HIGHWAY DESIGN REVIEWER
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Transportation
“Circulatory System” & Backbone of the society
Transportation Engineering
provides safe and efficient movement of people and goods
Types of Transportation Engineering
Port and Harbor Engineering
Highway and Traffic Engineering
Railway Engineering
Airport and Engineering
Scopes of Highway Engineering
Planning
Geometric Design
Pavement Engineering
Traffic Engineering
Construction, Maintenance ang Management
Goals of Transportation Engineering
Provide a high Level of Service (LOS) by minimizing travel time and delays
Provide a high Level of Safety (LOS) by minimizing accident and harmful effects to environment
Economic Growth
provide connectivity between regions
leads to increased trade, commerce and economic activity
Regional Development
improve access to remote and undeveloped areas
Improved Transportation
enables faster and more efficient transportation of goods and people
reduce travel time and cost
Safety
signage, signals, and safety measures reduce accidents and fatalities
Environment
helps minimize air and noise pollution
Highway Fragmentation
negative impact roads have on ecosystem
Classification of Roads
Expressways
Freeway
Arterial Road
Collector Road
Local Raod
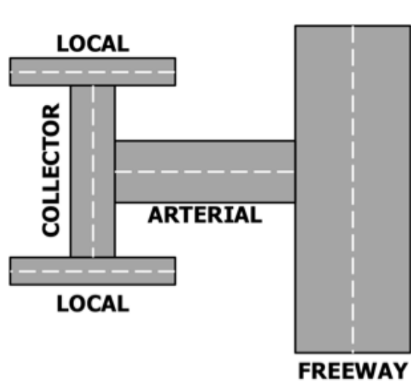
Expressways
generally with grade separation at major intersections
Full control of access
Partial control of access
Freeway
highspeed, fully-controlled-access highway with no at-grade crossing or intersections
have multiple lanes in each intersections
Arterial Road
with intersections and signal lights
connection of other roads to expressways
Collector Road
collects/connect local road to arterial or freeway
provides access to residential and commercial areas
Local Road
connects residential and other local roads to main road(collector road)
provides access to properties along the road
Road Patterns
Rectangular (or block) pattern
Radial (or star) & block pattern
Radial (or star) & circular pattern
Radial (or star) & grid pattern
Hexagonal
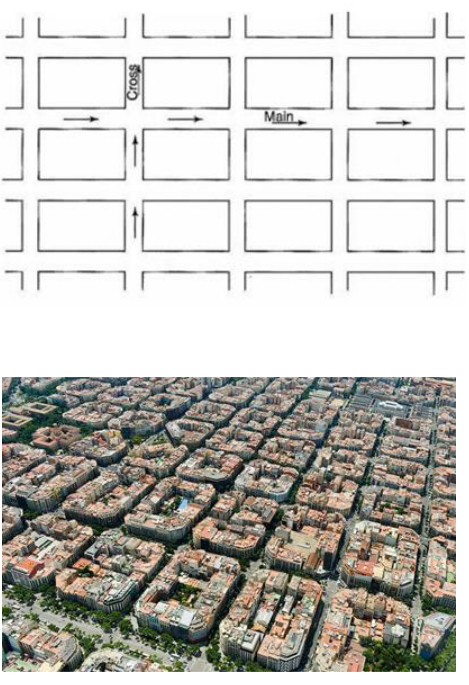
Rectangular (or Block) Pattern

Radial (or Star) & Block Pattern

Radial (or Star) & Circular Pattern
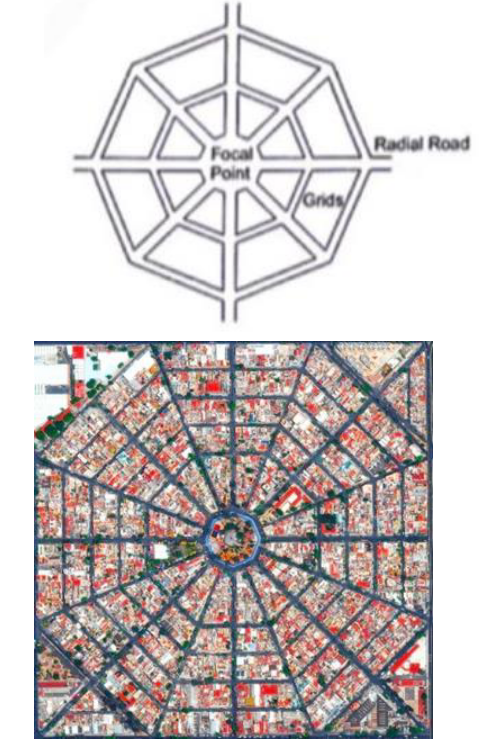
Radial (or Star) & Grid Pattern
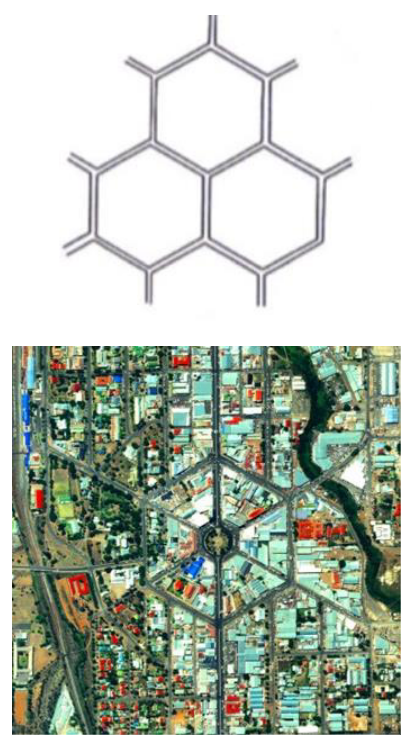
Hexagonal
Types of Planning Studies
Engineering Studies
Economic Studies
Financial Studies
Traffic Road Use Studies
Engineering Studies
assess technical feasibility of proposed project/infrastructure
site investigations
geotechnical surveys
structural design and parameters
cost estimate based on design specifications
Economic Studies
overall viability of a project & focus on how the project affects society at large
economic internal rate of return (EIIR)
cost-benefit analysis
socioeconomic impact
environmental & social considerations
Financial Studies
monetary aspects of a project
financial internal rate of return (FIRR)
project funding sources & structures
revenue forecasting & affordability
financial risk analysis
Traffic Road & Studies
how roads are currently used and predict future traffic patterns
traffic counts & vehicle classifications
