity
Fluid space that forms between embryoblast and trophoblast, eventually surrounding the embryo.
Epiblast
Columnar cell layer of the bilaminar disc adjacent to the amniotic cavity; precursor of ectoderm and mesoderm.
Hypoblast
Cuboidal cell layer of the bilaminar disc lining the blastocele; contributes to endoderm and yolk-sac roof.
Bilaminar embryonic disc
Two-layered embryo (epiblast + hypoblast) present during week 2.
Heuser’s (exocoelomic) membrane
Thin lining formed by cytotrophoblast and hypoblast cells that surrounds the primitive yolk sac.
Primitive (primary) yolk sac
First yolk-sac cavity bordered by Heuser’s membrane; later replaced by the definitive yolk sac.
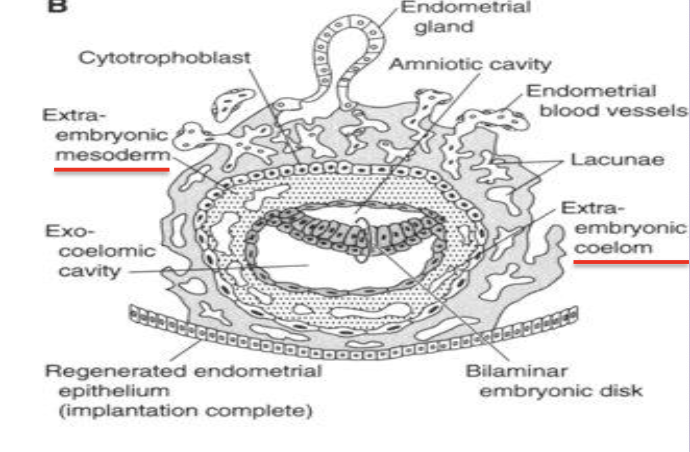
Extraembryonic mesoderm
Loose tissue between cytotrophoblast and yolk/amnion that splits to form the extraembryonic coelom.
Extraembryonic coelom (chorionic cavity)
Fluid cavity surrounding amnion and yolk sac except at the connecting stalk; becomes the chorionic sac.
Splits the extraembryonic mesoderm (lines trophoblast and covers amnion) into Somatic and Splanchnic/Visceral (covers yol sac)mesoderm
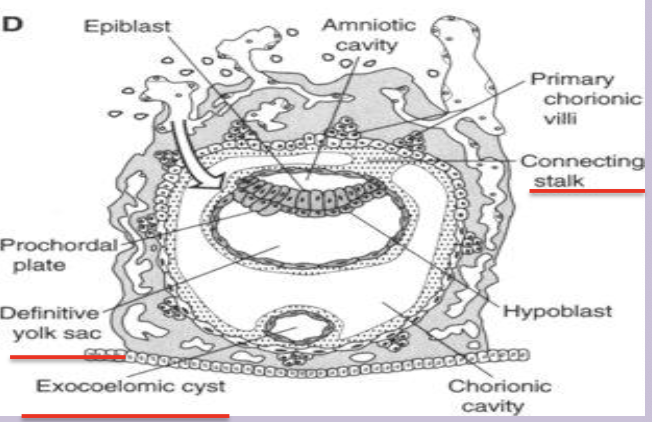
Connecting stalk
Band of extraembryonic mesoderm linking embryo to trophoblast; later forms the umbilical cord.
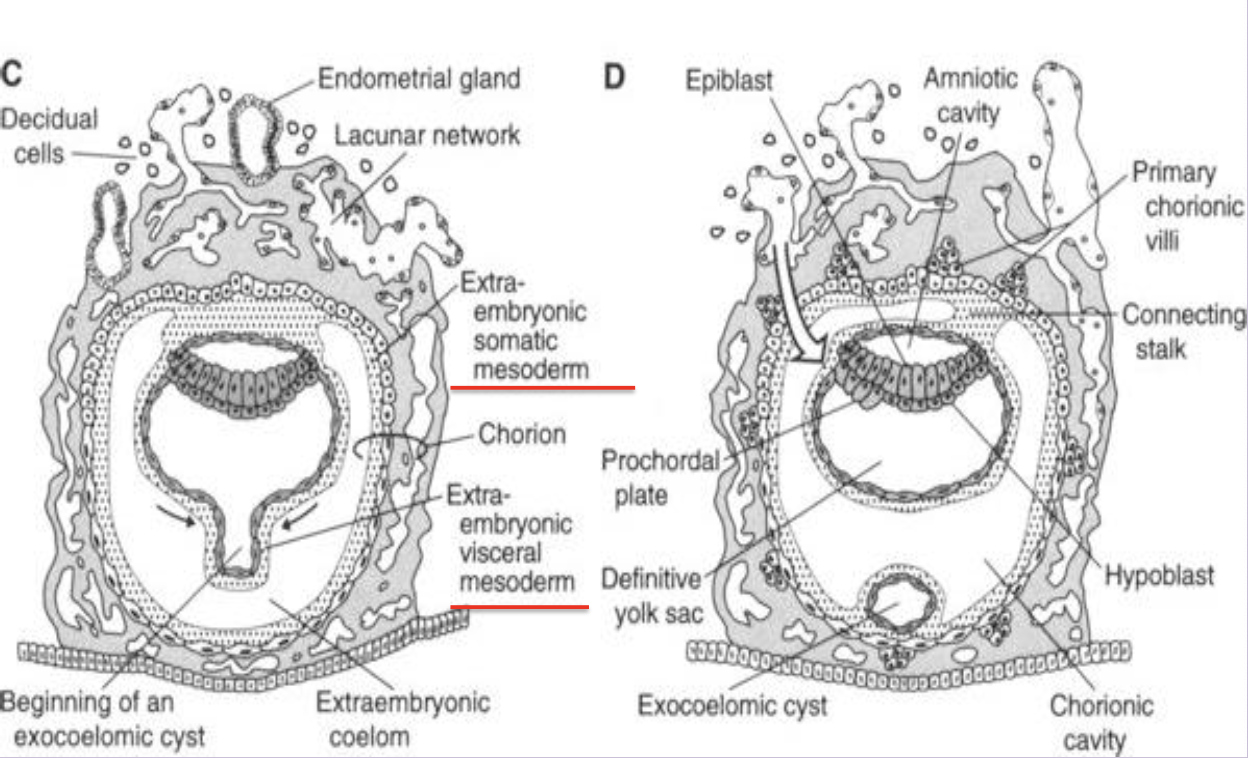
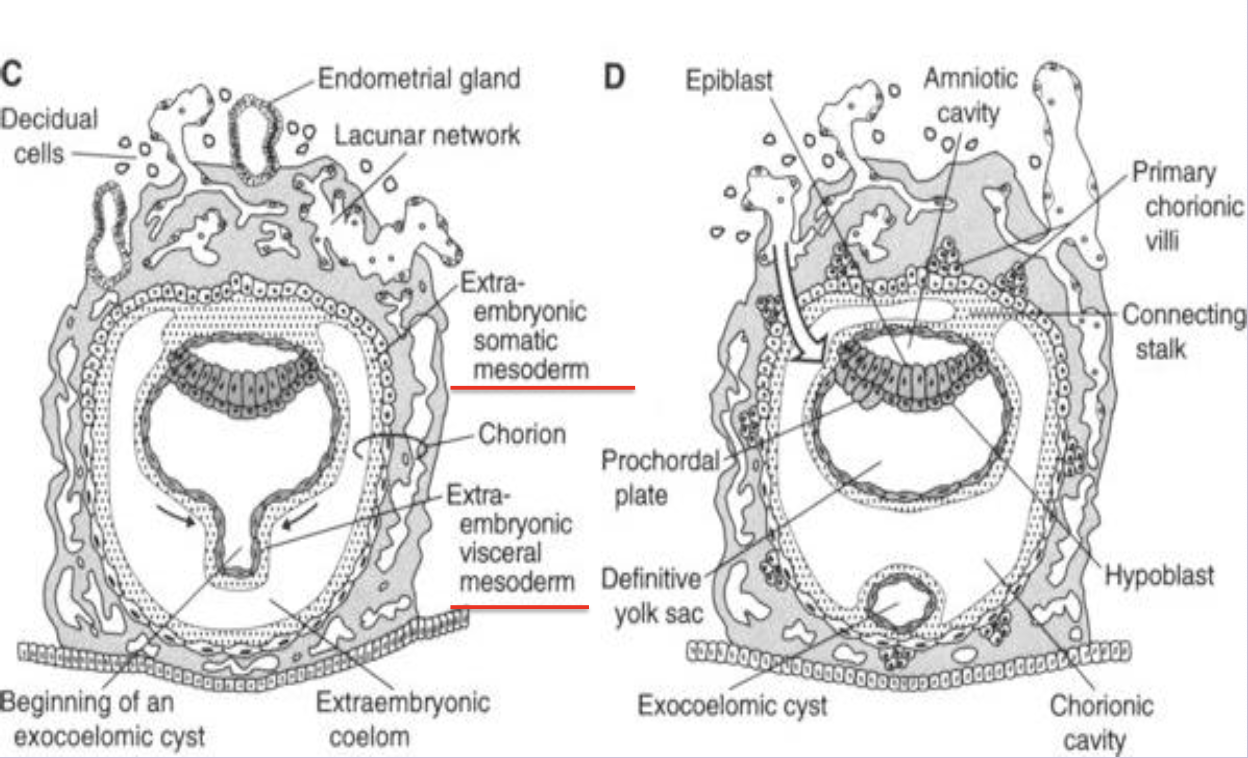
