AP Biology - Ch. 1-4
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
7 Characteristics of Life
Growth and development
Homeostasis
Heredity
Reproduce
Responds to stimuli
Metabolism
Cellular composition
GHHRRMC (Grimace)
Emergent Property
(N) properties that arise as a result of the combination and interactions of smaller parts that would not exhibit such properties individually
Biological Classification
Cells
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Organism
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biosphere
3 Domains of Life
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
Taxonomic Classification
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Dear King Phylum Calls Order For Grumpy Species
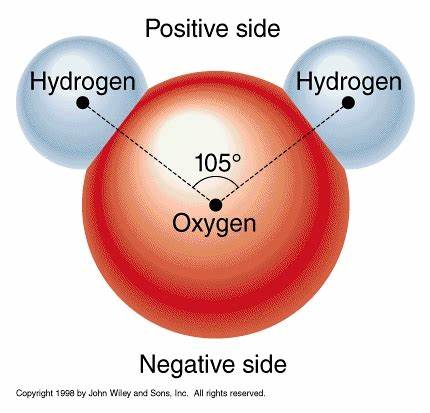
Polarity of H2O
Positive: 2H
Negative: O
Difference between Ionic, Covalent, and Hydrogen bonds
Ionic bonds occur when one atom transfers electrons to another atom. This bond occurs in large differences of electronegativity between atoms and is the strongest of bonds.
Covalent bonds occur when atoms share pairs of electrons. The strength of this bond varies.
Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces, or attractions, that occur between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom. This bond is the weakest of bonds.
Electronegativity
