Session 1: Introduction to Infection
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Microorganisms can be classified into...
- Bacteria
- Archae
- Fungi
- Helminths + parasites
- Protozoa
- Algae
Non-living pathogens
Viruses and prions
Bacteria are ___
Prokaryotes (no nucleus)
Are archaea prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic (no nucleus)
Eukaryotes contain what?
A nucleus
Three examples of eukaryotes
Fungi
Algae
Protozoa
Gram positive bacteria stain...
Blue/purple
Gram negative bacteria stain...
Pink/red
Why do Gram positive bacteria stain purple?
Thick layer of peptidoglycan retains the primary stain
Why don't Gram negative bacteria stain purple?
Thin layer of peptidoglycan does not retain the primary stain.
Can be counterstained pink/red.
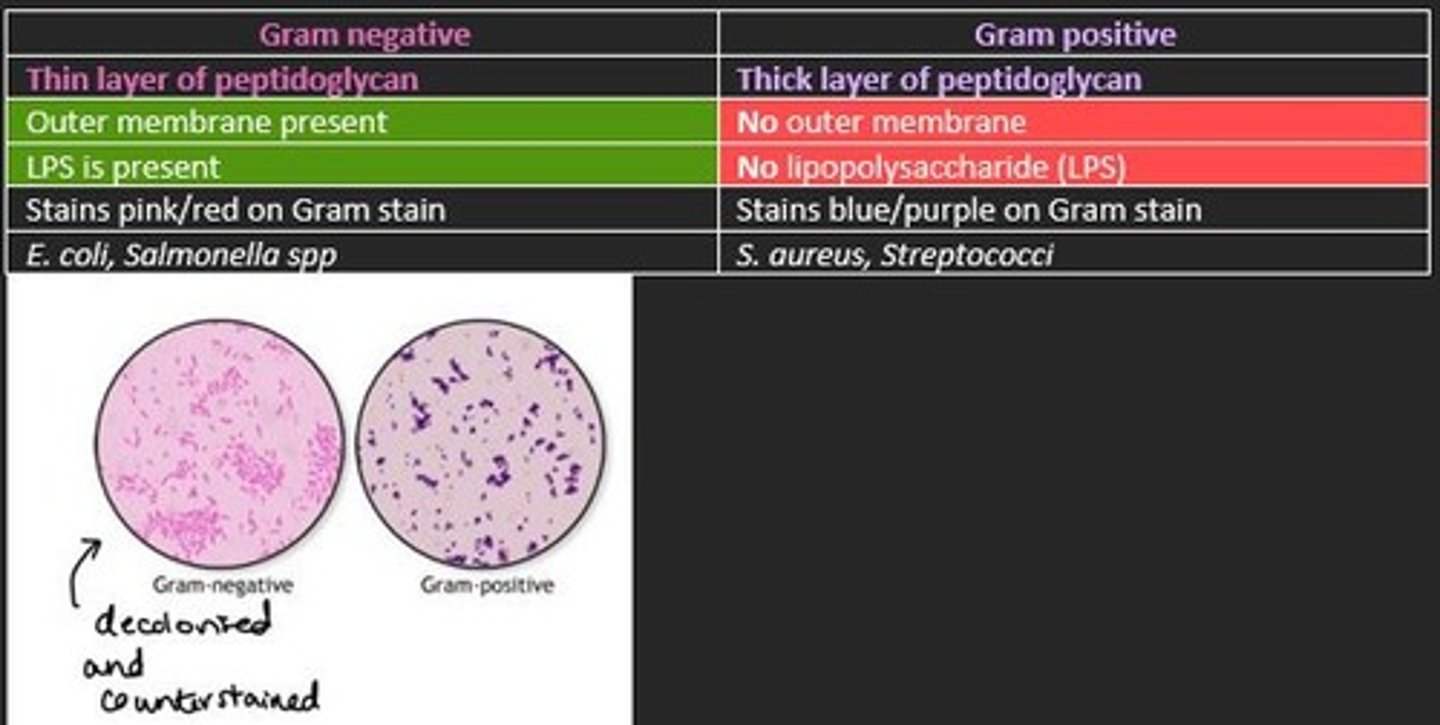
