Bones of the LE & Muscles
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
The functions of the lower extremity include supporting the weight of the body and producing _______ .
locomotion
The hip bones are formed by the __________, __________ , and __________.
ilium, ischium, pubis
The ________ is the meeting point of the three hip bones and includes a structure called __________.
acetabulum, tridirate ligament
The __________ is an opening for nerves and blood vessels created by the ________ and _______.
obturator foramen, ischium, pubis
The pubis is divided into a body, a __________ & __________ ramus
superior, inferior
__________ is a deformity where the angle of inclination is less than __________ degrees.
Coxa vara, 120
__________ is characterized by an angle of inclination usually above __________ degrees.
Coxa valga, 135
The ___ is located below the ASIS and aligns with the level of __.
AIIS, L4
The PIIS is located below the ___ and is at the level of ___
PSIS, S2
The ___________ ________ notch is located above and behind the acetabulum.
Greater sciatic
True or False: Anesthesia is typically administered at L4 to avoid the spinal cord.
True
True or False: When anesthesia is administered at L1 it will not cause paralysis.
False
The ischial tuberosity is the site for attachment of which muscle group?
Hamstring muscles
The ___, felt when sitting upright, is also known as the "sit bone."
Ischial tuberosity
What projects from the posterior border of the ischium between the greater and lesser sciatic notches?
Ischial spine
The ischial spine is used as a measurement site for what?
Pelvic opening
The greater and lesser sciatic notches become foramina when _______ & _______ ligaments are attached.
Sacrospinous, Sacrotuberous
The ___ of the pubis forms the upper border of its body and ends at the pubic tubercle.
Crest
The pubic _______ is where the bodies of both pubic bones meet.
symphysis
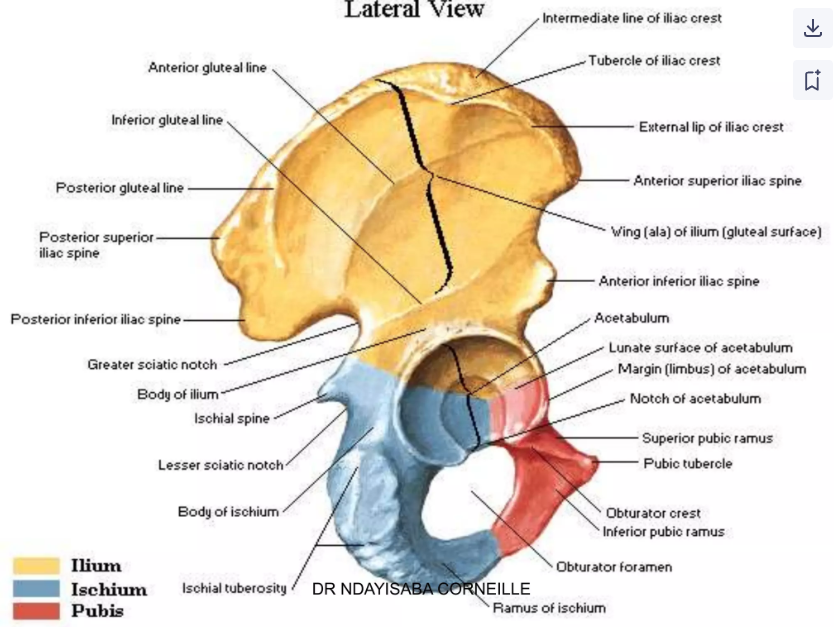
The _______ ramus of the pubis joins the _______ and _______ at the acetabulum.
Superior, ilium, ischium
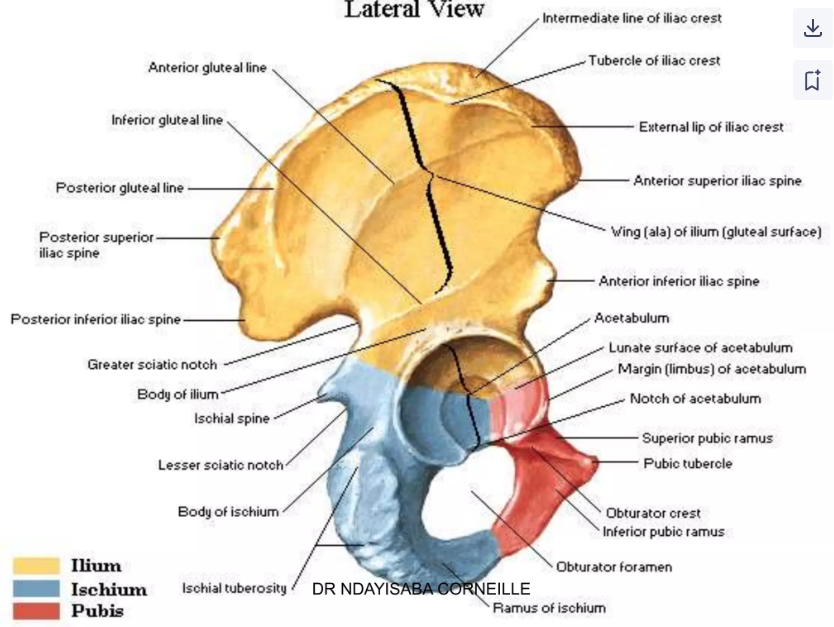
The _______ ramus of the pubis joins the ________ ________ below the _______ _________.
inferior, ischial ramus, obturator foramen
What is the depression on the outer surface of the hip bone where the three hip bones meet?
Acetabulum
The acetabulum is made up of more than 2/5 ____, less than 2/5 ____, and the remaining 1/5 by the ____.
Ischium, ilium, pubis
The lower boundary of the acetabulum is formed by the _____, upper boundary by ______ and midline by _____.
Ischium, ilium, pubis
The ___ is a circular, non-articular depression found at the inferior margin of the acetabulum.
Acetabular notch
The ___ is horseshoe-shaped and serves as the articulation site for the femoral head.
Acetabular fossa
The sacrum _________ (position) articulates with the 2 iliac bones at the __________ joints.
Laterally, sacroillac
How many vertebrae make up the sacrum?
5
The coccygeal cornua are remnants of the ___ and ___ processes.
Pedicles, superior articular
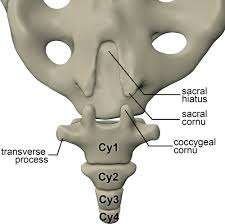
The coccygeal cornua articulate with the ___ cornua.
Sacral
True or False: All coccygeal vertebrae have transverse processes.
False
True or False: The first coccygeal vertebra has a rudimentary transverse process.
True
The _____ border or base of the sacrum articulates with __? (Level of vertebra)
upper, L5
The inferior border of the sacrum articulates with the _____
Coccyx
The coccyx consists of __ vertebrae fused…
4
The sacrum articulates laterally with the iliac bones at the ___.
Sacroiliac joints
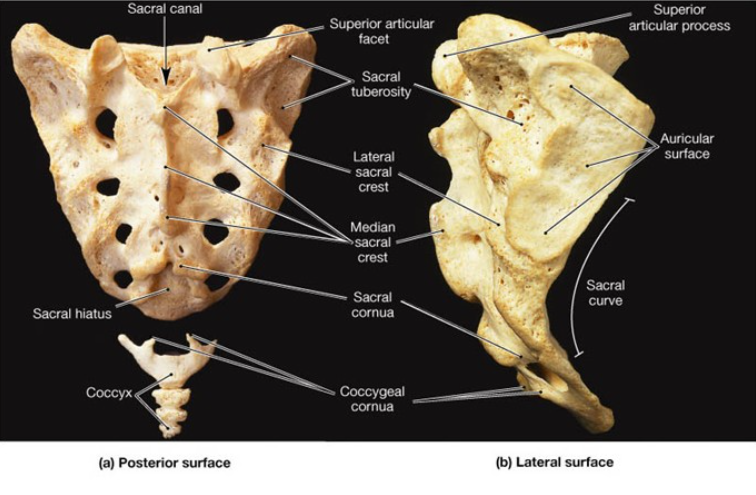
The ___ forms the anterior and upper margin of the sacrum, marking the _________ _______ _______.
