Pathophysiology II - Exam 4 - Substance Use Disorder 💊
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
to reduce stigma/negative bias and improve scientific accuracy, what should we say instead of "substance abuse" or "drug abuse"?
"substance use disorder" or specify the specific disease state (ex: alcohol use disorder)
to reduce stigma/negative bias and improve scientific accuracy, what should we say instead of "addict", "user", "drug abuser", "junkie", or "alcoholic"?
"person with SUD" or "person who uses drugs"
to reduce stigma/negative bias and improve scientific accuracy, what should we say instead of "clean"?
- "in remission or recovery"
- "tested negative on a drug screen"
- "abstinent from drugs"
to reduce stigma/negative bias and improve scientific accuracy, what should we say instead of "dirty" or "failed a drug test"?
"tested positive on a drug screen"
what is addiction, according to the ASAM?
a treatable, chronic medical disease involving complex interactions among brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual's life experiences
- non-specific term; doesn't mention substances!
what are the 6 general steps of the pathophysiology behind SUD/addiction?
① substance use or activity performed
② release of DA to the nucleus accumbens (reward center)
③ stimulation of DA-1 Rs
④ activation of cAMP
⑤ euphoria and pleasure occur
⑥ association developed between the substance and the feeling of euphoria/pleasure
what changes are observed in the brain during SUD on a neuronal level?
- increase in DA in the neuron synapse
- both NMDA Rs and AMPA Rs increase glutamate (excitatory NT)
- further modification of interconnected neural loops causes habit formation, which creates a hyper-excitable state when the substance is removed
which 2 NTs have a clear association with SUD? which 4 NTs are likely involved, but not well understood?
clear association:
- ★DA
- glutamate
likely association, but not well understood:
- GABA
- 5-HT
- ACh
- endogenous opioids and cannabinoid compounds
what is substance-use disorder?
a cluster of physiological, behavioral, and cognitive Sx associated with the continued use of substances DESPITE substance-related problems, distress, or impairment
what are substance-induced disorders? provide examples
conditions caused by a substance that occur in people who do NOT have an existing mental disorder
- intoxication
- withdrawal
- other substance-related mental disorders: anxiety, psychosis, sleep disorders, BPD, depressive disorders, sexual dysfunction, neurocognitive disorders, OCD
using the DSM-5 system, what are the 4 SUD criteria that fall under the category of "impaired control"?
- substance is taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than intended
- unsuccessful efforts to cut down/regulate substance use, despite persistent desire to control use
- significant amount of time spent obtaining/using/recovering from substance use
- cravings
using the DSM-5 system, what are the 3 SUD criteria that fall under the category of "social impairment"?
- recurrent use resulting in failure to fulfill major obligations at work/school/home
- continued substance use despite it leading to social or interpersonal problems
- reduced or missed social/occupational/recreational activities due to substance use
using the DSM-5 system, what are the 2 SUD criteria that fall under the category of "risky use of the substance"?
- continued use of the substance in potentially physically hazardous situations
- continued use despite knowledge that the substance has caused or worsened physical or psychological harm
using the DSM-5 system, what are the 2 SUD criteria that fall under the category of "pharmacologic indicators"?
- tolerance
- withdrawal
how many of the 11 criteria are needed to classify a case of SUD as mild, moderate, or severe?
minimum needed is 2
- mild: 2-3
- moderate: 4-5
- severe: 6+
what are cravings?
an intense desire or urge for a substance
- may occur at any time, but the environment is a common trigger
what is tolerance?
a decrease in response to a drug dose that occurs with continued use
- an increased amount of substance is needed in order to achieve the desired result
what is withdrawal? what influences the Sx?
the discomfort and distress that follow discontinuing the use of an addictive substance
- patient uses the substance (or a similar substance) to relieve or avoid withdrawal Sx
- substance-specific Sx
- influenced by an individual's tolerance and dose, route, and frequency of use
what is physical dependence?