Chorion
Composite of cytotrophoblast and extraembryonic somatic mesoderm forming the outer fetal membrane.
Primary chorionic villus
Solid column of cytotrophoblast projecting into syncytiotrophoblast (day 13–14).
Secondary chorionic villus
Primary villus whose core is invaded by extraembryonic mesoderm (week 3).
Tertiary chorionic villus
Villus containing fetal blood vessels that connect to the embryonic circulation; functional unit of placenta.
Prochordal Plade and derivation
Endodermal cells have become columnar to for thick circle area called Prochordal Plate
Future site of head and mouth region
Trilaminar Embryoblast
epiblast differentiates into ecto and mesoderm and hypoblast will differentiate into endoderm
Endometrial Cycle
Proliferative Phase - Estrogen
Secretory Phase - 2,3 days after ovulation
Menstrual Phase - shedding
Decidua
Endometrial stromal tissue that enlarges and accumulates glycogen/lipid around the implanted embryo.
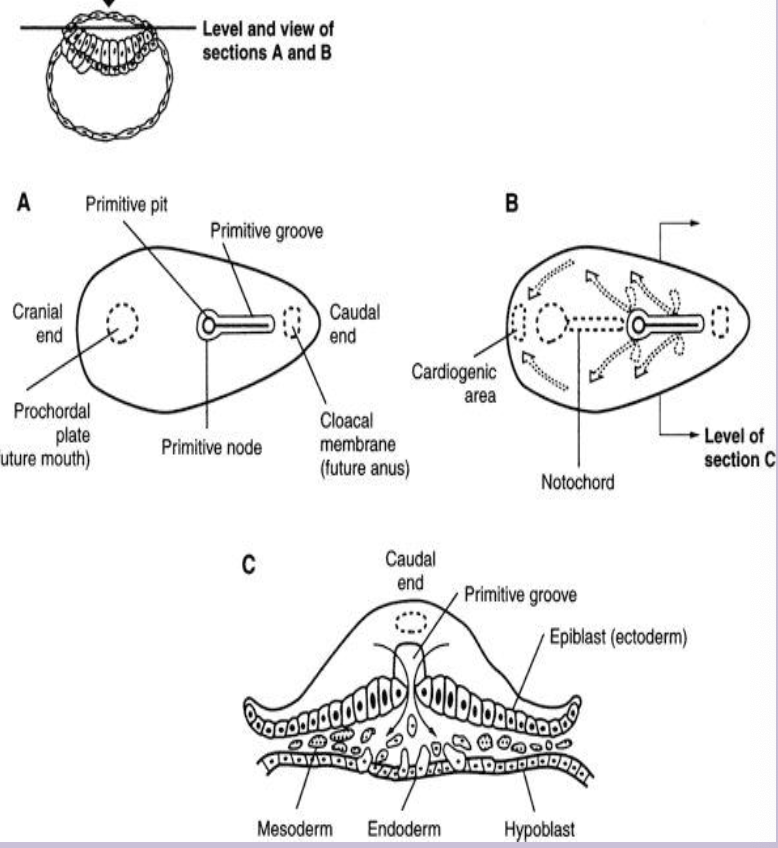
Gastrulation
Process in week 3 that forms the three definitive germ layers via the primitive streak.
Primitive streak
Linear band of thickened ectodermal cells appearing caudally; site of cell migration during gastrulation.
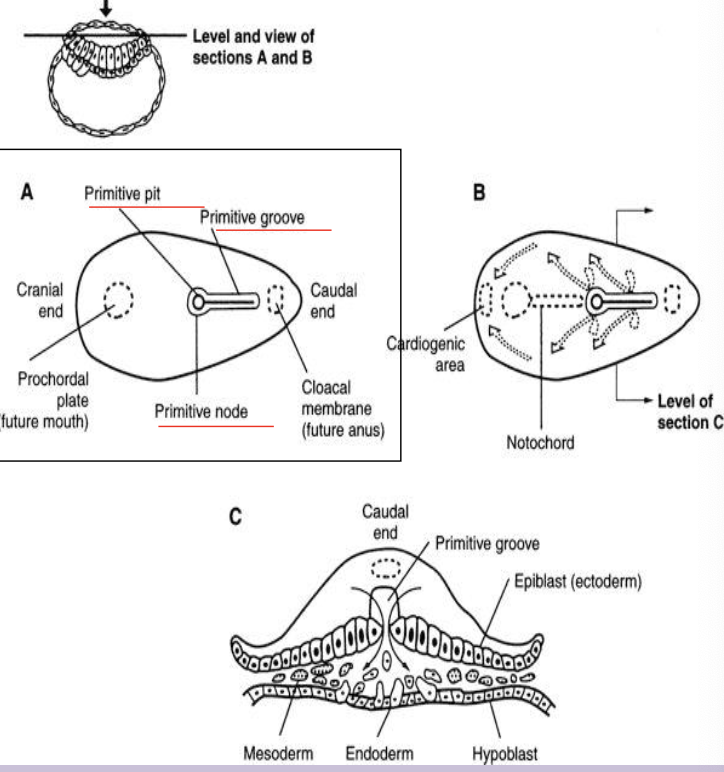
Primitive node
Cranial end of the primitive streak containing the primitive pit; organizer of axial structures.