Sacral promontory, posterior pelvic inlet
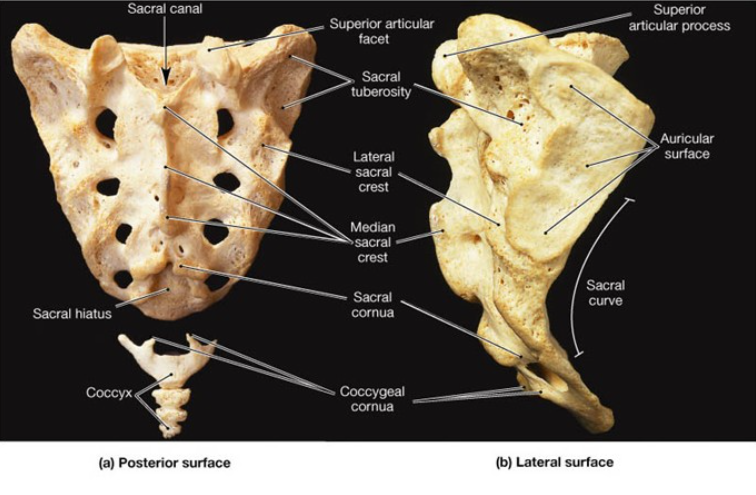
What level is the sacral promontory located at?…
S1
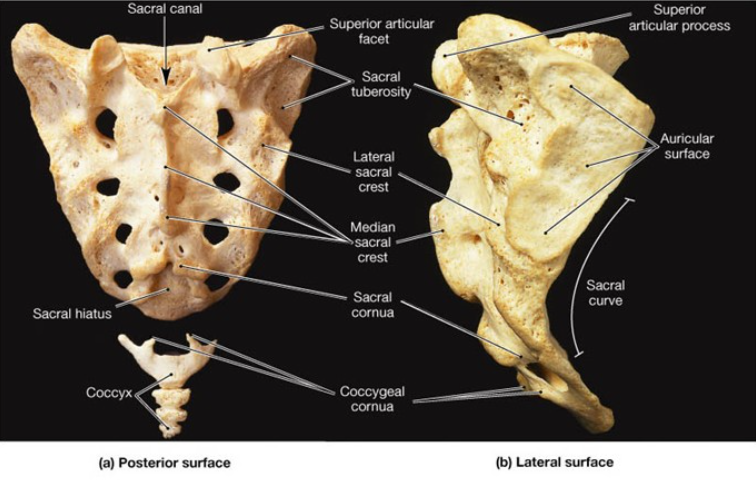
The laminae of ____ and ___ vertebrae fail to meet at the midline, forming the ______ _______?
S4, S5, sacral hiatus
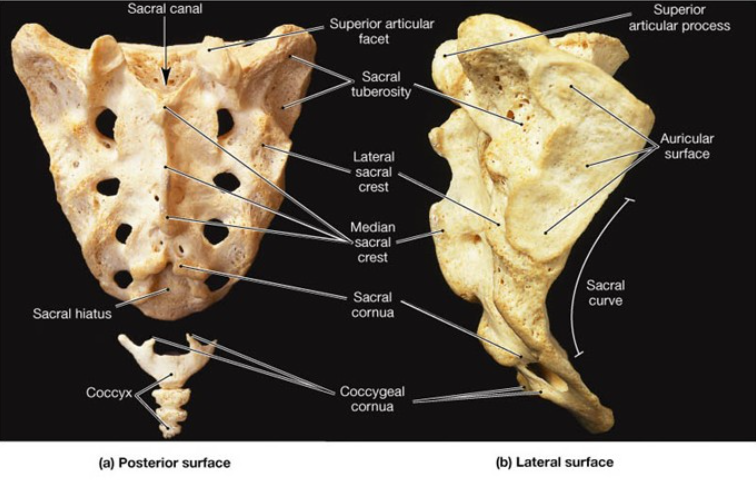
What are the other contents of the sacrum?
filum terminale, fibrofatty material
The sacrum has a _________ space and reaches up until the lower border of __ level.
Subarachnoid, S2
The vertebral foramina fuse together to form ______ _______?
Sacral canal
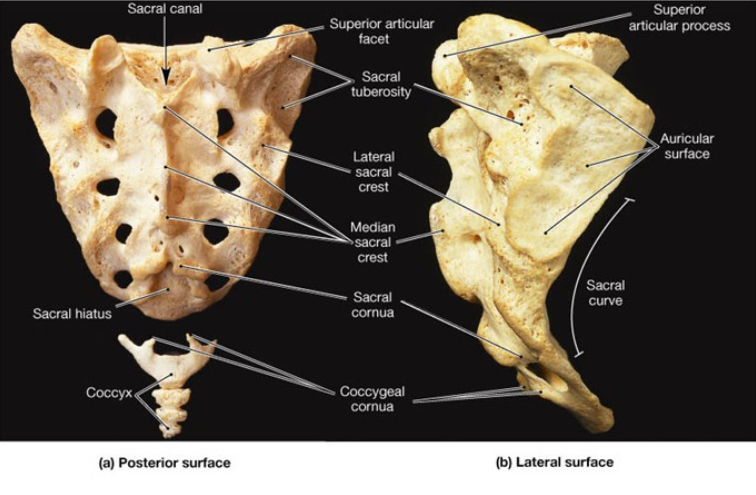
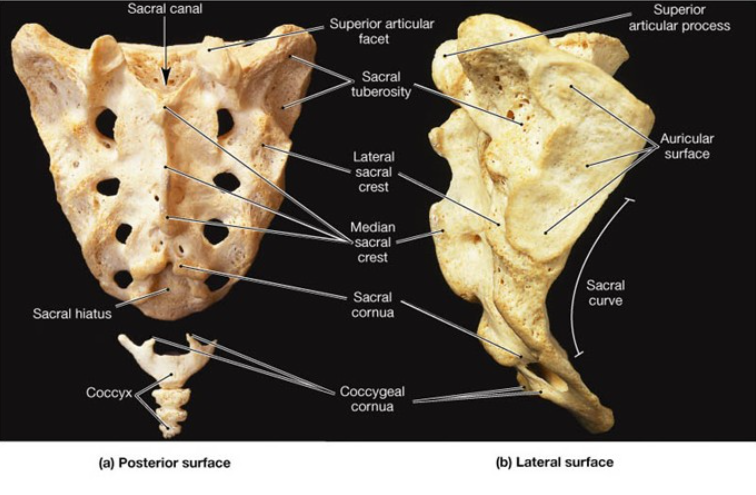
The sacral ______ contains the anterior and posterior roots of the ___, ___, and ___ nerves.
canal, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
The small depression on the head of the femur for attachment of ligamentum teres is called ___.
Fovea capitis
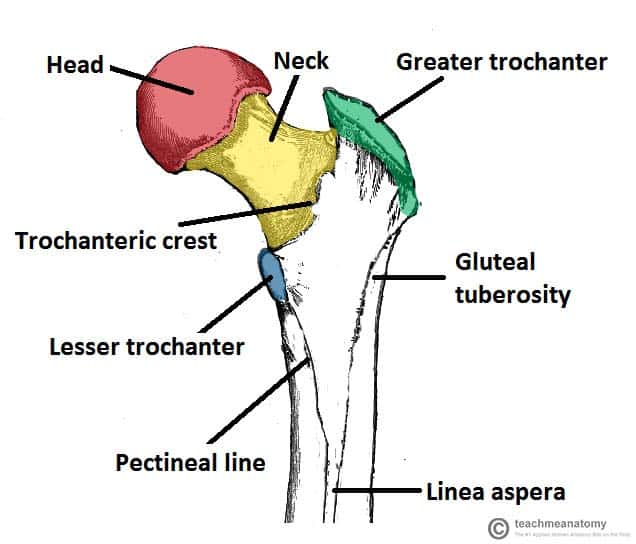
Upper end of femur contents (7 structures)
Head, neck, fovea capitis, greater and lesser trochanter, Intertrochanteric line, Quadrate tubercle
Middle third femur contents (6 structures)
Medial and lateral supracondylar ridge, linea aspera, gluteal tuberosity, shaft
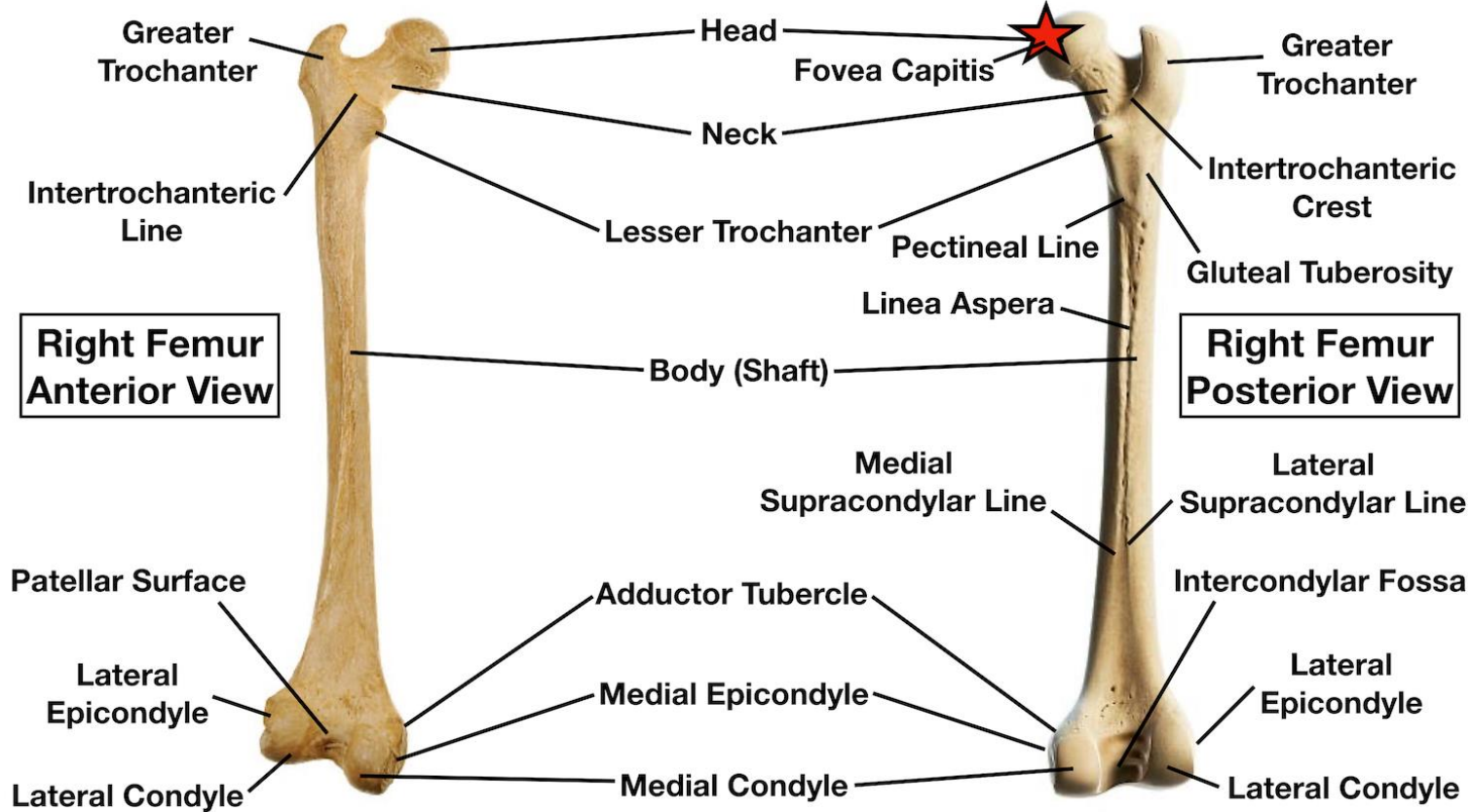
Which muscle attaches to the gluteal tuberosity?
