chapter 15: lipids and fatty acids
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
lipids consist of
fatty acids or steroid nucleus
lipids solubility
only soluble in organic solvents not in water
lipids important in
cell membrane, fat soluble vitamins, steroid hormones
steroid nucleus fused rings
lipids that are esters that can be hydrolyzed
waxes, fats, oils and phospholipids
give fatty acids and other molecules
long chains w/ carboxylic group attached
lipids that can not be hydrolyzed
steroids
no fatty acids
four fused carbon rings
fatty acid structures
long unbranched chains w/ carboxylic acid at the end
12-18 carbons long
saturated or unsaturated
fatty acids solubility in water
insoluble due to long carbon chain
saturated fatty acids
single bonds only
lauric acid
found in coconut
myristic acid
nutmeg
palmitic acid
palm
steric acid
animal fat
monounsaturated
only one double bond
palmitoleic acid
butter
oleic acid
olives
polyunsaturated fatty acids
2 or more double bond
linoleic acid
soybean and sunflower
linolenic acid
corn
arachidonic acid
meat, eggs and fish
cis and trans unsaturated fatty acids
can be drawn as cis and trans isomers
almost all naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids have one or more cis double bonds
essential fatty acids
cannot be synthesized by humans due to amount of polysaturated fatty acids
linoleic acid (omega 6)
linolenic acid (omega 3)
arachidonic acid
deficient in linoleate
mild skin scaling, hair loss and poor wound healing in rats
properties of saturated fatty acids
fit close together in a regular pattern
strong dispersion forces between carbon chains
high melting points and solids at room temp
properties of unsaturated fatty acids
cis double bond causes a kink = irregular shape
few interactions between molecules
low melting point
what is prostaglandins and function
hormone-like substances produced in cells
functions: lower or raise blood pressure, stimulate contractions and relax muscle of uterus
prostaglandins also known as
eicosanoids: formed from arachidonic acid
prostaglandins produce
inflammation and pain in a area where tissues are injured
what blocks prostaglandins
NSAIDs
waxes on plants
prevent loss of water and damage from plants
waxes on skin, fur and feathers
provide waterproof coating
waxes structures and parts
esters of saturated fatty acids and long chain alcohols
14-30 carbons
have 3 parts
fatty acid, ester bond, long chain alcohol
beeswax
honeycomb
used for candles
carnauba wax
Brazilian palm tree
used for cars
jojoba wax
jojoba bush
used for soaps, cosmetics
how are fatty acids stored in the body
triacylglycerol
what are triacylglycerols
esters of glycerol and fatty acids
formed when 3 OH groups of glycerol react with carboxyl group of 3 fatty acids. water is removed
naming triacylglycerols
change glycerol to glyceryl
name fatty acids as carboxylates (-oate)
major form of energy storage for animals
triacylglycerols
saturated fatty acid melting point
higher than unsaturated
packed more tightly
melting point of fat and location
solid at room temp
comes from animal sources, meat, milk
melting point of oil and location
liquid at room temp
comes from plant sources
palm and coconut oil
they consist mostly of saturated acids making them solids at room temperature
vegetable oils have low melting points
high percentage of unsaturated fatty acids than animal fats
hydrogenation reaction
double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids react with H2 to make single bonds
H2 is bubbled through heated oil in the presence of a catalyst
commercial hydrogenation
addition of H is stopped before all double bonds are lost
liquid to a soft semisolid fat
more saturated = higher melting point
trans fatty acids through hydrogenation
small number of cis double bonds turn into trans double bonds which are more stable
structure looks like saturated fatty acids
natural trans fatty acids
milk, eggs, beef
trans fatty acids in the body
behave like saturated fatty acids
raise LDL cholesterol (bad)
lowers HDL cholesterol (good)
2-4% of total calories
t/f: there are more unsaturated fats in vegetable oils