Cloacal membrane
Caudal end of embryo where ectoderm and endoderm fuse, marking future anus.
Oropharyngeal (prochordal) plate
Cranial fused ecto-endoderm area that marks future mouth region.
Intraembryonic mesoderm
New layer formed from epiblast cells migrating through the primitive streak between ectoderm and endoderm.
Separates ecto and endo everwhere BUT oropharyngeal membrane cranially, midline cranial to primitive node, cloacal membrane caudally
Teratoma
After 4th week the primitive streak diminshes
When it remains clusters of all 3 types of cells form teratomas (tumors)
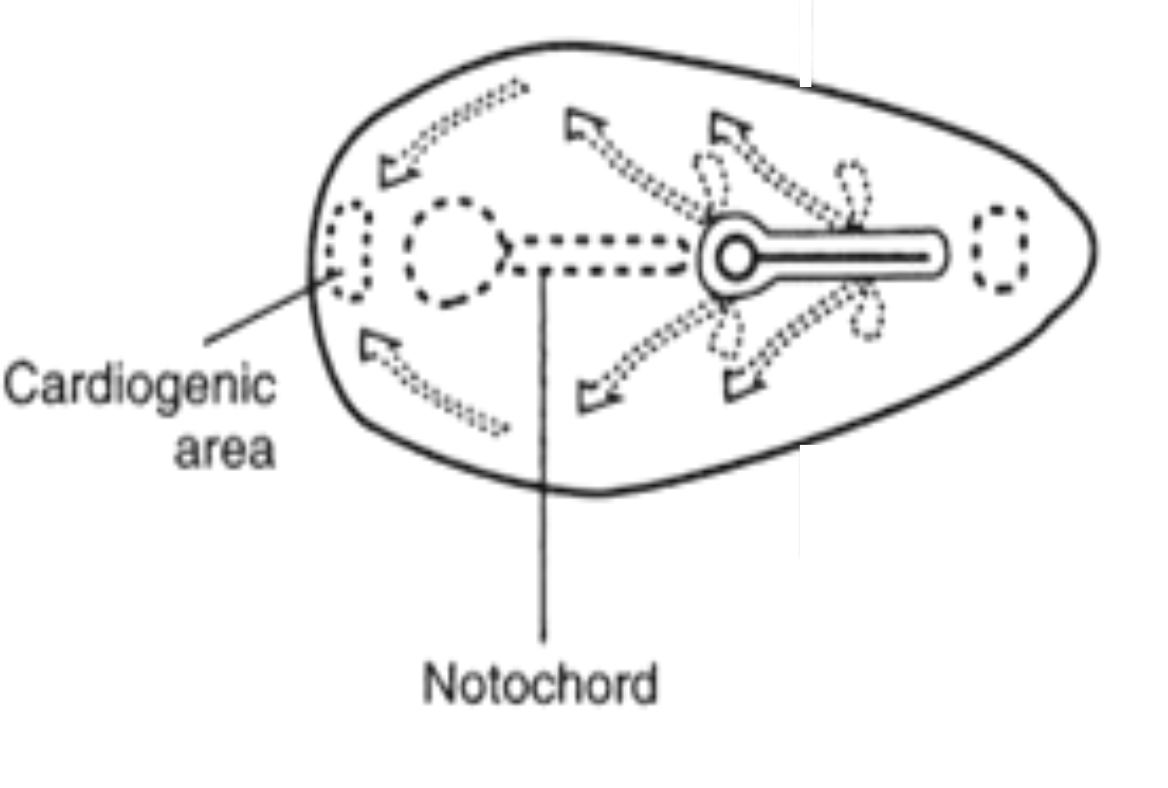
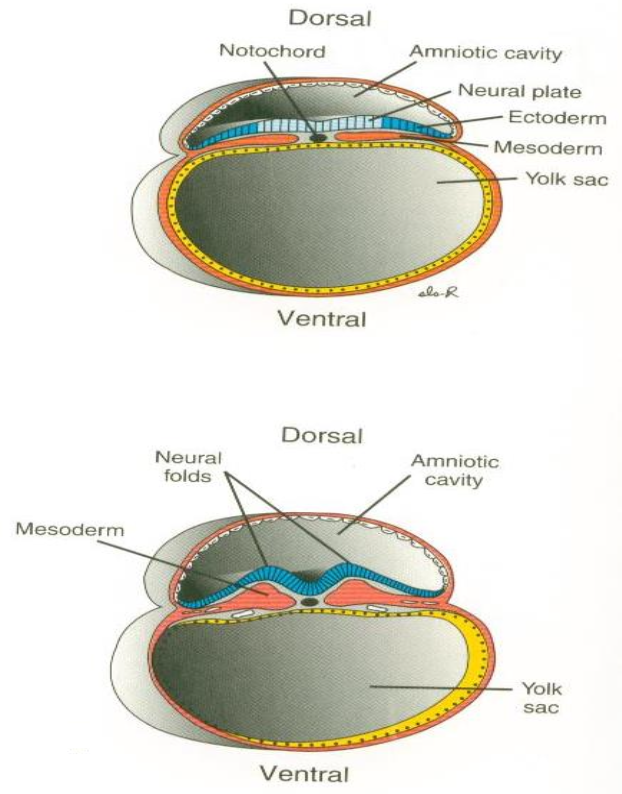
Notochord
Comes from primitive node
Midline rod derived from notochordal process; defines the primitive axis and induces neural plate; later nucleus pulposus.