a neurological adaptation manifested by a drug class-specific withdrawal syndrome
- Sx are produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug, and/or administration of antagonists
T/F: physical dependence and tolerance are inherently pathogenic
FALSE
- NOT inherently pathogenic, and NOT unique to drugs that can lead to SUD!
what is intoxication? what influences the Sx?
maladaptive change in behavior after acute substance exposure
- substance-specific
- influenced by an individual's tolerance and dose, route, and frequency of use
T/F: substance-induced disorders are usually temporary
TRUE
- temporary, but can be severe!
what are some classes of sedating drugs? what are the common Sx of intoxication vs. withdrawal?
sedatives, hypnotics, anxiolytics, alcohol
- intoxication: depressive disorders
- withdrawal: anxiety disorders
what are some examples of stimulating drugs? what are the common Sx of intoxication vs. withdrawal?
amphetamines, cocaine
- intoxication: substance-induced psychotic and/or anxiety disorders
- withdrawal: substance-induced major depressive episodes
T/F: both stimulating and sedating drugs are likely to cause significant (but temporary) sleep and sexual disturbances
TRUE
what has been in the local opioid supply, both historically and currently?
historically
- prescription opioids
- heroin (diacetylmorphine)
currently (Philly/Camden)
- illicit fentanyl (50-100x more potent than heroin!)
