PSYC2016 - Intelligence 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
1
New cards
The Two Disciplines Problem
Experimental Paradigm
Experimental Paradigm
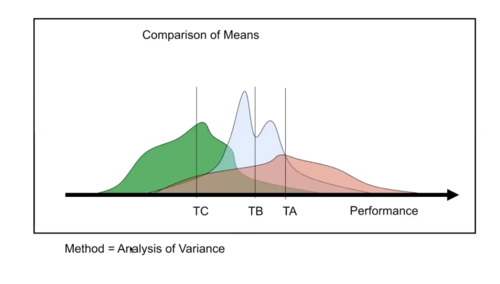
- Standardisation of "situational variables" through treatments and experimental conditions (IV's)
- Investigate cause and effect relations (on DV's) ... but on incomplete information ...
- CONTROL is the important feature
- But, what is the role of individual differences in an approach dominated by "Comparison of Means"?
- "The goal is to control behaviour and variation within treatments is proof the experimentalist has not succeeded ... Individual variation is cast into the outer darkness known as 'error variance'"
- Investigate cause and effect relations (on DV's) ... but on incomplete information ...
- CONTROL is the important feature
- But, what is the role of individual differences in an approach dominated by "Comparison of Means"?
- "The goal is to control behaviour and variation within treatments is proof the experimentalist has not succeeded ... Individual variation is cast into the outer darkness known as 'error variance'"
2
New cards
Experimental Psychology
treat variance as 'noise'
rather than individual difference
rather than individual difference
3
New cards
Correlational Psychology
'... is in love with just those variables the experimenter left home to forget.'
- Goal is to predict variation within a treatment
- Driven by the development of Factor Analysis
- Focus on relationship between performances on multiple tests
"His sophistication in data analysis has not been matched by sophistication in theory. The correlational psychologist was led into temptation by his own success, losing himself in practical prediction, and then in a narcissistic program of studying his tests as an end in themselves"
Cronbach
^ lack of theory
- Goal is to predict variation within a treatment
- Driven by the development of Factor Analysis
- Focus on relationship between performances on multiple tests
"His sophistication in data analysis has not been matched by sophistication in theory. The correlational psychologist was led into temptation by his own success, losing himself in practical prediction, and then in a narcissistic program of studying his tests as an end in themselves"
Cronbach
^ lack of theory
4
New cards
Cronbach's (1957) Lament
"Psychology continues to this day to be limited by the dedication of its investigators to one or the other method of inquiry rather than to scientific psychology as a whole"
A suggested solution...
Aptitude x Treatment Interaction
A suggested solution...
Aptitude x Treatment Interaction

5
New cards
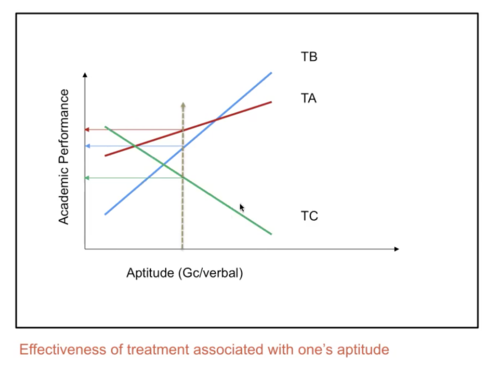
Cronbach (1957): Aptitude x Treatment Interaction
Effectiveness of treatment associated with one's aptitude
Average effects still hold, but they are qualified by aptitude
1. Over simplification - Difficult to replicate
2. Practical and resource constraints on individualisation
Average effects still hold, but they are qualified by aptitude
1. Over simplification - Difficult to replicate
2. Practical and resource constraints on individualisation
6
New cards
Attempts at Integration since 1956
Aptitude-Treatment Interactions
- Snow (1966; also Cronbach; Lohman)
Componential analyses: Correlatoin with psychometric tests
- Sternberg (1977); Hunt (1980)
Differences in skill learning as a function of aptitude
- Ackerman (1987)
WM and control processes in intelligence
- Embretson (1995)
Working memory, controlled attention, PFC, Gf
- Engle, Kane and Tuholiski (1999)
Working memory and bindings
- Oberauer et al (2003)
Latent-Trait Theory (between vs within)
- Bosboom et al (2004)
Relational integration and Gf
- Birney et al (2002; 2009; 2019)
- Snow (1966; also Cronbach; Lohman)
Componential analyses: Correlatoin with psychometric tests
- Sternberg (1977); Hunt (1980)
Differences in skill learning as a function of aptitude
- Ackerman (1987)
WM and control processes in intelligence
- Embretson (1995)
Working memory, controlled attention, PFC, Gf
- Engle, Kane and Tuholiski (1999)
Working memory and bindings
- Oberauer et al (2003)
Latent-Trait Theory (between vs within)
- Bosboom et al (2004)
Relational integration and Gf
- Birney et al (2002; 2009; 2019)
7
New cards
Have we succeeded?
As a discipline? NO...
- "Cognitive psychology promised to rescue differential psychology from psychometrics and return it to mainstream research. But this has not happened." (Lohman, 1994)
- "differential psychology was unable to achieve one of its central goals: The identification of the mental processes that underlie intelligent functioning. ... it was only recently that many in the field acknowledged that a research program dominated by factor analysis ... was incapable of producing and explanatory theory of human intelligence"
- "Cognitive psychology promised to rescue differential psychology from psychometrics and return it to mainstream research. But this has not happened." (Lohman, 1994)
- "differential psychology was unable to achieve one of its central goals: The identification of the mental processes that underlie intelligent functioning. ... it was only recently that many in the field acknowledged that a research program dominated by factor analysis ... was incapable of producing and explanatory theory of human intelligence"
8
New cards
Identification of Mental Processes
Individual Differences as a pathway to Process
- Factor Analysis [Spearmen (1904) Thurstone (1947)]
- Factors were primitive/core psychological functions
- Guildford (1967): "It is only by correlating scores on a test with scores on other tests that we can test any hypothesis as to what it measures psychologically"
- "In the search of meaning of aptitude factors, we can take one more easy but very significant step to tie factors ... to psychological theory. This step is to say that such a factor is also a psychological function"
But this assumption was RIGHTLY challenged
"studies of individual differences never come to grips with the process or operation by which a given organism achieves an intellectual response. Indeed, it is difficult to see how the available individual differences data can be used even as a starting point for generating a theory as to the process nature of general intelligence or of any other specified ability"
- Factor Analysis [Spearmen (1904) Thurstone (1947)]
- Factors were primitive/core psychological functions
- Guildford (1967): "It is only by correlating scores on a test with scores on other tests that we can test any hypothesis as to what it measures psychologically"
- "In the search of meaning of aptitude factors, we can take one more easy but very significant step to tie factors ... to psychological theory. This step is to say that such a factor is also a psychological function"
But this assumption was RIGHTLY challenged
"studies of individual differences never come to grips with the process or operation by which a given organism achieves an intellectual response. Indeed, it is difficult to see how the available individual differences data can be used even as a starting point for generating a theory as to the process nature of general intelligence or of any other specified ability"
9
New cards
Overview of the argument so far
1. Failure to identify processes of intelligence originated in the failure to consider aspects of tests that have an impact on performance during the test
2. Measurement models (structural process theory) of tests are needed; consider component processes of test performance
3. However, component scores have not been particularly useful, they don't explain individual differences
4. Tasks need to be developed that focus on qualitative differences between individuals
2. Measurement models (structural process theory) of tests are needed; consider component processes of test performance
3. However, component scores have not been particularly useful, they don't explain individual differences
4. Tasks need to be developed that focus on qualitative differences between individuals
10
New cards
David Lohman & Martin Ippel (1993)
Main Claim:
- Cognitive approach to measurement is most useful when applied to tasks designed to elicit responses that reveal qualitative differences between individuals in knowledge or strategy
Differential Test vs Cognitive Task
- Differential tests are not the same as cognitive tasks and attempts ot model one from the other have not worked well
- Experimental tasks are founded on differences between processes/conditions (e.g. list memory)
- Differential tasks are focused on differences between individuals (e.g. Raven's Matrices)
- Cognitive approach to measurement is most useful when applied to tasks designed to elicit responses that reveal qualitative differences between individuals in knowledge or strategy
Differential Test vs Cognitive Task
- Differential tests are not the same as cognitive tasks and attempts ot model one from the other have not worked well
- Experimental tasks are founded on differences between processes/conditions (e.g. list memory)
- Differential tasks are focused on differences between individuals (e.g. Raven's Matrices)
11
New cards
Factor Analysis:
Common Processes
Common Processes
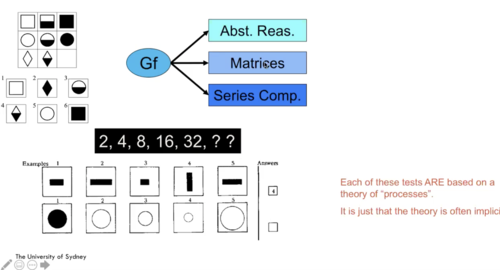
Each of these tests ARE based on a theory of 'processes'
It is just that the theory is often implicit
Not a sum
It is what they have in common
What is not in common is purer processes
It is just that the theory is often implicit
Not a sum
It is what they have in common
What is not in common is purer processes
12
New cards
Factor Analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person's total score.
