Diseases of nasal passages and paranasal sinuses
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
what nasal disorders do we see?
trauma - e.g. lacerations
facial nerve paresis / paralysis
nasal atheroma
alar fold collapse
what is the anatomy of the nares / nostrils?
alar folds - allows dilating of nostrils
supported by alar cartilages
input from facial nerve
nasal diverticulum
false nostril
what are clinical signs of facial nerve paresis / paralysis?
facial swelling
asymmetry
reduced airflow
nasal stertor
may get facial distortion
poor performance
how do we diagnose facial nerve paresis / paralysis?
observation
palpation

what side is the paralysis on?
right hand side of the image (horses left hand side)
drooping occurring on right side
when do we see facial nerve paresis / paralysis?
when under GA / recumbent - with pressure over facial nerve
iatrogenic - e.g. surgery of face
most often temporary and will resolve with time
what is needed for acute lacerations to the nares?
for full thickness defects - precise anatomical repair important to persevere ability to dilate fully
minimal debridement needed - good blood supply and want to preserve tissues
2 or 3 layer closure
monitor for rubbing of sutures
what is the significance of chronic scarring?
performance limiting - reduced nasal airflow
cosmesis may be important
reconstructive surgery possible
what are epidermal inclusion cysts?
cysts within nasal diverticulum (false nostril)
what are clinical signs of epidermal inclusion cysts?
no painful swelling at nasoincisive notch
how do we diagnose epidermal inclusion cysts?
history
visual appearance
histopathology
how do we treat epidermal inclusion cysts?
surgical removal - under local anaesthetic and standing sedation
formalin treatment - reported but risk of necrosis so not recommended
what is the prognosis for epidermal inclusion cysts?
excellent with surgical removal
likely to recur with simple drainage
what is alar fold collapse?
flaccid or redundant alar folds
what do we see with alar fold collapse?
respiratory tract noise at exercise
exercise intolerance in performance horses
how do we diagnose alar fold collapse?
fluttering sound during exercise (note - DDx = laryngeal / soft palate disorders)
temporary sutures - see if it makes a difference
how do we treat alar fold collapse?
can resect folds
what are key parts of nasal passage anatomy?
nasal septum and vomer bone separate nasal passages
dorsal and ventral conchae (terbinates)
thin scrolls of cartilage and bone
divide nasal passages into 3 meati - dorsal, middle and ventral
form conchal sinuses caudally
sinus drainage angle
narrow passageway where paranasal sinuses drain into nasal passages
usually 2-3mm diameter - cannot directly access paranasal sinuses in normal horse with endoscopy
ethmoidal turbinates
what are congenital disorders of nasal passages?
wry nose (nasal septum deviation)
choanal atresia (rare)
what are acquired disorders of the nasal passages?
trauma
progressive ethmoid haematoma
fungal rhinitis
foreign bodies (rare)
what are clinical signs of disease of nasal passages?
nasal discharge
abnormal respiratory noise
dyspnoea
malodorous smell
facial / nasal distortion
head shaking
snorting / rubbing nose
what can cause nasal trauma?
epistaxis
kick / blunt trauma
iatrogenic - trauma during nasogastric intubation / endoscopy (common)
how can we avoid iatrogenic trauma?
ensure tube placement is in the ventral meatus not middle
use a smooth tube
lubricant on end of tube
don’t force the tube when you meet resistance
what are progessive ethmoid haematomas?
(basically a blood clot)
encapsulated non-neoplastic mass
unknown aetiology
locally invasive - but don’t metastasise
grows into nasal passages / paranasal sinuses
what are clinical signs of progressive ethmoid haematomas?
epistaxis - usually intermittent, often slightly brown / red colour
may get facial swelling
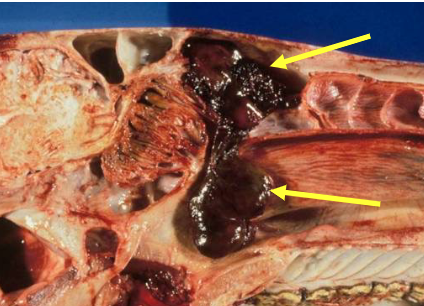
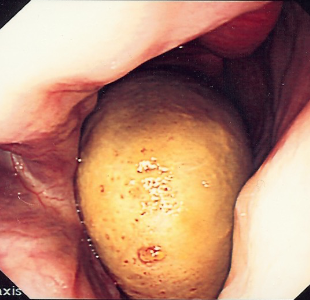
what do these images show?
progressive ethmoid haematoma
how do we diagnose nasal progressive ethmoid haematomas?
