Th II Exam 4
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
INACTIVE thyroid hormone =
T4 thyroxine
ACTIVE thyroid hormone =
T3 triiodothyronine
Thyroid hormones are mostly _________ (99% inactive)
protein bound
HYPOthyroidism lab values →
-T4, +TSH
HYPERthyroidism lab values →
+T4, -TSH
HYPOTHYROIDISM
-T4, +TSH
#1 cause in iodine-sufficient areas →
#1 cause worldwide →
s/s → “COLD FACTS”
hashimoto’s
iodide deficiency or excess
cold intolerance
overweight
low mood
dry skin
fatigue
abnormal heavy menses
constipation
thinning hair
slow HR
DRUG-ASSOCIATED CAUSES OF HYPOTHYROIDISM (ITALC)
*can also cause hyperthyroidism
interferons*
tyrosine kinase inhib
amiodarone*
lithium
carbamazepine
HYPOTHYROIDISM TREATMENT
________ is the drug of choice
Dose → ____ mcg/kg/day, may initiate lower
Titrate every ____ until TSH normalizes
Use _____ formulation/product each time!!
Counseling →
Side effects →
Drug interxns: DEC absorption → 6
INC T4 metabolism (higher concentration) → 4
DEC effectiveness → 1
May increase the effects of _________
levothyroxine (T4)
1.7
6-8w
same
take 30-60m b4 breakfast OR at bedtime (3h+ after evening meal); empty stomach
hyperthyroidism, cardiac
cations, orlistat, BAS, PPIs, H2RAs, sucralfate
rifampin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, SSRIs
beta blockers
anticoagulants
LEVOTHYROXINE SPECIAL POPULATIONS
-
-
Dosing ____ mcg/kg/day
Doses ____ are associated w +fracture risk in adults >70 yo
pre-existing cardiac/older adults
osteopenia/osteoporosis
1.6
>93 mcg/day
HYPOTHYROIDISM: OTHER AGENTS → 3
NOT recommended over levothyroxine!!
Cytomel/liothyronine
Armour Thyroid
Liotrix/Thyrolar
#1 cause of HYPERthyroidism
Graves’ disease
HYPERthyroidism s/sx → “SWEATING”
Sweating
*weight loss (despite +appetite, CARDINAL SIGN)
emotional instability
appetite +
tremor
intolerance to heat, irregular HR+
nervousness
goiter
DRUG-ASSOCIATED CAUSES OF THYROTOXICOSIS
longest lasting (month-yrs) to shortest (weeks-months)
amiodarone
lithium
IFNa
IL2
iodinated contrast
radioactive iodine
Subacute Thyroiditis
mod-sev pain in the thyroid that radiates to the ears, jaw, or throat after viral infection
Presentation? (malaise, low grade fever, pharyngitis sx, fatigue)
____ for mild pain
INTENSE pain, fever, and malaise → ______ 40 mg daily x 1-2w with gradual taper over 2-4w
Treatment →
prodrome sx
NSAIDs
prednisone
propranolol or nadolol
GRAVES’ DISEASE
_____ (bulging eyes)
Most common tx →
^ Contraindications →
exophthalmos
I131 ablation
preg/lactation, thyroid cancer
GRAVES’ DISEASE (cont.)
