VMCB 122 - FINALS
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Bulbar conjunctival injections are used to treat which stage of Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis (IBK)?
a. Stage 1
b. Stage 2
c. Stage 3
d. Stage 4
Stage 2
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of Stage 4 IBK?
a. Epiphora
b. Corneal clouding
c. Uveal prolapse
d. Corneal ulceration
Uveal prolapse
The bacterium formerly known as Haemophilus parasuis has been reclassified to:
a. Pasteurella parasuis
b. Actinobacillus parasuis
c. Glaesserella parasuis
d. Streptococcus parasuis
Glaesserella parasuis
Which bacterial species is the causative agent of Glanders?
a. Pseudomonaspseudomallei
b. Burkholderia mallei
c. Pseudomonas mallei
d. Burkholderia pseudomallei
Burkholderia mallei
Campylobacter species require which of the following for optimal growth in culture?
a. Candle jar system
b. CO₂ incubator
c. Gas generation pack
d. Vacuum-sealed anaerobic jar
Gas generation pack
Which clinical presentation helps differentiate Haemophilus parasuis (Glaesserella parasuis) infection from E. coli infection in guinea pigs?
a. Fever
b. Anorexia
c. Depression
d. Fibrinopurulent meningitis
Fibrinopurulent meningitis
What type of lesions can Actinobacillus species cause in swine, particularly in chronic cases?
a. Necrotic lesions
b. Abscesses
c. Granulomatous lesions
d. Hemorrhagic lesions
Granulomatous lesions
Which virulence factor of Actinobacillus enables it to evade the host's immune response, particularly within the lymphatic system?
a. RTX toxins
b. Pili
c. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
d. Antiphagocytic capsule
Antiphagocytic capsule
What microscopic finding is NOT associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae?
a. Fibrinous exudate
b. Necrotic debris
c. Neutrophils
d. Asteroid bodies
Asteroid bodies
Which characteristic enables Pasteurella species to thrive in the lungs?
a. They are obligate aerobes
b. They are obligate anaerobes
c. They are facultative anaerobes
d. They produce endospores
They are facultative anaerobes
Which bacterial genus exhibits satellitism with Actinobacillus species on blood agar?
a. Streptococcus
b. Enterococcus
c. Staphylococcus
d. Corynebacterium
Staphylococcus
Which bacterial species is frequently involved in atrophic rhinitis co-infection with Pasteurella multocida?
a. Haemophilus influenzae
b. Mannheimia haemolytica
c. Bordetella bronchiseptica
d. Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
Bordetella bronchiseptica
Which type of bacteria can act as both a primary and secondary agent in respiratory infections?
a. Streptococcus
b. Mycoplasma
c. Bordetella
d. Pasteurella
Bordetella
Which of the following bacterial genera is commonly a commensal in the respiratory tract of animals?
a. Mycoplasma
b. Pasteurella
c. Bordetella
d. Actinobacillus
Bordetella
Bordetella bronchiseptica is a key agent in which canine respiratory disease?
a. Canine Distemper
b. Canine Infectious Hepatitis
c. Kennel Cough
d. Canine Parainfluenza
Kennel Cough
Pasteurella multocida is a significant cause of which disease in cattle?
a. Haemorrhagic septicaemia
b. Blackleg
c. Mastitis
d. Foot Rot
Haemorrhagic septicaemia
In which year was Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale (ORT) discovered?
a. 1990
b. 2002
c. 1991
d. 2010
1991
Which anatomical structure is primarily affected by ORT in poultry?
a. Trachea
b. Lungs
c. Bronchi
d. Air sacs
Air sacs
What is the term for the specialized flagella found in Leptospira species?
a. Polar flagella
b. Peritrichous flagella
c. Lophotrichous flagella
d. Axial filaments
Axial filaments
Which cellular feature enables Moraxella bovis to attach to the corneal epithelium?
a. Fimbriae
b. Type 4 pili
c. Capsule
d. Lipopolysaccharide
Type 4 pili
Which family do Leptospira species belong to?
a. Leptospiraceae
b. Spirochaetaceae
c. Brachyspiraceae
d. Borreliaceae
Spirochaetaceae
Leptospira serovars manilae and losbanos belong to which species?
