12. Development of the Heart
1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
List the overall steps in the development of the heart and its vessels.
Formation of the heart tube
Cranio-caudal folding and positioning of the heart
Division of the heart tube
Bending of the bulbo-ventricular loop
Circulation through the primordial heart
Formation of the heart chambers
Partitioning of the heart
Formation of the heart tube; formation of endo-cardial tubes
When _______ folding of the embryo occurs, the __________ ____ move ________ to ____ with each other. It is followed by the __________ mesoderm.
The splanchnic mesoderm ________ in the cardiogenic area to form 2 solid _____-_______ _____.
Both cords start __________ to form ____-_______ tubes.
The 2 ends of the ________ (green) fuse together forming the ___.
lateral, endodermal ends, medially, fuse, splanchnic
thickens, angio-blastic cords
canalizing, endo-cardial
endoderm, gut
Formation of the heart tube
The 2 ____-_______ tubes start approaching each other in the _______.
At this stage, the developing heart is composed of a ____ ___________ ____ which forms the ____________ and the _________ mesoderm forms the __________.
The ___________ cells of the ___________ ______ forms the __________.
endo-cardial, midline
thin, endocardial tube, endocardium, splanchnic, myocardium
mesothelial, pericardial coelom, epicardium
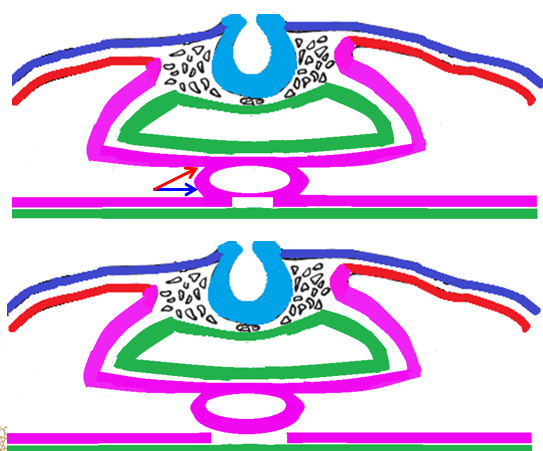
Formation of the heart tube
The 2 tubes fuse to form one ___________ tube. This tube lies _______ to the ___ (future _________ system).
The heart tube is connected to the _________ mesoderm:
Anterior through _______ (blue arrow) mesocardium
Posteriorly through ______ (red arrow) mesocardium.
After that, the ventral mesocardium __________ and a single __________ ______ is formed.
The pericardial cavity is the _____-_________ ______ around the heart.
endocardial, ventral, gut, digestive
splanchnic, ventral, dorsal
disappears, pericardial cavity
intra-embryonic coelom
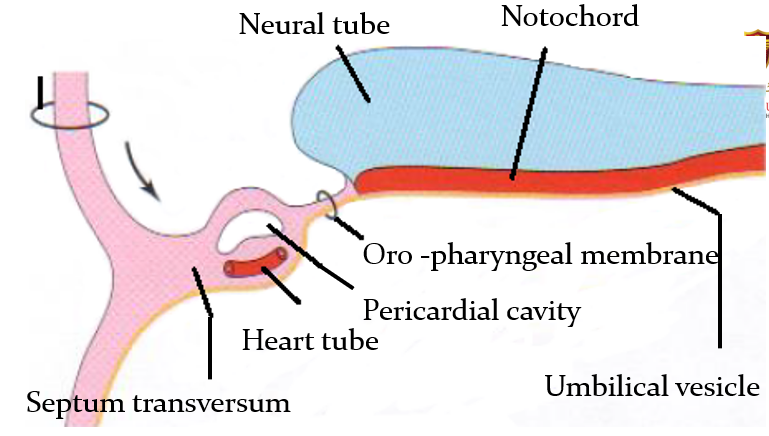
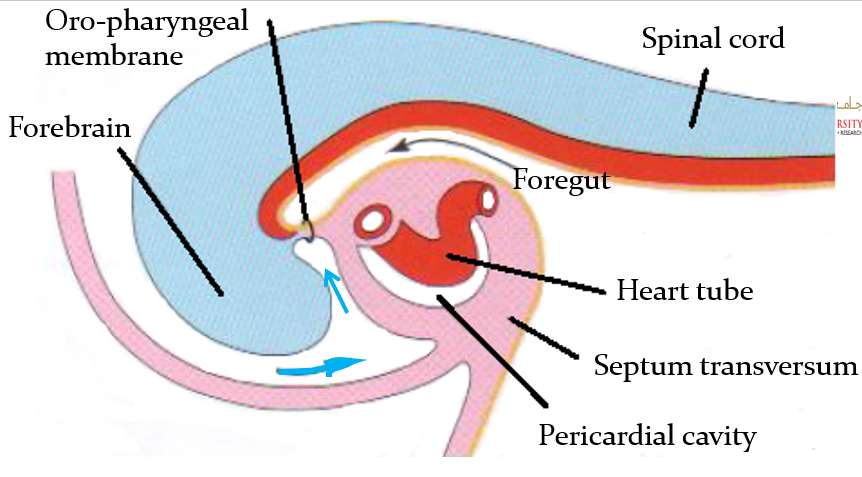
Describe the cranio-caudal folding and the position of the heart.