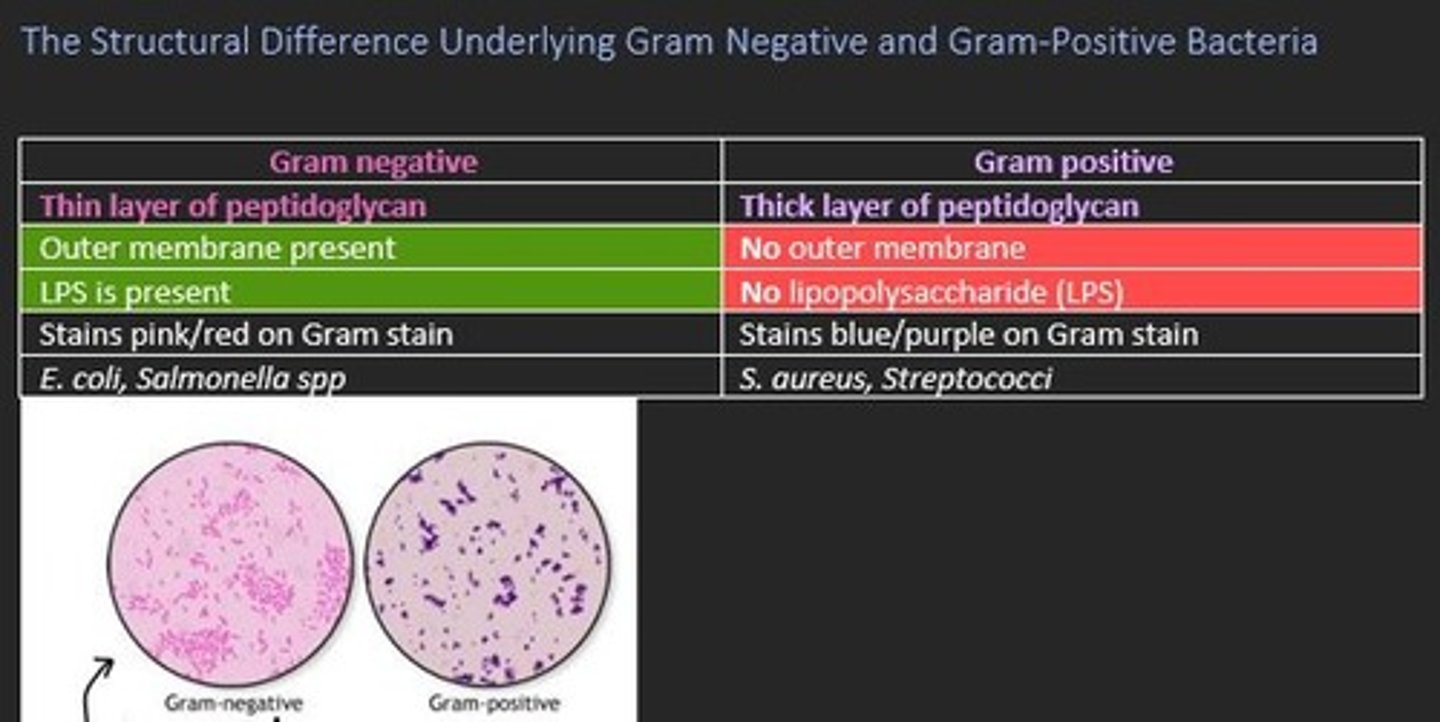
Some structural differences between Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria
Gram negative
- Thin layer of peptidoglycan = counterstains pink/red
- LPS present
- Outer membrane present
Gram positive
- Thick layer of peptidoglycan = stains purple
- No LPS
- No outer membrane
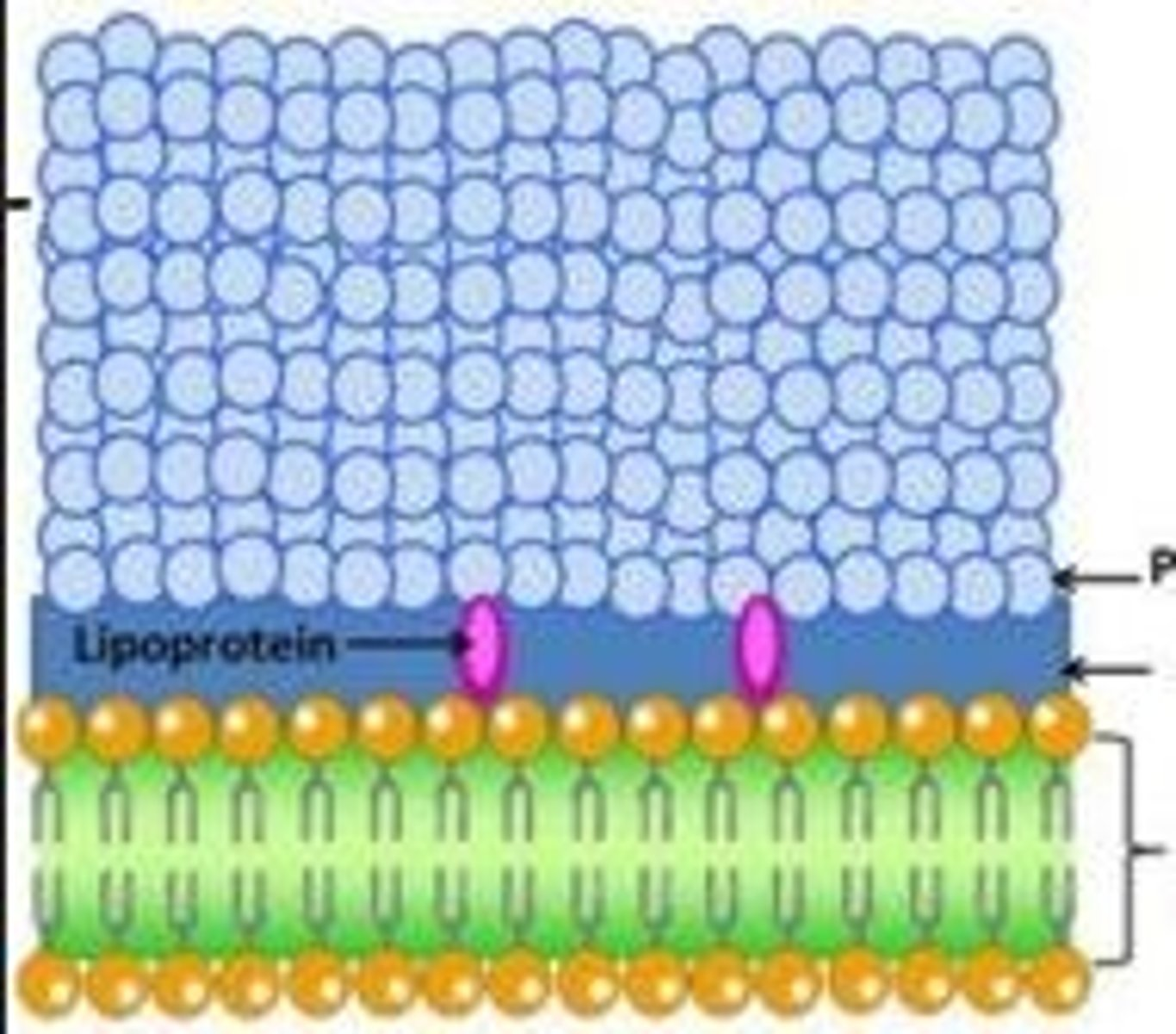
Is this Gram positive or Gram negative bacteria?