(N) an atom’s tendency to attract the electrons in a chemical bond to itself
Differentiate between Adhesion and Cohesion
Adhesion is the ability of water molecules to stick to other surfaces.
“Ad” means toward
Cohesion is the ability of water molecules to stick to each other
“Co" means together
Capillary Action
(N) slight upward movement of water in a narrow space
Meniscus
Differentiate between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic
Hydrophilic means to have a tendency to dissolve in water
Salt and sugar
Ionic and polar bonds
Hydrophobic means to repel water
Fats and oils
Non-ionic and non-polar bonds
Organic Chemistry
(N) the study of carbon compounds, which allow for a variety of structures to be built
# of valence electrons in:
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Carbon
1
2
3
4
HONC 📯📯📯
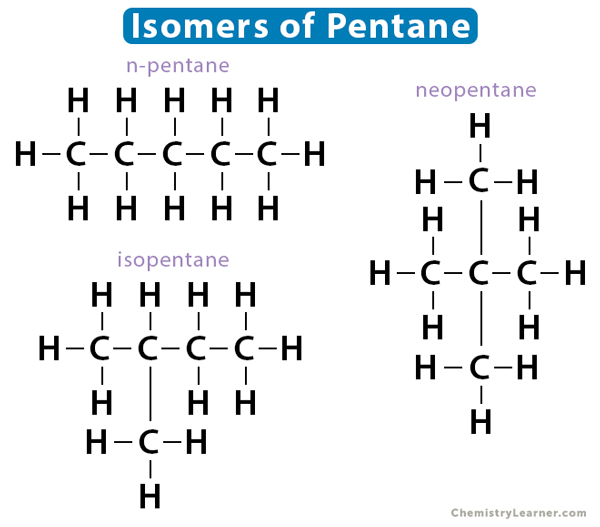
[Structural] Isomer
(N) compounds with identical chemical formulas but different chemical structures
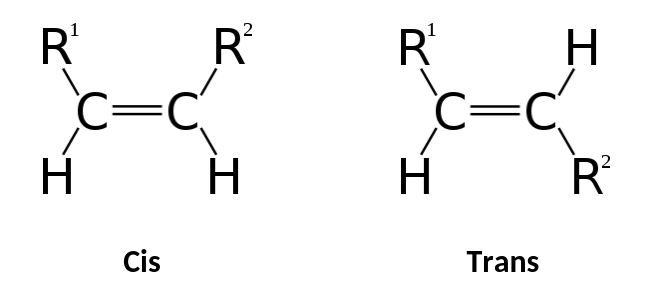
Geometric Isomer
(N) compounds with identical covalent partnerships differing in arrangements around a double bonded carbon
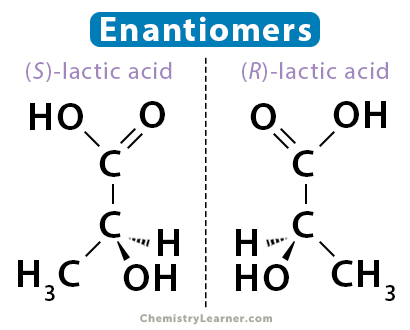
Enantiomers
(N) molecules that are mirror images
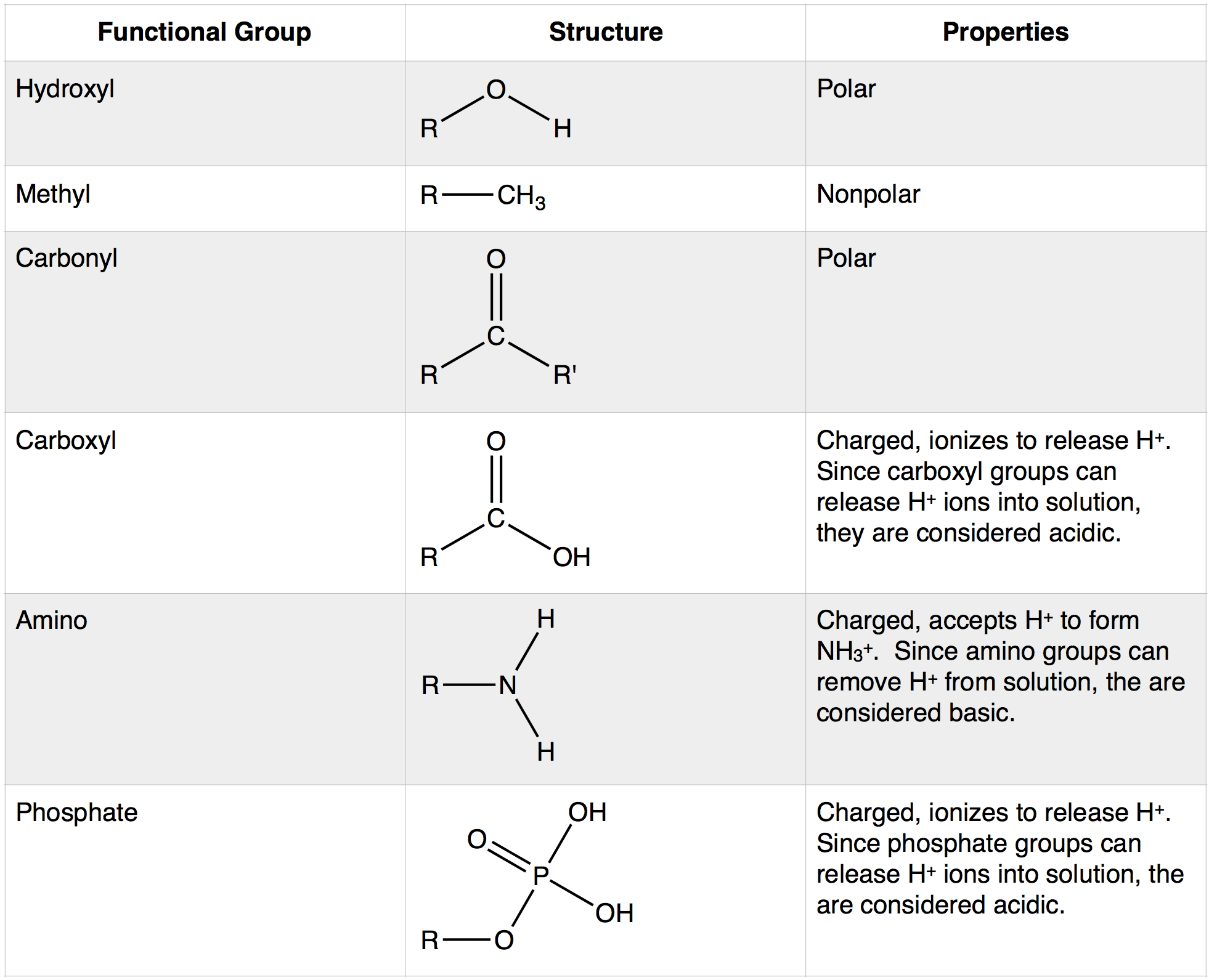
Functional Group
(N) specific group of atoms that's responsible for a molecule’s characteristics