true
t/f: vegetable oils have higher melting points than fats
false
t/f: hydrogenation of oils converts some cis double bonds to trans double bonds
true
t/f: animal fats have more saturated fats
true
hydrolysis meaning
act of separating chemicals when water is added
OH replaces the OR2 in the ester: leaves you with an acid and a alcohol
triacylglycerols undergoing hydrolysis
splits into glycerol and three fatty acids
needs a strong acid or enzymes called lipases
types of phospholipids
glycerophospholipids
sphingomyelin
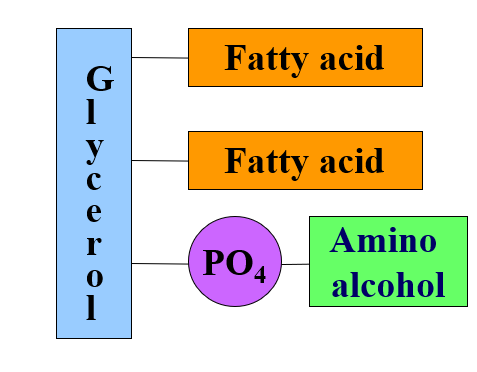
what is in a glycerophospholipid
glycerol
2 fatty acids
phosphate attached to amino alcohol
glycerophospholipids bonds
2 fatty acids that form ester bond with the first and second OH groups of glycerol
hydroxyl group that forms ester with phosphoric acid which forms another phosphoester bond with an amino alcohol
examples of glycerophospholipids and locations
cephalin: brain and nerve tissues
lecithin: egg yolk, soy and yeast
what is in a sphingomyelin
sphingosine (18 carbon amino alcohol) instead of glycerol
fatty acid, phosphate and a amino alcohol
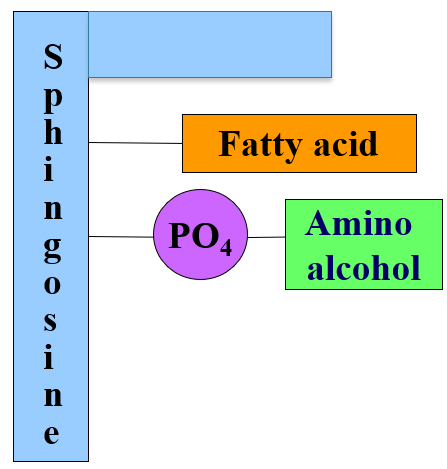
sphingomyelin bonds
amine group of sphingosine forms amide bond to a fatty acid
OH group forms ester bond with phosphate which bonds another phosphoester bond to choline or ethanolamine
where can sphingomyelin be found
abundant in white matter of myelin sheath
coating surrounding nerve cells
increases speed of nerve impulses and insulates and protects nerve cells
steroid nucleus
3 cyclohexane rings and 1 cyclopentane ring
fused
steroid nucleus rings
numbered starting from A
2 methyl groups at 18 and 19
cholesterol
abundant steroid in the body
where cholesterol comes from
diet: meats, milk and eggs
synthesized: in the liver
what is cholesterol needed for
cell membrane, brain and nerve tissue, steroid hormones and vitamin D
clog arteries when in high levels
elevated cholesterol
exceeds 200mg/dL
bile salts found in
synthesized in the liver from cholesterol and stored in gallbladder
large amounts of cholesterol = gallstones in gallbladder
help absorb cholesterol
bile salts characteristics
polar and nonpolar regions - act like soaps to make fat soluble in water
lipoproteins
combined with glycerophospholipids and proteins to form water-soluble complexes
function of lipoproteins
transport nonpolar fats, cholesterol, and triglycerides
surround nonpolar lipid with polar lipid and protein for transport to cells
make them soluble in water
examples of lipoproteins
HDL and LDL aka “high/low density”
changing milk to butter process
transforming fat in water emulsion (milk) to a water in fat emulsion (butter)
whole milk
dilute emulsion of fat globules surrounded by lipoproteins membranes that keep fat separate from each other
steroid hormones
chemical messengers: produced from cholesterol that communicate for the body
male sex hormones
testosterone and androsterone
female sex hormones
estrogens and progesterone
adrenal corticosteroids
from adrenal glands
mineralcorticoids
glucocorticoids
diffusion
aka passive transport
high concentration to a low one
facilitated transport
uses proteins channels that increase rate of diffusion
active transport
moves ions against a concentration gradient
low to high
saponification
reaction of a fat with a strong base in the presence of heat
forms soaps (salts of fatty acids)
saponification reaction
splits triacylglycerols into glycerol and sodium salts of fatty acids
NaOH with fat
solid soaps
KOH with fat
liquid soaps
cold process to make soap
mix fatty acids and lye (NaOH) together
high lye: high pH can burn the skin
not enough lye: greasy soap
takes 6 weeks
hot process to make soap
no exact measurements
soaps vs detergents
soaps: natural but leave a film and need warm water to work
detergents: manmade and leave no residue and preform well in any temp
surfactants
surface active agents
reduce surface tension and improve water ability to spread evenly
hard water and soap
forms scum
detergent vs soap structure
detergent: has a ionic group that is manmade
soap: carboxylic acid group