Unit 10- Hydronephrosis (Elie)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is Hydronephrosis of Urinary Tract Obstruction (UTO)
Dilation of pelvocalyceal system
Interconnected fluid-filled calyces
With UTO what does progressive obstruction do?
Compresses renal parenchyma
Compromising renal function
•When renal compromise is suspected, a renal US performed to R/O obstruction of what?
Collecting System
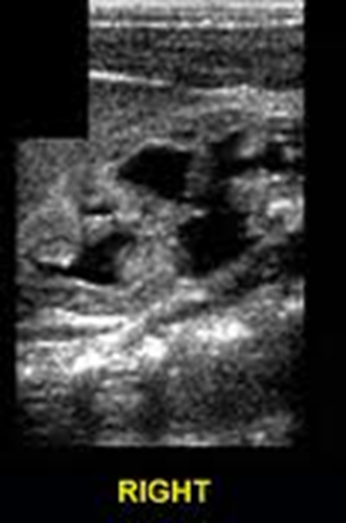
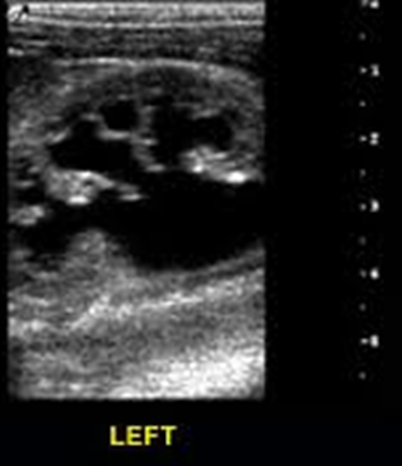
What is this image showing?
Hydronephrosis
