2- HUMAN EMBRYOLOGY: Teratogens & Parturition
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
The ____ weeks of embryonic development, when gastrulation and neurulation occur and most organ systems are being established, are especially sensitive to damage from _____ such as viruses, recreational drugs and medications, smoking, and alcohol.
3rd – 8th
teratogens
Recognize that fetal alcohol syndrome, of varying severity, affects as many as ______.
1 in 100 of live births.
Learn that the risk of spinal cord defects can be reduced by _____ taken during early pregnancy.
folic acid
Recognize the value of _____ as a tool for assessing the development of the embryo or fetus.
ultrasound scans
Learn the risks of _____ and understand the need to evaluate ____ in terms of gestational age.
low infant birth weight (<2500gms)
birth weight
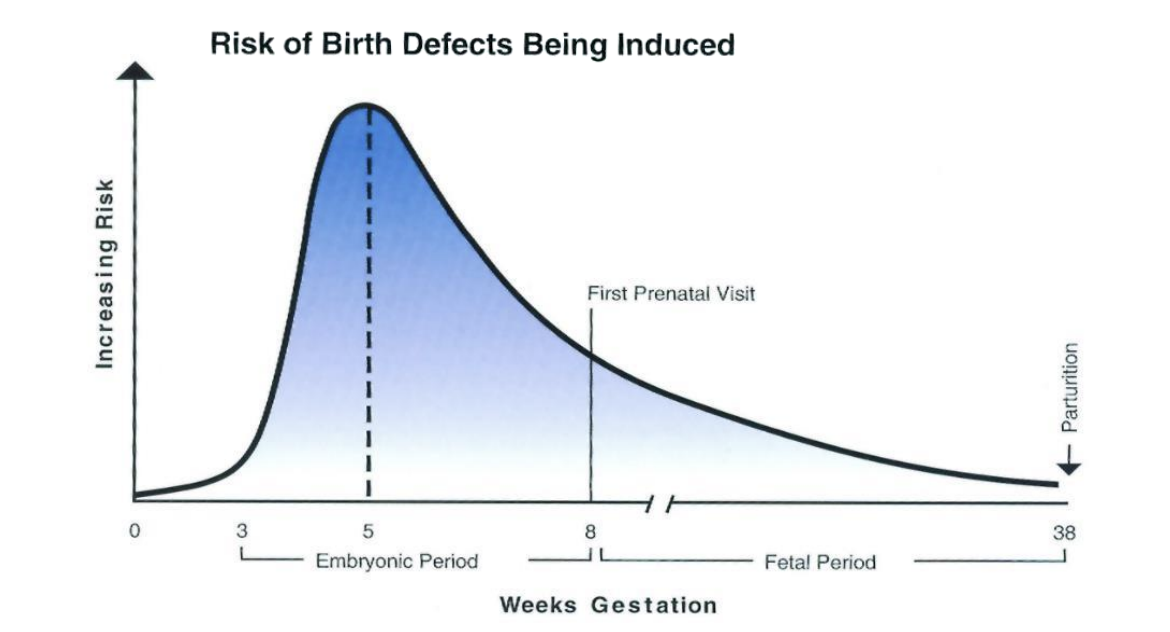
Timing of Birth Defects is
1. Most prominent between _____.
2. _____ throughout development
3. Prior to 3 weeks, the disruptions are so severe that _____.
3 – 8 weeks (most women do not know their pregnant)
Continues
miscarriage occurs
Review of Development (3 – 8 Weeks)
1. _____ forms at 2 – 3 weeks.
2. Primitive _____ field form.
Bilaminar embryo
streak and heart
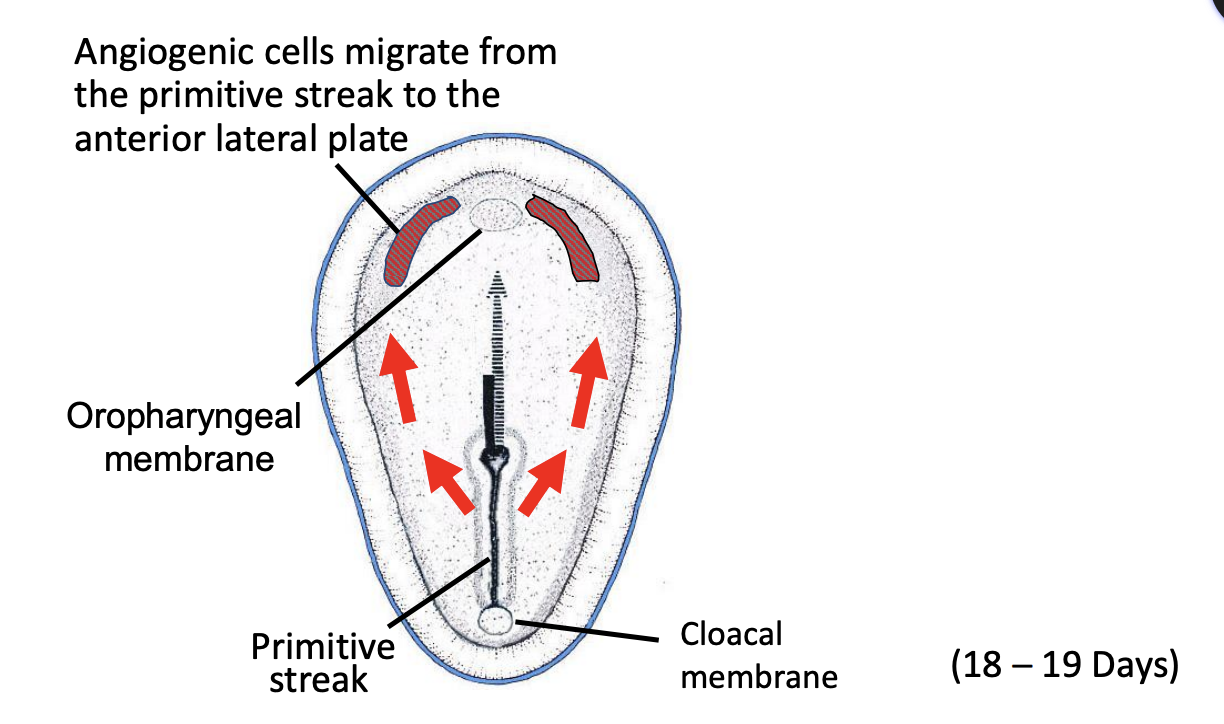
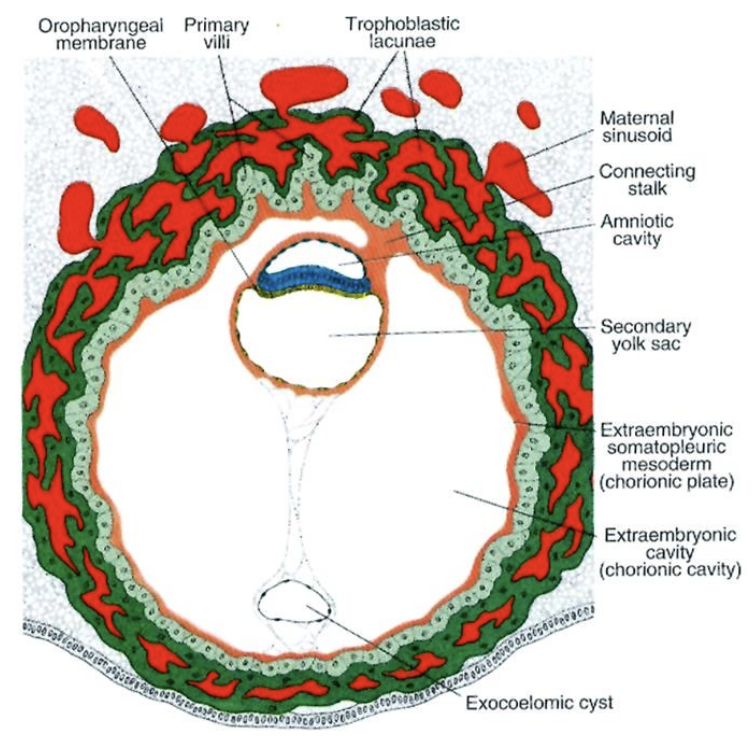
Review of Development (3 – 8 Weeks)
3. _____ at 3 weeks.
4. ________ begins to form.
Primitive heart field and blood islands
Neural plate (forms the brain and spinal cord)
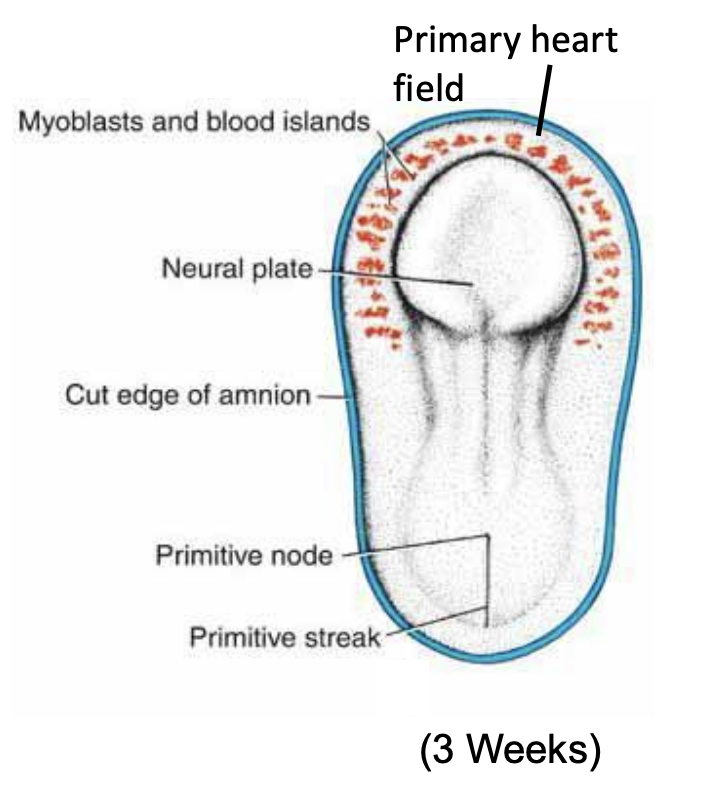