what qualities of opioids makes them the "perfect storm" for SUD?
- agonists at opioid Rs (mu, kappa, delta)
- lipophilic (rapid crossing of BBB)
- multiple routes of administration (intranasal, IV, subcut, IM, smoking)
- t1/2 shortens as tolerance builds, so withdrawal occurs faster after the last use
what is the onset of action of opioids when administered subcut/IM, intranasal/smoking, and IV?
- subcut/IM: 5-10 mins
- intranasal/smoking: 3-5 mins
- IV: <1 min
what are the common Sx of opioid intoxication?
- euphoria
- apathy
- lethargy
- somnolence (strong desire for sleep)
- impaired motor skills
what are the common signs of opioid intoxication?
- miotic (pinpoint) pupils
- drooping eyelids
- scratching/pruritis (histamine release)
- depressed respiratory drive
- LOC
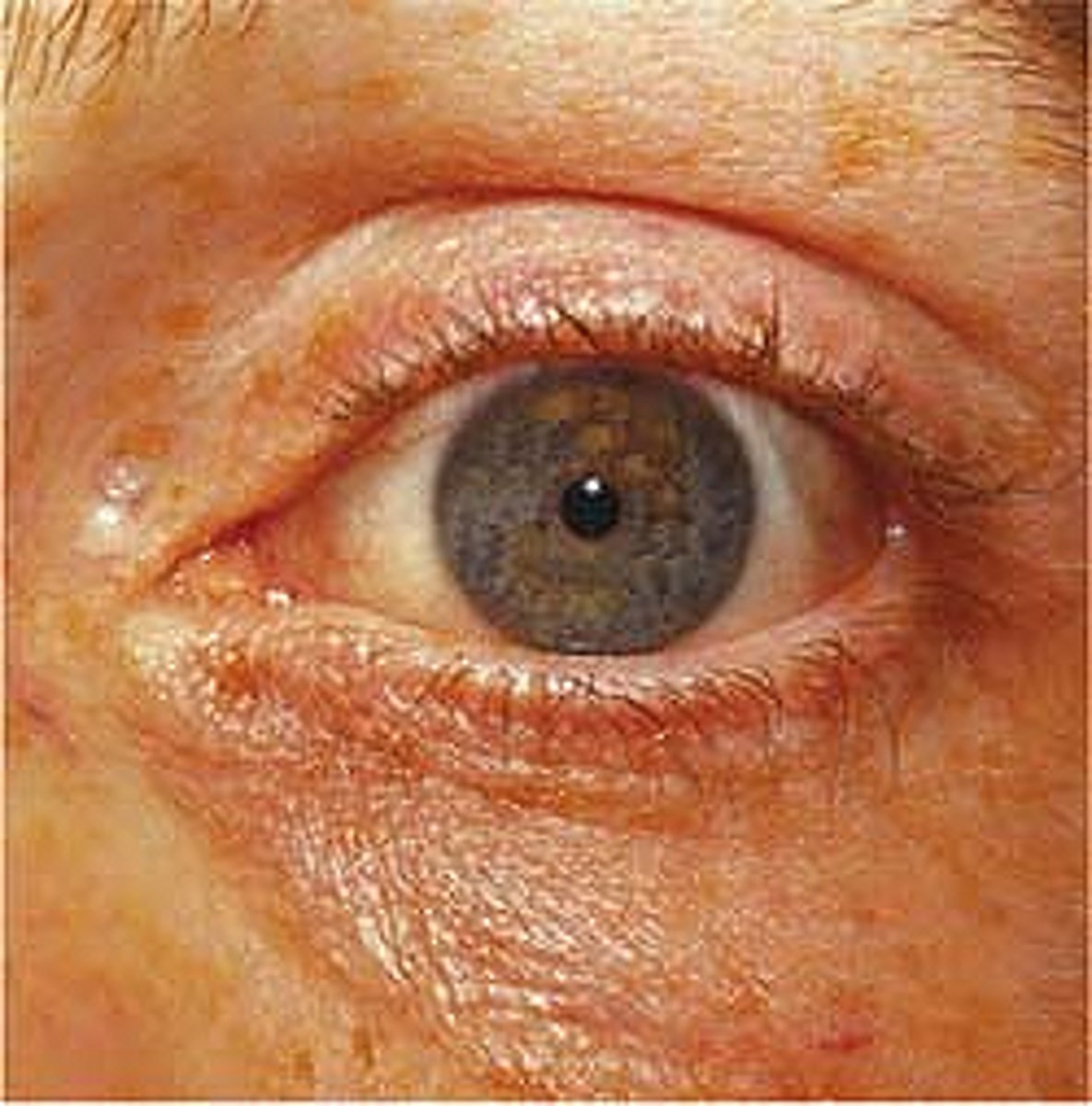
what are the signs of an opioid overdose?
- unresponsive
- not breathing or slow/shallow respirations
- pinpoint (constricted) pupils
- clammy skin
- cyanotic lips or nail beds
will rapidly progress to respiratory failure and cardiac arrest!
what are some of the common signs/Sx of opioid withdrawal (long list!)?
- irritability
- restlessness
- anxiety
- insomnia
- cravings
- pupil dilation
- lacrimation (crying)
- rhinorrhea
- yawning
- tachycardia
- HTN
- abdominal cramping
- N/V/D
- muscle and bone pain
- piloerection
- diaphoresis
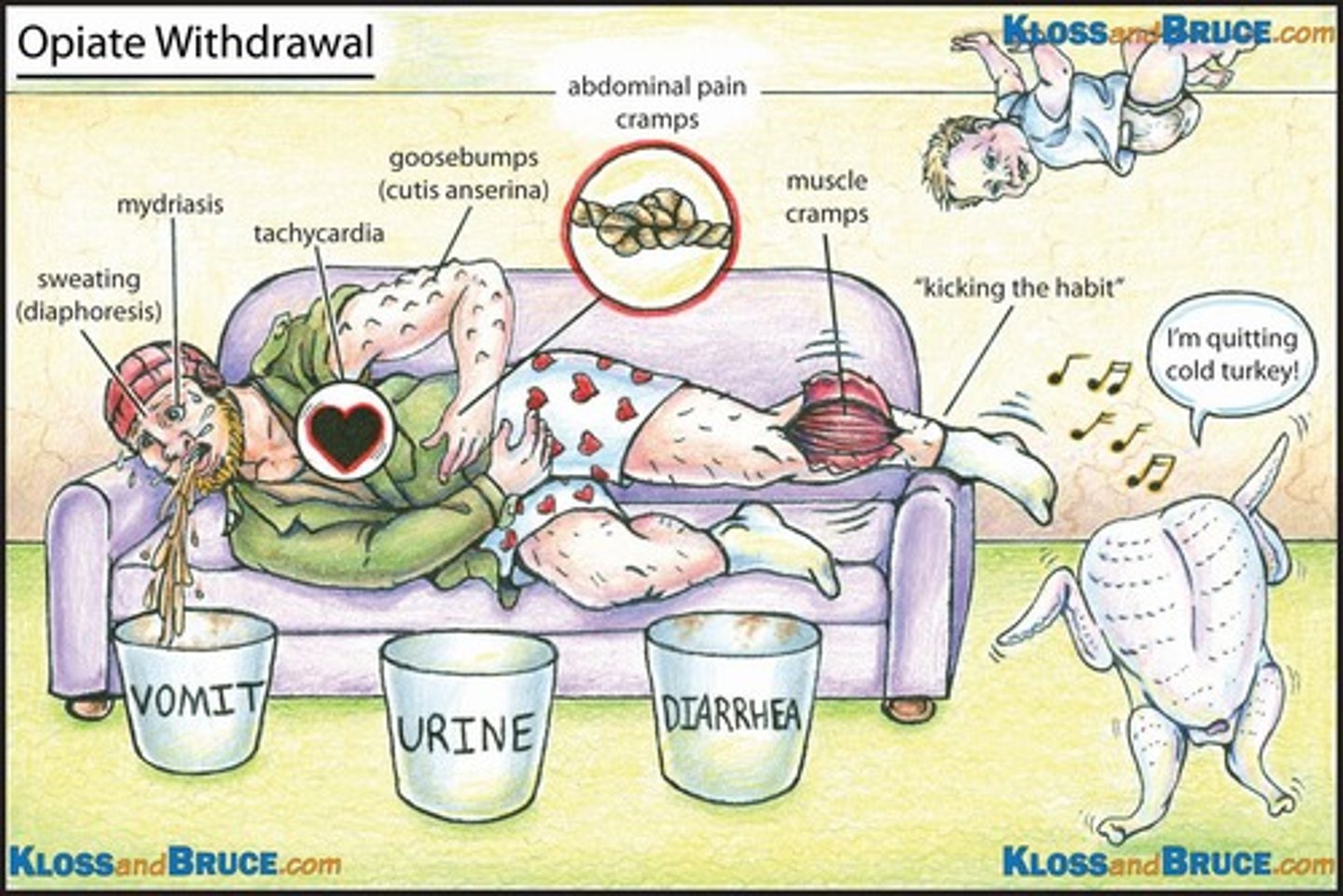
T/F: each opioid has its own unique set of signs/Sx of withdrawal