a. Leptospira biflexa
b. Leptospira interrogans
c. Leptospira nobukawae
d. Leptospira borgpetersenii
Leptospira interrogans
Which Leptospira species contains pathogenic and parasitic serovars?
a. Leptospira biflexa
b. Leptospira interrogans
c. Leptospira weilii
d. Leptospira kirschneri
Leptospira interrogans
Which of the following control measures is effective in eliminating the asymptomatic carrier state of Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis in bulls?
a. Antibiotic treatment
b. Vaccination
c. Bacterins
d. Isolation and culling
Bacterins
Why is the proliferation of Leptospira in the kidneys advantageous for bacterial transmission?
a. It allows the bacteria to evade the host immune response
b. It causes chronic kidney disease, weakening the host
c. It facilitates shedding of the bacteria in urine
d. It provides a stable environment for bacterial growth
It facilitates shedding of the bacteria in urine
Which pathogen causes Proliferative ileitis in pigs?
a. Brachyspira hyodysenteriae
b. Lawsonia intracellularis
c. Salmonella enterica
d. Escherichia coli
Lawsonia intracellularis
Which age group of pigs is most susceptible to Proliferative ileitis?
a. Suckling piglets
b. Weaned pigs
c. Grower pigs
d. Finisher pigs
Weaned pigs
Which specific disease in poultry is caused by Pasteurella multocida?
a. Infectious Coryza
b. Fowl Cholera
c. Avian Mycoplasmosis
d. Newcastle Disease
Fowl Cholera
Which bacterial species is a common cause of rat-bite fever?
a. Spirillum volutans
b. Streptobacillus moniliformis
c. Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae
d. Bartonella henselae
Streptobacillus moniliformis
Which bacterium produces a pigment that gives colonies a characteristic blue-green colour on agar plates?
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Staphylococcus aureus
c. Escherichia coli
d. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Which toxin produced by Bordetella bronchiseptica contributes to tissue damage?
a. Tracheal cytotoxin
b. Dermonecrotic toxin
c. Adenylate cyclase toxin
d. Pertussis toxin
Dermonecrotic toxin
Which virulence factor of Campylobacter jejuni is responsible for causing diarrhoea?
a. Cytolethal Distending Toxin (CDT)
b. Enterotoxin
c. Lipopolysaccharide
d. Flagella
Enterotoxin
Which clinical sign is NOT typically associated with Riemerella anatipestifer infection in ducks?
a. Diarrhoea
b. Ataxia
c. Respiratory signs
d. Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic feature of Campylobacter species?
a. S-shaped morphology
b. Gram-negative staining
c. Asymptomatic carriage in all hosts
d. Motility via polar flagella
Asymptomatic carriage in all hosts
Which statement regarding Taylorella equigenitalis is incorrect?
a. It causes contagious equine metritis (CEM)
b. It can lead to temporary infertility in mares
c. Sexual transmission is unclear
d. Stallions can be asymptomatic carriers
Sexual transmission is unclear
Which bacterial species is responsible for placentitis, abortion, and metritis in cattle?
a. Campylobacter jejuni
b. Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus
c. Brucella abortus
d. Chlamydia abortus
Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus
Which of the following antibiotics is used against mycoplasma?
a. Macrolides
b. Penicillin
c. Ampicillin
d. Bacitracin
Macrolides
Which of the following is NOT caused by organisms in the order Rickettsiales?
a. Avian Chlamydiosis
b. Rocky Mountain spotted fever
c. Potomac horse fever
d. Canine monocytic ehrlichiosis
Avian Chlamydiosis
Which of the following is the smallest prokaryote, lacks a cell wall, and is ubiquitous in nature?
a. Mycoplasma
b. Mycobacterium
c. Rickettsia
d. Chlamydia
Mycoplasma
Which of the following Chlamydia spp. is not prominent to humans?
a. C. trachomatis
b. C. pneumoniae
c. C. psittaci
d. C. abortus
C. abortus
Which of the following is associated with Johne's disease?
a. Respiratory distress
b. Diarrhea and weight loss
c. Sudden death
d. Lameness and joint swelling
Diarrhea and weight loss
Which of the following is not paired correctly?
