Mendel’s 3 Laws of Genetics, and Inheritance Patterns
1/5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Law of Dominance
Ex: in a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits (RR x rr), only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation. In this case all the offspring will be heterozygous and express only the dominant trait (RR x rr yields all Rr)
Law of Segregation
During the formation of gametes (eggs or sperm), the two alleles responsible for a trait separate from each other. Alleles for a trait are then recombined at fertilization, producing the genotype for the trait of the offspring. Ex: Tt x Tt cross
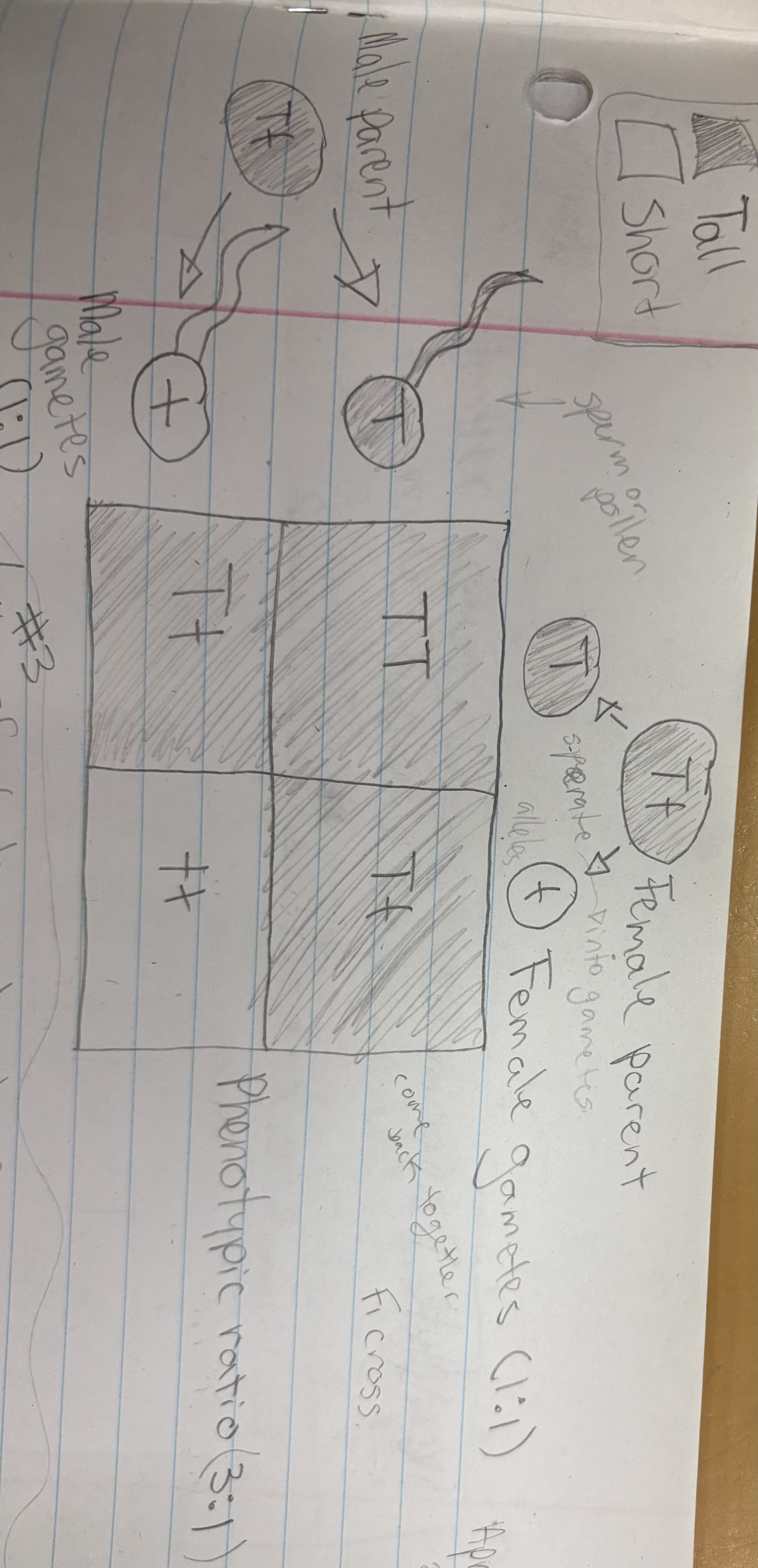