Tx option 2 (offers control, not a cure)
DRUG OF CHOICE* →
Other drug option →
Contraindications → 2
Monitoring → BASELINE (4)
Monitoring → subsequent
Length of therapy: _________ if TSH and TRAb levels are normal
thioamides
methimazole → 2nd/3rd tri
PTU (propylthiouracil) → 1st tri
neutrophil <500, liver >5x ULN
CBC, liver, TSH, free T4
free T3+T4 q 4-8w, CBC w febrile illness
12-18m
METHIMAZOLE VS PTU
_________ than PTU → may be given DAILY
_________ compared to PTU
t1/2 longer
less hepatotox
PTU → ***BBW for severe _____ injury and acute failure
liver
SUBCLINICAL HYPERTHYROIDISM
asymptomatic with normal T4 and -TSH
Tx: wait _____ and check TSH again
1 yr
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY GOUT
________ is the byproduct of the breakdown of purines
Most common cause
^ can crystallize when serum levels are ____ mg/dL
Crystalls deposit into ____ and _____ triggering inflammatory response
uric acid
-urate excretion (kidneys)
>6.8
joints, cartilage
GOUT CLINICAL PRESENTATION
_________
labs → 2
complications → 3
monoarticular arthritis
+uric acid, leukocytosis
nephrolithiasis, gouty neuropathy, tophi
RISK FACTORS FOR DEVELOPING GOUT
Conditions → 6
Lifestyle → 4
MEDICATIONS → 5
alcoholism, DM, CVD, dyslipidemia, hypothyroid, renal
obesity, +animal purine intake, high fructose foods/drinks, alc
thiazides, low-mod dose ASA, vit B12, cyclosporine, levodopa
GOUT PHARM MANAGEMENT
Acute tx →
May use ____ as adjuvant tx
Chronic tx →
NOT 1ST LINE tx →
NSAIDs, corticosteroids, colchicine IF attack began w/in 36h
ice
XO inhib (allopuriol, febuxostat), uricosurics (probenecid)
biologics
GOUT MEDICATIONS
______ blocks formation of uric acid
______ breaks down uric acid
______ +excretion of uric acid in urine
_____________ -degree of inflammation
allopurinol
uricase
probenecid
NSAIDs, colchicine, steroids
ACUTE GOUT ATTACK
Initiate pharmacologic tx within ____ of acute gout onset for optimal results
Ongoing ULT therapy should NOT be interrupted
24h
WHEN TO USE MONOTHERAPY? → 2
colchicine, NSAIDs, corticosteroids
mild-mod pain
attack of 1/few small joints/1-2 large joints
NSAIDS/COX-2 inhibitors
AVOID FOR … (7)
eGFR <60
hyperK
GI ulcer
poorly controlled HTN
mod/sev CHF
cirrhosis
anticoagulation
ORAL CORTICOSTEROIDS
AVOID FOR … (3)
*MONOTHERAPY NOT REC
brittle DM
recent surgery w unhealed wound
suspected concurrent infxn
INTRAARTICULAR CORTICOSTEROIDS
AVOID FOR … (4)
>2 affected joints
small joints in hands/feet
lack of timely access to provider
suspected joint infxn
COLCHICINE (COLCRYS)
MOA: inhib inflam response by inhibiting ______ and _______
Toxicities: NV, myalgia, _______, _______, ______
AVOID FOR … (2)
Drug interactions → INCREASE colchicine levels
MT polymerization, inflam mediators
diarrhea, neuropathy, BMS
CrCL<10, kidney/hepatic impair
CYP/Pgp inhib
WHEN TO USE COMBINATION TX?
For _____ pain or ________ attack
Combination therapy →
WHY AVOID NSAIDS + ORAL STEROIDS?
