Bio 75: Human Development - Lecture 1 Overview
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Scientific literacy
The ability to understand and apply scientific knowledge in everyday life.
Williams syndrome
A rare genetic aberration that occurs once in every 7,500 births, resulting in atypical body and profoundly asymmetrical mind.
Howard Lenhoff
A biochemistry professor who advocated for the musical talents of individuals with Williams syndrome, including his daughter Gloria.
Global warming
A long-term rise in the average temperature of the Earth's atmosphere due to human activities.
Antibiotic resistance
The ability of bacteria to resist the effects of an antibiotic to which they were once sensitive.
Conception
The process by which a sperm fertilizes an egg, leading to the formation of a zygote.
Development
The series of changes that occur from conception to birth, including cell division, differentiation, and growth.
Birth
The act or process of delivering a baby from the womb.
Fertilization
The process that triggers the creation of human life when the human egg and sperm join.
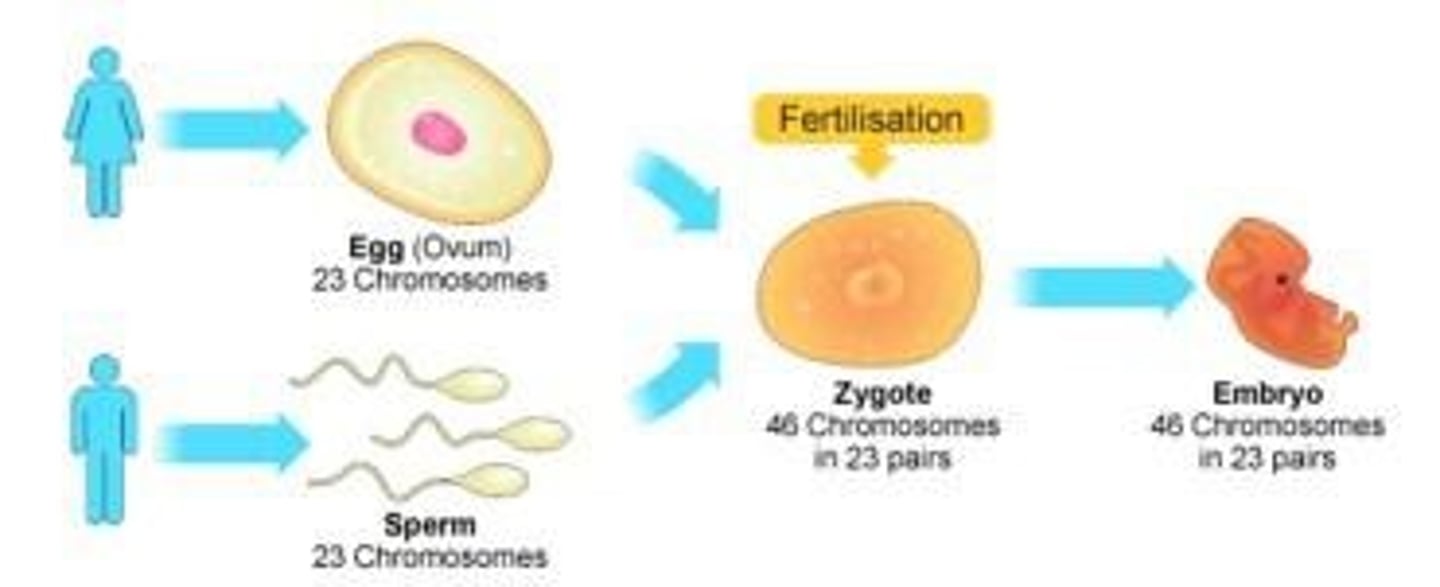
Sexual Reproduction
A mode of reproduction that involves the combination of genetic material from two parents.
Asexual Reproduction
A mode of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes and results in offspring genetically identical to the parent.
Male Reproductive System
The system in males that produces sperm and hormones.
Female Reproductive System
The system in females that produces eggs and hormones.
STIs
Sexually transmitted infections that can affect reproductive health.
Fertility
The natural capability to produce offspring.
Contraception
Methods or devices used to prevent pregnancy during or following sexual intercourse.
Mitosis
The process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
The process of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse gametes.
Genetic Engineering
The direct manipulation of an organism's genes using biotechnology.
Biotechnology
The use of living systems and organisms to develop or make products.
Implantation
The process by which a fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus.
Definition of life - scientific
Life is a characteristic that distinguishes physical entities that have biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from those that do not.
Reproduction
A characteristic of life that requires a 'blueprint' = genetic info, DNA, passed down through generations = inheritance.
Synthetic Life
Self-replicating species whose parent is a computer.
Inanimate entities
Entities that do not have biological processes and are classified as not living.
Self-sustaining processes
Biological processes that allow an entity to maintain itself.
Genetic information
The blueprint required for reproduction, typically in the form of DNA.
Inheritance
The process by which genetic information is passed down through generations.
Clones
Individuals that are genetically identical to the parent organism.
Gametes
Reproductive cells (sperm and egg) that unite during fertilization.
Somatic cells
Any cells of a living organism other than the reproductive cells (gametes).
Germ cells
Reproductive cells that give rise to gametes.
Parthenogenesis
A form of asexual reproduction where an egg develops into an individual without fertilization.
