Blinn College - Geology 1403 - 316 - Dr.Mosely - Final Exam
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Name and distinguish between the two broad subdivisions of geology
1.) physical - examines materials composing earth & processes that operate beneath and upon the surface
2.) historical - understand the origin of earth and its development through time
What are geologic hazards?
volcanoes, floods, tsunamis, earthquakes, and landslides
Whats the difference between catastrophism and uniformitarianism?
catastrophism - belief that earths landscapes were shaped by great catastrophes
uniformitarianism - the present is key to the past
How old is earth?
4.5 billion years
Why is the understanding of the magnitude of geologic time important for geologist?
How is a scientific hypothesis different from a scientific theory?
hypothesis - a tentative or untested explanation
theory - a well tested and widely accepted that explains certain hypothesis with facts
What are the basic steps followed in scientific investigations?
1.) a question is raised
2.) scientific data is collected
3.) one or more working hypotheses are developed
4.) observations & experiments are developed to test the hypotheses
5.) the hypotheses are accepted, modified, or rejected
6.) data and results are shared w/ scientific community
What explains the fact that continental drift is considered a hypothesis but plate tectonics is considered a theory?
continental drift was a hypothesis because many people were very skeptic - but with time it was tested and became a theory with a new name of plate tectonics
List and describe earth's four spheres
1.) hydrosphere - water portion of the planet
2.) atmosphere - the gaseous portion of the planet
3.) biosphere - includes all life on earth
4.) geosphere - the solid earth
Compare the height of the atmosphere to the thickness of the geosphere
atmosphere is a very thin layer - but the geosphere is very thick (4000 miles)
How much of earths surface do oceans cover?
71 %
What percentage of earths total water supply do oceans represent?
97 %
To which sphere does soil belong to?
geosphere
What is a system?
a group of interacting, or interdependent, parts that form a complex whole
What are three examples of a system?