sev, polyarticular
colchicine+NSAIDs, colchicine+oral steroids
GI tox
STRONG RECOMMENDATION FOR URATE-LOWERING THERAPY (ULT)
______ subcutaneous tophi
________ damage attributable to gout
freq gout flares ______
Conditional rec for ULT →
1+
radiographic
>/= 2 a yr
>1 flare but infreq (<2 a yr), 1st flare +CKD or urolithiasis
CHRONIC GOUT MANAGEMENT (ULT)
1st line =
2nd line =
last line =
allopurinol > febuxostat
probenecid
peloticase, rasburicase
ULT TX GOALS
serum urate goal of ______, assess every _____ while titrating
<6 mg/dL, 2-6w
ANTI-INFLAM PROPHYLAXIS THERAPY DURING ULT
1ST LINE option
2ND LINE option
Continue concomitant prophylaxis for atleast _____
low dose colchicine, low dose NSAIDs + PPI (if indicated)
prednisone/prednisolone <10mg/day
3-6m
ALLOPURINOL (ZYLOPRIM)
USE CAUTION in patients with ____
Monitoring → 4
ADEs → 3
STOP IF ______ DEVELOPS
*Hypersens can occur → __________ testing prior to initiation
CVD
uric acid, LFTs, SCr, CBC
dyspepsia, headache, diarrhea
pruritic maculopapular rash
HLA-B*5801
FEBUXOSTAT (ULORIC)
USE CAUTION in patients with ____
Greater efficacy at -uric acid BUT more _____
Monitoring →
ADEs → 4
CVD
side effects
uric acid, LFTs, CBC → baseline, 2m, 4m, periodically
+LFTs, nausea, arthralgia, rash
URICOSURIC AGENTS: PROBENECID
ineffective in patients with CrCL _____
AVOID IN PATIENTS WITH _______ or _____
ADEs → 3
<50
kidney stones, CKD
rash, precipitation of gouty arthritis, nephrolithiasis
BIOLOGIC OPTIONS (NOT 1ST LINE)
__________ for acute gout flares in pts who cannot use 1st line/inadequate response → anakinra (KINERET), canakinumab (ILARIS)
__________ chronic hyperuricemia only w failure of other agents/freq flares/non-resolving tophi → peloticase (KYSTEXXA), rasburicase (ELITEK)
IL1 inhib
uricase
BBW FOR RASBURICASE →
hypersens
GOUT
Disease process → break down of …
Host factor →
Joints affected →
_____ inflammation
Morning stiffness?
Labs →
cartilage, localized uric acid crystal deposits
M>W
asymmetrical
local
if during/after recent attack
+uric acid and ESR
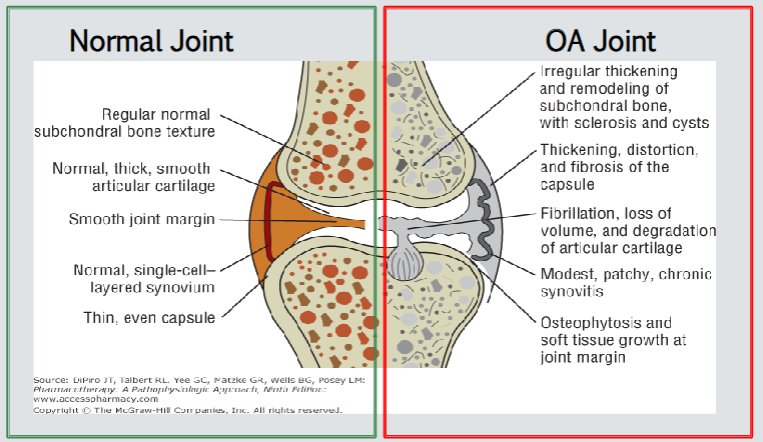
OSTEOARTHRITIS
Diagnosis (3)
NO specific ______ for OA
Symptoms resolve with …
RECURS with …
Duration ______
sx, hx, radiographic
labs
motion
rest
<30m
OSTEOARTHRITIS (OA)
Disease process → break down of …
Host factor →
Joints affected →
_____ inflammation
Morning stiffness?
Labs →
cartilage
+age
symmetrical/asymmetrical
local
NO
none specific
OA NON PHARM TX
________ for ALL
________ and _________ programs for ALL
Hand
Knee
Hip
exercise
self-efficacy, self-management
CMC orthosis
weight loss, tai chi, cane, TF knee brace
weight loss, tai chi, cane
When to use TOPICAL AGENTS?