Review of Development (3 – 8 Weeks)
5. _____ and primitive _____ during third week
6. _____ forming in third week
Cardiac looping, heart beat
Neural tube
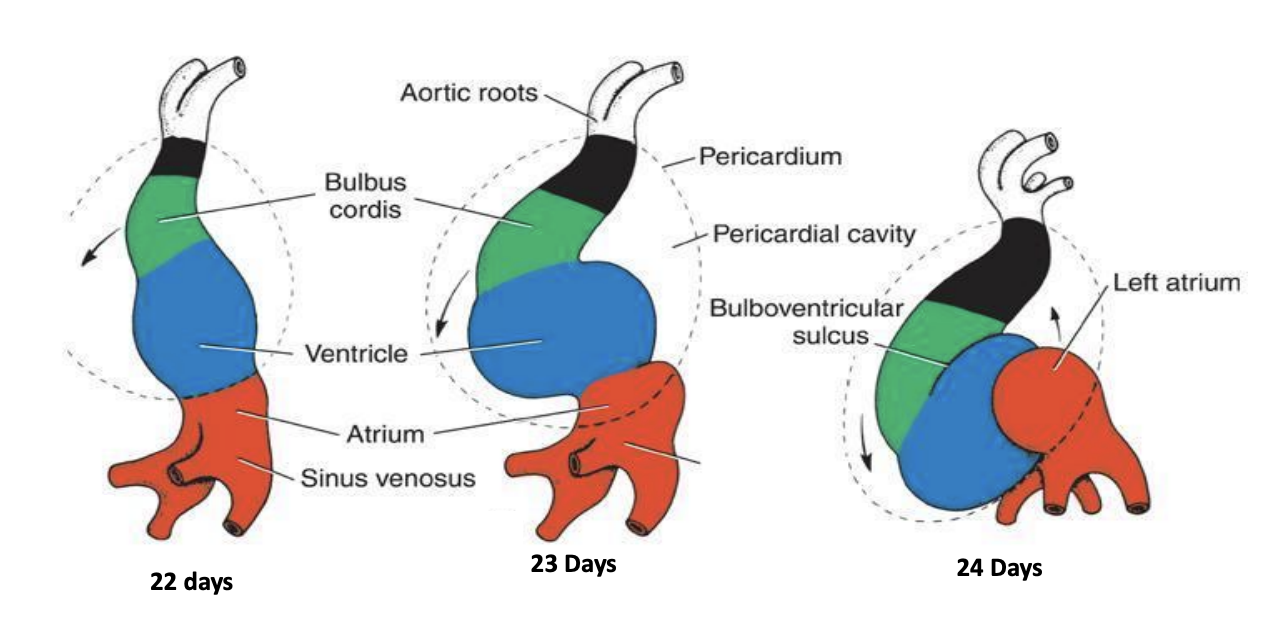
Review of Development (3 – 8 Weeks)
7. _____ formation begins during third week
8. _____ occurs during third week
Somite (“let’s grow a…”) (vetebral level)
Gastrulation (folding & rounding to hold cavity organs)
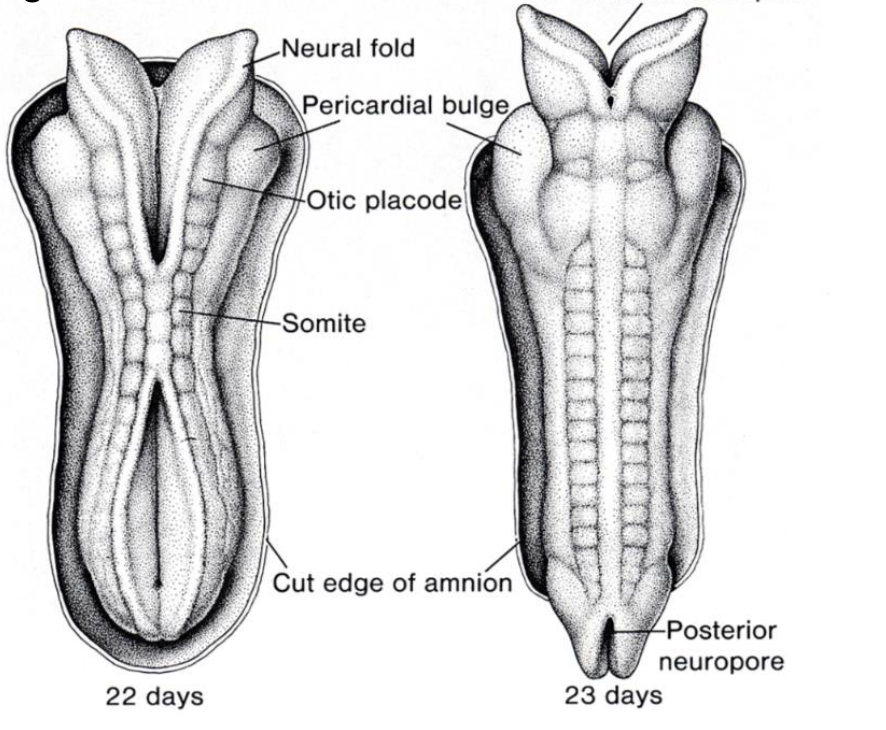
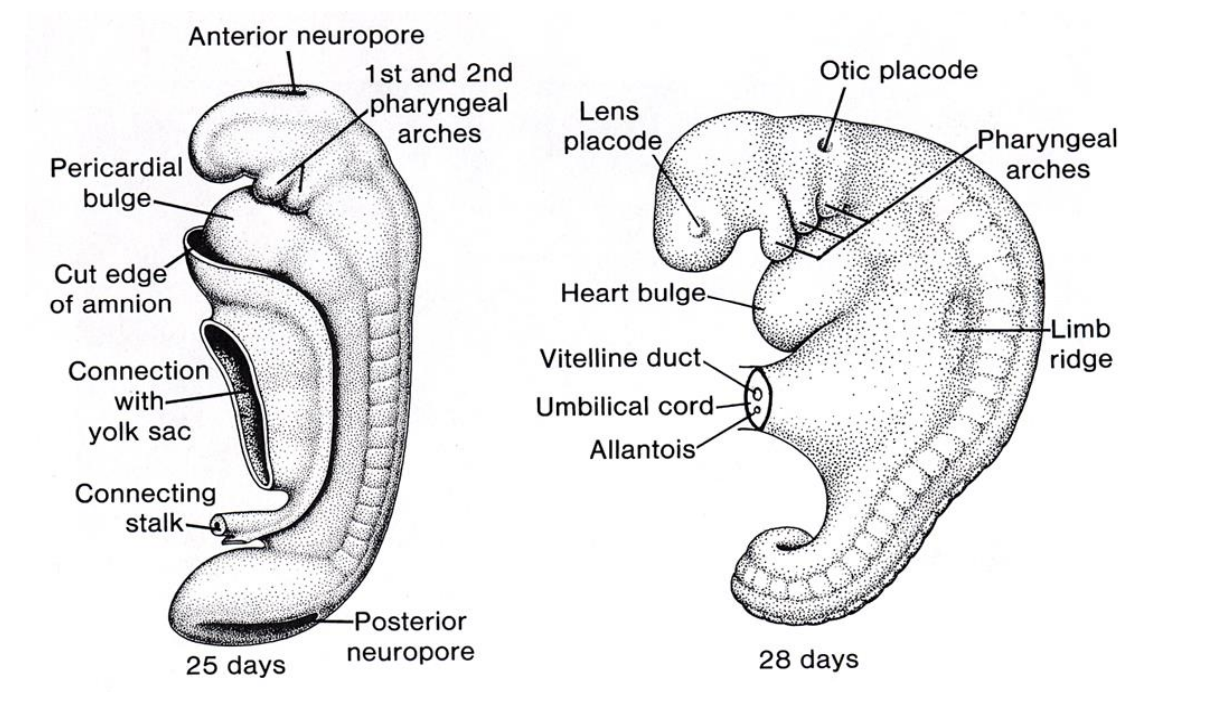
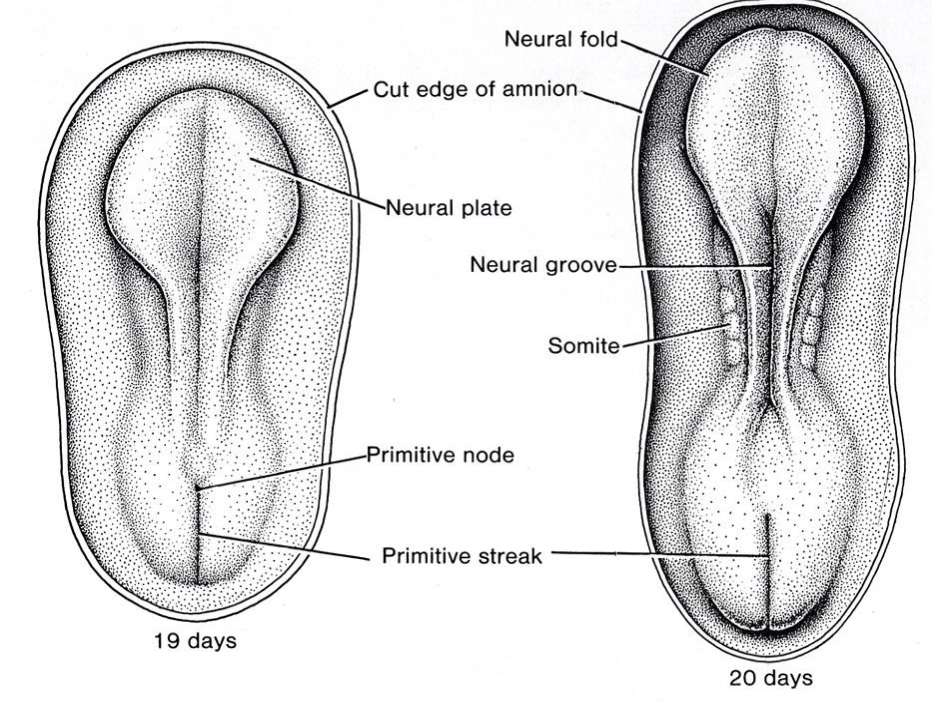
Review of Development (3 – 8 Weeks)
9. By 8 weeks, the embryo has a human form and _____. ____ development then begins.
Any damage during this period is very dangerous since this is the period that _____.
