Head and Neck Anatomy Terms & Definitions Pre-Exam Study
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
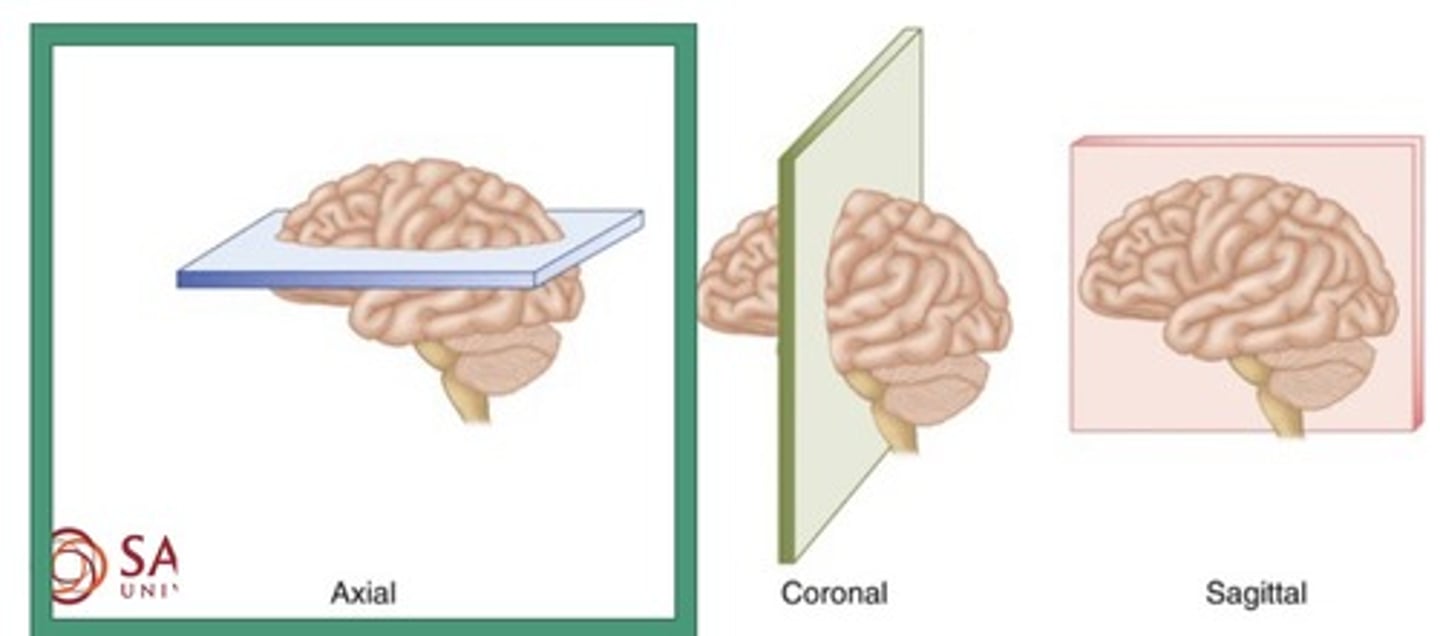
Planes of the body
1. Coronal
2. Sagittal
3. Axial
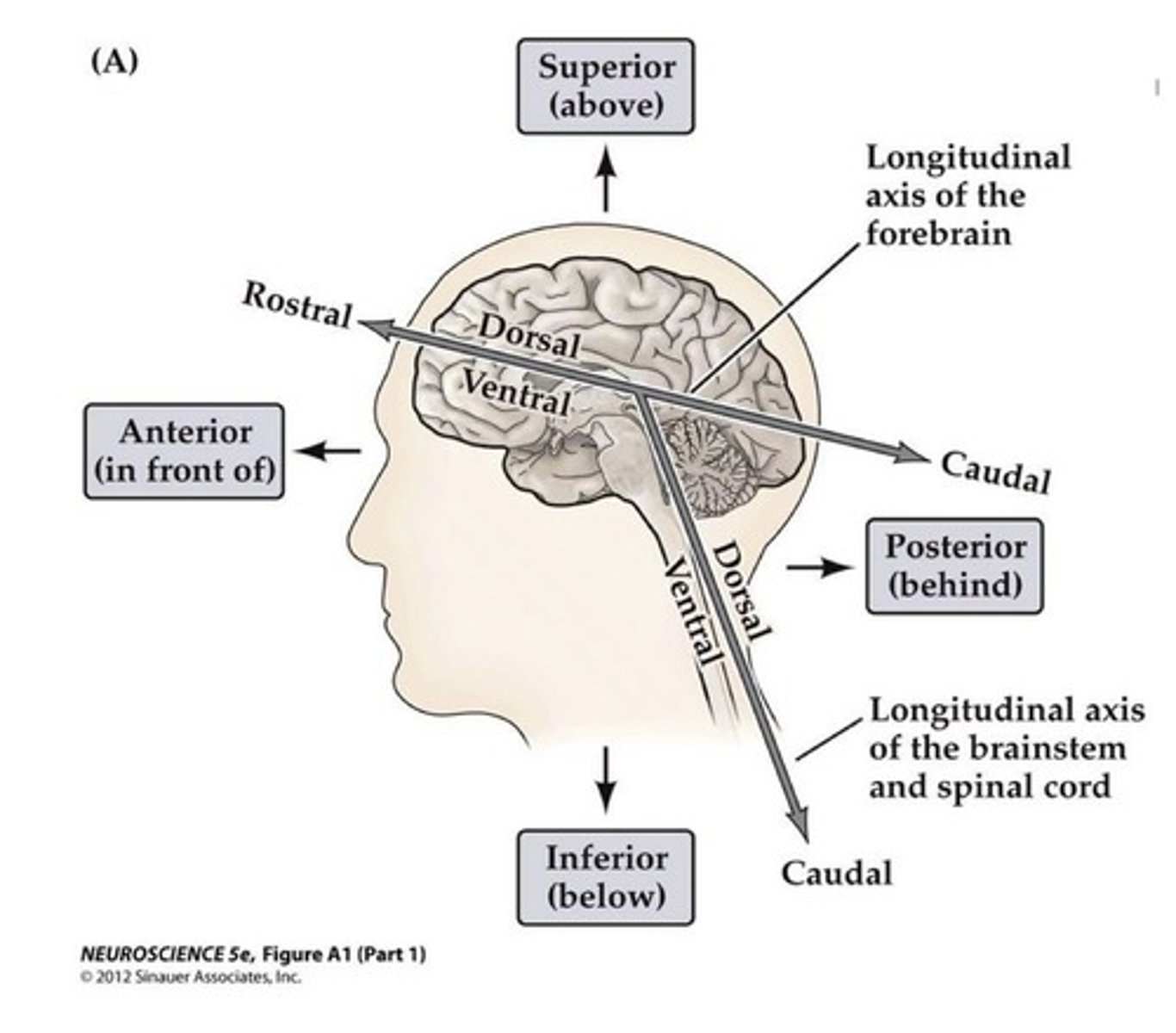
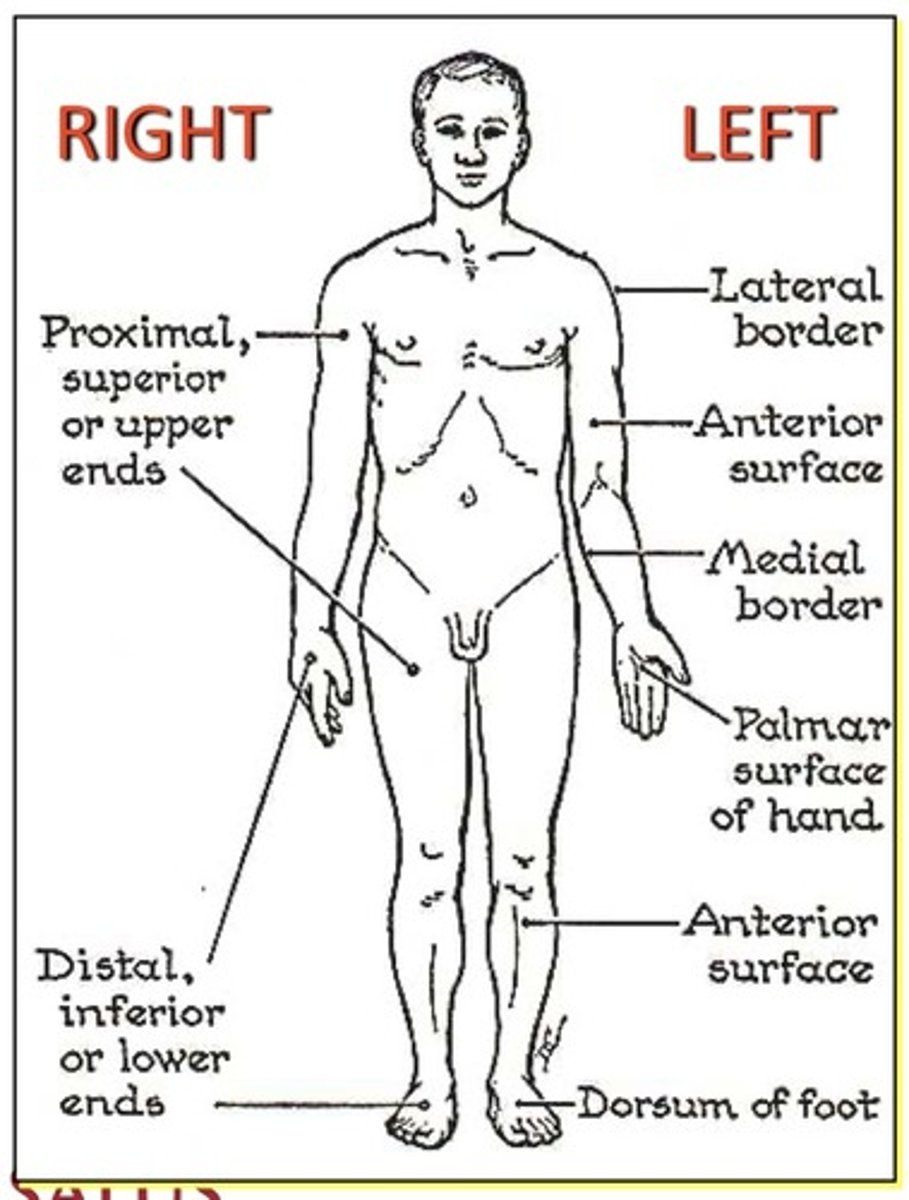
Terms of Direction
1. Ventral
2. Dorsal
3. Rostral
4. Caudal
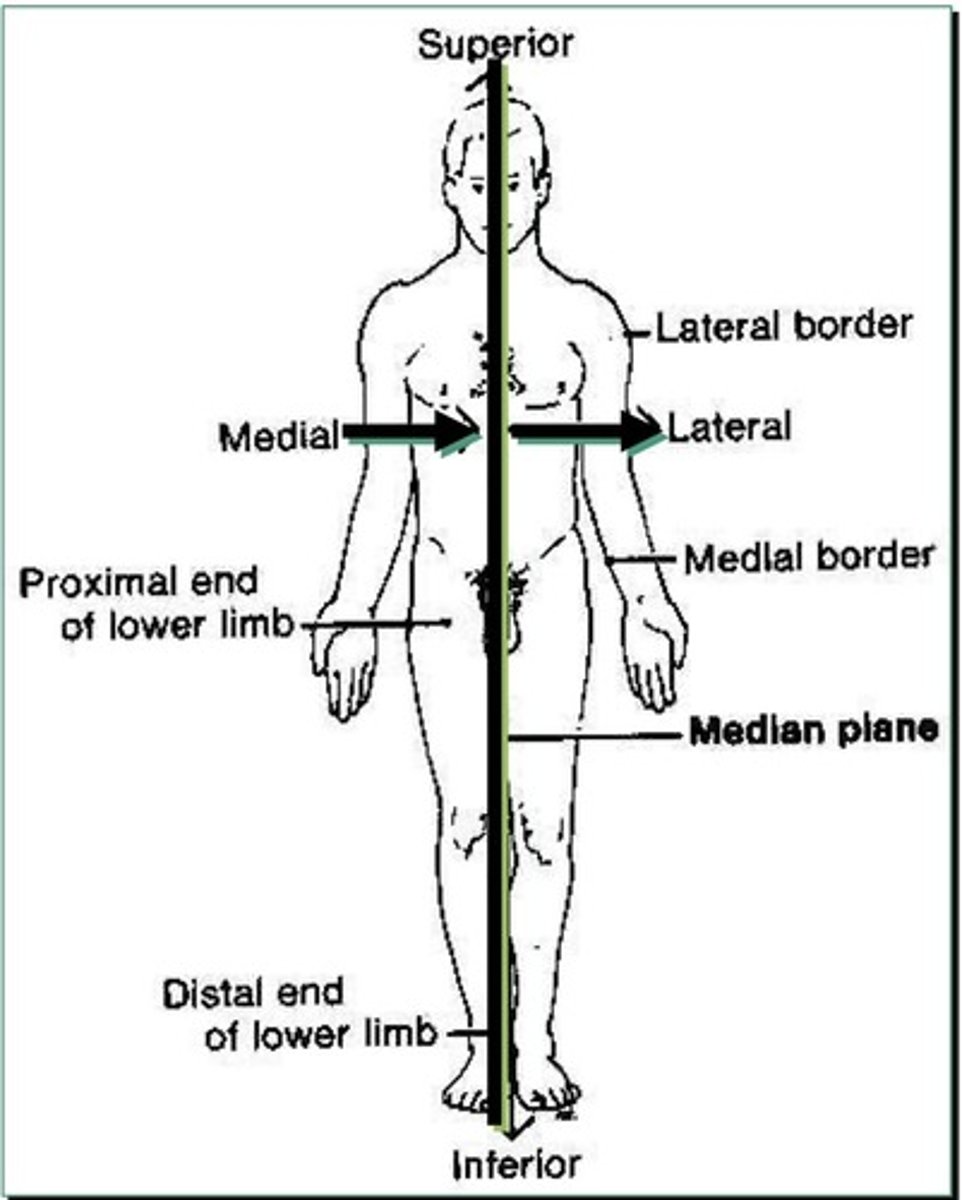
Terms of Direction
1. Medial: toward midline
2. Lateral: away from midline
3. Superficial: closer to the surface
4. Deep: away from surface
5. Proximal: towards the attachment
6. Distal: away from the attachment
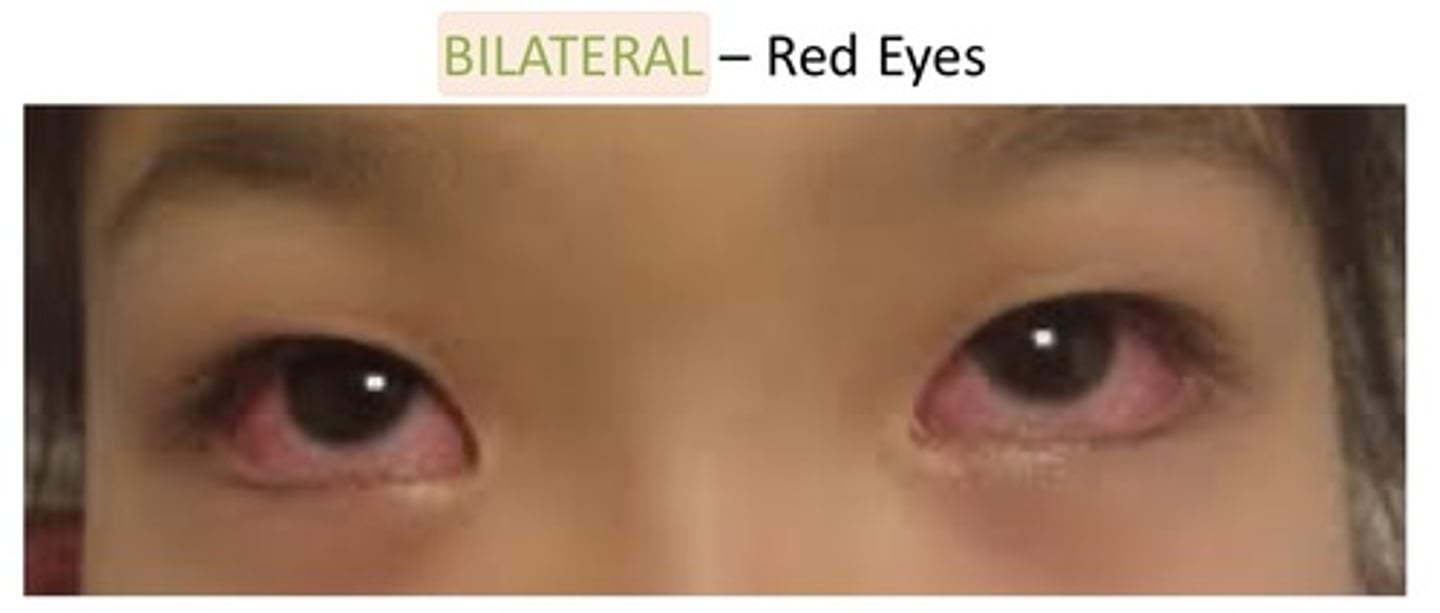
Bilateral
1. Both sides of an anatomic structure
2. Used to describe if both eyes are red
3. Used to describe if both sides of the body are weak
Anatomical position
1. Body is standing or lying erect
2. Eyes are forward
3. Feet are forward
4. Palms are forward and thumbs are out
Coronal
1. Divides into a front and back
2. An anatomic cut from ear to ear
3. An anatomic cut through the both eyes
4. An anatomic cut through the mouth
Axial
1. Divides into top and bottom
2. An anatomic cut from ear to ear
3. An anatomic cut through both eyes
4. An anatomic cut through the mouth
5. Also called a transverse cut
6. Also called a horizontal cut
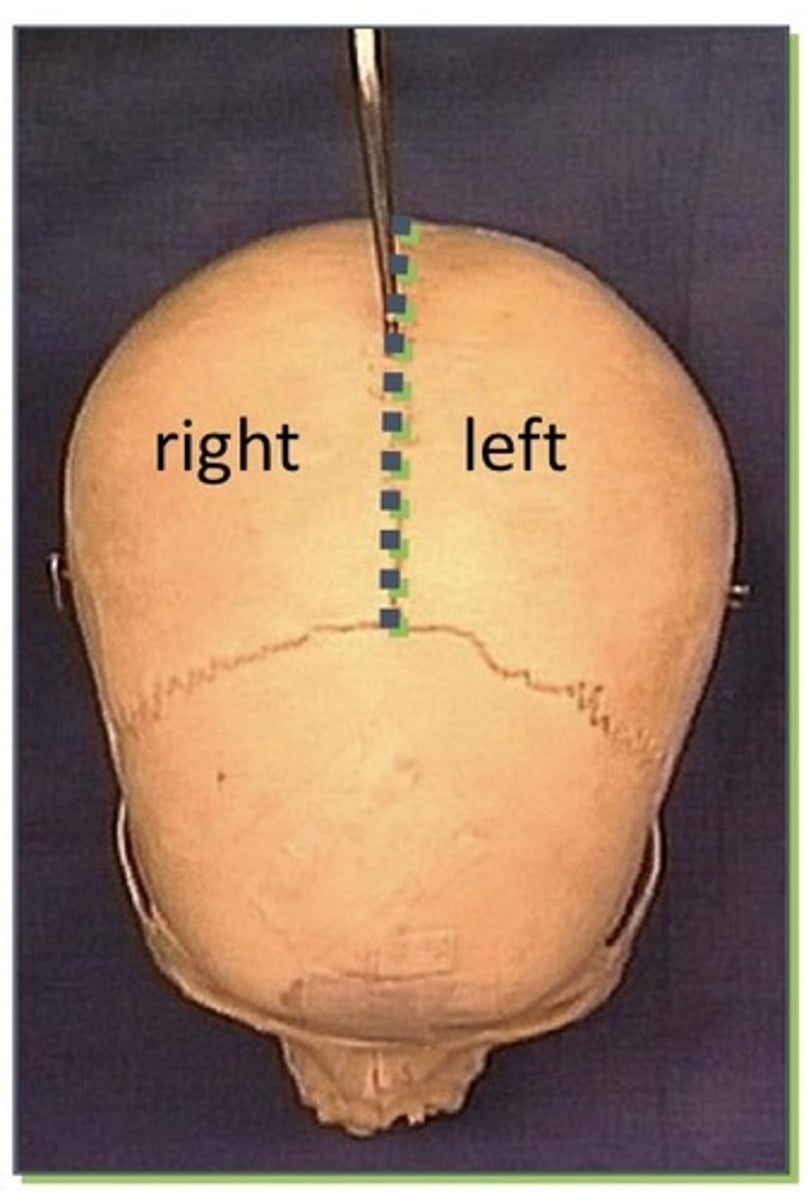
Sagittal
1. Divides into right and left
2. An anatomic cut from the nose to the back of the head
3. An anatomic cut through only one eye
4. An anatomic cut through only one ear
5. An anatomic cut through the mouth
Dorsal
1. Also known as posterior
2. Refers to the back of the anatomical structure
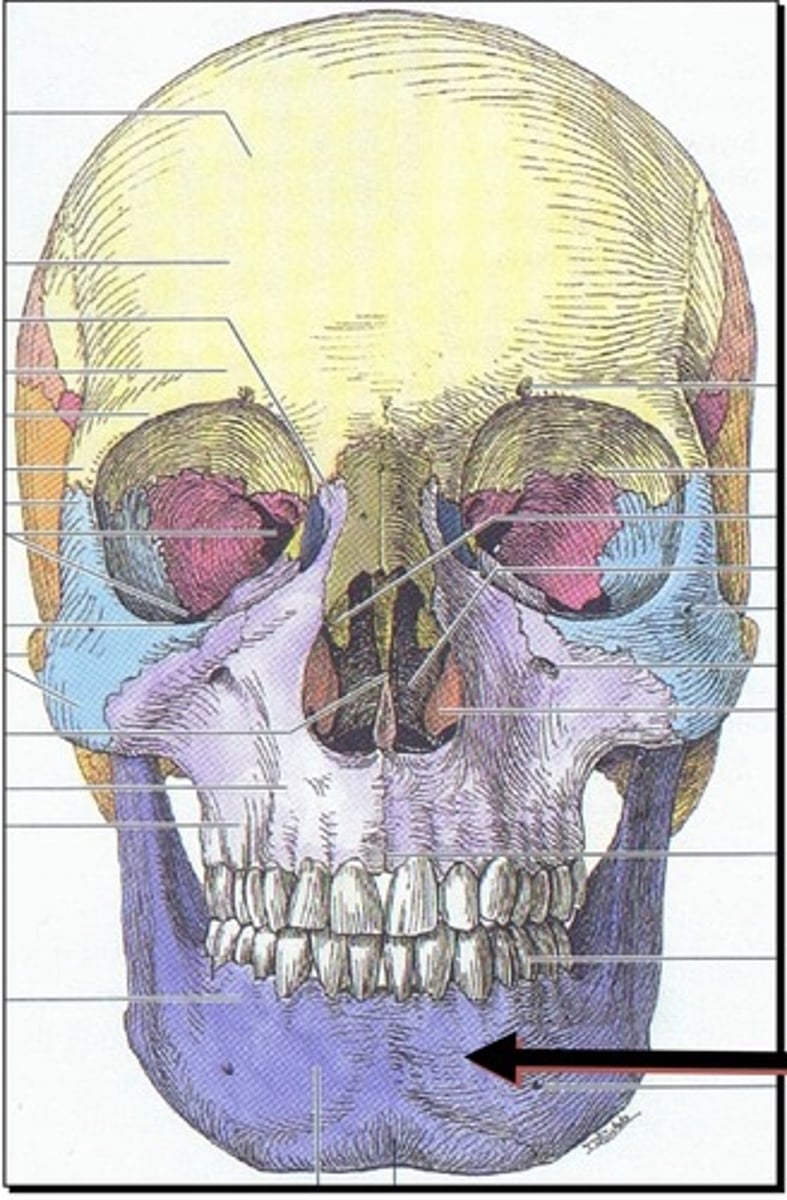
Bones of the face (14)
1. Nasal (x2)
2. Maxillary (x2)
3. Lacrimal (x2)
4. Palatine (x2)
5. Zygomatic (x2)
6. Vomer
7. Inferior nasal conchae (x2)
8. Mandible
Ventral
1. Also known as anterior
2. Refers to the front of an anatomical structure
Cranial
1. Also known as superior
2. Also known as cephalic
3. Indicates towards the head of the human
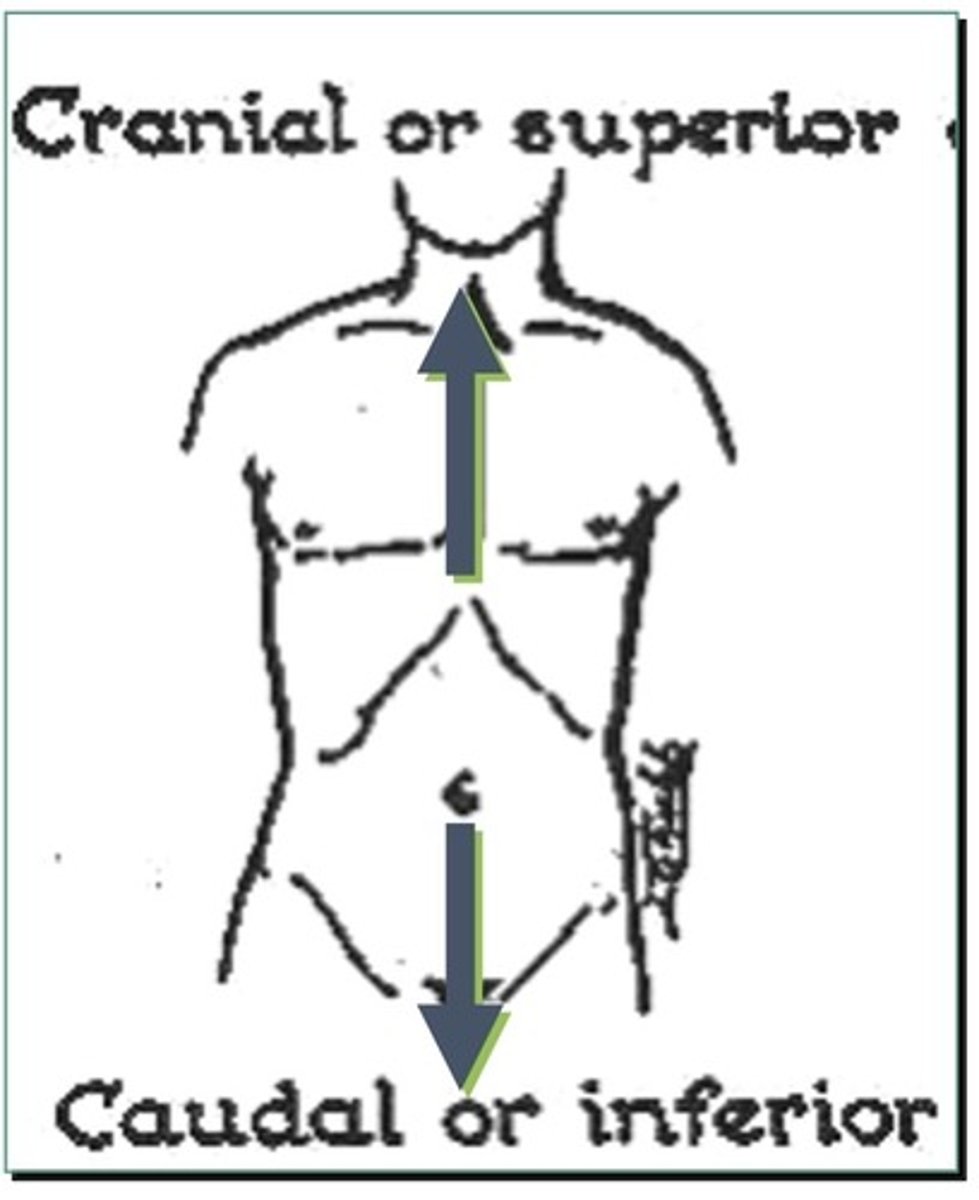
Caudal
1. Also known as inferior
2. Also known as "to the tail"
3. Indicates towards the tail/bone of a human
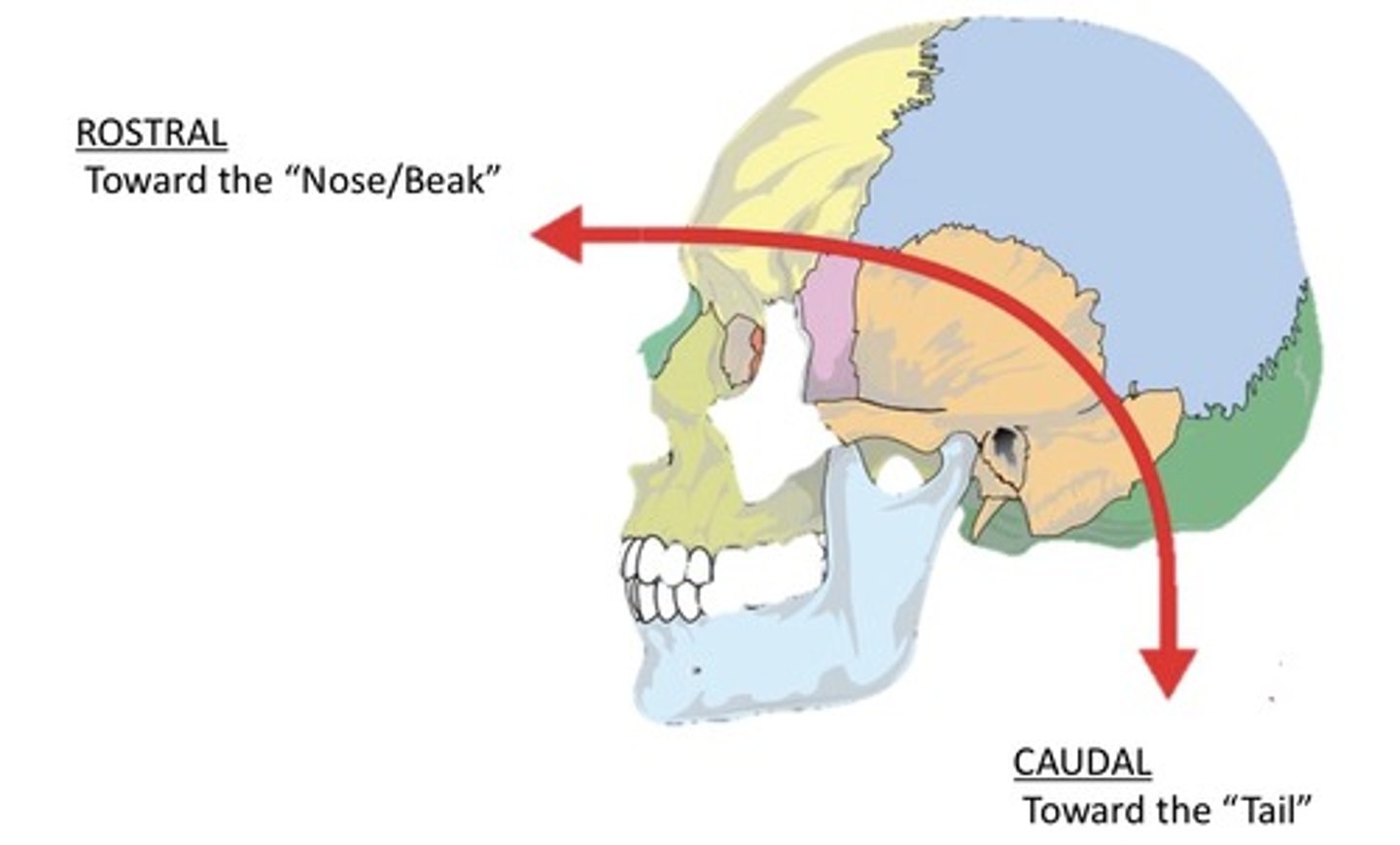
Rostral
Indicates towards the nose/beak
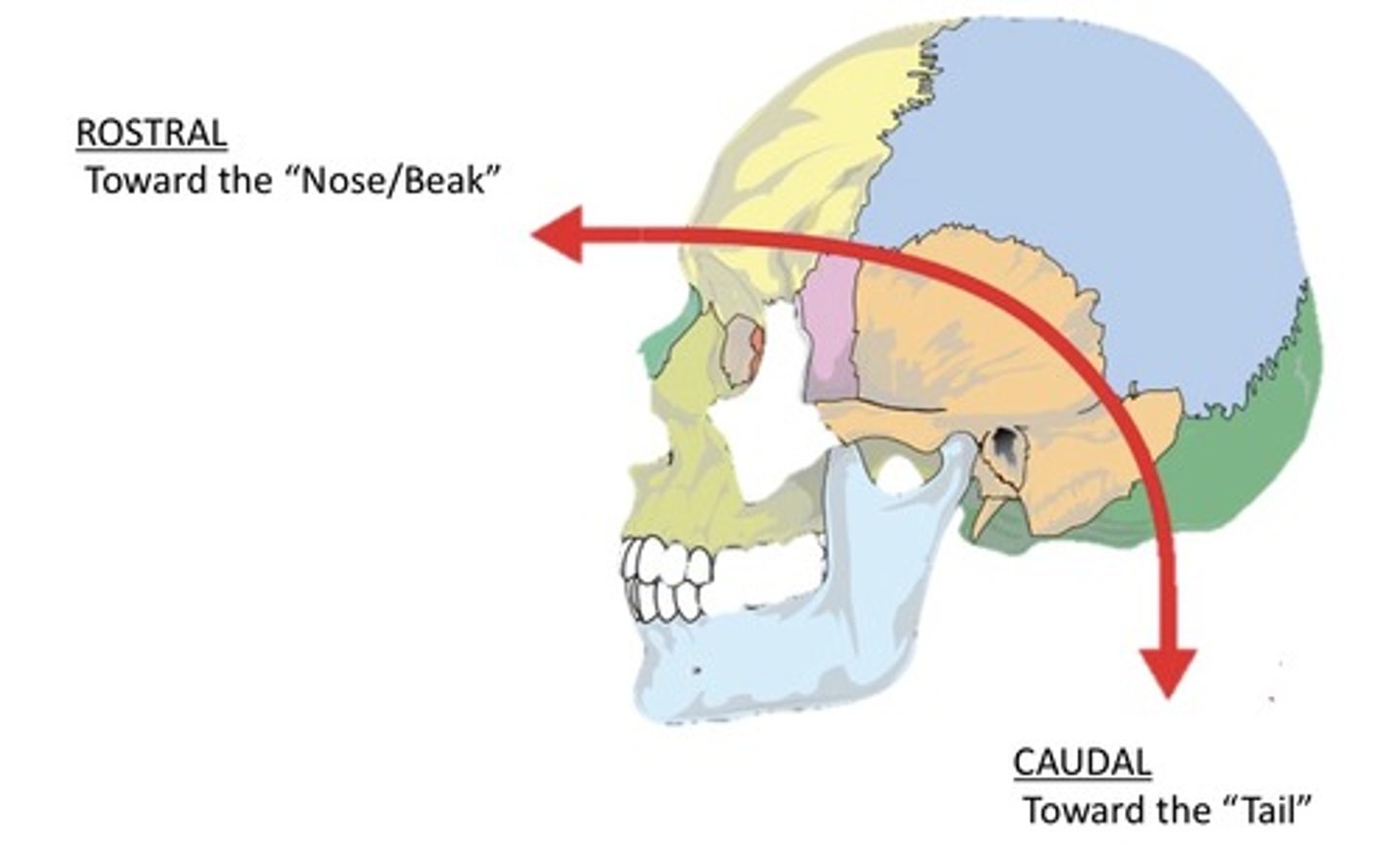
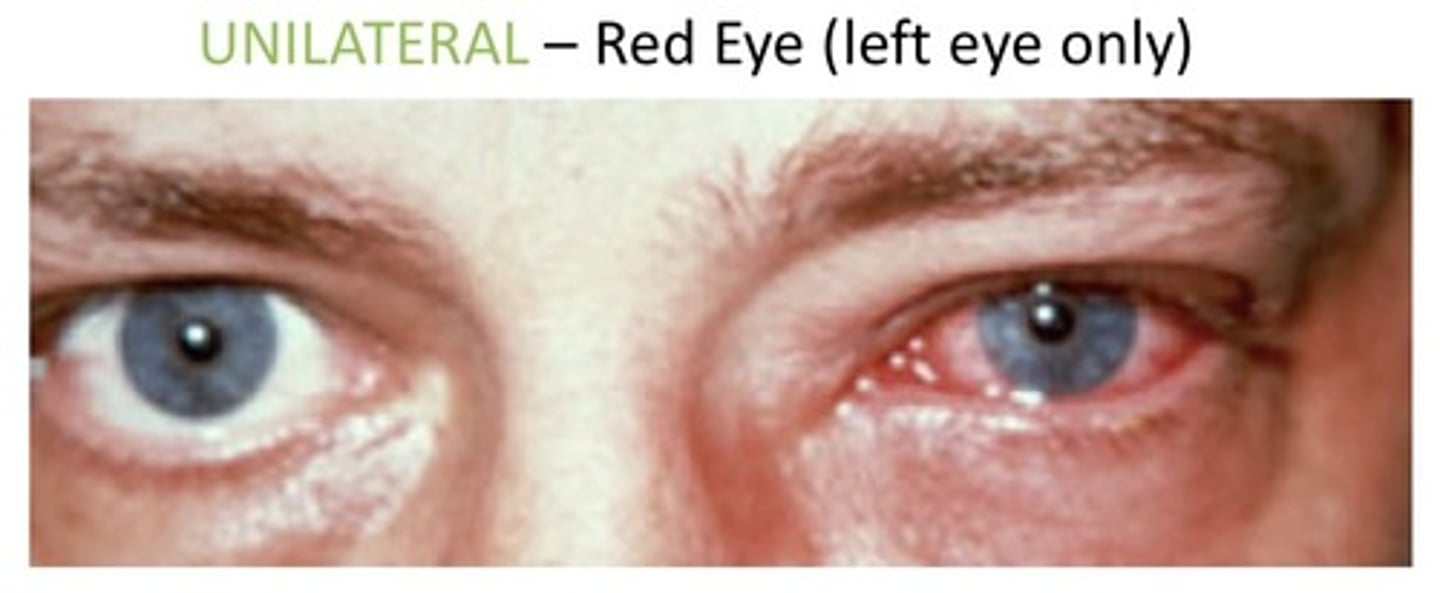
Unilateral