Gluteus maximus
Lower third femur contents (4 structures)
Medial and lateral condyle, intercondylar notch, adductor tubercle
Is the adductor tubercle located laterally or medially?…
Medially
The angle of inclination between the femoral neck and shaft is about ___ degrees.
125
At birth, the angle of inclination of the femur is about _______ degrees and begins to change when a child ______.
180, stands
What is the hip deformity called when the angle of inclination is less than 120 degrees?
Coxa Vara
What is the hip deformity called when the angle of inclination is greater than 135 degrees?
Coxa Valga
In Coxa Valga, the limb length discrepancy typically results in a ___ limb.
Longer
What is the largest sesamoid bone in the body that helps elongate the tendon?
Patella
The patella is part of which tendon?
Quadriceps tendon
What connects the apex of the patella to the tuberosity of the tibia?
Ligamentum patellae
Which is the large weight-bearing bone in the leg.
Tibia
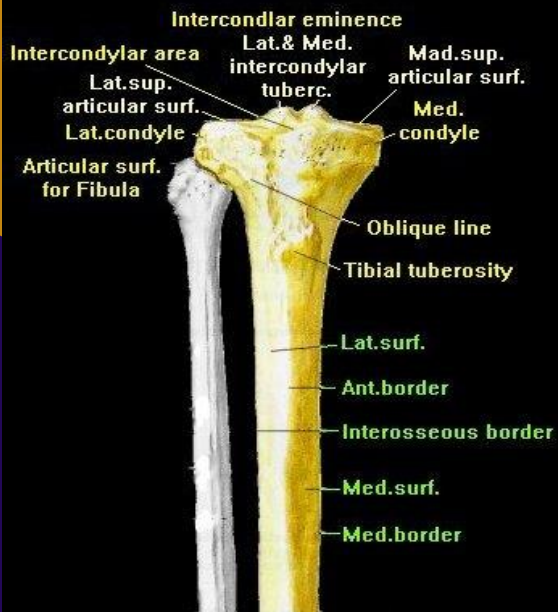
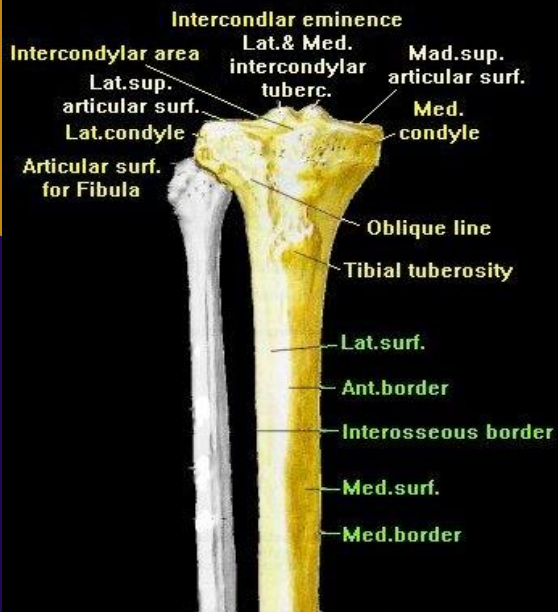
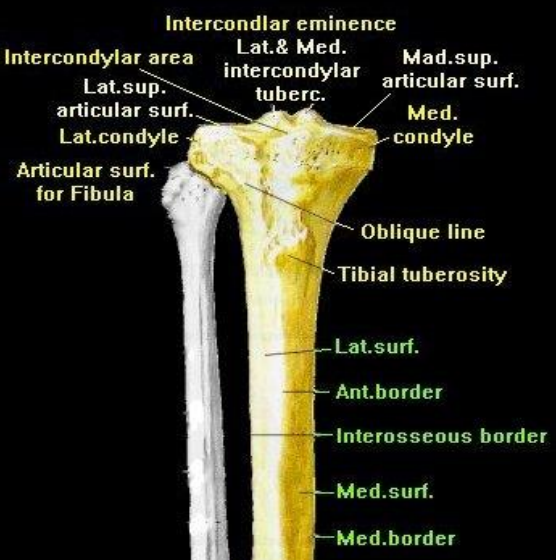
Proximal third tibia contents (6 structures)
Medial and lateral condyles, Intercondylar eminence, lateral fibular facet, interosseous border, tibial tuberosity
Distal third tibia contents (3 structures)
Medial malleolus, lateral border, soleal line
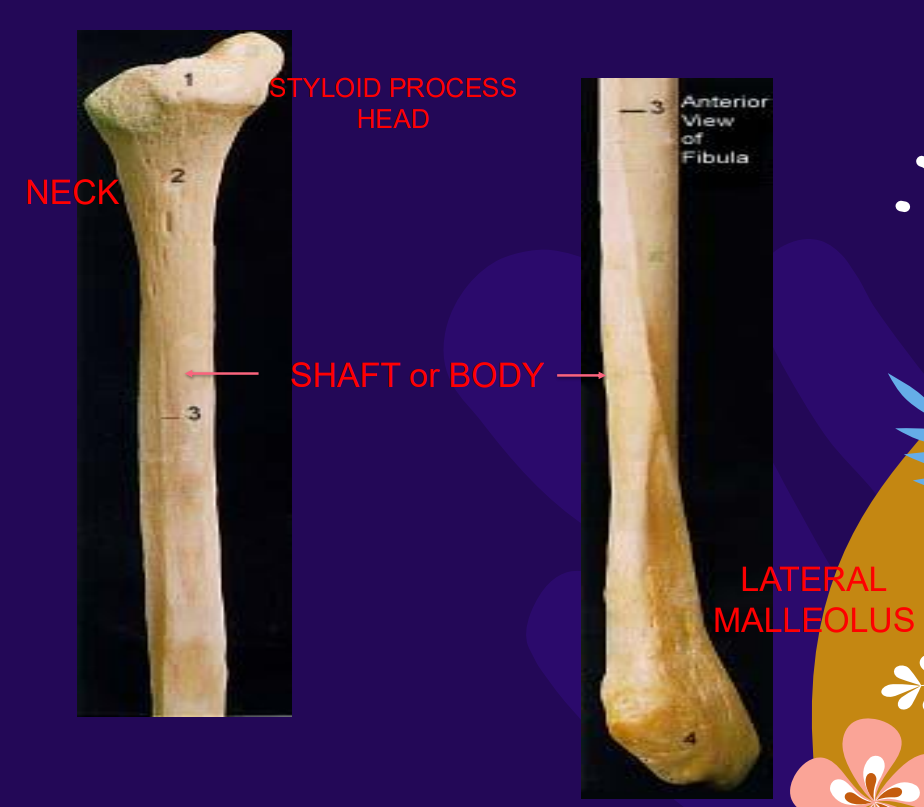
The fibula is a slender bone that is located ______ in the leg.
Laterally
Upper third fibula contents (5 structures)
Medial border, articular surface, styloid process, shaft, head
Lower third fibula contents (2 structures)
Lateral malleolus, malleolar fossa
Yes or No: Does the fibula participate in articulation at the knee joint?
No
The fibula participates in the ___ joint below the knee.
Ankle
Where does the peroneal nerve pass.
Head of the fibula
The _____ of the fibula provides attachment for the _____ membrane.
shaft, interosseous
Which bone is the largest in the foot and forms the prominence of the heel?
Calcaneum
What bone does the calcaneum articulate with above and in front respectively?