all of the organ systems have begun developing
Fetal (things just get bigger)
tells everything where to form.
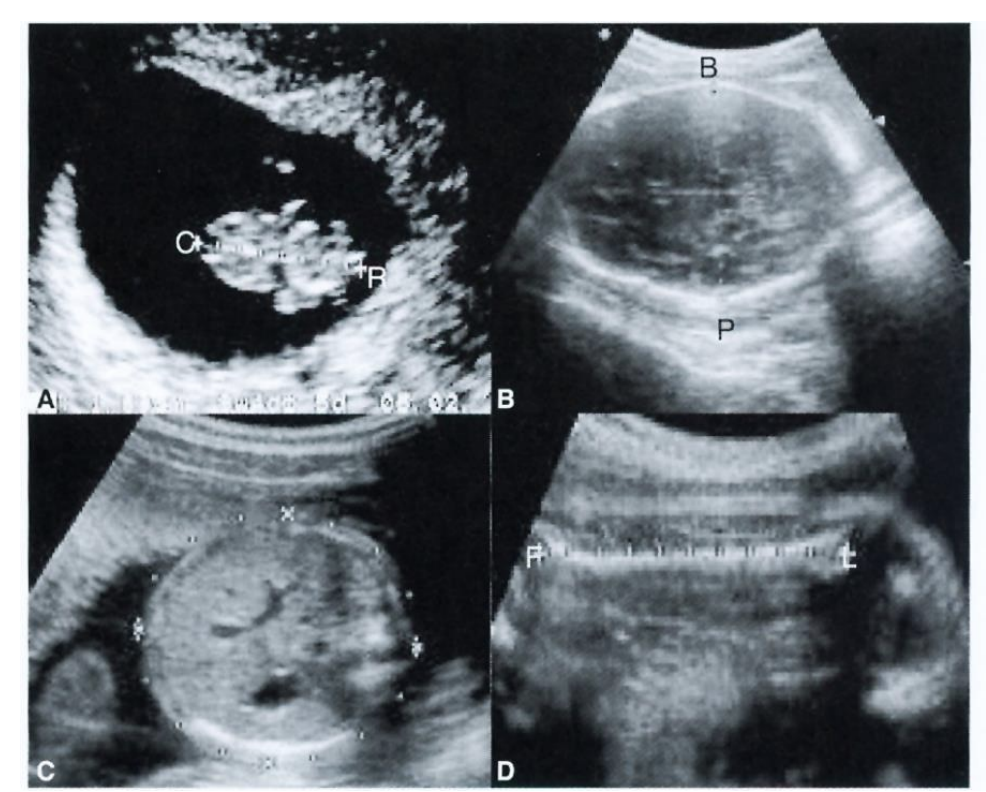
The Use of Ultrasound in Development is
1. ______ means of evaluating fetus
2. Can observe normal ____
3. Can measure _____, _____ of the skull, _____ circumference and _____ to assess growth rate
4. Can be used to guide _______
Non-invasive, non-isotopic
anatomy and anomalies
crown – rump (CR) length, bi-parietal diameter, abdominal, femur length
needle for amniocentesis
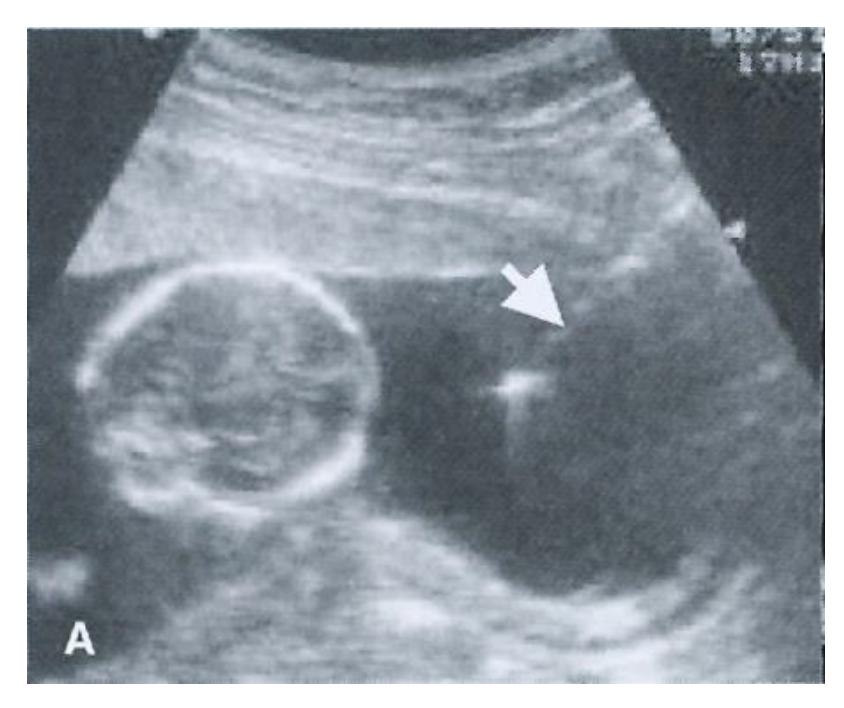
Amniocentesis procedure is not usually performed before _____, since 20 - 30 ml of amniotic fluid is withdrawn. The risk of fetal loss is around _____, but may be less for highly skilled individuals and centers.