_________ joints affected
Especially ________ OA
Hand = _____ recommendation
Knee = _____ recommendation
Hip = _____ recommendation
1 or few
knee and/or hand
conditional
strong
NO
TOPICAL NSAIDS
VOLTAREN = diclofenac _____
PENNSAID = diclofenac _____
FLECTOR PATCH = diclofenac _____
^ which one for ACUTE PAIN indication only?
Monitoring → 3
1% gel
1.5 or 2% soln
1.3% patch
patch
LFTs 4-8w after initiation, CBC, renal fx
TOPICAL: CAPSAICIN
CONDITIONALLY RECOMMEND AGAINST _____ OA
MOA: induces release of ________ from peripheral sensory neurons; repeated application leads to prevention of re-accumulation
_______ (Qutenza) APPLIED BY HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL
hand
substance P
8% patch
T or F:
Acetaminophen may no longer be considered the 1st line analgesic for the tx of knee and hip OA.
T
WHEN TO USE ORAL NSAIDS?
Patients w ________ sx relief or unable to use topical NSAIDs
Patients w symptomatic OA in ________ and/or patients with ____ OA
inadequate
multiple joints, hip
ORAL NSAIDS
diclofenac, naproxen, celecoxib
_____ recommendation in hand, knee, hip OA
CONTRAINDICATED IN …
BBW
Consider use of _____ if used for chronic management
strong
CKD IV or V
CV and GI risk
PPI
WHEN TO USE TOPICAL > ORAL NSAIDs? → 4
CKD IV or V
hand or knee OA
CVD
PUD
____________ considered for multiple joint OA + concomitant comorbidities that may contraindicate oral NSAIDs
beneficial for depression
duloxetine
HERBAL AGENTS
__________ → recommended against
__________ → recommended against EXCEPT hand (conditional rec)
If patient still wants to use, suggest DC if no benefit in _____
glucosamine
chondroitin sulfate
6m
TRAMADOL (ULTRAM)
hand, knee, hip → recommendation?
schedule →
Warning →
conditional, 2ND LINE
IV
SS, seizures
INTRAARTICULAR CORTICOSTEROIDS
Indication: OA of …
RISKS → 4
knee, hip
crystal synovitis, post inj flares, cartilage atrophy, joint sepsis
OSTEOPOROSIS RISK FACTORS
Women
Men
Body type
Social history
65+, estrogen deficiency
70+, androgen deficiency
-BMI, calorie-restricted weight loss
smoking, alc, high caffeine
OSTEOPOROSIS DRUG-INDUCED CAUSES → 9
antiepileptic/anticonvulsant
immunosupp
lithium
PPIs
systemic coticosteroids
SSRIs, TCAs
TZDs
aromatase inhib
loop diuretics
OSTEOPOROSIS PREVENTION: CALCIUM INTAKE
Dietary → 8
Calcium carbonate (___ elemental)
Calcium citrate (___ elemental)
Tolerability →
Safety →
__________ preferred in chronic gastric acid-suppression therapy
should be used for patients receiving chronic ____________ therapy
should be admin w appropriate _____ supplement
dairy, leafy greens, OJ, cereals, fish w bones, almonds, tofu, broccoli
40%
21%
constipation, GI
may +risk of MI, hypercalc in late stage CKD
calc citrate
systemic corticosteroid
vit D
OSTEOPOROSIS PREVENTION: VIT D INTAKE
Dietary → 6
vit D2 (_________) available RX