Urinary Tract Obstruction (UTO)
What is Grade 1 of Hydronephrosis?
Small fluid-filled separation of renal pelvis “splaying”
What is Grade 2 of Hydronephrosis?
Extension into some but not all major & minor calyces “bear-claw”
What is Grade 3 of Hydronephrosis?
Complete pelvocaliectasis, echogenic line separating collecting system from renal parenchyma
What is Grade 4 of Hydronephrosis?
Massive dilation of collecting system
Loss of renal parenchyma
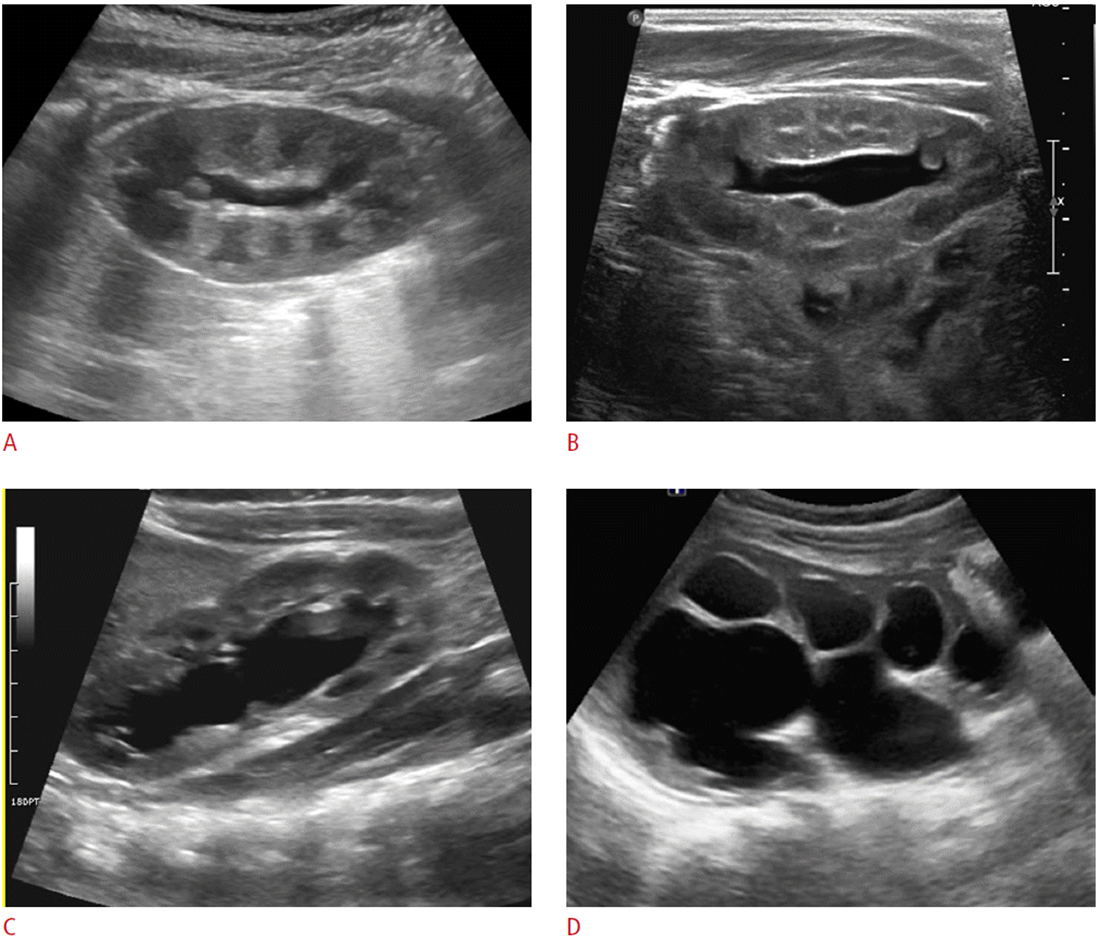
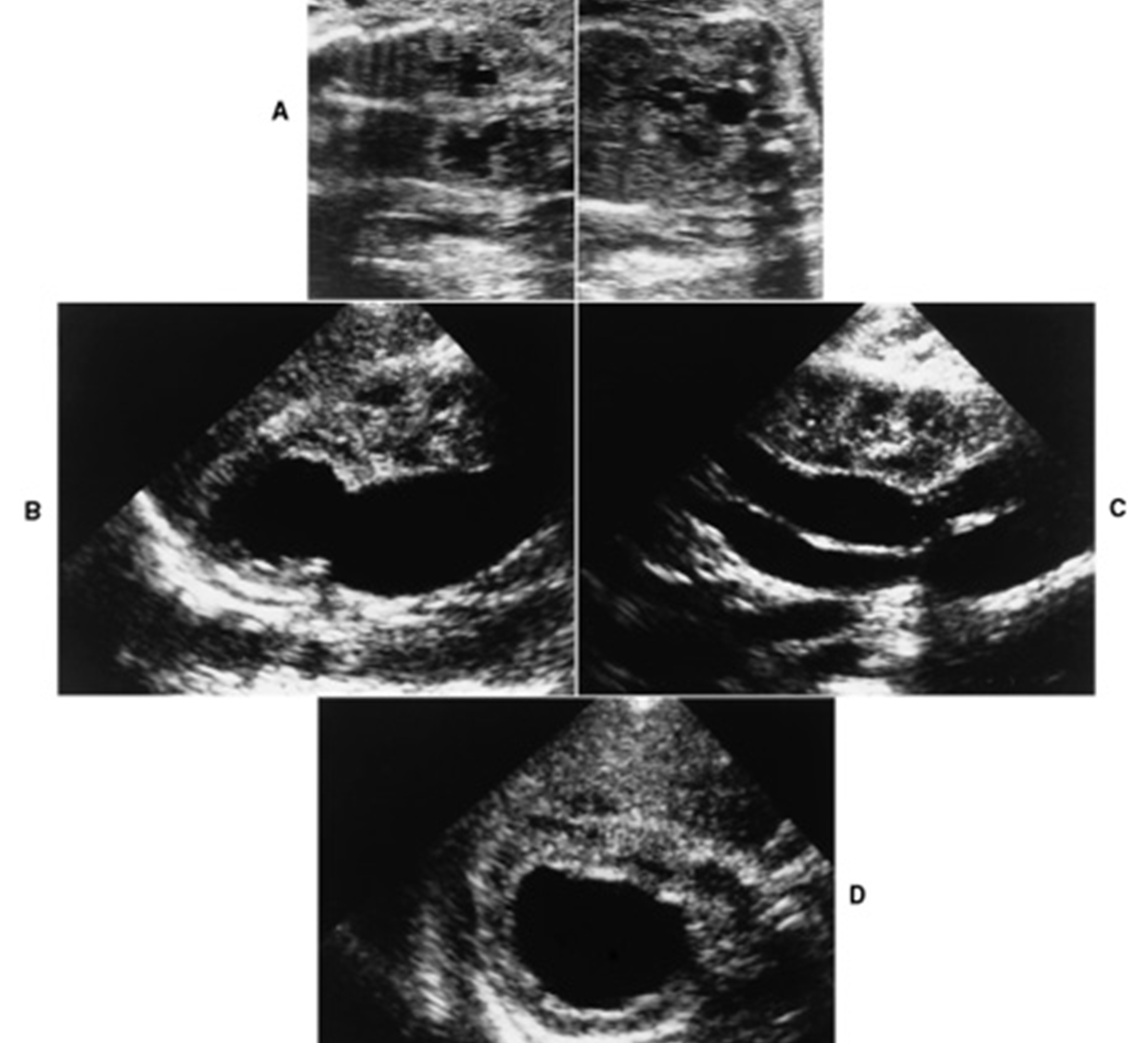
What are these images showing?