Talus, Cuboid
What surface of the calcaneum forms the prominence of the heel and provides attachment for the Achilles tendon?
Posterior surface
What is the roughened groove separating the articular facets on the superior surface of the calcaneum called?
Sulcus calcanei
What is the name of the large, shelf-like process on the medial surface of the calcaneum?
Sustentaculum tali
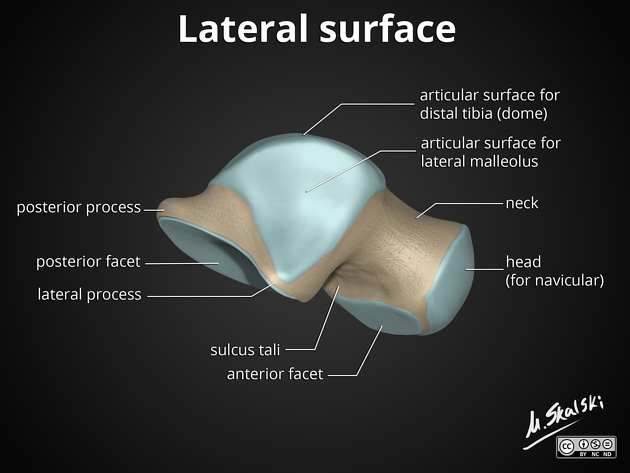
The talus consists of which three parts?
Head, neck, body
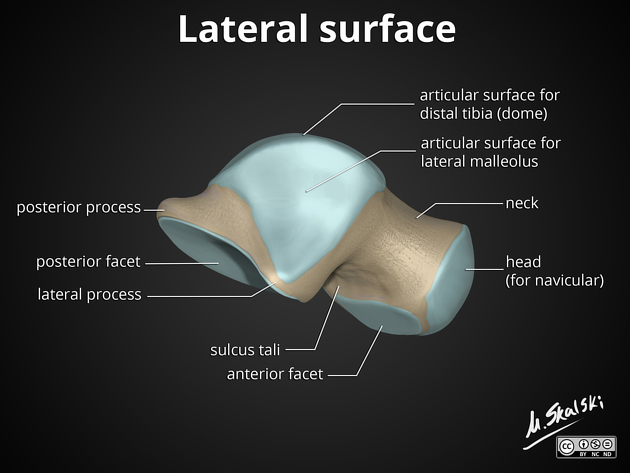
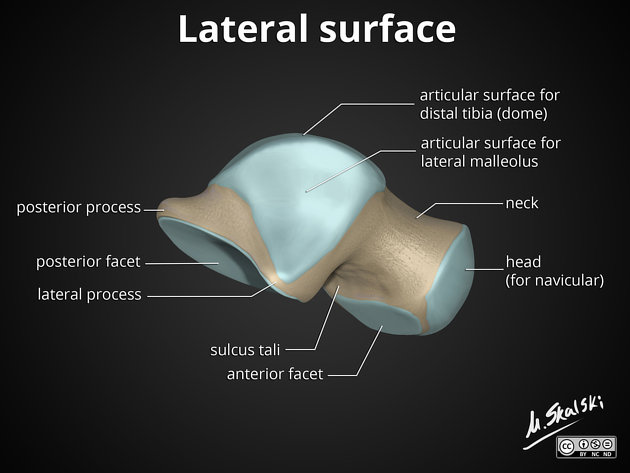
Which part of the talus articulates distally with the navicular bone?
Head
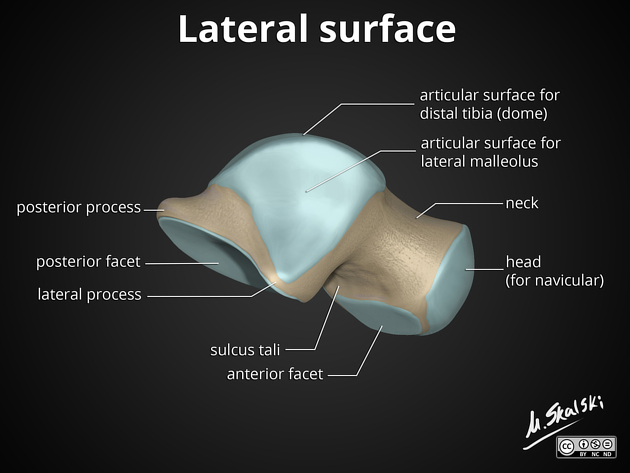
The _______ surface of the calcaneum is for fascia at the foot area
Inferior
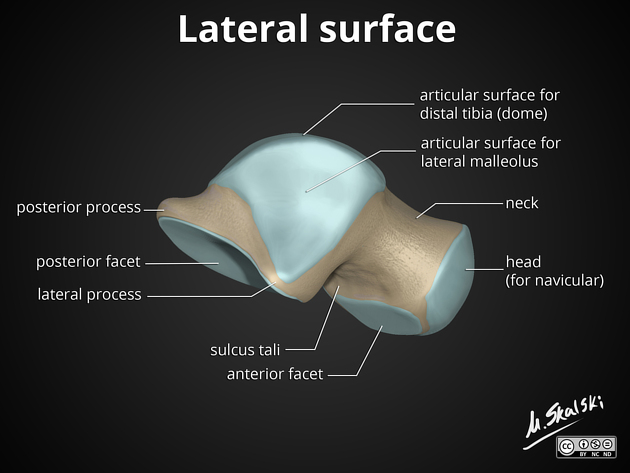
The inferior surface of the calcaneum has an ________ ________ in the midline and a large ______ and a smaller _____ tubercle at the junction of the inferior and posterior surfaces
anterior tubercle, medial, lateral
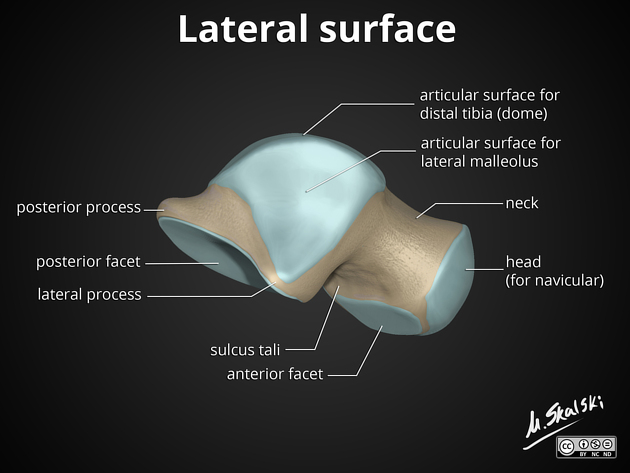
What does the superior surface of the talus articulate with? (Be specific)
Distal end of tibia
The superior surface of the talus is ___ from before backward and ___ from side to side.
Convex, concave
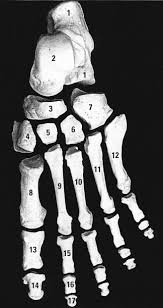
Name all 7 bones of the foot and ankle
Calcaneus
Talus
Navicular
Medial cuneiform
Intermediate cuneiform
Lateral cuneiform
Cuboid
Fascia that is responsible for the prominence of the buttock.