1. One side of an anatomic structure
2. Used to describe if one eye is red
3. Used to describe if one sides of the body are weak
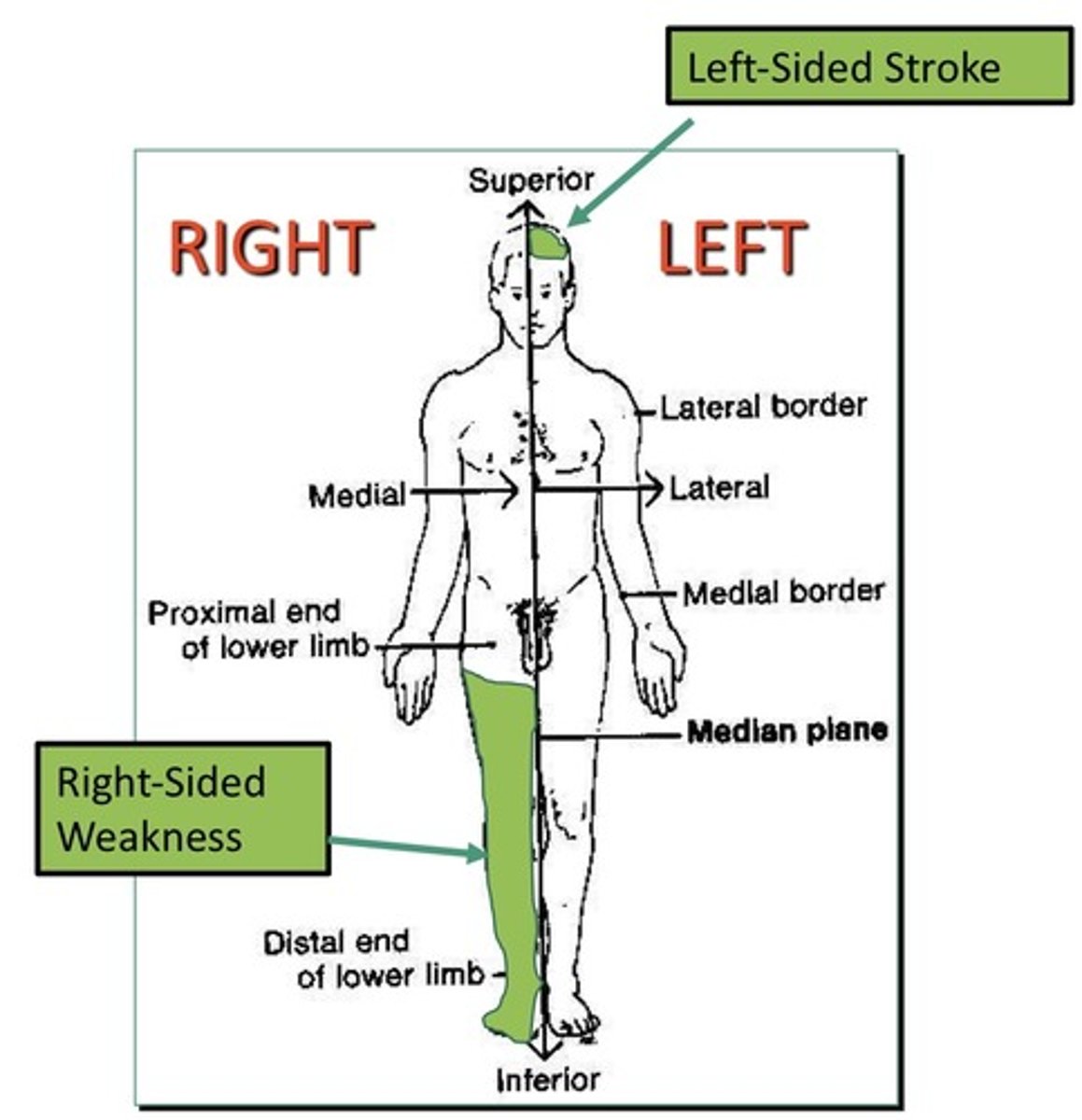
Ipsilateral
1. Refers to the lesion and deficit on the same side of the body
2. Can describe the relationship between the right eye and right ear
3. Refers to two things on the same side of the body
Contralateral
1. Refers to the lesion and deficit on the opposite side of the body
2. Can describe the relationship between the right eye and left ear
3. Refers to two things on the opposite side of the body
Bones that can be seen from the superior cranium
1. Frontal
2. Parietal
3. Occipital
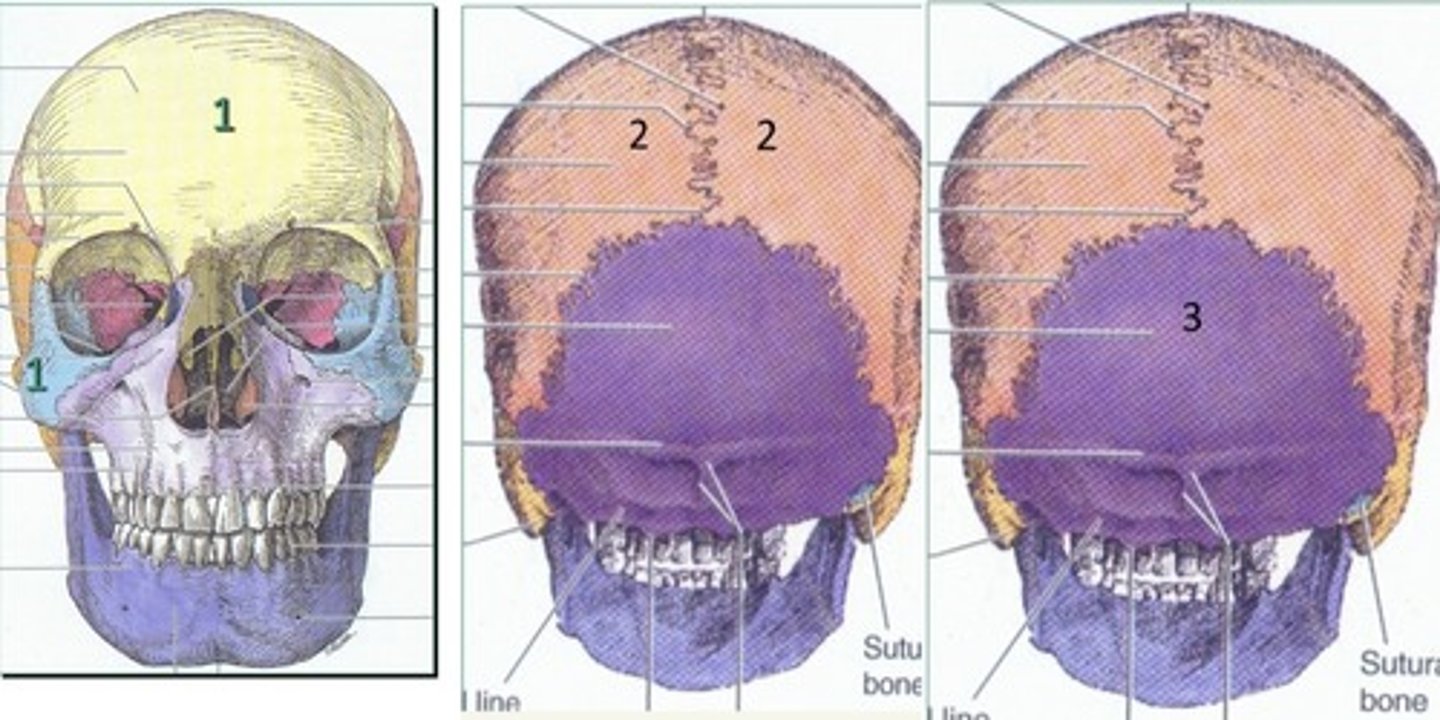
Bones that can be seen on the lateral cranium
1. Sphenoid
2. Temporal
3. Occipital
4. Frontal
5. Parietal
6. Zygomatic
Paired bones (8): My New Potty Trained Zebra Peed In Lake
1. Maxillary
2. Nasal
3. Parietal
4. Temporal
5. Zygomatic
6. Parietal
7. Inferior nasal conchae
8. Lacrimal
Solitary bones (6) VOMSEF
1. Vomer
2. Occipital
3. Mandibular (Mandible)
4. Sphenoid
5. Ethmoid
6. Frontal
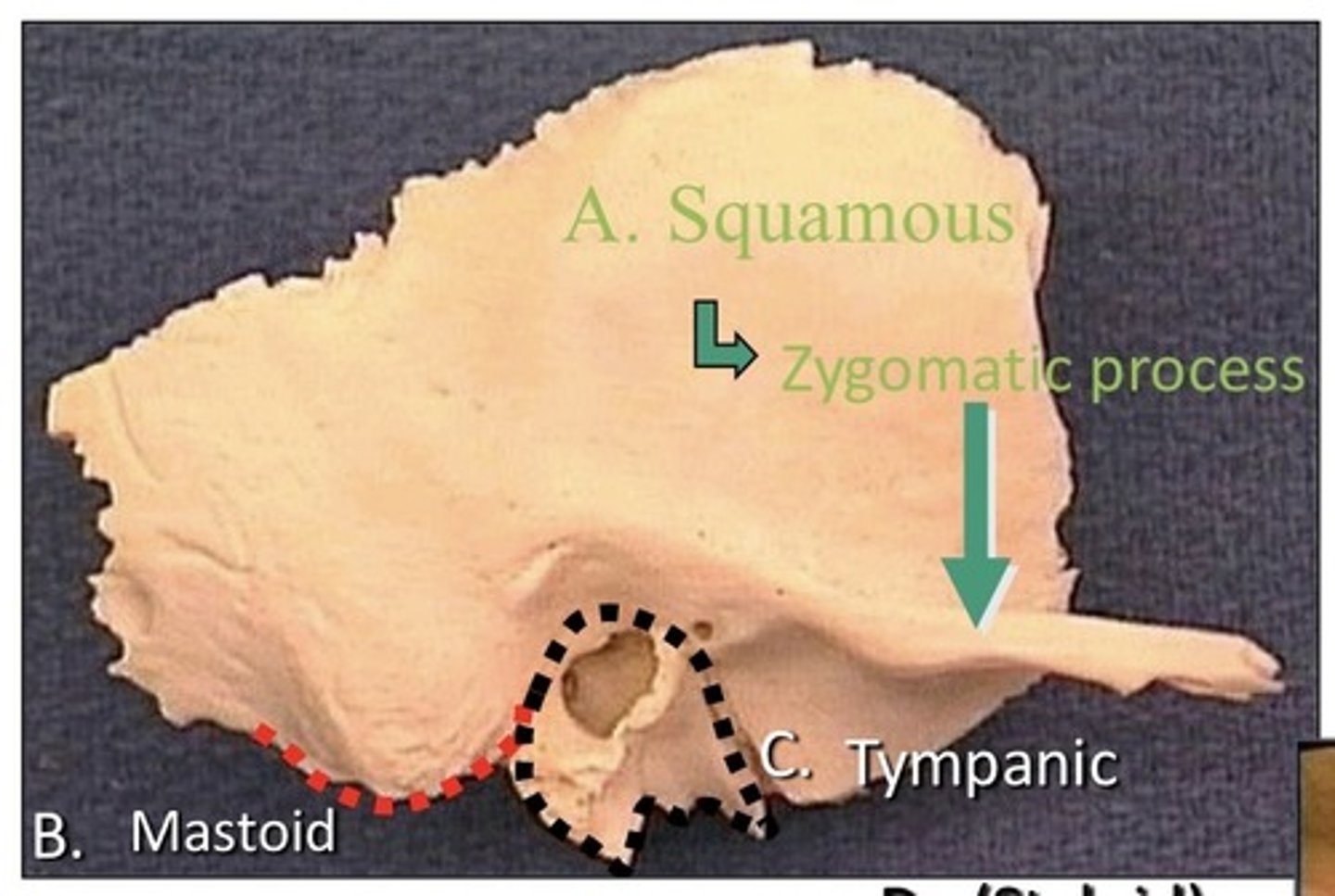
Temporal bone
1. Squamous
2. Tympanic
3. Petro-mastoid
4. Styloid
5. Has 4 parts
6. Paired bone
7. Lateral to sphenoid bone
8. Located in the middle cranial fossa
9. Anterior to occipital bone
10. Posterior to the frontal bone
11. Inferior to the parietal bone
12. Surrounds external auditory meatus
13. On the lateral aspect of the skull
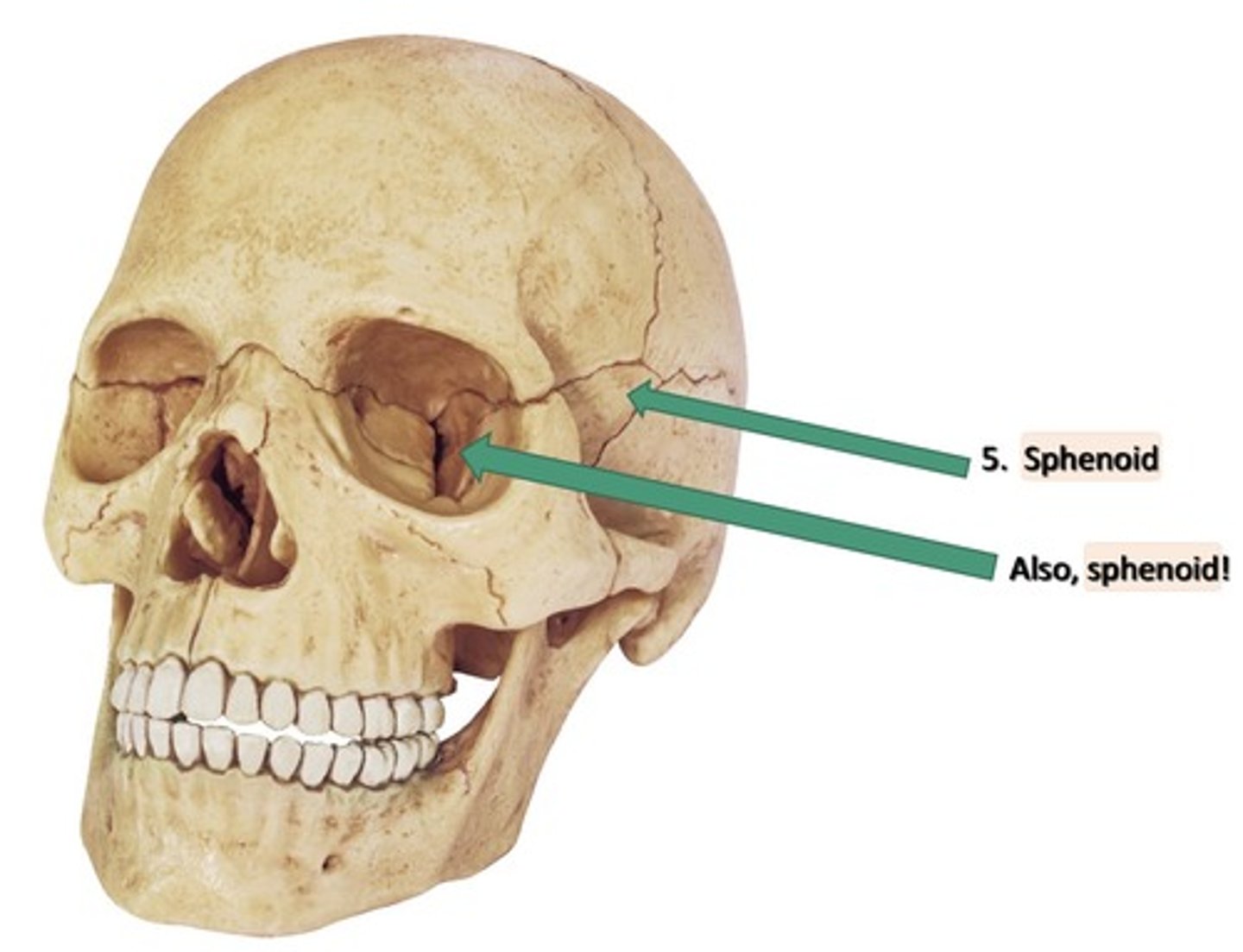
Sphenoid
1. On the lateral aspect of the skull
2. Inferior to the frontal bone
3. Anterior to the temporal bone
4. Posterior to the maxillary bone
5. Superior to the mandible
6. Lateral to the ethmoid
7. Has 4 parts:
8. Lesser wing
9. Greater wing
10. Pterygoid process (allows for jaw movement)
11. Body of this bone
12. Solitary
13. In the middle cranial fossa
14. Contains a sinus
15. In the lateral wall of the orbit
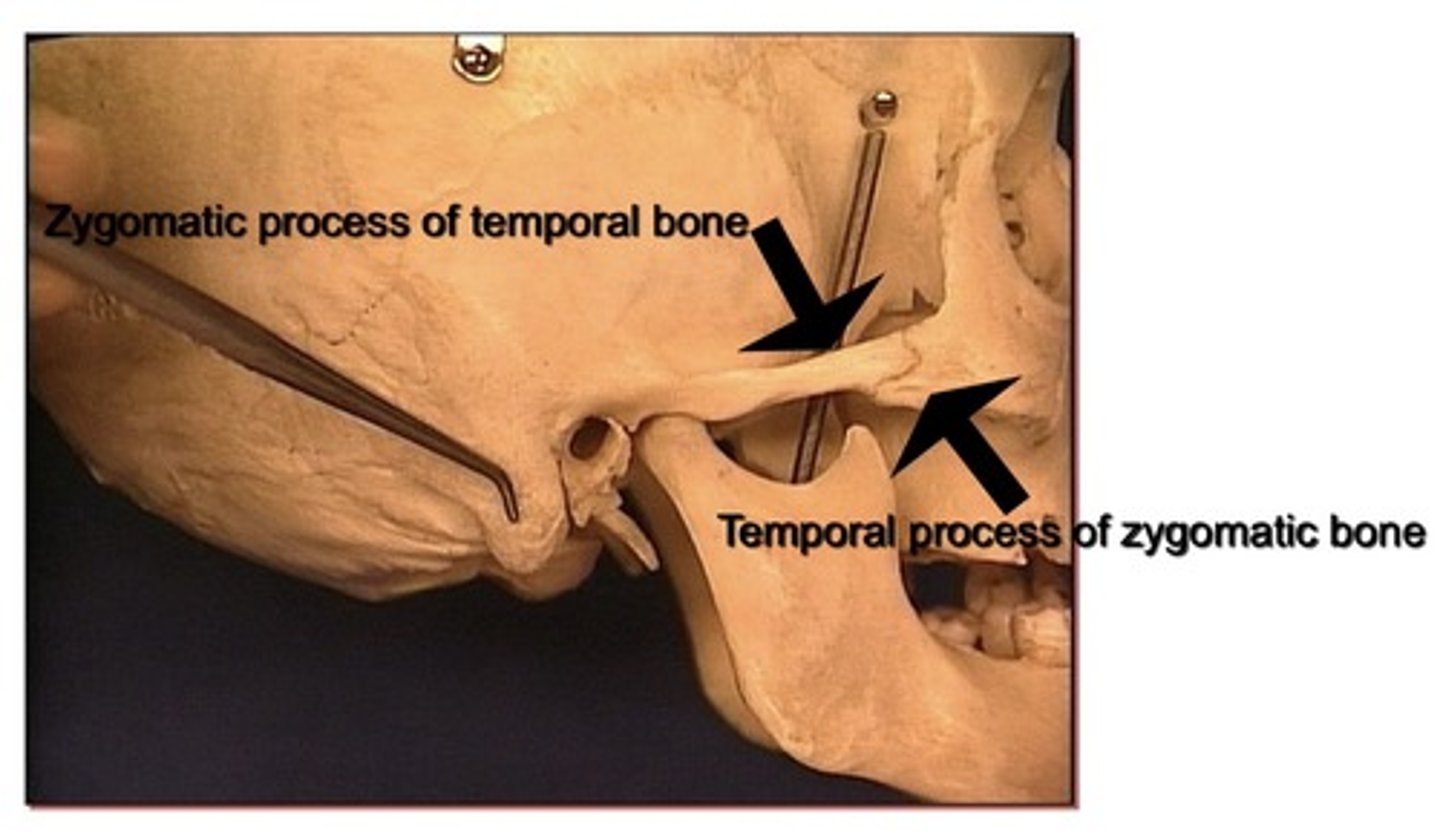
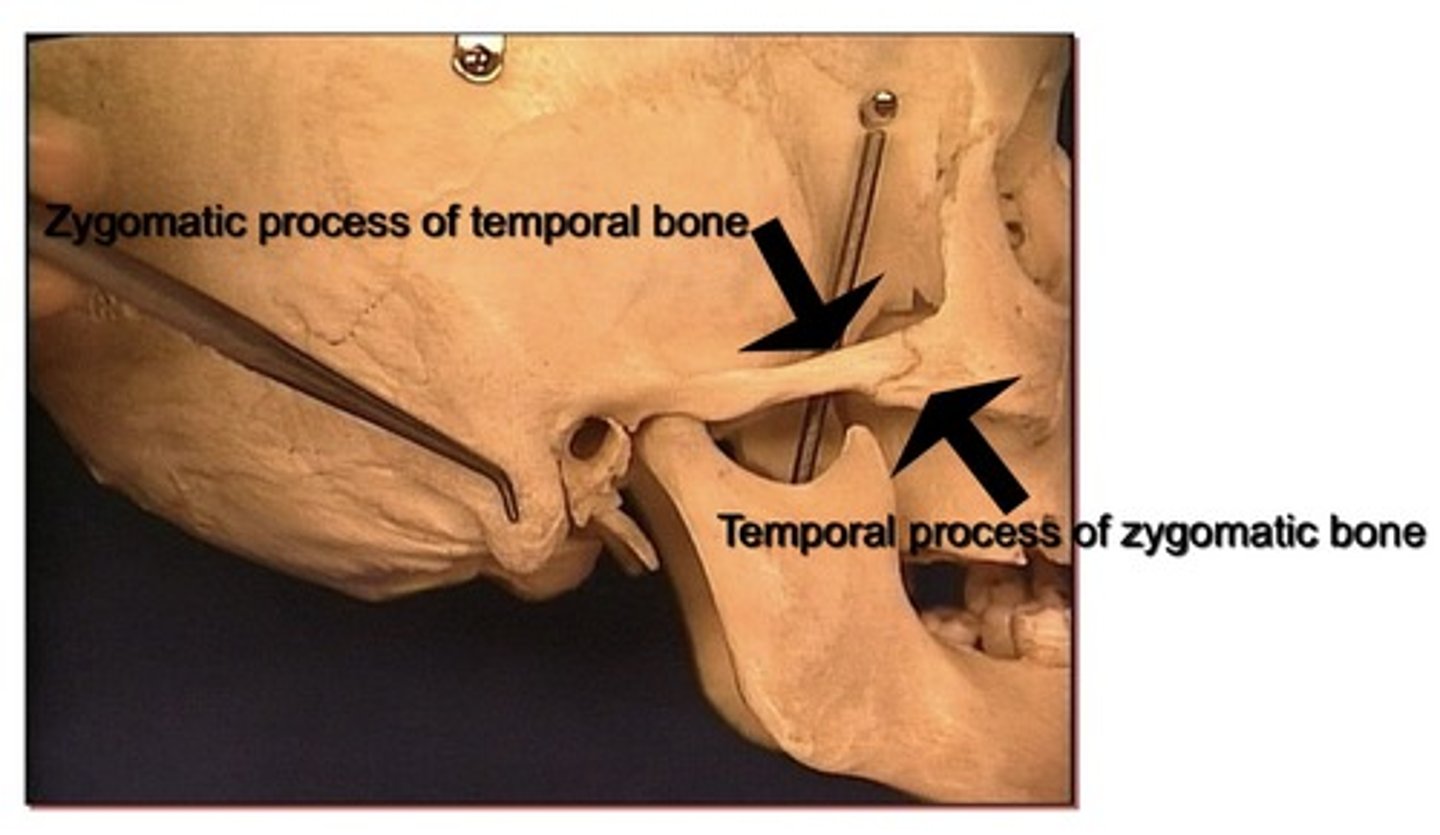
Bones that form zygomatic arch
1. Temporal process of the zygomatic (closer to the face)
2. Zygomatic process of the temporal
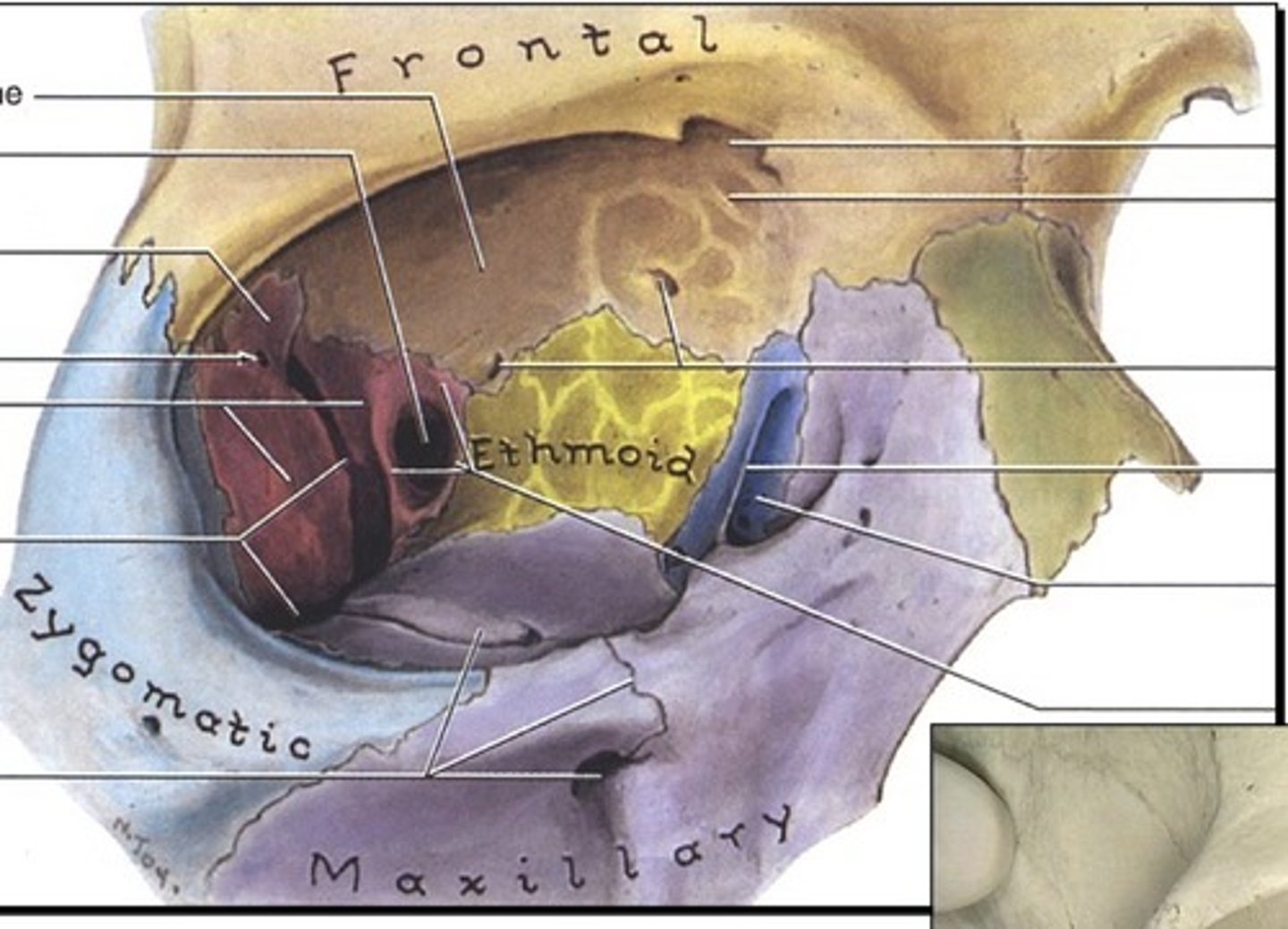
Bones of the inferior orbit
1. Maxillary
2. Zygomatic
3. Palatine
Bones of the medial orbit
1. Sphenoid
2. Ethmoid
3. Lacrimal
4. Maxillary