A- Grade 1
B- Grade 2
C- Grade 3
D- Grade 4
Grade 1 Hydronephrosis is also called what?
Mild Hydronephrosis
Splaying of calyces indicates hydronephrosis rather than an ________ _____
Extrarenal Pelvis
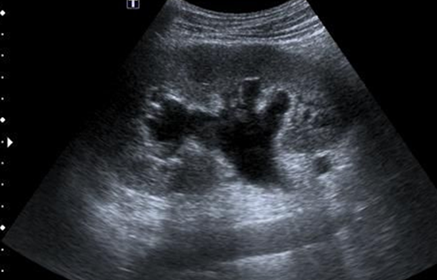
What grade of hydronephrosis is this?
Grade 2
What is this image showing?
Hydronephrosis Pelvis- Ureter
What are the US findings for Hydronephrosis?
Dilation of fluid filled renal pelvis & calyces
Fluid-filled areas conform anatomically to calyces & renal pelvis
With hydronephrosis where should scan?
Document level of obstruction
Mass or stone identified
While scanning for hydronephrosis, if the bladder is full, the patient should void and what should happen for the rest of the scan?
Kidneys are rescanned to R/O transient hydronephrosis vs obstruction
What does a sonographer need to differentiate between when scanning?
Hydronephrosis, extrarenal pelvis, and peri/parapelvic cysts
What must be documented when a sonographer differentiates between hydronephrosis, extrarenal pelvis & peri/parapelvic cysts?
Connection with calyces must be documented
Evaluation of ureters & bladder must be included
What are the clinical findings for Obstructive Hydronephrosis?
Renal insufficiency
Decreased urine output
HTN
What are the findings for an Acute Obstruction of hydronephrosis?
Intrarenal RI increased for 48 – 72 hours
> 0.7 then returns to normal
Compare with contralateral side
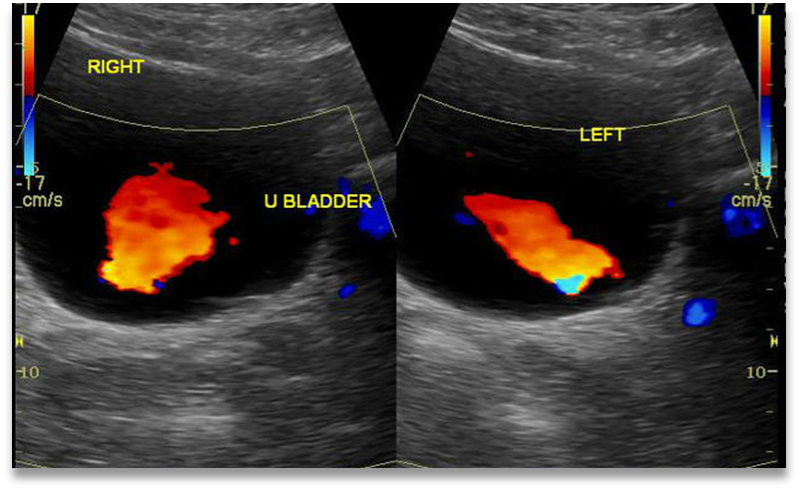
What is this image showing?