Superficial fascia
_____ fascia where lateral surface it thickens to form a strong wide band, and forms the ______ tract
Deep, Iliotibial
________ forms the “sheet” of the tensor _____ _____ muscle.
Iliotibial tract, fascia latae
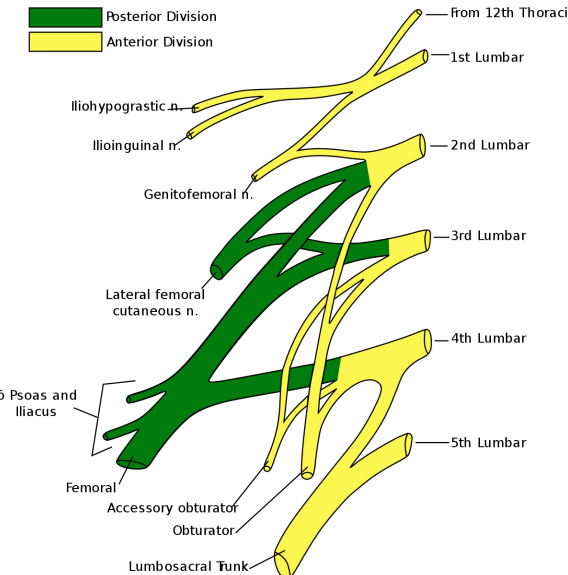
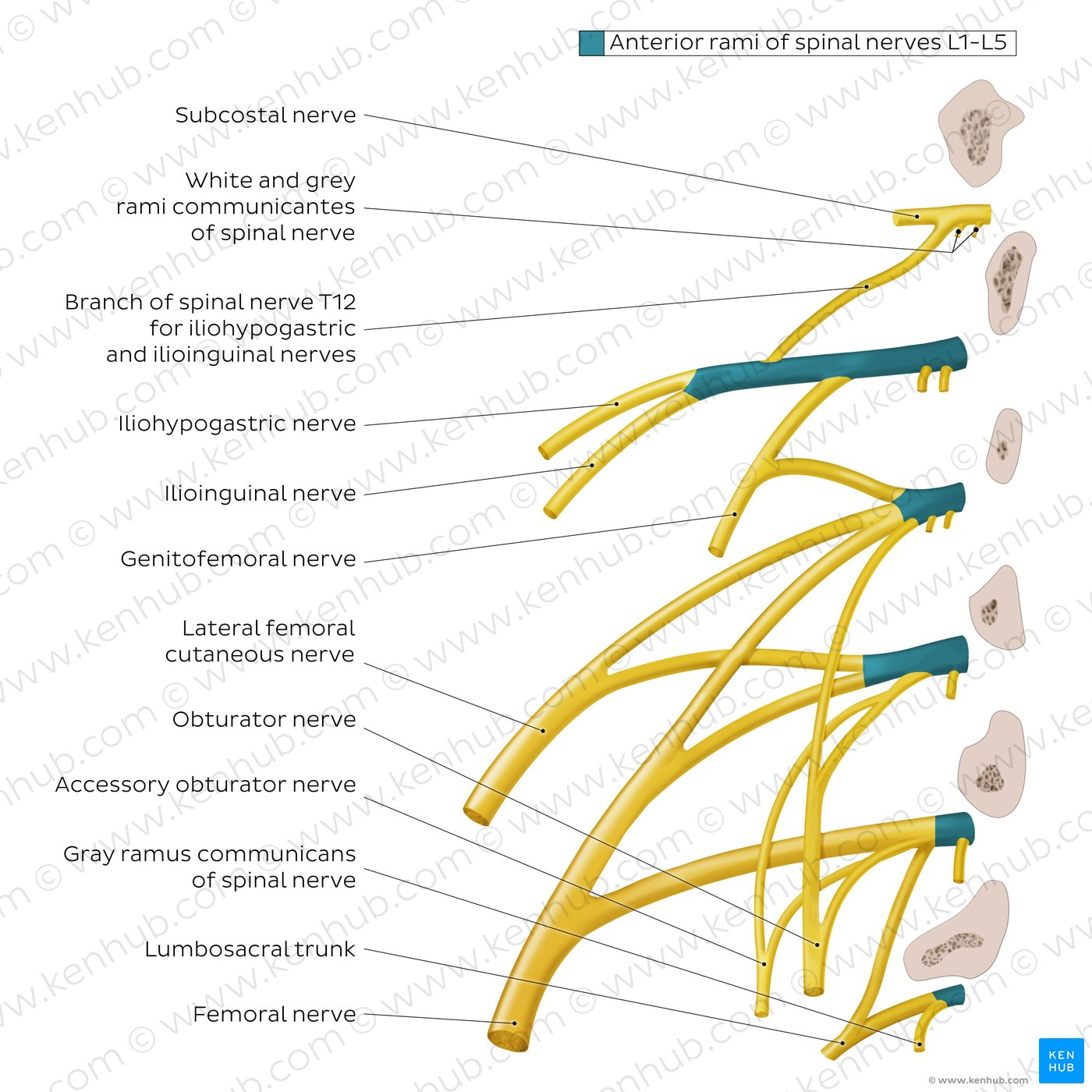
Which nerve arises from L1?
Iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal
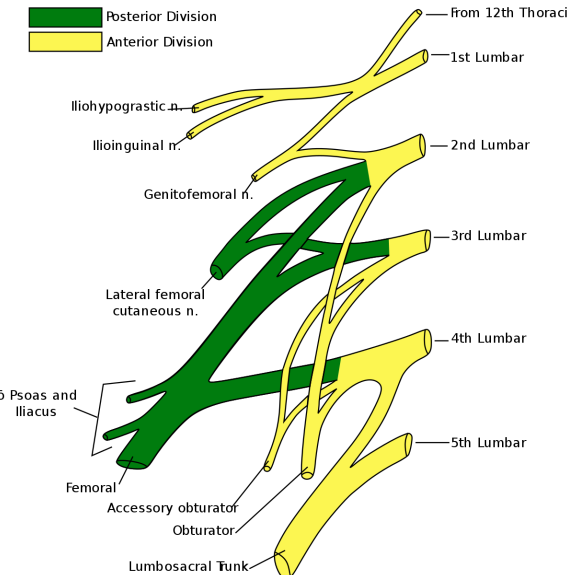
Which nerve arises from L1-2?
Genitofemoral
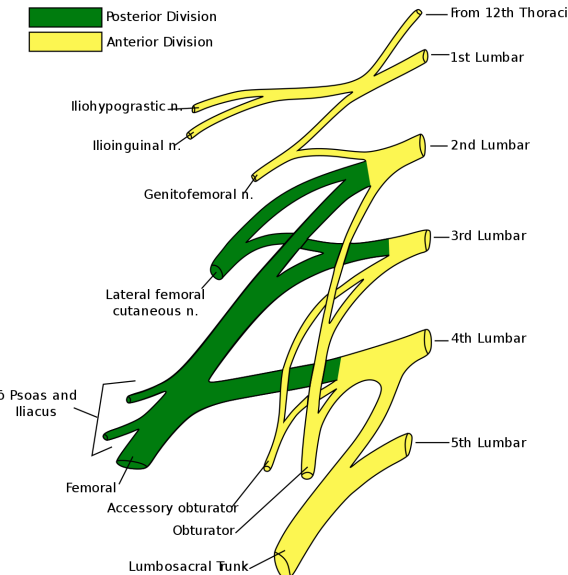
Which (Posterior) nerve arises from L2-3?
Lateral femoral cutaneous
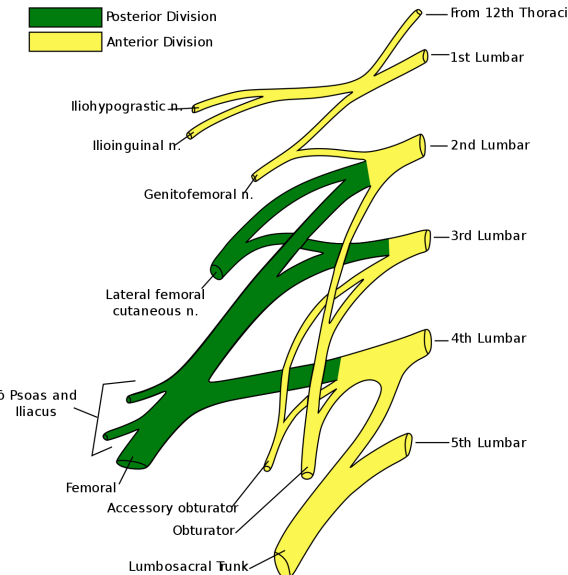
Which nerve arises from L2,3,4 ?
Obturator nerve
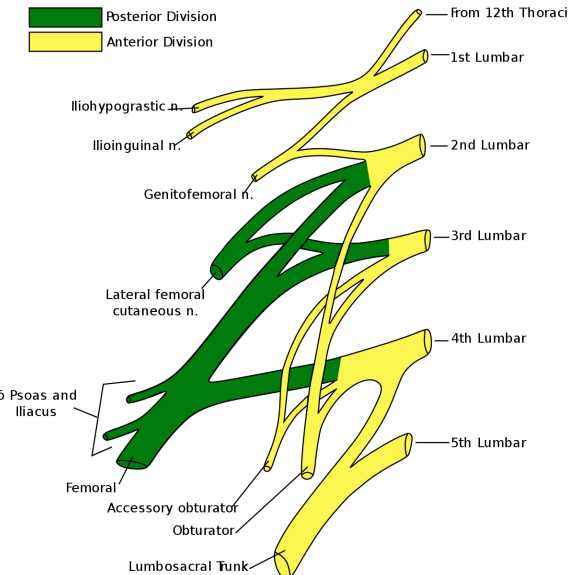
Which (Posterior) nerve arises from L2,3,4 ?
Femoral nerve
Which nerve has roots L4-S1?