peak hour studies
origin-destination surveys
road safety & capacity analysis
Alignment
laying out of the centerline of a proposed highway on the ground
Requirements of Highway Alignment
Directness
Ease of Construction, Maintenance & Operation
Safety
Economy
Special Considerations
Horizontal Alignment
alignment of highway/roadway in horizontal plane
Vertical Alignment
change in gradient calls for curves in vertical plane
Horizontal Curve
for smoothening change of direction
Vertical Curve
for smoothening change of longitudinal gradients
Stages of Engineering Surveys for Highway Location
Map Study
Preliminary Survey
Final Location & Detailed Survey
Map Study
to conduct initial evaluation using topographic & thematic maps
to identify possible corridors for highway
helps ruling out unsuitable areas
Preliminary Survey
to inspect shortlisted routes on the ground
involves reconnaissance survey & basic field investigation
Final Location & Detailed Survey
to finalize the highway alignment
detailed survey is conducted along chosen route
Highway Economics
involves evaluating cost & benefits associated with highway projects
to maximize the economic benefits to society while minimizing cost
PPPs (Public - Private Partnerships)
helps mobilize additional resources & improve efficiency
Cost Components in Highway Projects
Capital Cost
Maintenance & Operating Cost
User Cost
External Cost
Capital Cost
one-time expenditures
Maintenance & Operating Costs
keep the highway in good condition & endure safety
User Costs
incurred by road users
vehicle operating costs
travel time costs
accident costs
External Costs
unintended consequences
environmental degradation
social impacts
Economic Evaluation Methods
Cost - Benefit Analysis (CBA)
Life Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA)
Shadow Pricing & Economic Costs
Sensitivity & Risks Analysis
Costs - Benefit Analysis (CBA)
a systematic approach to comparing the benefits & costs of a project
Components of Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA)
Net Present Value (NPV)
Benefit-Costs Ratio (BCR)
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Financial Benefit (FB)
Non-Financial Benefit (NFB)
Life Cycle Costs Analysis (LCCA)
economic evaluation method that evaluates total costs of ownership over a highway’s lifespan
Components of Life Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA)
initial construction costs
routine & periodic maintenance
rehab or replacement costs
salvage value
Shadow Pricing & Economic Costs
economic evaluation method that converts financial costs to economic values using conversion factors to adjust for market distortions such as taxes or subsidies
Sensitivity & Risks Analysis
economic evaluation method that tests how results change with variations in key assumptions
Components of Highway Project Financing
Public Sector
Private Sector
Public Sector
highway project financing sector that financing ensures social equity by funding roads that may not be financially viable but have high economic & social benefits
Private Sector
highway project financing sector that is mobilized through PPPs
Common PPP Project Model
Build - Operate - Transfer (BOT)
