Crystal Systems, Counting Atoms, Lattice +Basis
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Cubic
a=b=c/ x,y,z = 90 degrees
Hexagonal
a=b not C/ x=120 y,z=90
Tetragonal
A=B not C/ x,y,z=90
Orthorhombic
a not equal b not equal C/ x,y,z=90
Rhombohedral (trigonal)
a=b=c/ x,y= 90 z= something?
Monoclinic
a not equal b not equal c/ x not equal 90, y,z=90
Triclinic
a not equal b not equal c/ x not equal y not equal z
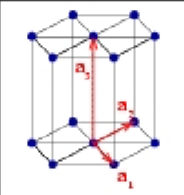
Lattice parameter
physical side length of a unit cell (a,b,c). usually in angstroms or nanometers
Interaxial angles
Physical angles between the three primary axes.
Primitive lattice (p)
lattice points (“atoms”) only at the corners
Body centered
Lattice points with atom in the center
Based centered
Lattice points with 2 atoms on opposite sides of the same axis
Face centered
atoms on all the surfaces or “faces” of the unit cell
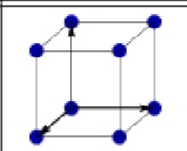
What is this?
Primitive Cubic
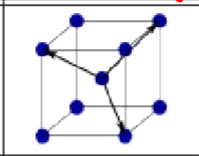
What is this?
Body centered cubic
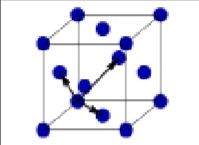
What is this?
Face centered cubic
What is this?
primitive hexagonal
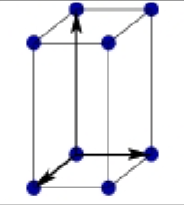
What is this?
Primitive Tetragonal
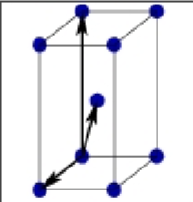
What is this?
Base centered tetragonal
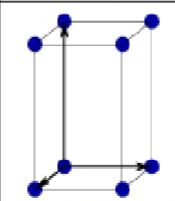
What is this?
Primitive centered Orthorhombic
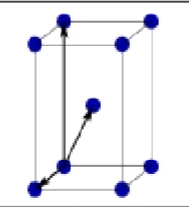
What is this?
Body centered Orthorhombic
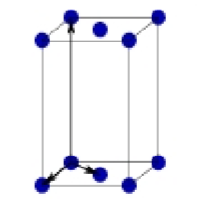
What is this?
Based centered Orthorhombic
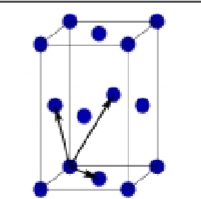
What is this?
Face centered Orthorhombic
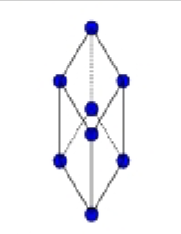
What is this?
Primitive centered Rhombohedral/Trigonal
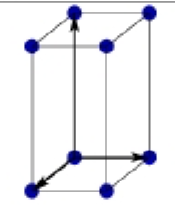
What is this?
primitive centered monoclinic
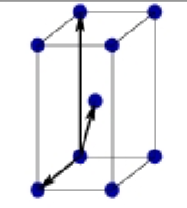
What is this?
Based centered monoclinic
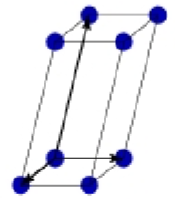
What is this?
Primitive based triclinic
What are point groups?
They are orientations that take into account rotations, reflections, and inversions
What are space groups?
accounts for same orientations as point groups but also takes into account for screw glide.
What is a conventional unit cell?
A unit cell that is NOT the smallest repeatable unit but it is selected because it is convenient for other reasons.
if HCP, FCC, or BCC not closed packed?
BCC is not closed packed.
How much of corner atom is in a cubic lattice?
1/8th
How many atoms in Body cubic centered?
2 atoms?
How many atoms in face centered?
4 atoms
What is a lattice?
a regular collection of equivalent sites in Euclidian space that only describes symmetry.
What is a basis?
What we put in the lattice site/ the composition of the sites.
What is a basis usually equal to?
The stoichiometry of the molecule.
What is an important fact about lattice sites?
They MUST be equivalent.