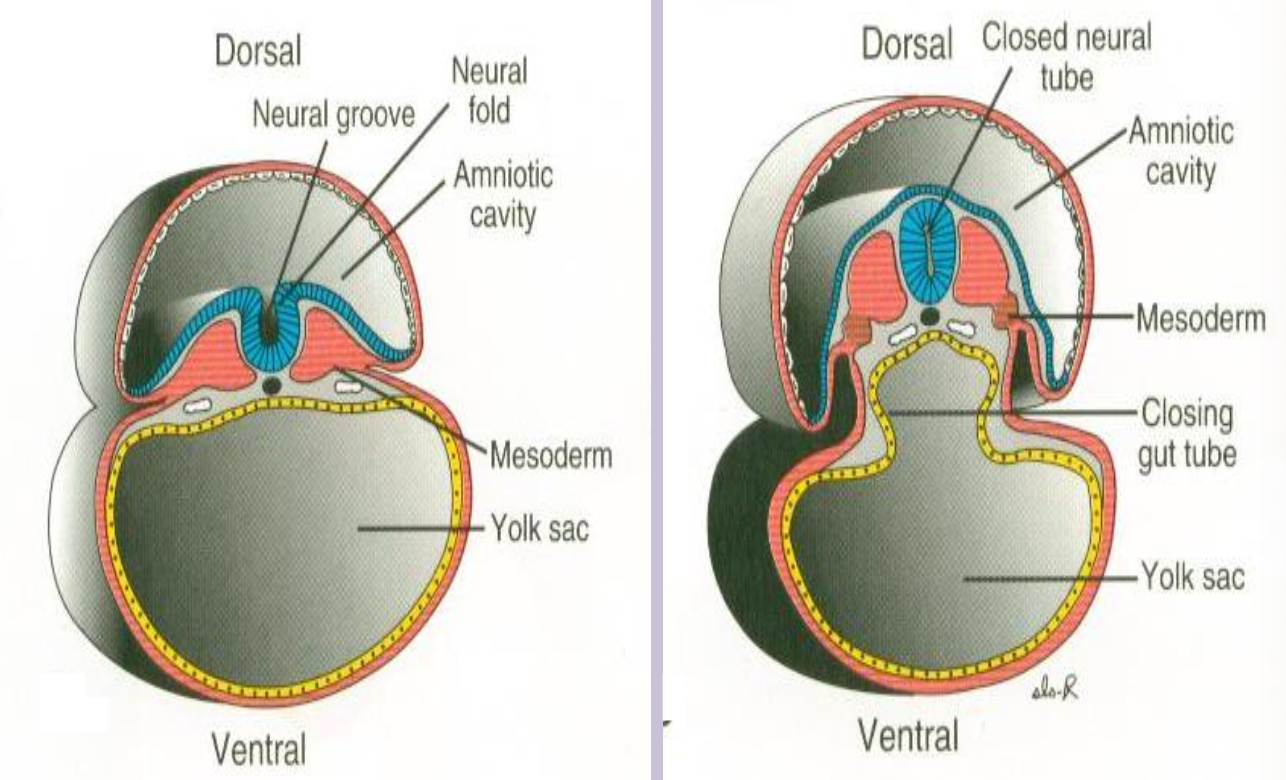
Neurulation
Formation and closure of the neural tube from neuroectoderm (weeks 3–4).
Neural tube —> brain and spinal cord
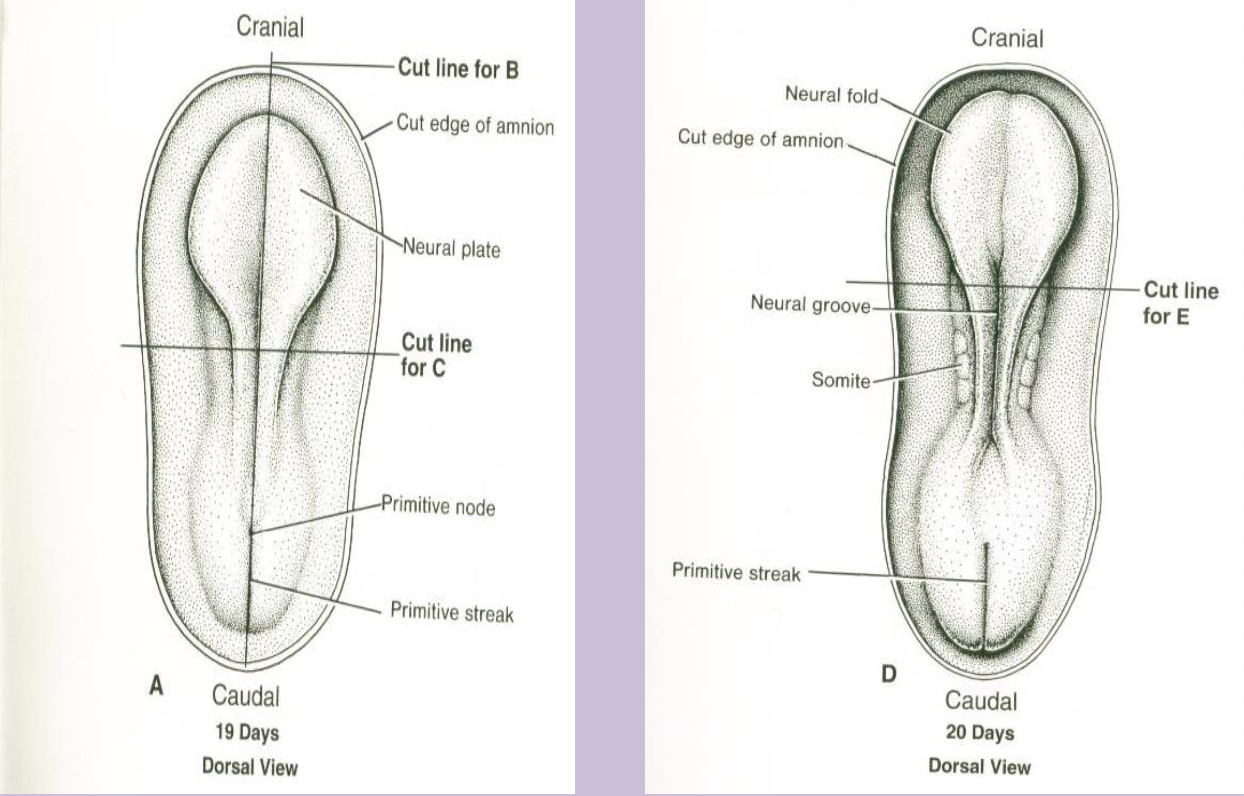
Neural plate
Thickened ectoderm induced by the notochord that folds into the neural tube.
Anterior neuropore
Cranial opening of the neural tube that closes ~day 25; failure causes anencephaly.
