Physiological Psychology Lab Exam 1
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
Two division of the nervous system
Central Nervous System/CNS
Peripheral Nervous System/PNS
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
all the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord
Division of the peripheral nervous system
Somatic
Autonomic
Somatic Nervous System
controls voluntary body movements and processes incoming sensory information from the skin, muscles, joints, etc.
Autonomic Nervous System
regulates involuntary physiological processes of the body, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, respiration, etc.
Parts of the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Sympathetic Division
division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the “fight or flight” response
Parasympathetic Division
division of the peripheral nervous system that helps the body relax and conserve energy, referred to as “rest and digest”
Efferent Neurons
motor neurons that carry information from the brain to the rest of the body
Afferent Neurons
sensory neurons that carry sensory information from the body to the brain.
Blood-Brain Barrier
protects the CNS from harmful substances entering the brain or spinal cord from the blood in our body
Meninges and Bones
help to protect the CNS
Hindbrain Divisions
Myelencephalon and Metencephalon
Hindbrain Structures
Medulla, Pons, Cerebellum
Myelencephalon
division of the hindbrain that includes the medulla
Metencephalon
division of the hindbrain that includes the pons and cerebellum
Midbrain Division
Mesencephalon
Midbrain Structures
Tectum and Tegmentum
Mescencephalon
division of the midbrain including the tectum and tegmentum
Forebrain Divisions
Diencephalon and Telencephalon
Forebrain Structures
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Cerebral Cortex
Basal Ganglia
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Diencephalon
division of the forebrain that includes the thalamus and hypothalamus
Telencephalon
division of the forebrain that includes the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, hippocampus, and amygdala
Four Cortical Lobes of the Brain
frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal
Frontal Lobe
one of the cortical lobes that contains:
Frontal and motor cortices
Superior, Middle, Inferior Gyri
Central Sulcus
Precentral Gyrus
motor cortex
Postcentralm Gyrus
somatosensory cortex
Parietal Lobe
one of the cortical lobes that contains:
Superior Parietal Lobule
Inferior Parietal Lobule
Occiptial Lobe
one of the cortical lobes that contains:
Parieto-occipital sulcus
Calcarine fissure
Cuneus
Temporal Lobe
one of the cortical lobes that contains:
Lateral Sulcus
Superior or Temporal Gyrus
Middle Temporal Gyrus
Inferior Temporal Gyrus
Order of the Meninges
Dura Mater (closest to the outside, skull) —> Arachnoid Mater —> Pia Mater (closest to the inside, brain)
Neurons
functional cellular unit of the nervous system that transmits information via action potentials and neurochemical release
Glia
provide structural and metabolic support for neurons (modulate, support, insulate, etc.)
Glia of the CNS
Oligodendrocytes and Ependymal
Glia of the PNS
Schwann and Satelite Cells
Glia of both the CNS and PNS
Astrocytes and Microglia
Macroglia
glial cell type containing astrocytes, oligodendrocyte, schwann cells, and staelite cells
Astrocyte
macroglia cell of the CNS and PNS that provides physical and nutritional support to neurons
Oligodendrocyte
macroglia cell of the CNS that forms Myelin sheaths and provides guidance
Schwann Cell
macroglia cell of the PNS that forms myelin sheaths and provides guidance
Satelite Cell
macroglia cell of the PNS that provides physical support to neurons
Ependymal
type of glial cell found in the CNS that lines the ventricles
Microglia
type of glia cell found in the CNS and PNS that is responsible for tissue repair, debris removal, and defense
Grey Matter
divided into “horns” (dorsal and ventral); some axons but mostly cell bodies
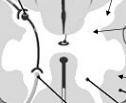
White Matter
composed of only myelinated axons, surrounds central grey matter
Ways to Classify Neurons
Based on the number of extensions that extend from the neuron’s soma
Unipolar - touch, pain neurons
Bipolar - vision, hearing neurons
Multi-polar - Most neurons in the brain
According to their connections
Sensory (afferent) and Motor (efferent) (reside partly in CNS and PNS)
Interneurons (local info) and Projection neurons (reside entirely in the CNS)
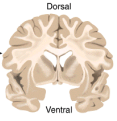
Coronal Section
divides the brain into dorsal and ventral sections
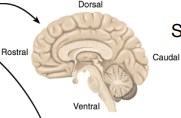
Sagittal Section
vertical plane that divides the brain into left and right sections
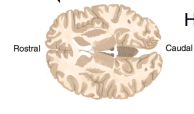
Horizontal Section
horizontal plane that divides the brain into upper and lower sections.