Bones of the lateral orbit
1. Zygomatic
2. Great wing of sphenoid
Bones of the superior orbit
1. Frontal
2. Lesser wing of sphenoid
Located in the posterior cranial fossa
1. Occipital lobe
2. Cerebellum
Located in the middle cranial fossa
1. Sphenoid bone
2. Temporal bone
3. Temporal lobe
Located in the anterior cranial fossa
1. Frontal bone
2. Ethmoid bone
Maxillary
1. Contains a sinus
2. In the inferior wall of the orbit
3. Immediately lateral to the nasal bone
4. Immediately medial to the zygomatic
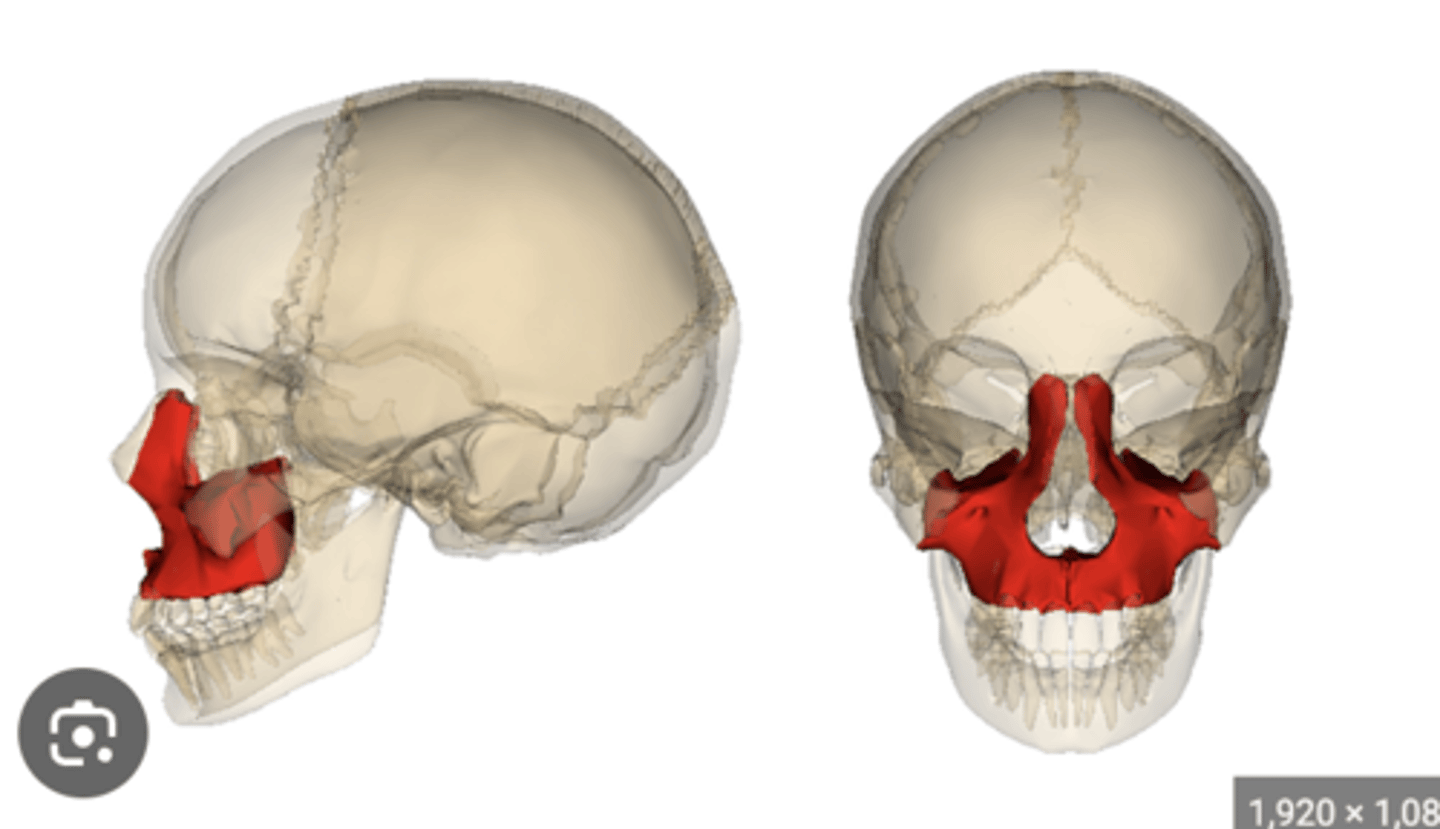
Ethmoid
1. Solitary
2. Cristal galli
3. Cribriform plate
4. Horizontal plate
5. Orbital plate
6. Air cells
7. Perpendicular plate
8. Has more than 4 parts
9. Middle Nasal Concha
10. Superior Nasal concha
11. In the anterior cranial fossa
12. Is in the medial wall of the orbit
13. Immediately superior to the inferior nasal conchae
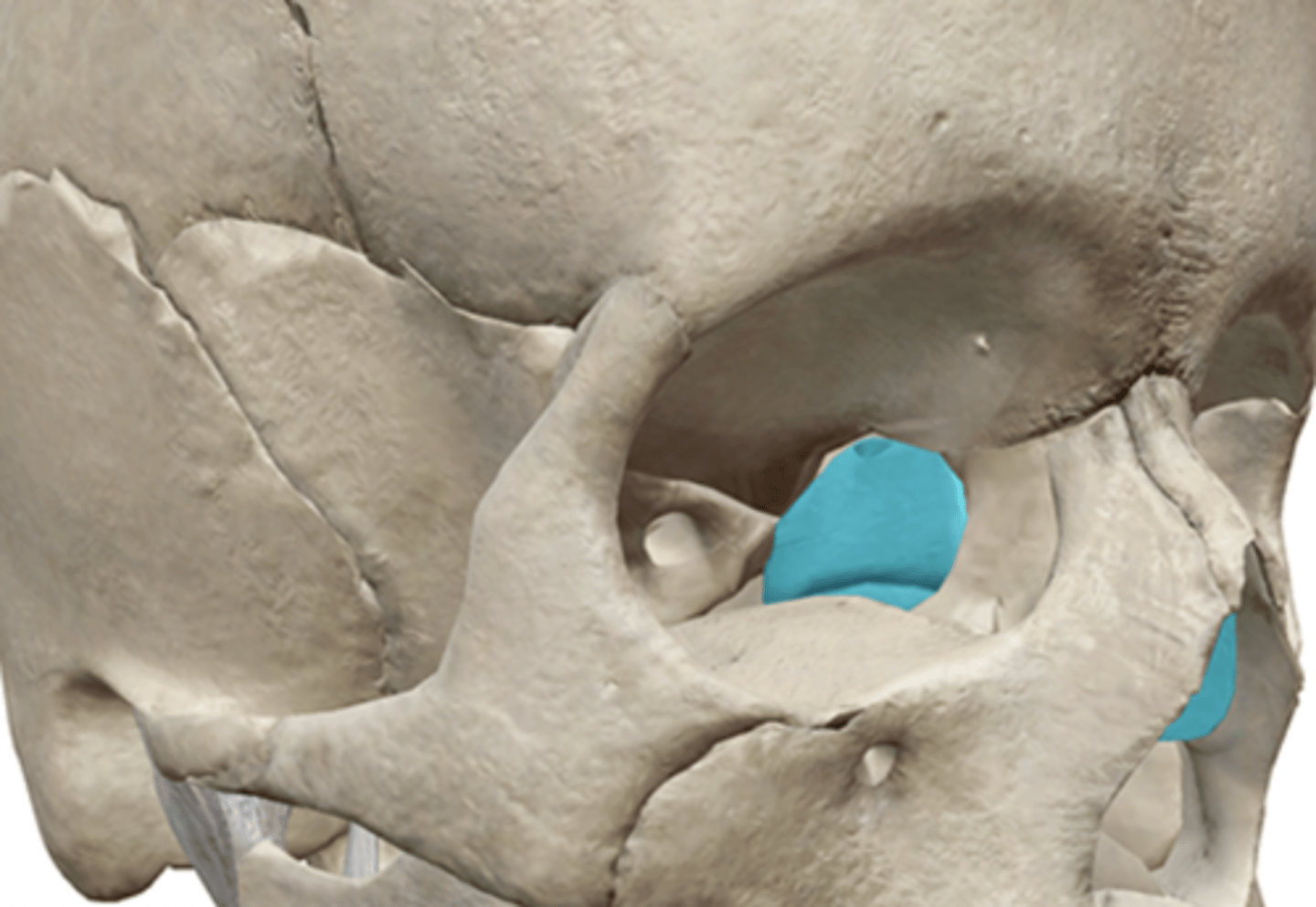
Lacrimal Bone
1. Paired bone
2. In the medial wall of the orbit
3. Immediately posterior to the maxillary bone
4. In the orbit
5. Bone between the maxillary and ethmoid
Mandible
1. Coronoid process
2. Condyle
3. Angle
4. Body
5. Ramus
6. More than 4 parts
Vomer
1. Latin for plowshare
2. Inferior to the nasal bones
3. Immediately superior to the mandible
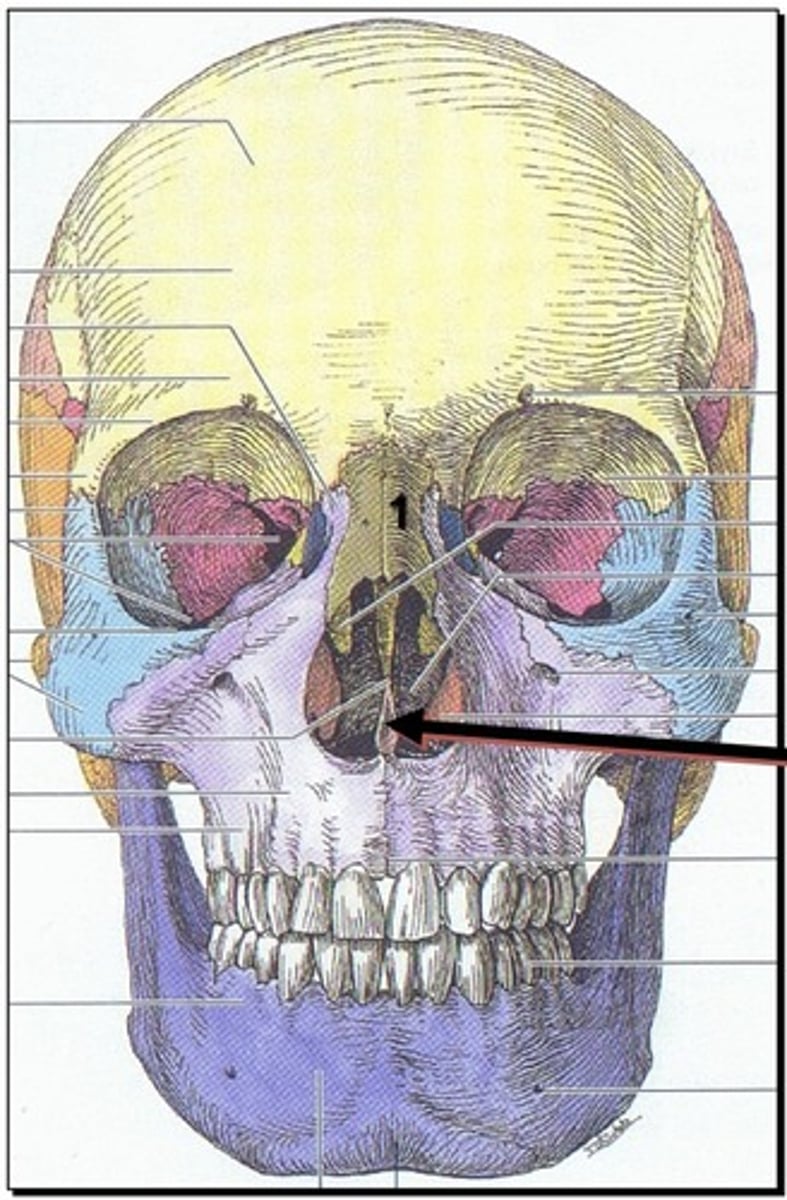
Zygomatic bone
1. Immediately lateral to the maxillary bone
2.Inferior lateral to the frontal bone in the orbit.
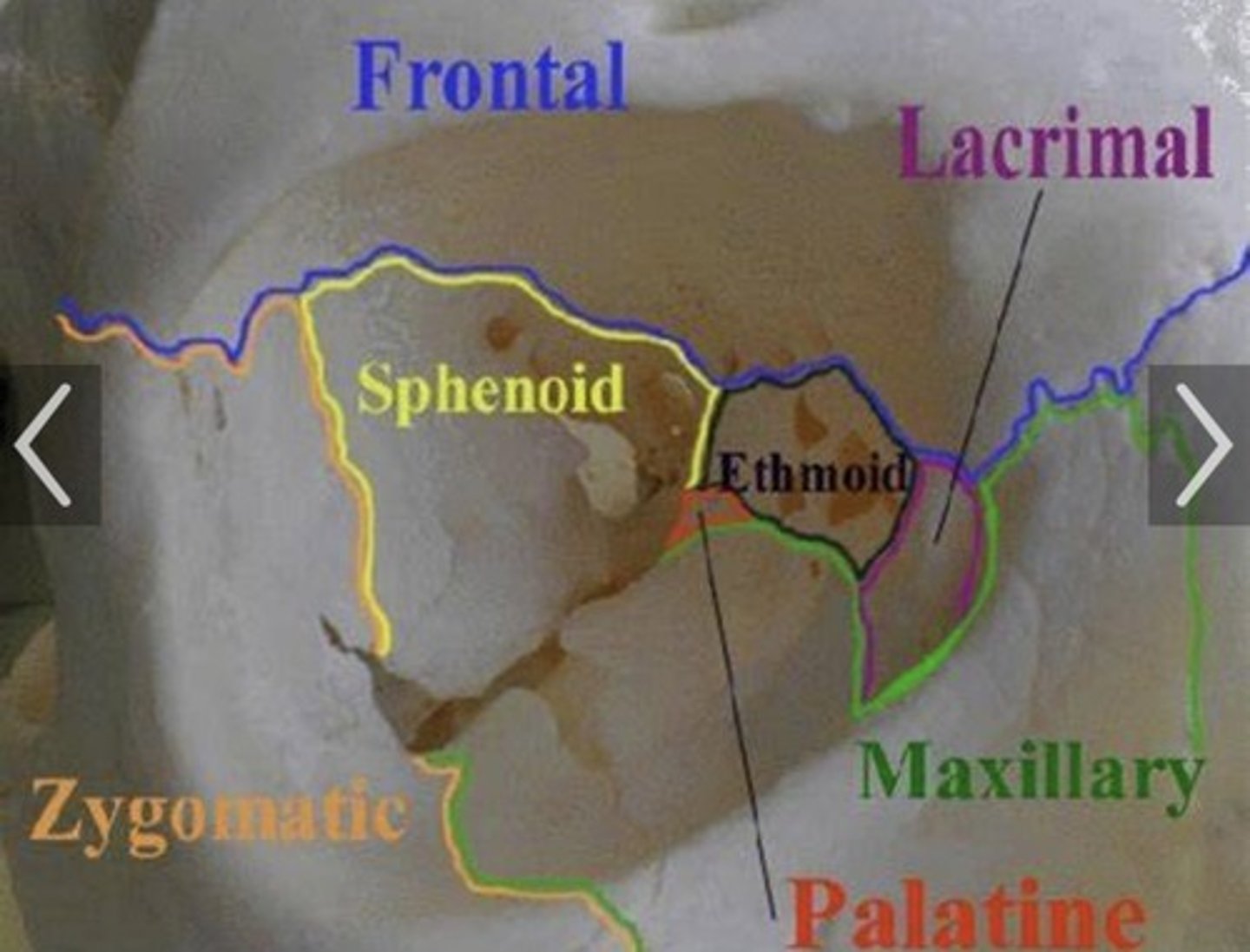
Bones of the orbital margin
1. Frontal
2. Maxillary
3. Zygomatic
4. Ethmoid
5. Sphenoid
6. Palatine
7. Lacrimal
What angle can you see the frontal lobe from?
1. Top
2. Lateral
What angle can you see the parietal lobe from?
1. Top
2. Side
3. Back
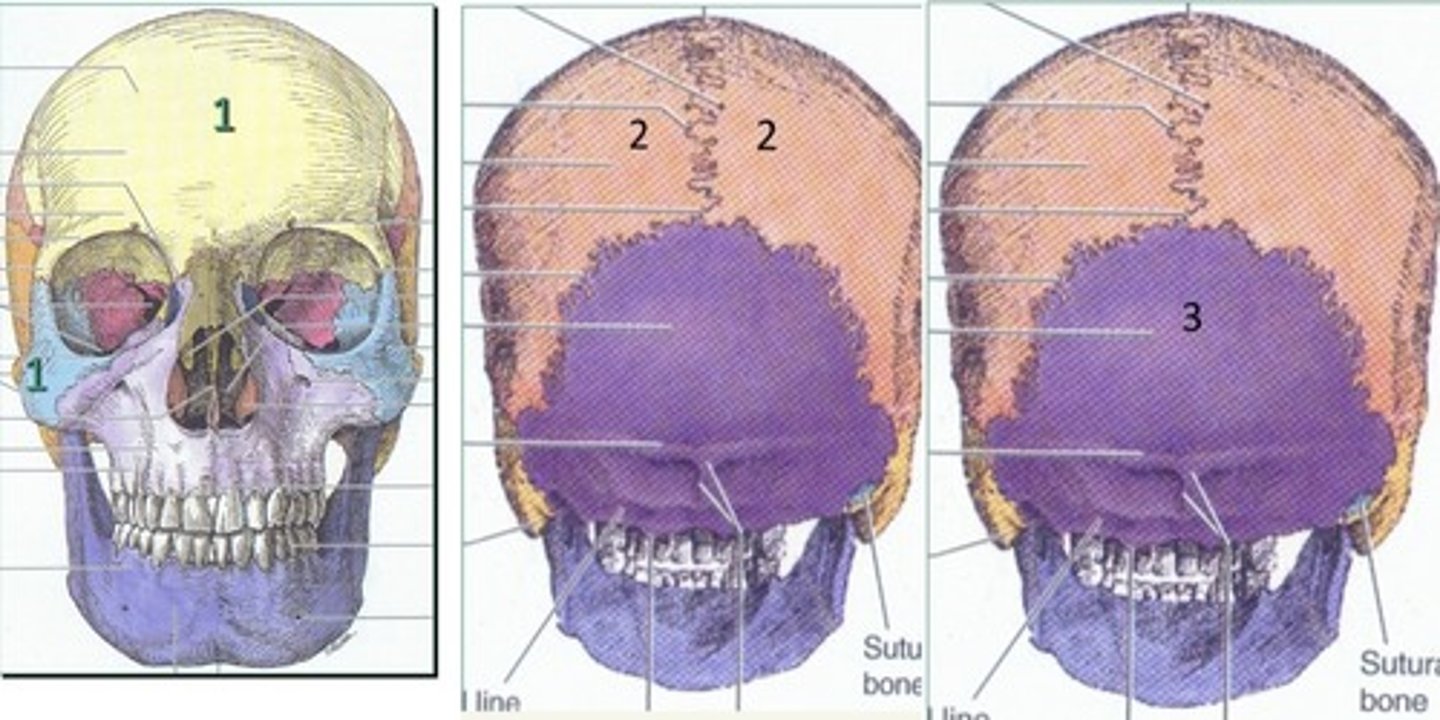
What angle can you see occipital lobe from?
1. Top
2. Side
3. If you flip it
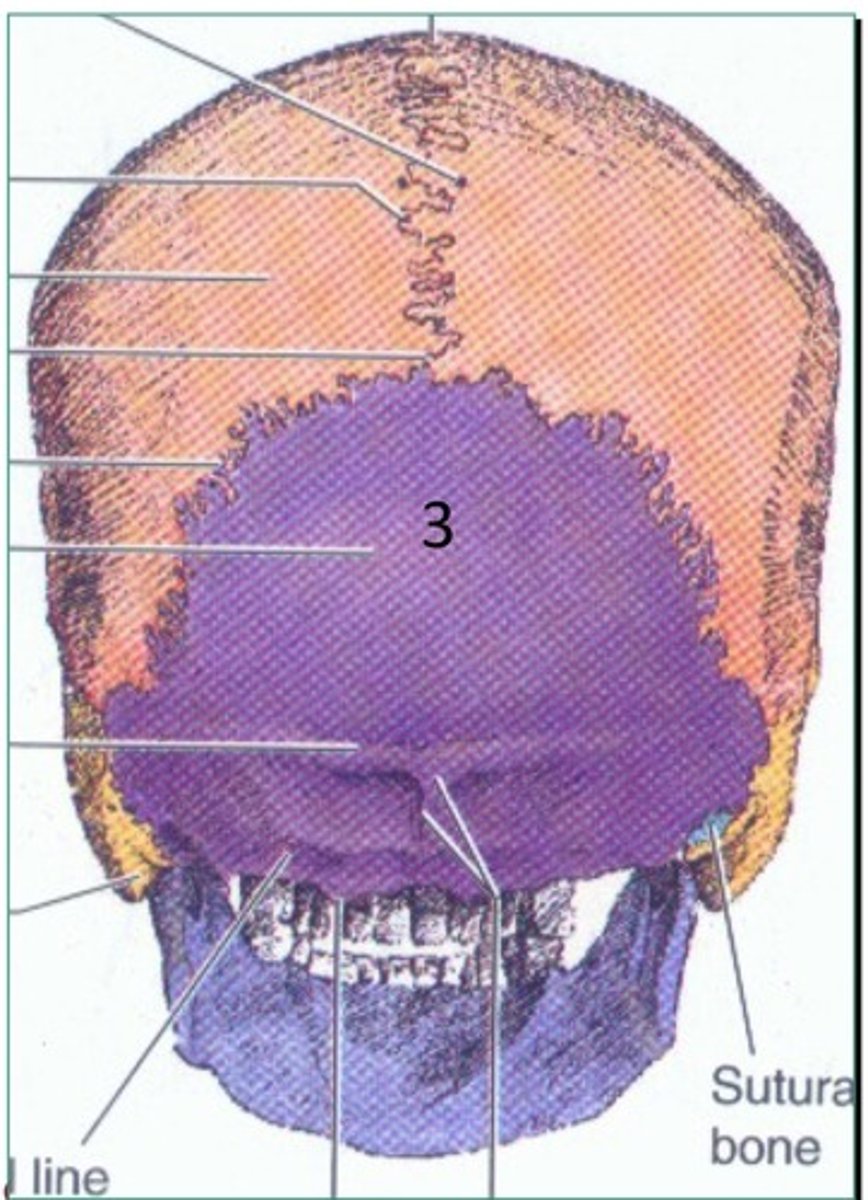
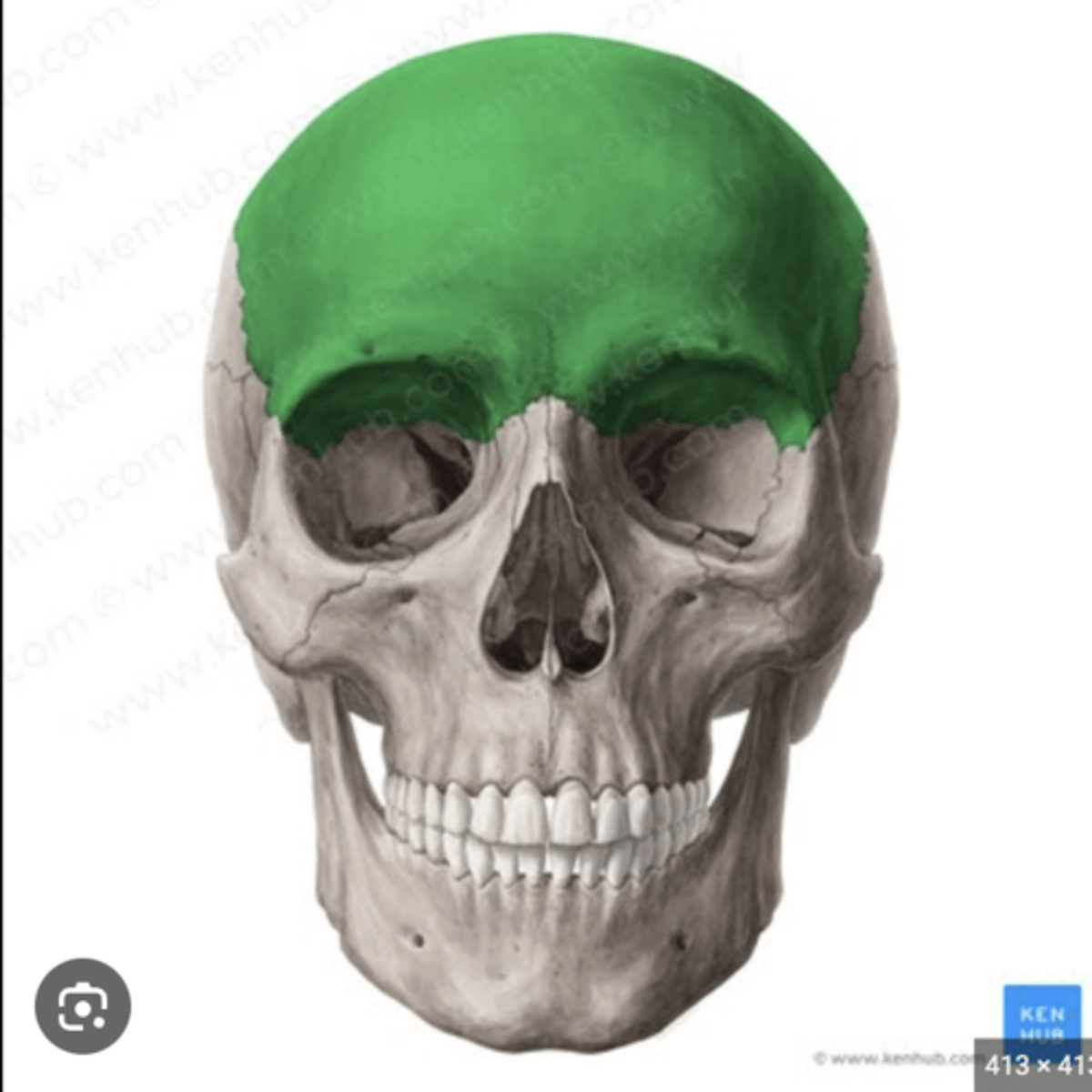
Frontal bone
1. Anterior to the occipital bone
2. Forms the roof of the orbit
3. In the anterior cranial fossa
4. Contains a sinus
5. In the superior wall of the orbit
6. Immediately anterior to parietal bone
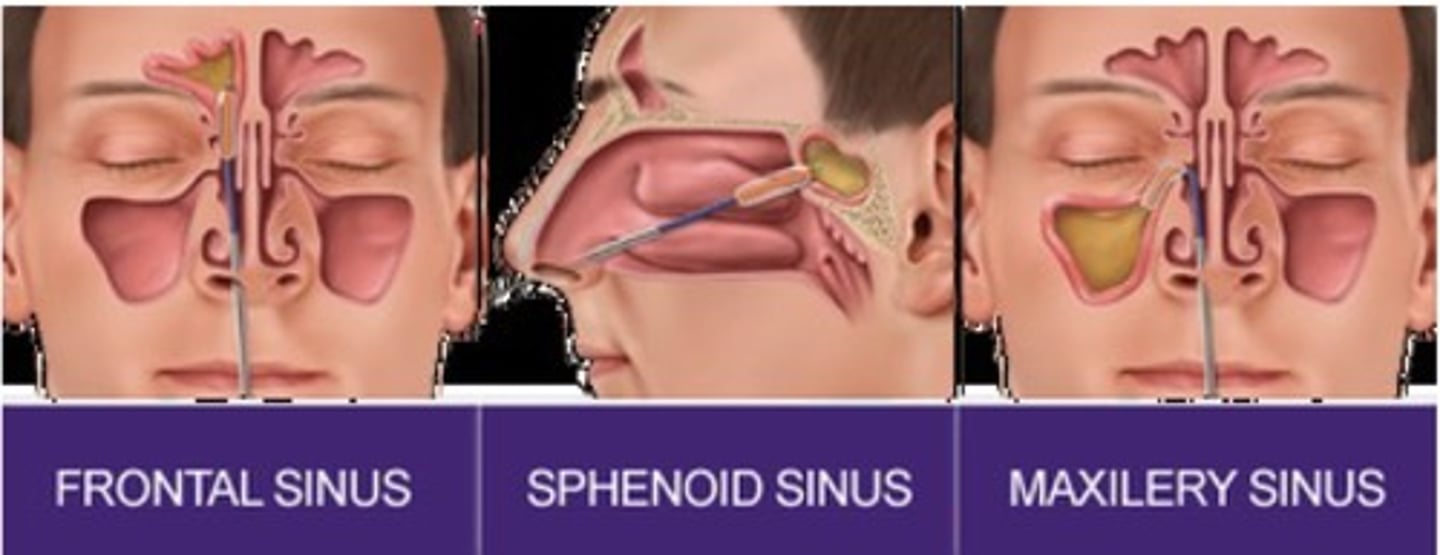
Sinuses
1. Frontal
2. Sphenoid
3. Maxillary
Which of the following bones cannot be seen from a lateral view of the skull?
Ethmoid
Which one is in middle cranial fossa?