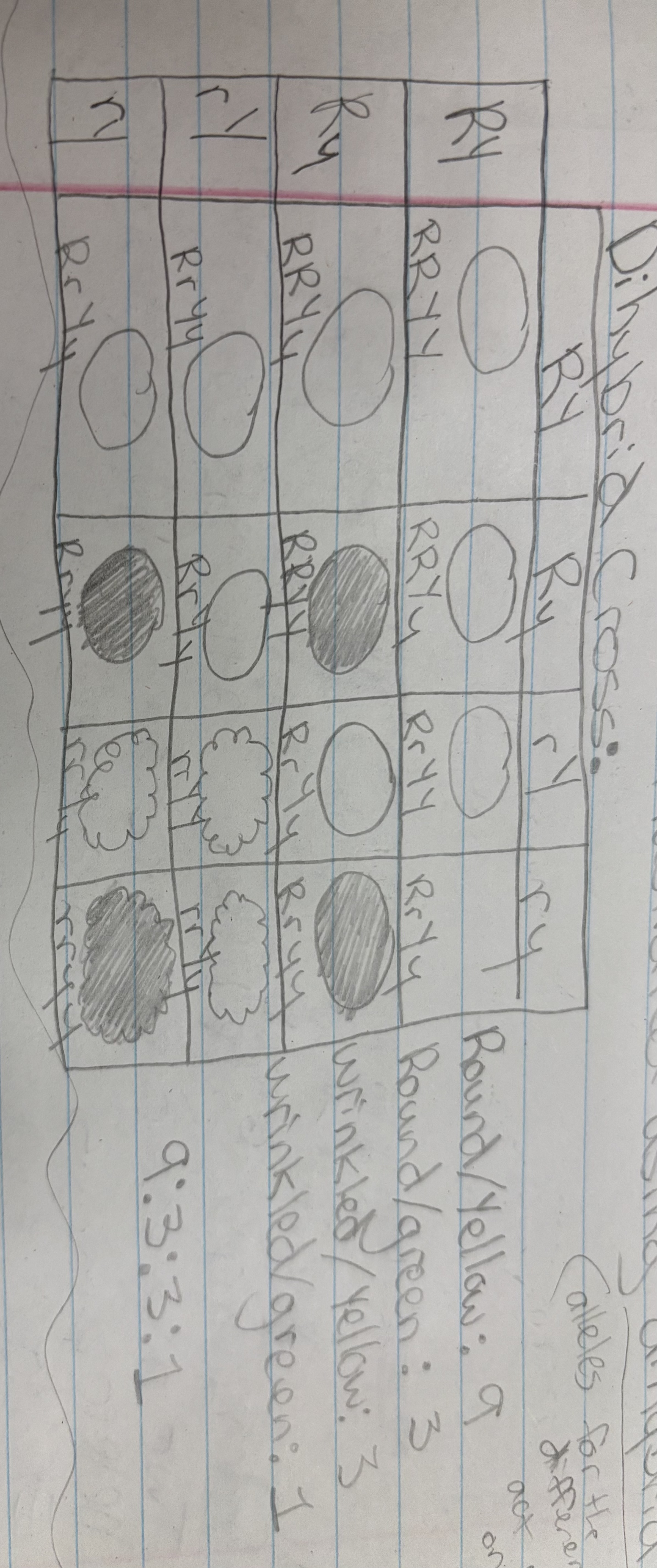
Law of Independent Assortment
Alleles for different traits are distributed to sex cells (and offspring) independently of one another. This law can be illustrated using dihybrid crosses. Alleles for the different traits act completely on their own. Traits on separate chromosomes jumble up separately.
Autosomal dominant
The disease is passed from the father to the son, and this never happens with X-linked traits. The disease occurs in three consecutive generations, this never happens with recessive traits. And males and females are affected with roughly the same probability. Lot’s of shaded shapes.