a. Fumonisin - Porcine edema
b. Tetracycline (TCN) - Equine leukoencephalitis
c. Ochratoxin - Nephropathy
d. Mycotoxin (MS) - Liver toxicity
Tetracycline (TCN) - Equine leukoencephalitis
Which of the following causes nerve damage and skin lesions?
a. M. leprae
b. M. lepraemurium
c. M. tuberculosis
d. M. bovis
M. leprae
Who is primarily affected by Trichophyton verrucosum?
a. Cattle
b. Sheep
c. Goats
d. Horses
Cattle
Which causes Potomac Fever?
a. Rickettsia rickettsii
b. Neorickettsia risticii
c. Neorickettsia helminthoeca
d. Anaplasma marginale
Neorickettsia risticii
Which type of dermatophyte growth occurs on the external hair shaft?
a. Ectothrix
b. Endothrix
c. Favus
d. Tinea
Ectothrix
Which dermatophyte is associated with fluorescence under a Wood's lamp?
a. Microsporum
b. Trichophyton
c. Epidermophyton
d. Candida
Microsporum
Which of the following statements is true?
a. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are always pathogenic to humans
b. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are sometimes called typical mycobacteria
c. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) cause tuberculosis in humans
d. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are found only in soil
Non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are sometimes called typical mycobacteria
Which of the following organisms affect cats?
a. Mycoplasma canis
b. Ehrlichia ewingii
c. Anaplasma phagocytophilum
d. Babesia canis
Mycoplasma canis
Which of the following is not a dimorphic fungi?
a. Pythium insidiosum
b. Sporothrix schenckii
c. Candida albicans
d. Blastomyces dermatitidis
Pythium insidiosum
Which organism is the cause of pseudoglanders?
a. Histoplasma capsulatum var. farciminosum
b. Burkholderia mallei
c. Brucella melitensis
d. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Histoplasma capsulatum var. farciminosum
Which of the following is the main cause of human dermatophytes?
a. Zoophilic
b. Geophilic
c. Anthropophilic
d. Microsporotic
Anthropophilic
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched?
a. Aflatoxins - Aflatoxicosis
b. Zearalenone - Oestrogenism
c. Trichothecenes - Trichothecene Toxicosis
d. Ochratoxin - Neurotoxin
Ochratoxin - Neurotoxin
Which of the following is not part of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex?
a. M. africanum
b. M. canetti
c. M. avium
d. M. bovis
M. avium
Rickettsia species typically infect which host cell?
a. RBC
b. Vascular endothelial cells
c. Monocytes and macrophage
d. Granulocytes
Vascular endothelial cells
Which of the following is not true about Aflatoxin?
a. It is known to be toxic, carcinogenic, teratogenic, and mutagenic
b. Primarily affects the reproductive system
c. It is produced by Aspergillus spp.
d. There are 4 types of Aflatoxin - B1 is the most toxic
Primarily affects the reproductive system
Which of the following is a true statement?
a. Yeast grows best at 37°C, while mold grows best at 30°C.
b. Asexual reproduction includes karyogamy and meiosis.
c. Yeast forms pseudohyphae, which are elongated chains of yeast cells that fail to separate after budding.
d. Candida albicans has vegetative septate hyphae
Yeast forms pseudohyphae, which are elongated chains of yeast cells that fail to separate after budding.
Which of the following are methods for detecting Mycobacterium?
a. Tuberculin Skin Test (Mantoux)
b. PCR
c. Direct visualization
d. A and B
A and B
Which of the following is true for Chlamydia?
a. Tetracycline
b. Cytotoxins
c. Griseofulvin
d. Beta-lactams
Tetracycline
What disease is caused by Claviceps purpurea?
a. Ergotism
b. Aspergillosis
c. Tinea corporis
d. Candida infections
Ergotism
Griseofulvin inhibits the assembly of which structure?
a. Microtubules
b. Cell wall synthesis
c. DNA replication
d. Protein synthesis
Microtubules
What is the type of infection associated with chronic localized infection of skin and subcutaneous tissue following traumatic implantation?
a. Systemic mycoses
b. Superficial mycoses
c. Subcutaneous mycoses
d. Opportunistic mycoses
Subcutaneous mycoses
Which of the following statements is true?
a. There is a strong correlation between age and disease.
b. Ehrlichia canis primarily affects dogs.
c. Anaplasma marginale is the more pathogenic strain.
d. None of the above.