Thick peptidoglycan layer - Gram positive
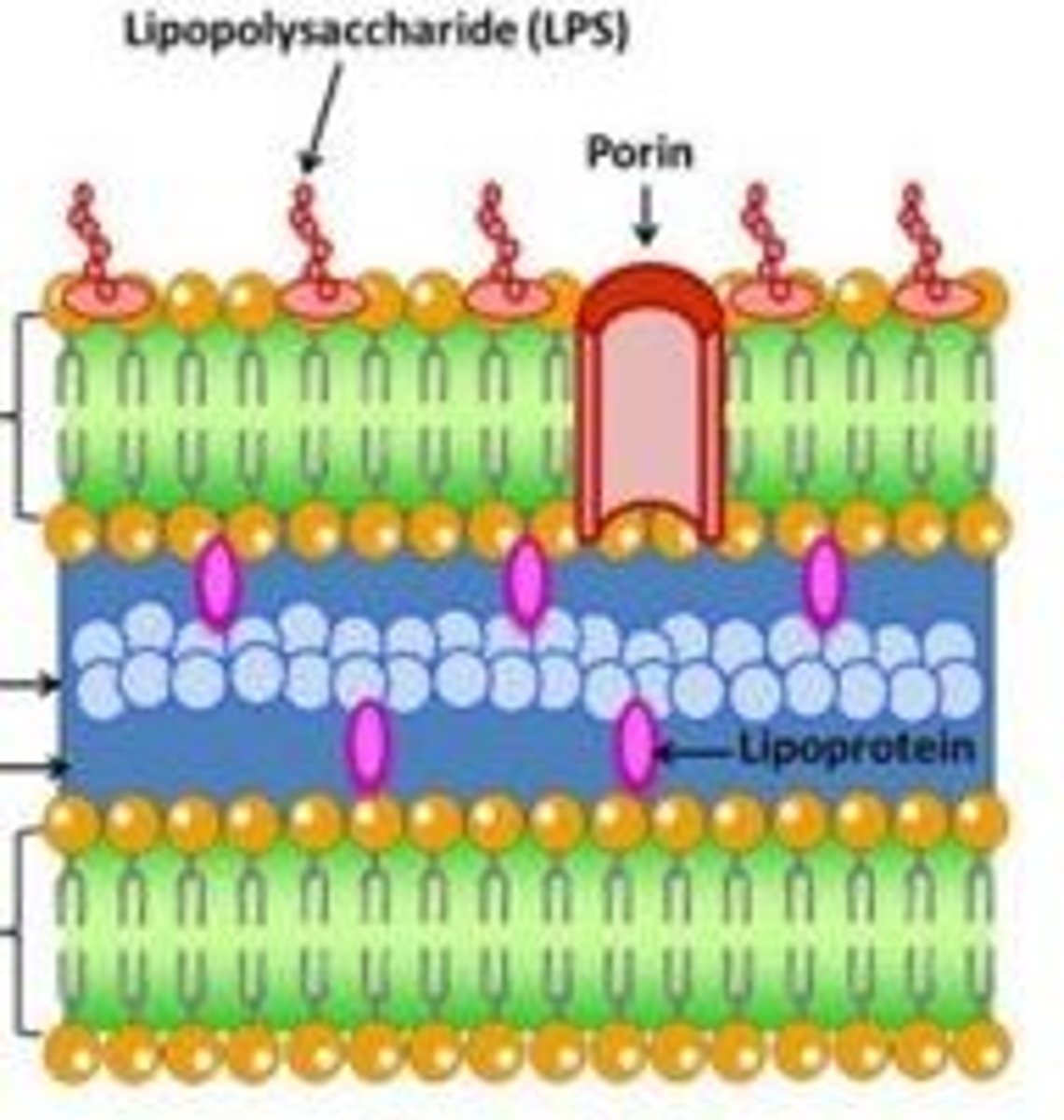
Is this Gram positive or Gram negative bacteria?
Thin peptidoglycan layer - Gram negative
LPS is present
Why is it important to know if bacteria causing an infection is Gram negative or Gram positive?