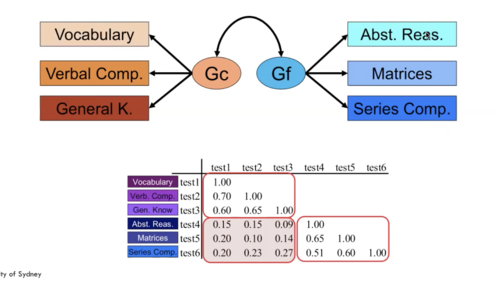
13
New cards
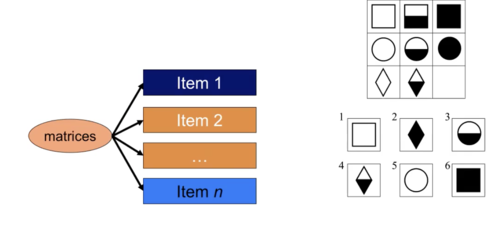
Ability tests from an item perspective
A major criterion is Reliability (repeatability of measurement)
14
New cards
The main problem with the individual differences approach to the study of intelligence was
that it did not have a clear conception of what a 'process' might be, or how particular aspects of a test might elicit those processes
Lohman & Ippel (1993, p43)
Lohman & Ippel (1993, p43)
15
New cards
Inidividual differences as a way to understand processes
Heitz, Unsworth & Engle (2005, p74)
" The most puzzling realisation is that we have good reason to implicate attention in Gf, but we are devoid of a suitable explanation of how attention comes into play when performing tasks such as the Raven (matrices test)"
" The most puzzling realisation is that we have good reason to implicate attention in Gf, but we are devoid of a suitable explanation of how attention comes into play when performing tasks such as the Raven (matrices test)"
16
New cards
Within-Subject Process Design
- Borsboom, Mellenbergh & van Heerden (2004)
- Theories based on between-subject designs (factor analysis) cannot tell us about what is happening within a given individual
- Borsboom (2015)
- Birney, Beckmann. Beckmann (2019)
- Theories based on between-subject designs (factor analysis) cannot tell us about what is happening within a given individual
- Borsboom (2015)
- Birney, Beckmann. Beckmann (2019)
17
New cards
Mental Processes as Information Processes
Definition
- Information-Processing approach treats mental activities as different operations performed on symbols and symbol structures (mental representations)
Central Assumptions
1. Mental activities are decomposable into a series of relatively independent processes or operations
2. For each mental operation, a set of task conditions exist, that when varied, will exert a selective influence on these particular processes
3. These internal processes may produce externally observable effects on behaviour
- Information-Processing approach treats mental activities as different operations performed on symbols and symbol structures (mental representations)
Central Assumptions
1. Mental activities are decomposable into a series of relatively independent processes or operations
2. For each mental operation, a set of task conditions exist, that when varied, will exert a selective influence on these particular processes
3. These internal processes may produce externally observable effects on behaviour
18
New cards
In order to benefit from the information-processing perspective, we need to reconceptualize the measurement processes
- Not so much as, Measurement as applied statistics
- But more like, Measurement as substantive theory
- But more like, Measurement as substantive theory
19
New cards
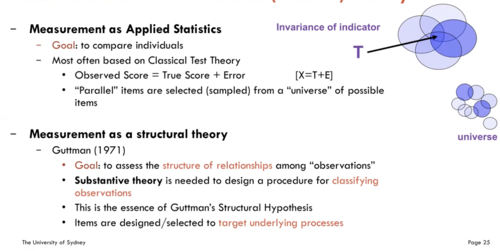
Measurement as a Structural (Process) Theory
Measurement as applied statistics
- Goal to compare individuals
- Most often based on Classical Test Theory
Measurement as a structural theory
Guttman (1971)
- Goal: to assess the structure of relationships among 'observations'
- Substansive theory is needed to design a procedure for classifying observation
- This is the essence of Guttman's Structural Hypothesis
- Items are designed/selected to target underlying processes
- Goal to compare individuals
- Most often based on Classical Test Theory
Measurement as a structural theory
Guttman (1971)
- Goal: to assess the structure of relationships among 'observations'
- Substansive theory is needed to design a procedure for classifying observation
- This is the essence of Guttman's Structural Hypothesis
- Items are designed/selected to target underlying processes
20
New cards
What is a Structural (Process) Hypothesis?
Need to ask the question: What processes or operations are instantiated when people solve a cognitive task?
21
New cards
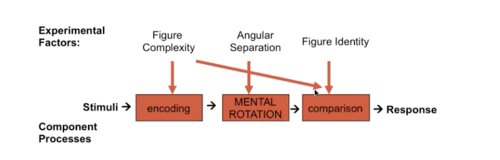
How do people make responses?
Mental Rotation Experiment (example)
Component Processes
Building a process theory and testing
Component Processes
Building a process theory and testing
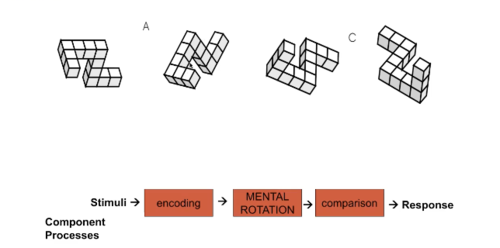
22
New cards
Structural Theory: Component Processes
Performance =
average mental rotation ability + something to deal with encoding + something to deal with mental rotation + something to deal with comparison + something to deal with an interaction
average mental rotation ability + something to deal with encoding + something to deal with mental rotation + something to deal with comparison + something to deal with an interaction
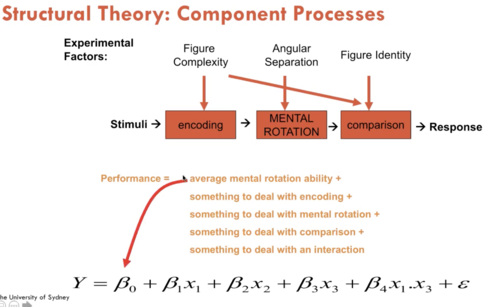
23
New cards
Two implications to consider
1. Observational Design
- Judicial selection of items to measure
2. Assumption of behaviour consistency
- Differential psychology assumption that latent dimensions are stable
- Judicial selection of items to measure
2. Assumption of behaviour consistency
- Differential psychology assumption that latent dimensions are stable
24
New cards
Observational Design
Random selection of items from the universe of possible items is not appropriate
a) Bias in measurement by specific items "ending up" in the test
b) Bias for some individuals if they have different profiles of strengths on the different processes
Suggests that different responses by the same person on different items may be systematic
- Within-subject variability (in part) due to different structural features of the task
TESTING COMPONENT PROCESSES
a) Bias in measurement by specific items "ending up" in the test
b) Bias for some individuals if they have different profiles of strengths on the different processes
Suggests that different responses by the same person on different items may be systematic
- Within-subject variability (in part) due to different structural features of the task
TESTING COMPONENT PROCESSES
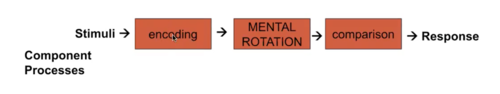
25
New cards
Measurement Design (what to score?)
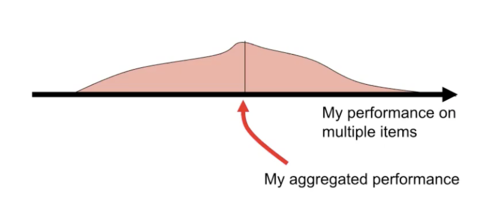
Traditionally (psychometric), the object of measurement is simply the person
- e.g. some aggregate score (total, mean) from "randomly" selected items
BUT, process analysis allows multiple objects of measurement to be specified
- Using total score aggregates within-subject variance across items and relegates it to the residual
- e.g. some aggregate score (total, mean) from "randomly" selected items
BUT, process analysis allows multiple objects of measurement to be specified
- Using total score aggregates within-subject variance across items and relegates it to the residual
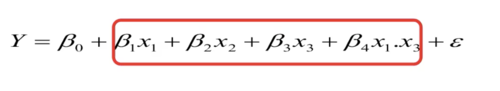
26
New cards
Assumption of behaviour consistency
Dimensional/Factor Analytic Theories
- Assumption: An individual's score/value on a factor (latent dimension) is a stable characteristic (of that person) that explains behaviour consistencies across relevant situations (in a test, items!)