14 weeks of gestation
1 in 300-500 overall
What are Teratogens & the different types?
compounds/drugs that impact development
Different types:
1. Infectious agents
2. Physical agents
3. Chemical agents
4. Hormones
3 important teratogen infectious agents are:
Rubella
Cytomegalovirus
Toxoplasmosis
Rubella:
Cytomegalovirus:
Toxoplasmosis:
was formerly a major problem, but is now well-controlled by a vaccine.
is a serious threat. Mothers are often asymptomatic, but newborns can be seriously ill or die from defects apparent at birth or may be delayed until later.
causes brain defects; symptoms may first appear at birth or later.
An important teratogen physical agent is:
X-rays
Ionizing radiation from X-rays:
is a potent teratogen, producing almost any type of birth defect depending upon the dose and stage of development.
4 important teratogen chemical agents are:
Thalidomide
Alcohol
Lead
Tylenol
Thalidomide:
used as anti-nausea / sleep aid in Europe in 1960’s
Produced amelia / meromelia (loss of limbs)
Not in US, due to FDA reviewer
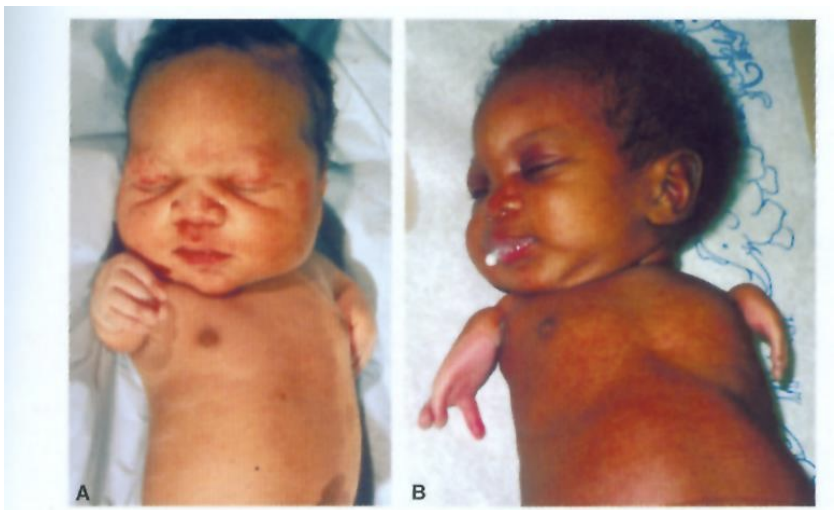
Alcohol causes:
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD)
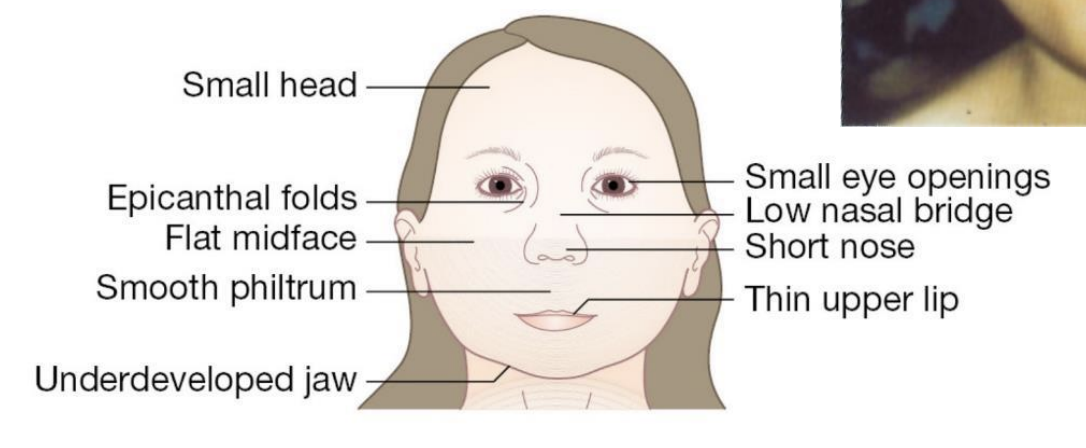
Tylenol (acetaminophen):
asthma, attention deficit disorder (ADHD)
Not sure of mechanism, small risk
2 important teratogen hormone agents are
Diethylstilbestrol (DES)
Endocrine disruptors
Diethylstilbestrol (DES) :
is a synthetic estrogen that was used to prevent abortion. Women exposed to DES in utero had higher incidences of carcinomas of the vagina and cervix as well as higher incidences of malformations of the uterine tubes, uterus, and upper vagina. Male embryos exposed in utero were also affected, though less severely
Endocrine disruptors:
interfere with the interaction of estrogen with its receptors and cause developmental disruptions. Today, environmental estrogens largely derived from industrial chemicals and pesticides are becoming more prevalent and can affect many aspects of sexual development, both anatomical and behavioral, in males and females.