FALSE
- similar signs and Sx regardless of which opioid is used
T/F: opioid withdrawal is NOT fatal unless the patient has a concurrent medical issue
TRUE
what signs/Sx are taken into account in the Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS)?
- resting HR (often increased)
- sweating
- restlessness
- pupil size (often dilated)
- bone/joint aches
- runny nose
- GI upset
- tremors
- yawning
- anxiety/irritability
- goosebumps
what is the typical onset of opioid withdrawal? how does it change with short-acting vs. long-acting drugs?
ranges from hours to days
- short-acting (heroin, fentanyl): 8-24 hours
- long-acting (methadone): 24-36 hours (may peak up to 96 hours after the last dose)
how long can the acute and post-acute opioid withdrawal phases last?
- acute: 3-14 days
- post-acute (cravings, irritability): weeks-months
what Rs does alcohol bind to in the CNS?
GABA Rs (inhibitory NT)
- induces sedative effect
T/F: alcohol use disorder (AUD) is inheritable
TRUE
- 50% of the risk of AUD is inheritable
T/F: the criteria for AUD is essentially the same as the criteria for general SUD
TRUE
- minimum of 2 criteria needed within 12 months
what is the CAGE questionnaire for AUD? what does the pneumonic CAGE stand for?
one of the many methods used to identify patients at risk for developing or who have already developed AUD; 2+ of the following may indicate AUD:
- have you ever felt the need to Cut down on your drinking?