As folding of the head region occurs, the heart and the pericardial cavity become ventral to the foregut and caudal to the oro-pharyngeal membrane
The pericardial cavity is ventral to the heart
(blue arrow is stomodeum)
Division of the heart tube
The tubular heart elongates and develops alternate dilations and constrictions which are arranged from above downwards. List the divisions.
The bulbus cordis
The ventricle
The atrium
The sinus venosus
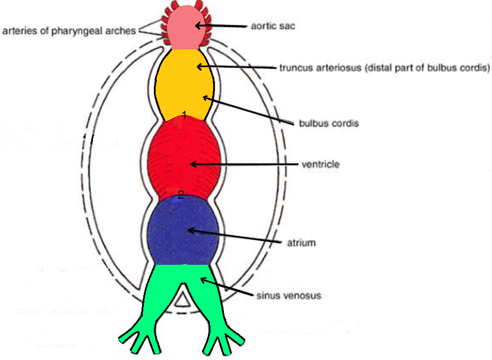
Division of the heart tube
From above downwards, the bulbus cordis is consisted of 3 things. List them.
The truncus arteriosus
The conus arteriosus
The conus cordis
Division of the heart tube
The arterial end of the heart is the _______ _________.
The venous end of the heart is the _____ _______.
truncus arteriosus
sinus venosus
Bending of the bulbo-ventricular loop
Because the ______ ______ (yellow) and the _________ (red) grow faster than the other regions, the heart bends (to the _____) on itself, forming a U-shaped _________________ loop.
Bulbus cordis moves _________, ________ and _____.
The _________ moves to the left.
The ______ (dark blue) and the _____ _______ (green) move upwards and posterior.
As the heart tube bends, the atrium and sinus venosus become ______ and _____ to the bulbus cordis, while they become ______ and ____ to the ventricle.
bulbus cordis, ventricle, right, bulbo-ventricular
downwards, forwards, right
ventricle
atrium, sinus venosus
dorsal, right, dorsal, left
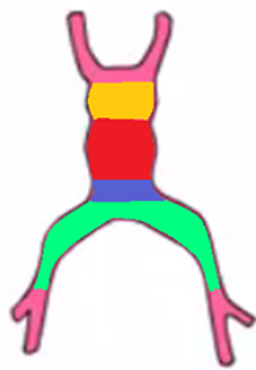
Circulation through the the primordial heart
The heart is formed of the _____ _______ (green), common ______ (blue), common ________ (red), and _______ ______ (yellow).
The blood moves from the _____ _______, to the _____, and then to the ________, and finally to the ______ _____.
sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, bulbos cordis
sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, bulbos cordis
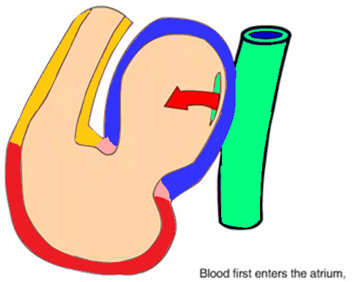
Formation of the heart chambers
How is the right atrium formed?