vit D3 (_________) available RX and OTC
Tolerability →
fatty fish, milk, OJ, cereal, egg yolks, mushroom
ergocalciferol
cholecalciferol
hypercalc, constipation
OSTEOPOROSIS SCREENING RECOMMENDATION
Women _______
Postmenopausal women __________
Risk factors → 5
65+
<65 + 1 or more risk factors
hx of fracture/falls, smoking, alc, low body weight, long term corticosteroid use
OSTEOPOROSIS DIAGNOSIS
T-score vs Z-score → how many standard deviations separate the patient’s BMD from …
T = same sex young healthy adult
Z = matched age, sex, ethnicity
OSTEOPOROSIS DIAGNOSIS
T-SCORES
normal
osteopenia
osteoporosis
sev or established osteoporosis
>/= -1.0
-1.0 to -2.5
</= -2.5
</= -2.5 + hx fracture
OSTEOPOROSIS DIAGNOSIS
Z-SCORES
considered within the expected range for patient’s age
considered BELOW the expected range
>/= -2.0
< -2.0

OSTEOPOROSIS: BISPHOSPHONATES
COUNSELING:
EXCEPTION →
Remain upright for ________
EXCEPTION →
IV therapy (zoledronic acid) → counsel on adequate _______ before/after infusion
Side effects → 3
Safety
NOT REC FOR CrCL _____
All dosage forms and intervals equally effective EXCEPT ______
take w 6-8 oz water atleast 30-60m before food/meds
Atelvia take after breakfast
30m after admin
ibandronate 60m
hydration
GI, eye inflam, acute phase rxns w infusion
osteonecrosis of jaw, atypical femur fractures → >5yr use
<30 to 35 → zoledronic acid CI in <35
ibandronate
Ibandronate is effective ONLY for preventing _________ fractures
vertebral
HIGH FRACTURE RISK
Consider a drug holiday after _____ of oral bisphos therapy
after _____ of IV bisphos therapy
5y
3y
VERY HIGH FRACTURE RISK
Consider a drug holiday after _____ of IV zoledronate
During holiday, _____ can be used
6y
raloxifene
RALOXIFENE (EVISTA)
MOA
prevention & tx of osteoporosis in ________
-incidence of ________ fractures
SAFETY → 6
SERM
postmenopausal women
vertebral
+risk DVT, +hot flashes, leg cramps, arthralgias, peripheral edema, +risk fatal stroke (hx CAD)
TERIPARATIDE (FORTEO)
MOA
FDA approv tx of osteoporosis in _______
reduces risk of __________ fractures
Dosage form
Side effects → 3
Safety
PTH recomb
M+W
vertebral+non
SQ → do not exceed 2y, refrigerate
leg cramps, nausea, orthostasis
abrupt bone loss when DC, DO NOT USE in +risk osteosarcoma
ABALOPARATIDE (TYMLOS)
MOA
FDA approv tx of osteoporosis in _______
Dosage form
Side effects + safety same as teriparatide
PTH analog
postmenopausal women
SQ → do not exceed 2y, refrigerate then after 1st dose store at room T up to 30d
PTH AGENTS NOTES
_______ efficacy if used concurrently w a bisphos
After DC or completion of therapy, antiresorptive therapy must be initiated to preserve BMD benefits →
AVOID USE in patients with … (4)
diminished
bisphos or Prolia/denosumab
+ALP, open epiphyses, Paget, prior skeletal radiation
DENOSUMAB (PROLIA)