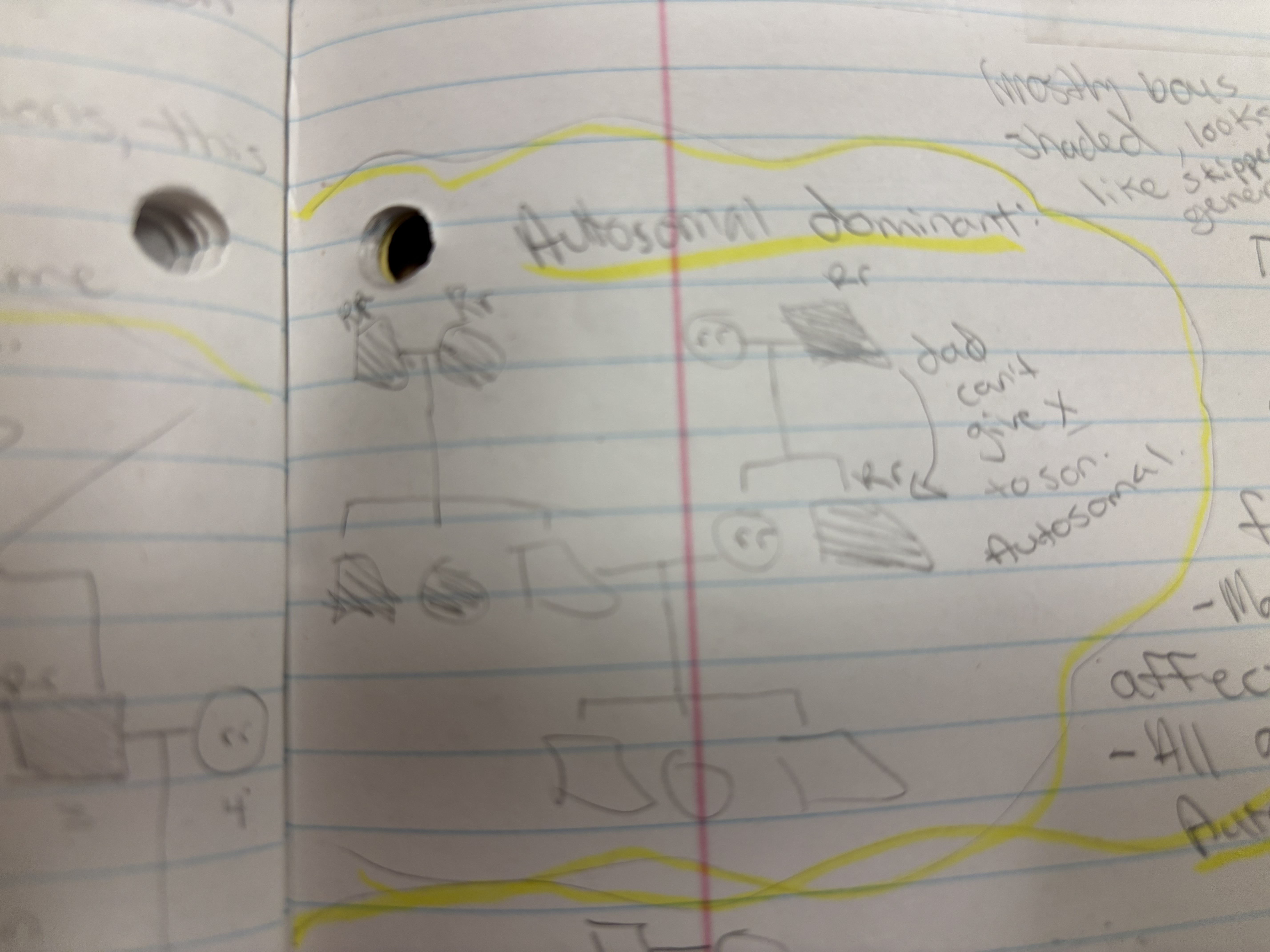

Autosomal recessive and Sex-linked recessive
Males and females are equally likely to be affected. The recurrence risk to the unborn sibling is 1/4 , a.k.a not gonna show up that much cause parents are homozygous. Parents of affected children may be related. The rarer the trait in the general population, the more likely a consanguineous mating is involved (incest).
Sex- linked: mostly boys shaded, looks like skipped a generation, half shaded female=carrier