Sphenoid
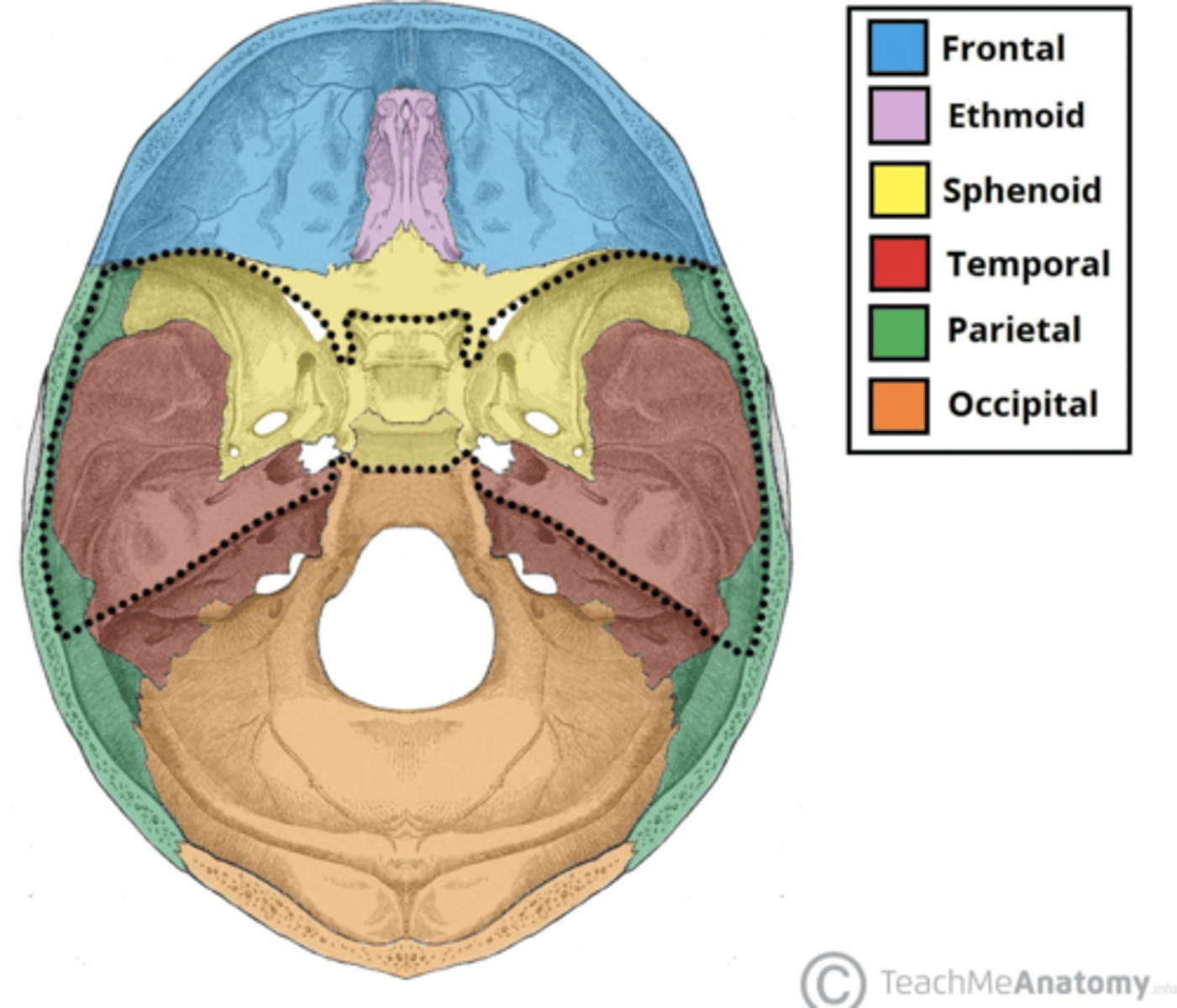
Know where parietal bone is on the skull
posterior the frontal lobe
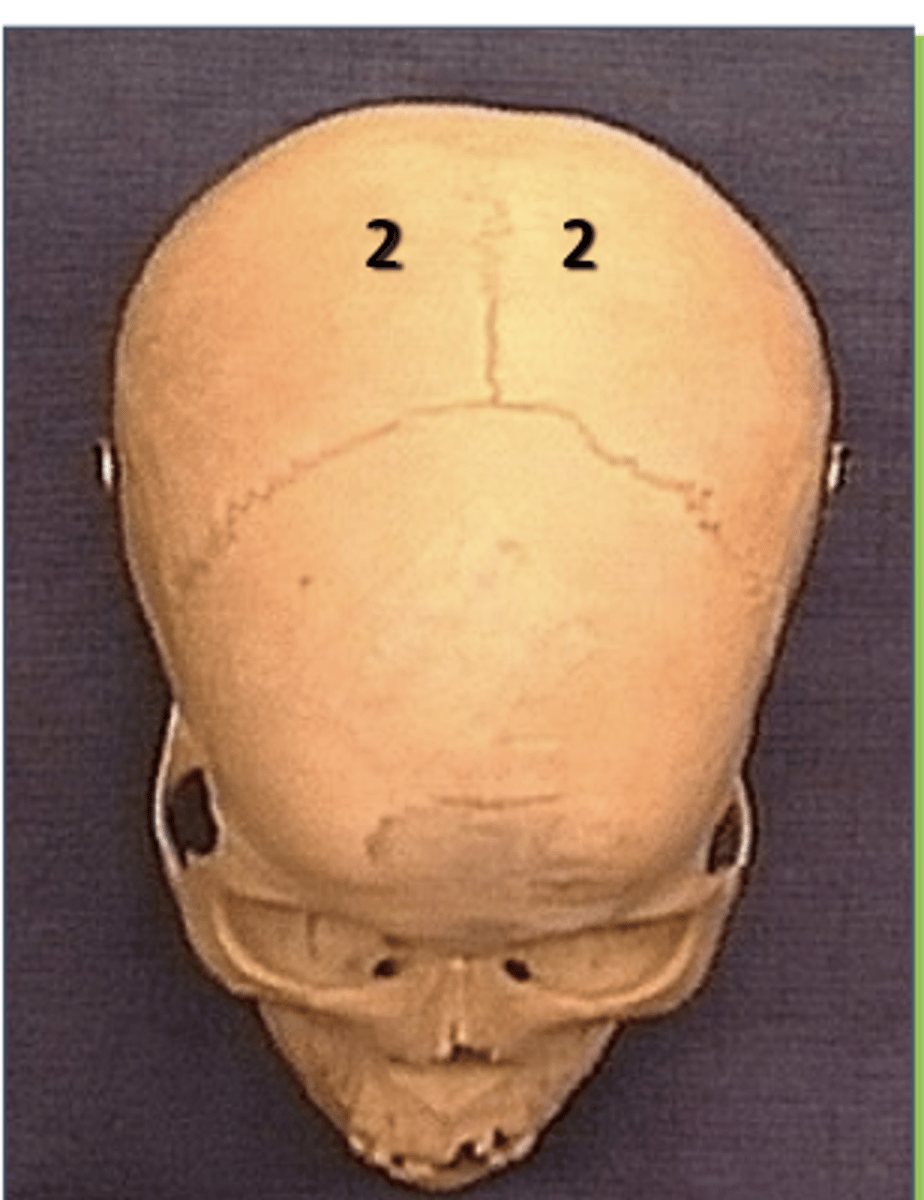
Know where the occipital bone is on the skull
posterior to the parietal lobe
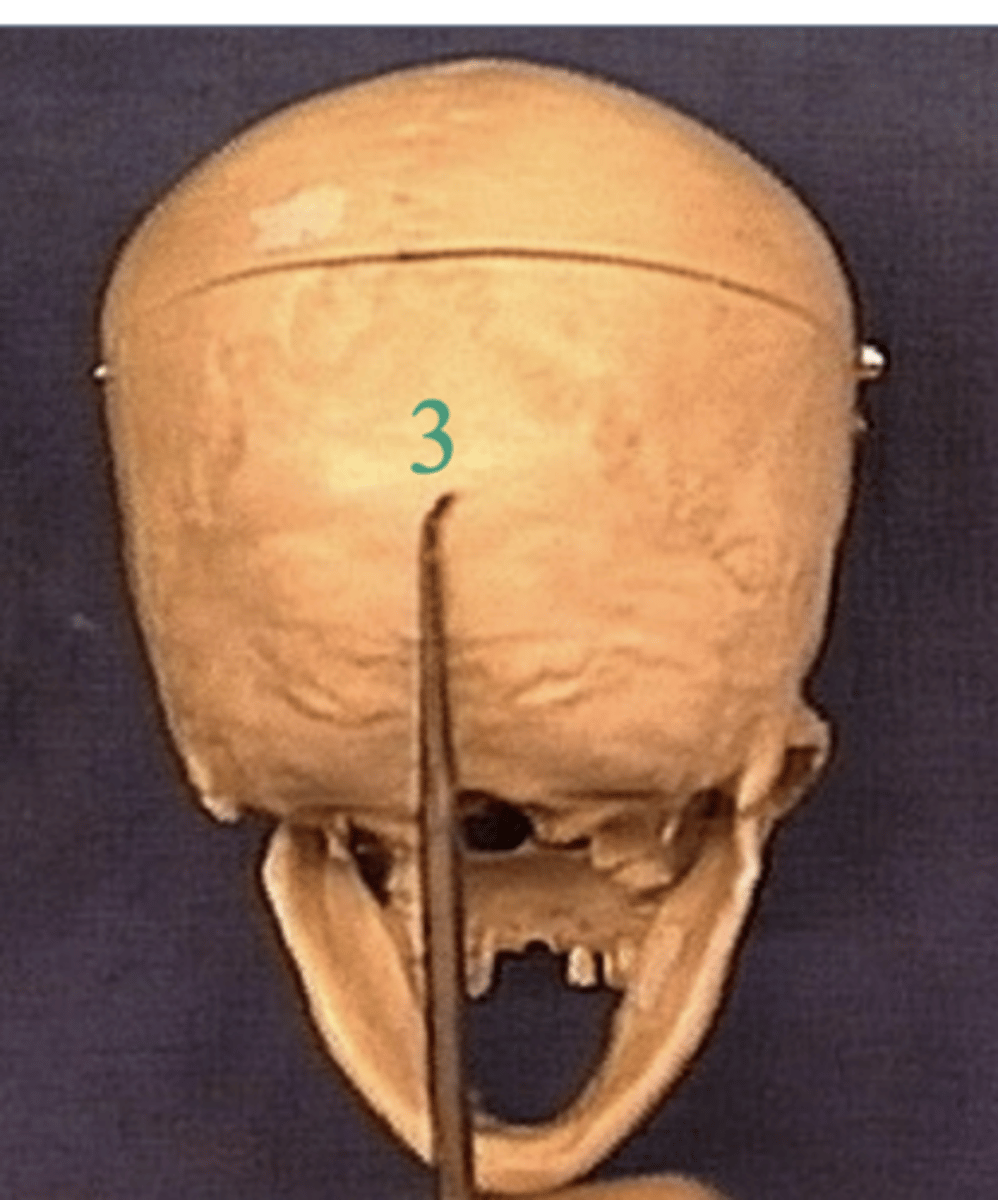
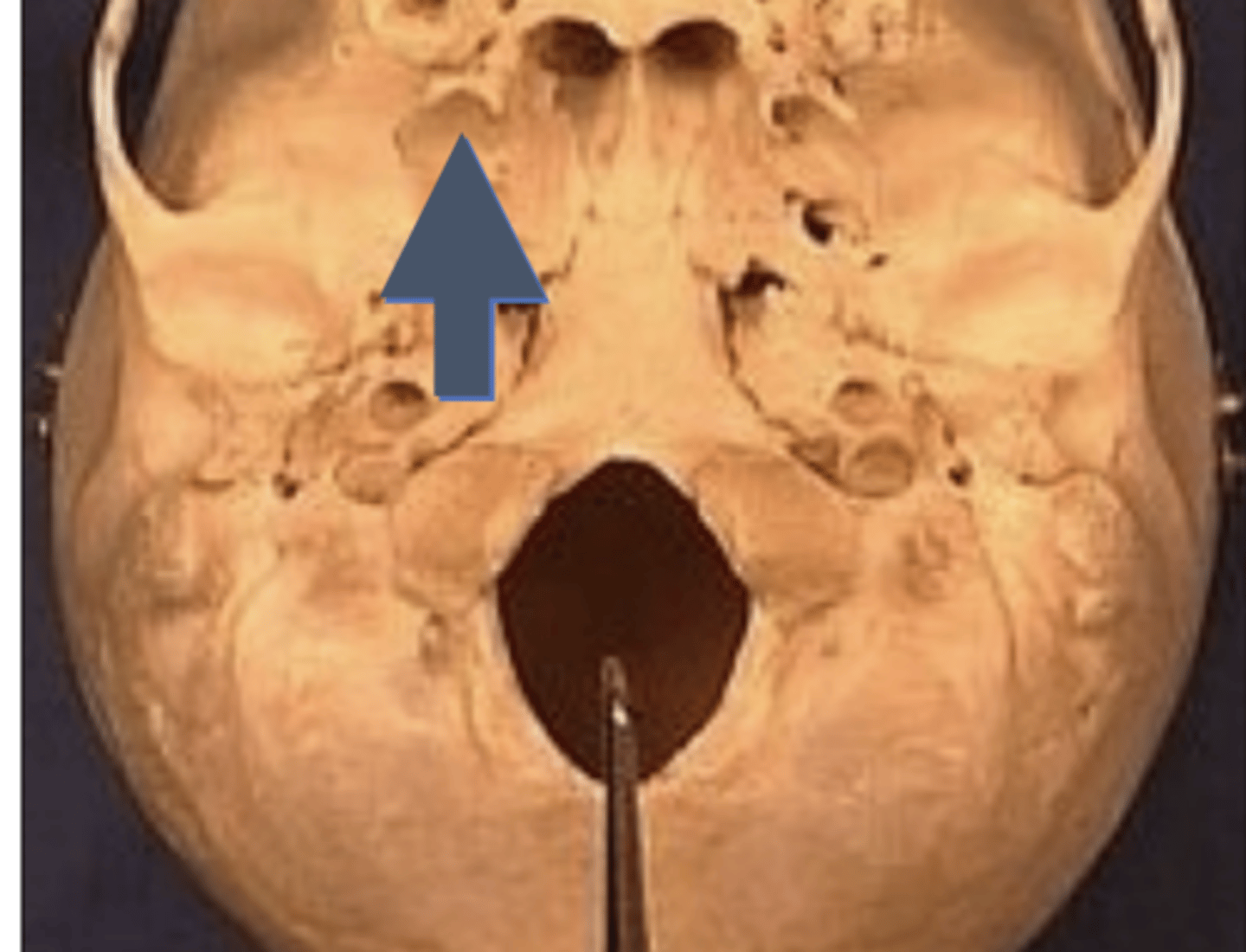
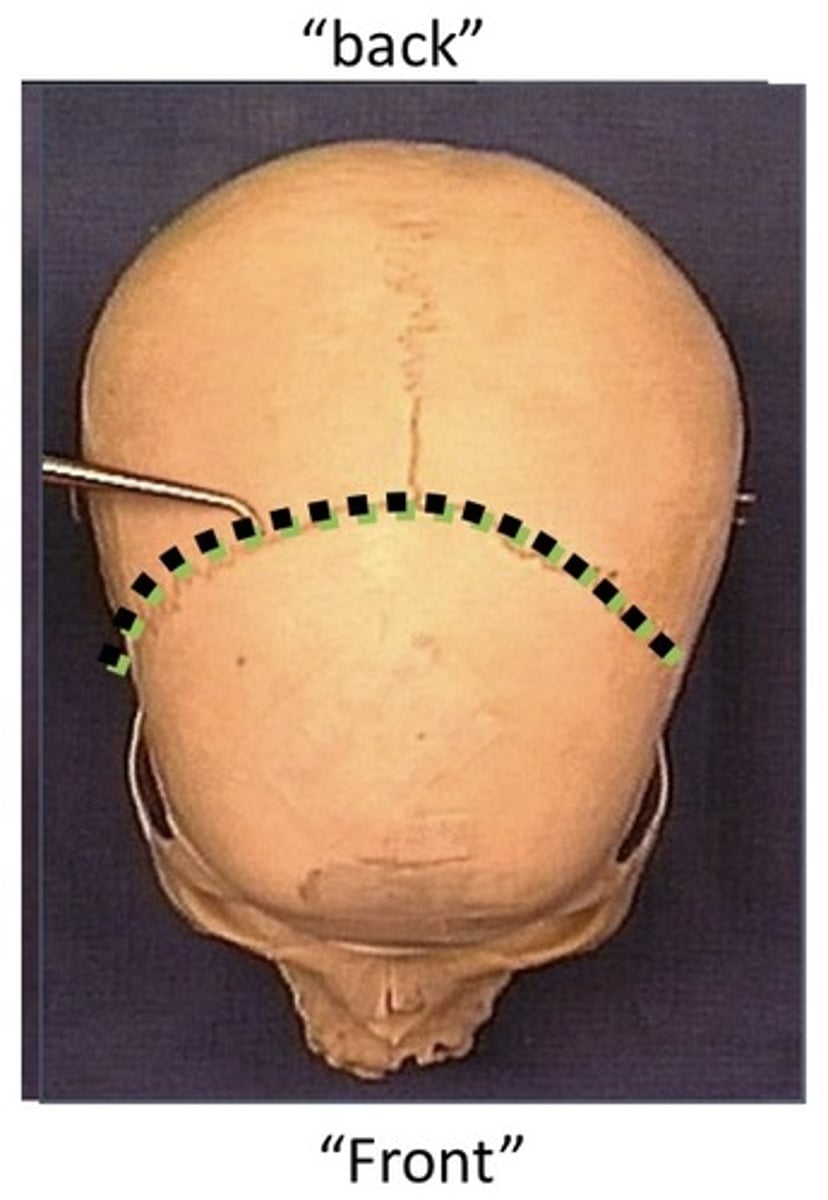
What type of cut is this picture?
axial
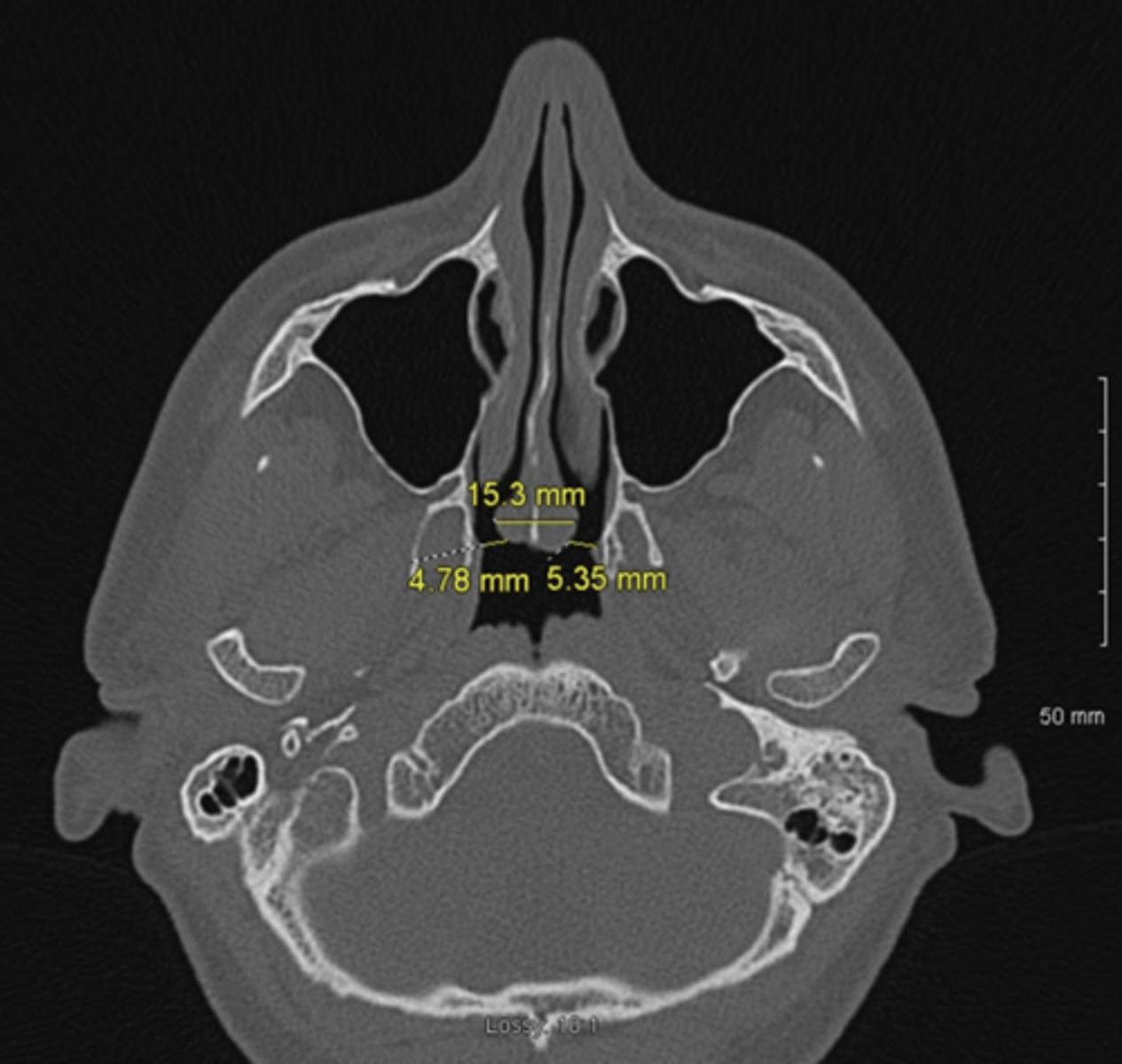
Foramen
Hole
Fissure
Opening, "Ditch" with length
Name the fissures
1. Superior orbital fissure
2. Petrotympanic fissure
3. Pterygomacillary fissure
Superior orbital fissure
1. Located superior in the orbit
2. Formed by the lesser and greater wing of sphenoid
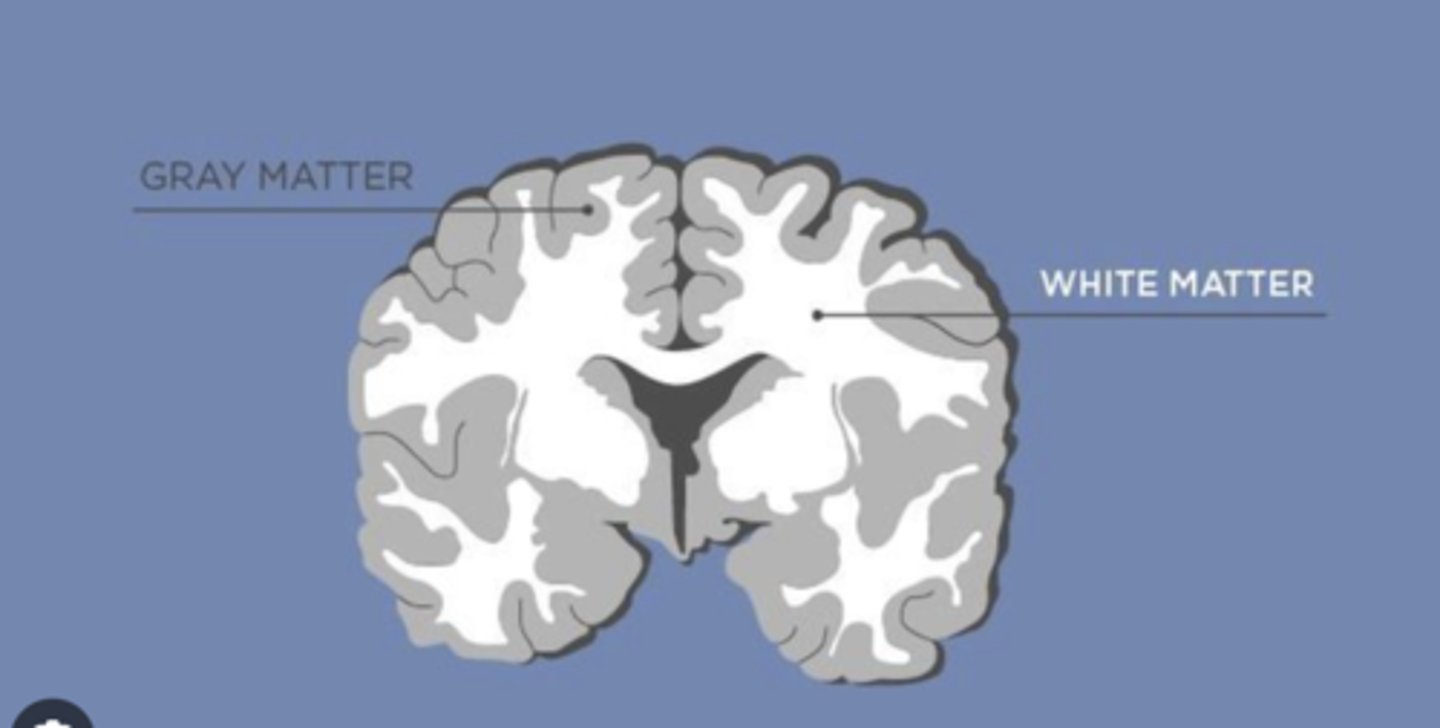
In the brain, we refer to gray matter as:
1. Neuronal cell body
2. Where the cell body is (more external)
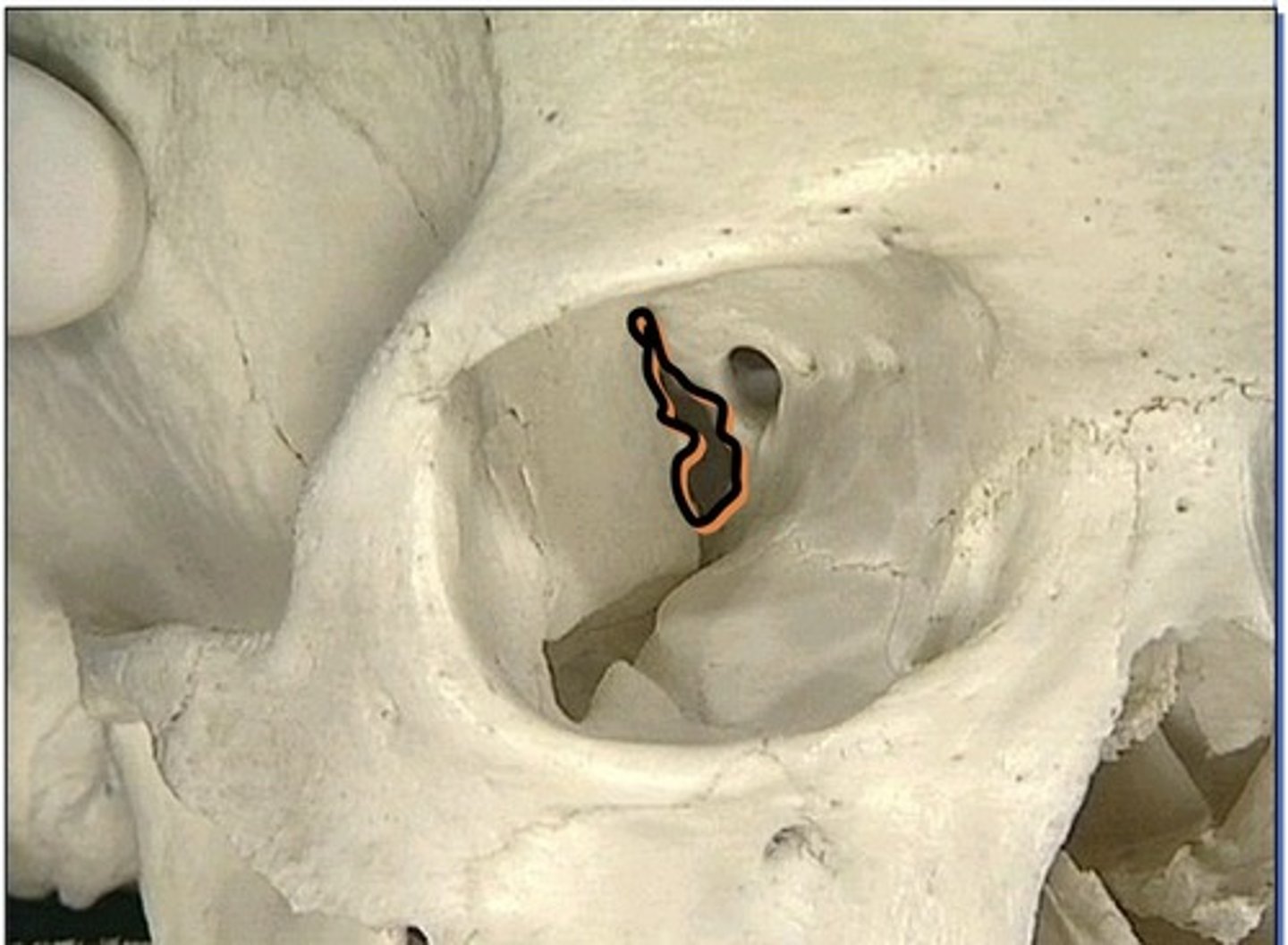
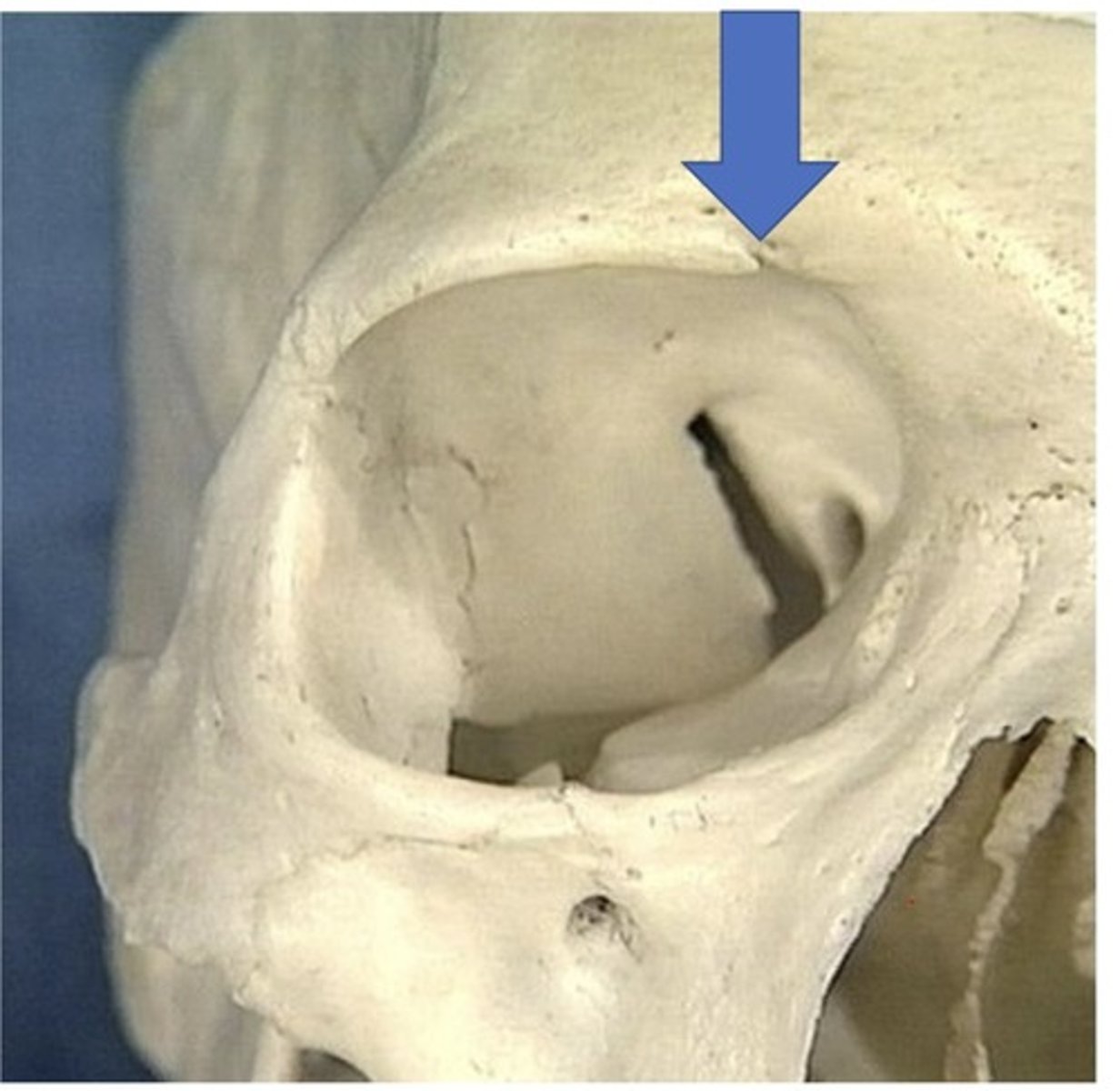
Supraorbital foramen
1. May be a notch instead of a foramen in some
Name the foramens
1. Optic foramen
2. Infraorbital foramen
3. Supraorbital foramen
4. Anterior ethmoidal foramen
5. Posterior ethmoidal foramen
6. Zygomatic-orbital foramen
7. Zygomatic-facial foramen
8. Zygomatic-temporal foramen
9. Foramen rotundum
10. Foramen ovale
11. Foramen spinosum
12. Foramen lacerum
13. Foramen Jugular
14. Foramen Magnum
15. Anterior condyloid foramen (hypoglossal)
16. Posterior condyloid foramen
17. Stylomastoid foramen
18. Carotid foramen
Optic foramen