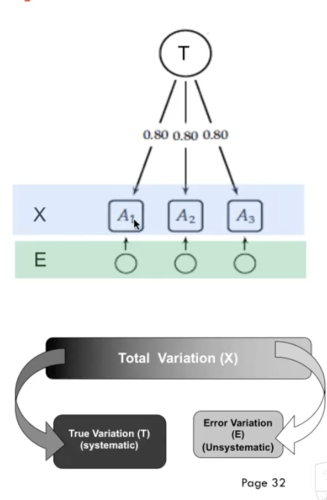
- A structural hypothesis is not relevant because attribute is assumed constant (X = T + E)
- That is, the score is assumed identical across all observation conditions
- AND: this is implemented statistically in test theories (such as Classical Test Theory)
- Assumption: An individual's score/value on a factor (latent dimension) is a stable characteristic (of that person) that explains behaviour consistencies across relevant situations (in a test, items!)
- A structural hypothesis is not relevant because attribute is assumed constant (X = T + E)
- That is, the score is assumed identical across all observation conditions
- AND: this is implemented statistically in test theories (such as Classical Test Theory)
27
New cards
Assumption of Behaviour Consistency
Factor Analytic Theories
Factor Analytic Theories
Assumption of Behaviour Consistency conflicts with the assumption made in research that aims to DESCRIBE HOW subjects achieve the responses they give (i.e. information-processing approaches)
28
New cards
Summary
Information processing approaches
Information processing approaches
Information-processing approaches rest on a view of measurement that is fundamentally different from that of dimensional theories of individual differences
29
New cards
Observational and Measurement Design
Observational Design
-The purpose of the observational design is to structure selection of items so that defensible inferences about the theoretical constructs or attributes can be made. Validity!
-The purpose of the observational design is to structure selection of items so that defensible inferences about the theoretical constructs or attributes can be made. Validity!
30
New cards
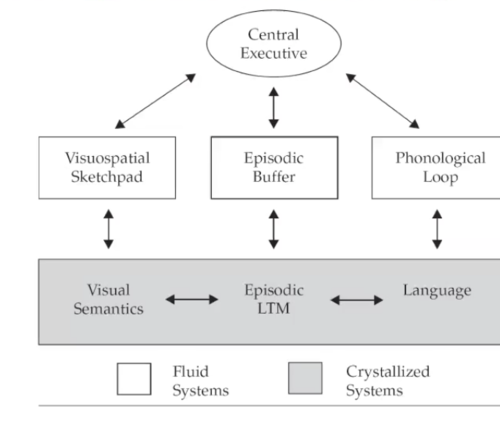
Fluid Intelligence and Working Memory Capacity
- A long-standing issue in fluid intelligence research is the need to define its nature at a deeper level than "novel problem-solving ability"
- Working-Memory (WM) Capacity has been seen as a candidate account
- Research into WM has concentrated on one of two complementary but different approaches
1. Experimental (Analytic) Approach
2. Psychometric Approach
- Each has strengths and weaknesses
- Working-Memory (WM) Capacity has been seen as a candidate account
- Research into WM has concentrated on one of two complementary but different approaches
1. Experimental (Analytic) Approach
2. Psychometric Approach
- Each has strengths and weaknesses
31
New cards
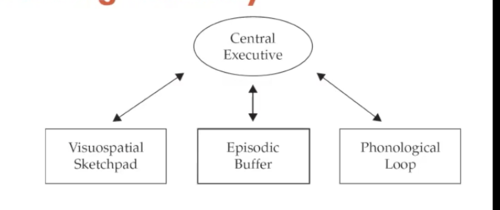
Experimental Approach to working-memory
Definition: Most effort devoted to the "slave systems"
Tasks: Dual-task methodology (using fairly simple tasks)
- reasoning + span-task
- interference task (articulatory suppression)
Test of theory: Dissociation through Dual-Task or Neuropsychological evidence
Advantages: Can be applied to analyse the constituent processes of the slave systems
Disadvantages: has made less head-way in teasing apart the complexities of the central executive (partly due to less research on this topic)
Tasks: Dual-task methodology (using fairly simple tasks)
- reasoning + span-task
- interference task (articulatory suppression)
Test of theory: Dissociation through Dual-Task or Neuropsychological evidence
Advantages: Can be applied to analyse the constituent processes of the slave systems
Disadvantages: has made less head-way in teasing apart the complexities of the central executive (partly due to less research on this topic)
32
New cards
Psychometric Approach to Working Memory Capacity
Definition: WM as a system necessary for concurrent storage and manipulation of information
Tasks: devised to combine storage and processing
Test of theory: Extent to which WM tasks predict a range of cognitive skills, such as reading, comprehension, and reasoning
Advantaged: Can (better?) tackle the central executive; work directly on problems of practical significance (reading comprehension; educational and clinical applications)
Disadvantages: Somewhat arbitrary construction of tasks that do not readily lend themselves to detailed analysis of component processes
Tasks: devised to combine storage and processing
Test of theory: Extent to which WM tasks predict a range of cognitive skills, such as reading, comprehension, and reasoning
Advantaged: Can (better?) tackle the central executive; work directly on problems of practical significance (reading comprehension; educational and clinical applications)
Disadvantages: Somewhat arbitrary construction of tasks that do not readily lend themselves to detailed analysis of component processes
33
New cards
Working Memory and Gf
Since the 1980s
- major theoretical and empirical developments of the construct of working memory as distinct from rote or span memory (short-term memory)
- several investigators began to argue that WM and intellectual abilities are highly related or even identical constructs
Daneman & Carpenter (1980)
- Relationship between individual differences in working memory and reading comprehension
- Using reading span tasks
- major theoretical and empirical developments of the construct of working memory as distinct from rote or span memory (short-term memory)
- several investigators began to argue that WM and intellectual abilities are highly related or even identical constructs
Daneman & Carpenter (1980)
- Relationship between individual differences in working memory and reading comprehension
- Using reading span tasks
34
New cards
Reading Span (Daneman & Carpenter, 1980)
"When at last his eyes opened, there was no gleam of triumph, no shade of anger"
"The taxi turned up Michigan Avenue where they had a clear view of the lake"
Assumption: It is a WM task because it requires processing and storage
Processing: Does the sentence make sense?
Storage: Recall the final words of each sentence
"The taxi turned up Michigan Avenue where they had a clear view of the lake"
Assumption: It is a WM task because it requires processing and storage
Processing: Does the sentence make sense?
Storage: Recall the final words of each sentence
35
New cards
Daneman & Carpenter (1980)
Hypothesis
- Individual differences in reading comprehension reflect differences in working memory capacity
- Trade-off between processing and storage functions
Factor Analysis
- Latent variables ...
- Represent variance that is shared among all the tasks that are being used to identify the construct
- Task-specific variance that is unique to each task is removed, resulting in a relatively pure measure of the latent construct of interest
Results
- WM (reading) span correlated with three reading comprehension measures
- Similar correlations with a listening span task
- the correlation is not specific to reading (i.e. comprehension)
Traditional digit span and word span measures which DO NOT correlate with comprehension
- Individual differences in reading comprehension reflect differences in working memory capacity
- Trade-off between processing and storage functions
Factor Analysis
- Latent variables ...
- Represent variance that is shared among all the tasks that are being used to identify the construct
- Task-specific variance that is unique to each task is removed, resulting in a relatively pure measure of the latent construct of interest
Results
- WM (reading) span correlated with three reading comprehension measures
- Similar correlations with a listening span task
- the correlation is not specific to reading (i.e. comprehension)
Traditional digit span and word span measures which DO NOT correlate with comprehension

36
New cards
Kyllonen & Christal (1990)
Reasoning ability is (little more than) working-memory capacity?!
Reasoning ability is (little more than) working-memory capacity?!
Operationalising WM
- Needed a well formulated theory of the task requirements of different WMC tasks
- Theory available?
> Experimental psychology literature: Yes
> Differential psychology: Very little
- An important point!
- Used a 'varied-content and varied-process' approach to select WMC tasks
- Makes some sense to select a wide range of tasks (different content and process), and derive a latent variable from them all
Latent Variables
- Identifies what is common!
- There is a problem with this approach (i.e. selecting tasks using a weak theory):
1. Difficult to ascertain key cognitive mechanisms underlying performance on the tasks contributing to the latent variable
2. This makes it difficult to account for the covariation between WMC and g in terms of cognitive processes
- Needed a well formulated theory of the task requirements of different WMC tasks
- Theory available?
> Experimental psychology literature: Yes
> Differential psychology: Very little
- An important point!
- Used a 'varied-content and varied-process' approach to select WMC tasks
- Makes some sense to select a wide range of tasks (different content and process), and derive a latent variable from them all
Latent Variables
- Identifies what is common!