Formed partly from the common atrium and the right horn of the sinus venosus
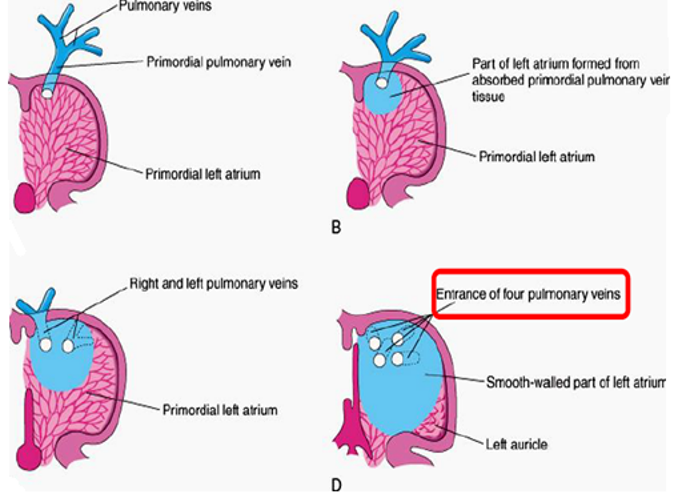
How is the left atrium formed?
Formed partly from common atrium absorption of the primordial pulmonary vein
How is the right ventricle formed?
Formed from the common ventricle and the conus cordis
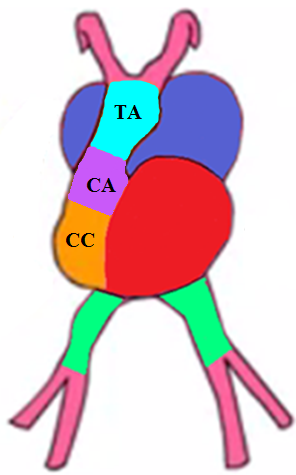
How is the left ventricle formed?
Formed from the common ventricle and the conus cordis
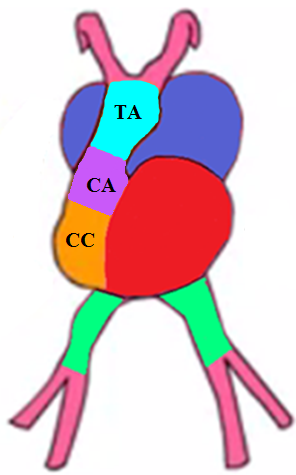
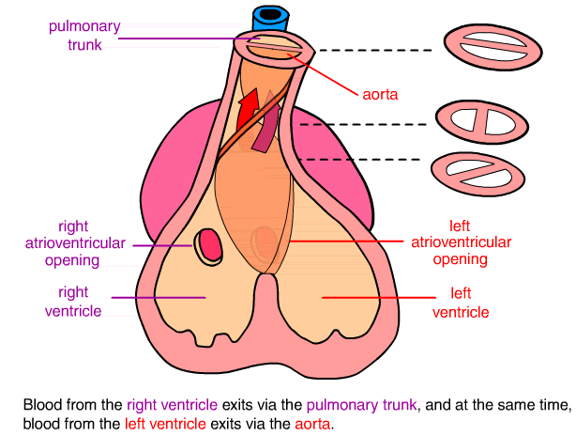
How are the ascending aorta and pulmonary artery formed?
Formed by the truncus arteriosus
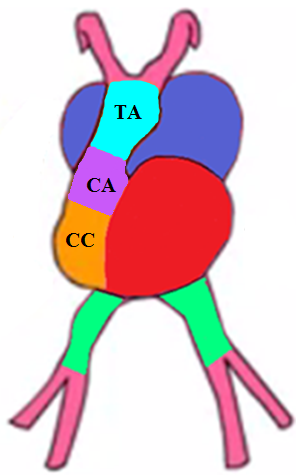
How are the aortic and pulmonary valves formed?
Formed by the conus arteriosus
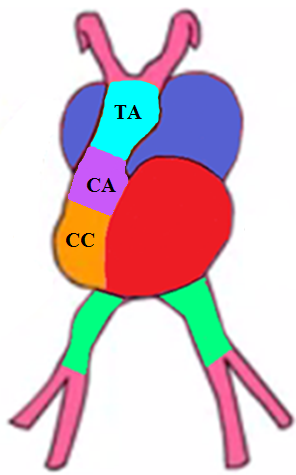
List the partitions of the heart.
