Genetic Engineering
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are restriction endonucleases?
Restriction enzymes
They are enzymes used to cut the desired gene from DNA.
What can the desired gene also be called?
cDNA
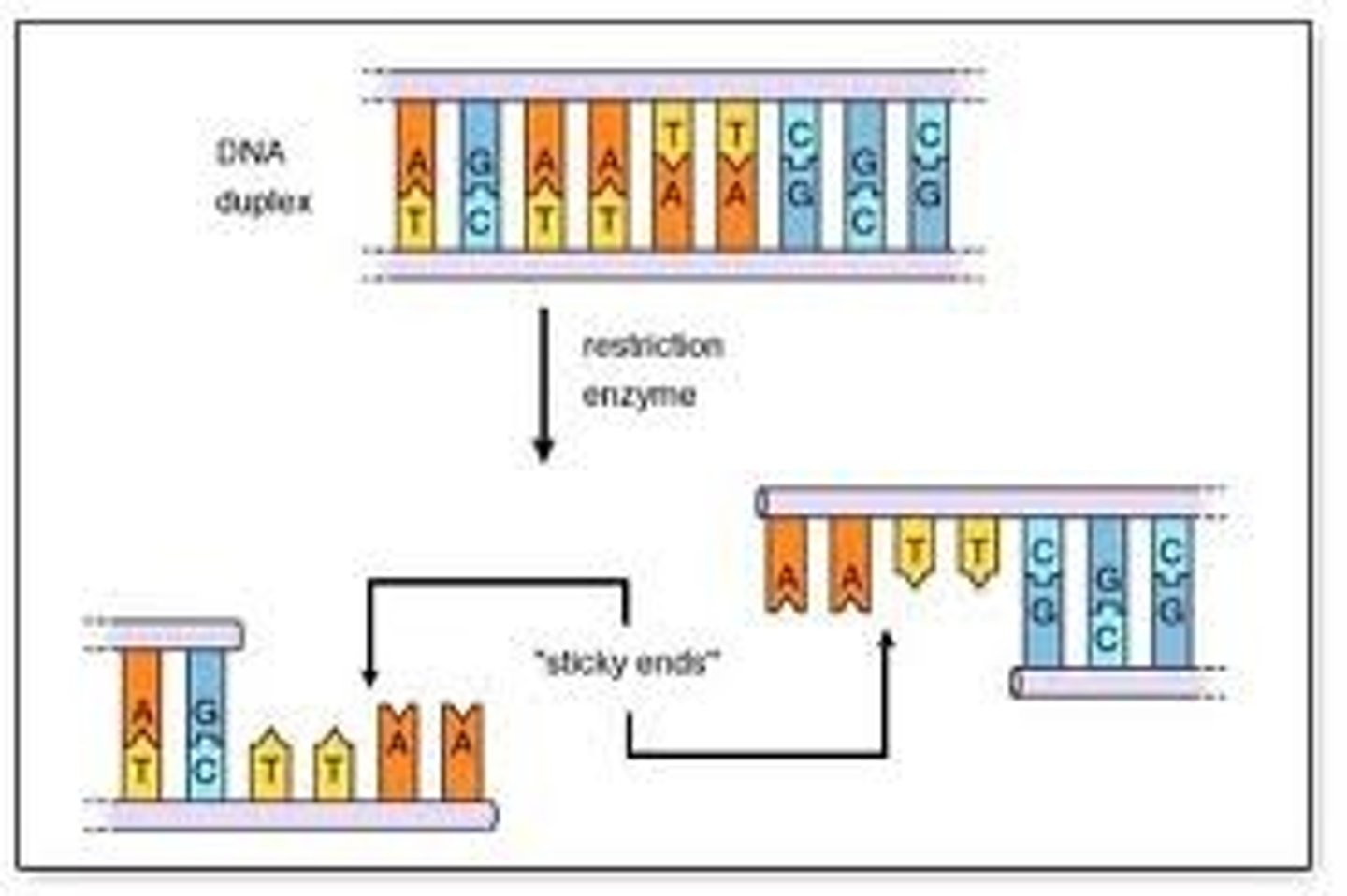
1) Isolating the desired gene
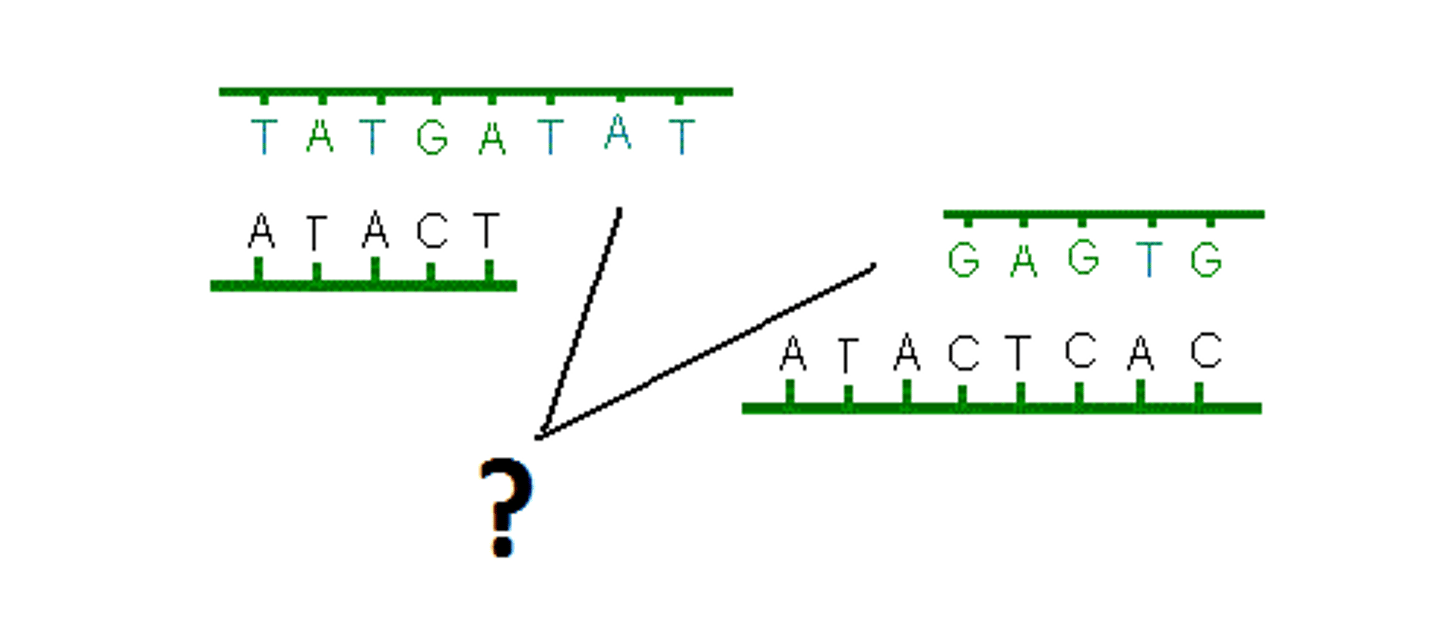
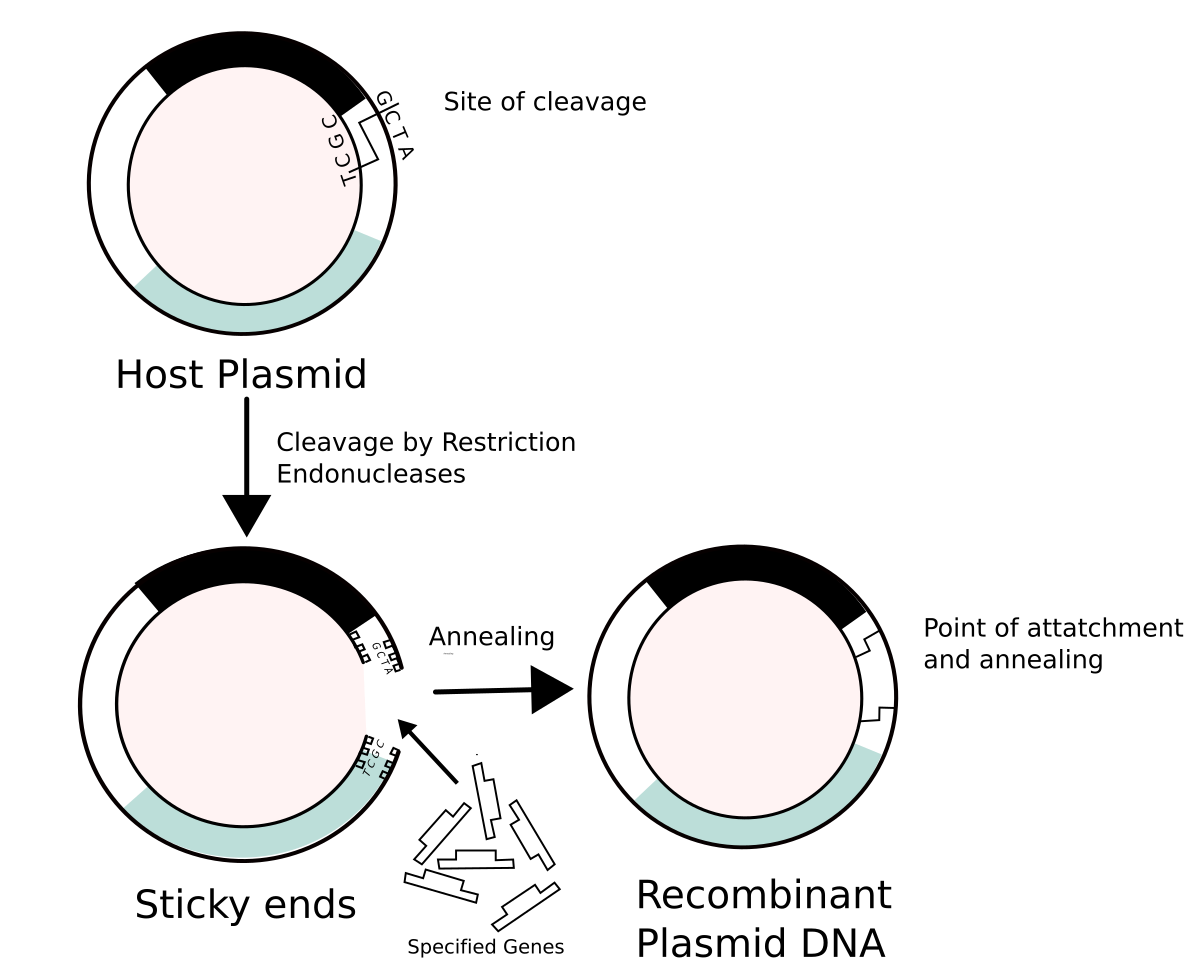
Restriction endonucleases are used to cut the desired gene from DNA. This creates sticky ends, which makes it easier for the gene to be inserted elsewhere.
What is a plasmid in this process?
It is a circular piece of DNA used as a vector
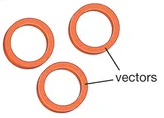
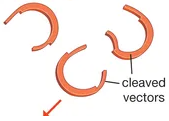
2) Plasmid
A plasmid is cut using the same restriction enzymes.
This produces complementary sticky ends that match the gene.
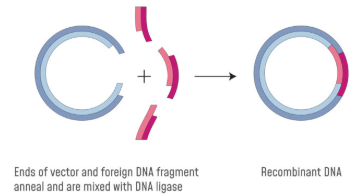
3) Recombinant DNA
The desired gene (cDNA) is inserted into the plasmid.