- There is a problem with this approach (i.e. selecting tasks using a weak theory):
1. Difficult to ascertain key cognitive mechanisms underlying performance on the tasks contributing to the latent variable
2. This makes it difficult to account for the covariation between WMC and g in terms of cognitive processes
37
New cards
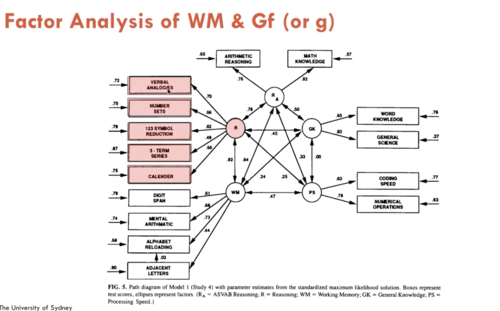
Factor Analysis of WM & Gf (or g)
grouping mental processes
latent variables
- R
- GK
- WM
- PS
testing relationships between ^
Collected data on these different tasks
Correlations:
- Reasoning & WM r = 0.82
- Reasoning and General Knowledge r = 0.45
- WM and GenKnow r = 0.24
- Reasoning and ProcSpeed r = 0.25
- WM & ProcSpeed r = 0.47
Evidence for differentiation of the WM and Reasoning factors
latent variables
- R
- GK
- WM
- PS
testing relationships between ^
Collected data on these different tasks
Correlations:
- Reasoning & WM r = 0.82
- Reasoning and General Knowledge r = 0.45
- WM and GenKnow r = 0.24
- Reasoning and ProcSpeed r = 0.25
- WM & ProcSpeed r = 0.47
Evidence for differentiation of the WM and Reasoning factors
38
New cards
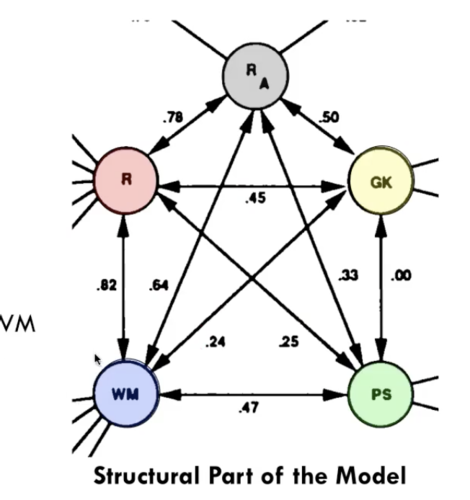
Factor Analysis of WM & Gf (or g)
Structural component of model
Structural component of model
Correlations:
- Reasoning & WM r = 0.82
- Reasoning and General Knowledge r = 0.45
- WM and GenKnow r = 0.24
- Reasoning and ProcSpeed r = 0.25
- WM & ProcSpeed r = 0.47
Evidence for differentiation of the WM and Reasoning factors
- Reasoning & WM r = 0.82
- Reasoning and General Knowledge r = 0.45
- WM and GenKnow r = 0.24
- Reasoning and ProcSpeed r = 0.25
- WM & ProcSpeed r = 0.47
Evidence for differentiation of the WM and Reasoning factors
39
New cards
Kyllonen & Christal (1990) Conclusions
The central message: g = WM
- But also evidence for some dissociation
1. Reasoning had higher correlation with Knowledge than did the WM
2. WM had a higher correlation with Processing Speed than did Reasoning
- That is, differentiation on the basis of convergent and discriminant validity evidence with General Knowledge and Processing Speed
"...we do not see 'g' as a separate factor driving the correlation between WM and Reasoning. Rather, we believe 'g' can be identified with either WM or Reasoning"
"We concede to a certain degree of arbitrariness in creating tasks according to such a broad and vague definition of their requirements, and readers may find fault with the way we operationalised the working memory factor. But without well-developed models of information-processing requirements of the tasks, we can only proceed with what is available"
- But also evidence for some dissociation
1. Reasoning had higher correlation with Knowledge than did the WM
2. WM had a higher correlation with Processing Speed than did Reasoning
- That is, differentiation on the basis of convergent and discriminant validity evidence with General Knowledge and Processing Speed
"...we do not see 'g' as a separate factor driving the correlation between WM and Reasoning. Rather, we believe 'g' can be identified with either WM or Reasoning"
"We concede to a certain degree of arbitrariness in creating tasks according to such a broad and vague definition of their requirements, and readers may find fault with the way we operationalised the working memory factor. But without well-developed models of information-processing requirements of the tasks, we can only proceed with what is available"
40
New cards
Baddeley (1992)
Individual differences approach use somewhat arbitrary construction of tasks that do not readily lend themselves to detailed analysis of component processes
41
New cards
Engle/Kane/Conway et al Studies
- Follow a similar method to Kyllonen & Christal, but on a tighter theoretical basis of WM
- Conclude that WM and 'g' are highly related, but not identical (~ 50-80% shared variance)
- Executive Attention view of WMC (controlled attention)
- Conclude that WM and 'g' are highly related, but not identical (~ 50-80% shared variance)
- Executive Attention view of WMC (controlled attention)
42
New cards
Differential Findings
STM -> not related to gf
WM -> related to gf
WM -> related to gf
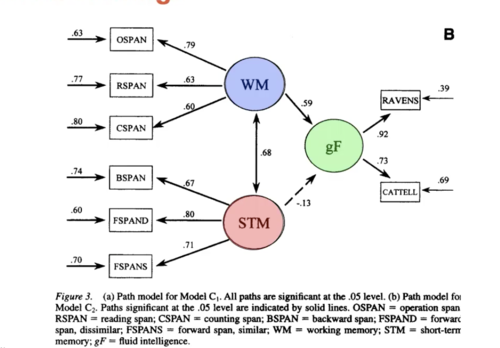
43
New cards
Alternative Methodological Approach
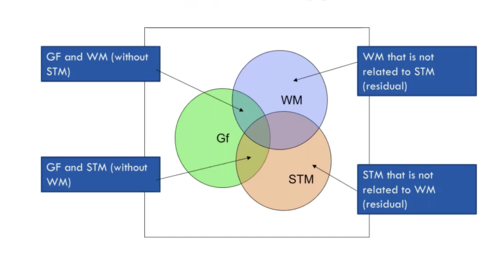
44
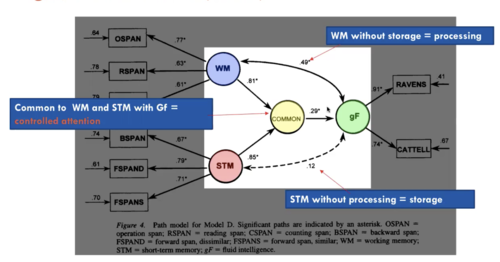
New cards
Engle, Tuholski et al (1999)
what is common?
How is this different?
postulating a common factor and see how this relates to WM, STM, gF
How is this different?
postulating a common factor and see how this relates to WM, STM, gF
45
New cards
Critical Findings from Engle et al
1. STM storage and rehearsal factors cannot account for the relation between WMC and Gf
2. WMC and STM tasks yield correlated but separate factors
3. WMC factor is more strongly associated with Gf than is STM
- Empirical Question: If the storage, rehearsal, processing and strategic processes tapped by WMC tasks do not explain (all) the correlations with ability, then what does?
- The 'common-secret ingredient' is an attention-control capability that is elicited by WMC tasks to a greater degree than by STM tasks (controlled-attention)
2. WMC and STM tasks yield correlated but separate factors
3. WMC factor is more strongly associated with Gf than is STM
- Empirical Question: If the storage, rehearsal, processing and strategic processes tapped by WMC tasks do not explain (all) the correlations with ability, then what does?
- The 'common-secret ingredient' is an attention-control capability that is elicited by WMC tasks to a greater degree than by STM tasks (controlled-attention)
46
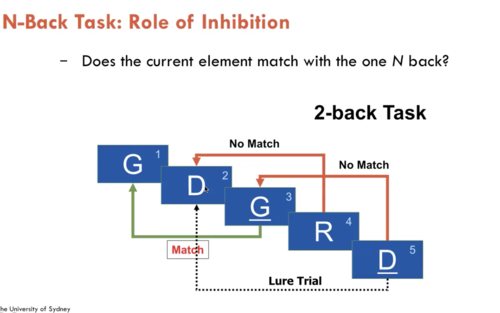
New cards
N-back Task: Role of Inhibition
Does the current element match with the one N back?