What are two sources of energy for the earth system?
1.) the sun - drives external processes that occur
2.) heat - rom earths interior
Predict how a change in the hydrologic cycle, such as increased rainfall in an area, might influence the biosphere & geosphere in that area
Name and briefly outline the theory that describes he formation of our solar system
nebular theory - the bodies or our solar system evolved fro an enormous rotating cloud called the solar nebula
What are the inner planets?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
What are the outer planets?
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Explain why density and buoyancy were important in the development of earths layered structure
List and describe the three major layers defined by their chemical composition
1.) crust - low density rock
2.) mantle - high density rock
3.) core - iron and nickel
Whats the difference between the lithosphere and asthenosphere?
lithosphere - the rigid outer layer of earth includes the mantle & upper mantle
asthenosphere - a subdivision of the mantle above the lithosphere
Distinguish between the outer core and the inner core
outer core - liquid
inner core - solid
List two rock characteristics that are used to determine the processes that created rock
1.) minerals
2.) texture
Basic rock cycle
- cooling, crystallization
- weathering (transport, deposition)
- lithification (compaction, cementation)
- metamorphism (heat, intense pressure)
- melting
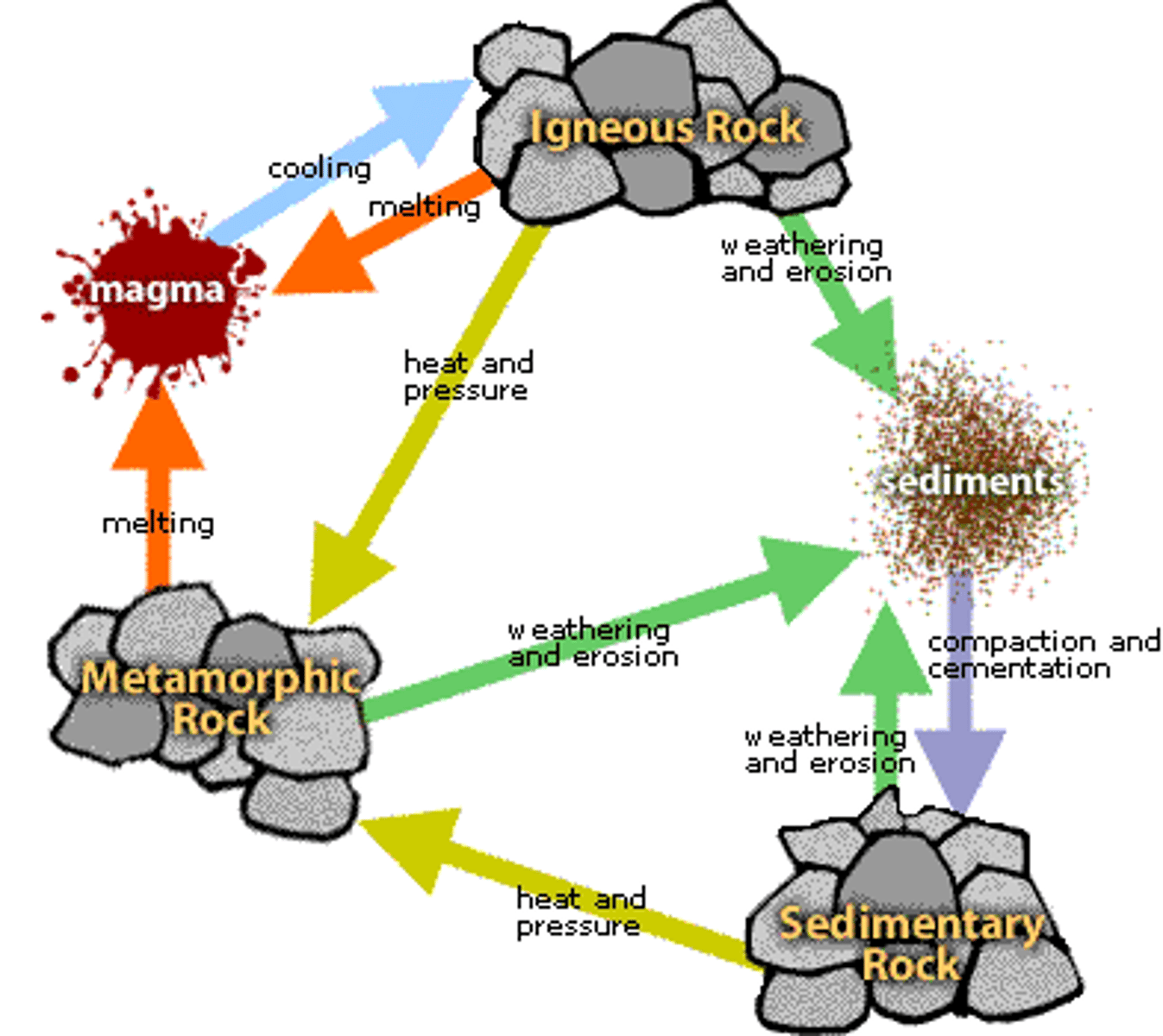
How is one rock the raw material for another?
because one type of rock can go into a phase and become another type
Compare and contrast continents and ocean basins
continents - flat features that have the appearance of plateaus protruding above sea level
one basins - lower the the average elevation of the continents and covered in water
Describe the general distribution of earths youngest mountains
tend to be long, narrow, and less than 100 million years old
What is the difference between shields and stable platforms?
shields - flat regions composed largely of deformed igneous and metamorphic rocks
stable platforms - like shields but are thin veneer of sedimentary rocks
What are the three major regions of the ocean floor, and what are some features associated with each?