Atrio-ventricular (AV) canal
Inter-atrial septa
Inter-ventricular septum
Bulbar septum
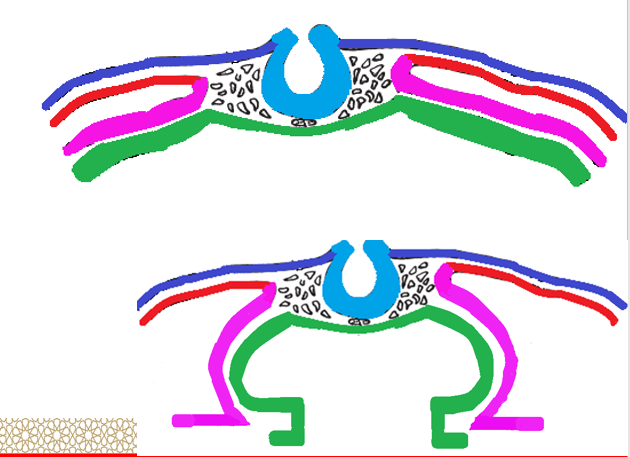
Atrio-ventricular (AV) canal
Anterior and posterior __________ _______________ ________ project from the anterior and posterior walls of the AV canal.
They approach each other and ____ to form the AV ______, dividing the AV canal into _____ and ____ AV canals.
endocardial atrio-ventricular cushions
fuse, septum, right and left
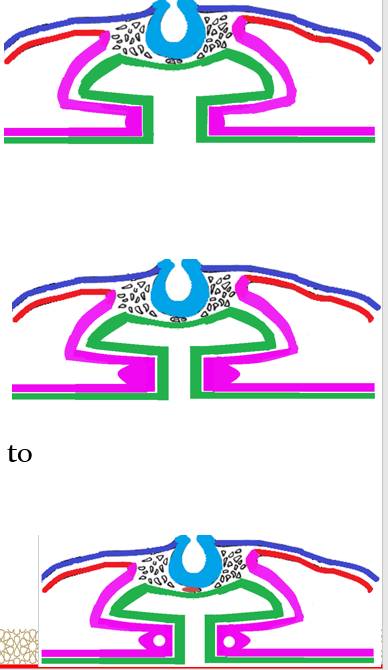
Inter-atrial septa
The __________ atrium is divided into right and left atria by the formation and ______ of 2 septa; septum ______ and septum ________ by the ___ week.
primordial, fusion, primum, secundum, 5th
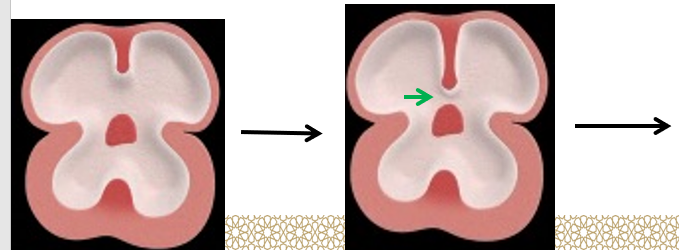
Septum primum
Grows from the _________ ______ towards the fusing AV _______, partially dividing the atrium into right and left halves.
This septum develops a large _______ called the _______ ______ (green arrow), between its lower free edge and the AV ___________ _________.
This foramen _________ in size gradually until it __________ when the septum primum is completed by the ___________ _______ of the AV ______.
Before the foramen ______ disappears, another upper opening called the _______ ________ (blue arrow) appears.
primordial atrium, cushions
opening, foramen primum, endocardial cushions
decreases, disappears, endocardial cushion, septum
primum, foramen secundum
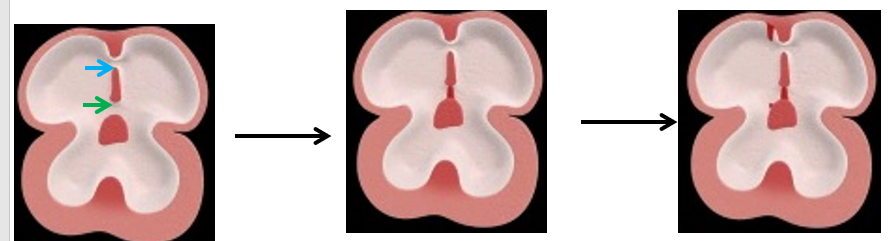
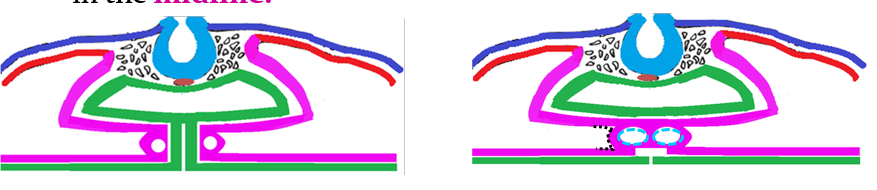
Septum secundum
Is a ____, ________ septum, which starts to grow to the _____ of the septum primum.