1. In the lesser wing of sphenoid

Infraorbital foramen
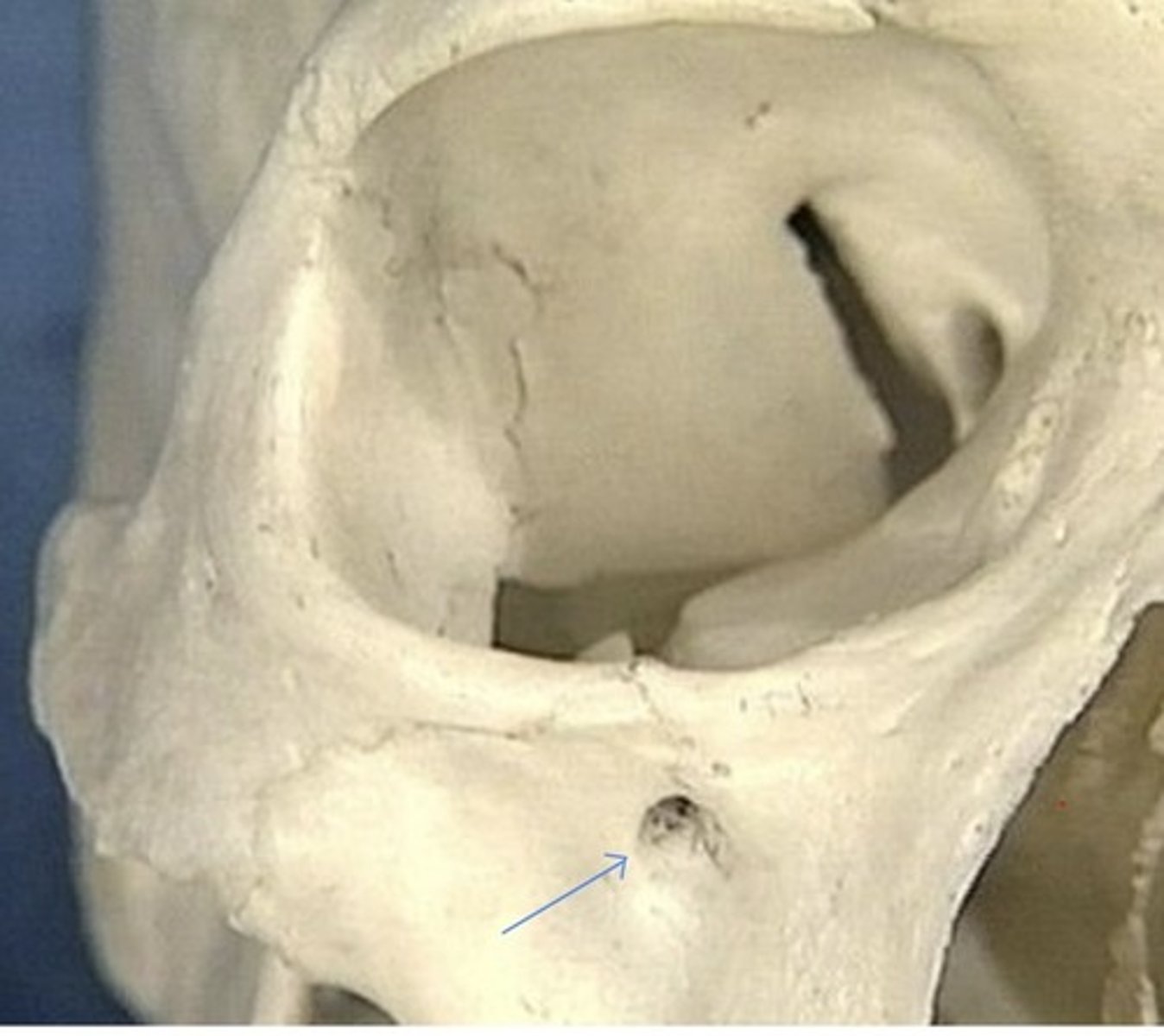
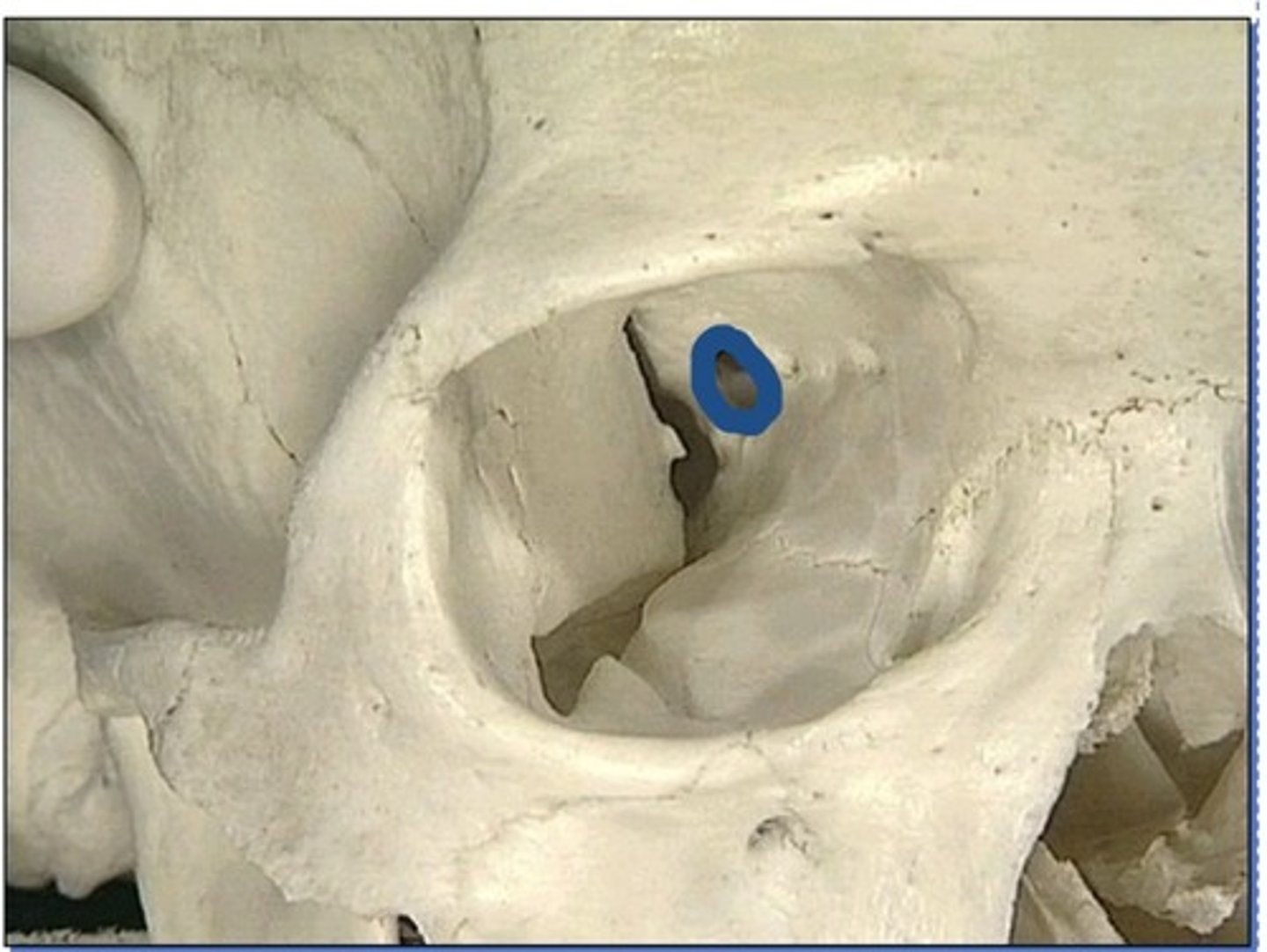
Foramen in medial orbit
1. Anterior ethmoidal foramen
2. Posterior ethmoidal foramen
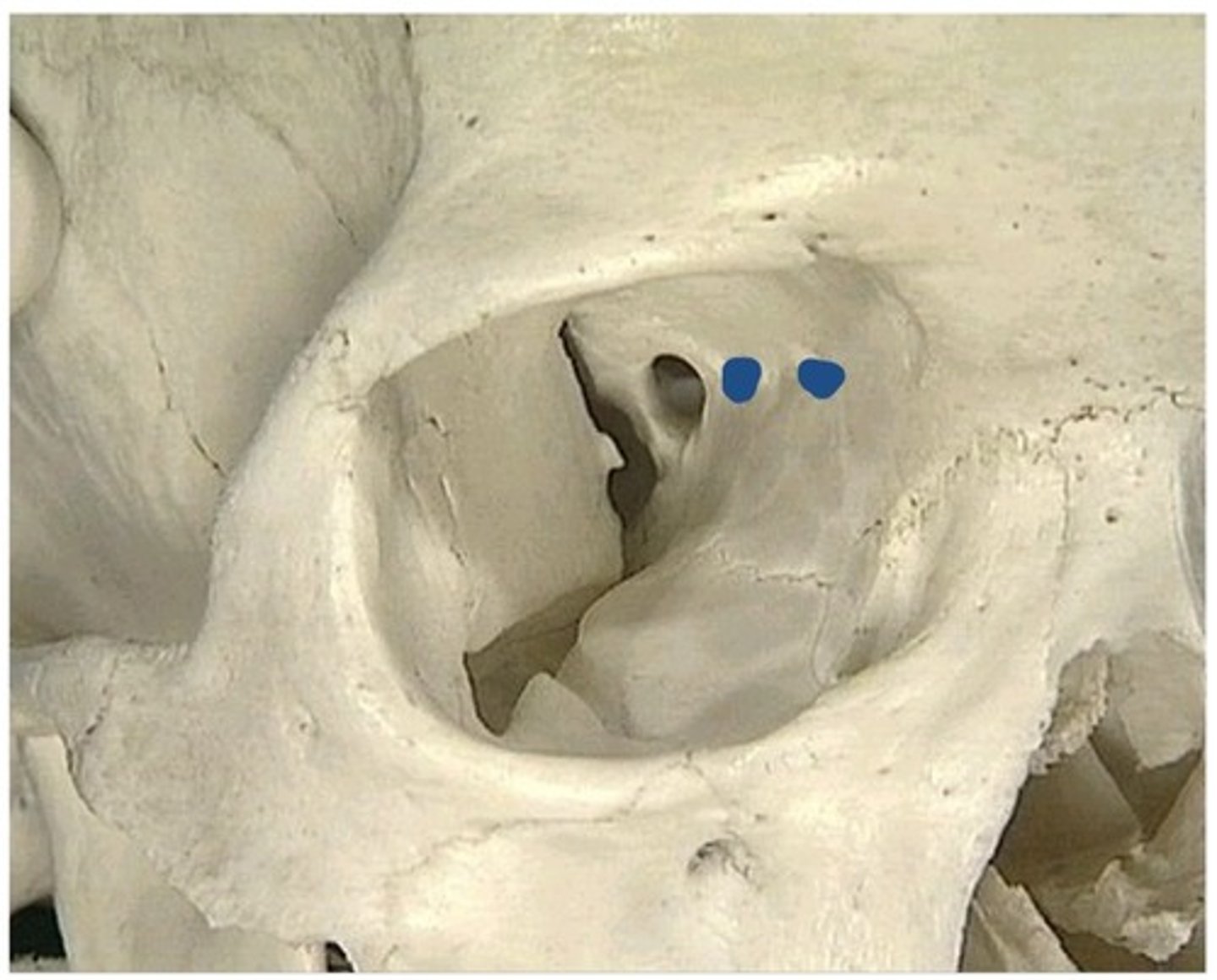
Orbital openings
1. Nasolacrimal canal
2. Zygomatico-orbital foramen (lateral)
3. Anterior ethmoidal foramen (medial)
4. Posterior ethmoidal foramen (medial)
Zygomatico-facial foramen
1. In zygomatic bone, on the face
2. There are 2 more small foramen like this
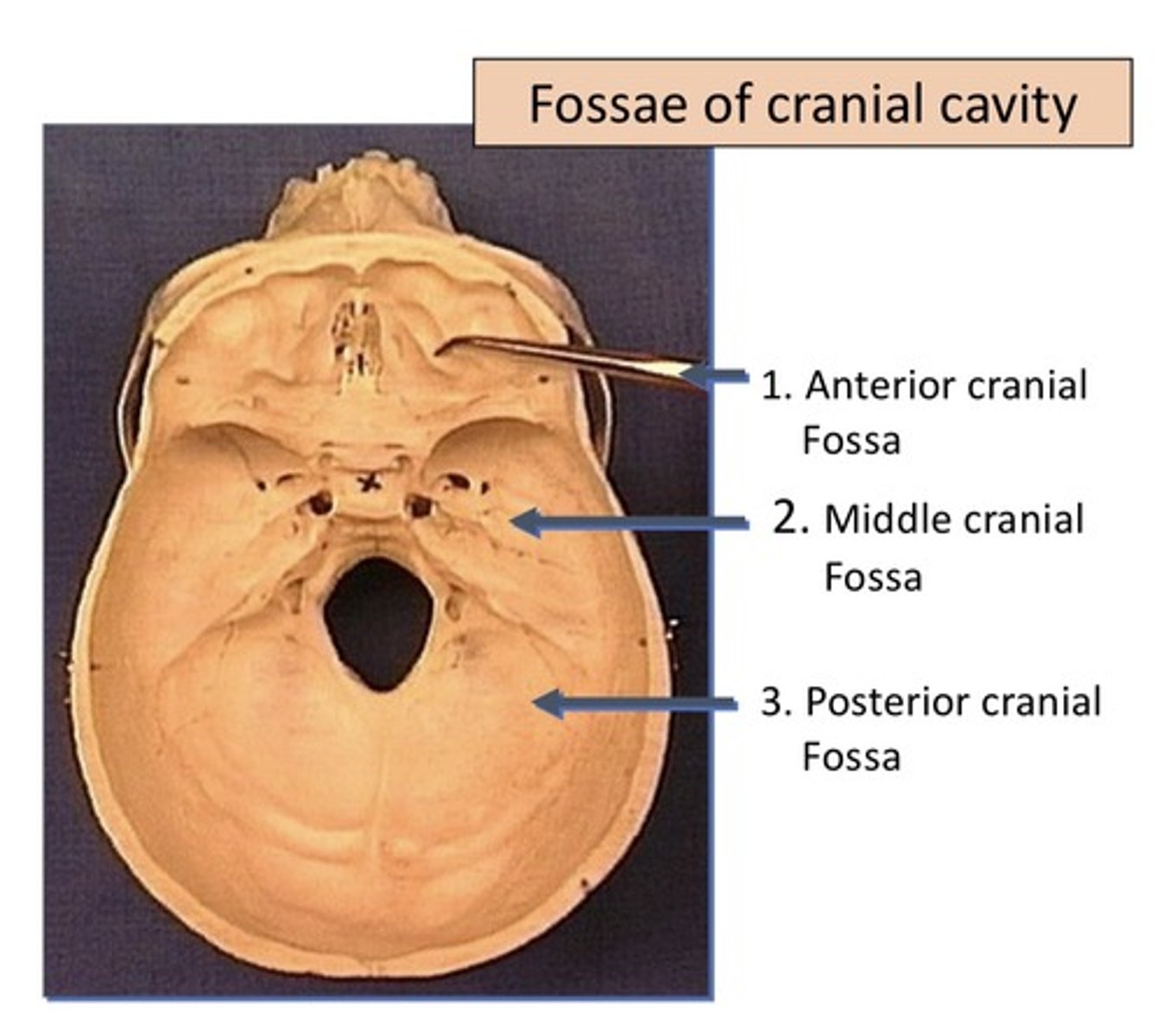
Fossae of cranial cavity
1. Anterior cranial fossa
2. Medial cranial fossa
3. Posterior cranial fossa
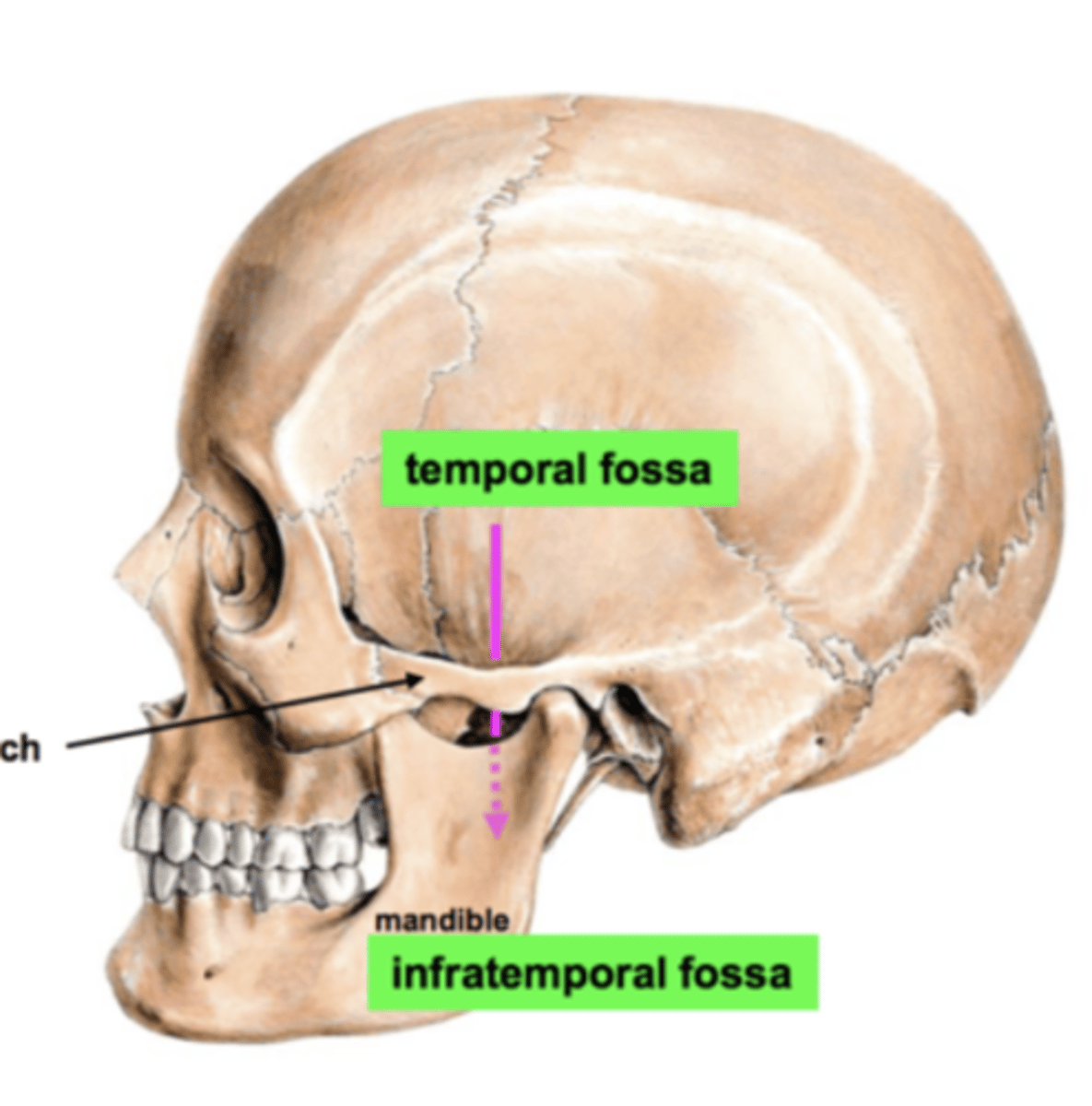
Temporal Fossa
above the zygomatic arch
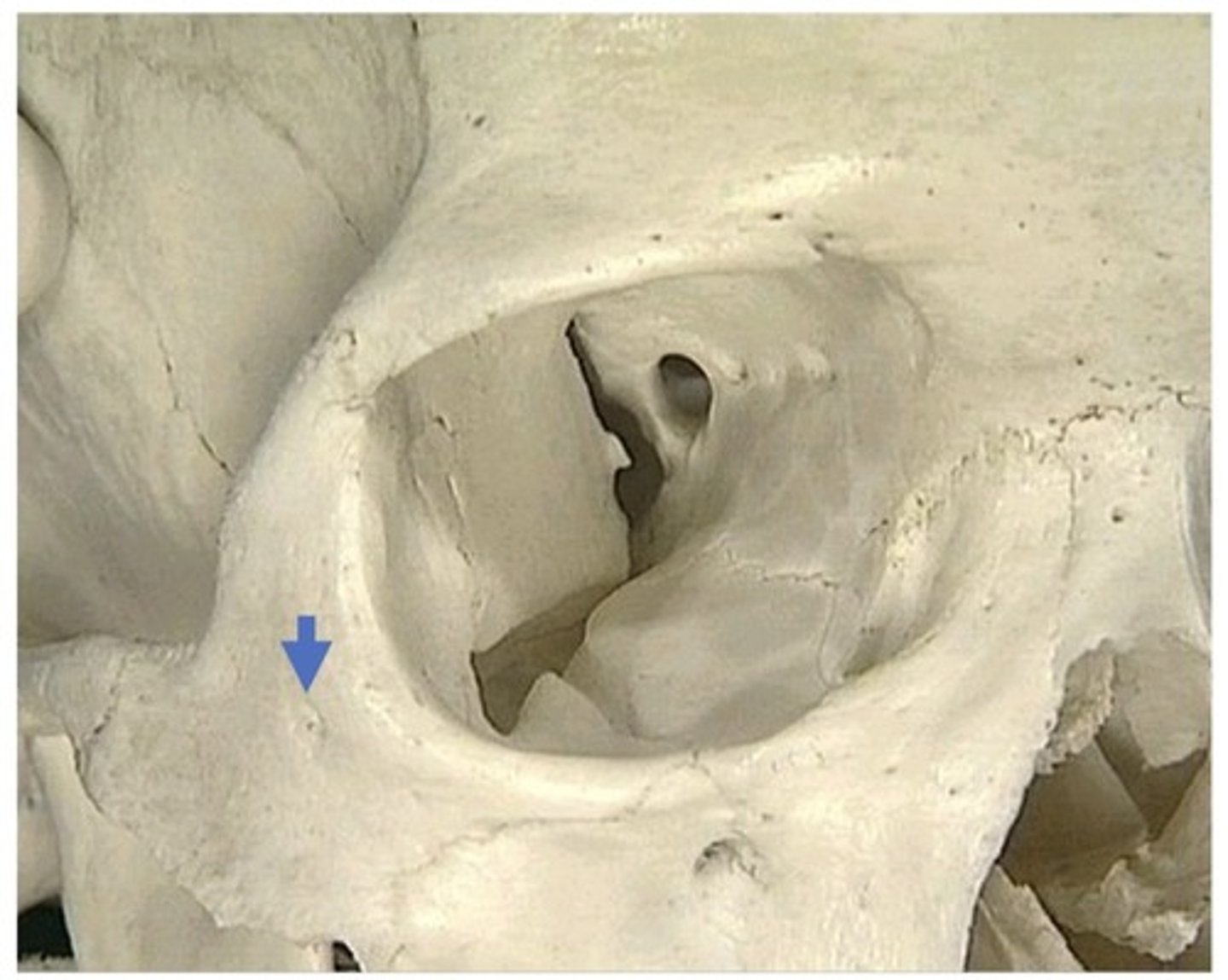
Foramen Ovale
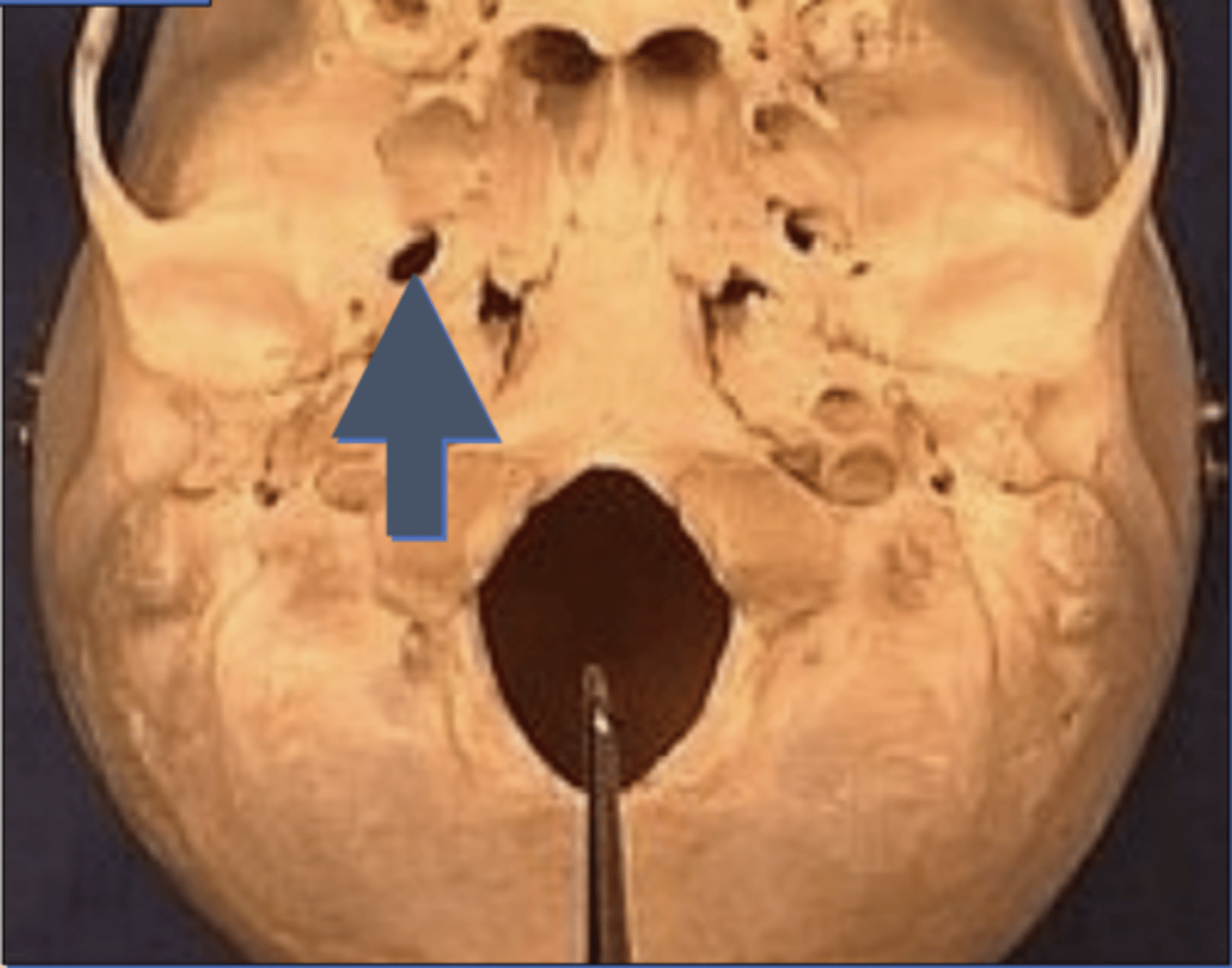
Zygomatico-temporal foramen
1. In zygomatic bone, in the region of your temple
2. There are 2 more small foramen like this
3. Behind the cheek bone
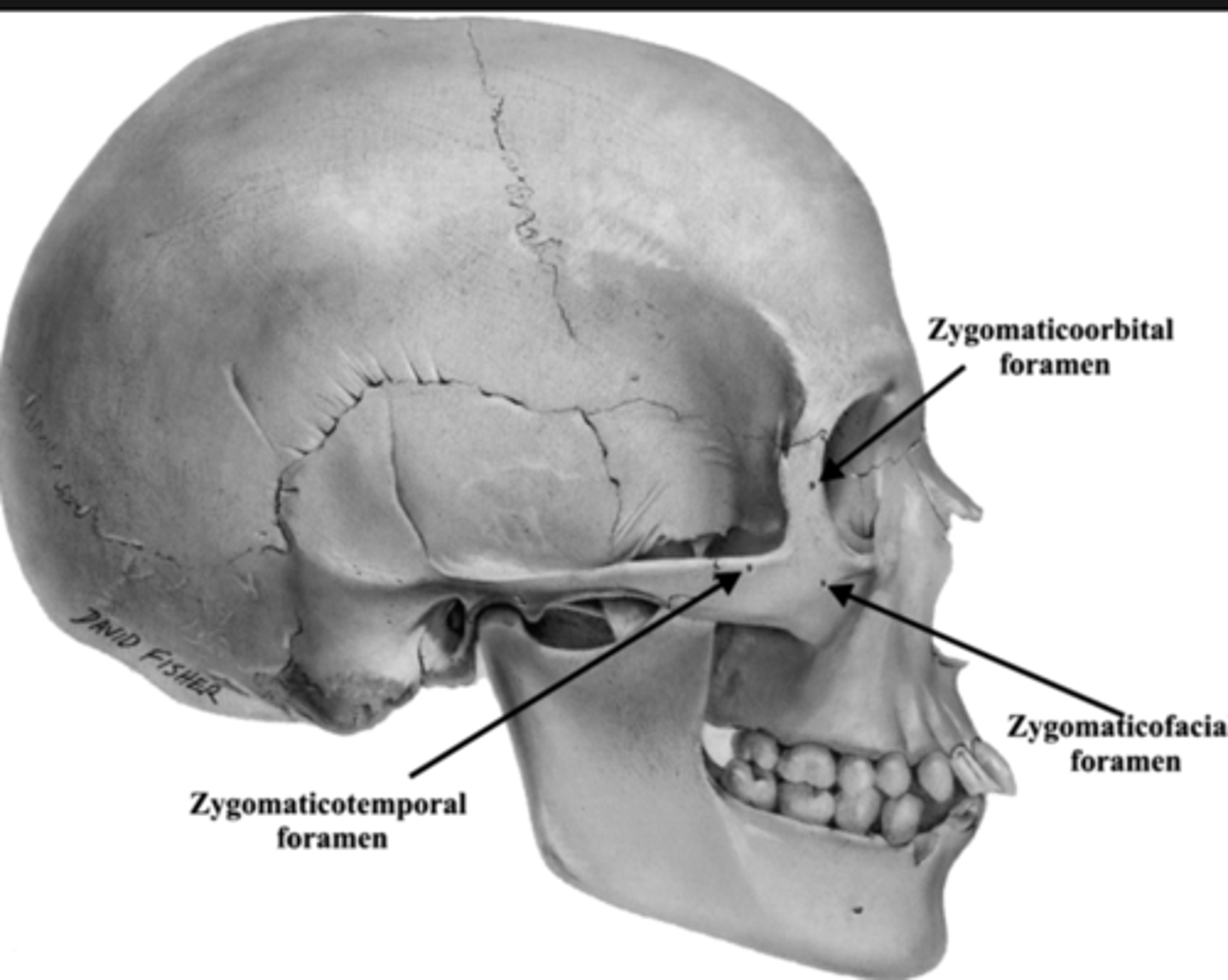
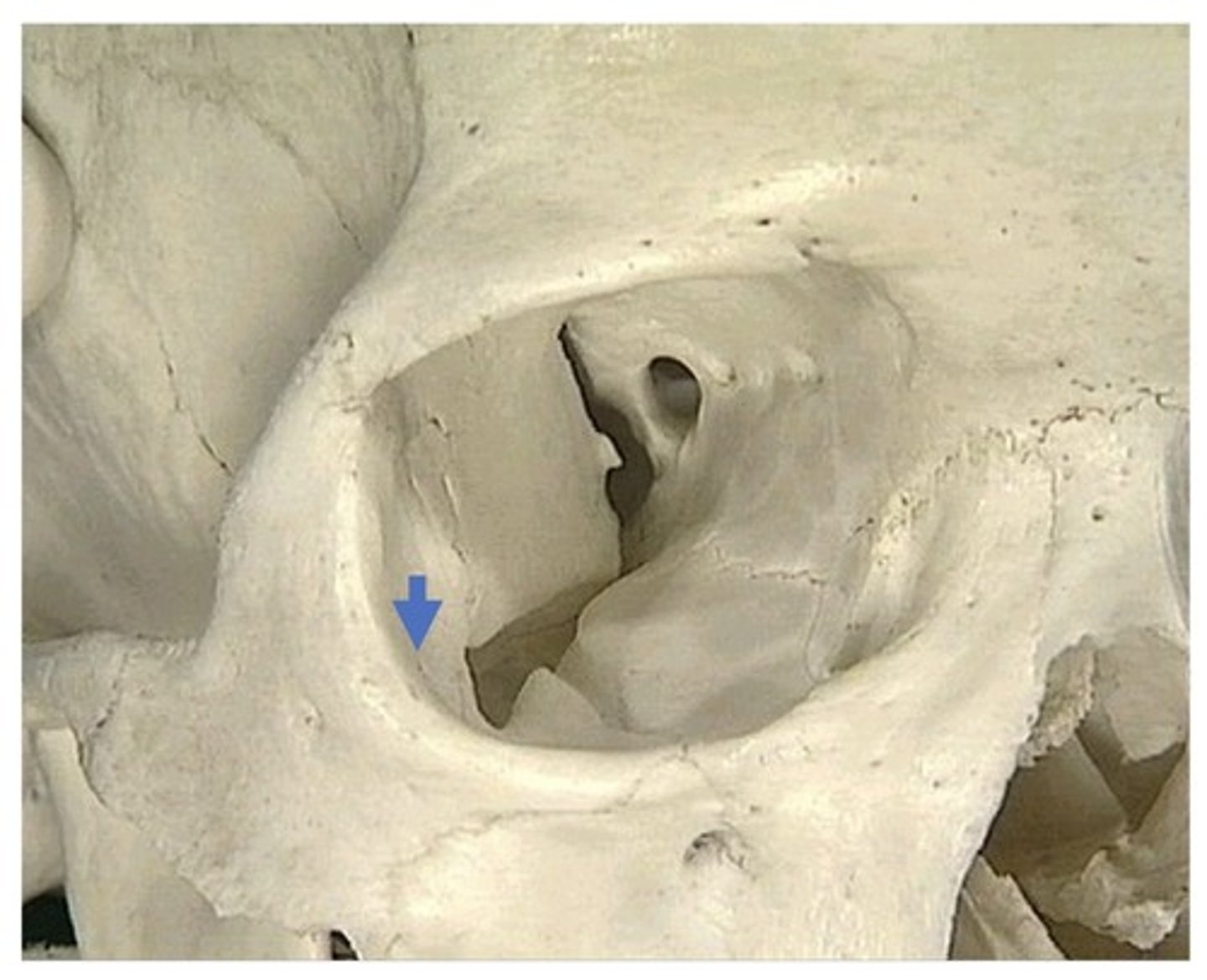
Zygomatico-orbital foramen
1. In zygomatic bone, within the orbit
2. There are 2 more small foramen like this
Openings of the anterior cranial fossa
1. Cribriform plate
Cribriform plate
1. Related to olfactory nerves by the olfactory bulbs that overly it
2. Gives the sense of smell
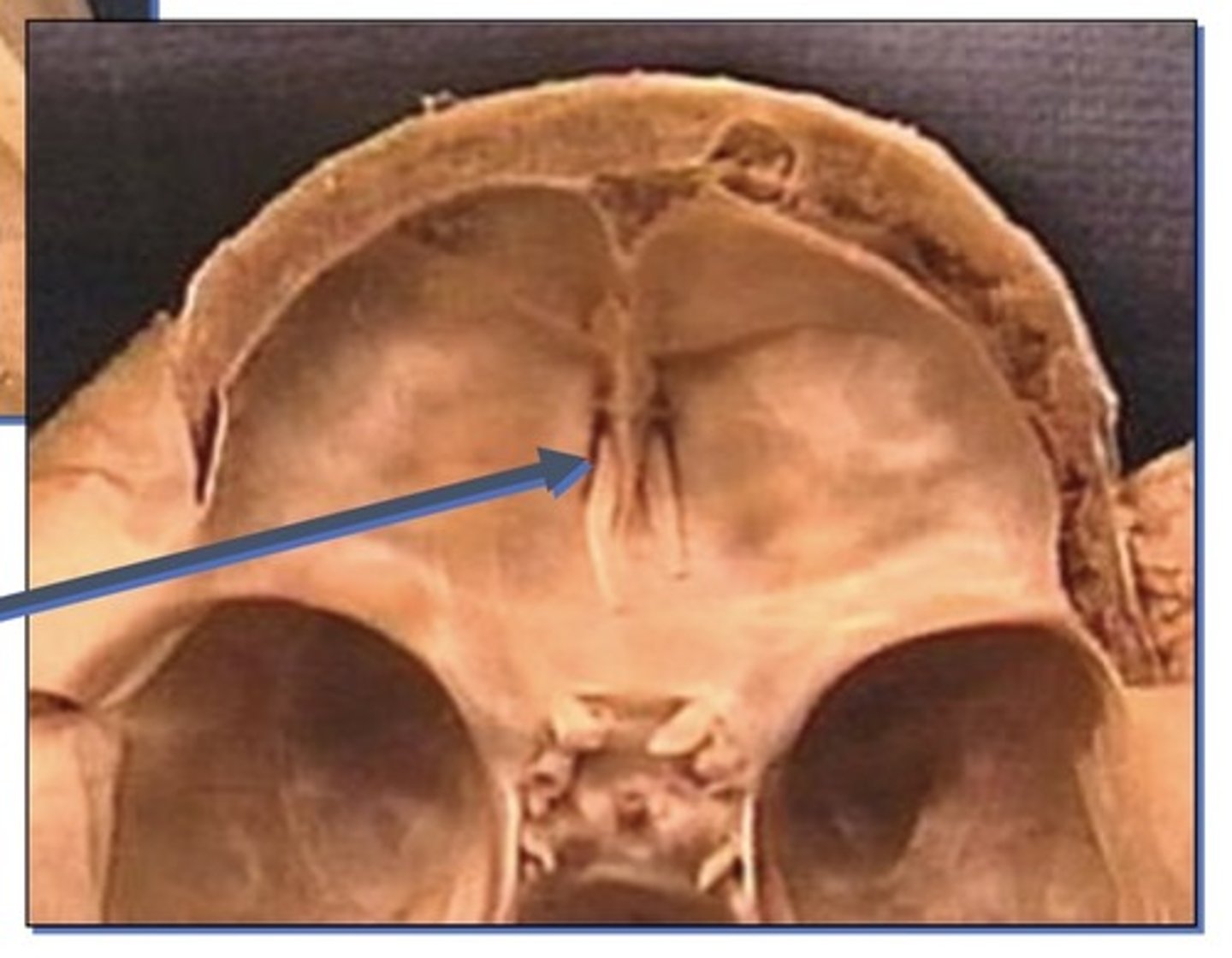
Landmarks of the anterior cranial fossa
1. Crista galli
2. Orbital plate of the frontal bone roof