1.) continental margin - the portion of the seafloor adjacent to major landmasses (continental shelf, slope, and rise)
2.) deep ocean basins - lay between the continental margins and oceanic ridges (30% of earths surface)
3.) oceanic ridges - a continuous mountainous ridge on the floor of all major ocean basins (divergent plate boundaries)
Briefly describe the view held by most geologists regarding the ocean basins and continents prior to the 1960's
had fixed geographic positions and were of great antiquity, came to realize that the continents are not static - instead they gradually migrate across the globe
What group of geologists were the least receptive to the continental drift hypothesis?
geophysicists & geochemists
What was the first line of evidence that led early investigators to suspect that the continents were once connected?
the shorelines of South America and Africa, and the seaward edge of the continental shelfs
Explain why the discovery of the fossil remains of mesosaurus in both South American and Africa, but nowhere else, supports the continental drift hypothesis
they couldn't cross vast oceans, therefore the two must have been connected
What was the prevailing view of how land animals migrated across vast expanses of open ocean?
island stepping stones
What analogy did Wegener use to describe how the continents move though the ocean floor?
the gravitational forces of the moon and sun the produced earths tides were also capable of moving the continents
What two aspects of Wegener's continental drift hypothesis were objectionable to most of earth scientists?
1.) continents do not break through the ocean floor