False responses due to lure
False responses due to lure
47
New cards
Burgess, Gray, Conway and Braver (2011)
Lure activities
- (failed) Inhibition
- Gf and WM
- (failed) Inhibition
- Gf and WM
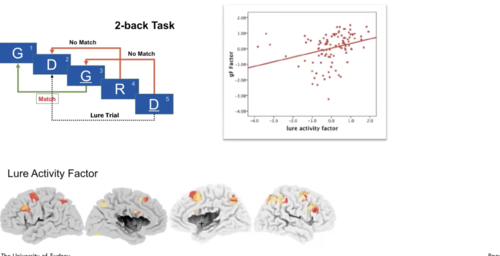
48
New cards
Gray et al (2003) - 3-back task
Performance on Lure trials
1. Lure trials are more difficult than non-lure trials
2. Lure trials predict individual differences in performance on Ravens (Gf) over and above performance on other trials
3. Correlations between brain activity and Gf were greatest in high interference (lure) trials
4. Brain activity was more focused to specific areas in lure trials than in non-lure trials
1. Lure trials are more difficult than non-lure trials
2. Lure trials predict individual differences in performance on Ravens (Gf) over and above performance on other trials
3. Correlations between brain activity and Gf were greatest in high interference (lure) trials
4. Brain activity was more focused to specific areas in lure trials than in non-lure trials
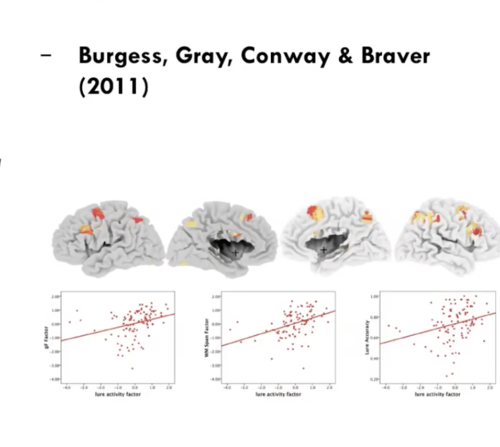
49
New cards
Brain activity and lure activities
causal model
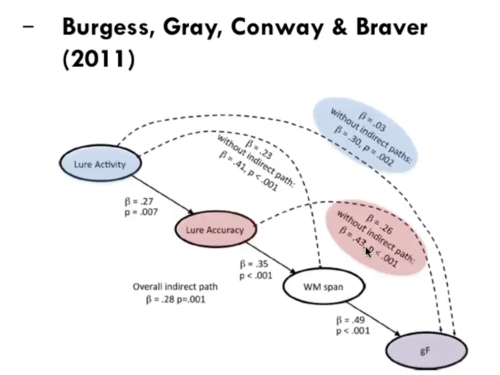
50
New cards
General Findings
Individual differences in performance on WMC tasks predict a variety of hugher order cognitive abilities (learning; comprehension; reasoning)
Even when:
- WMC and ability tests bear no surface similarity to each other
- So these factors cannot account for the relationship between WMC and ability
People with lower WMC show poorer control over thought and action than do those with higher WMC
1. Fail more often to prevent or recover from prepotent (automatic) responses
2. Show slower and less flexible allocation of attention to objects
Even when:
- WMC and ability tests bear no surface similarity to each other
- So these factors cannot account for the relationship between WMC and ability
People with lower WMC show poorer control over thought and action than do those with higher WMC
1. Fail more often to prevent or recover from prepotent (automatic) responses
2. Show slower and less flexible allocation of attention to objects
51
New cards
Shipstead & Engle (2018)
- Tests of working memory capacity place primary demand on the maintenance related aspects of the working memory system and secondary demand on the disengagement aspects
- Fluid intelligence tests place demand in the reverse order
- Thus, the observed constructs of working memory capacity and fluid intelligence do not represent separate cognitive abilities, so much as they represent different and sometimes contradictory functions that are necessary for information processing
- Fluid intelligence tests place demand in the reverse order
- Thus, the observed constructs of working memory capacity and fluid intelligence do not represent separate cognitive abilities, so much as they represent different and sometimes contradictory functions that are necessary for information processing
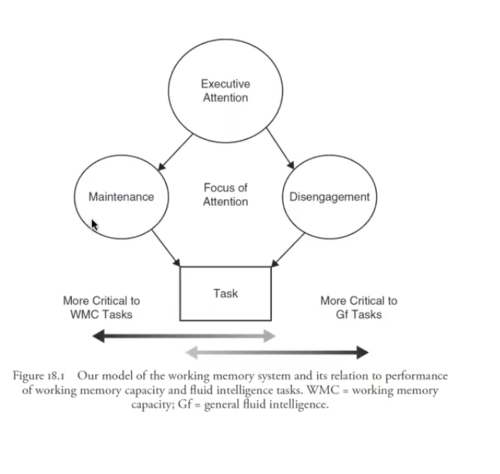
52
New cards
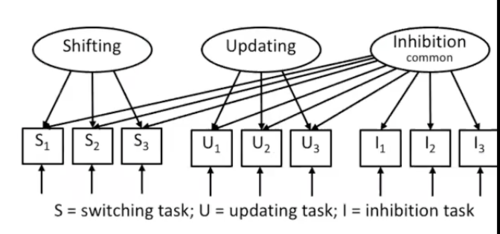
Executive Functions: Miyake, Emerson et al 2000
Shifting
- shifting between mental sets or operations by disengaging from an irrelevant mental set and actively engaging in a set relevant to the current task
Updating
- active process of monitoring incoming information and 'updating' items held in working memory by replacing irrelevant information with task-relevant information
Inhibition
- active and deliberate overriding of a dominant or automatic response in order to complete a task
Unity-Diversity EF Framework (Miyake and Friedman 2012)
- Unity is represented by the arrows from the distinct inhibition factor linking all tasks
- Diversity is represented as each factor is linked by arrows to their respective tasks (and only their tasks for updating and shifting)
- shifting between mental sets or operations by disengaging from an irrelevant mental set and actively engaging in a set relevant to the current task
Updating
- active process of monitoring incoming information and 'updating' items held in working memory by replacing irrelevant information with task-relevant information
Inhibition
- active and deliberate overriding of a dominant or automatic response in order to complete a task
Unity-Diversity EF Framework (Miyake and Friedman 2012)
- Unity is represented by the arrows from the distinct inhibition factor linking all tasks
- Diversity is represented as each factor is linked by arrows to their respective tasks (and only their tasks for updating and shifting)
53
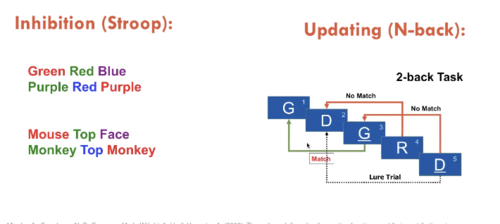
New cards
Example of inhibition and updating tasks
+ Wisconsin card sorting task
54
New cards
Dynamic Model of General Intelligence
(Conway and Kovacs, 2018)
(Conway and Kovacs, 2018)
Process Overlap Theory
- Motivated by Gf-Gc theory
- Gf Working Memory relationship
WM Processes most likely reflect individual differences in executive attention
g is 'not a thing' but instead is the consequence of a set of overlapping cognitive processes sampled by a battery of tests
- Different intelligence tasks require multiple domain-general processes (explain positive manifold, and 'g')
- Overlap in these different processes has been demonstrated to lead to positive manifold
Therefore 'g' is:
- an index rather than a causal factor (cf Gottfredson)
- result of measurement
POT is influenced by the executive attention theory of WM
- Motivated by Gf-Gc theory
- Gf Working Memory relationship
WM Processes most likely reflect individual differences in executive attention
g is 'not a thing' but instead is the consequence of a set of overlapping cognitive processes sampled by a battery of tests
- Different intelligence tasks require multiple domain-general processes (explain positive manifold, and 'g')
- Overlap in these different processes has been demonstrated to lead to positive manifold
Therefore 'g' is:
- an index rather than a causal factor (cf Gottfredson)
- result of measurement
POT is influenced by the executive attention theory of WM
55
New cards
Executive Functions and CHC
56
New cards
Expertise
Ackerman
- Adult Intelligence
- Knowledge and expertise
- Conative dispositions are important
> Personality
> Interests
Ericsson
- Adult expertise
- Arrested Development
- Deliberate Practice
Learning Objectives
- Understand Ackerman's view on the importance of non-cognitive variables on the intelligence as knowledge, and evidence for this view
- Understand the concepts of automatisation, arrested development and developing expertise
- Adult Intelligence
- Knowledge and expertise
- Conative dispositions are important
> Personality
> Interests
Ericsson
- Adult expertise
- Arrested Development
- Deliberate Practice
Learning Objectives
- Understand Ackerman's view on the importance of non-cognitive variables on the intelligence as knowledge, and evidence for this view
- Understand the concepts of automatisation, arrested development and developing expertise
57
New cards
A Broader Conceptualization of Individual Differences
Some Puzzling Facts
- Correlations between measures of intelligence and uni GPA rarely exceed 0.50 (i.e. 75% unexplained variance)
- Research in gerontology show that adults perform poorly on several tests of intellectual abilities, BUT function quite well in day-to-day activities
^ more to intelligence than just test results
- Teachers identification of over achievement and under achievement
- Expertise is not simply a function of g
- Correlations between measures of intelligence and uni GPA rarely exceed 0.50 (i.e. 75% unexplained variance)
- Research in gerontology show that adults perform poorly on several tests of intellectual abilities, BUT function quite well in day-to-day activities
^ more to intelligence than just test results
- Teachers identification of over achievement and under achievement
- Expertise is not simply a function of g
58
New cards
Academic vs 'Real-World'
In contrast with
- Multiple Intelligences (Gardener)
- Creative and Practical Intelligence (Sternberg)
- Emotional Intelligence (Mayer & Salovey)
- Multiple Intelligences (Gardener)
- Creative and Practical Intelligence (Sternberg)
- Emotional Intelligence (Mayer & Salovey)
59
New cards
Phillip Ackerman: PPIK Theory
Summary of Ackerman's Arguments
- Under-appreciation of the importance of knowledge
- Inappropriate to use the methodology of child assessment for the assessment of adult intellect
- Intelligence Tests we use do not assess knowledge very well
- Broader conceptualization of knowledge is needed
- Personality and interests contribute to knowledge acquisition
- Under-appreciation of the importance of knowledge
- Inappropriate to use the methodology of child assessment for the assessment of adult intellect
- Intelligence Tests we use do not assess knowledge very well
- Broader conceptualization of knowledge is needed
- Personality and interests contribute to knowledge acquisition
60
New cards
PPIK
P: Intelligence as Process
P: Personality
I: Interests
K: Intelligence as Knowledge
P: Personality
I: Interests
K: Intelligence as Knowledge
61
New cards
Justifications for taking knowledge seriously
1. Lay definitions (our implicit/intuitive theories of intelligence)
- Person's intellect often defined as what things an individual can perform or achieve hence, performance on 'intelligence tests' is just a small part of implicit theories
In contrast,
- other competencies characterise broader aspects of adult intellect, such as being able to:
> figure out financial markets
> build a house
> write an article or novel
> perform scientific experiments
> and so on...