Different antibiotics used for different infections due to the structure of the peptidoglycan cell wall
This can confer sensitivity to specific antibiotics
Two examples of Gram negative bacteria
E.coli
Salmonella spp
Two examples of Gram positive bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococci
MRSA is an example of a Gram ___ bacteria
Positive
MRSA is treated with...
Vancomycin
Fungi are classified as...
Eukaryotes
Fungi are commonly associated with what specific types of infection?
Opportunistic infections in people who are immunocompromised or immunosuppressed
Examples of diseases caused by fungi
Athlete's foot
Ringworm
Pneumonia (think of CF - opportunistic)
Examples of some fungi
Candida albicans
Cryptococcus neoformans
Aspergillus fumigatus
What are helminths
Large multicellular eukaryotic organisms (worms) that can be free-living or parasitic
Examples of helminths
Tapeworm
Hookworm
Pinworm
Protozoa are classified as...
Eukaryotic, unicellular which can be free-living or parasitic
Examples of some diseases caused by protozoa
Malaria
Toxoplasmosis
Cryptosporidiosis
Trichomoniasis
Examples of some protozoa which cause disease
Plasmodium spp = Malaria
Toxoplasma gondii = Toxoplasmosis
Trichomonas vaginalis = Trichomoniasis
What are the five characteristics of a living organism?
1) One or more cells with DNA
2) Capable of reproducing, growing & developing
3) Capable of capturing & using energy/raw materials
4) Able to sense/respond to environment
5) Capable of evolving over generations
What is a prion
An infectious misfolded protein
Why are prions not considered as living infectious agents?
Prions do not contain any nucleic acids such as DNA/RNA so it is non-living
Example of disease caused by prion protein
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
Example of causes of acquired CJD (rare)?
Blood transfusions
Contaminated instruments in brain surgery
Infected tissue transplants
Can prion diseases be genetic?
Prion diseases can be sporadic, genetic or acquired
Describe structure of viruses
Acellular (non-living)
Contain short strands of genetic material (DNA/RNA)
Encapsulated with protein coat
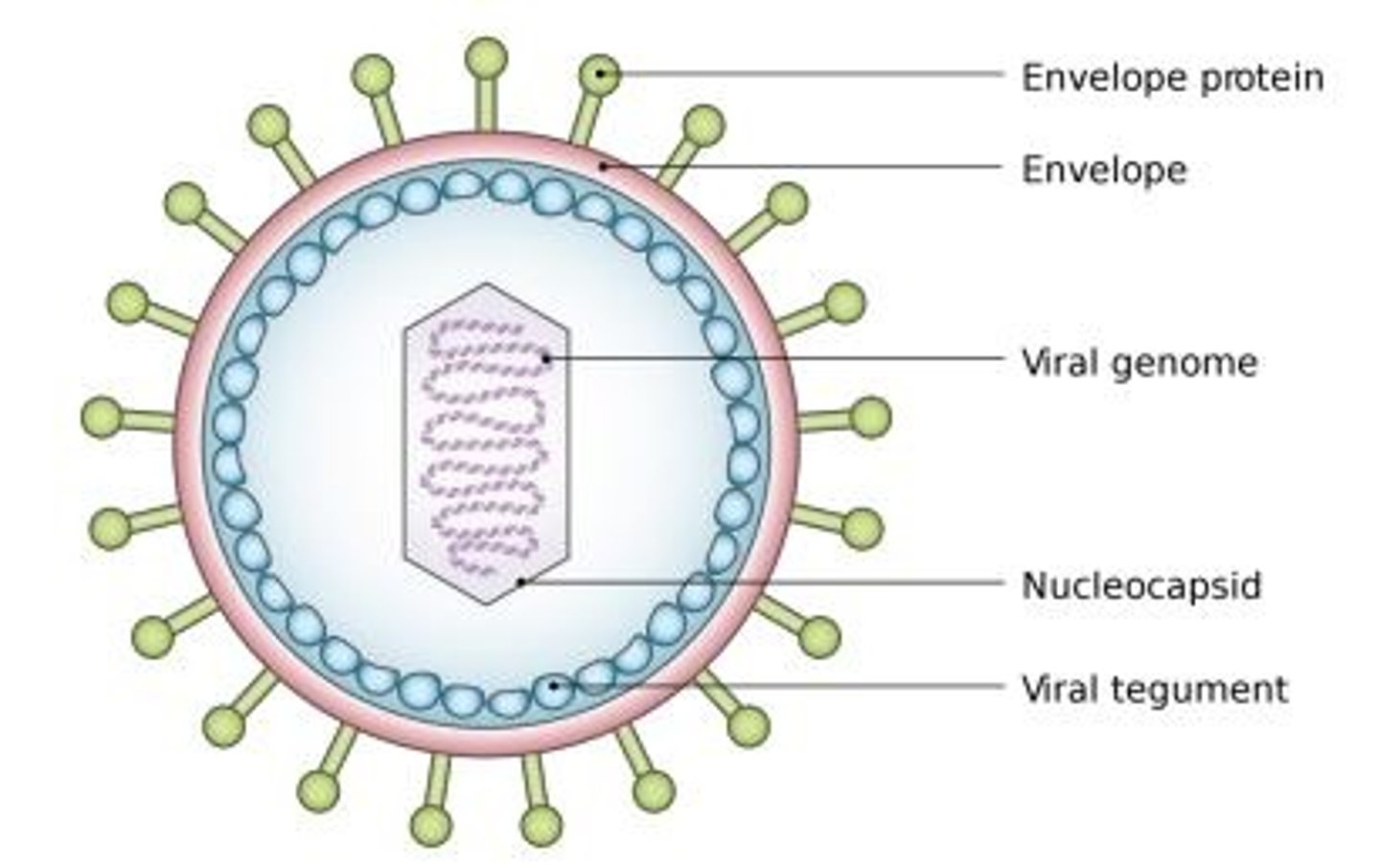
Why are viruses considered non-living?
They cant survive or reproduce on their own, and are not made of cells.