It gradually ________ the _______ ________ in the septum primum.
It has an ____foramen lower down (foramen _____) (light blue arrow) between the 2 _____.
thick, muscular, right
overlaps, foramen secundum
oval, ovale, atria
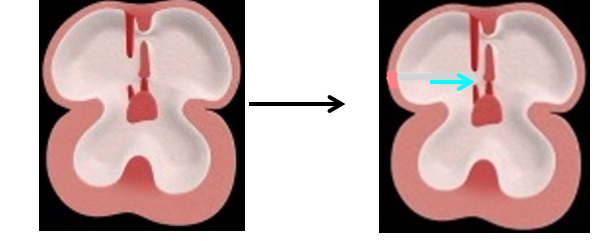
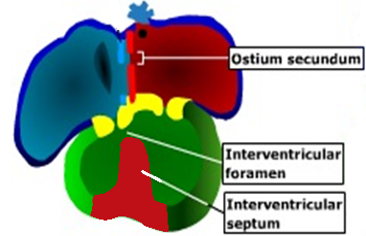
Interventricular septum
Has 2 parts; muscular part and membranous part.
Muscular part
A median _____ or fold grows from the _____ of the primordial _________, near its ____.
It represents the ______ 2/3 of the ______.
Membranous part
It develops from 2 sources:
Its anterior 1/3 comes from the ________ ______ ______ (yellow).
The posterior 2/3 comes from the _________ ___ ______(green).
ridge, floor, ventricle, apex
lower, septum
proximal bulbar septum
posterior AV cushion
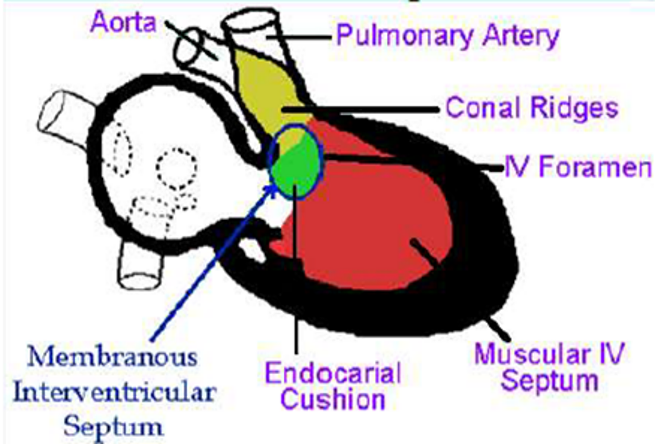
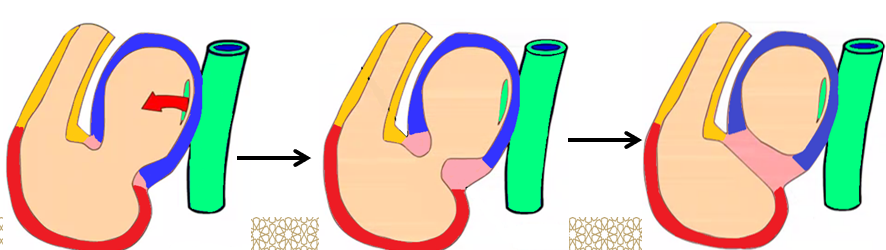
Bulbar septum
Is ______ in shape.
Formed of ________ part and ______ part.
spiral
proximal, distal
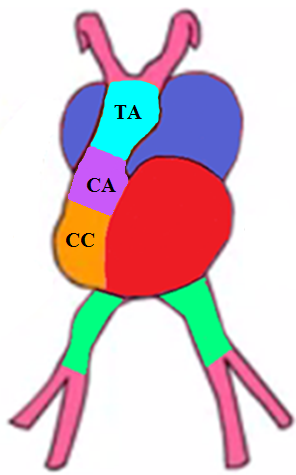
Proximal bulbar septum
Divides the _____ ______ into:
Right half _____________ of the right ventricle.
Left half _________ of the left ventricle.
Distal bulbar septum
Divides the _____ __________ into:
_________ valve (anteriorly) and ______ valve (posteriorly).
It divides the _______ __________ into:
_________ artery (anteriorly) and _________ _____ (posteriorly).
conus cordis
infundibulum
vestibule
conus arteriosus
pulmonary
aortic
truncus arteriosus
pulmonary, ascending aorta