tx postmenopausal women, +bone mass in men at high risk of fracture
MOA
side effects → 4
safety →
_________ IS NOT RECOMMENDED!
RANKL inhib
hypocal, +risk skin infxn and rash, osteonecrosis of jaw, atypical femur factures
bone loss rapid if DC
drug holiday
CALCITONIN (MIACALCIN, FORTICAL)
MOA
FDA approved to tx osteoporosis in women who are ______ postmenopausal when other tx not suitable
DOES NOT -RISK OF _________ fractures
Dosage form →
Safety → ____________ in calcitonin-salmon-treated pts
ADEs → 3
NOT _______
PTH antag
>/= 5yr
non-vertebral
nasal spray
+risk malignancy
rhinitis, epistaxis, allergic
routinely used
ROMOSOZUMAB (EVENITY)
MOA
Considered a __________ for pts at very high fracture risk
BBW →
duration of therapy
Side effects → 7
sclerostin inhib
rescue drug
+risk MI
12m
hypocal, osteonecrosis of jaw, arthralgias, headache, inj site rxns, hypersens, CV
OSTEOPOROSIS PHARM THERAPY RECOMMENDED FOR
10-yr major osteoporotic fracture risk _____
OR hip fracture ____
>/= 20%
>/= 3%
OSTEOPOROSIS HIGH RISK/no prior fractures pharm tx
1st line + duration →
Adj tx →
alternate →
alendronate or risedronate x 5yr, zoledronate x 3yr, denosumab indefinitely
calc + vit D
ibandronate, raloxifene
OSTEOPOROSIS VERY HIGH RISK/prior fractures pharm tx
Indicators → 5
1st line + duration →
Alternate therapy →
+age, frailty, glucocorticoids, very low T score, +fall risk
abaloparatide or teriparatide x 2y then transx, denosmab until no longer high risk then transx, romosozumab x 1y then transx, zoledronic acid x 6y
alendronate, risedronate
_____________________ are the key substances in the initiation and continuance of rheumatoid inflammation
→
pro-inflammatory cytokines
TNF, IL1, IL6
RA CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Morning stiffness that lasts _________ & may persist all day
_______ joint involvement
Disease process
Host factor
Labs
>30m
symmetrical
systemic, autoimmune
smoking
+ESR/CRP, RF may be present, anti-CCP
RA SYMPTOM CONTROL → 2 choices
NSAIDs → equally effective, celecoxib less GI → consider +PPI
</= 10 mg prednisone/day → calc/vit D supp to prevent bone loss
3 CLASSES OF DMARDS
Conventional (c ) → 4
Targeted synthetic (ts) → 3
Biologic (b)
MTX, hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, leflunomide
tofacitinib/Xeljanz, baricitinib/Olumiant, upadacitinib/Rinvoq
-mabs
METHOTREXATE (MTX)
1st line for DMARD naive with ________ disease activity
Time to benefit
Counseling
MOA
BBW → 3
CONTRAINDICATED IN _________
AVOID in CrCL ____
Drug interxns → 6
mod-high
2-4w
ONCE WEEKLY, +folic acid 1 mg/day except day of MTX admin
DHFR inhibitor
serious infxns, BMS, GI/liver/lung/kidney tox
preg
<30
PPIs, NSAIDs, salicylates, bactrim, acitretin, alcohol
MTX should be stopped _____ prior to attempting to become pregnant, INCLUDING MEN!
3m
MTX MONITORING
______ and ______ function
___________ for first few months
-
-
-
renal, liver
CBC q 2-4w
preg test
hep B and C
TB screening
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE (HCW)
1st line for DMARD naive with ______ disease activity
Time to benefit
MOA
Common ADEs → 2
Rare ADEs → 2
low
8-12w → give 6m trial of benefit
inhib polymorphonuclear leukocytes
GI, itchy skin rash
vision, tinnitus
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE MONITORING
Complete _____________ (repeat annually for high risk patients)
^ High risk = 3
other → 3
AVOID IN _______
Drug interxns →
eye exam w/in 1yr of tx
liver disease, retinal disease, age 60+
CBC, LFTs, SCr
preg
may +digoxin levels