2.) for any theory to gain wide acceptance it must withstand critical testing from all areas of science
The global extent of what major ocean floor feature did oceanographers discover after World War II?
oceanic ridge system
List the seven largest lithospheric plates
1.) North American
2.) South American
3) Pacific
4.) African
5.) Eurasian
6.) Australian-Indian
7.) Antarctic
List the three types of plate boundaries and describe the relative motion at each of them
1.) divergent plate boundaries - two plates move apart
2.) convergent plate boundaries - two plates move together (oceanic lithosphere beneath overriding plate)
3.) transform plate boundaries - two plate grind past each other
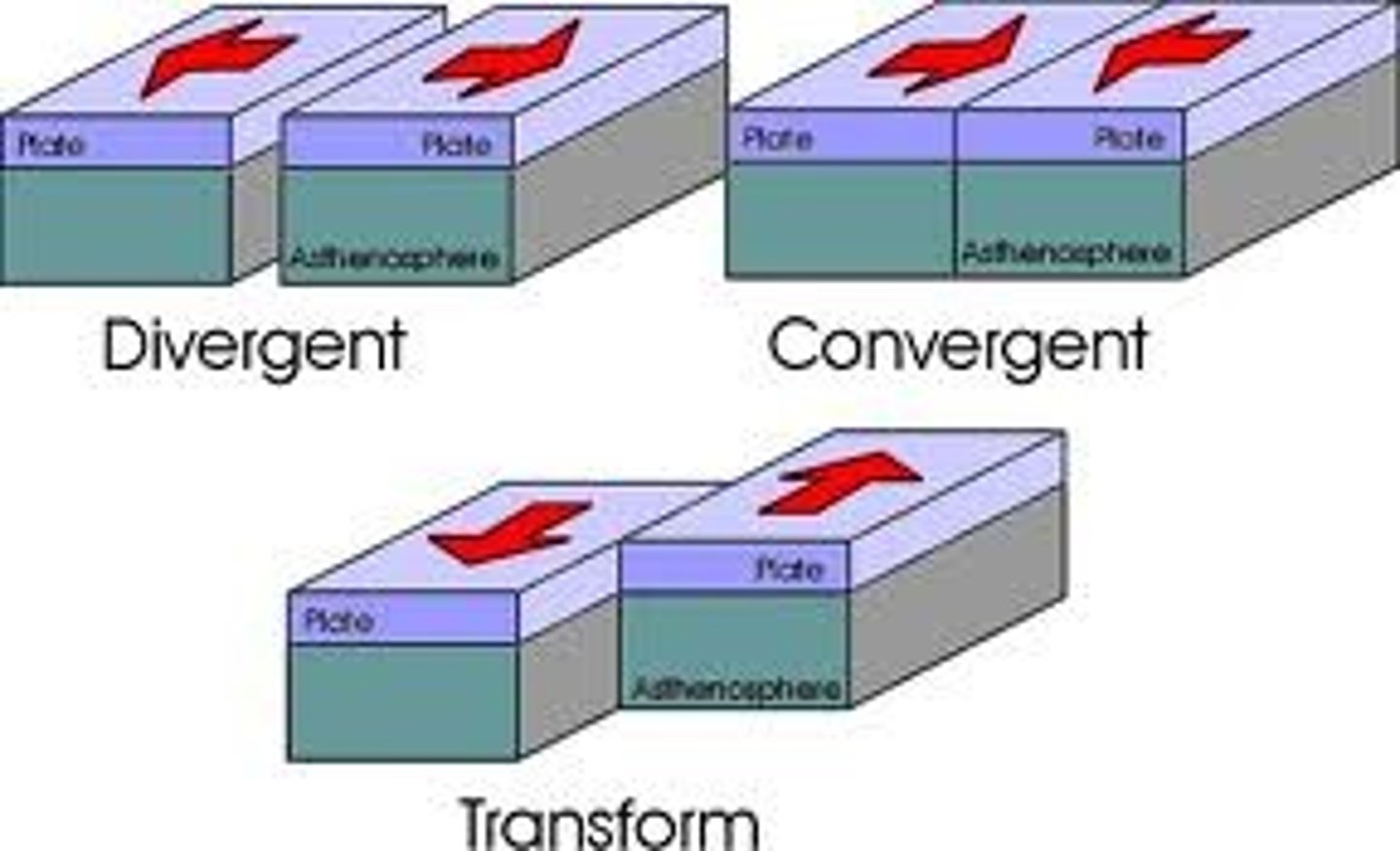
What is the average rate of seafloor spreading in modern oceans?
5 centimeter (2 inches) to 15 centimeters (6 inches) per year
List four facts that characterized the oceanic ridge system
Where does continental rifting occur today?
East African Rift
Compare a continental volcanic arc and a volcanic island arc
continental volcanic arc - mountains formed in part by igneous activity (oceanic under continental)
volcanic island arc - a chain of volcanic islands generally located a from a trench (oceanic under oceanic)
Why does oceanic lithosphere subduct, while continental lithosphere does not?
oceanic lithosphere tends to be dense and sink to the mantle, the buoyancy of continental material inhibits it from being subjected
Briefly describe how mountain belts such as the Himalayas form
the continental crust buckles & fractures and generally shorten horizontally and thicken vertically