Ehrlichia canis primarily affects dogs.
Which mycotoxin is associated with estrogenic effects, leading to vulvovaginitis and precocious mammary development in prepubertal gilts?
a. Fumonisin
b. F1 toxin
c. F2 toxin
d. Aflatoxin
F2 toxin
Which fungi have a clear capsule visible under the microscope?
a. Cryptococcus neoformans
b. Candida albicans
c. Coccidioides immitis
d. Sporothrix schenckii
Cryptococcus neoformans
Which of the following organisms is an opportunistic pathogen that is part of the normal flora of animals but can cause infections such as otitis externa and seborrheic dermatitis?
a. Aspergillus fumigatus
b. Sporothrix schenckii
c. Malassezia pachydermatis
d. Microsporum canis
Malassezia pachydermatis
Which of the following is true about Malassezia pachydermatis?
a. It thrives in a lipid-rich environment.
b. It is commonly found in households with dogs and cats.
c. It causes systemic infections in healthy pets.
d. It is primarily a zoonotic pathogen.
It thrives in a lipid-rich environment.
How is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever transmitted in dogs that have been infected and moved to the Philippines?
a. Direct contact
b. Airborne transmission
c. Ticks
d. Rodents
Rodents
How could a dog from another country acquire Rickettsia?
a. Direct contact with infected animals