Two ways in which viruses are classified?
1) Baltimore classification = based on manner of m-RNA synthesis
2) Whether viral genome is DNA or RNA based
Give three examples of DNA viruses and the associated disease they cause
1) Herpes simplex virus = Cold sores, herpes
2) Varicella-Zoster virus = Chickenpox
3) Hepatitis B virus = Hepatitis
Give three examples of RNA viruses and the associated disease they cause
1) HIV virus = HIV, AIDS
2) Influenza virus = Influenza
3) Coronavirus = Covid-19, SARS, MERS
Name two eukaryotic infectious agents
Bacteria
Protozoa
What are the main differences between Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria?
Gram positive stain purple with crystal violet dye due to thick peptidoglycan wall.
Gram negative bacteria do not stain purple, but are counterstained red/pink (thin peptidoglycan wall).
Gram negative bacteria also have LPS present and have an outer membrane present, unlike gram positive which do not.
Give an example of Gram negative bacteria
E.coli
Salmonella spp
Name one disease caused by fungi
Athlete's foot
Explain why viruses aren't classed as living organisms
Viruses cannot reproduce without a host cell.
Viruses lack the machinery needed to carry out the functions of life. therefore, they are classified as non-living infectious agents and are not placed in the biological classification system.
Streptococcus bacteria are gram negative
True or false?
False
When classifying Escherichia coli using the hierarchic scale, Class, Order, Family, Genus or Species, which group is the coli assigned to?
Species
When considering relative sizes, which pathogen is the smallest?
Virus
What category of bacterial pathogen exploits the deficiencies of immunocompromised hosts to become pathogens?
Opportunistic
3 multiple choice options
When classifying microbes, to which group would you associate the term mycology?
Fungi
3 multiple choice options
Infectious agents can be classified as cellular or acellular.
An example of a acellular infectious agent may include...
Prion
3 multiple choice options
The majority of microbes which can cause human infection are found to have a cellular structure including organelles, however some infectious agents do not have organelles.
Which organism might this be?
Virus
3 multiple choice options