Virus
A microscopic infectious agent that can only replicate inside the living cells of an organism.
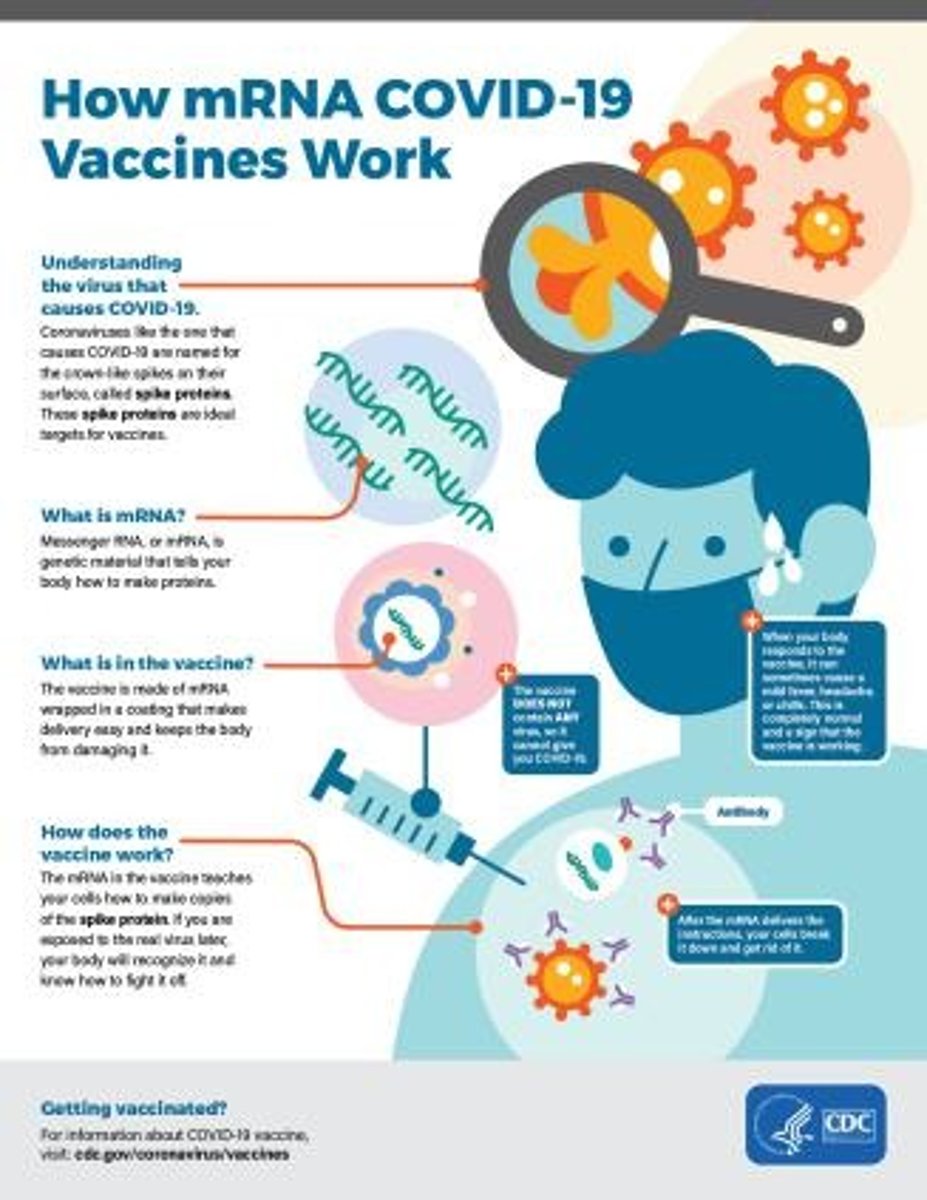
mRNA vaccines
Vaccines that use messenger RNA to instruct cells to produce a protein that triggers an immune response.
Classic Platforms
Traditional methods for vaccine development, often involving the use of inactivated or weakened viruses.
Spike protein
A protein on the surface of the coronavirus that facilitates entry into host cells.
Unfertilized egg cell
In parthenogenesis, an embryo develops from this type of cell.
Examples of parthenogenesis
Includes animals such as bees, wasps, ants, and some species of birds and lizards.
Asexual reproduction examples
Includes organisms like Amoeba, Bacteria, Sweet potato, Flowering plants, and Hydra.
Stem cells
Cells that can be induced to become any body cell type, generated from embryos.
Clone
An organism that is genetically identical to its parent.
Lateral bud
A structure in potato plants that can grow into a new plant.
parthenogenesis
reproduction in gametes without fertilization by sperm.
Examples of asexual reproduction
Virus, Cellular organisms, Parthenogenesis (uses gametes).
Trisomy 21
Also known as Down Syndrome, characterized by a range of symptoms.
Male gamete
Sperm.
Female gamete
Egg.
Male germ cell
The cell that develops into a male gamete.
Female germ cell
The cell that develops into a female gamete.
Genetic variability
Introduced by sexual reproduction, allowing for evolution and adaptation.
Advantages of sexual reproduction
Offspring resemble the parents but are not genetically identical.
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction
Lack of genetic variability.
chromatin
DNA is combined with proteins and organized into a compact structure called _____
Chromosome length
1.5 inches long.
Cell nucleus
The structure that contains the cell's genetic material.