So, our implicit theories about intelligence suggest a broader conceptualisation
- Person's intellect often defined as what things an individual can perform or achieve hence, performance on 'intelligence tests' is just a small part of implicit theories
In contrast,
- other competencies characterise broader aspects of adult intellect, such as being able to:
> figure out financial markets
> build a house
> write an article or novel
> perform scientific experiments
> and so on...
So, our implicit theories about intelligence suggest a broader conceptualisation
62
New cards
Second justification for taking knowledge seriously
2. Research
a) Investigation into knowledge-based and skill-based differences in experts and novices
- Declarative Knowledge: Knowing that/what (most Gc tasks measure this)
- Procedural Knowledge: Knowing how
- Tacit Knowledge and Practical Intelligence: Knowing with
b) Expertise is predicated on long study and practice to develop rich, specific knowledge structures
a) Investigation into knowledge-based and skill-based differences in experts and novices
- Declarative Knowledge: Knowing that/what (most Gc tasks measure this)
- Procedural Knowledge: Knowing how
- Tacit Knowledge and Practical Intelligence: Knowing with
b) Expertise is predicated on long study and practice to develop rich, specific knowledge structures
63
New cards
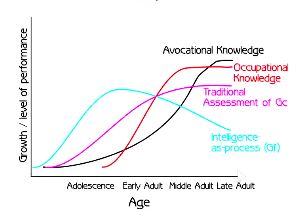
Influences on the development of PPIK: Gf/Gc
Fluid Intelligence (Gf)
- The ability to grasp relations between things
- Nonverbal abilities, inductive and deductive reasoning
- Culture free (????? in theory, but not in practice)
Crystallised Intelligence (Gc)
- Acquired knowledge and skills
- acculturated knowledge requires exposure to culture, formal/informal education
- may require some investment of fluid intelligence
Knowledge (Gc) develops out of an investment of Gf
- The ability to grasp relations between things
- Nonverbal abilities, inductive and deductive reasoning
- Culture free (????? in theory, but not in practice)
Crystallised Intelligence (Gc)
- Acquired knowledge and skills
- acculturated knowledge requires exposure to culture, formal/informal education
- may require some investment of fluid intelligence
Knowledge (Gc) develops out of an investment of Gf
64
New cards
Intelligence as Process: Maximal Performance
Intelligence-as-Process
- Speed of processing; memory; reasoning
- Classic Gf conceptualization has problems
- Some tasks are Gf for some people (Children) and Gc for others (Adults)
Note: General ability tests attempt to remove the benefits of specific expertise
- Sampling is very broad and content is not associated with expertise
Without the application of directed cognitive effort toward knowledge acquisition, performance on specific achievement tests will suffer
- Speed of processing; memory; reasoning
- Classic Gf conceptualization has problems
- Some tasks are Gf for some people (Children) and Gc for others (Adults)
Note: General ability tests attempt to remove the benefits of specific expertise
- Sampling is very broad and content is not associated with expertise
Without the application of directed cognitive effort toward knowledge acquisition, performance on specific achievement tests will suffer
65
New cards
Personality
- Weakly related to intelligence-as-process
- Intelligence-as-knowledge is associated with two related personality traits
- Openness to experience (Big five factor)
- Need for Cognition
Need for Cognition Scale
- Like to solve complex problems
- Need things explained only once
- Love to think up new ways of doing things
- Love to read challenging material
x
- Have difficulty understanding abstract ideas
- Try to avoid complex people
- Avoid philosophical discussions
- Intelligence-as-knowledge is associated with two related personality traits
- Openness to experience (Big five factor)
- Need for Cognition
Need for Cognition Scale
- Like to solve complex problems
- Need things explained only once
- Love to think up new ways of doing things
- Love to read challenging material
x
- Have difficulty understanding abstract ideas
- Try to avoid complex people
- Avoid philosophical discussions

66
New cards
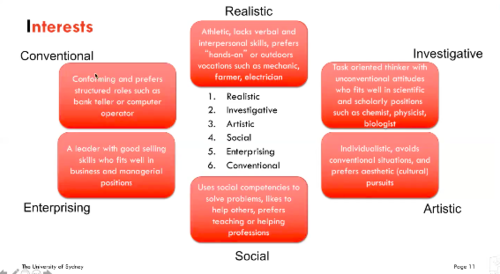
Interests
1. Realistic
2. Investigative
3. Artistic
4. Social
5. Enterprising
6. Conventional
2. Investigative
3. Artistic
4. Social
5. Enterprising
6. Conventional
67
New cards
(Intelligence as) Knowledge
1. Similar to Gc but broader and more encompassing (not just academic)
2. Gc is often determined 'historically'
3. Test of intellectual performance that is contextual
4. Developmental trajectory similar to Gc
- Argument is not that these (PPIK) are all measuring aspects of the same thing (which is one way to interpret correlations)
- These distinct attributes contribute interactively in the development of abilities, competencies and expertise
2. Gc is often determined 'historically'
3. Test of intellectual performance that is contextual
4. Developmental trajectory similar to Gc
- Argument is not that these (PPIK) are all measuring aspects of the same thing (which is one way to interpret correlations)
- These distinct attributes contribute interactively in the development of abilities, competencies and expertise
68
New cards
Development of Personality, Interests and Intelligence
Abilities and Interests develop in tandem
1. Ability levels determine the probability of success in a particular task domain
2. Personality and interest determine the motivation for attempting a task
3. With subsequent successful attempts at task performance, interest increases and knowledge in the task increases
With subsequent unsuccessful attempts at task, interest declines
1. Ability levels determine the probability of success in a particular task domain
2. Personality and interest determine the motivation for attempting a task
3. With subsequent successful attempts at task performance, interest increases and knowledge in the task increases
With subsequent unsuccessful attempts at task, interest declines
69
New cards
During Childhood
Common (educational) experiences limit inter-individual differences in specialised knowledge
- The extent that hobbies and interest in other extra-curricular activities develop, and are motivating, expertise develops
- As one moves away from homogenous experience, differentiation in skills and knowledge increases - (inter)-individual differences grow
Therefore, in assessing ability, content is important
- The extent that hobbies and interest in other extra-curricular activities develop, and are motivating, expertise develops
- As one moves away from homogenous experience, differentiation in skills and knowledge increases - (inter)-individual differences grow
Therefore, in assessing ability, content is important
70
New cards
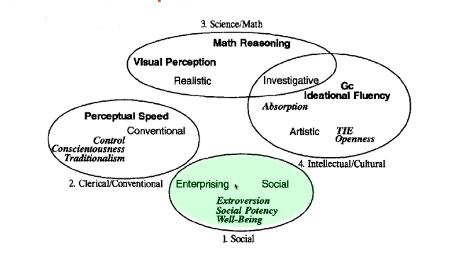
Evidence 1. trait complexes
clusters
- abilities
- personalities
- abilities
- personalities
71
New cards
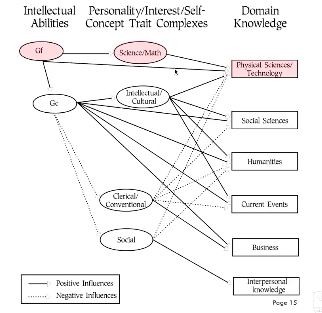
Evidence 2
Relations between abilities, trait complexes, and knowledge
positive AND negative
positive AND negative
72
New cards
Ackerman's Research Conclusions
1. Middle-aged adults more knowledgeable on several broad and specific domains compared with young adults
- Supports notion that focused cognitive investment over extended periods of time yields clear differences between individuals in depth and breadth of expertise