Build - Own - Operate - Transfer (BOOT)
Build - Own - Operate (BOO)
Management Agreement / Operations & Maintenance (O&M)
Design - Build - Finance - Operate - Maintain (DBFOM)
Design - Build - Lease (DBL)
Highway Design
Designed to provide safe roads for all road users
“Man is the reference standard”
roads must be adapted to the limitations of human capacity
Principles of Highway Design
Road Characteristics
Driver Characteristics
Vehicle Characteristics
Road Characteristics
Consistency
Highway Capacity
Average Annual Daily Traffic (AADT or ADT)
Cross-section of Typical Highway
Pavement
Cross Slope / Crossfall
Road Shoulder
Cut or Fill Slope
Interchanges
Highway Intersection at Grade
Road Shoulder
portion of roadway between the edge of traffic lane where vehicle can stop when disabled
Driver Characteristics
Human Sensory Process
Driver Perception - Reaction Time (PIEV Time)
Visual Acuity
Lateral Displacement
Human Sensory Process
information received to process
Types of Human Sensory Process
Visual (Sight)
Kinesthetic (Movement)
Vestibular (Equilibrium)
Auditory (Hearing)
Perception
detection
Intellection
Identification
Emotion
Decision
Volition
Response
Visual Acuity
sharpness with which person can see the object
Lateral Displacement
driver’s tendency to displace laterally away from the object
2 Primary Opposing Forces
Tractive Effort
Resistance
Tractive Effort
force available at roadway to perform at roadwork
Resistance
force impending at vehicle motion
3 Major Vehicle Resistance
Aerodynamic Resistance
Rolling Resistance
Grade Resistance
Aerodynamic Resistance
resistance force that can have significant impact on vehicle performance
Rolling Resistance
resistance generated from vehicles internal mechanical friction, and pneumatic tires and interaction with roadway surface
Grade Resistance
simply gravitational force acting on vehicle
Inertia
tendency of vehicle to resist acceleration
Curve
force required to cause vehicle to move along curve
function of curvature and speed
Vehicle Maximum Tractive Effort
results in spinning tires and does not overcome resistance or accelerate the vehicle
Vertical Alignment
establishing the transition of roadway elevation between two grade
Types of Vertical Alignment
Crest Vertical Curve
Sag Vertical Curve
Stopping Sight Distance (SSD)
sufficient sight distance to allow them to safely stop their vehicles
Breaking Distance
distance needed to stop vehicle from instant break application begins
Height of driver’s eye through passenger vehicles
3.50ft (1.08m) above road surface
Height of driver’s eye through truck driver
7.60ft (2.33m) above road surface
Horizontal Alignment
directional transitional between two straight sections of roadway (cornering capabilities of the vehicle)
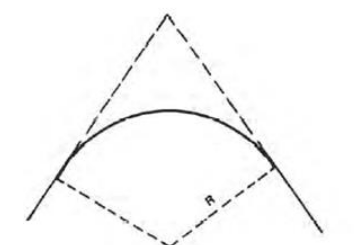
Simple Curve
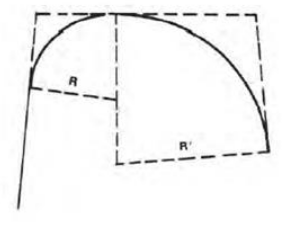
Compound Curve
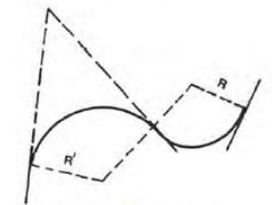
Reverse Curve
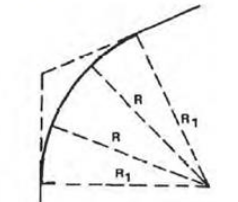
Spiral Curve
Passing Sight Distance (PSD)
shortest distance required for a vehicle to pass a vehicle travelling in the same direction
Superelevation
intentional tilting of road surface on a curve (banking)