Constituents of the atom & force interactions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is an Isotope?
An atom of an element that has the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons.
What is Specific Charge?
The ratio of a particles charge to its mass (CKg^-1)
Which constituents have the highest and lowest charge to mass ratio?
Highest - Electron
Lowest - Neutron
What is an Ion?
An atom that has become charged by losing or gaining an electron.
What forces act on the Nucleus?
Electromagnetic force, gravitational force and strong force.
What does the electromagnetic force cause?
Causes positively charged protons to repel eachother.
What does the gravitational force cause?
Causes all the nucleons in the nucleus to attract each other due to their mass.
What does the strong nuclear force cause?
Attractive force that holds the nucleus together (stronger than the electromagnetic force).
When is the strong force repulsive?
For very small separations (0.5 fm)
When is the strong force attractive?
Past 0.5fm and reaches max at 3fm.
What is the force carrier for the strong force and what does it act on?
Gluons
Quarks and gluons
What is the force carrier for the electromagnetic force and what does it act on?
Photons
Electrically charged particles
What is the force carrier for the weak force and what does it act on?
W+, W- and Z
Quarks and leptons
What is the force carrier for the gravitational force and what does it act on?
Gravitons
Particles with mass
What forces have an infinite range?
Gravitational and Electromagnetic forces.
What is the first thing you do when you see a feynman diagam?
Check which axis is time and space
What does a feynman diagram represent?
The particles interacting with each other by exchanging an exchange particles (different based on the force).
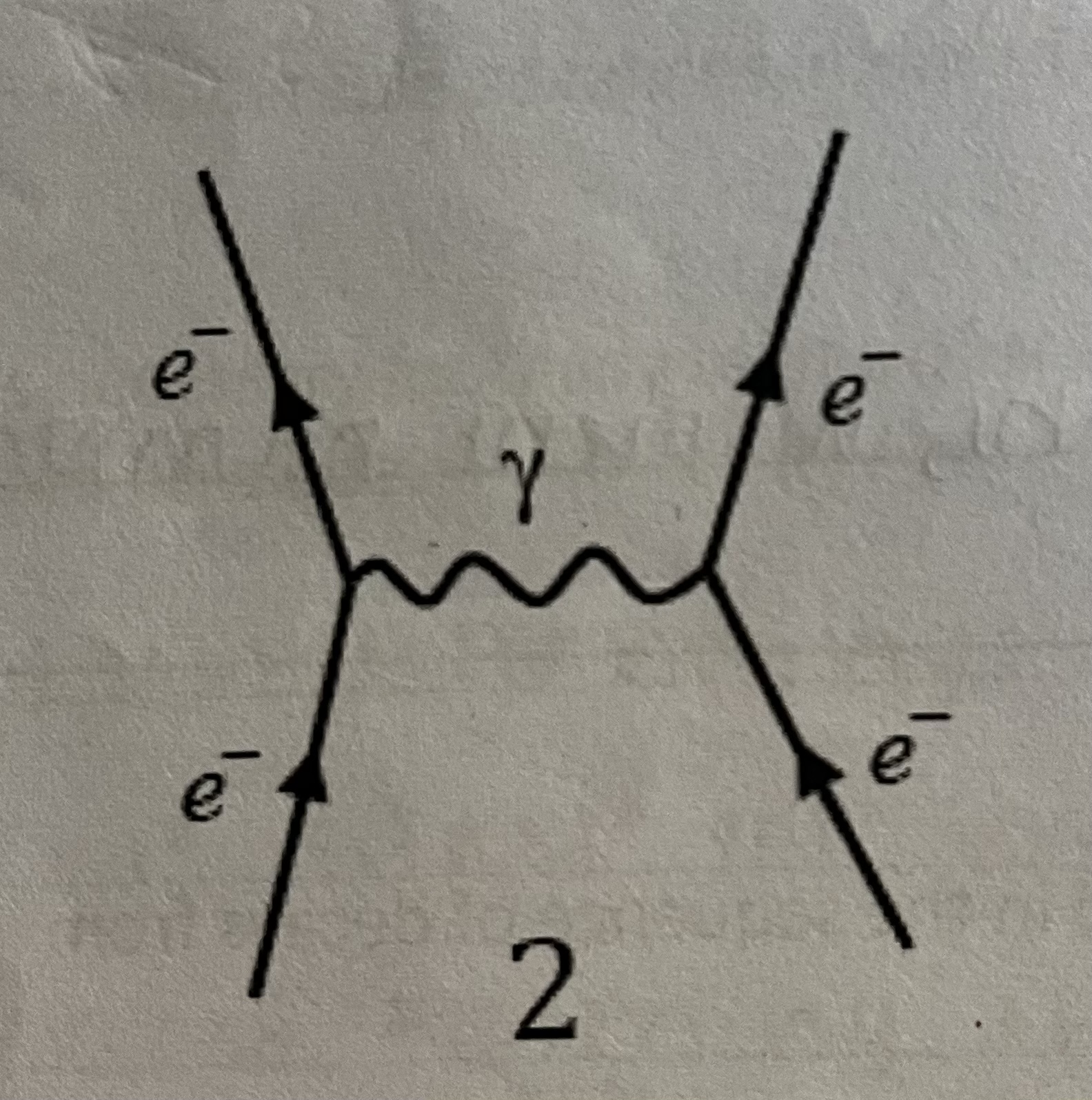
Feynman diagram for the electromagnetic interaction
-To electrons repel eachother by exchanging a virtual photon
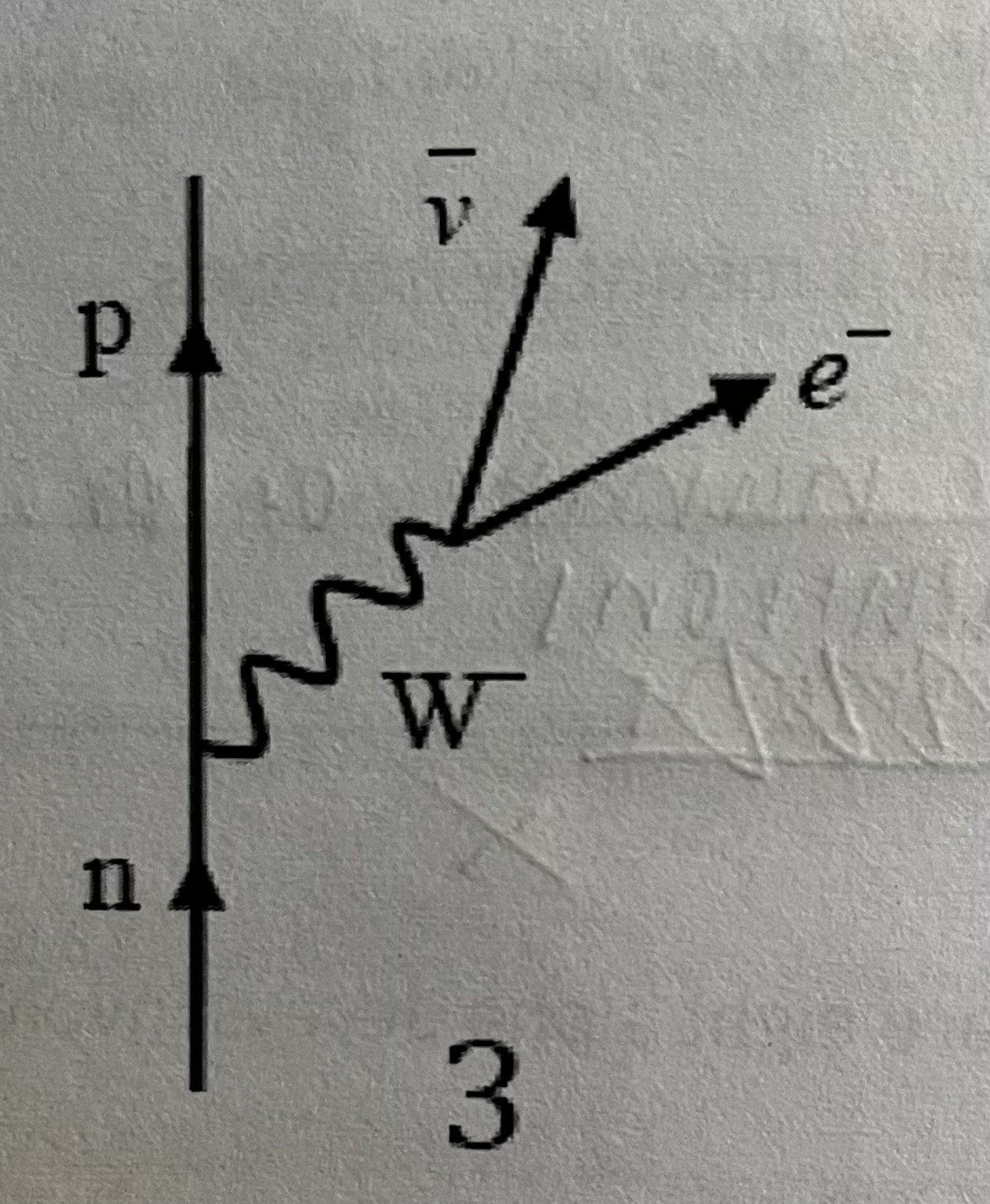
Feynman diagram for beta minus decay
-A neutron decays via the weak interaction into a proton, electron and antineutrino
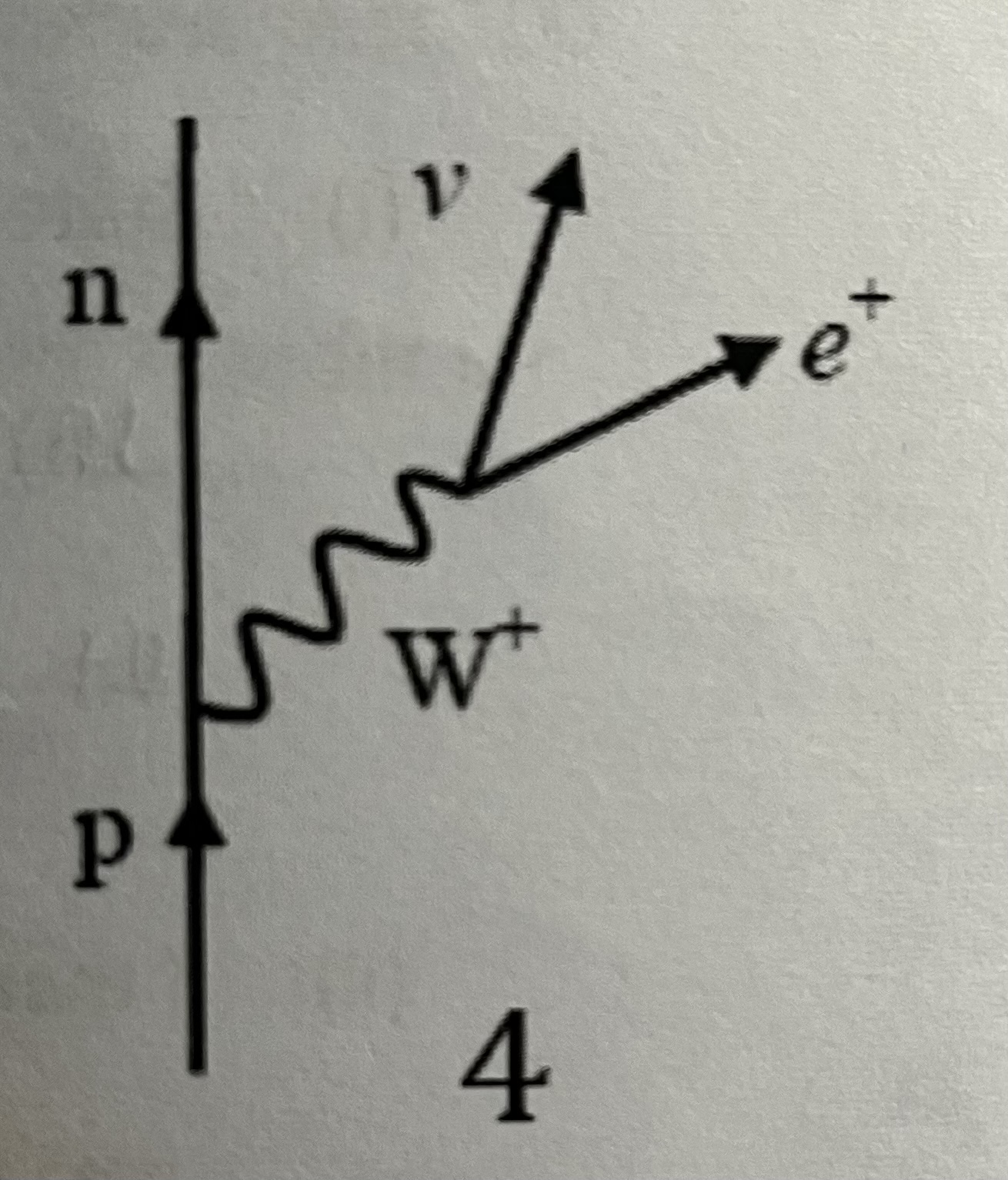
Feynman diagram for beta plus decay
-A proton decays via the weak interaction into a neutron, positron and electron neutrino.