2. Measures of Gf, which declines as adults enter middle age, fail to fully account for individual differences in knowledge structures or that middle-age adults know more
- Gc is more predictive, but doesn't capture rich breadth and depth of domain-specific knowledge
3. Science/Math and Intellectual/Cultural trait complexes are supportive of domain-knowledge acquisition, whereas Social and Clerical/conventional impede acquisition
- Supports notion that focused cognitive investment over extended periods of time yields clear differences between individuals in depth and breadth of expertise
2. Measures of Gf, which declines as adults enter middle age, fail to fully account for individual differences in knowledge structures or that middle-age adults know more
- Gc is more predictive, but doesn't capture rich breadth and depth of domain-specific knowledge
3. Science/Math and Intellectual/Cultural trait complexes are supportive of domain-knowledge acquisition, whereas Social and Clerical/conventional impede acquisition
73
New cards
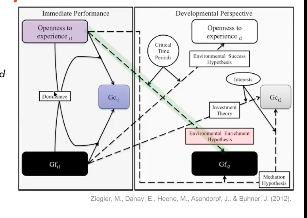
Cattell's Investment Theory: Gf and Gc
1. Historical and present-day Gc
- Ackerman: "For adults, historical abilities (or school version abilities) are those that are assessed by most standardised group tests used in schools - those that focus on the kind of knowledge and skills developed prior to adulthood"
2. Gc is experiential
- Influenced by time invested in intellectual pursuits over development, and by historical and current interests and memory
Open people are more likely to be attracted to more learning opportunities which positively affect Gf
- Gf positively affects Openness because the skills afforded by Gf are more likely to lead to success in novel, complex situations
- Ackerman: "For adults, historical abilities (or school version abilities) are those that are assessed by most standardised group tests used in schools - those that focus on the kind of knowledge and skills developed prior to adulthood"
2. Gc is experiential
- Influenced by time invested in intellectual pursuits over development, and by historical and current interests and memory
Open people are more likely to be attracted to more learning opportunities which positively affect Gf
- Gf positively affects Openness because the skills afforded by Gf are more likely to lead to success in novel, complex situations
74
New cards
Summary
Development of adult intellect
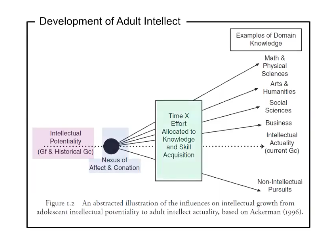
75
New cards
K.Anders Ericsson: Deliberate Practice
Modifiability of performances
- the biological mechanisms underlying performances can be improved substantially
Mechanisms
- Expert performance is mediated by complex modificable representations that allow experts to exhibit
> faster speed
> superior selection of actions, and
> more precise motor execution
Substantial Practice Effects
1. Short-term Memory Task
- Tested repeatedly every second day for many weeks and months
all improved 200%
Interpretation
- Acquired skill for storing and accessing LTM
- Expanded their functional working-memory
2. Physical Activity
push-ups
- the biological mechanisms underlying performances can be improved substantially
Mechanisms
- Expert performance is mediated by complex modificable representations that allow experts to exhibit
> faster speed
> superior selection of actions, and
> more precise motor execution
Substantial Practice Effects
1. Short-term Memory Task
- Tested repeatedly every second day for many weeks and months
all improved 200%
Interpretation
- Acquired skill for storing and accessing LTM
- Expanded their functional working-memory
2. Physical Activity
push-ups
76
New cards
Mechanisms mediating superior performance of experts
the ability to
1. select superior actions
2. generate rapid reactions
3. control movement production
1. select superior actions
2. generate rapid reactions
3. control movement production
77
New cards
1. Select superior actions
Analysis of verbal think aloud reports
1. Performance of experts is mediated by increasingly complex control processes
- More extensive planning, reasoning, evaluation (expert chess players can follow chess games in their head)
2. Rapidly encode and store information so that it can be more effectively accessed and manipulated
1. Performance of experts is mediated by increasingly complex control processes
- More extensive planning, reasoning, evaluation (expert chess players can follow chess games in their head)
2. Rapidly encode and store information so that it can be more effectively accessed and manipulated
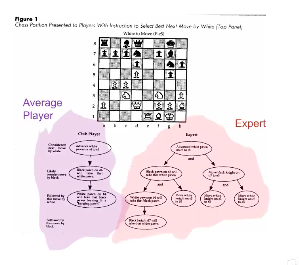
78
New cards
Stages of Learning (for typical performance)
First stages of learning
- Try to understand what is going on and avoid making mistakes
Middle phase
- Gross errors become rare
Later phase
- Performance becomes 'automated'
- Further skill acquisition is minimised
- Risk of 'arrested development'
- Try to understand what is going on and avoid making mistakes
Middle phase
- Gross errors become rare
Later phase
- Performance becomes 'automated'
- Further skill acquisition is minimised
- Risk of 'arrested development'
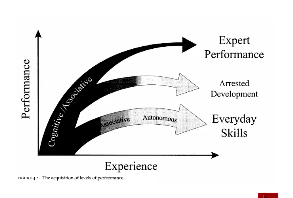
79
New cards
Typical Learning Process
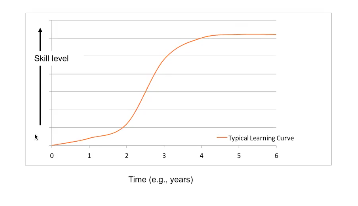
80
New cards
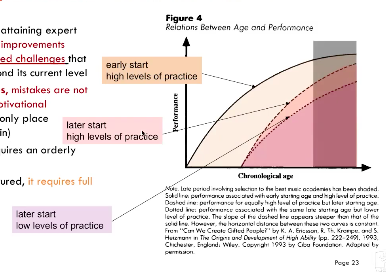
Arrested Development and Deliberate Practice
- The principal challenge for attaining expert performance is that further improvements require continuously increased challenges that raise the performance beyond its current level
- Challenges create mistakes, mistakes are not enjoyable and creates a motivational challenge (pretty much the only place motivation comes in)
- Acquisition of expertise requires and orderly and deliberate approach
- Deliberate practice is structured, it requires full concentration
10 year rule?!
- Challenges create mistakes, mistakes are not enjoyable and creates a motivational challenge (pretty much the only place motivation comes in)
- Acquisition of expertise requires and orderly and deliberate approach
- Deliberate practice is structured, it requires full concentration
10 year rule?!
81
New cards
Dynamic Assessment
Binet (1909); Thorndike (1924); Andre Rey (1934)
- Necessity to measure 'ability to learn'
- Suggested testing educability
Lev Vygotsky (1943/1962)
- Zone of Proximal Development
- An interaction between social context and individual
- What can be achieved with scaffolding instruction
Rueven Feuerstein (1970's)
- Mediated Learning Experience
- "Cognitive modifiability' is achieved through mediation of the complexities of the environment (task) to the individual
- Necessity to measure 'ability to learn'
- Suggested testing educability
Lev Vygotsky (1943/1962)
- Zone of Proximal Development
- An interaction between social context and individual
- What can be achieved with scaffolding instruction
Rueven Feuerstein (1970's)
- Mediated Learning Experience
- "Cognitive modifiability' is achieved through mediation of the complexities of the environment (task) to the individual
82
New cards
Lecture 9 Overview
Learning potential as cognitive flexibility
- Working-memory and Gf
- Structural process hypothesis
- Conative determinants of learning
- Working-memory and Gf
- Structural process hypothesis
- Conative determinants of learning
83
New cards
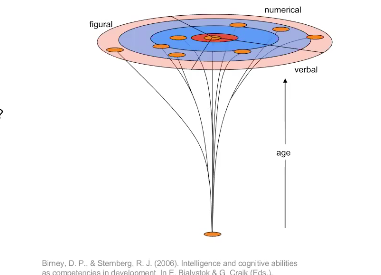
Dynamic Assessment of Learning Potential
Ability as competencies in development
- Assessment as a snapshot in time
Dynamic Assessment as Intervention
- What can be achieved with feedback?
