The Gas Phase
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
When do gases deviate from ideal behavior?
Hi Pressure, Lo Temp, Lo Volume = Not Ideal
What is the volume of 1 mole of an ideal gas at STP?
At STP, a mole is plenty-four — twenty-two point four!
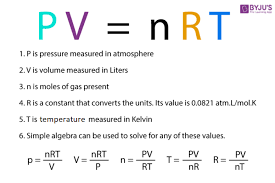
What is the Ideal Gas Law equation and what do each of its variables represent?
PerVy = nRT
What are the main characteristics of an ideal gas?
No PIE, Constant Temperature!
• No Particle volume
• Intermolecular forces? None!
• Elastic collisions
• Constant motion
• Temperature = KE
How do you calculate the number of moles of a substance?
Mass divided by molar mass — gives you moles, nice and fast!
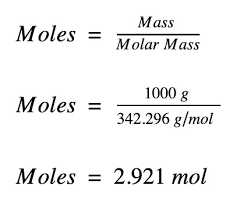
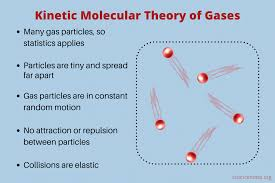
What are the key points of the Kinetic Molecular Theory of gases?
KMT is the theory behind the Ideal Gas Law!
What is Henry's Law and what is its equation?
More pressure, more gas dissolves! ~ just like soda
Cool People (C = kP) Keep Pressure!

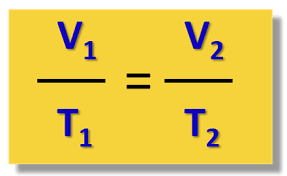
What is Charles' Law and what is its equation?
As Temp goes ↑, Volume goes ↑ (and vice versa) — if pressure stays the same
V over T = V over T
How do you calculate the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture?
Total Times Fraction = Partial Pressure
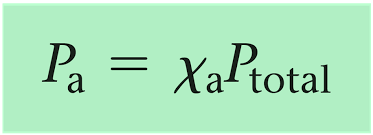
How to calculate mole fraction?
Part over Whole = Mole Fraction Goal!

What is the SI unit for pressure, and how is it defined?
Pressure is the push (force) over a patch (area) — that's a pascal!
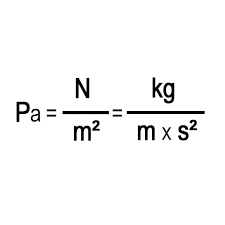
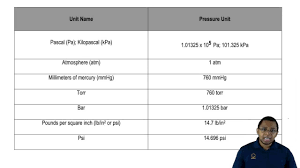
What are the common pressure units and how do they convert?
A Tiger Might Hunt Powerful Kangaroos
Atm =
Torr =
MmHg =
Hundred-one-three kPa =
Pascals = 101,325
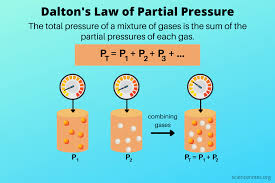
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
States that the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture.
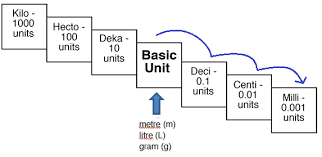
How do you convert between base units in the metric system?
Applied to metric order (left to right):
Kilo - Hecto - Deca - Base - Deci - Centi - Milli
King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk
Tip:
Move the decimal right when going from larger to smaller units (e.g., g → mg)
Move the decimal left when going from smaller to larger (e.g., mg → g)
What is Gay-Lussac's Law?
When temp goes up, pressure goes up!
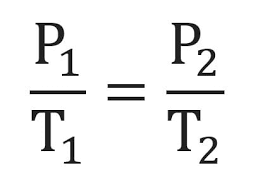
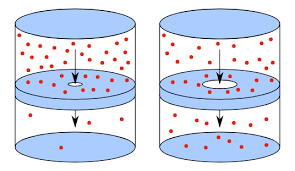
What is effusion?
Effusion = Escape through a pinhole
What is the Van der Waals equation and why is it used instead of the Ideal Gas Law?
Pressure Up? Add a! Volume Down? Subtract b!
a fixes pressure (due to attractions pulling particles in)
b fixes volume (accounts for particles taking up space)