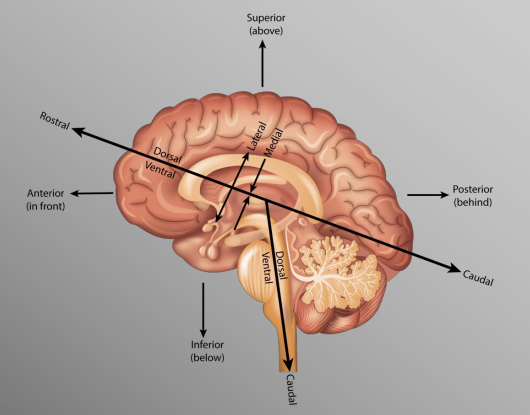
Human Brain Orientation
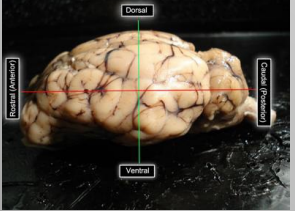
Sheep Brain Orientation
Focus on anterior and posterior rather than rostral and caudal since we are using sheep brains
Why does the orientation of the CNS change moving from the spinal cord to the brain in humans?
the evolution of bipedalism requires a different spatial understanding for human brains versus the brain of an animal that moves on all fours.
Cortical Folding
creates “hills” (gyri) and “valleys” (sulci) on the surface of the brain to increase cortical surface area in more advanced organisms, allowing for more complex processes.
Lissencephalic
smooth brain
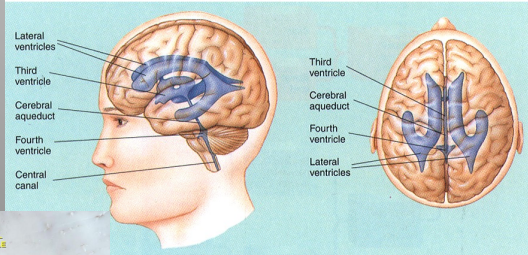
Ventricles
contain cerebral spinal fluid
Different types of ventricles
Lateral Ventricles
Third Ventricle
Cerebral Aqueduct
Fourth Ventricle
Central Canal
Steps in Histological Preparation of Tissue
Fixing
Processing
Embedding
Slicing
Staining
Fixation
Blood is drained from the body (by means of saline)
Fixative solution (usually formalin) is pumped into vascular system to replace remaining fluid
Stabilize tissue, disable intrinsic molecules and enzymes to prevent degredation, and increase tissue strength for further processing
Processing
Embedding in paraffin/ wax (microtome), or
Treatment with sugars to prevent cell damage during freezing (cryostat)
Does not occur when using a vibratome and is optional with the cryostat
Slicing
VIbratome, can section unprocesed tissue
Cryostat is relatively fast and does not require embedding
Microtome provides high quality for thin sections/high mag resolution
Staining
Nissl stain provides good general tissue contrast, stains cell bodies (nissl)
Myelin stains affect white-matter only (luxol blue)
Golgi/Silver stains highlight just a few neurons in full detail
Cresyl Violet Nissl Staining Method
Hydration helps the stain fix in the tissue because cell bodies are full of water
Dehydration with ethanol solutions help differentiate the Nissl stain by decoloring high myelinated areas of the brain
Dehydration if done from less (70%) to more concentrated (100%) to avoid damaging the tissue due to dramatic changes in the environment where the tissue was previously exposed (distilled water and cresyl violet)
Epidural Space
Area between the periosteum of the spinal column and the dura mater of the spinal cord containing mostly adipose tissue.