Describe the process that leads to the formation of deep-ocean trenches
Describe a transform fault
faults that have slide past each other but also consist of divergent and convergent boundaries
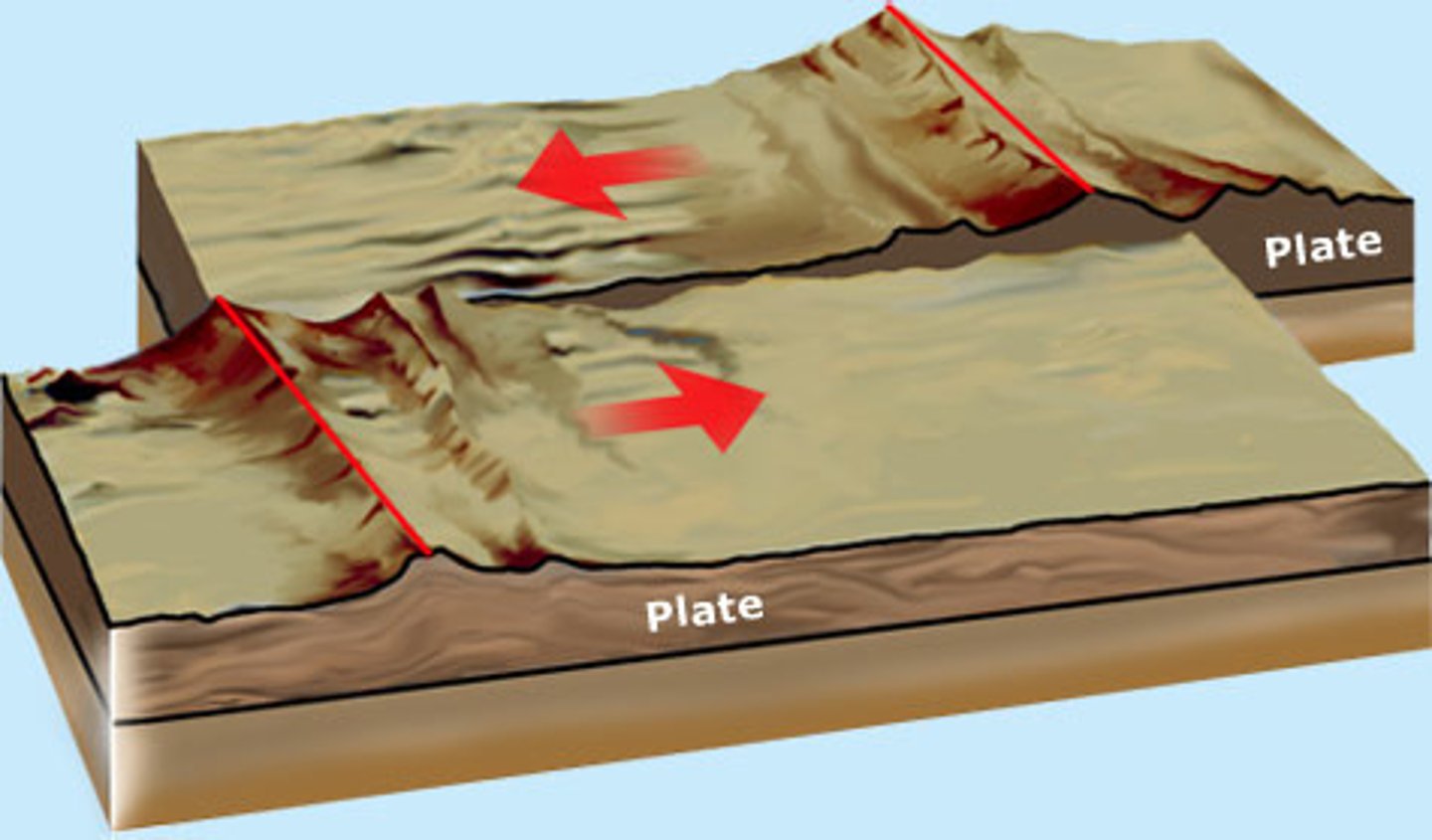
What two plates are growing in size?
African and Antarctic plates
Which plate is shrinking in size?
Pacific plate
What new ocean basin was created by the breakup of Pangaea?
the Atlantic
Briefly describe changes in the positions of the continents if we assume that the plate motions we see today continue 50 million years into the future
- Afica with collide with Eurasia and will close the Mediterranean
- Australia & New Guinea will be astride to the equator
- North & South America with begin to separate
- Atlantic & Indiana Ocean will grow
- Pacific Ocean will decrease
(could be another supercontinent)
What is the age of the oldest sediments recovered using deep-ocean drilling?
180 million years
How do the ages of these sediments compare to the ages of the oldest continental rocks?
the oldest rock is 4 billion years old
Assuming that hot spots remain fixed, in what direction was the pacific plate moving while the Hawaiian islands were forming?
northwestward
How do sediment cored from the ocean floor support the concept of seafloor spreading?
you can see how some of the floor is young while other is old - supporting the fact that the floor is growing (spreading)
Describe how Fred Vine and D.H. Matthews related the seafloor spreading hypothesis to magnetic reversals
What do transform faults that connect spreading centers indicate about plate motion?
What three plates exhibit the highest rates of motion?