Normal Ureteral Jets
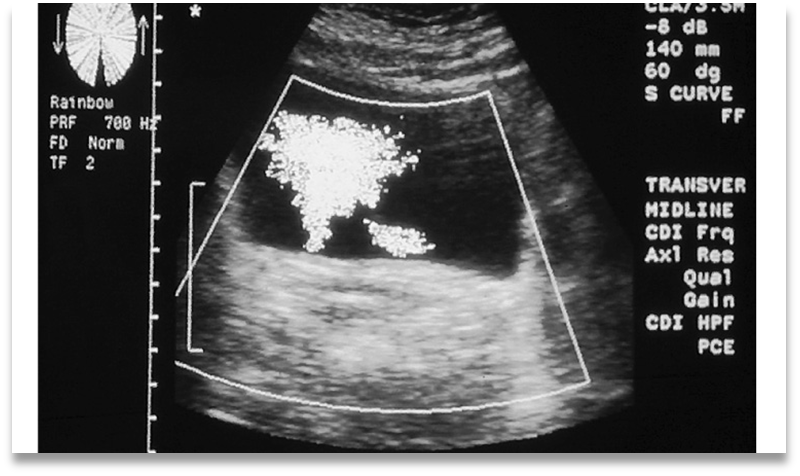
What is this image showing?
Partially obstructed left ureter with decreased flow
What may cause Nonobstructive Hydronephrosis?
Reflux
Infection
Polyuria
Overhydration
Post obstruction atrophy
Pregnancy- usually on right
Distended bladder =
Transient hydronephrosis
US findings for Nonobstructive Hydronephrosis:
Ureteral jets indicate non-obstructive hydronephrosis
Use color Doppler for jets
What can Localized Hydronephrosis be secondary to?
Strictures
Calculi
Focal masses
Duplex collecting system with ectopic insertion of ureter
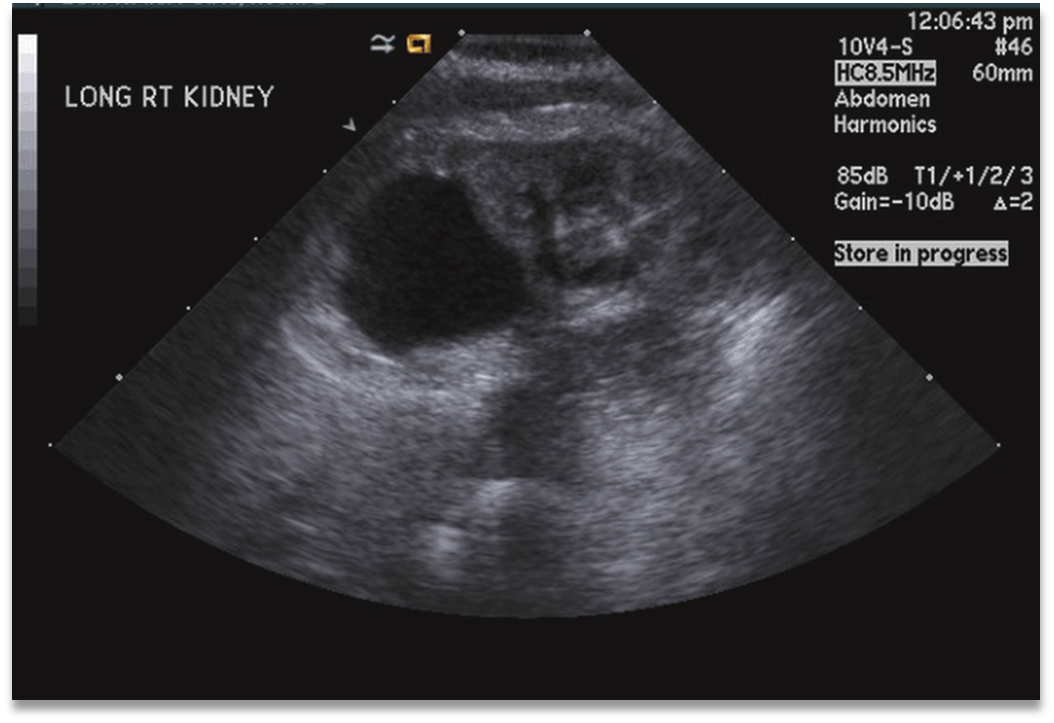
What is this image demonstrating?
Localized Hydronephrosis
What are the similar appearing conditions for False-Positive Hydronephrosis?