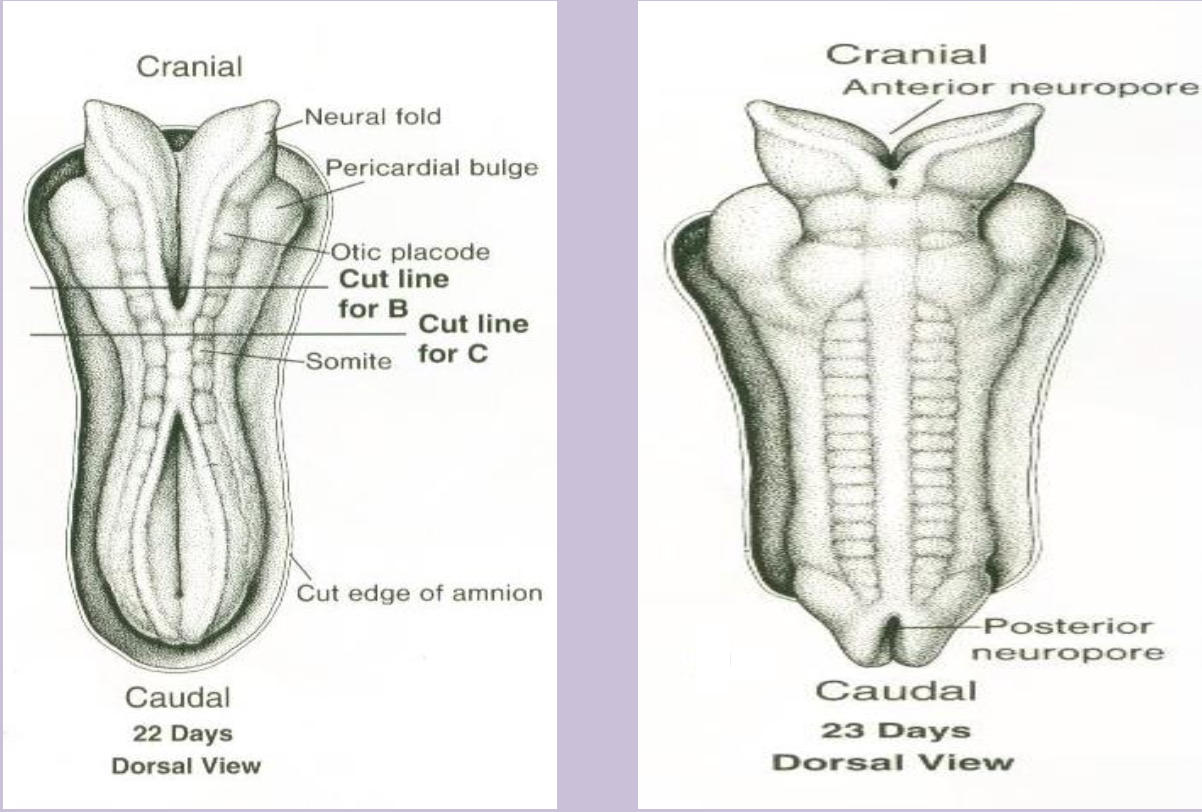
Posterior neuropore
Caudal opening of the neural tube that closes ~day 27; failure leads to spina bifida/meningomyelocele.
Anencephaly
Severe neural-tube defect due to failure of anterior neuropore closure, resulting in absence of much of the brain and skull.
Meningomyelocele
Form of spina bifida where spinal cord and meninges protrude through a vertebral defect.
Paraxial mesoderm
Comes from Intraembryonic Mesoderm
Mesoderm flanking the neural tube that segments into somites.
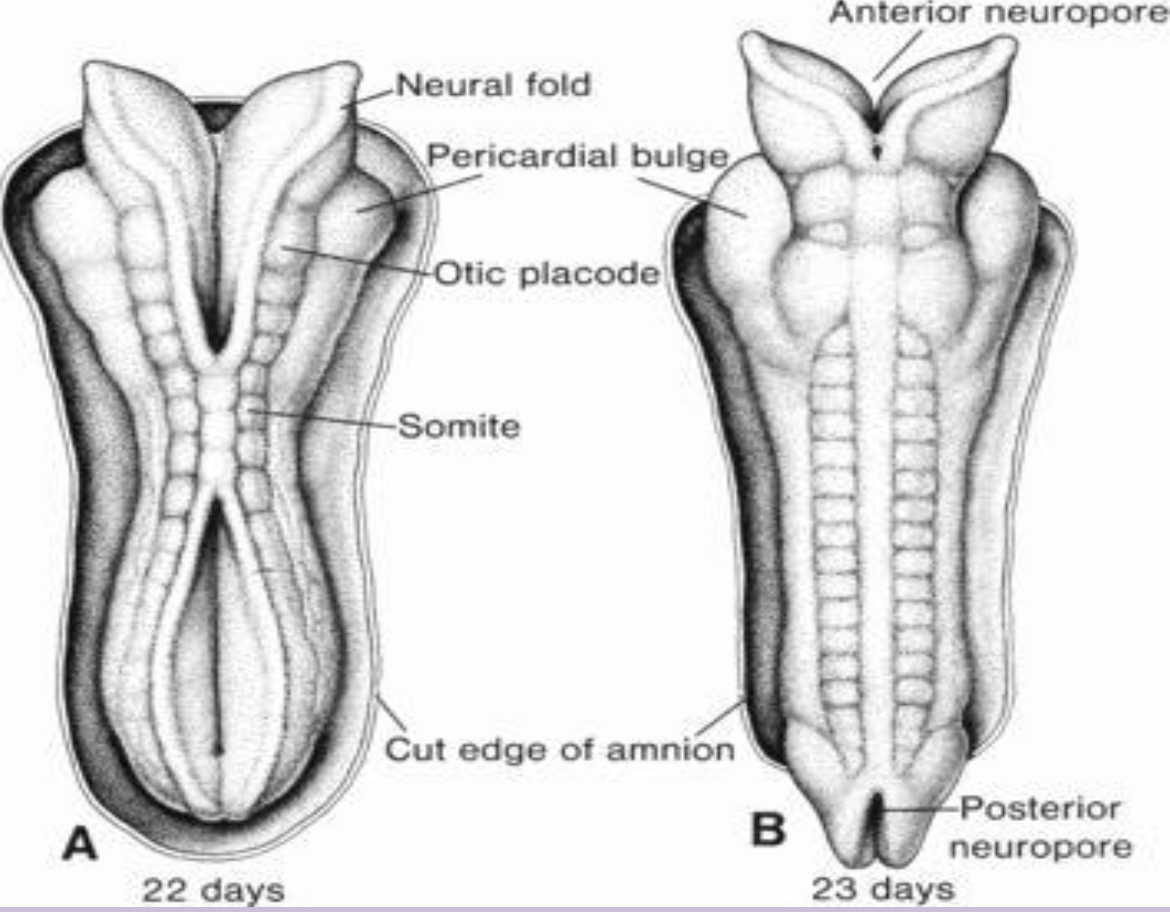
Somite
Paired block of paraxial mesoderm giving rise to sclerotome, myotome, and dermatome (most axial skeleton and musculature and skin dermis)
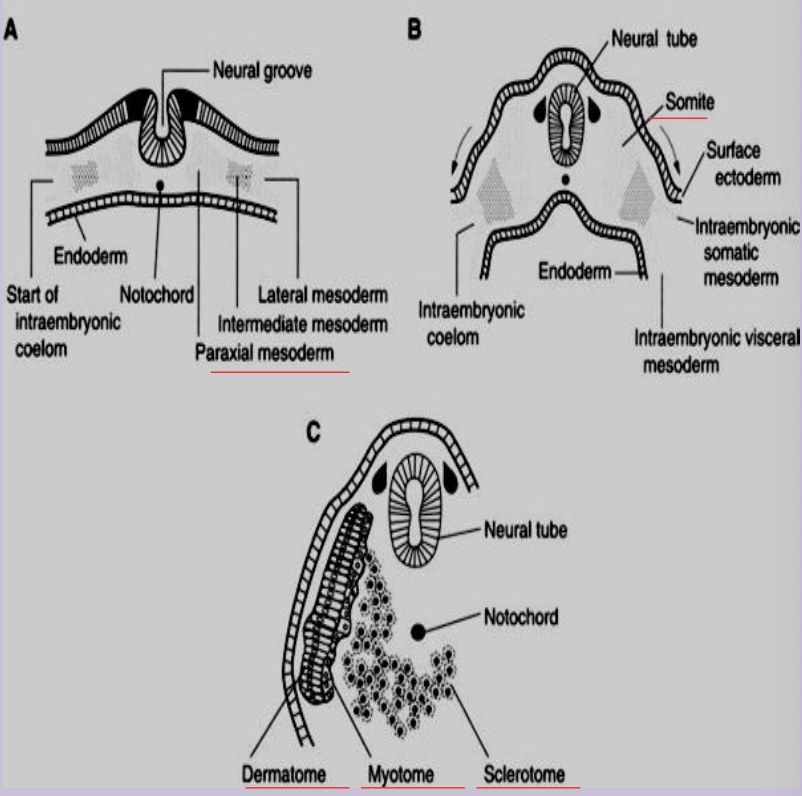
Sclerotome
Medial part of a somite forming vertebrae and ribs and skin and cartilgae
Myotome
Portion of a somite that forms skeletal muscle of body wall and limbs.