The complementary base pairs anneals using the enzyme DNA ligase.
It forms recombinant DNA.
4) Marker
A marker is often included with the desired gene. This helps identify which cells have successfully taken up the new DNA.
Give examples of a marker
Fluorescent marker
Gene for antibiotic resistance
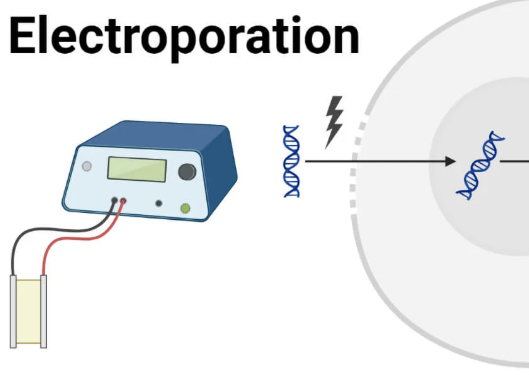
5) Electroporation
The recombinant DNA is inserted into the host cell using electroporation.
An electric shock makes the cell surface membrane temporarily porous, so the plasmids can enter the host cell.
6)
The host cell divides by mitosis, reproducing the recombinant DNA too and producing the desired protein.
What’s electrofusion?
Electrofusion combines 2 different cells.
1 cell with the desired gene, 1 host cell.
The cells are placed next to each other and given an electric pulse.
The electric shock will cause their membrane to temporarily break, allowing them to fuse into 1 hybrid cell.
The new hybrid cell contains genetic material from both original cells.
This hybrid can be grown into a GM organism.
7) Testing for marker
Finally, scientists test the cells to check if the gene was successfully taken up.
If a fluorescent marker was used, they check for fluorescence
If an antibiotic resistance marker was used, they grow the cells in antibiotics. Only the ones with the gene will survive.
Alternative methods to extract the desired gene
Using reverse transcriptase
Reverse transcriptase
You start with the mRNA (rather than the desired DNA) and you reverse it using reverse transcriptase to return to the cDNA (complementary DNA).
cDNA can now be inserted into a plasmid just like a normal gene.
What is recombinant DNA?
DNA combined from 2 sources
Vectors for Plants
Plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Vectors for Bacteria
BAC (Bacteria artificial chromosome), virus
Vectors for Animals
BAC, plasmids, virus