Basics of Fungi
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Taxonomy
the science of physical classification
Phylum
-mycota
Class
-mycetes
Order
-ales
Family
-acae
Genus/species
contain no word rules
Hyphae
Branching filaments
Septate
Hyphae that are divided into cells by internal walls
Ceonocitic/aspetate
contain no walls in hyphae and the nuclei flow freely
Mycelium
mass of hyphae that forms a network (vegatative body of fungus)
Cell Walls
rigid walls that provide support and protection, made of chitin
Plasma Membrane
Fungal membrane, similar to eukaryotes, but contains a different lipid of ergosterol, instead of cholesterol.
Osmotrophy
absorb soluble nutrition from surroundings
Decomposers
Fungi obtain nutrients from decomposing dead organic matter and recycling the nutrients back into the environment.
Sexual Reproduction
stages:
1a. Anastomosis
1. Plasmogamy
2. Karyogamy
3. Result in sexual spores
Anastomosis
Fusion of hyphae
Plasmogamy
Fusion of cytoplasm
Karyogamy
Fusion of nuclei
Parasites
Feed off the living hosts and cause disease
Mutualists
Form beneficial relationships for both the fungi and the host.
Nonmotile
can not move around
Dimorphic
They can exist in either unicellular or multicellular forms depending on the environment
Heterotrophic
Feeds on other organisms
Interphase
1. Growth Phase
2. DNA replication
3. Growth and Seperation for Division
Prophase
chromosomes condense around the centromere

Metaphase
chromosomes move to the middle
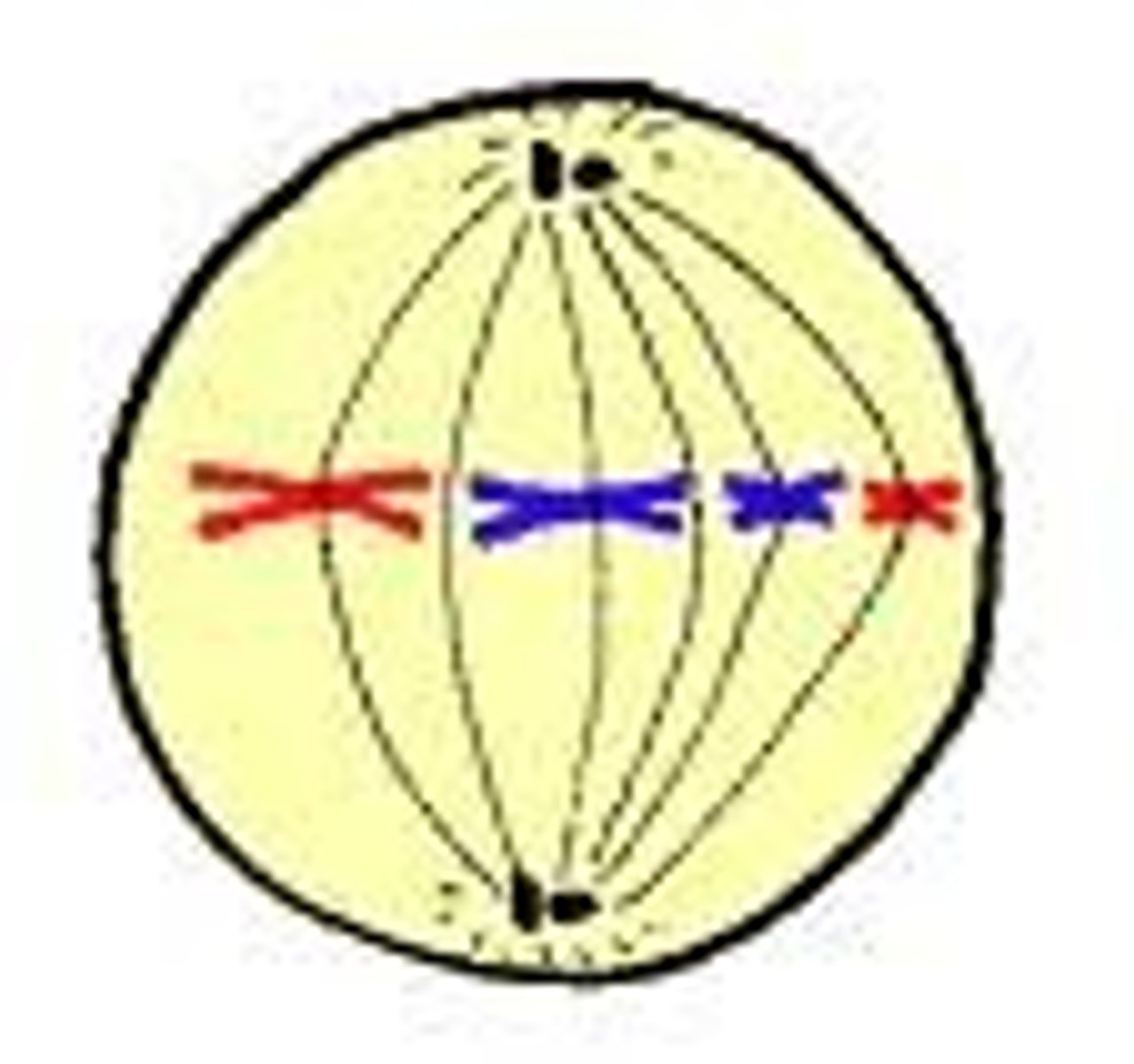
Anaphase
chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cells
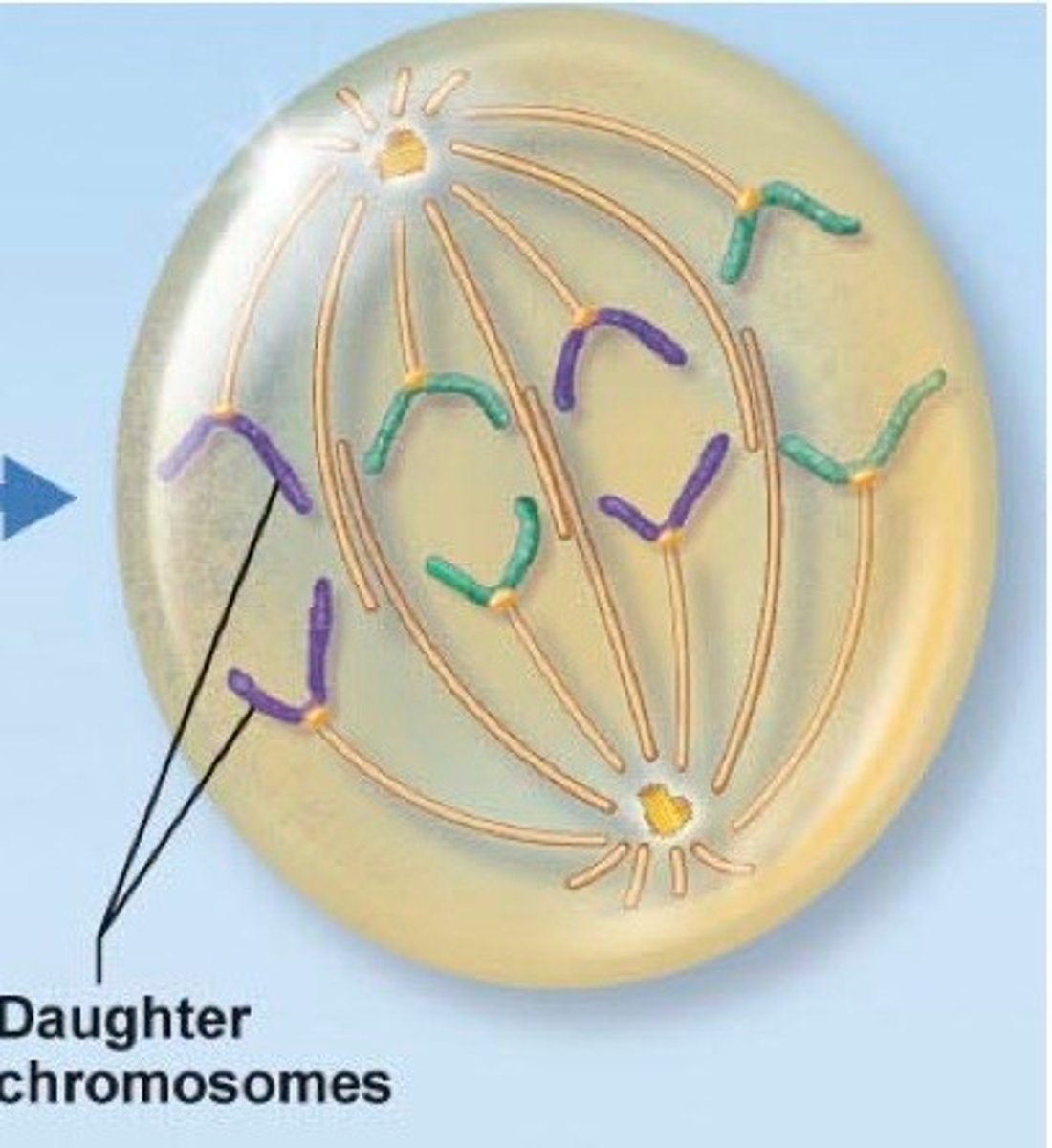
Telophase
Contractile creates a channel for duplicated nuclei to move over to the other septate
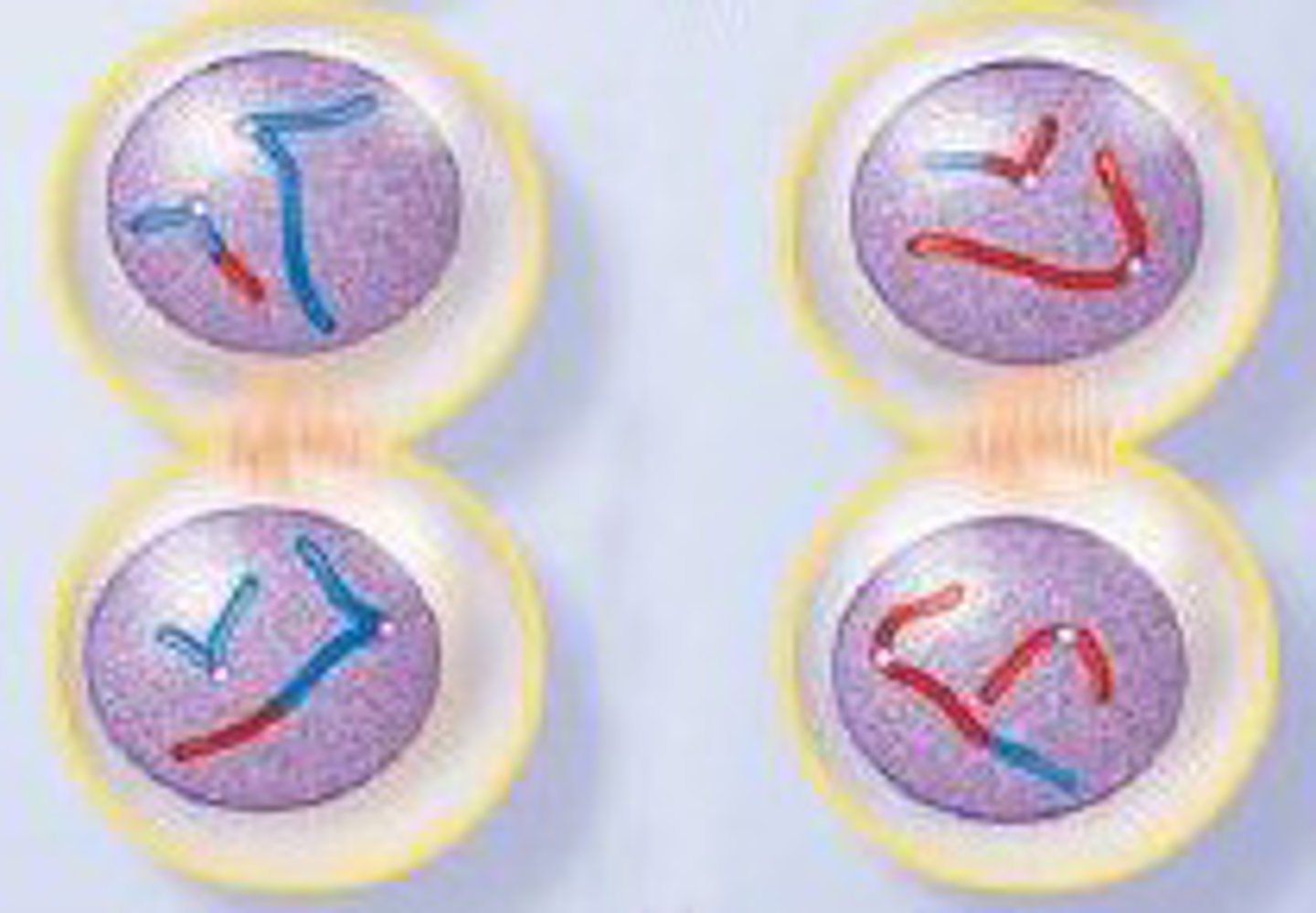
Cytokinesis
The 2 nuclei split into two different cells.