Dermatome
Lateral somite region that forms dermis of skin.
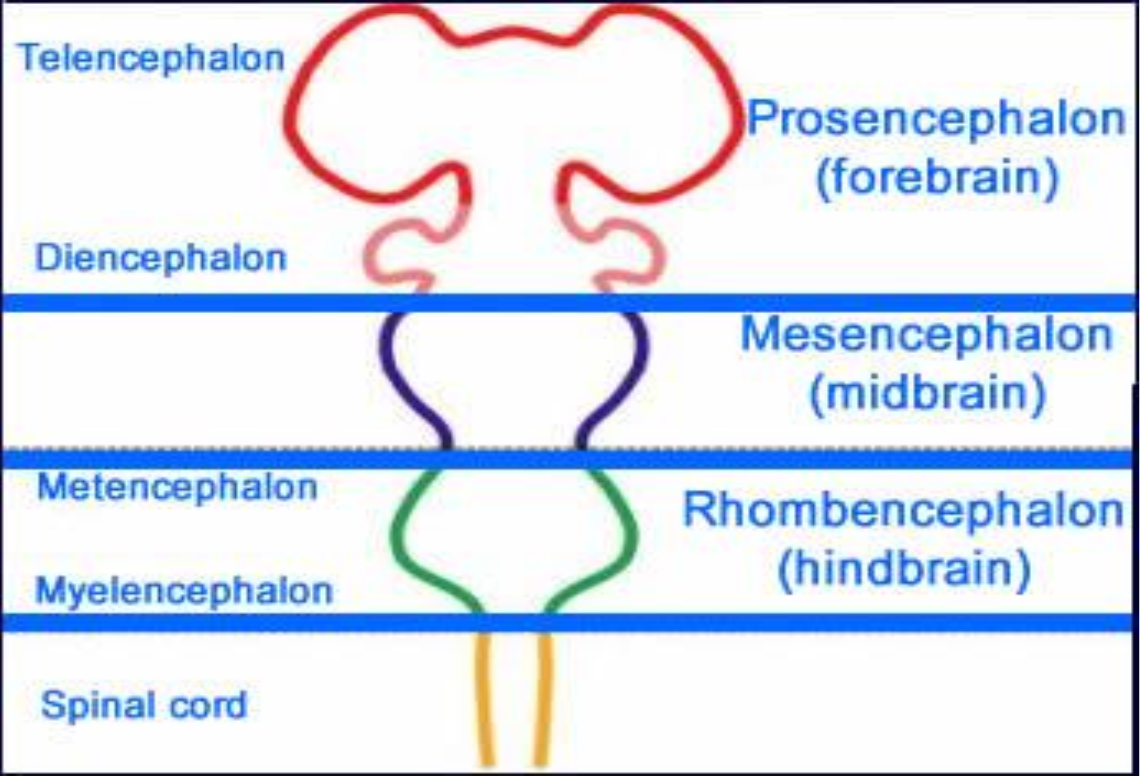
Prosencephalon
Embryonic forebrain that subdivides into telencephalon and diencephalon.
Mesencephalon
Midbrain region of the neural tube; remains undivided.
Rhombencephalon
Hindbrain that splits into metencephalon (pons, cerebellum) and myelencephalon (medulla).
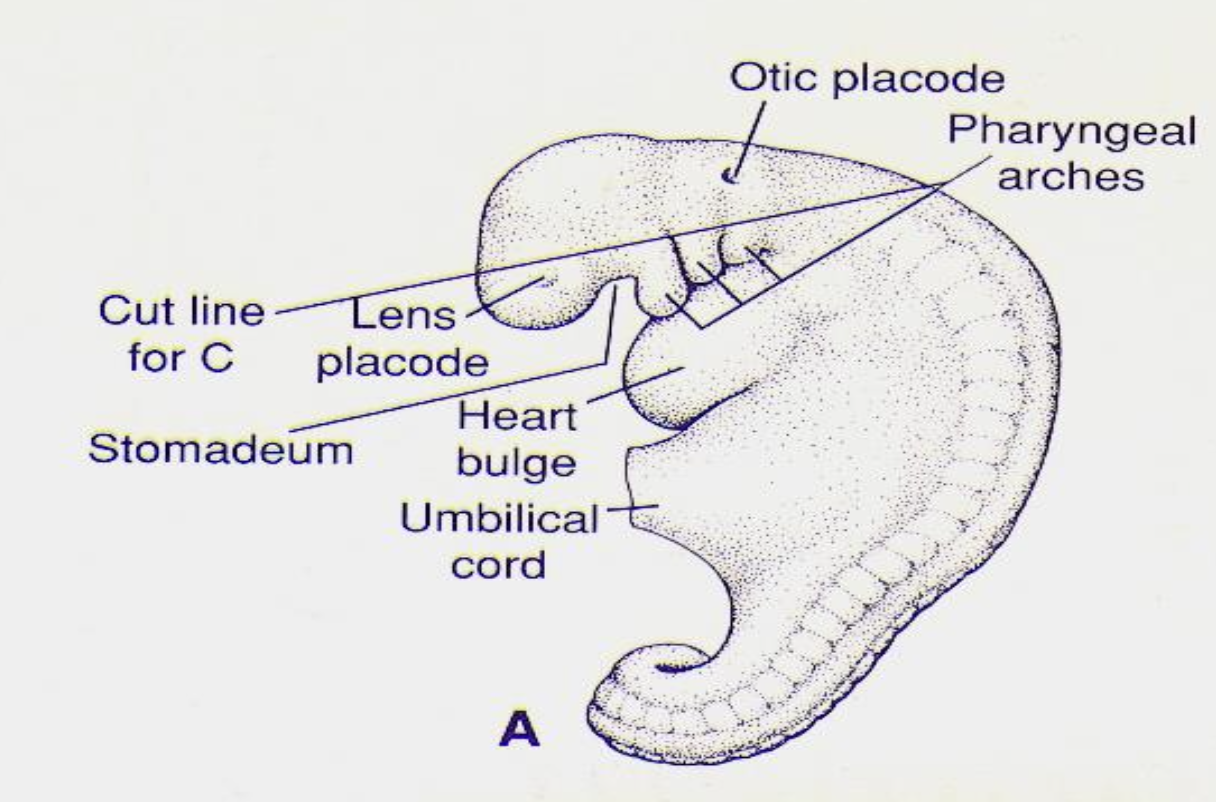
Pharyngeal arches
Series of 6 mesodermal/ectomesenchymal arches in week 4 that form head and neck structures.