1.) North American plate
2.) Eurasian plate
3.) African plate
Describe the slab pull and ridge push, which one appears to contribute more to plate motion?
slab pull - cold slabs of oceanic crust and is the major driving force of plate motion
ridge push - a gravity driven force that results from the elevated position of the ridge
What role are mantle plumes thought to play in the convective flow in the mantle?
transporting heat away from earths interior to the surface, where it is eventually radiated into space
Briefly describe the two models proposed for mantle-plate convection
1.) whole mantle model - oceanic crust sinks and stirs the entire mantle, downward flow is balanced by buoyantly rising mantle plumes
2.) layer cake model - has two largely disconnected convective layers, the layers don't mix
List five characteristics an earth material must have in order to be considered a mineral
1.) naturally occurring
2.) generally inorganic
3.) solid substance
4.) orderly crystalline structure
5.) definite chemical composition
Define the term rock
any solid mass of mineral, or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally
How do rocks differ from minerals?
rocks are made up of minerals
List three main particles of an atom and explain how they differ from one another
1.) protons
2.) neutrons
3.) electrons
protons & neutrons are very dense particle
Be able to sketch an atom & label the three main parts
nucleus, protons, electrons
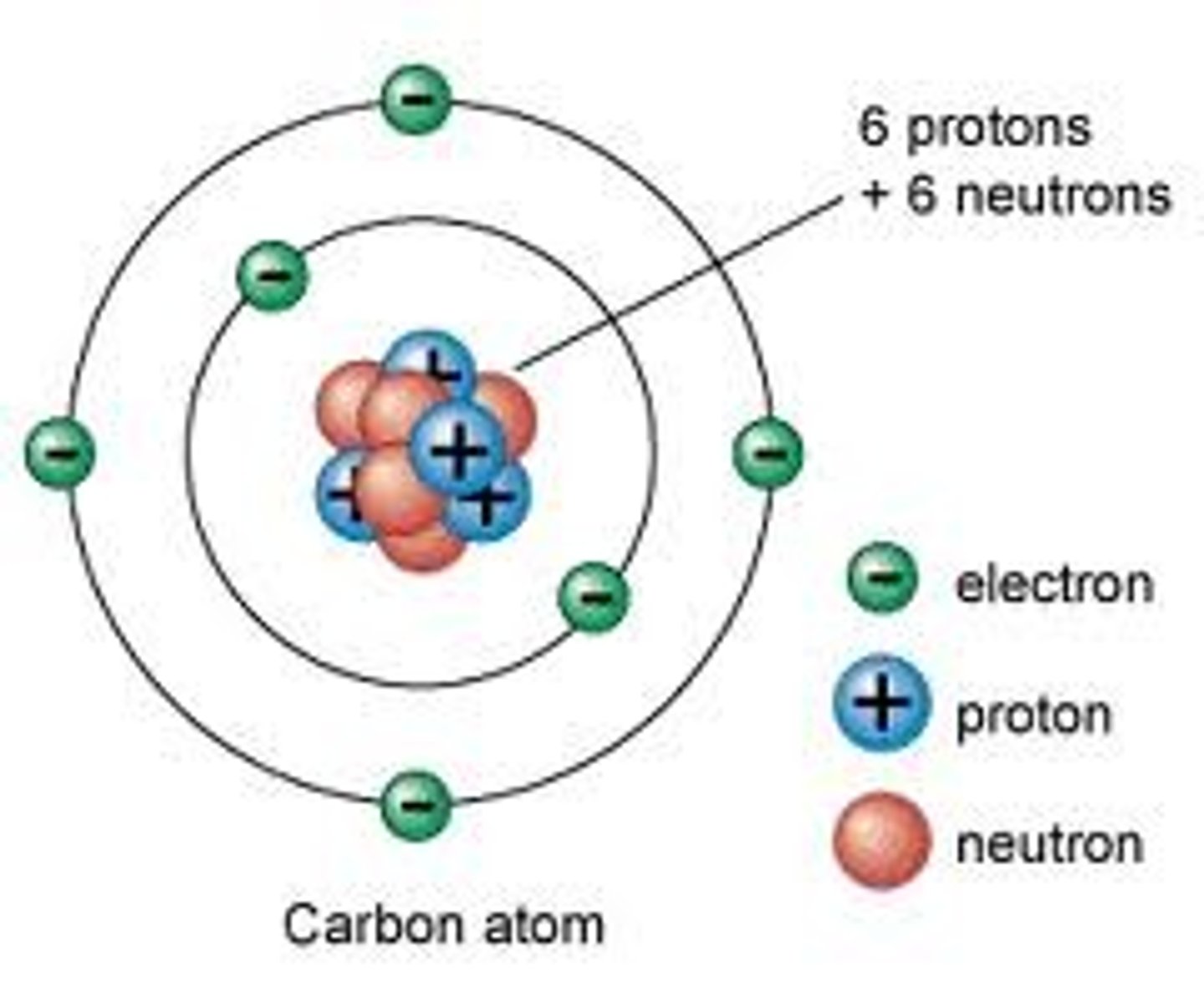
What is the significance of valance electrons?
