Law of mass action
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Law of mass action

Given by law of mass of action
Peter Waage and Cato Guldberg
Molar concentration or active mass
It is the ratio between mole and volume
Unit of m.c or a.m
Moledm-³ and mol/lDerivattion
Suppose a reversible reaction in which recatnats A and B react to form recatnats C and D

Derivattion reaction
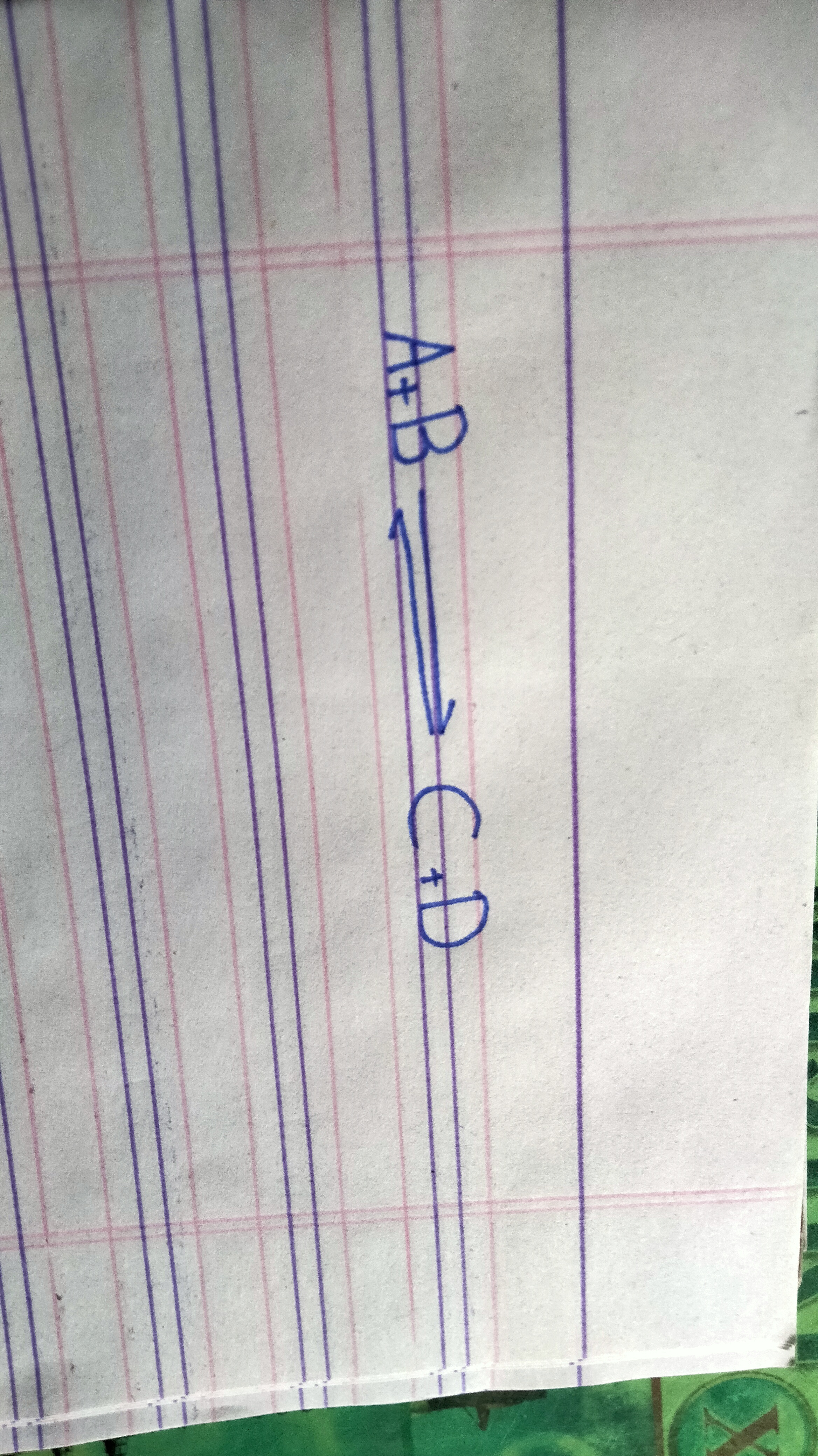
Rate of forward reaction
Rate of forward reaction is directly proportional to the active mass of A and B
Rate of reverser reaction
The rate of reverse recation is directly proportional to the active mass iof c and D
Mathematically Rf