each have their own CN innervation and blood supply
separated by clefts externally and 5 pouches internally
Mandibular arch (First arch)
First pharyngeal arch forming maxilla, mandible, malleus, incus, and muscles of mastication and meckel’s cartilage ear bones maleus and incus
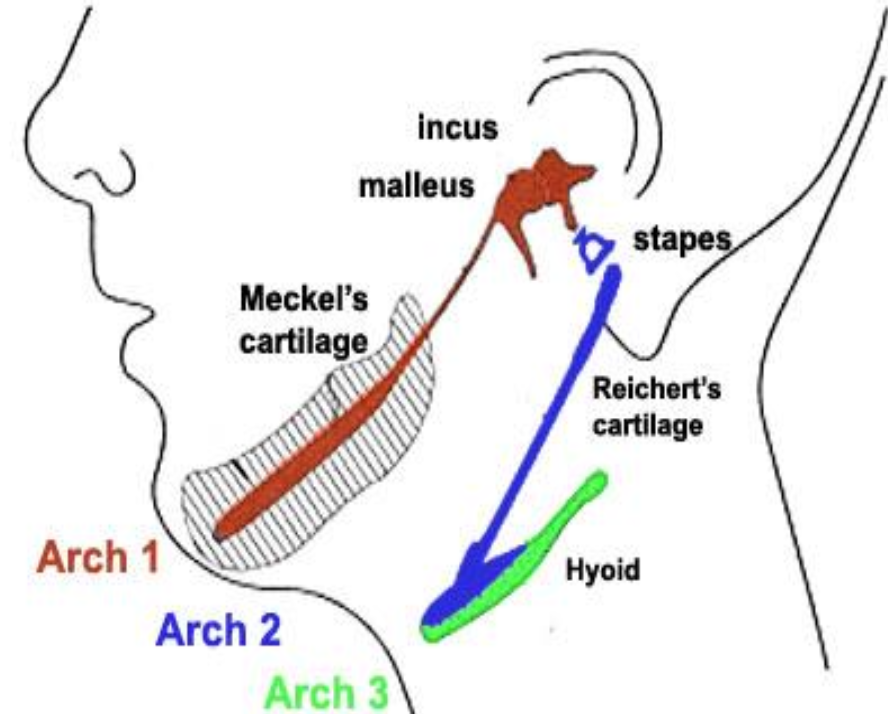
Hyoid arch (Second arch)
Second arch forming stapes, styloid process, lesser horn of hyoid, muscles of facial expression, Reichert’s cartilage, and muslces of facial expression
Meckel’s cartilage
Cartilaginous bar in first arch that contributes to malleus, incus, and template for mandible.
Reichert’s cartilage
Cartilage of second arch giving rise to stapes, styloid process, and part of hyoid bone.
Third pharyngeal arch
Forms greater horn of hyoid bone and portion of thymus; supplied by CN IX.
Fourth pharyngeal arch
Contributes to thyroid and epiglottic cartilages and muscles of soft palate; supplied by superior laryngeal branch of CN X.
Fifth Arch
Only briefly exists - no human structures results —> No 5th arch in humans
Sixth pharyngeal arch
Forms intrinsic laryngeal muscles and remaining laryngeal cartilages; supplied by recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Pharyngeal pouches
Endoderm-lined outpocketings between arches that form internal neck organs.
First pharyngeal pouch
Forms auditory meatus,(Eustachian) tube, tympanic cavity, and contributes to tympanic membrane.
Second pharyngeal pouch
Gives rise to palatine tonsils and tonsillar fossa.
Third pharyngeal pouch
Produces thymus (ventral) and inferior parathyroid glands (dorsal).
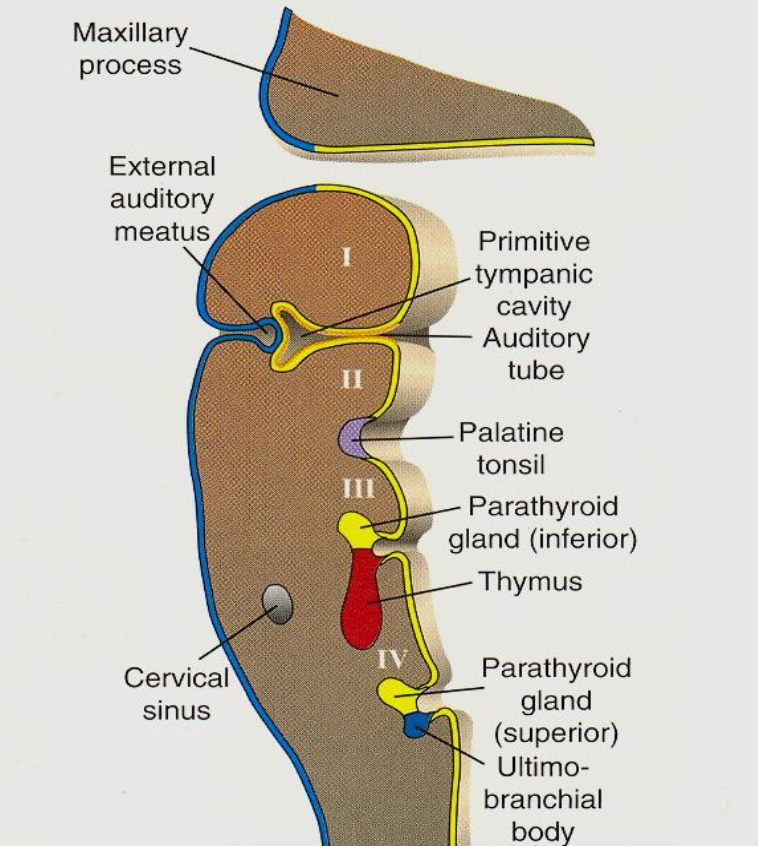
Fourth pharyngeal pouch
Forms superior parathyroid glands.