electrons that interact with other atoms to form chemical bonds
What is the difference between an atom and an ion?
atom - the smallest particle that exists as an element
ion - an atom or a molecule that possesses an electric charge
What occurs in an atom to produce a positive ion?
when an atom loses electrons
What occurs in an atom to produce a negative ion?
when an atom gains electrons
Briefly distinguish among ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding and the role that electrons play in each
ionic bond - when valence electrons are transferred between the elements to form ions
covalent bond - when the electrons are shared between the atoms
metallic bond - when the valence electrons are shared among all the atoms in a substance
Define luster
the appearance o quality of light reflected from the surface of a mineral
Why is color not always a useful property in mineral identification?
slight impurities in the common minerals give it a variety of tints
What differentiates cleavage from fracture?
cleavage - the tendency of a mineral to break along planes of weak bonding
fracture - any break or rupture in rock along which no appreciable movement has taken place
What do we mean when we refer to a minerals tenacity?
a minerals resistance to breaking, bending, cutting or other forms of deformation
What four terms describe tenacity?
1.) brittle
2.) malleable
3.) sectile
4.) elastic
What simple chemical test is useful in the identification of the mineral calcite?
a drop of hydrochloric acid
What is the difference between rock-forming minerals and economic minerals?
rock forming minerals - the minerals that make up the earth crust
economic minerals - other minerals extensively in the manufacture of products
List the eight most common elements in earths crust
1.) oxygen
2.) silicon
3.) aluminium
4.) iron
5.) calcium
6.) sodium
7.) potassium