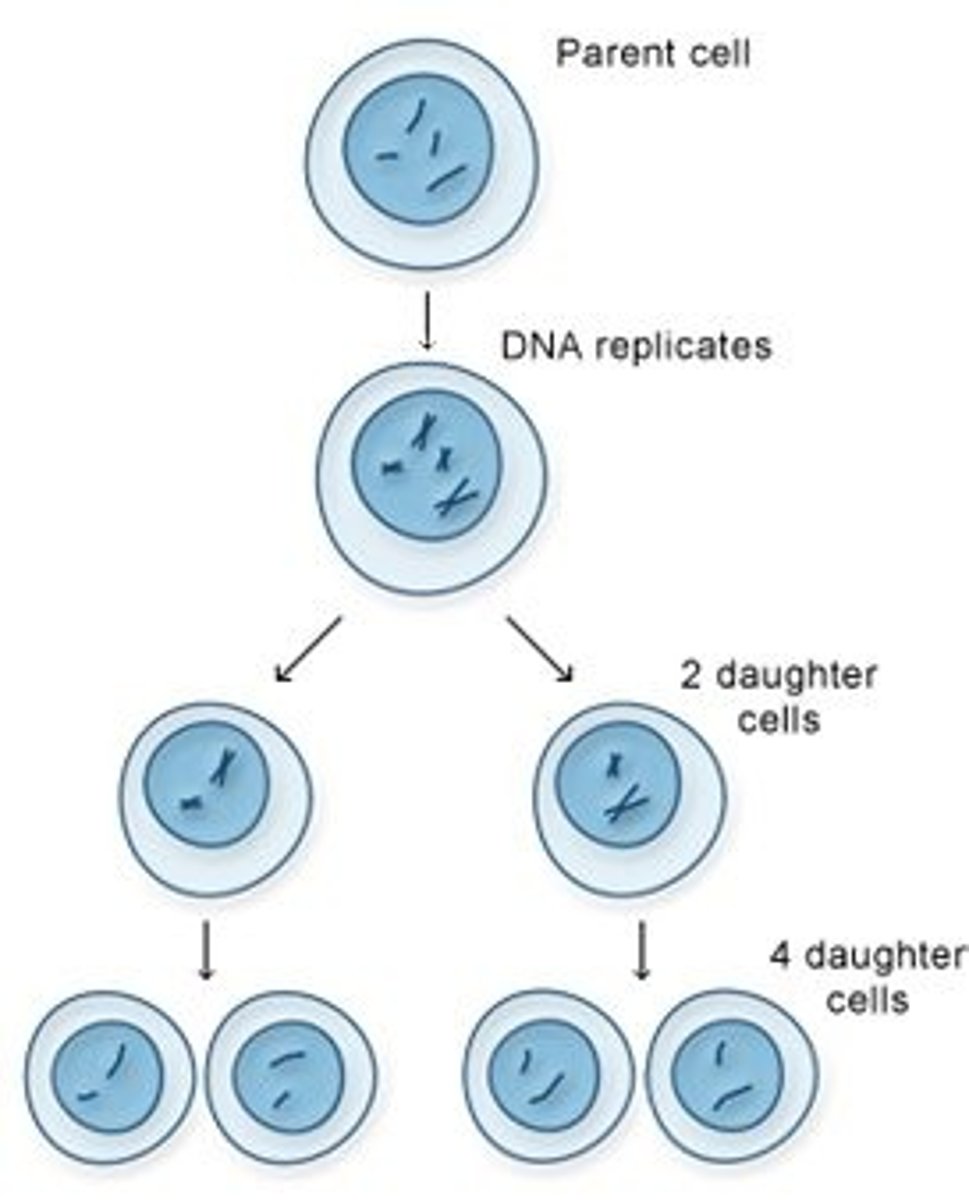
Mitosis
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
5. Cytokinesis
Meiosis
Enables recombinations, starts with a diploid cell and duplicates chromosomes, chromosomes find their homologous pairs and cross over.
