econ chapter ``11: unemployment
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
working age population
those age 16 or older who are not in the military or institutionailized
employed
working age people who are working
unemployed
working age people without jobs who are trying to get jobs
labor force
the employed plus the unemployed
not in the labor force
those in the working age population who are neither employed nor unemployed
labor force participation rate
the percentage of the working age population that is either employed or unemployed
labor force participation rate formula
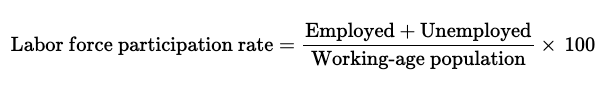
unemployment rate
the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed
unemployment rate formula
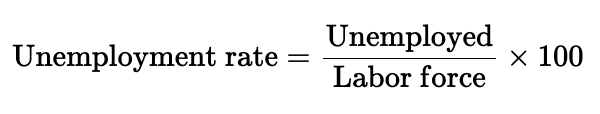
equilibrium unemployment rate
the long run unemployment rate to which the economy tends to return
long term unemployed
people who have been unemployed for 6 consecutive months or longer
marginally attached
someone who wants a job and who has looked for a job within the past year, but who isn’t counted as unemployed because they aren’t currently searching for work
underemployed
some who has some work but wants more hours, or whose job isn’t adequately using their skills
involuntarily part time
someone who wants full time work and is working part time because they haven’t found a full time job
frictional unemployment
unemployment due to the time it takes for employers to search for workers and for workers to search for jobs
structural unemployment
unemployment that occurs because wages don’t fall to bring labor demand and supply into equilibrium
cyclical unemployment
unemployment that is due to a temporary downturn in the economy
efficiency wage
a higher wage paid to encourage greater worker productivity
hysteresis
when a period of high unemployment leads to a higher equilibrium unemployment rate