Superior gluteal nerve, Nerve to quadratus femoris
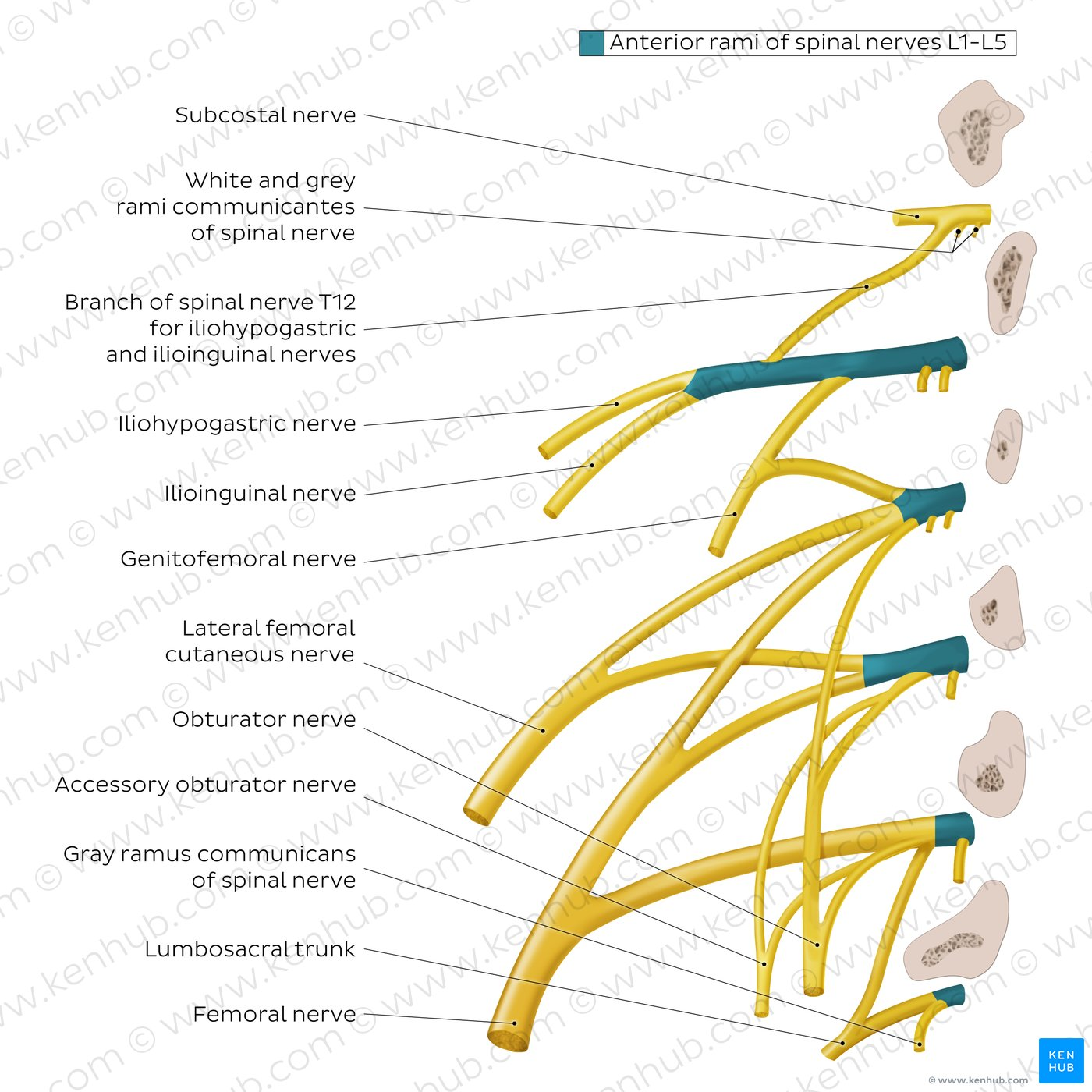
Which nerves has roots L4-S3?
Sciatic nerve, Tibial nerve, Common fibular (peroneal) nerve
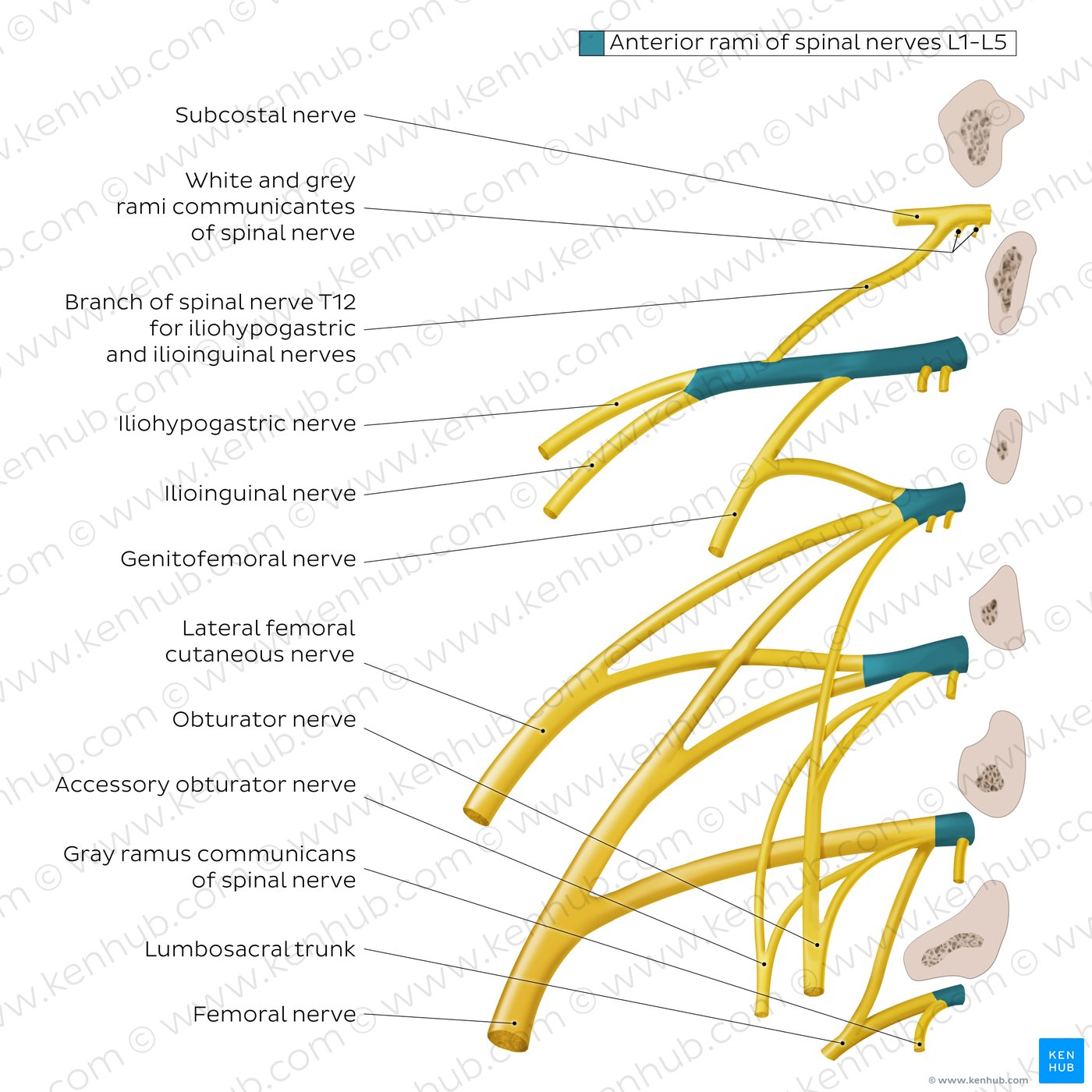
Which nerves has roots L5-S2?…
Inferior gluteal nerve, Nerve to obturator internus
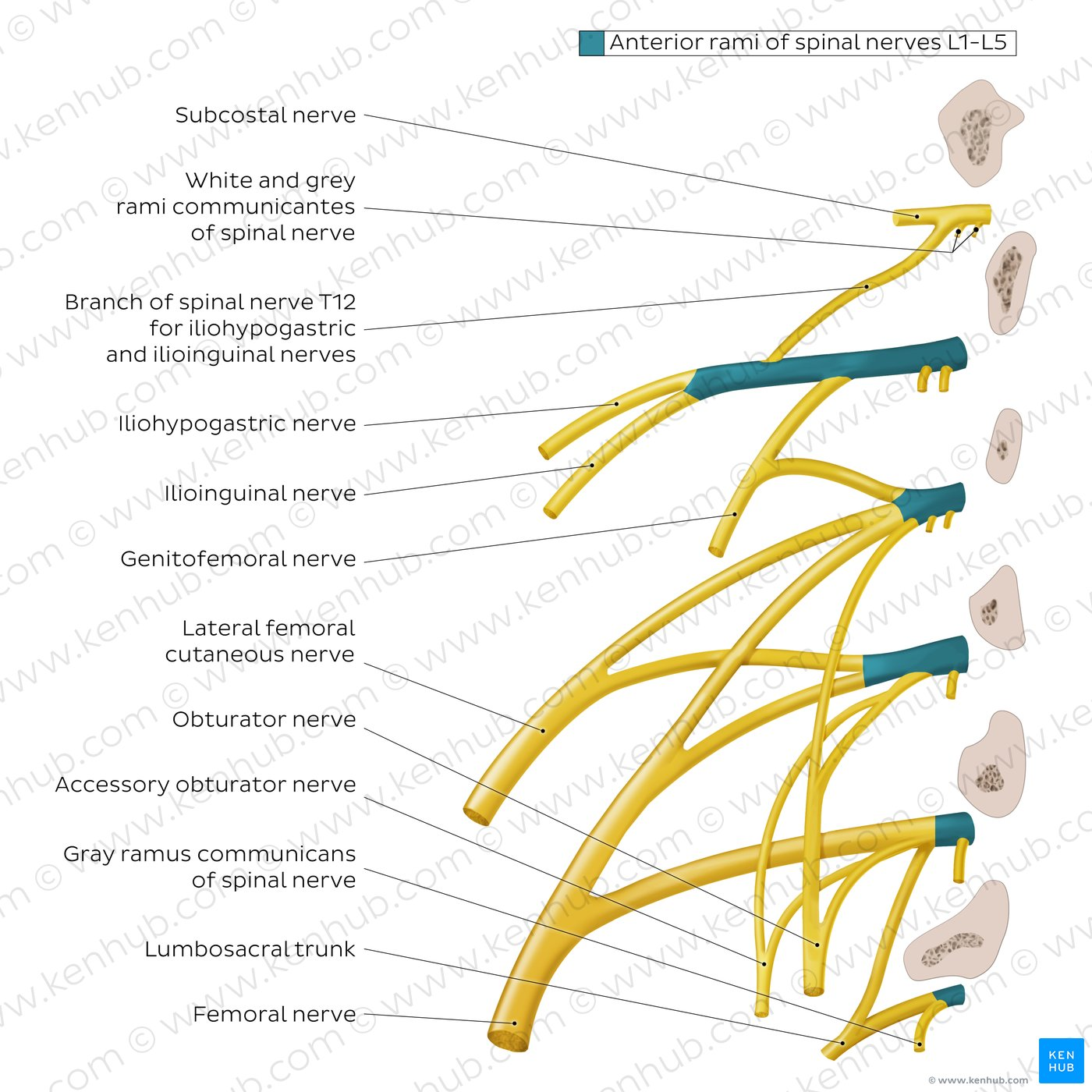
Which nerve has roots S1-S2?