Lack of Proper Nutrition like Folic acid causes:
neural tube defects (spina bifida)
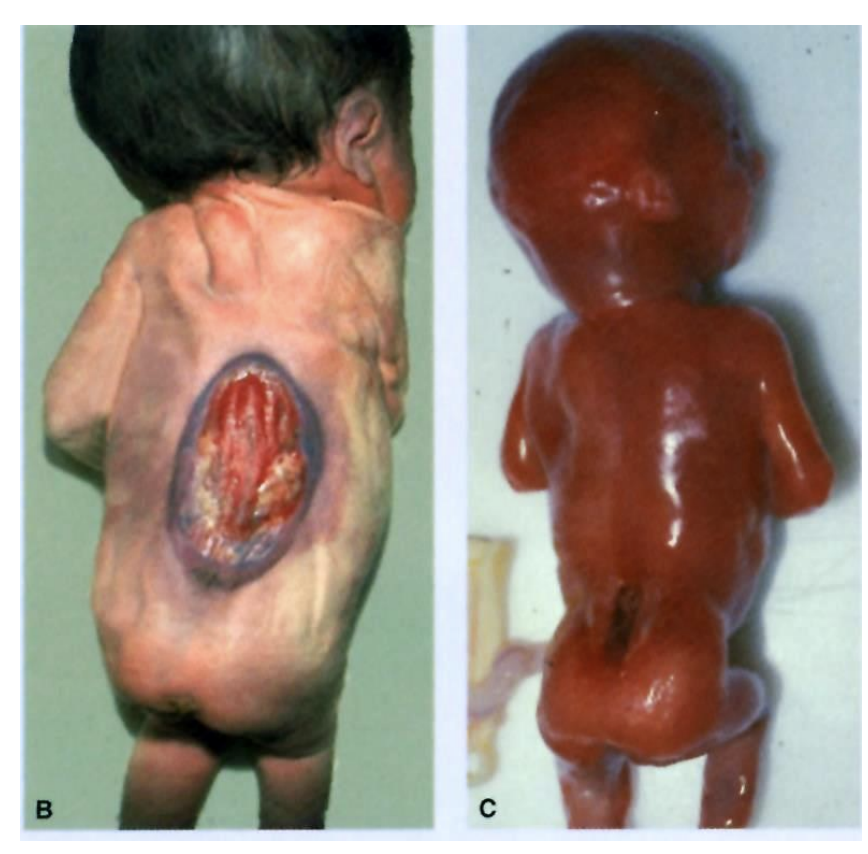
____ reduces occurrence of NTDs by 50 - 70% if taken by women of child-bearing age.
Folic acid (400 ug daily)
Low Birth Weight
1. Normal newborn size at delivery ranges from ____, with a CRL of ____.
2,500 to 4000 g (6 - 9 lbs)
51 cm (20 inches).
Low Birth Weight
2. _____ refers to a birth weight of < 2500 g, regardless of gestational age (includes pre-term infants). In contrast, ______ and ______ take into account gestational age.
Low birth weight (LBW)
intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
small for gestational age (SGA)
Low Birth Weight
3. IUGR applies to infants who do not attain their ____, are ____ small, and are at ____.
optimal intrauterine growth
pathologically
risk for poor outcomes.
Low Birth Weight