Extrarenal pelvis
Parapelvic cysts
Reflux
Multicystic kidney
Transient diuresis
Congenital megacalyces
Papillary necrosis
Renal artery aneurysm – use color Doppler
Arteriovenous malformation – use color Doppler
Duplex collecting system
What are the False- Negative Hydronephrosis?
•Distinction of renal pelvis from dilated calyces
•Polycystic Kidney Disease
•Transient obstructive process
Once obstruction has been ruled out for False Negative Hydronephrosis, what should be considered next?
Renal medical disease as cause of renal dysfunction
What is Pseudohydronephrosis from and what should the sonographer do?
From over distended urinary bladder
Have patient urinate, then rescan to check for drainage & change
Document pre & post void
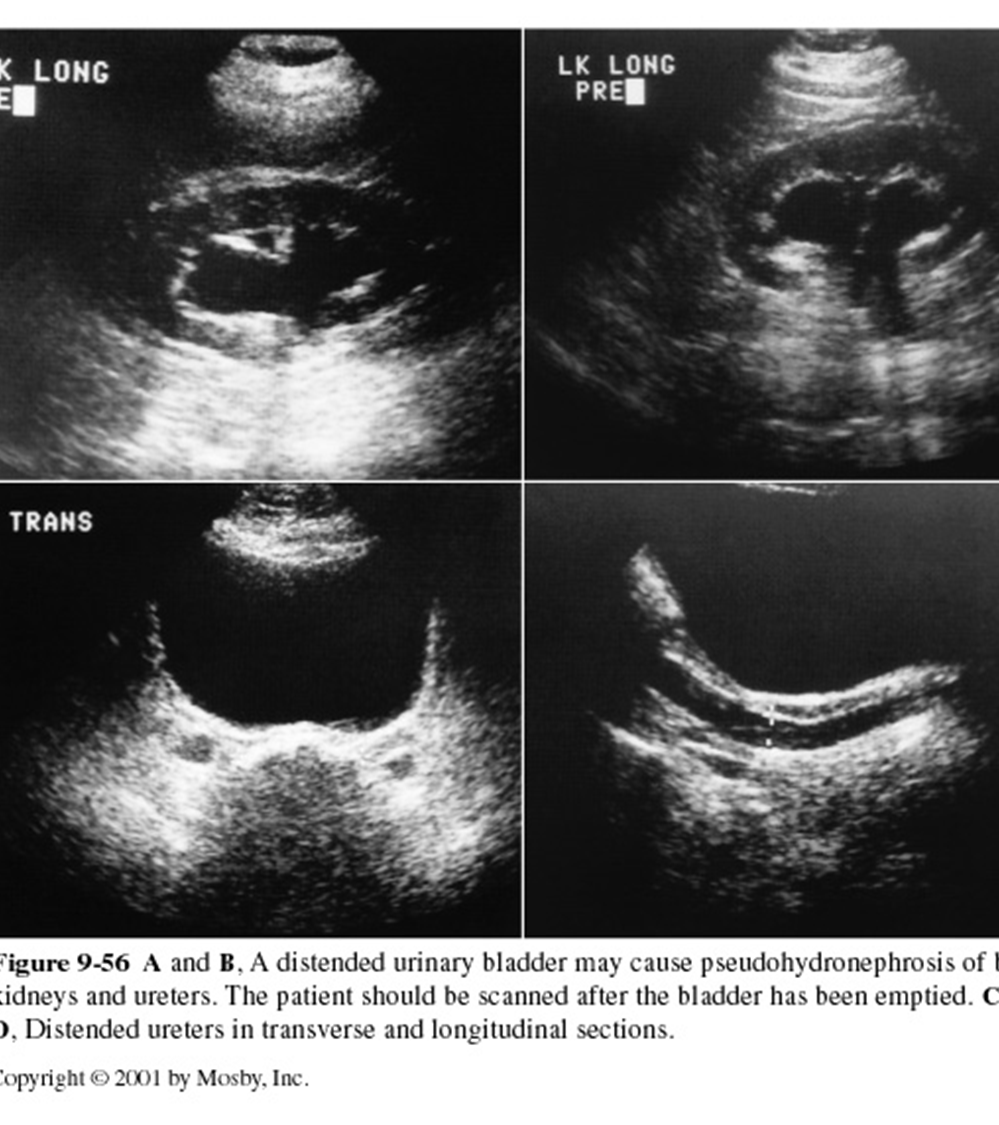
What are these images showing?
Pseudohydronephrosis