b. Airborne transmission
c. Tick bite
d. Ingestion of contaminated food
Tick bite
What is the required incubation period for a tuberculin sensitivity test?
a. 24 hours
b. 48-72 hours
c. 96 hours
d. 1 week
48-72 hours
Which of the following is a recommended management strategy for suspected fungal toxicity?
a. Stop feeding the suspected contaminated feed.
b. Replace the suspected contaminated feed with good-quality feed.
c. Dilute remaining contaminated feed with good-quality feed.
d. All of the above.
All of the above.
Which of the following is a correct type of asexual spore?
a. Conidia
b. Chlamydospores
c. Sporangiospores
d. Arthrospores
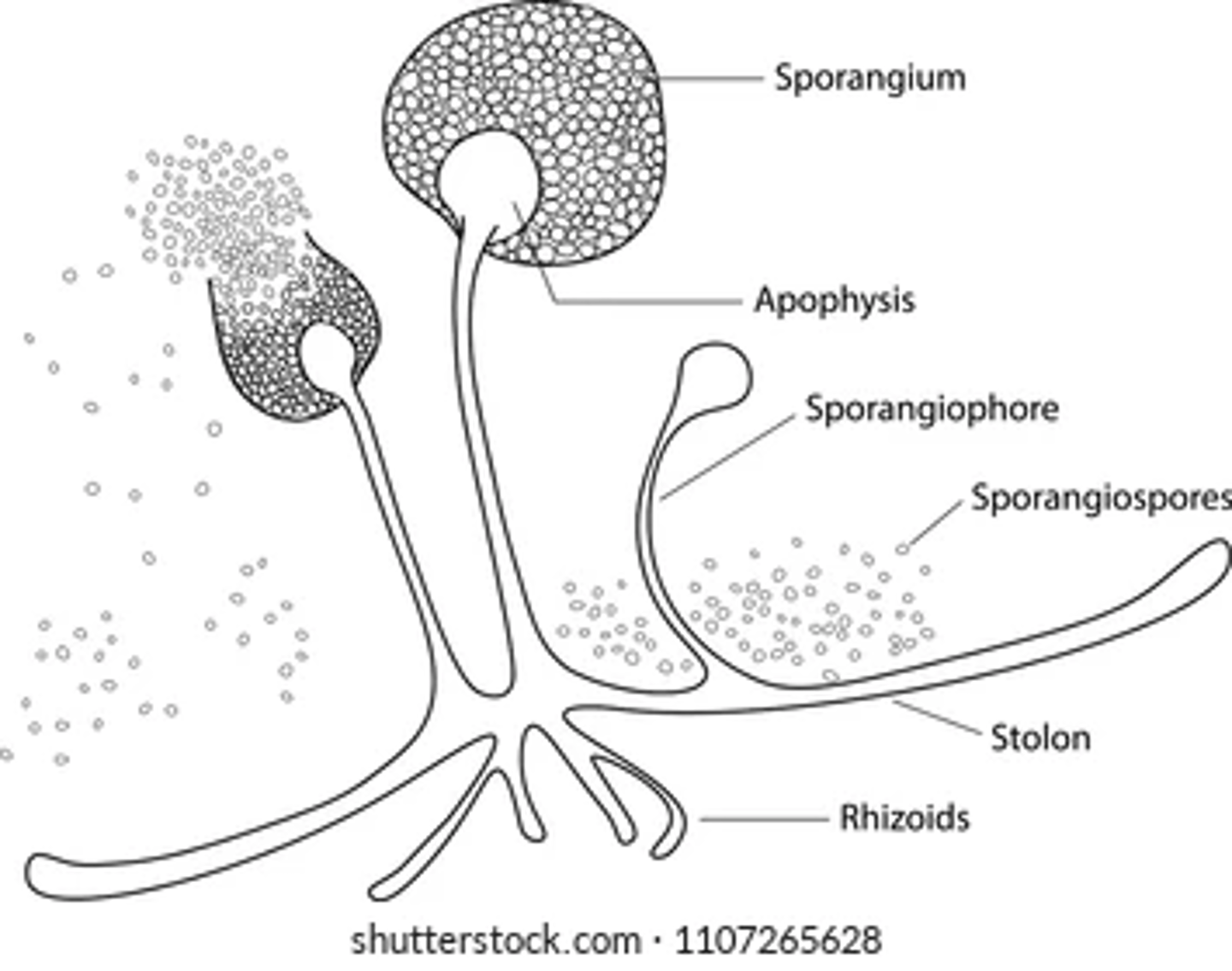
Sporangiospores
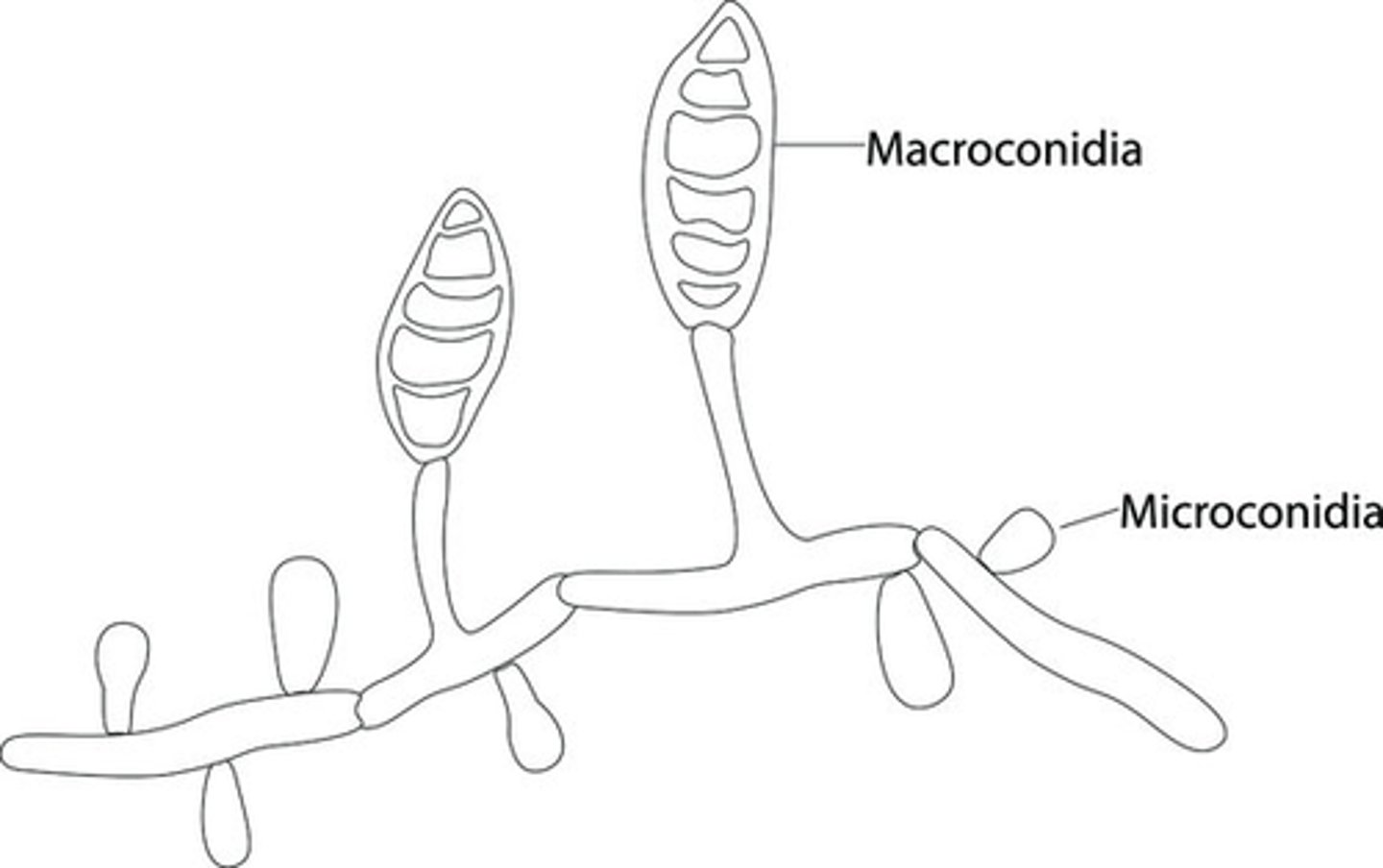
Which of the following is the correct type of asexual spore?
a. Microconidia
b. Macroconidia
c. Conidia
d. Zygospores
Macroconidia
Which of the following describes the asexual reproduction process in yeasts?
a. Fragmentation
b. Fission
c. Budding
d. Spore formation
Budding
Which of the following is not a sexual spore?
a. Arthrospore
b. Ascospore
c. Basidiospore
d. Zygospore
Arthrospore
What is the primary mechanism of the Ziehl-Neelsen stain?
a. Uses heat
b. Uses acid alcohol
c. Uses methylene blue
d. Uses a fluorescent dye
Uses heat
Which of the following groups of organisms does the Runyon classification scheme categorize?
a. Mycobacterium avium complex
b. Nontuberculous Mycobacterium
c. Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC)
d. Dimorphic fungi
Nontuberculous Mycobacterium
It is a chronic, localized infections of the skin and traumatic implantation subcutaneous tissue following traumatic implantation
a. Subcutaneous mycoses
b. Systemic mycoses
c. Dermatophytes
d. Opportunistic mycoses
Subcutaneous mycoses
Which of the following organisms is an example of an Oomycete that is not a true fungus or bacteria?
a. Candida albicans
b. Aspergillus flavus
c. Pythium insidiosum
d. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Pythium insidiosum
A pig presents with diamond-shaped, raised, reddish skin lesions. What is the most likely bacterial cause?
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Besides the skin, what other organs or systems can be affected by E. rhusiopathiae in pigs?
septicemia, arthritis, endocarditis
What are the common routes of transmission for E. rhusiopathiae?
ingestion or wounds, shedding in feces and secretions, and survival in the environment
What is the drug of choice for treating E. rhusiopathiae infection? What are some alternative antibiotics that could be used?