4. SGA infants have birth weight below the ____ for their gestational age. They may have ____ or they may be constitutionally_____. The challenge is to distinguish between the two so as not to subject healthy infants to _____ for IUGR.
10th percentile
IUGR
small and still healthy
unnecessary high risk protocols
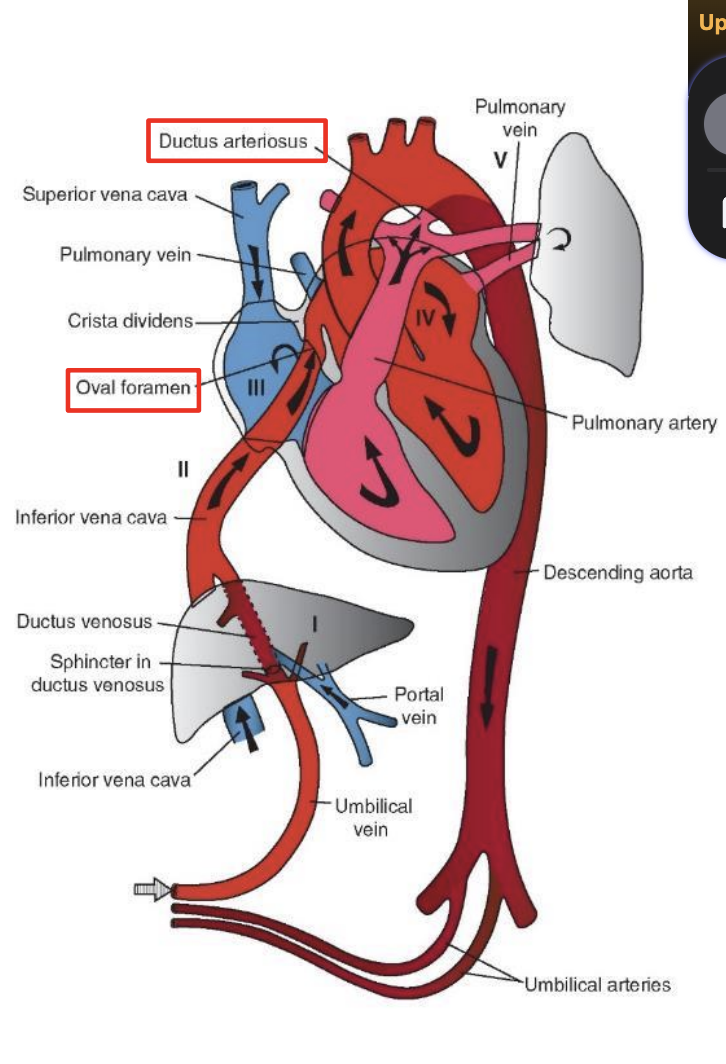
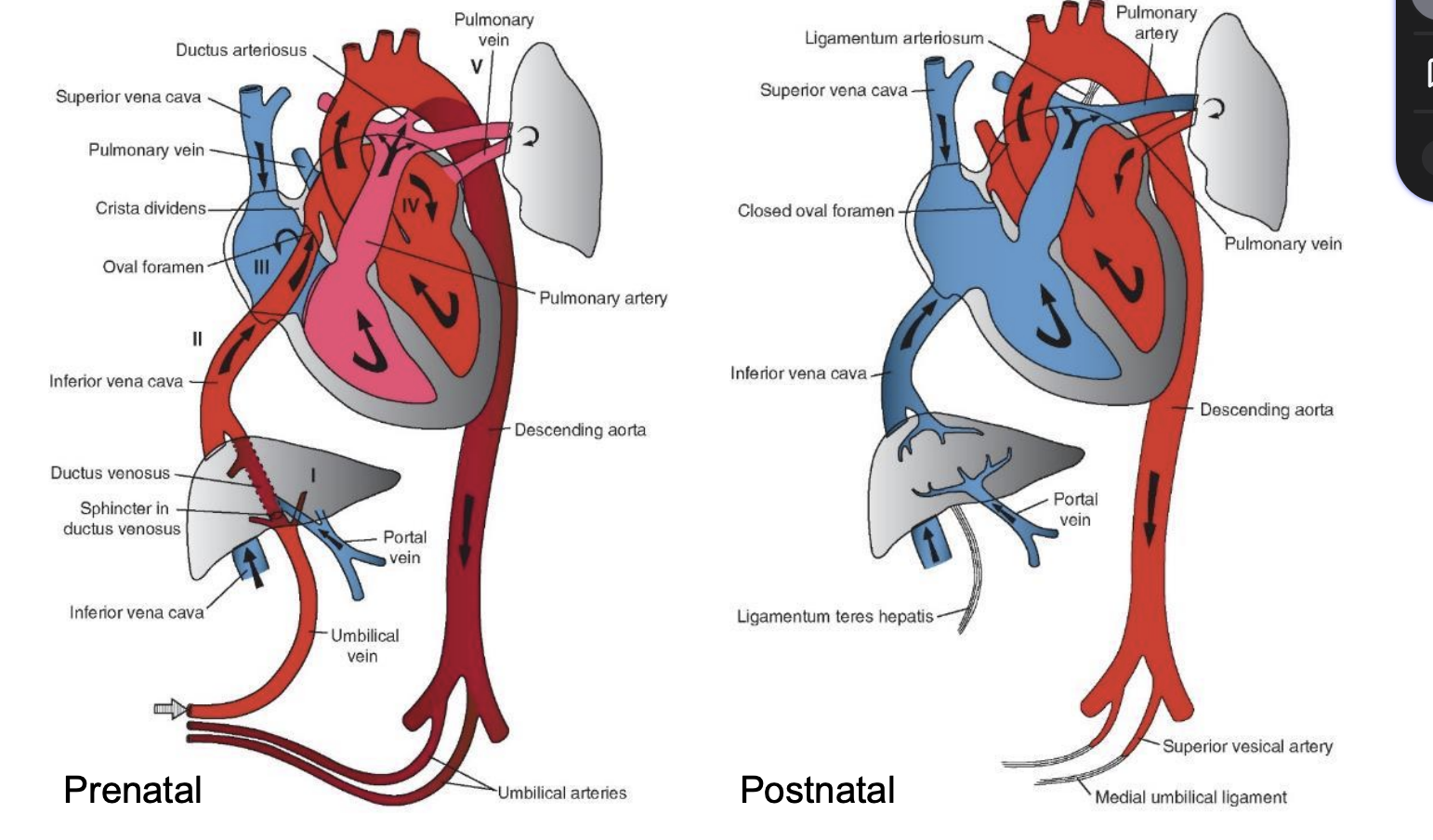
Changes in Circulation at Birth
1. Functional closure of _____ within a few minutes by smooth muscle contraction in their walls. Actual obliteration of the lumen by fibrous proliferation takes 2 - 3 months; vessel remnants become median umbilical ligaments.
2. Closure of the _____ occurs shortly after that of the umbilical arteries. Blood from the placenta may enter the newborn for some time after birth. The umbilical vein forms the ligamentum teres hepatis, and the ductus venosus forms the ligamentum venosum in the liver.