Subarachnoid Space
space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater of the spinal cord that contains cerebrospinal fluid.
Anasthesia in the Subarachnoid Space
Considered more dangerous due to punturing the meninges around the spinal cord
More widespread effect due to the circulating CSF
Can cause headaches in patients after waking up due to the circulation of the CSF
Anasthesia in the Epidural Space
Considered safer since the meninges of the spinal cord are not punctured
More of a local anasthetic, can pinpoint the exact nerves you want to target and select where to do the injection along the spinal column
Cevical Vertebrae
8 (C1 - C8). Generally involved with the head, neck, shoulders, diaphragm, radial side of arm, and hands.
Thoracic Vertebrae
12 (T1 - T12). Generally involved with the trunk, muscles, chest wall, organs, and ulnar side of the arm.
Lumbar Vertebrae
5 (L1 - L5). Generally involved with lower back, legs, and feet.
Sacral Vertebrae
5 (S1 - S5). Generally involved with bowel, bladder, sexual functions, and heels.
Coccygeal Vertebrae
only 1 at the coccyx
Complete Spinal Cord Injury
no movement or sensation below injury
Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury
partial damage to cord (movement/no sensation or vice versa)
Hangman’s Fracture
spinal cord injury at C2; usually fatal due to brain stem injury (medulla)
SCI below brainstem, but above C3, C4, C5
usually leads to asphyxiation
Quadriplegia
loss of feeling in most of the body
Paraplegia
loss of lower extremities
SCI between C1 and C5
paralysis of some or all muscles used for breathing and all arm and leg muscles. Typically, fatal unless ventillator is used.
SCI between C5 and C6
Paralysis of the legs, trunk, hands, wrists. Weakness of the muscles that move the shoulder and elbow.
SCI between C6 and C7
paralysis of the legs, trunk, and part of the wrists and hands. Normal movement of the shoulders and elbows.
SCI between C7 and C8
Paralysis of the lefs, trunk, and hands
SCI between C8 and T1
Paralysis of the legs and trunk. Weakness of the muscles that move fingers and hands. Horner’s syndrome (drooping eyelid, constricted pupil, and reduced sweating on one side of the face). Possibly normal movement of shoulders and elbows.
SCI between T2 and T4
paralysis of the legs and trunk. Loss of sensation below the nipples. Normal movement of the shoulders and elbows
SCI between T5 and T8
paralysis of the legs and lower trunk. Loss of sensation below the rib cage
SCI between T9 and T11
paralysis of the legs. loss of sensation below the navel.
SCI between T11 and L1
paralysis of and loss of sensation in the hips and legs
SCI between L2 and S2
various patterns of leg weakness and numbness, depending on the prcise level of injury
SCI between S3 and S5
numbness in the perineum
A severe injury at any level of the spinal cord can
cause loss of bladder and bowel control
Dermatome
an area of skin/the body associated with a single spinal cord segment (sensory and motor region)
Decussation
the crossing of two things, usually in the form of an X.
Pyramidal Decussation
when motor fibers pass from the brain to the medulla spinalis and medulla oblongata
Dorsal Root
sensory axons and interneuron cell bodies, ascending
Ventral Root
motor cell bodies, descending
Horns
present in gray matter and divided into dorsal and ventral
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
preferentially affects cervical spinal cord (dorsal areas). Body’s immune cells attacking myelin leading to inflammation around nerves. Symptoms include:
Ascending numbness, starting in feet
Bilateral hand numbness
Numbness on one side of the body
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Loss of lower motor neurons in the ventral horn
Degredation of lateral column pathways in spinal cord
Muscle atrophy
No changes in intellect or memory
Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges leading to headache, stiff neck, high fever. Massive immune response in the CNS leads to swelling and cell death. Detected through spinal tap to check for bacteria in CSF. Also referred to as “Dorm Disease”
Encephalitis
a serious brain inflammation that can occur due to an infection or autoimmune resonse. Can create a variety of symptoms, including headaches, seizures, and confusion. In severe cases can lead to brain damage, stroke, or death.