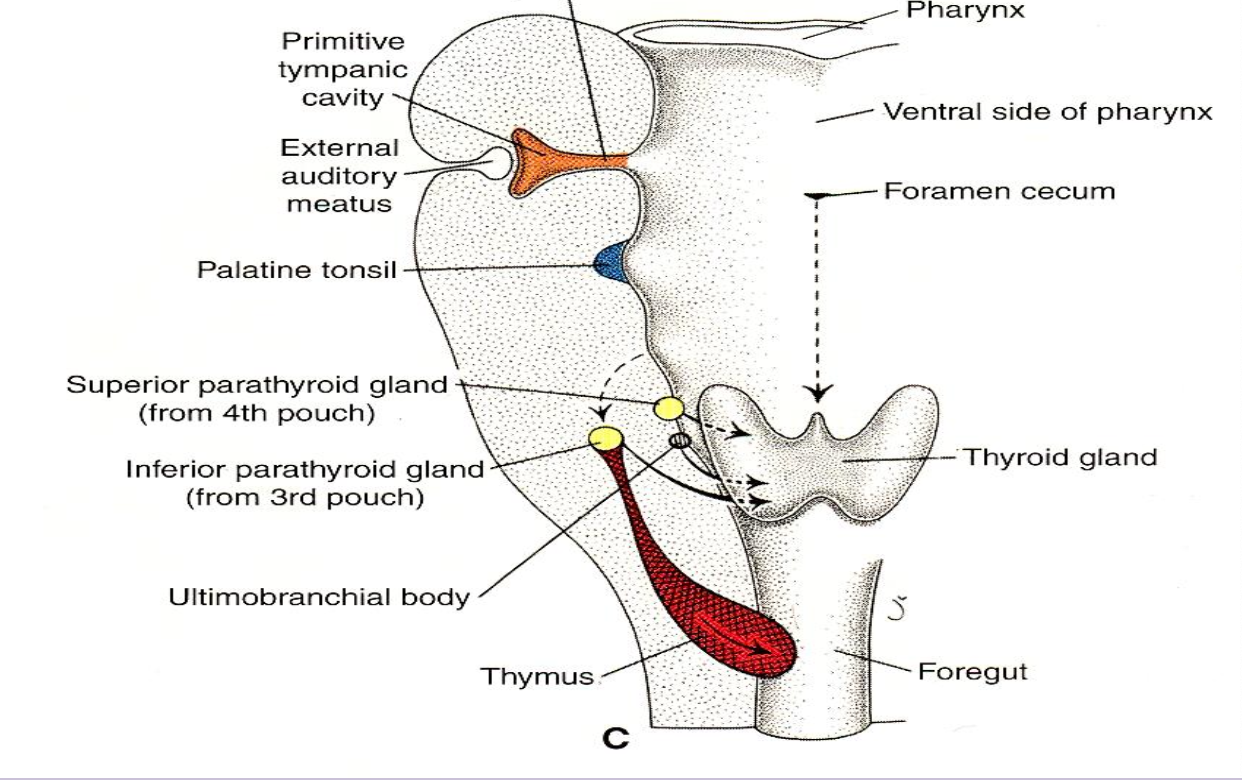
Fifth pharyngeal pouch
Part of fourth pouch
Forms ultimobranchial body which incorporates into thyroid as parafollicular cells - They secrete calcitonin
Ultimobranchial body
Derivative of caudal fourth pouch that becomes thyroid parafollicular (C) cells producing calcitonin.
Fontanelle
Fibrous membrane-covered gap between skull bones in newborns; six exist, largest is anterior fontanelle.
Metopic (frontal) suture
Suture between the two frontal bones that may persist into adulthood.
Sagittal suture
Midline suture between parietal bones.
Coronal suture
Suture between frontal and parietal bones.
Lambdoid suture
Suture between parietal bones and occipital bone.
Squamous (temporal) suture
Suture between temporal and parietal bones.
Ectoderm derivatives
Gives rise to organs and structures that contact outside world, CNS, PNS, sensory epithelium of ear/eye/nose, epidermis, hair, nails, glands, enamel of teeth.
Mesoderm derivatives
Forms muscle, bone, cartilage, dermis, cardiovascular system, blood cells, kidneys, gonads, spleen, adrenal cortex.
Endoderm derivatives
Produces epithelial lining of GI and respiratory tracts, bladder, auditory tube, and parenchyma of thyroid, liver, pancreas.
Anterior fontanelle
Largest fontanelle at junction of sagittal, coronal, and metopic sutures; closes ~2 years.
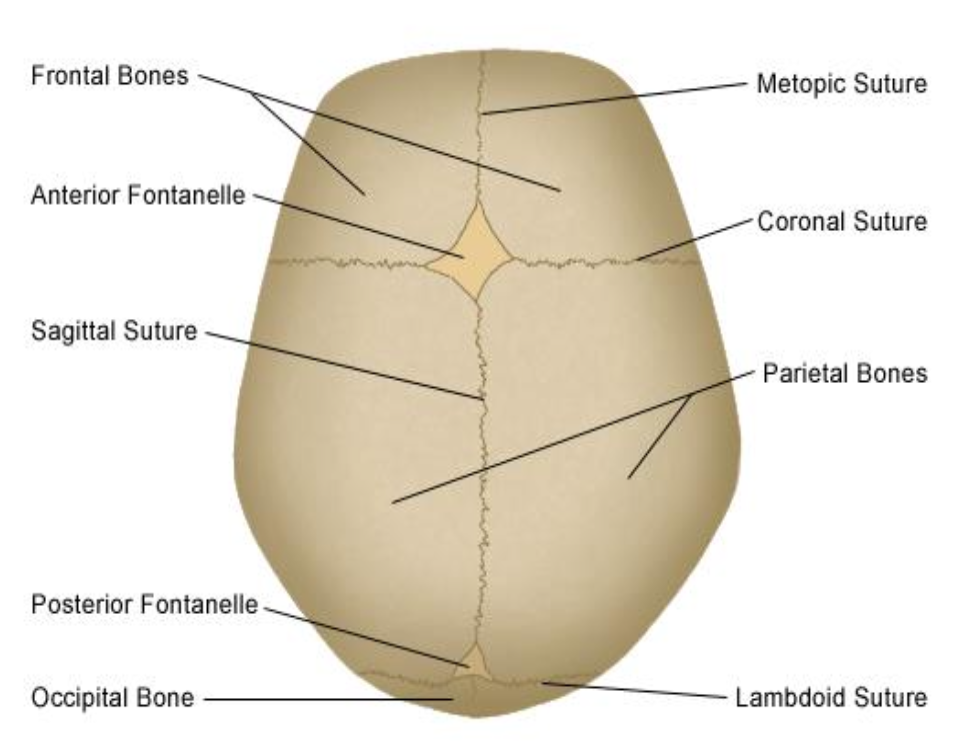
Posterior fontanelle
Small fontanelle at junction of sagittal and lambdoid sutures; closes ~6 months.
(Also have 2 sphenoid - 6 months close and 2 mastoid fontanelles - 2 years closes)
Primary villus
Early chorionic villus consisting solely of cytotrophoblast covered by syncytiotrophoblast.