SULFASALAZINE (SSZ)
Indication
Time to benefit
Common ADEs → 2
Most serious ADEs → 5
Monitoring →
Caution in patients with _________
Drug interxns →
2nd line for low-disease
1-3m
GI, rash
liver tox, sev skin rash, -blood counts, -sperm counts, kidney stones
CBC, LFTs (avoid if >2x ULN), SCr
G6PD def
-digoxin, give folate 1mg/day
LEFLUNOMIDE (LEF)
Indication
Time to benefit
Monitoring → 4
Contraindications
Check LFTs …
Initiate _______ if LFTs >3x ULN + monitor weekly until normal
Drug interxns
2nd line for low-disease
4-12w
CBC, LFTs, SCr, Hep B/C testing in high risk
preg, sev hepatic impair >2x ULN
monthly x 6m then q 6-8w
cholestyramine
inhib diclofenac and ibuprofen metabolism, smokers have +clearance
All JAK inhibitors (tsDMARDs) are _________ (dosage form)
oral tabs
tsDMARDs (JAK inhibitors) Safety
Inc risk of _________
___________
___________
BMS, hepatotox, caution in kidney disease, +lipids
MONITORING →
_______ requires dose adjustments for DRUG INTERXNS
Dose reduction for mod-sev _______
MAY BE USED AS ____________ for RA
serious infxns
malignancies
thrombosis
baseline CBC, LFTs, Hgb, lipids within 1-2m; CBC, LFTs, Hgb q 3m
tofacitinib (Xeljanz)
renal impair
monotherapy or combo w cDMARD
Anti-TNF DMARDS
______ choice for bDMARDs
_____________ with other bDMARDs
Agents → 5
Time to benefit
ADEs → inj/infusion rxns, +risk serious infxn, _____, _____, _______
Monitoring →
1st line
should not be used in comb
Enbrel/etanercept, Remicade/infliximab, Humira/adalimumab, Simponi/golimumab, Cimzia/certolizumab
few days to months
URTI, headache, worsening HF
CBC, LFTs, SCr
Which anti TNF inhibitor is a fusion protein?
A. Enbrel/etanercept
B. Remicade/infliximab
C. Humira/adalimumab
D. Simponi/golimumab
E. Cimzia/certolizumab
A
Which anti TNF inhibitor is a PEGylated recombinant Fab?
A. Enbrel/etanercept
B. Remicade/infliximab
C. Humira/adalimumab
D. Simponi/golimumab
E. Cimzia/certolizumab
E
ANTI-TNF bDMARDs SAFETY
Associated with reactivation of _____ → test for latent before/during therapy
Increase risk of invasive _____________
Increase risk of __________
Linked to new or worsening __________
TB
bacterial/fungal infxns
malignancies
HF
Which are preferred for overlapping inflammatory bowel disease? (Select all)
A. Enbrel/etanercept
B. Remicade/infliximab
C. Humira/adalimumab
D. Simponi/golimumab
E. Cimzia/certolizumab
B, C, E
Which are preferred for preconception, pregnancy, and breastfeeding? (Select all)
A. Enbrel/etanercept
B. Remicade/infliximab
C. Humira/adalimumab
D. Simponi/golimumab
E. Cimzia/certolizumab
A, E
NON-TNF BIOLOGICS → 4
Orencia/abatacept
Rituxan/rituximab
Actemra/tocilizumab
Kevzara/sarilumab
T-cell inhibitor bDMARD =
Indication
Safety →
ADRs → 5
Orencia/abatacept
alt to MTX w mod-high disease
COPD, +risk infxn
infxns, pneumonia, cellulitis, UTIs, bronchitis
Anti-CD20 bDMARD =
Indication →
Monitoring → 5
PRE-MEDICATE WITH …
BBW → deaths due to infusion rxn, ________, sev mucocutaneous rxns
ADEs → 6
Rituxan/rituximab
inadequate response to MTX & anti-TNF
CBC+platelets, TB screening, infusion rxn, cardiac, high risk screen HBV/HCV
glucocorticoid, acetaminophen, antihistamine
tumor lysis syndrome
HTN, nausea, arthralgia, pyrexia, pruritus, hep B reactivation
IL6 INHIBITOR bDMARDs =
Monitoring → LFTs, CBC+platelets, TB screening, s/s infxn, ________
ADEs → 4
AVOID USE IN … 3
Acetemra/tocilizumab, Kevzara/sarilumab
Lipid panel
URTI, hypersens, dyslipidemia, neutropenia/TC
ANC<2000, platelets <100k, ALT or AST >1.5x ULN