3. Ethmoid (orbital plate, orbital cavity)
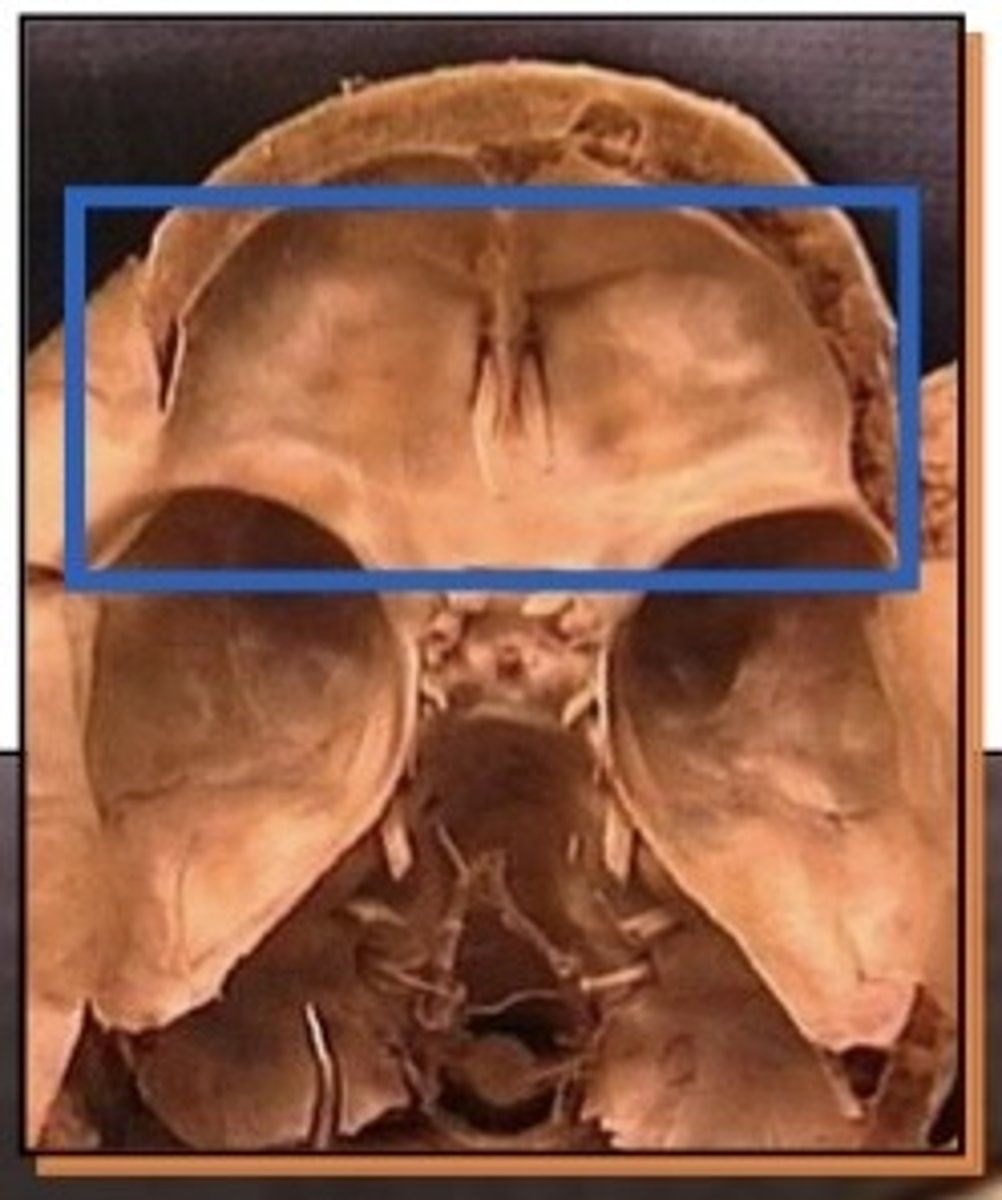
Landmarks in the lateral skull
temporal fossa, infratemporal fossa,
Orbital plate of the frontal bone roof
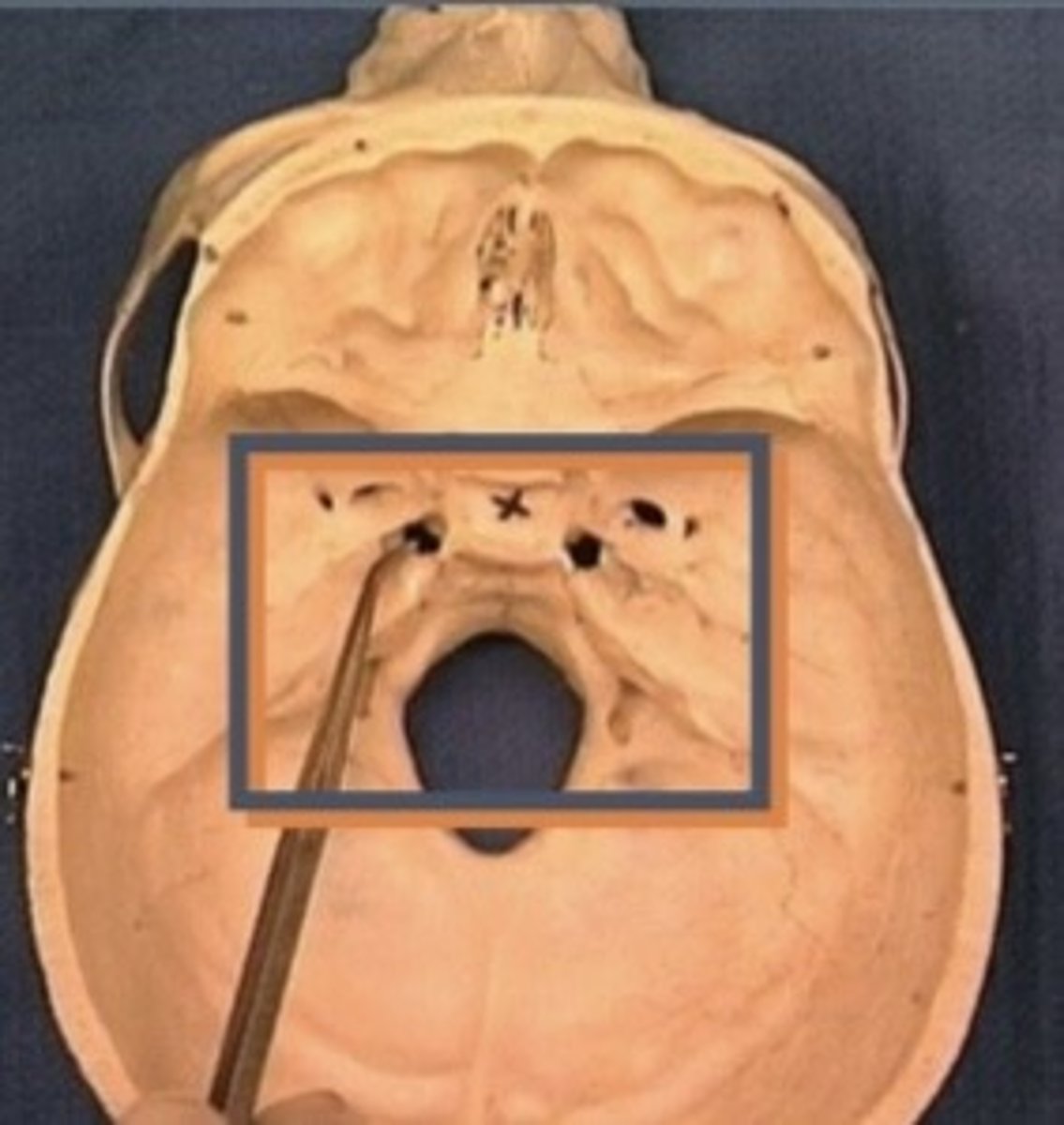
Openings of the middle cranial fossa
1. Optic foramen
2. Foramen rotundum
3. Foramen ovale
4. Foramen spinosum
5. Foramen lacerum
6. Hiatus of facial canal
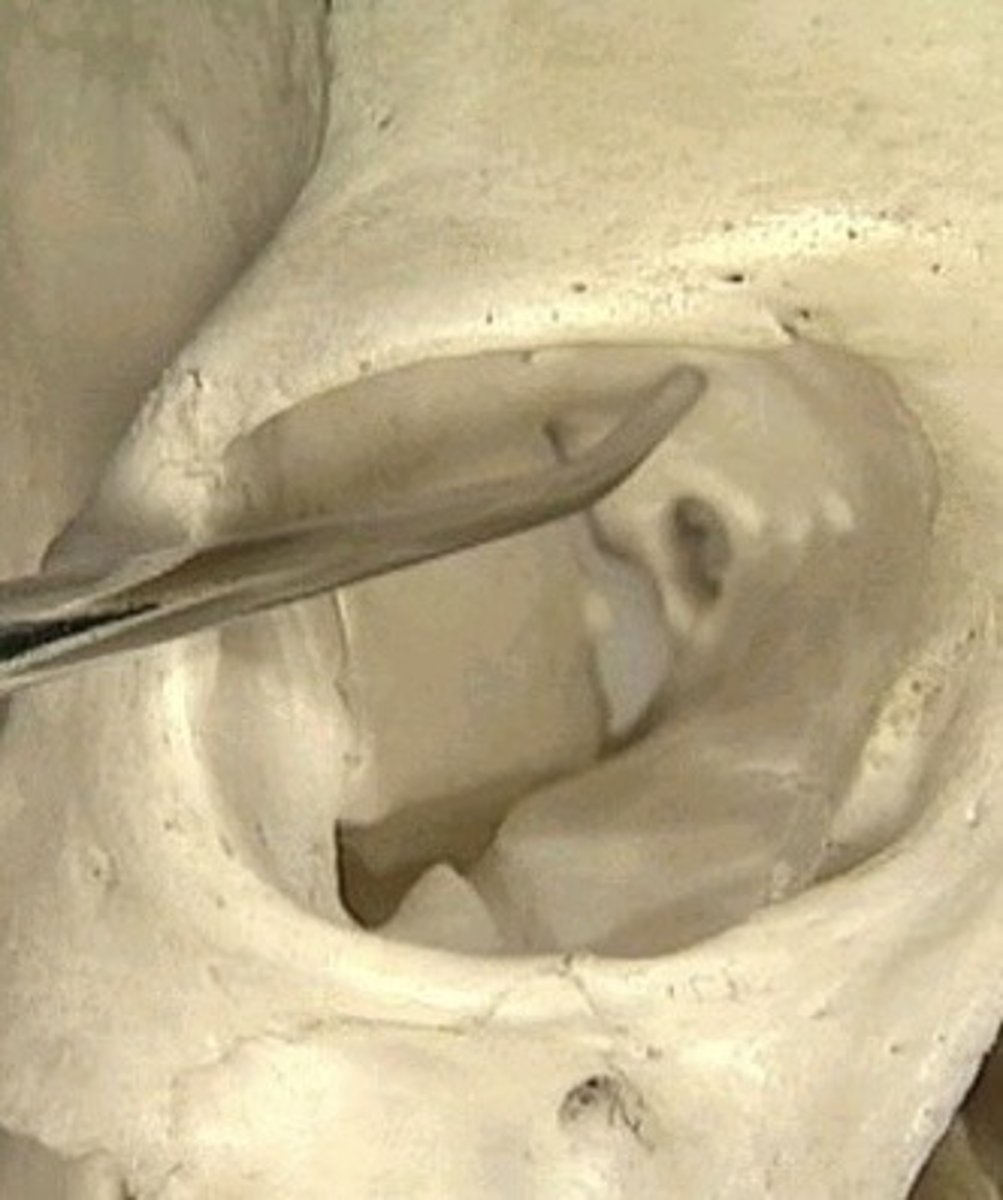
Hiatus of facial canal
1. Very small opening
2. Inside temporal bone
3. Nerve that leaves facial
Find petrous portion of temporal bone and look for small opening on the side of the mountain in the middle cranial fossa
Crista galli
1. Attachment site dura
2. Sticks out like a mountain
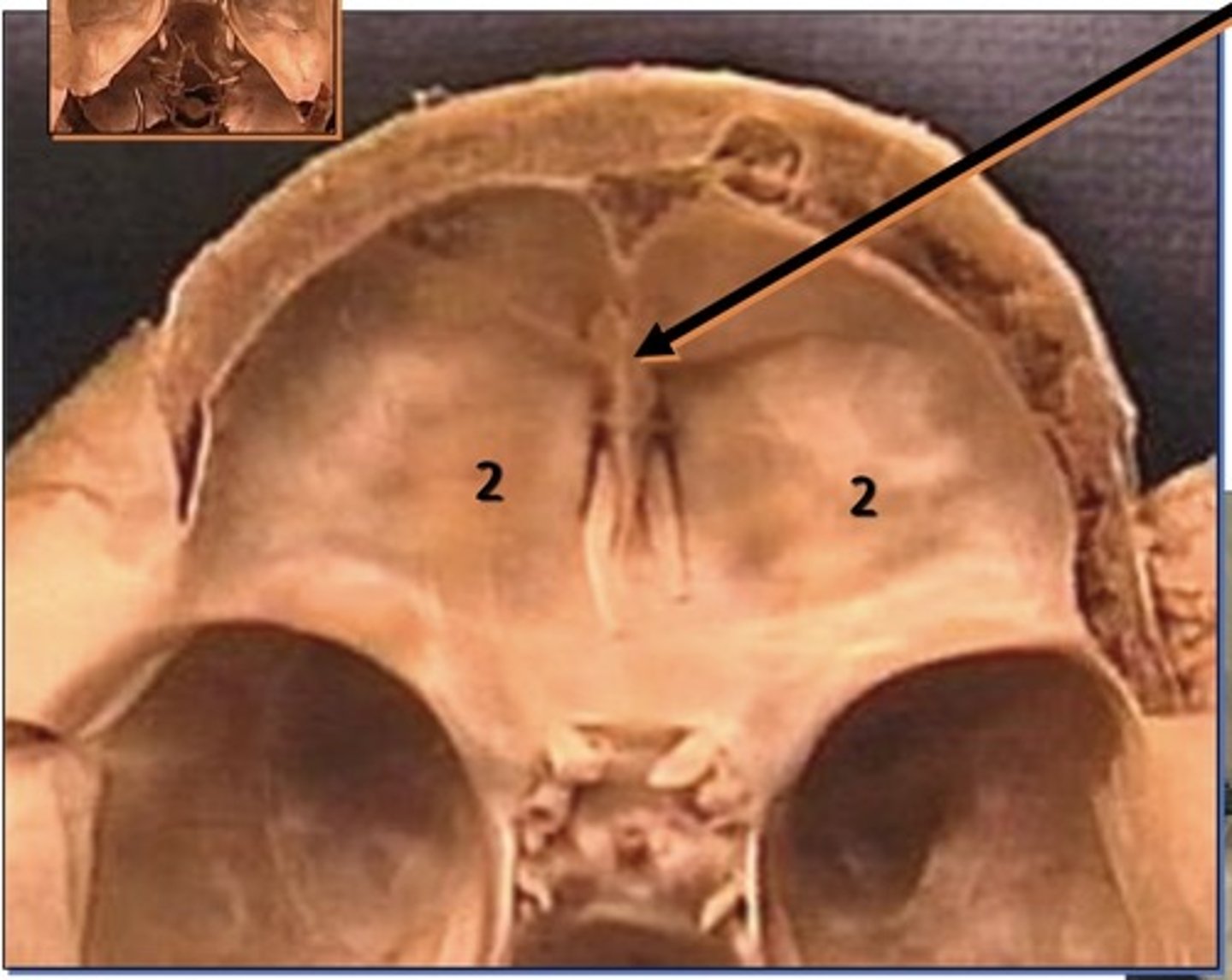
Foramen rotundum
1. Small round opening in sphenoid bone
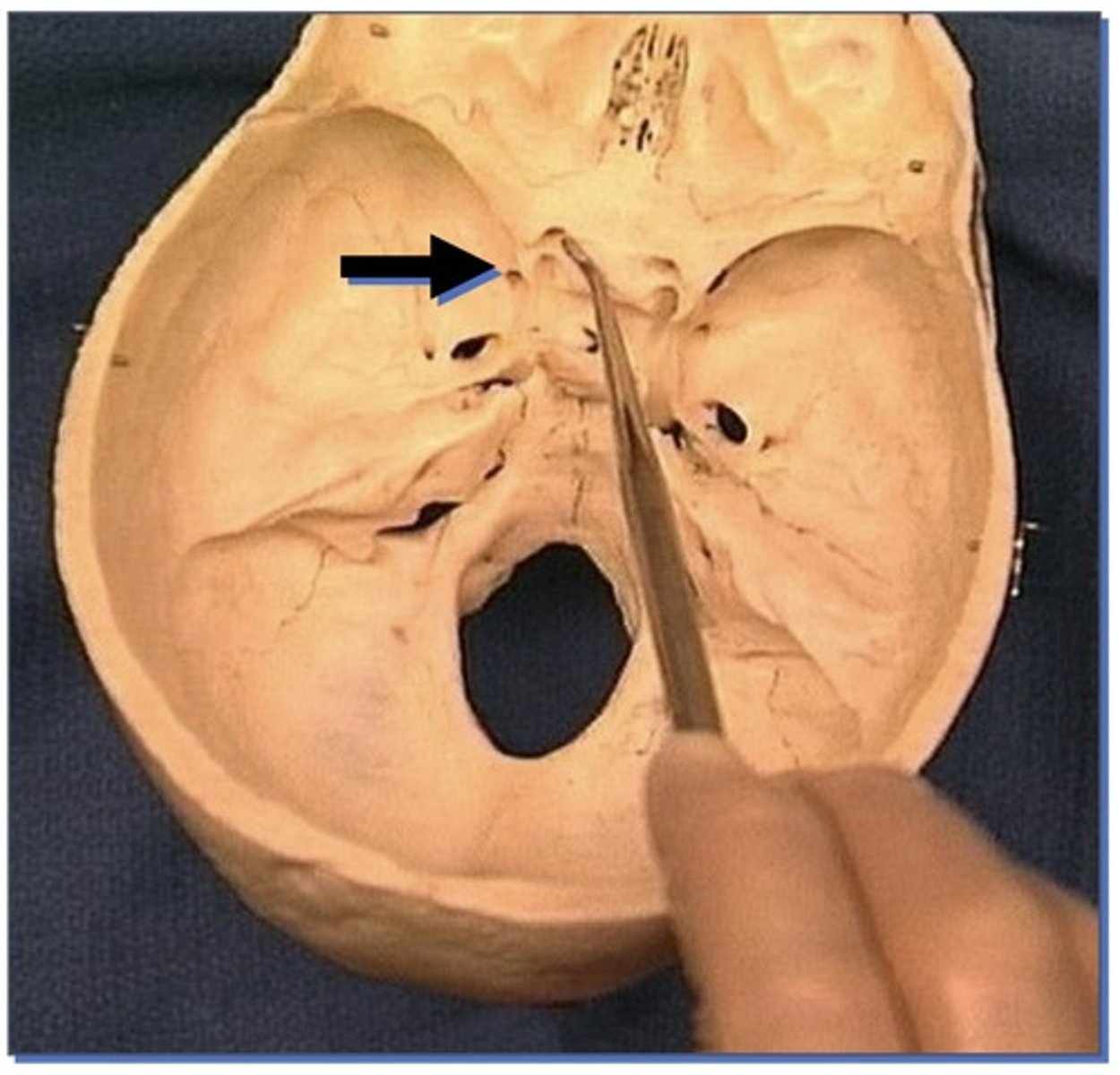
Foramen ovale
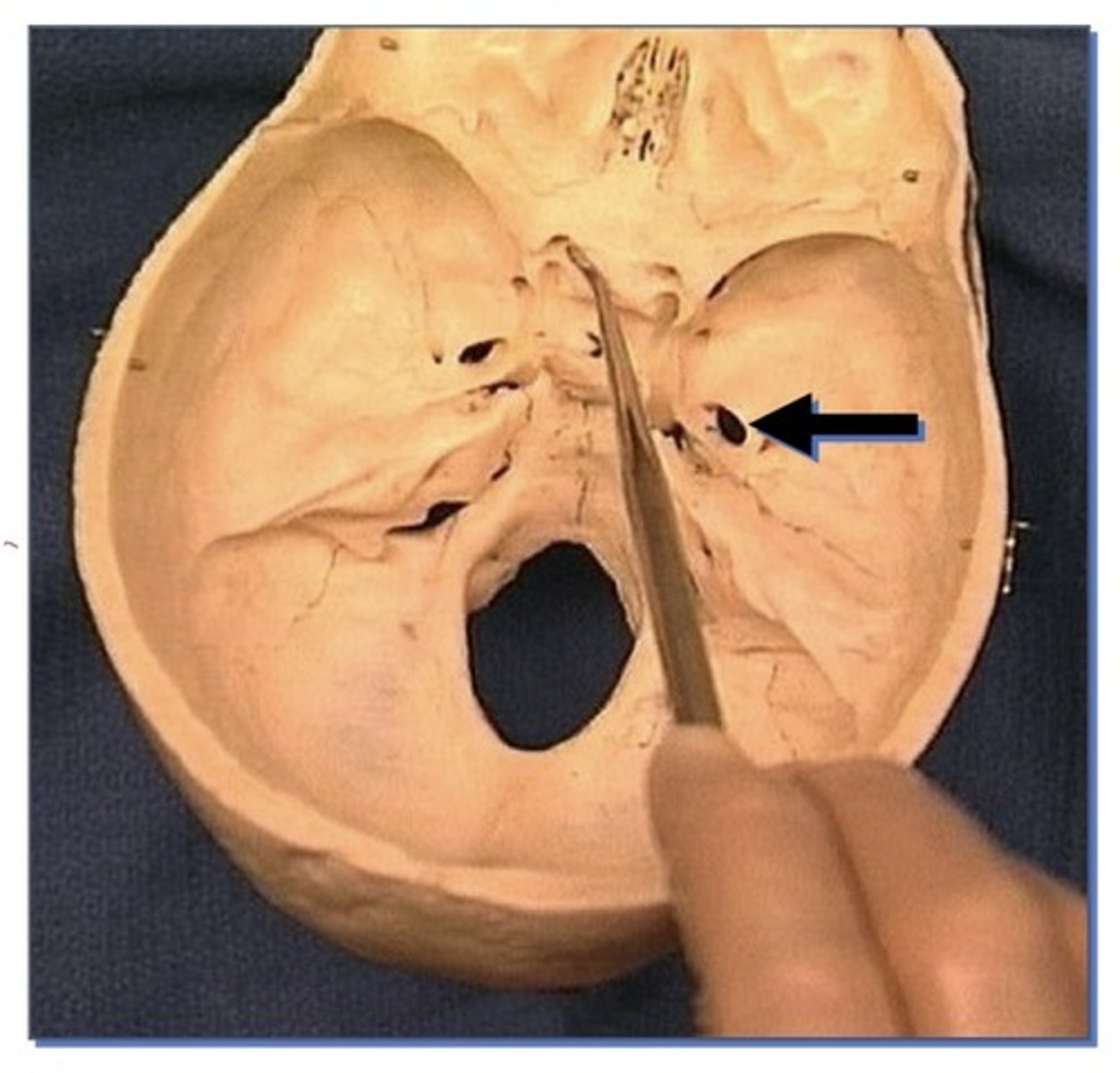
1. Larger, oval opening
2. Posterior aspect of Sphenoid bone
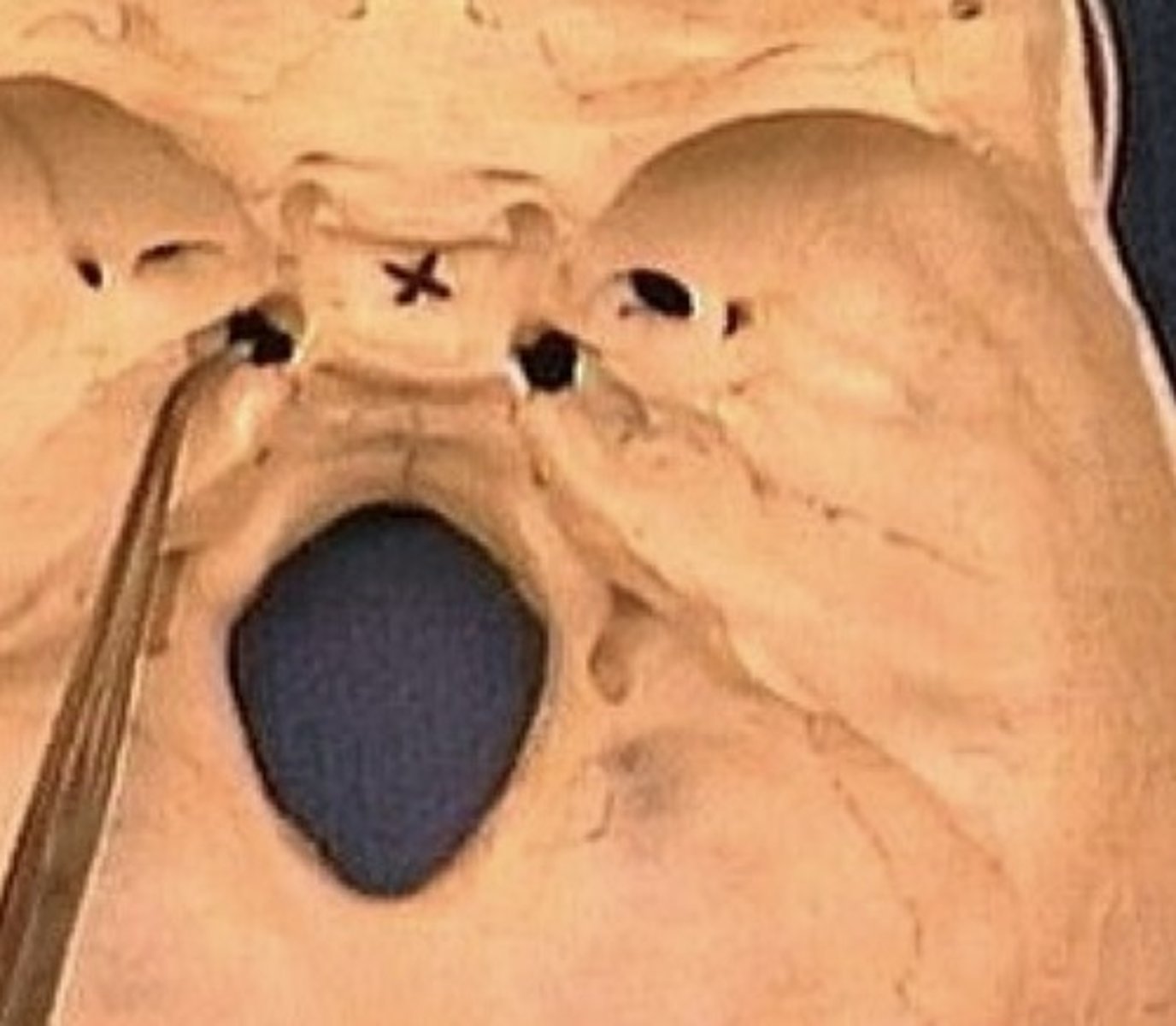
Foramen lacerum
1. Appears lacerated (jagged edge)
2. Not a true foramen
3. Formed between sphenoid and temporal bone
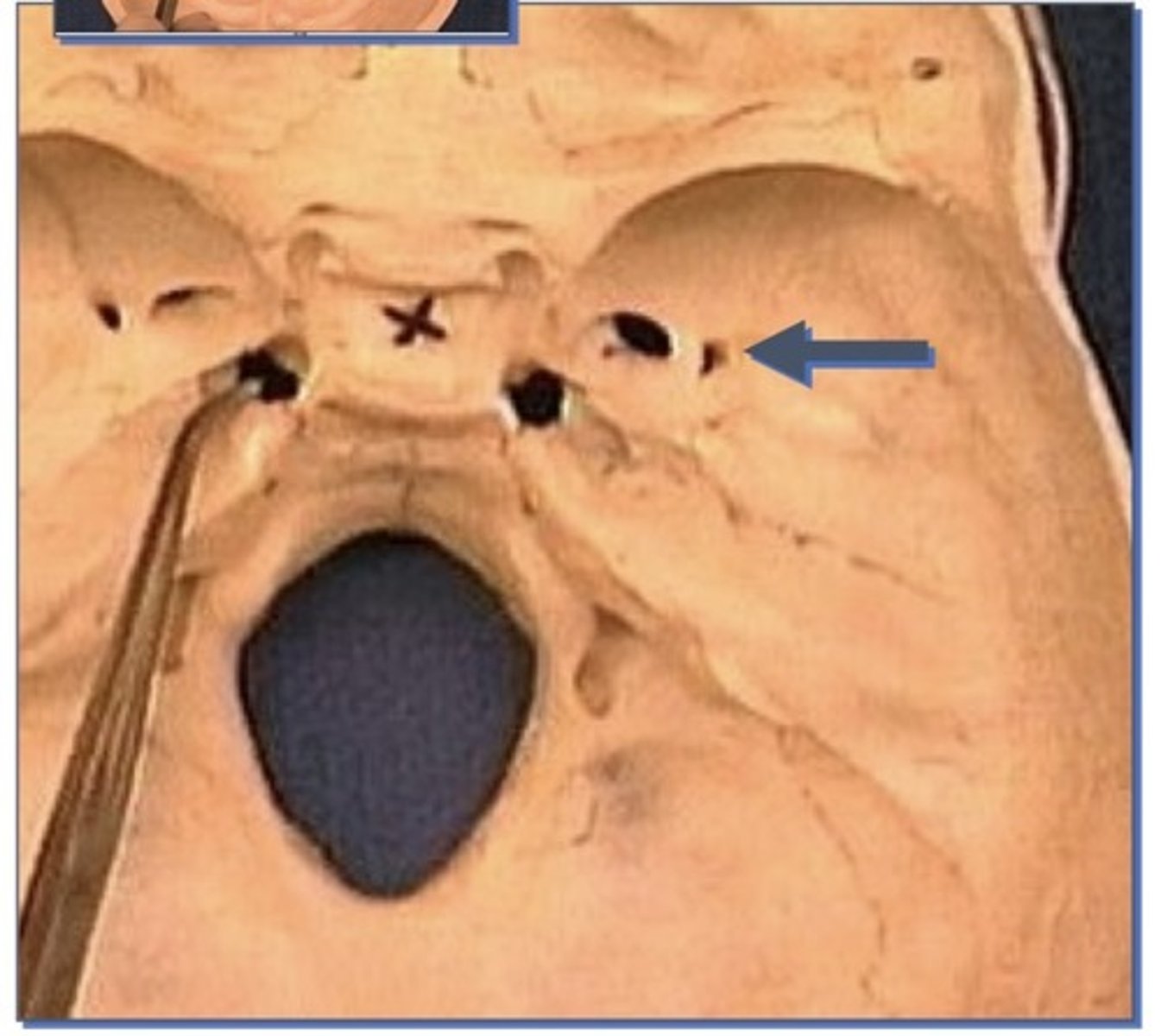
Foramen spinosum
1. Small opening immediately lateral to Ovale
2. In sphenoid bone
3. Next to sphenoid spine
Sinuses in the fossa part 1
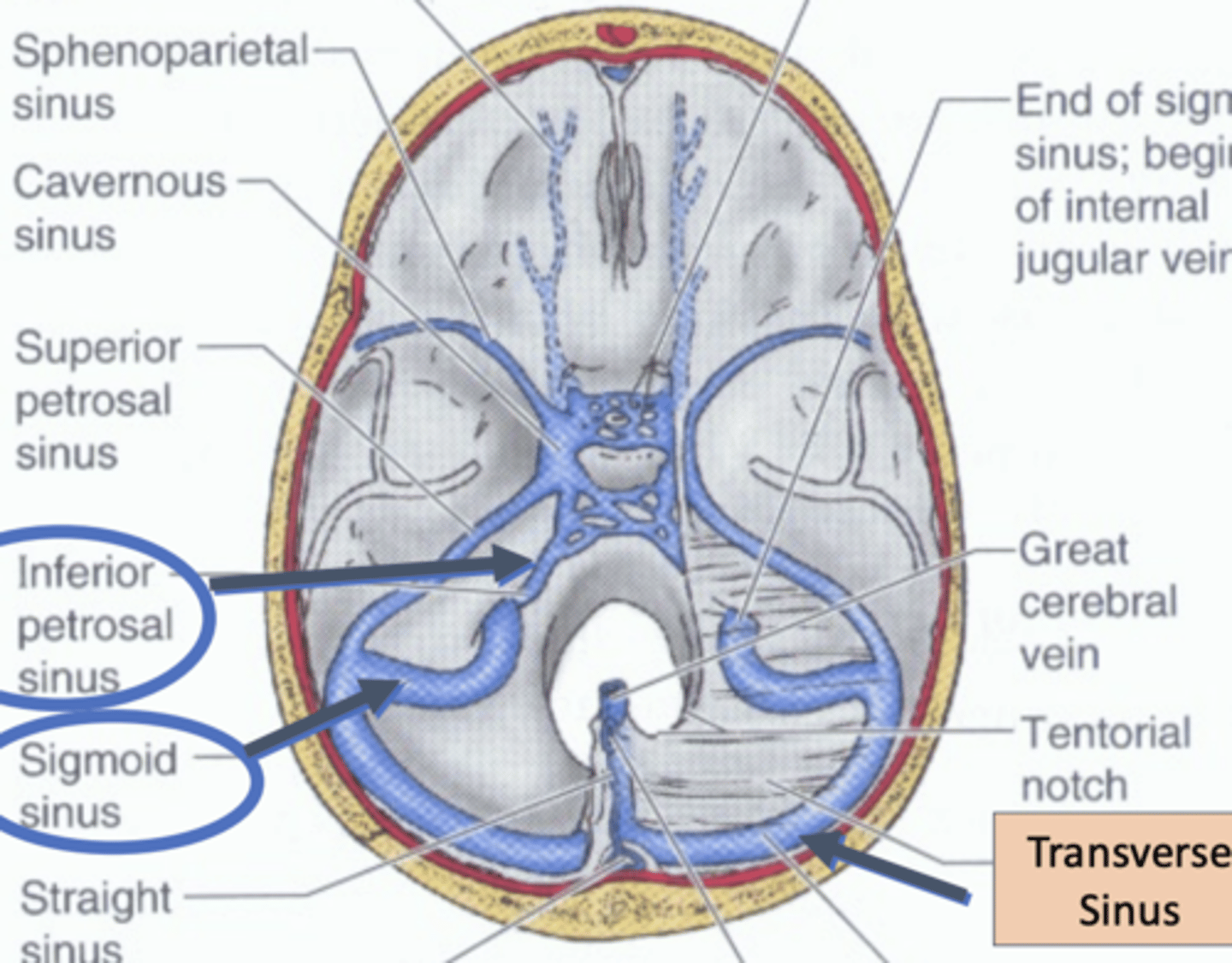
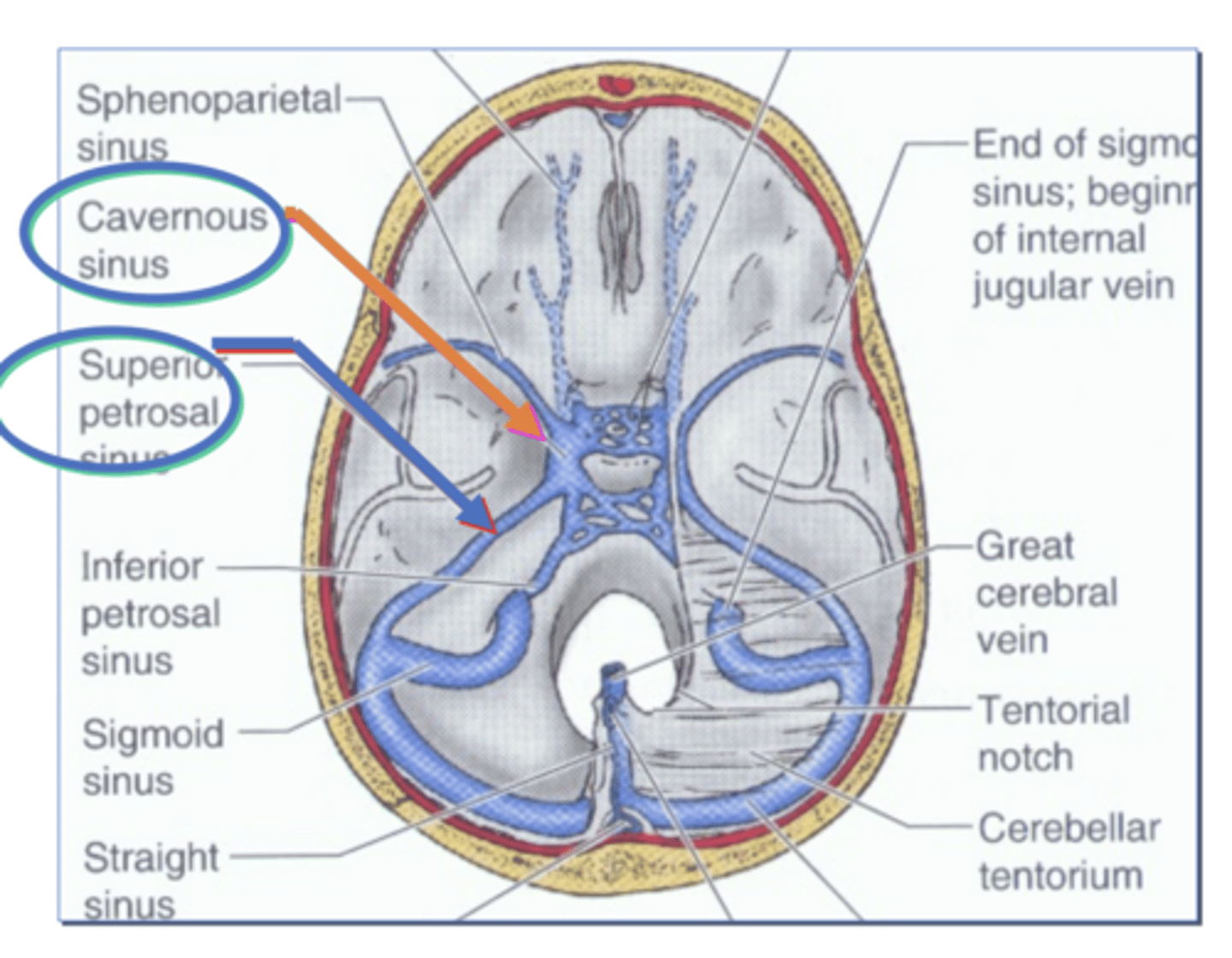
Sinuses in the fossa part 2
Landmarks of the posterior cranial fossa
1. Clivus (occipital bone)
2.