Penicillin
What bacterial species can endure harsh environments due to its ability to form resistant endospores?
a. Streptococcus
b. Staphylococcus
c. Bacillus
d. Listeria
Bacillus
Which of the following media is commonly used for the isolation of Enterobacter species?
a. Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
b. Blood Agar (BAP)
c. MacConkey Agar (MCA)
d. Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA)
MacConkey Agar (MCA)
Which of the following is a common virulence factor associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae?
a. Capsule
b. Hemolysin
c. Coagulase
d. Exfoliative toxin
Capsule
Which bacterial species is MOST likely to be isolated from a stool sample of a patient experiencing bloody diarrhoea and abdominal cramps?
a. Salmonella Typhimurium
b. Escherichia coli
c. Shigella sonnei
d. Proteus vulgaris
Shigella sonnei
What is the oxygen requirement for the growth of Corynebacterium species?
a. Obligate anaerobes
b. Aerobic or facultatively anaerobic
c. Microaerophilic
d. Aerotolerant anaerobes
Aerobic or facultatively anaerobic
Which of the following bacteria causes spastic paralysis due to the production of a potent neurotoxin?
a. Clostridium perfringens
b. Clostridium botulinum
c. Clostridium tetani
d. Bacillus anthracis
Clostridium tetani
A patient presents with muscle spasms, paralysis, and a "sawhead" formation. What bacteria is the MOST likely cause of the patient's symptoms?
a. Clostridium perfringens
b. Clostridium botulinum
c. Clostridium tetani
d. Bacillus anthracis
Clostridium tetani
The patient with muscle spasms, paralysis, and a "sawhead" formation is most likely experiencing these symptoms due to a toxin secreted by the bacteria. What toxin is responsible for these symptoms?
a. Botulinum toxin
b. Anthrax toxin
c. Tetanospasmin
d. Alpha toxin
Tetanospasmin
Which clinical sign is MOST commonly associated with Dermatophilus congolensis?
a. Diarrhea
b. Respiratory distress
c. Neurological signs
d. Thick, crusty scabs on the skin
Thick, crusty scabs on the skin
Which animal is MOST commonly affected by Dermatophilus congolensis?
a. Cattle
b. Sheep
c. Horses
d. All of the above
All of the above
What species of Actinomyces is responsible for lumpy jaw?
a. Actinomyces viscosus
b. Actinomyces bovis
c. Trueperella pyogenes
d. Actinobacillus lignieresii
Actinomyces bovis
Which of the following describes the common characteristics of Actinomyces species?
a. Gram-negative cocci, fast-growing, motile
b. Gram-positive rods, spore-forming, anaerobic
c. Gram-positive branching filaments, slow-growing, non-motile
d. Gram-negative rods, encapsulated, facultative anaerobes
Gram-positive branching filaments, slow-growing, non-motile
Explain pathogenesis of e. Coli
Intestinal Pathogenic E. coli (InPEC)
These strains colonise the intestinal tract and produce toxins that cause diarrhoea. Virulence factors include fimbrial antigens for adherence to host cells and exotoxins like heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins, which disrupt fluid balance in the intestines.
Extra-intestinal Pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC)
ExPEC strains cause infections outside the intestinal tract, such as urinary tract infections, sepsis, and meningitis. Virulence factors include the capsule for evading phagocytosis, endotoxin, which triggers inflammation, and siderophores for iron acquisition.
Explain T3SS mechanism
The Type III Secretion System (T3SS) is a complex mechanism used by some Gram-negative bacteria, including certain strains of Salmonella and E. coli, to inject effector proteins directly into host cells. The sources do not provide a comprehensive explanation of the T3SS mechanism, but they do offer some insights into its function:
Effector molecules rearrange the actin cytoskeleton of the host cell, leading to membrane ruffling. This facilitates bacterial uptake into the host cell.
T3SS effector proteins can destabilize tight junctions between host cells, compromising the integrity of the epithelial barrier.
Bacteria-mediated endocytosis occurs, leading to bacterial uptake into the host cell. This process is facilitated by T3SS effector proteins.
T3SS also triggers an inflammatory response in the host. It does this by inducing the release of proinflammatory cytokines that upregulate polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs).
In essence, the T3SS acts like a molecular syringe, delivering effector proteins that manipulate host cell processes to the benefit of the bacterium. This can include facilitating invasion, suppressing immune responses, and promoting bacterial survival and spread.
Present name of corynebacterium renale type II
Corynebacterium pilosum
CAMP test with C. pseudotuberculosis (horizontal) drawn across ____ demonstrates synergistic hemolysis
Rhodococcus equi
CAMP test with C. pseudotuberculosis (horizontal) drawn across ____ demonstrates inhibition of the effect of the staphylococcal hemolysin
Staphylococcus aureus