- have people Annoyed you by criticizing your drinking?
- have you ever felt Guilty about your drinking?
- have you ever had a drink the first thing in the AM ("Eye opener")?
T/F: the CAGE criteria for AUD is diagnostic
FALSE
- just indicates the need for evaluation using the DSM-5 criteria
what Sx are typically observed in individuals with a BAC of 0.002-0.05?
- mild speech/memory/attention/coordination/balance impairment
- relaxation
- sleepiness
- nystagmus (rapid eye movement)
what Sx are typically observed in individuals with a BAC of 0.06-0.15?
- impaired speech/memory/attention/coordination/balance
- risk of aggression
- significantly impaired driving skills (legal limit is 0.08!)
- increased risk of injury to self or others
what Sx are typically observed in individuals with a BAC of 0.16-0.30?
- impaired reaction time and balance
- driving skills are dangerously impaired
- judgement and decision making are dangerously impaired
- LOC, blackouts, vomiting
what Sx are typically observed in individuals with a BAC of 0.31-0.45?
- LOC
- danger of life-threatening alcohol poisoning
- significant risk of death
describe the pathophysiology of alcohol withdrawal; what are the primary NTs involved?
imbalance between excitatory glutamate and inhibitory GABA
- balanced in a healthy brain
- decreased GABA production with alcohol dependence; supplemented with alcohol itself
- extreme imbalance in NTs (excessive glutamate, deficient GABA) with removal of alcohol/withdrawal
what is the typical onset of alcohol withdrawal?
4-12 hours after last alcohol use
- peak in intensity during the 2nd day of abstinence
- generally resolve within 4-5 days
what are the key signs/Sx of alcohol withdrawal?
- tremors
- tachycardia
- HTN
- low-grade fever
- agitation
- seizures
- delirium tremens (delirium + visual hallucinations)
electrolyte imbalances are common in AUD due to...? a deficiency in what vitamin is particularly associated with syndromes?
inadequate nutrition and shifts in fluid volume
- syndromes are cause by thiamine (vit B1) deficiency
what is Wernicke's encephalopathy?
extreme confusion and loss of muscle coordination (ataxia)
- may progress to coma and death
what is Korsakoff's psychosis?
severe memory loss and inability to make new memories
- hallucinations (delirious)
what are some common examples of benzodiazepines (benzos)? how do they induce sedative effects?
alprazolam, clonazepam, diazepam, lorazepam
- increase the affinity of GABA to its R and augment GABA-mediated inhibitory signaling to induce sedative effects
what are some common signs/Sx of benzo intoxication?
- memory impairment, confusion
- drowsiness
- slurred speech
- poor coordination
- bloodshot eyes
what are the 3 major signs of benzo overdose?
- excessive sedation
- amnesia
- respiratory depression
what are the common signs/Sx of benzo withdrawal?
Sx
- agitation, restlessness
- sleep disturbances
- impaired memory and concentration
- hallucinations
signs
- sweating
- HTN
- tachycardia
- tremors
- seizures
how long can minor withdrawal Sx from benzos last? what mild Sx typically persist?
several weeks or longer
- anxiety
- insomnia
- irritability
- photosensitive, phonosensitivity
- muscle spasms
what is the FDA boxed warning on benzos?
increased risk of sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death with concomitant use of benzos + opioid
- using both at the same time increases the likelihood of fatal overdose!!
what Rs does cocaine interact with in the CNS?
α and β adrenergic stimulation increases the activity of catecholamines (NE, DA)
- CNS and cardiac stimulants
how long does the high from cocaine typically last?