endoscopy - characteristic yellow / green lesion on ethmoid
can use computed tomography
how do we diagnose sinus progressive ethmoid haematomas?
radiography
sinoscopy
computed tomography - to assess cribriform plate
often bilateral so check both sides
how do we treat nasal progressive ethmoid haematomas?
intra-lesional formalin
need to CT first to assess the cribiform plate
multiple formaline injections
laser excision / ablation
can be done if it is small
can be done post formalin treatment
how do we treat sinus progressive ethmoid haematomas?
sinus flap surgery
treat sinusitis
remove lesions - can use laser
what is fungal rhinitis due to?
can be primary - but uncommon in UK
secondary - fungal disease secondary to bacterial sinusitis
what are clinical signs of fungal rhinitis?
unilateral purulent / haemorrhagic nasal discharge
malodorous smell
occasionally nasal stertor
how do we diagnose fungal rhinitis?
endoscopy
fungal culture
how do we treat fungal rhinitis?
removal of fungal plaques and necrotic bone
topical anti-fungal treatment - e.g. enilconazole lavage
what are the two groups of paranasal sinuses?
rostral group
caudal group
sinuses within each group share drainage into nasal passages
note - no communication between groups - separated by oblique bony septum
what sinuses are in the rostral group of paranasal sinuses?
rostral maxillary
ventral conchal
what sinuses are in the caudal group of paranasal sinuses?
caudal maxillary
frontal
dorsal conchal
sphenopalatine
ethmoid sinus
why is the proximity of nasal sinuses to other structures significant?
can cause disease in close structures - e.g. intrasinus PEH can extend into the brain
diseases may extend from these structures to the nasal sinuses - e.g. periapical regions of the teeth can lead to secondary sinusitis
what disease of the paranasal sinus do we see?
primary sinusitis
secondary sinusitis - due to fungal or periapical infection
sinus cysts
sinus PEH
neoplasia
trauma
what clinical signs are common for paranasal sinus diseases?
nasal discharge - usually unilateral
serous, purulent, mucopurulent or haemorrhagic
may get facial swelling, facial deformity or decreased nasal airflow
how do we diagnose paranasal sinus disease?
using history, clinical signs, physical examination, and external examination of the head - lymph nodes, facial symmetry, nasal airflow, percussion of sinuses
endoscopy
can see sinus drainage angle
radiography
laterolateral or dorsoventral
computed tomography
sinoscopy
when do we usually see primary sinusitis?
40% of cases are primary
occurs often with previous URT infection
most common cause - Streptococcus spp
when treating secondary sinusitis, what should we consider?
need to treat sinusitis and the primary cause, e.g:
dental disease
sinus cyst
PEH
neoplasia
fungal sinusitis
how would we diagnose sinusitis on endoscopy?
visualise purulent material coming from sinus drainage angle
how would we diagnose sinusitis by radiography?
fluid lines on lateral views
increases radiodensity in sinuses on dorsoventral views
(poor sensitivity for identifying cause of secondary sinusitis)
what are advantages of computed tomography for diagnosis of sinusitis?
allows differentiation of primary vs secondary sinusitis
has greater sensitivity when imaging the teeth
useful for pre-operative planning
how would we treat primary sinusitis?
antimicrobials - one course only (poor response indicates further investigation required)
do culture and sensitivity testing to rule out Strep. equi var equi infection (strangles)
NSAIDs - e.g. phenylbutazone
feed from ground to encourage drainage
dust free management - reduce YRT inflammation
turn out as much as possible - encourage drainage and reduce inflammation
surgical drainage may be required in cases that don’t respond to other treatments
how do we treat secondary sinusitis due to dental disease?
removal of infected tooth
management of sinusitis
how do we diagnose secondary sinusitis due to dental disease?
computed tomography gold standard
computed tomography is difficult to interpret
what are paranasal sinus cysts?
uncommon
seen in young horses most commonly
aetiology is unknown
cysts filled with yellow, viscous fluid
causes erosion and distortion as it expands
nasal passage deformity
facial swelling
what are clinical signs of paranasal sinus cysts?
how do we diagnose paranasal sinus cysts?
how do we treat paranasal sinus cysts?
what common types of sinus neoplasia do we see?
what are clinical signs of sinus neoplasia?
how do we diagnose sinus neoplasia?
how do we treat sinus neoplasia?
how do we diagnose sinus trauma?
how do we treat sinus trauma?
what are advantages of sinoscopy for nasal sinuses?
how do we perform sinus surgery - sinus flaps?
what are potential complications of sinus surgery?
what is empyaemia of conchal bullae?
chronic infection of dorsal or ventral conchal bulla
surgical techniques for drainage of bullae
what is suturitis?