Covalent Bonding
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Covalent Bonding
The strong, electrostatic forces of attraction between shared paired of electrons and the bonded atom’s nuclei
Covalent Bonding between atoms
Non-metallic
Compounds of non-metallic elements
Polyatomic ions
Covalent Bond - orbital overlap
It is the overlap of atomic orbitals, each containing 1 electron, to provide a shared pair of electrons
Covalent Bond - attraction
The attraction is localised (it acts solely between the shared pairs of electrons and the nuclei of the 2 bonded atoms - forms a molecule)
Displayed Formula
A structure showing the relative positioning of atoms and bonds between them as lines
Lone Pair
Paired electrons that are not shared
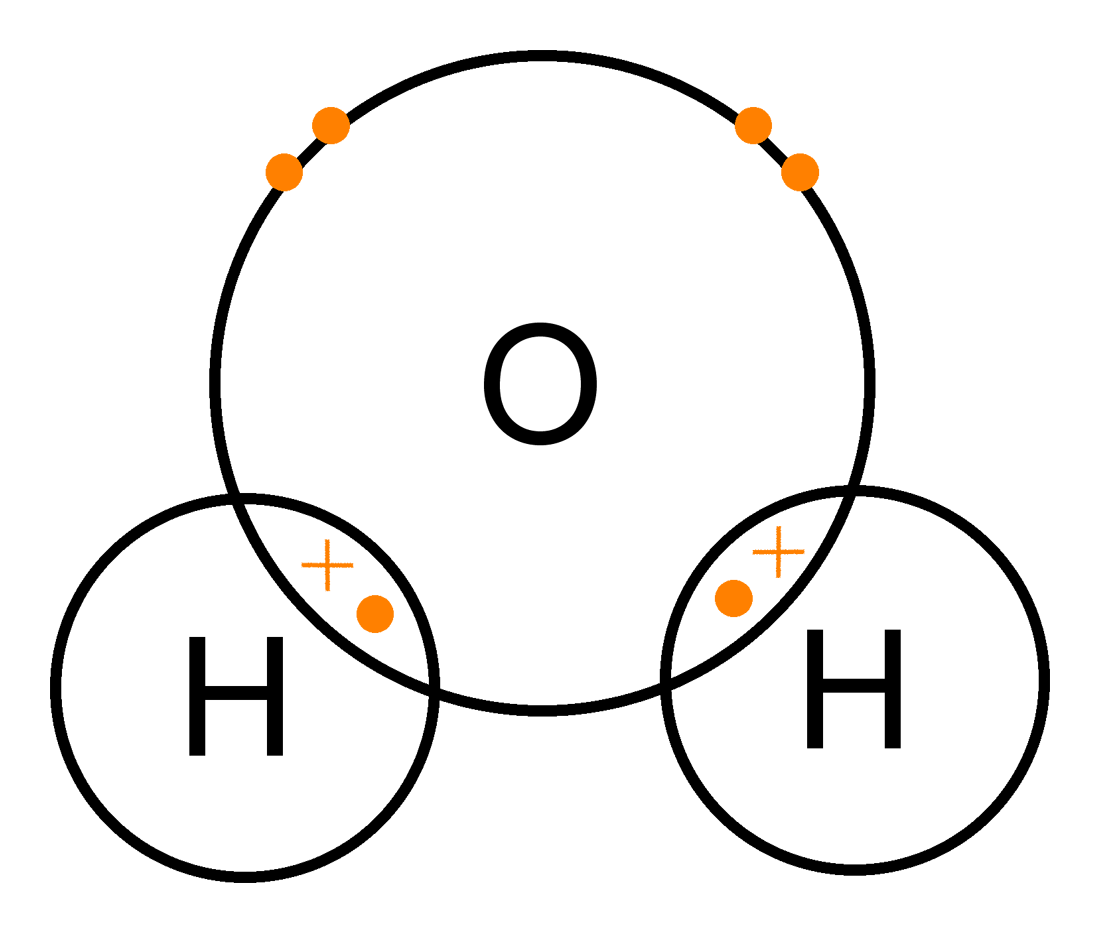
H2O Covalent Bond
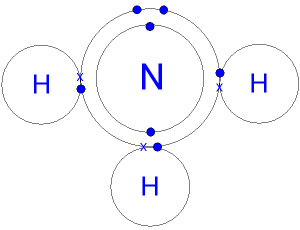
NH3 Covalent Bond
Number of Covalent Bonds (common elements)
C - 4 bonds
N - 3 bonds
O - 2 bonds
H - 1 bond
Elements in Period 2
Maximum 8 electrons in the outer shell
Elements in Period 3
Can have more than 8 electrons in the outer shell (octet)
Multiple Covalent Bonds
2 atoms sharing more than 1 pair of electrons
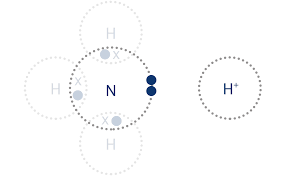
Dative Covalent Bonds
When the shared pair of electrons have been supplied by one of the bonding atoms only (e.g, NH4)
Formation of Dative Covalent Bonds
The shared electron pair was originally a loan pair of electrons
E.g, formation of an ammonium ion - ammonia donates the loan pair of electrons to an H+ ion (shown by an arrowhead)
Average Bond Enthalpy
A measurement of covalent bond strength