Nerve to piriformis
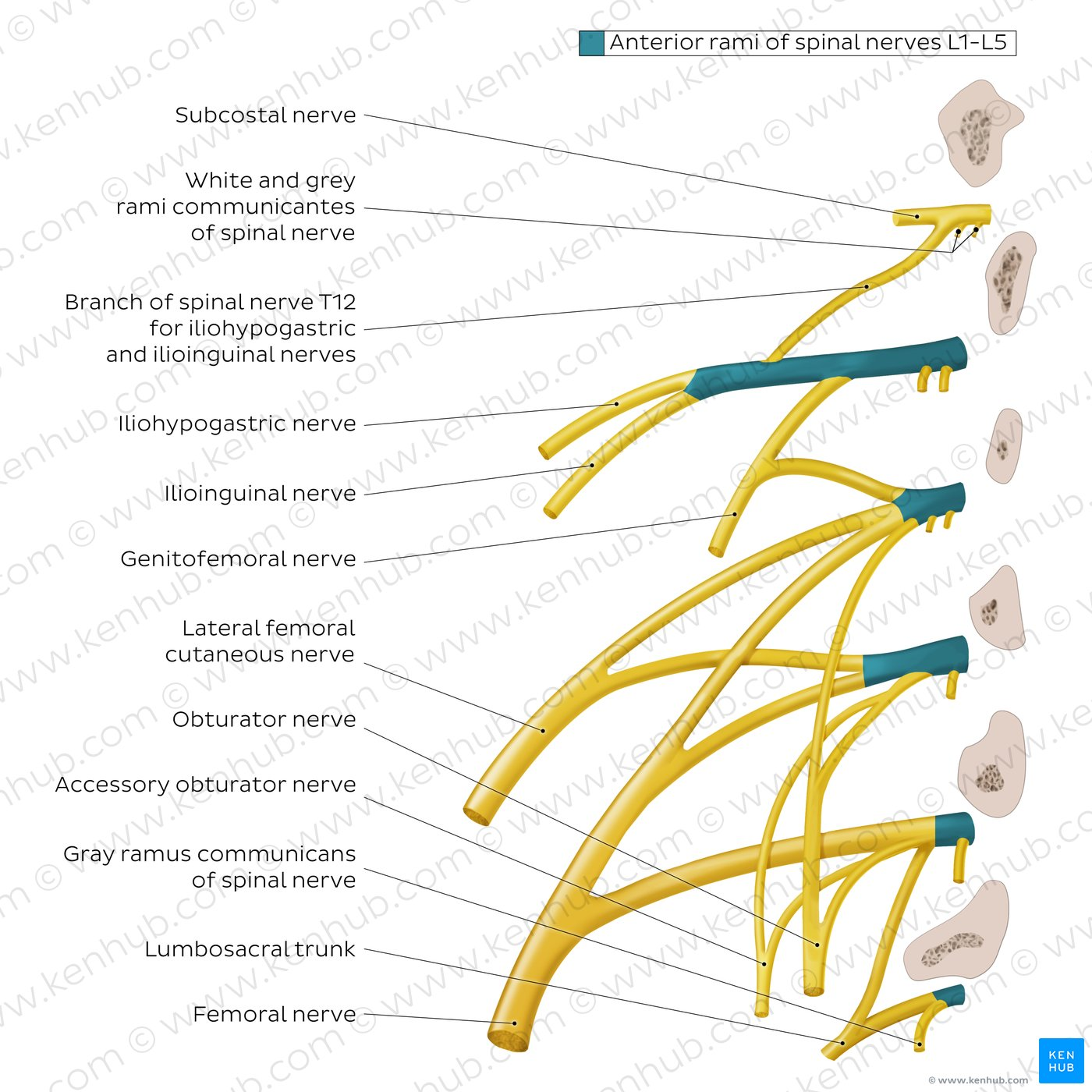
Which nerve from S1-S3 provides sensation to the posterior thigh?
Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh
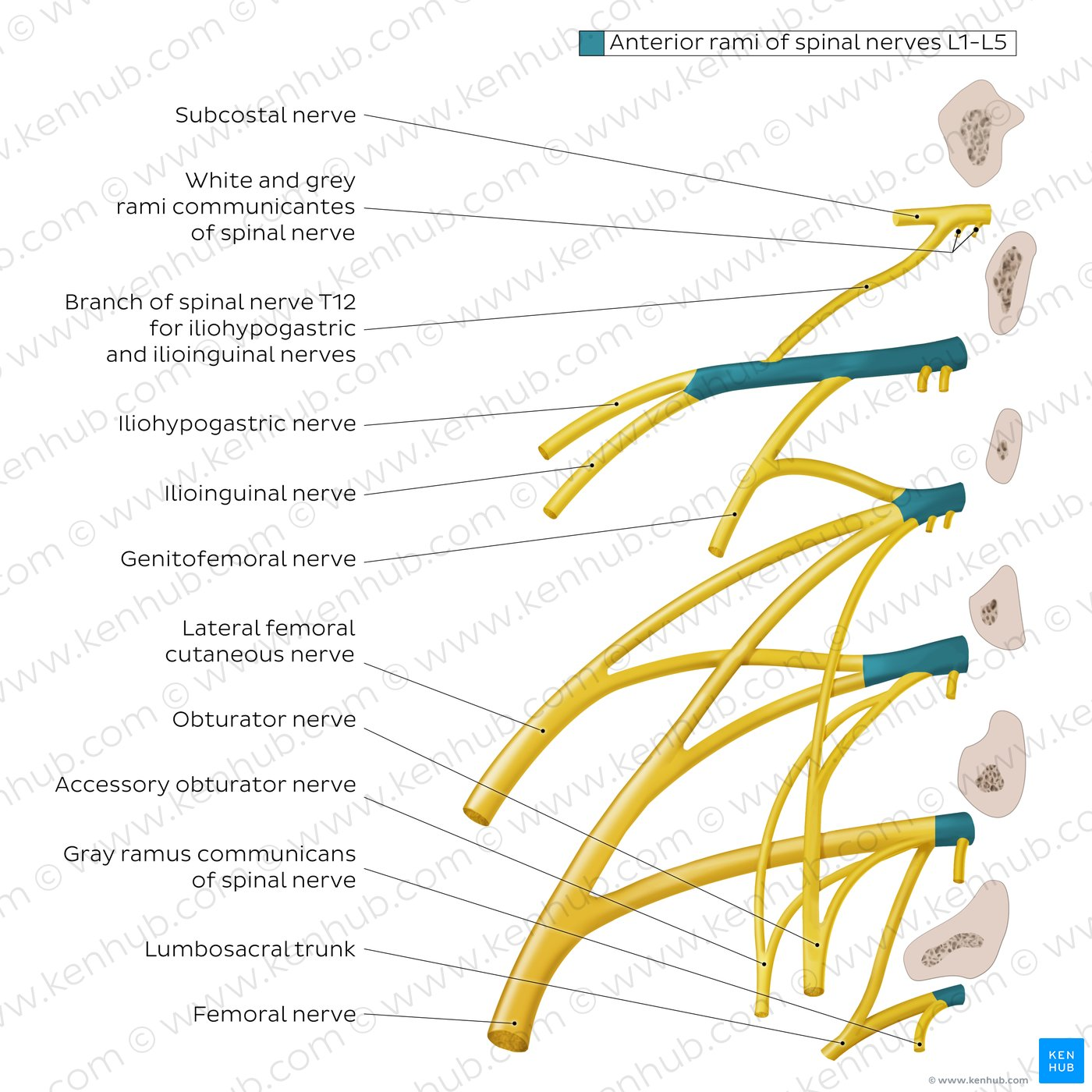
Which nerve has roots S2-S3 and supplies sensation to the skin over the buttocks?