Feynman diagram for electron capture
-A proton captures and electron and becomes a neutron and and electron neutrino
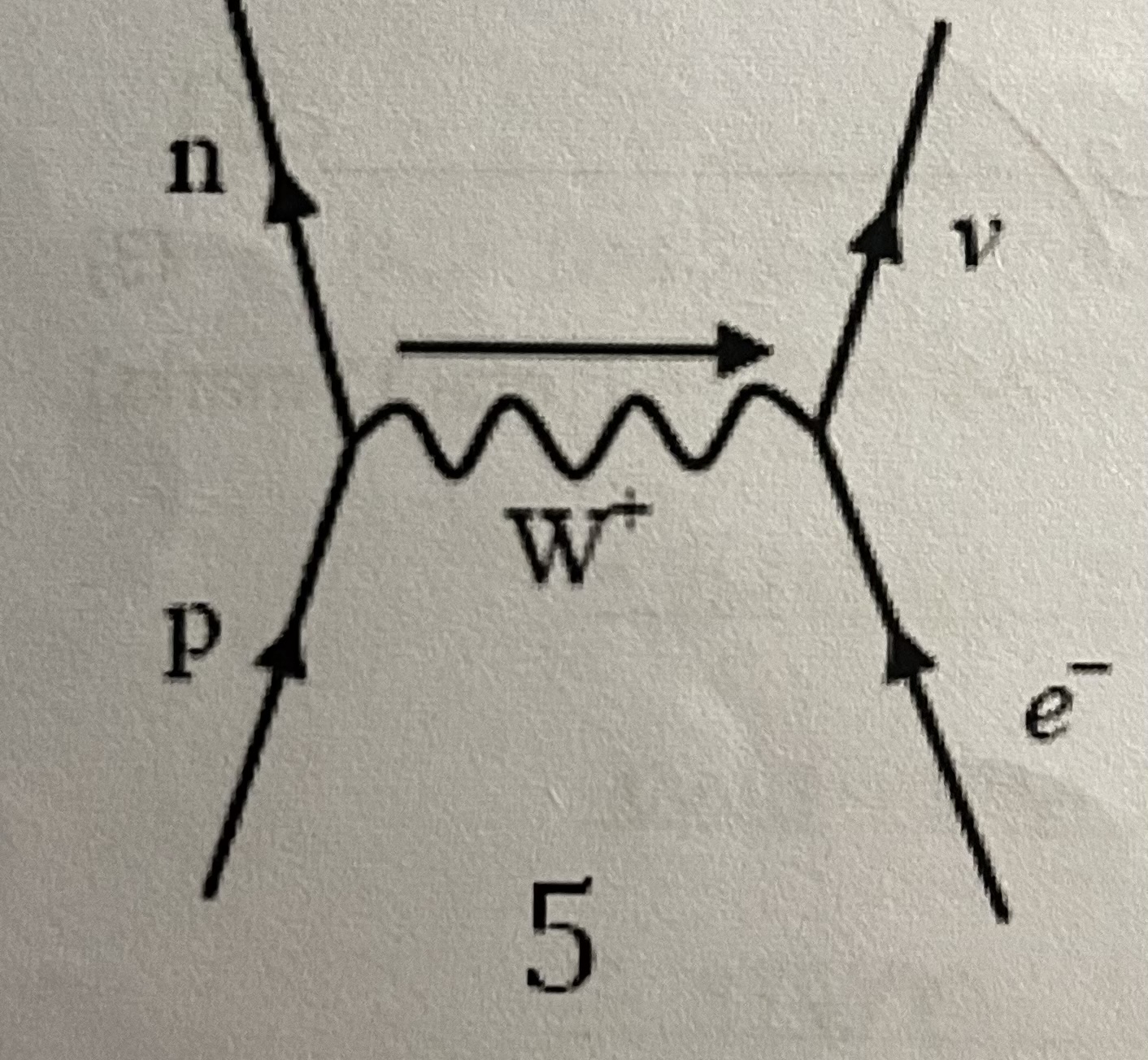
Feynman diagram for electron-proton collision
-Collide and emit a neutron and electron neutrino