Homologs
Same genes , different alleles
Meiosis 1
Pairs are separated into 2 different cells
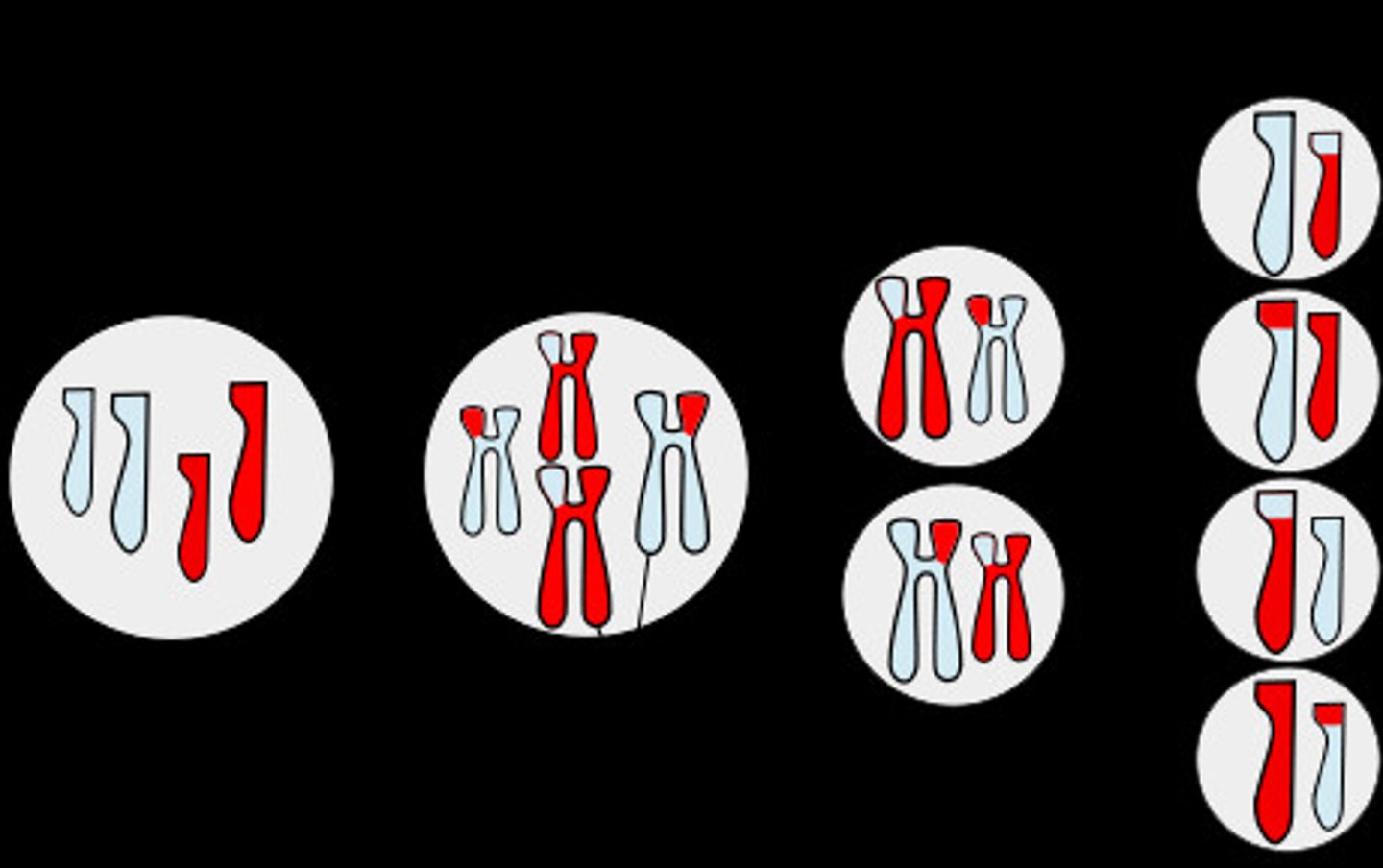
Meiosis 2
Same as mitosis
Heterokaryotic
Having genetically different nuclei
Asexual Reproduction
Fragmentation, budding, or producing asexual spored (conidia)