Perforating cutaneous nerve
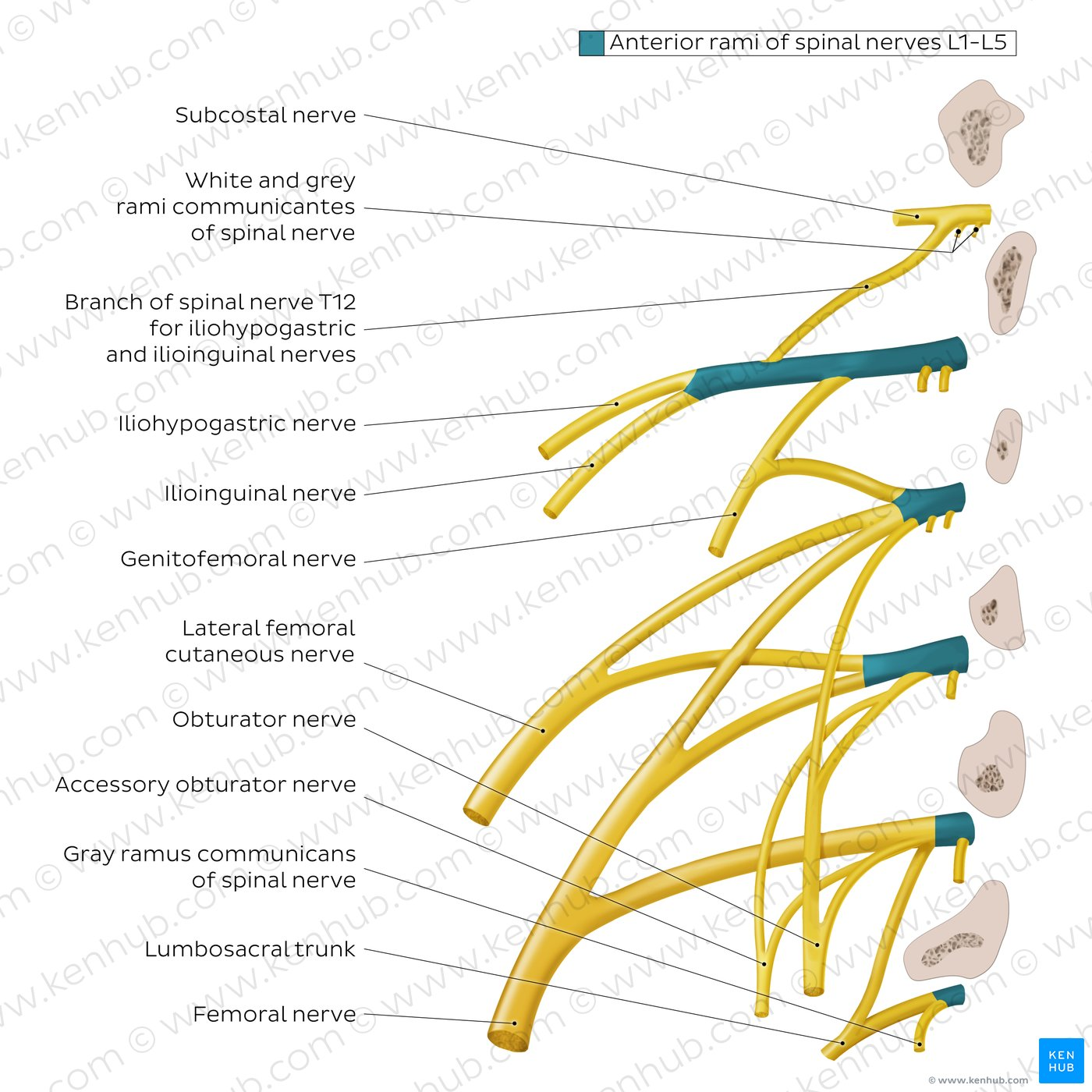
Which nerve has roots S2,3,4 and supplies the perineum?
Pudendal nerve
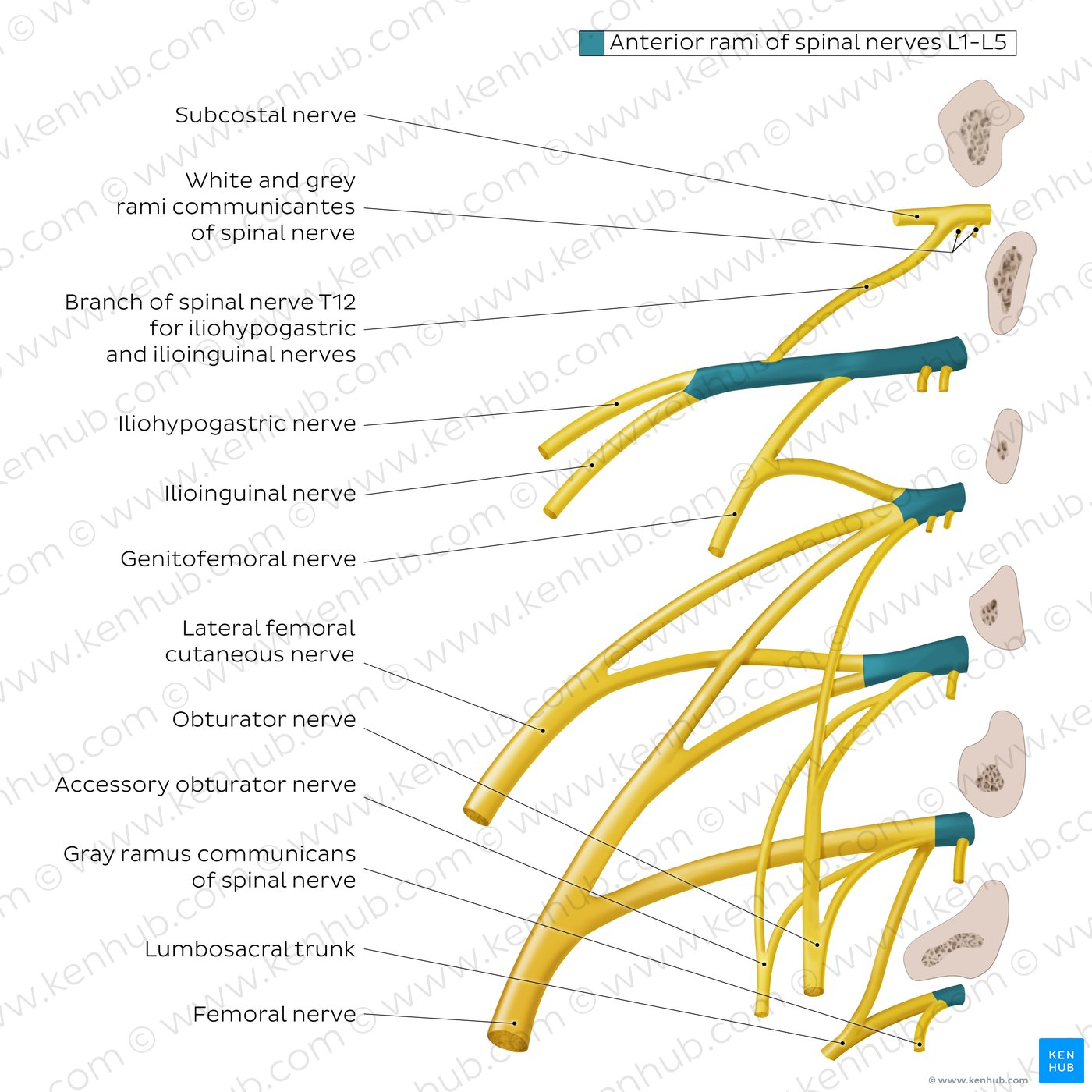
Which nerve has roots S4-Co1 and supplies the coccygeal region?
Coccygeal nerve
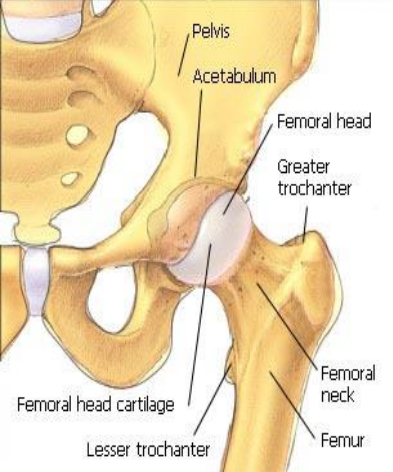
What type of joint is the hip joint?
Multiaxial ball and socket
The retinacula attaches to the ___.
Intertrochanteric lines
Which ligament is Y-shaped and prevents hip hyperextension?
Iliofemoral ligament
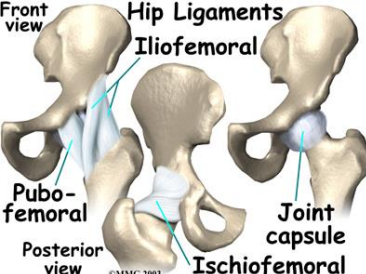
The iliofemoral ligament attaches at the ___ and intertrochanteric line.
AIIS
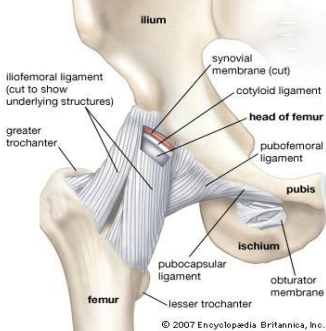
True or False: The pubofemoral ligament limits hip abduction and extension.
True