15-30 mins (snorted) or 10-15 mins (smoked)
- many experience intense drug use cycling (rapid repeating of doses until money/supply is exhausted)
most cocaine-related deaths are from...? how does the concomitant use of alcohol increase the risk of death?
cardiac arrest or seizures
- in the presence of alcohol, cocaine is metabolized into cocaethylene, which is longer-acting and increases the risk of death!
what are the 2 major formulations of cocaine?
- cocaine HCl (salt form; typically snorted)
- cocaine base ("crack cocaine", typically smoked)
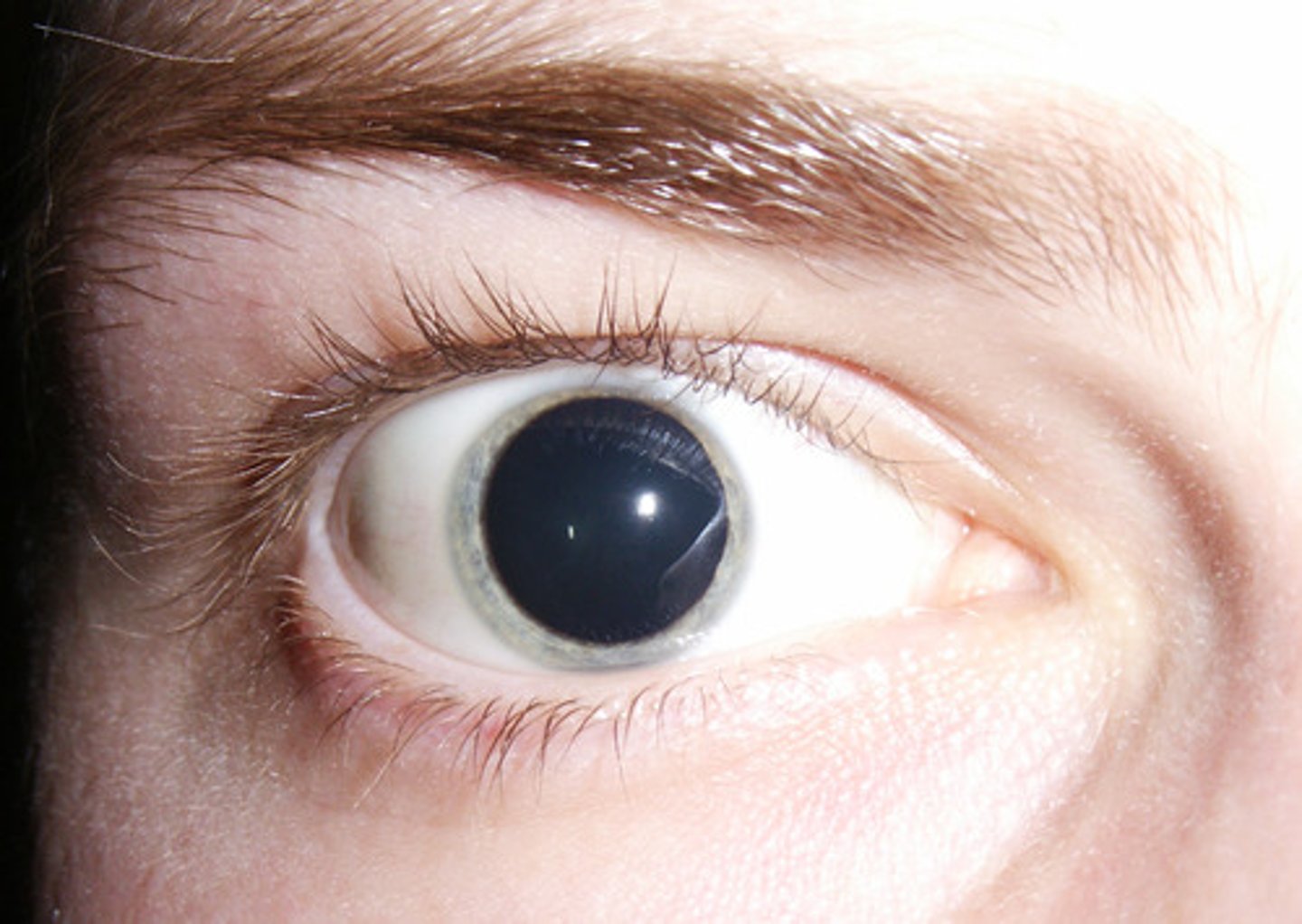
what are the common signs/Sx of cocaine intoxication?