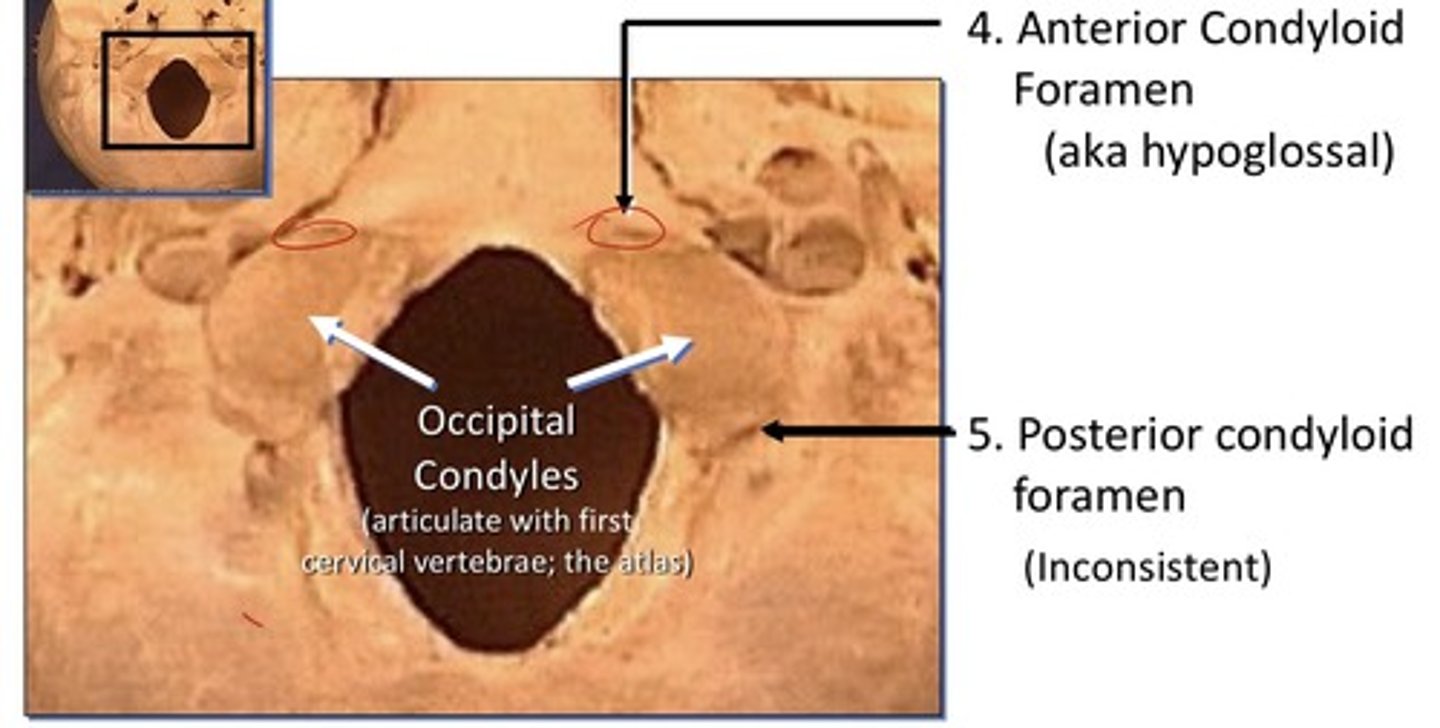
Structures traversing openings of the posterior cranial fossa
1. Anterior condyloid foramen (aka hypoglossal)
2. Posterior condyloid foramen (inconsistent)
3. Occipital condyles: (articulate with first cervical vertebrae; the atlas)
-Sometimes they communicate
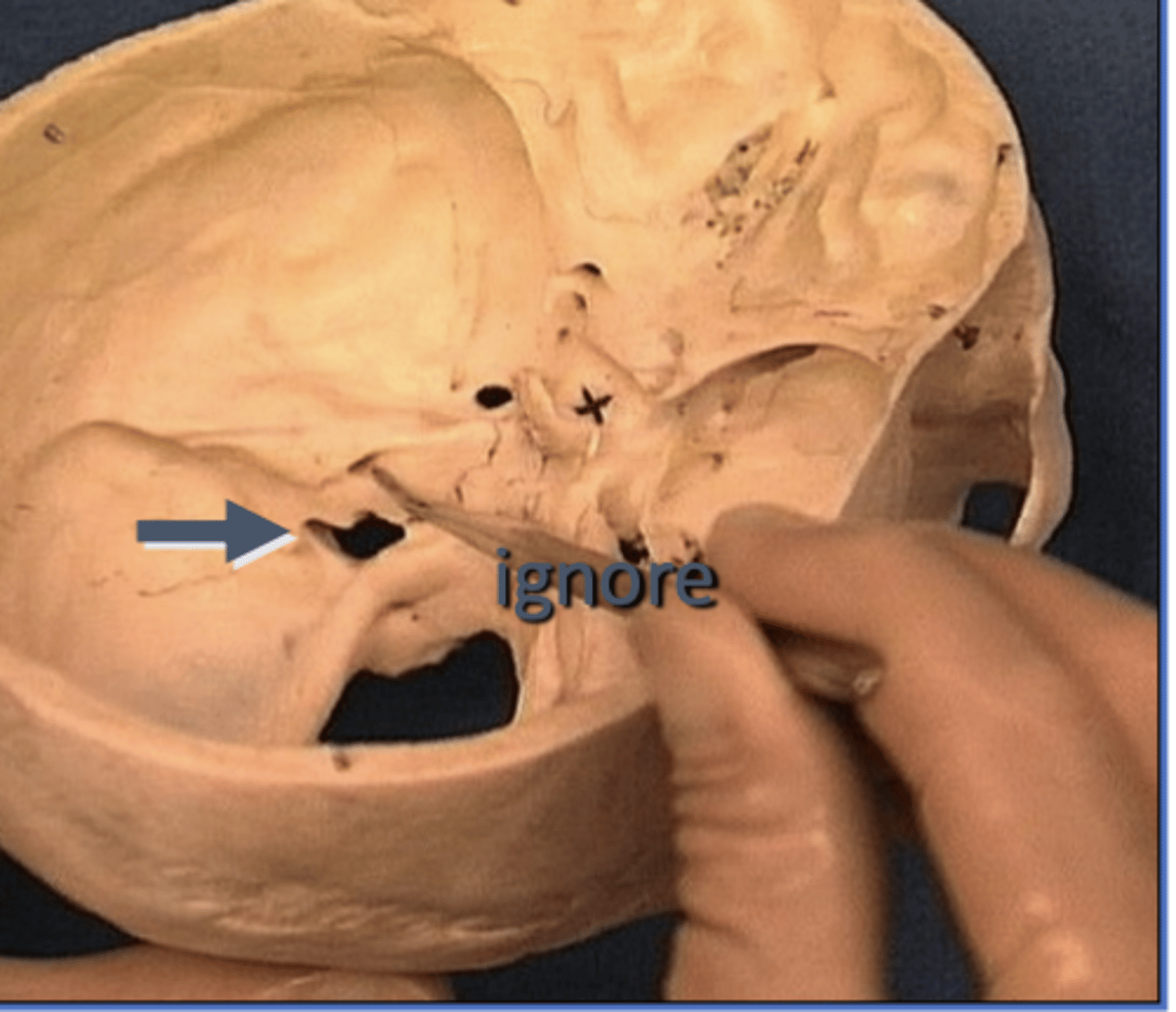
Openings of the posterior cranial fossa
Internal auditory meatus, foramen magnum (in occipital bone), jugular foramen, anterior and posterior condyloid foramens
jugular foramen
formed by the junction of the temporal and occipital bone
Landmarks of the middle cranial fossa
1. Sella turcica (Turkish saddle)
2. Dorsam sellae
3. Tuberculum sellae
4. Anterior clinoid process
5. Posterior clinoid process
6. Chiasmatic groove
7. Carotid groove
8. Arcuate eminence
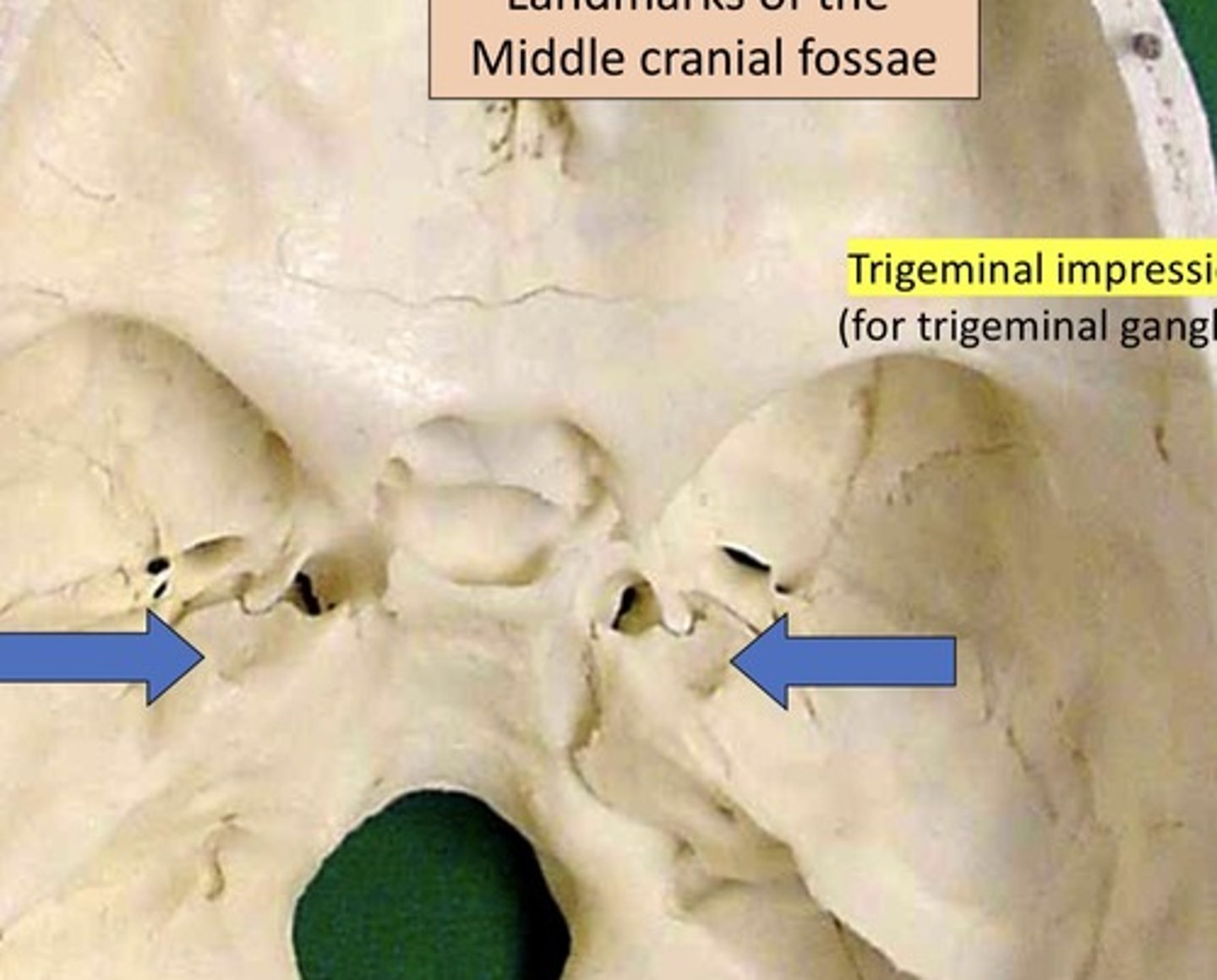
9. Trigeminal impression
Posterior clinoid process
1. In between saddle
Sella turcica (Turkish saddle)
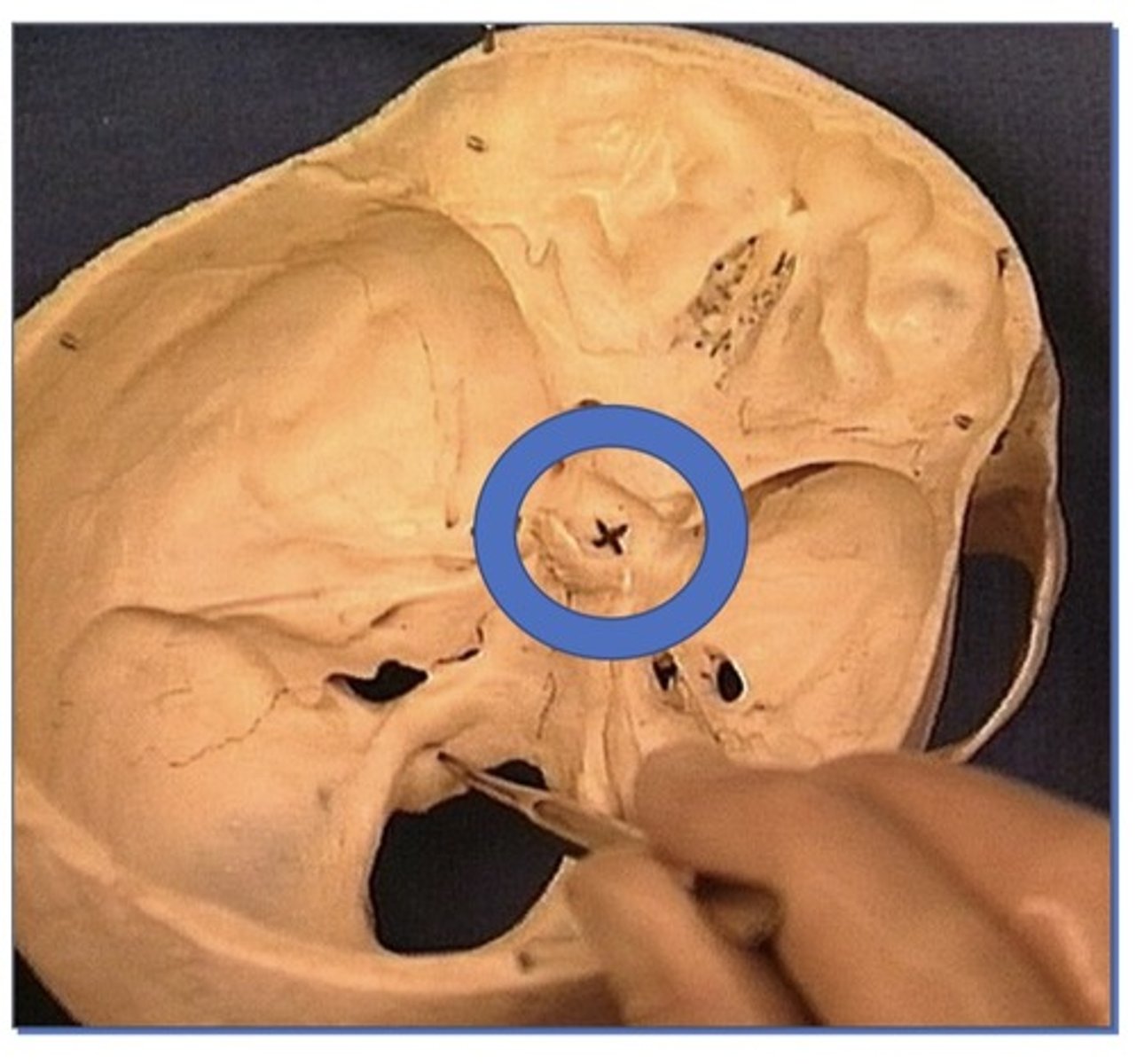
Trigeminal impression
1. For Trigeminal ganglion
2. Where sensation nerve sits
3. Medial center of skull
4. Sits on petrous bone
clivus
occipital bone
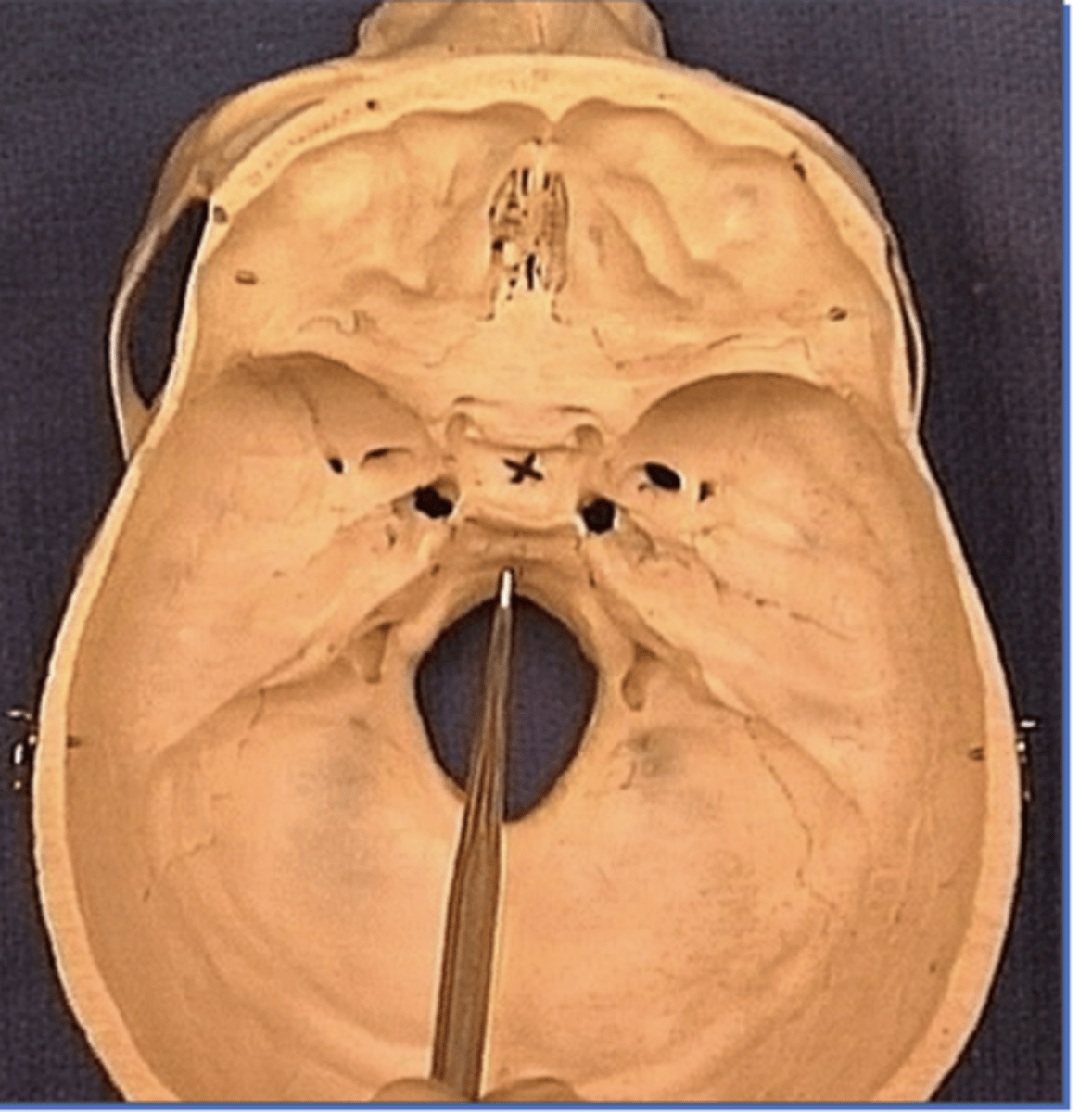
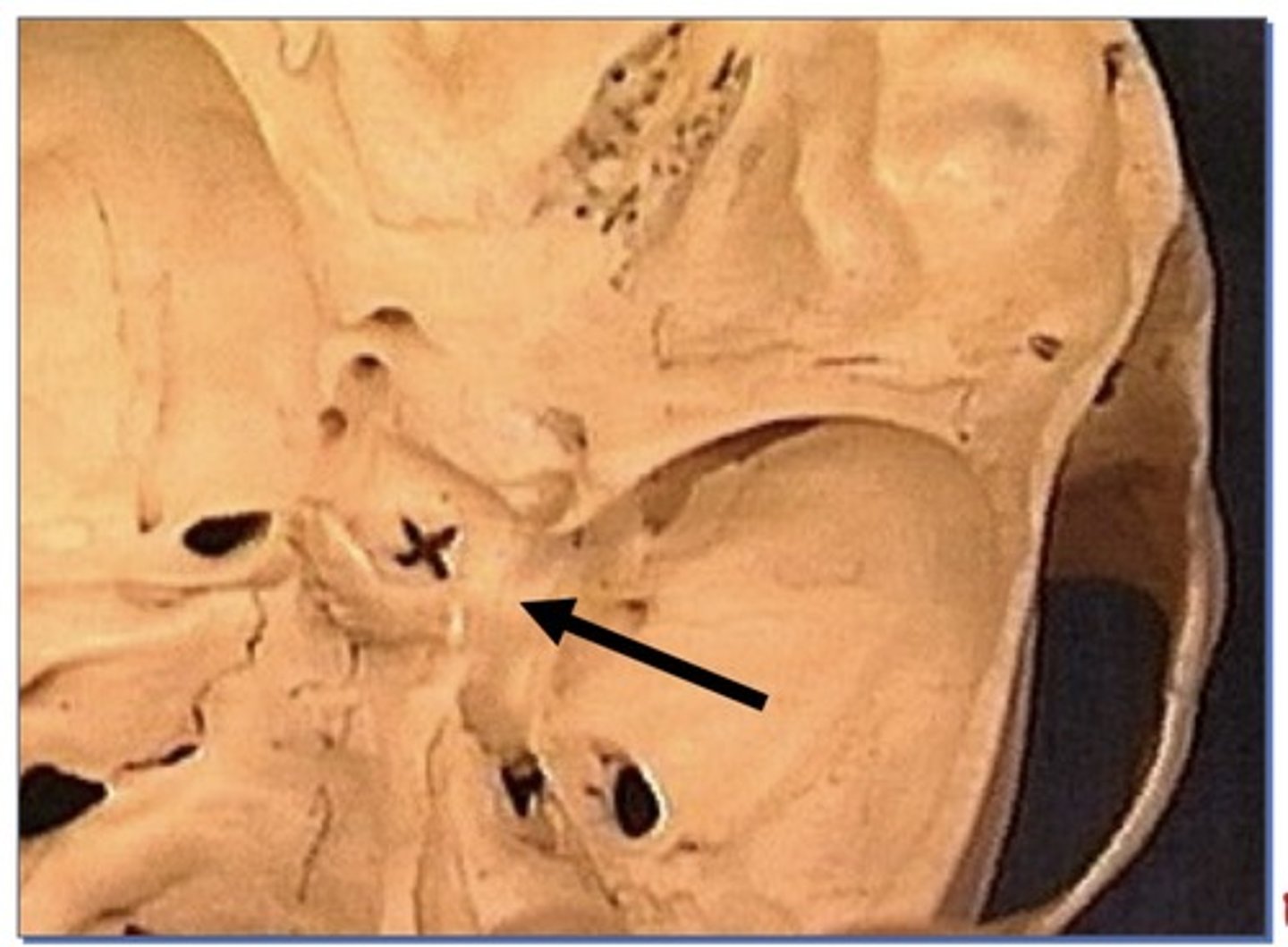
Carotid groove