umbilical arteries
umbilical vein and ductus venosus
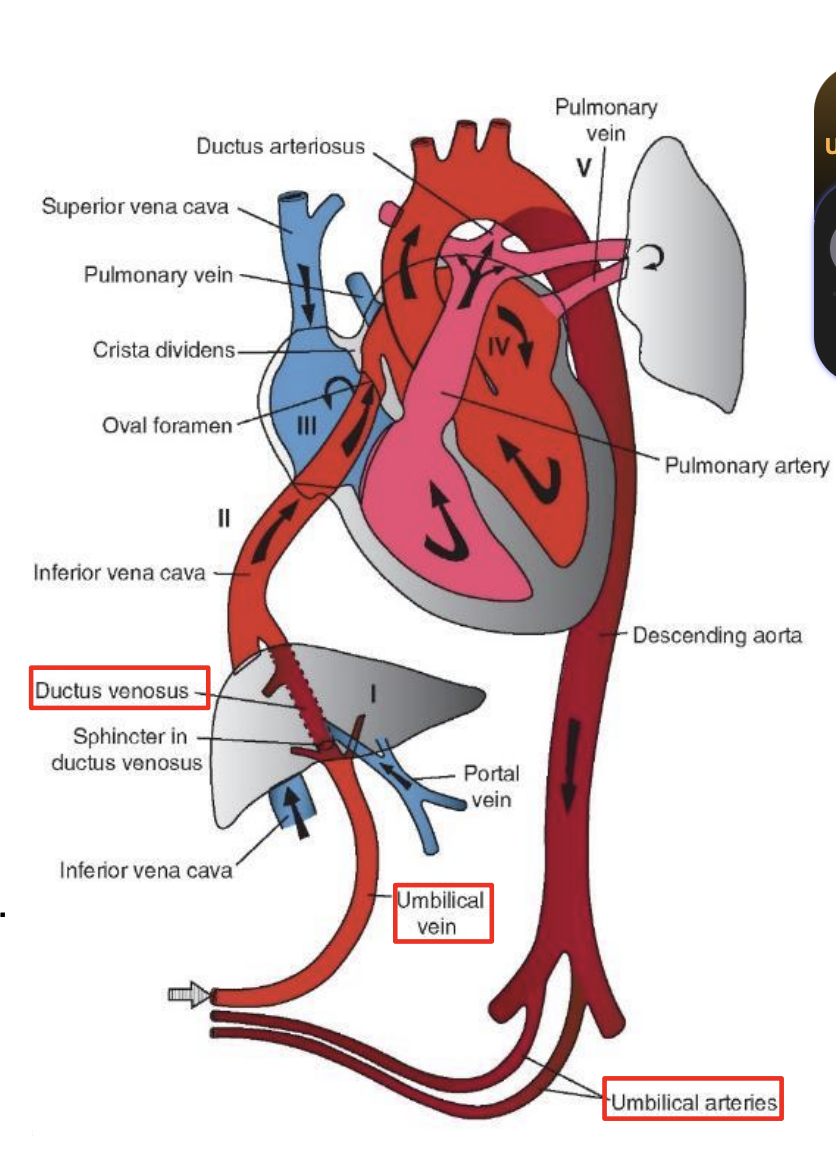
Changes in Circulation at Birth
3. Closure of the _____ by contraction of its muscular wall occurs immediately after birth. Complete anatomical obliteration takes 1 - 3 months, with the remnant becoming the ligamentum arteriosum.
4. Closure of the ____ is caused by increased pressure in the left atrium along with decreased pressure in the right atrium. The____ compresses the septum primum against the septum secundum. During the first days of life, this closure is ______ can create a shunt from right to left that accounts for cyanotic periods in the newborn. Fusion of the two septa occurs within a year, although in 20% of individuals complete anatomical closure may never occur.
ductus arteriosus
foramen ovale
first breath
reversible, and crying
Changes in Circulation at Birth:
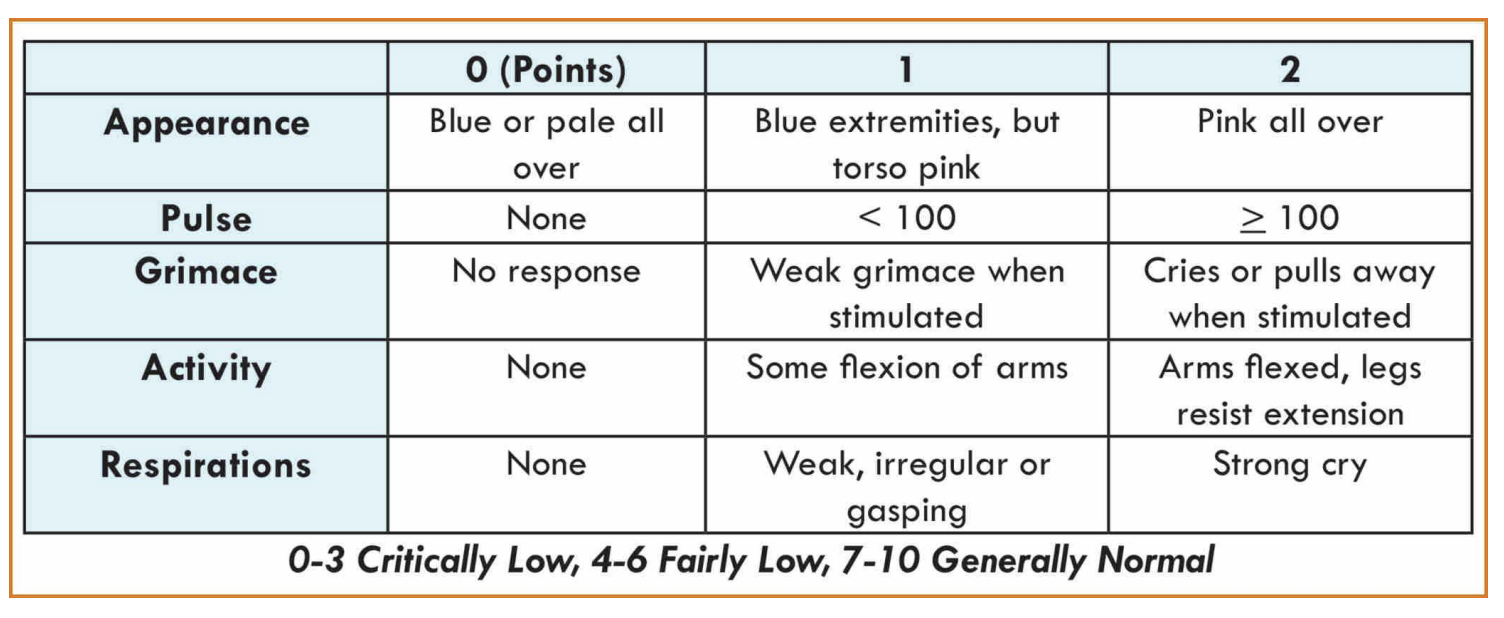
What is the APGAR Score?
a medical assessment of a newborn's health that evaluates 5 characteristics
What are the 5 characteristics of the APGAR Score?
A = appearance
P = pulse
G = grimace
A = activity
R = respiration
Each criteria of the APGAR scores ____ for a total of ___ points. It is performed at ____ after birth.
0 – 2
10
1 and 5 minutes
Interpretation for the APGAR Score
____= normal
____= low
____= critically low
7 - 10 = normal
4 - 6 = low
0 - 3 = critically low