signs
- tachycardia, HTN
- mydriasis (dilated pupils)
- cardiac abnormalities (arrhythmias, MI)
Sx
- motor agitation
- elation, euphoria
- sweating
- paranoia
what are the common signs/Sx of cocaine withdrawal?
signs
- bradyarrhythmia
- tremors
Sx
- fatigue
- sleep disturbances, nightmares
- depression
- changes in appetite
what is the duration of action and routes of administration of methamphetamine (meth)?
- effects are similar to cocaine, but meth has a longer duration of action of ~12 hours
- routes of administration: intranasal, IV, smoking, oral, rectal
what are the negative consequences of meth use?
- anxiety, agitation
- insomnia
- HA
- palpitations
- tachycardia, HTN
- confusion, paranoia
- convulsions
- "meth mouth" (pattern of dental decay from smoking meth)
what Rs does nicotine bind to in the body, and what are its effects?
binds to nicotinic ACh Rs in the CNS AND PNS
- causes increased alertness and cognitive functioning, as well as feelings of pleasure and relaxation
when does nicotine withdrawal typically start, and what are the common withdrawal Sx?
occurs within 24 hours of last use and can last from days-weeks
- anxiety, irritability, hostility
- difficulty concentrating
- insomnia
- strong cravings
- "hedonic dysregulation" (state of malaise or inability to experience pleasure)
what is the safe dose of caffeine per day?
up to 400 mg/day is considered safe in healthy adults
- NOT associated with CV, behavioral, reproductive, or developmental AEs
- there are ~100-125 mg of caffeine in a normal coffee, but can vary significantly!
T/F: caffeine use is categorized as a SUD per DSM-5
FALSE
- NOT categorized as a SUD per DSM-5
what is caffeinism?
syndrome of anxiety, psychomotor alterations, sleep disturbances, mood changes, and psychophysiological complaints
- associated with daily intake of ~1000-1500 mg/day (increased risk starts at >500 mg/day!)
what are the criteria of caffeine intoxication?
- exceeding 250 mg
- 5+ Sx during/shortly after consumption of caffeine
what are the common signs/Sx of caffeine intoxication?
signs
- sweating
- muscle twitching
- tachycardia, arrhythmias
- seizures
Sx
- N/V/D
- restlessness, nervousness
- flushing
to classify as caffeine withdrawal, an individual requires ____ of 5 Sx; what are these Sx?
3+ of 5 Sx:
- HA
- marked fatigue or drowsiness
- altered mood (depressed, irritable, dysphoric)
- difficulty concentrating
- flu-like Sx (N/V, muscle pain/stiffness, etc.)
cannabis affects the ______________ system of NTs; what physiologic processes are regulated by this system?
endocannabinoid system
- appetite
- immune system regulation
- mood/anxiety
- sleep
- cognition
what are the 2 common active cannabinoid compounds? describe their effects
- THC: euphoric/psychoactive effects; downregulates the body's endogenous endocannabinoid system
- CBD: NO psychoactive effects
when do the effects of cannabis peak?
- smoking/vaping: 10 mins
- oral: 2 hours
what are the negative consequences associated with cannabis use?
more associated with synthetic cannabinoids (THC)!
- anxiety, agitation
- tachycardia, HTN
- tremors
- seizures
- hallucinations
- paranoia
- cannabis hyperemesis syndrome (repeated episodes of projectile vomiting due to high daily intake of THC for a chronic duration)
what are the common signs/Sx of cannabis withdrawal?
- anxiety
- dysphoria
- sleep changes
- irritability
- anorexia