1. Impression made by the Internal carotid artery as it travels through the cavernous
Dorsam sellae
1. Posterior to sella turcica
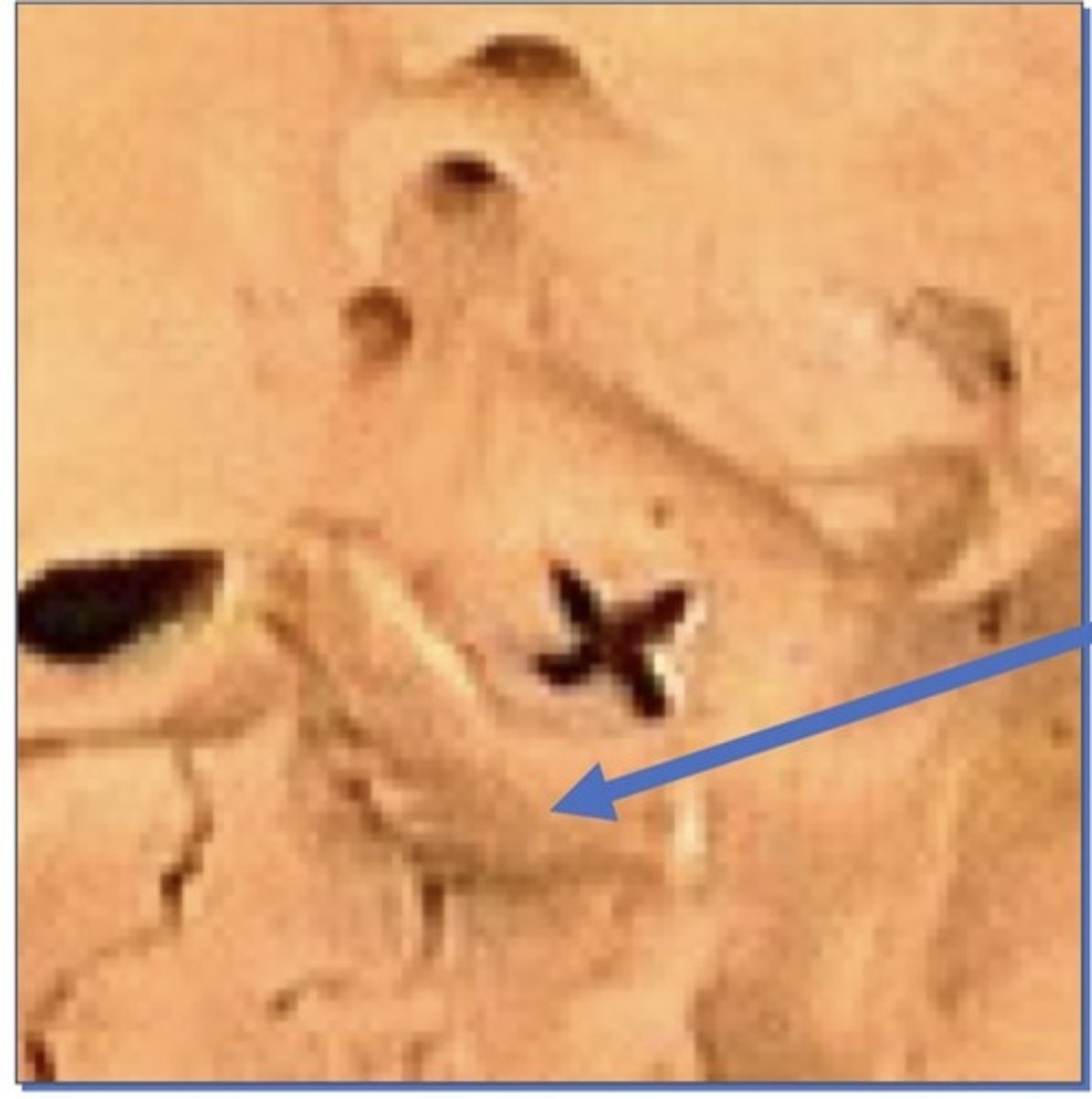
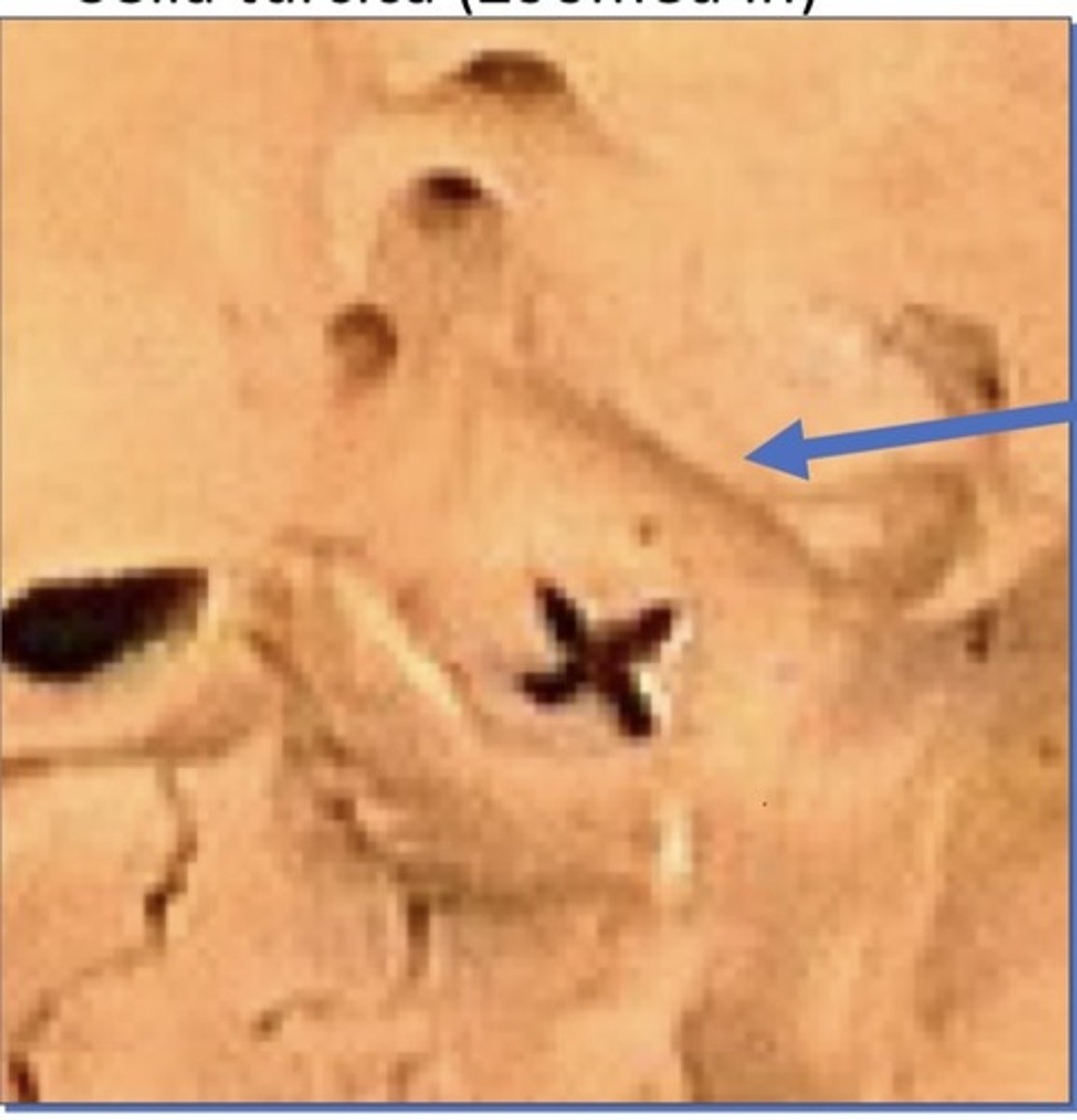
Arcuate eminence
1. On petrous portion of temporal bone
2. Semicircle canal under it, giving it a bump
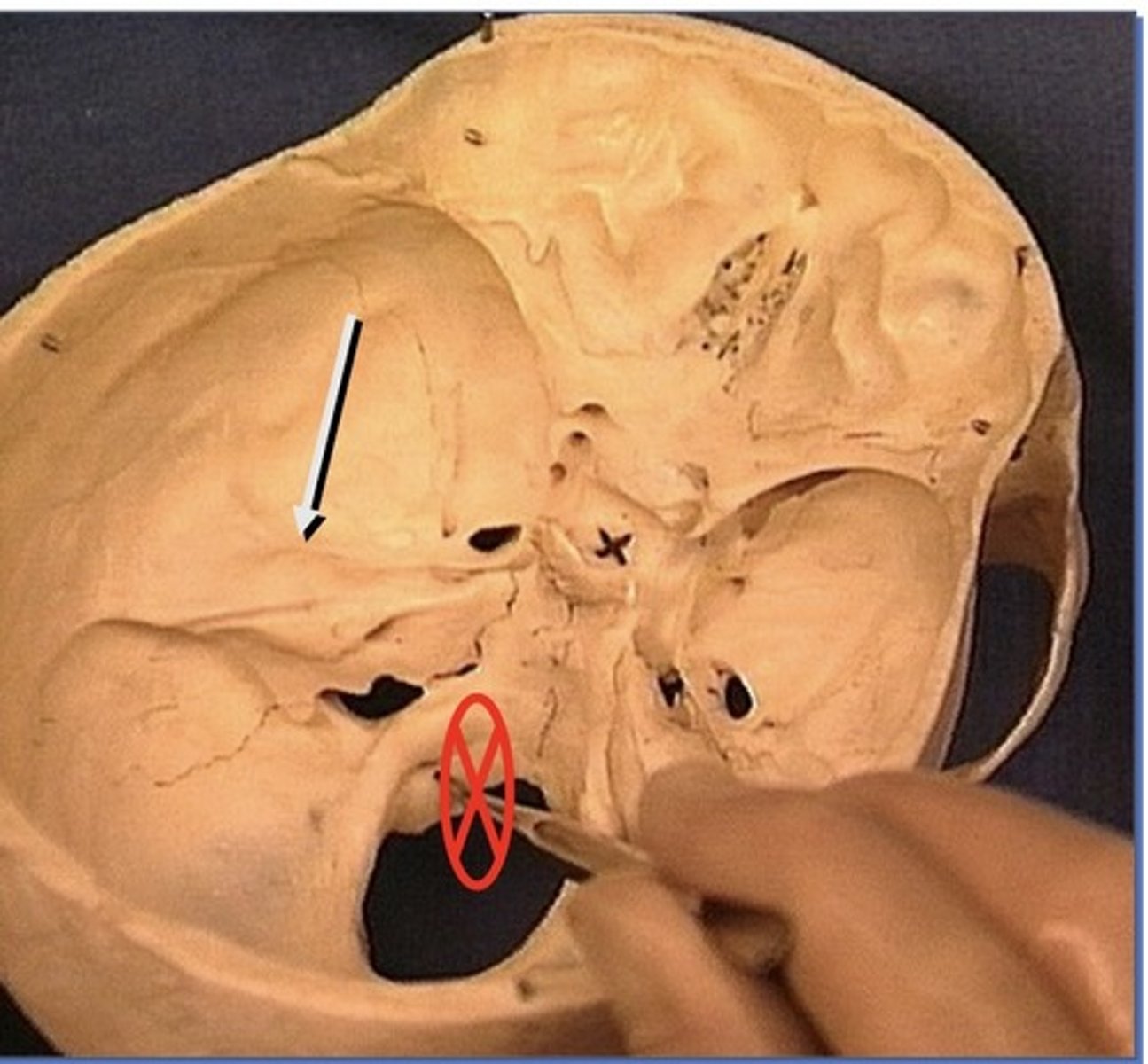
Cavernous Sinus
on each side of the sella turcica
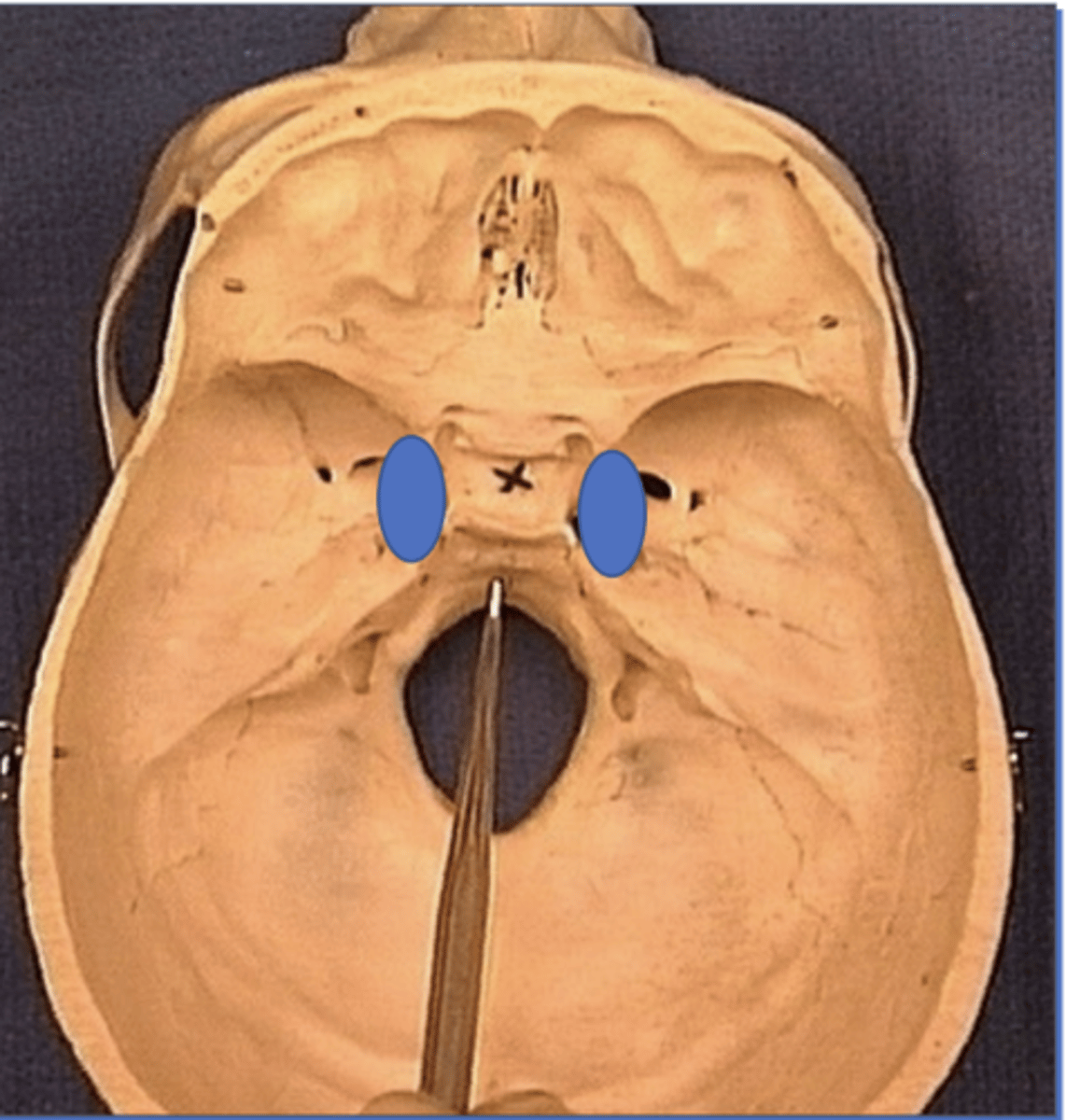
Tuberculum sellae
2. Anterior to sella turcica
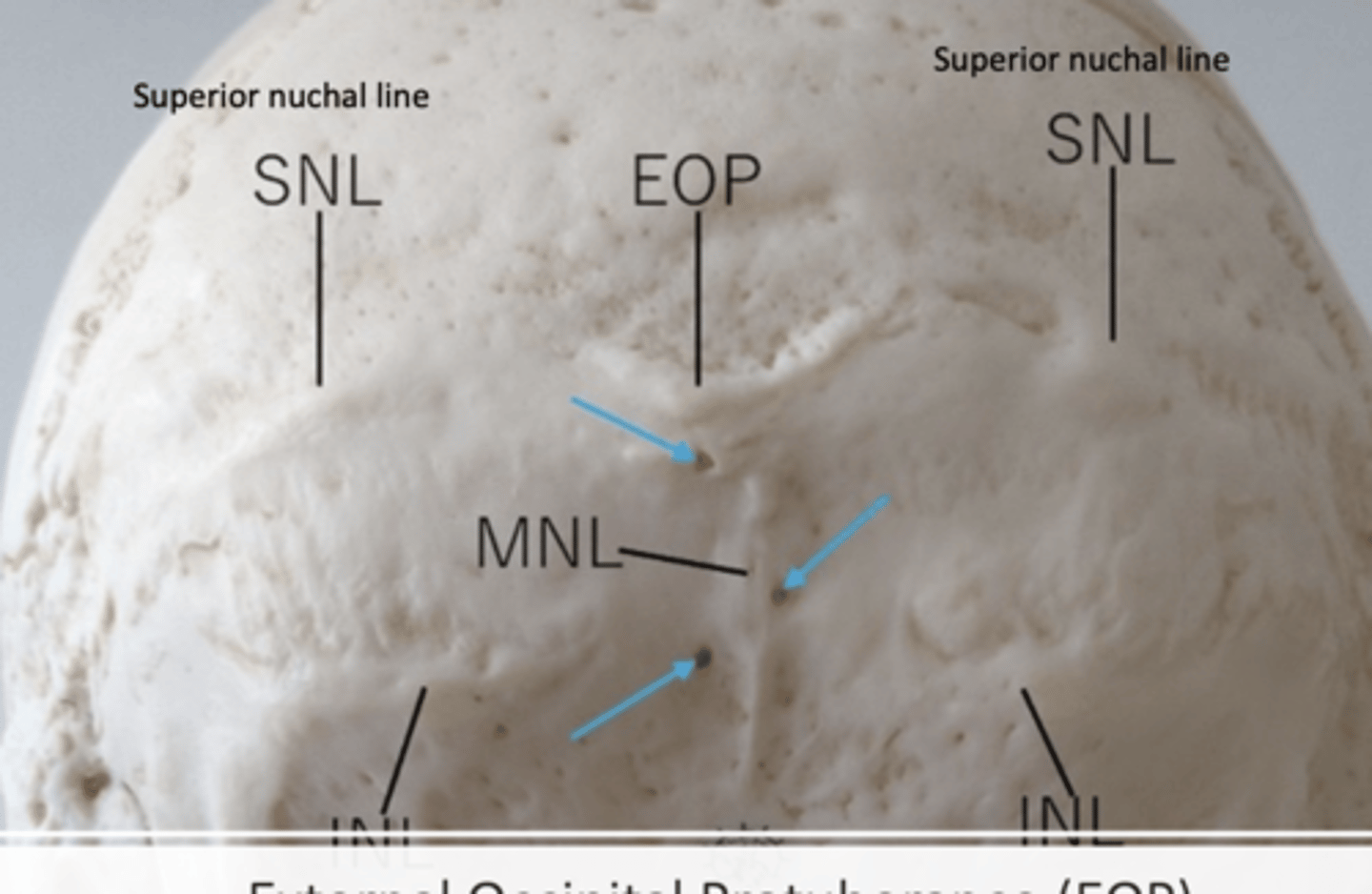
Landmarks of the back of the skull
SNL (superior nuchal line)
MNL (medical nuchal line)
INL (inferior nuchal line)
EOP (external occipital protuberance)

Anterior clinoid process
1. Edge of sella turcica
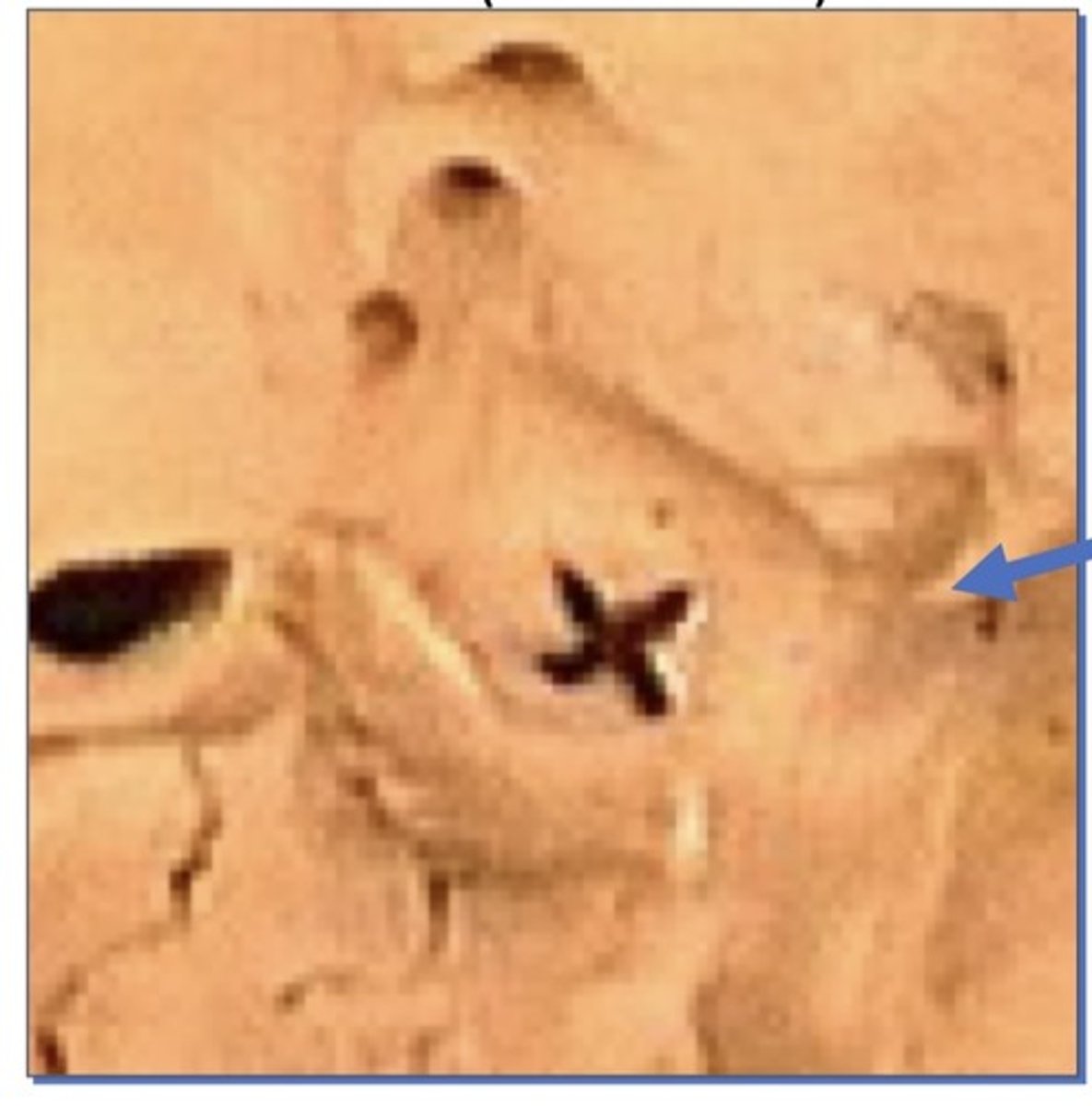
opening of pterygoid canal
it is in the medial aspect of the pterygoid process, very small opening at the base. Opens to the pterygoid canal that moves towards the plate.
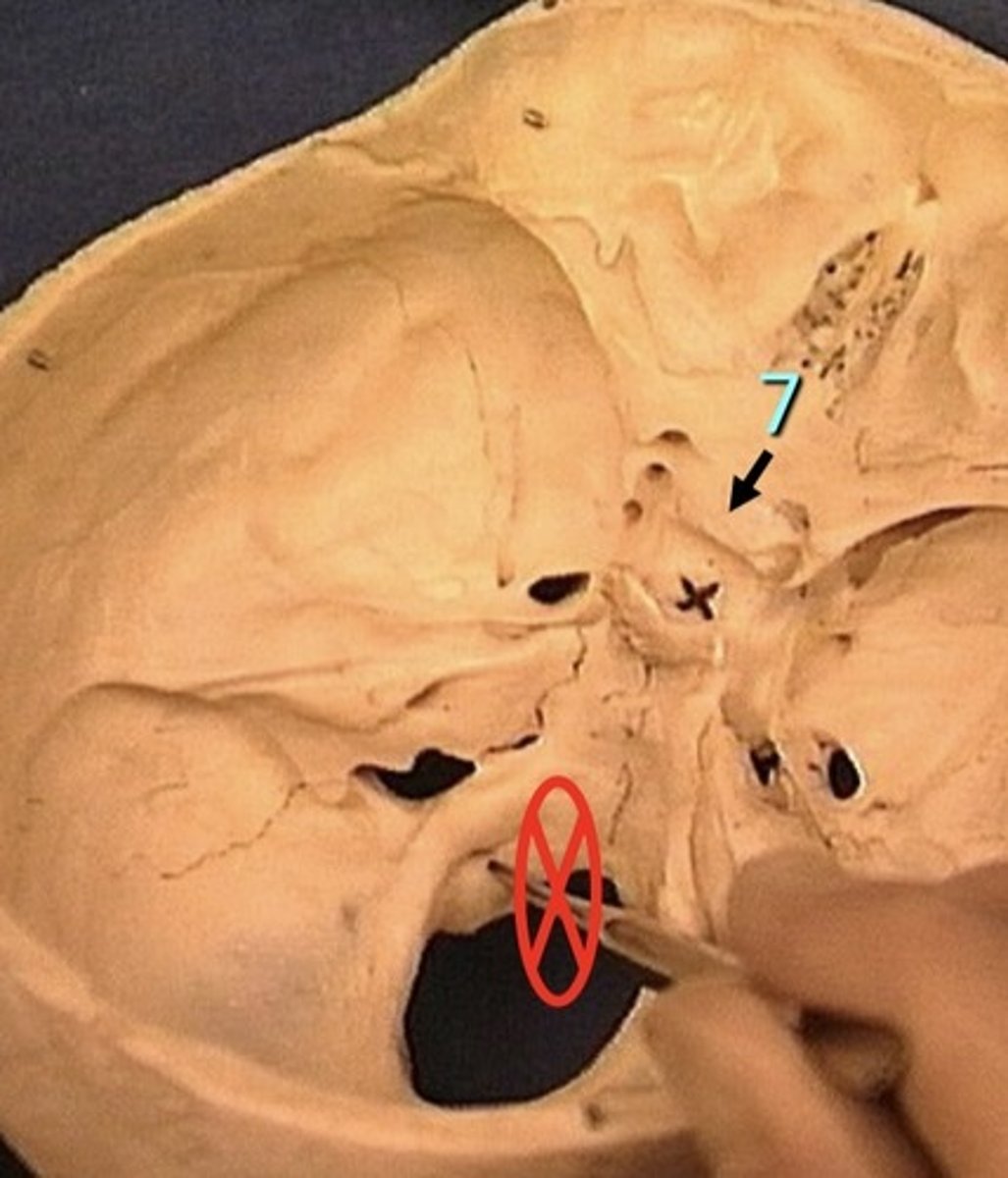
Chiasmatic groove
1. Connects the 2 optic nerves of the eye
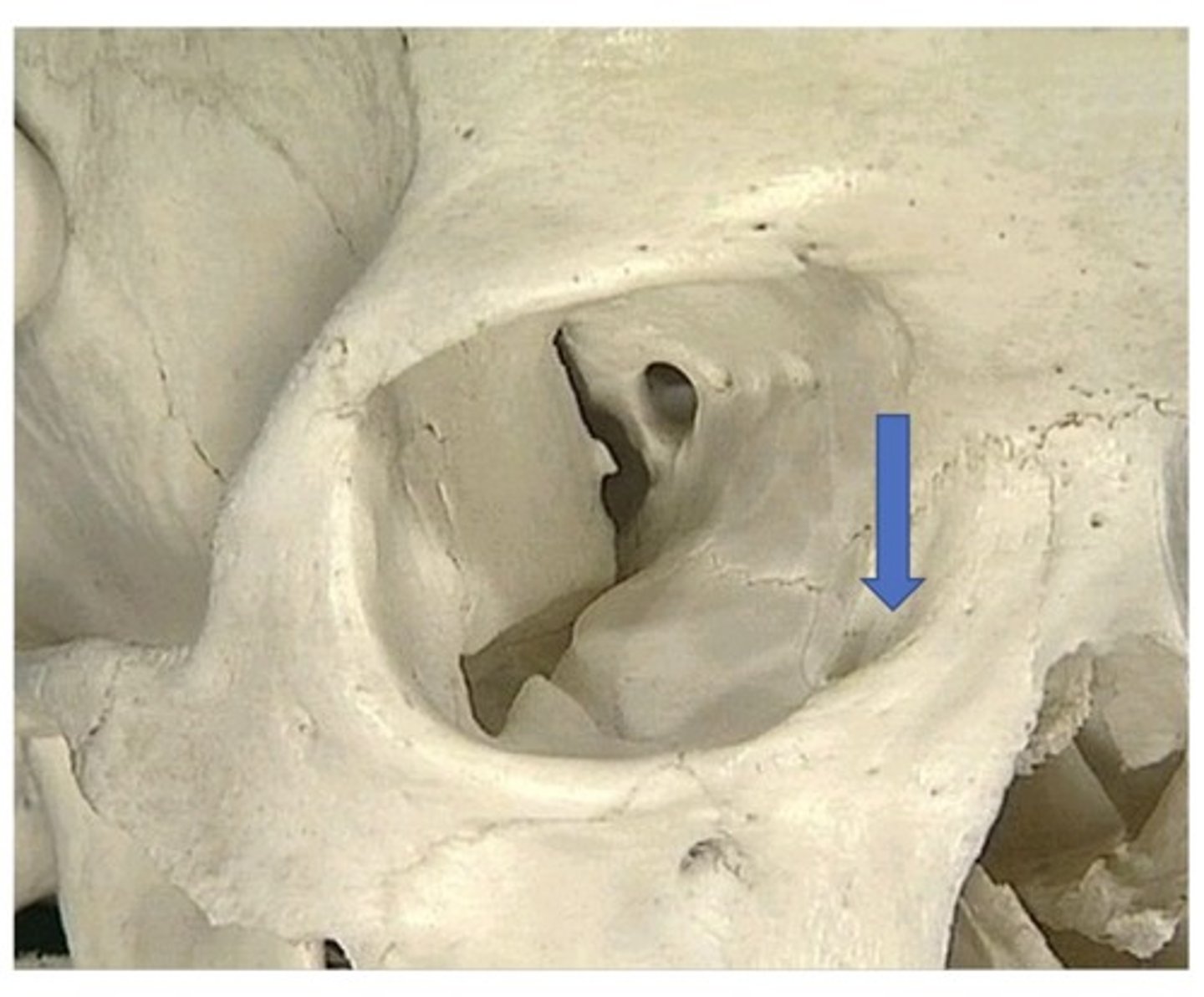
Nasolacrimal canal
1. Anterior and medial in the orbit
2. Allows the orbit to drain tears to the nose
3. When you cry, your nose gets stuffy
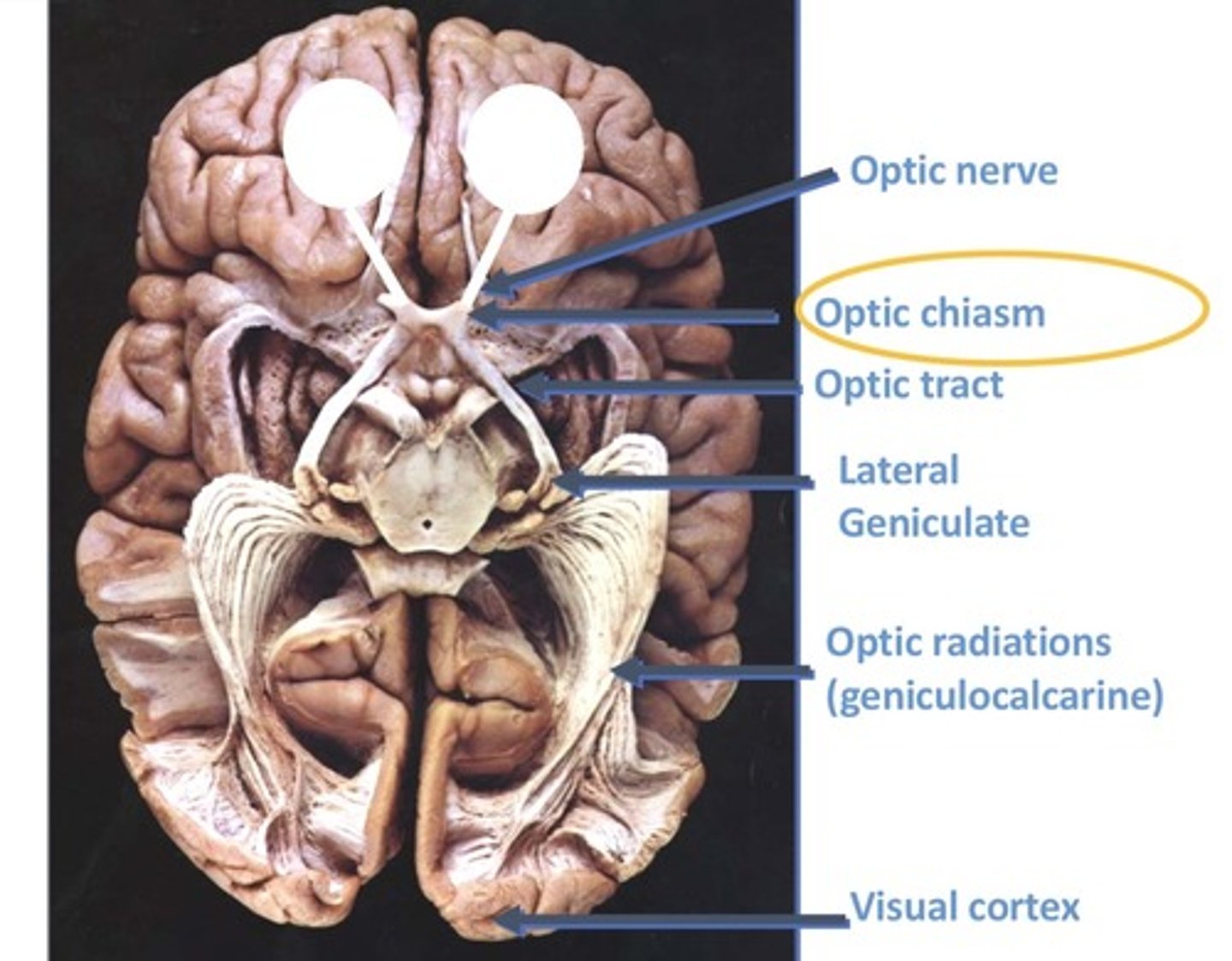
Visual pathway
Pterygoid Process