- How much is feedback needed to achieve?
begins unitary, becomes much more diverse
- Assessment as a snapshot in time
Dynamic Assessment as Intervention
- What can be achieved with feedback?
- How much is feedback needed to achieve?
begins unitary, becomes much more diverse
84
New cards
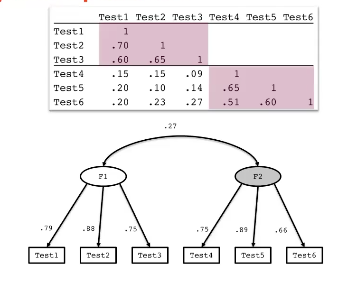
A paradigm for studying dynamic processes
Structural Process Hypothesis
1. Historically, understanding intelligence has been a between-person endeavor
2. Psychometrics are unable to identify the mental processes that underlie intelligent functioning
3. Within-person level processing must be incorporated in between-person measurement models
4. Need theoretically substantive structural process hypotheses and experimental manipulations
1. Historically, understanding intelligence has been a between-person endeavor
2. Psychometrics are unable to identify the mental processes that underlie intelligent functioning
3. Within-person level processing must be incorporated in between-person measurement models
4. Need theoretically substantive structural process hypotheses and experimental manipulations
85
New cards
Cognitive Flexibility
Cognitive flexibility as an executive function assessed through shifting and set-switching tasks
- BUT .. this is an incomplete perspective, and maybe too narrow
(Wisconsin Card Sorting Test)
The extant literature suggests understanding cognitive flexibility as
- A cognitive approach to novelty processing
- A conative disposition towards novelty
- BUT .. this is an incomplete perspective, and maybe too narrow
(Wisconsin Card Sorting Test)
The extant literature suggests understanding cognitive flexibility as
- A cognitive approach to novelty processing
- A conative disposition towards novelty
86
New cards
Wisconsin Card Sorting Task Scoring
The task
Sort 64 cards to match either
- colour rule (red, blue, yellow or green)
- form rule (crosses, circles, triangles or stars)
- number rule (one, two, three, or four figures)
The sorting rule changes without notice
Requirement
- Monitor for rule changes
- Shift sets accordingly
- Sort cards following the new sorting rule
Scoring (most common)
- Set shifting (flexibility) difficulties indicated by total number of preservative errors
Sort 64 cards to match either
- colour rule (red, blue, yellow or green)
- form rule (crosses, circles, triangles or stars)
- number rule (one, two, three, or four figures)
The sorting rule changes without notice
Requirement
- Monitor for rule changes
- Shift sets accordingly
- Sort cards following the new sorting rule
Scoring (most common)
- Set shifting (flexibility) difficulties indicated by total number of preservative errors
87
New cards
Cognitive flexibility definition
Cognitive flexibility is reflected in adaptive performance as a strategic response to novelty in dynamic environments
We can operationalise this
- Correlates of problem solving that almost exclusively relies on between-subjects designs, is limited in its capability to serve as the foundation for understanding dynamic decision making
- So use within-subjects designs
We can operationalise this
- Correlates of problem solving that almost exclusively relies on between-subjects designs, is limited in its capability to serve as the foundation for understanding dynamic decision making
- So use within-subjects designs
88
New cards
Lecture 9
Advantages of...
- Investigation of repeated observations
- under systematic conditions (experimental control; structural process hypothesis)
Entails...
- Within-subject designs and analytics
Hypothesis Testing ...
- Experimental manipulations hypothesized a priori to make differential demands on intelligence
Why ... ?
- To better understand the dynamic nature of processes underlying intelligence
Case Study 1
- Latin Square Task
Case Study 2
- Raven's (Psychometric Assessment)
Case Study 3
- Complex Problem Solving (Microworld)
Moderators: Gf, Personality, Emotional Intelligence, Conative Mindsets
- Investigation of repeated observations
- under systematic conditions (experimental control; structural process hypothesis)
Entails...
- Within-subject designs and analytics
Hypothesis Testing ...
- Experimental manipulations hypothesized a priori to make differential demands on intelligence
Why ... ?
- To better understand the dynamic nature of processes underlying intelligence
Case Study 1
- Latin Square Task
Case Study 2
- Raven's (Psychometric Assessment)
Case Study 3
- Complex Problem Solving (Microworld)
Moderators: Gf, Personality, Emotional Intelligence, Conative Mindsets
89
New cards
Case 1: Manipulations of Working Memory in the Latin Square Task
Simultaneous storage and processing
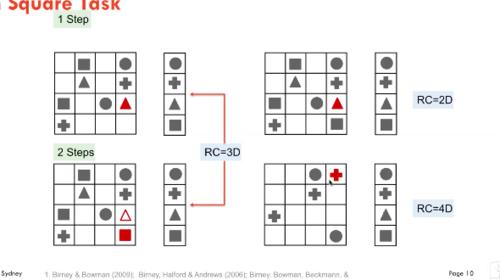
90
New cards
Case 1: Results
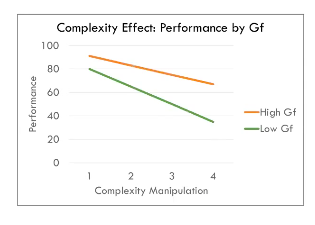
Complexity Effect
- Is the relationship between Gf and performance moderated by task manipulation (i.e., RC and Steps)?
- Is the relationship between Gf and performance moderated by task manipulation (i.e., RC and Steps)?
91
New cards
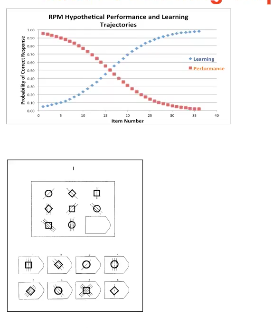
Case 2: Learning Trajectories
Can we explain the individual variance?
- Cognitive Difficulty - arousal?
- Learning from experience - worry?
Neuroticism
- Cognitive Difficulty - arousal?
- Learning from experience - worry?
Neuroticism
92
New cards
Learning Trajectories
93
New cards
Case 3: Complex Problem Solving (CPS) & Microworlds
Simulation variables
Input variables
- Decision variables
- Those for which the problem solver or learner sets the values
Output variables
- consequences of the input decisions plus effect due to intervening relationships within the model
Input variables
- Decision variables
- Those for which the problem solver or learner sets the values
Output variables
- consequences of the input decisions plus effect due to intervening relationships within the model
94
New cards
Complex Problem Solving (cps)

95
New cards
Microworlds

96
New cards
Microworlds: Examples in Business Education

97
New cards
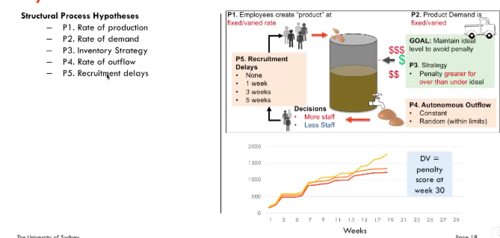
Dynamic Performance Parameters
Microworlds (Dynamic Systems)
Input variables
- Decisions
Output variables
- Cumulative penalty
Input variables
- Decisions
Output variables
- Cumulative penalty
98
New cards
Dynamic Performance Parameters
variables
variables
- Penalties
- Attempts
- Attempts
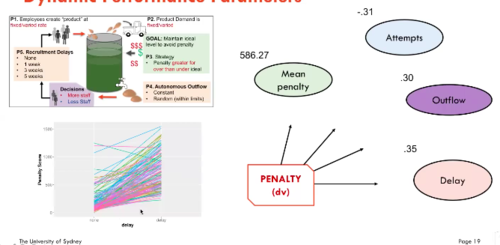
99
New cards
Case 3: Results
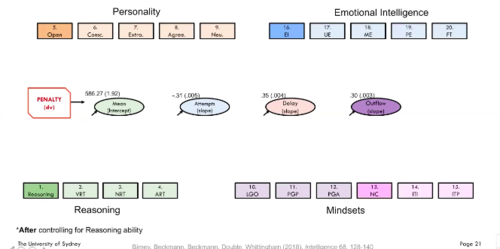
100
New cards
Summary
Cognitive Flexibility
Cognitive Flexibility
Cognitive flexibility as learning potential
- Limitations of the use of correlations and factor analysis alone
- Structural process hypothesis
- Working memory and Gf
- Conative determinants of learning
- Limitations of the use of correlations and factor analysis alone
- Structural process hypothesis
- Working memory and Gf
- Conative determinants of learning