8.) magnesium
Sketch the silicon-oxygen tetrahedron
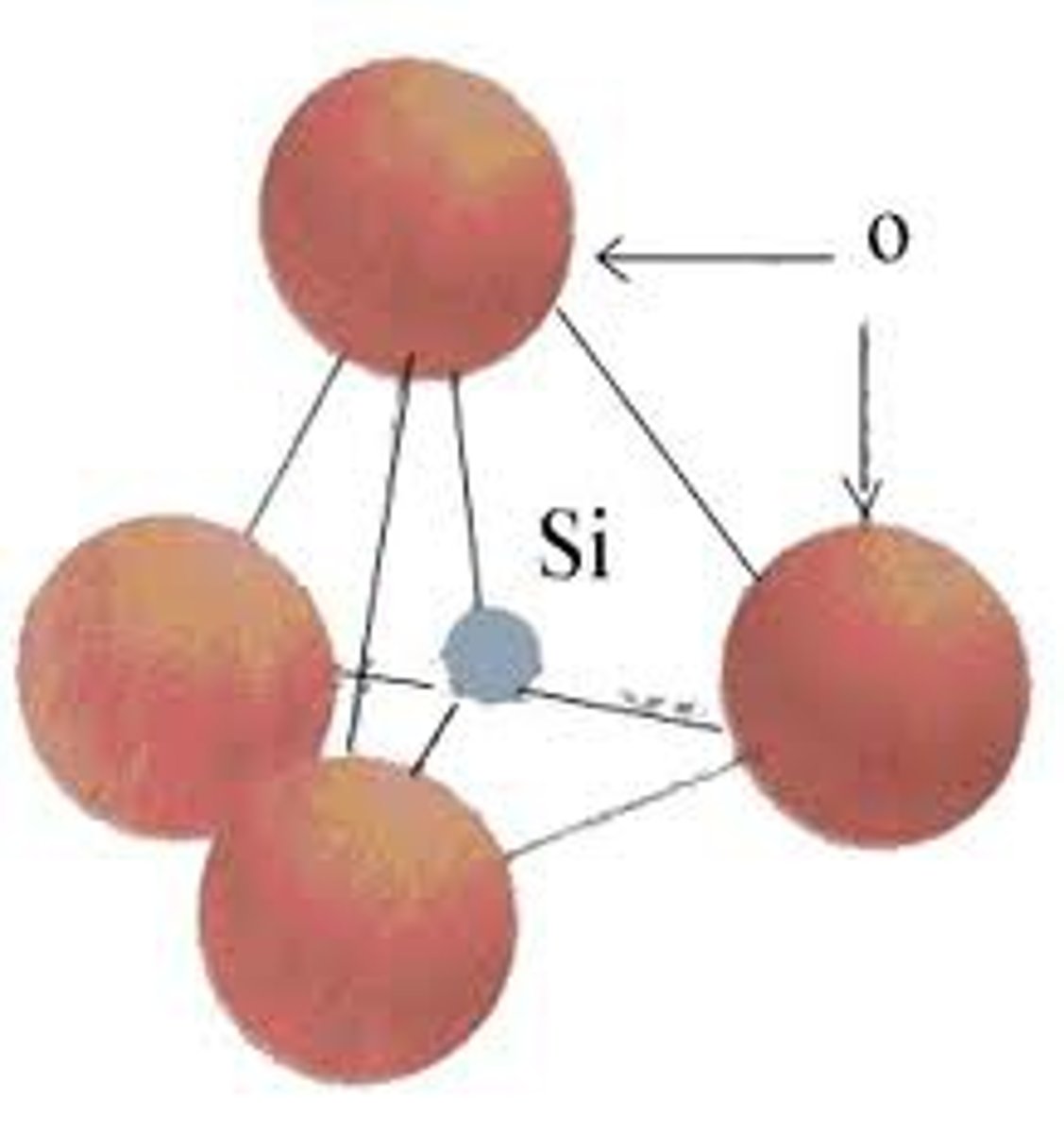
What differences in their silicate structures account for the different properties of quartz and talc?
How do most silicate minerals form?
when molten rock cools and crystallized
What is one main distinction between light and dark silicates?
light silicates don't contain iron & magnesium and have a lighter specific gravity than dark silicates
What do muscovite and biotite have in common? How are they different?
same - has a sheet structure that has excellent cleavage in one direction, glassy or pearly
different - muscovite is light in color biotite is dark in color
Is color a good way to distinguish between orthoclase (potassium) and plagioclase feldspar? If not, what is a better way?
no - instead look for a multitude of fine parallel lines, some are found on plagioclase but not orthoclase (potassium)
List five common non-silicate mineral groups
1.) carbonates (calcite, dolomite)
2.) halides (halite, fluorite)
3.) oxides (hematite, limonite)
4.) sulfides (galena, sphalerite, pyrite)
5.) sulfates (gypsum)
What is the most common carbonate mineral?
calcite, dolomite
List nine common non-silicate minerals
1.) calcite
2.) dolomite
3.) halite
4.) gypsum
5.) hematite
6.) magnetite
7.) galena
8.) chalcopyrite
9.) fluorite
List three examples of renewable resources
1.) flowing water
2.) wind
3.) sun
List three examples of nonrenewable resources
1.) oil
2.) natural gas
3.) coal
Compare and contrast a mineral resource and an ore deposit
mineral resources - occurrences of useful minerals that are formed that can eventually be extracted
ore deposit - naturally occurring concentration of one or more metallic minerals that can be extracted economically
Explain how a mineral deposit that previously could not be mined profitably might be upgraded to an ore deposit