Mathematically Rr

At equilibrium
Rate of forward reaction =rate of reverse reaction
Rf= Rr
Proof mathematically
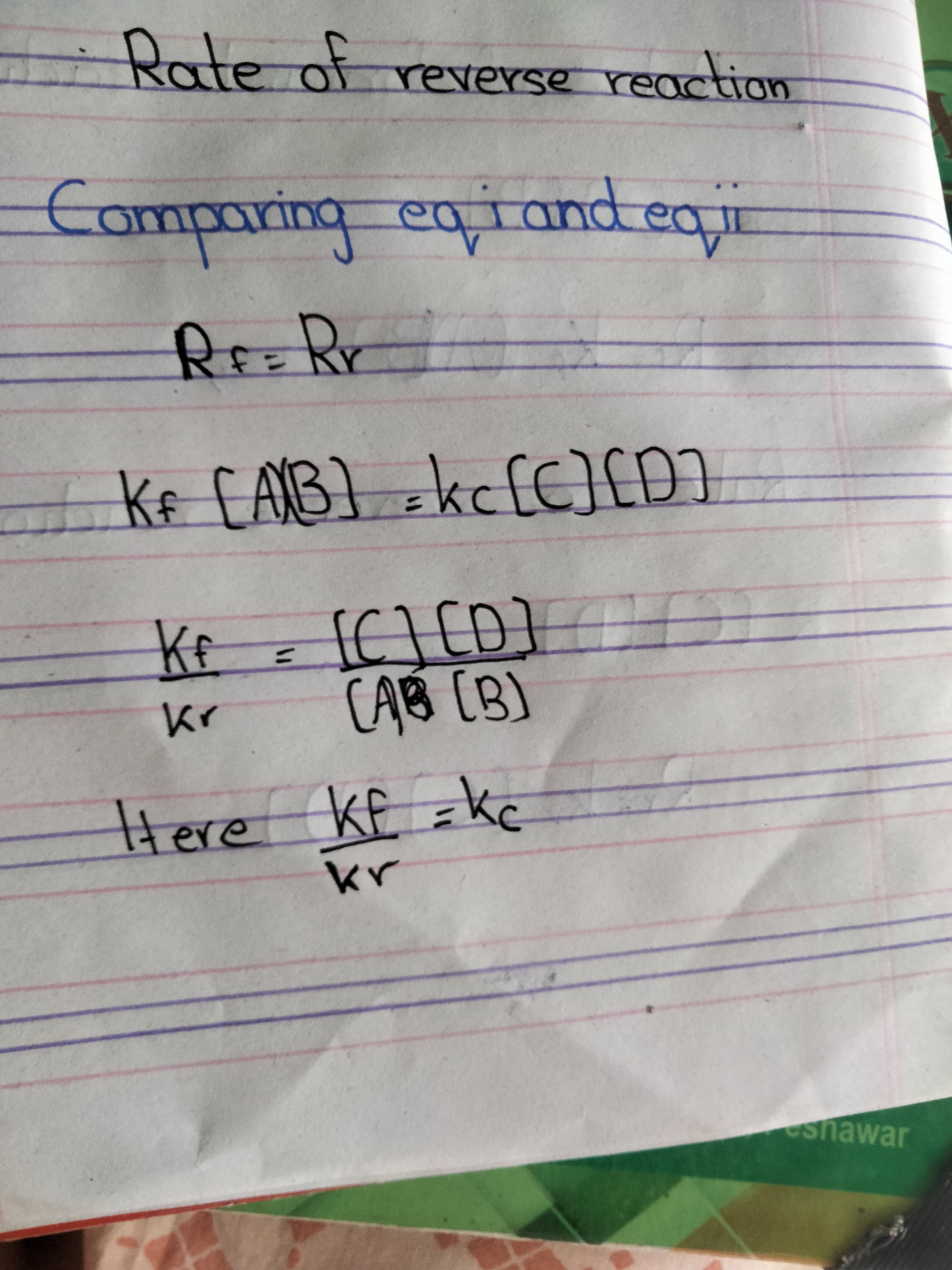
Equation of equilibrium constant
Example of equilibrium constant