2.1.2 (a)how hydrogen bonding occurs between water molecules, and relate this, and other properties of water, to the roles of water for living organism
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To include roles that relate to the properties of water; solvent, transport medium, coolant and as a habitat AND roles illustrated using examples of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Learners should be able to apply their knowledge and understanding in the context of prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Importance of water:
A universal solvent – many substances can dissolve in water
It is the medium in which all metabolic reactions take place in cells
It acts as a transport medium
A relatively high specific heat capacity
A relatively high latent heat of vaporisation
Water is less dense when a solid (ice floats on water and can act as a habitat for animals such as polar bears)
Water has high surface tension and cohesion
It acts as a reagent
water molecular properties
2 hydrogen combine with one oxygen molecule by sharing electrons (covalent bonding)
dipole moment: due to oxygen having a higher affinity for electrons,
The oxygen atom attracts the electrons more strongly than the hydrogen atoms resulting in:
a weak negatively charged region on the oxygen atom (δ-)
and a weak positively charged region on the hydrogen atoms (δ+),
this also results in the asymmetrical shape
is a polar molecule
polarity of water:
When a molecule has one end that is negatively charged and one end that is positively charged
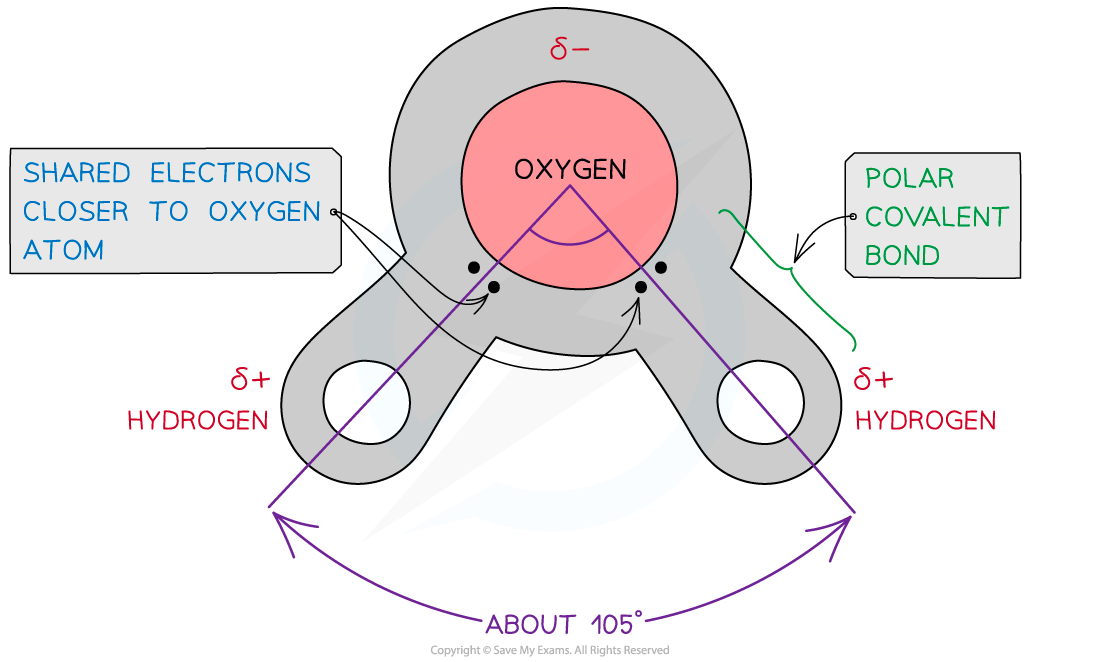
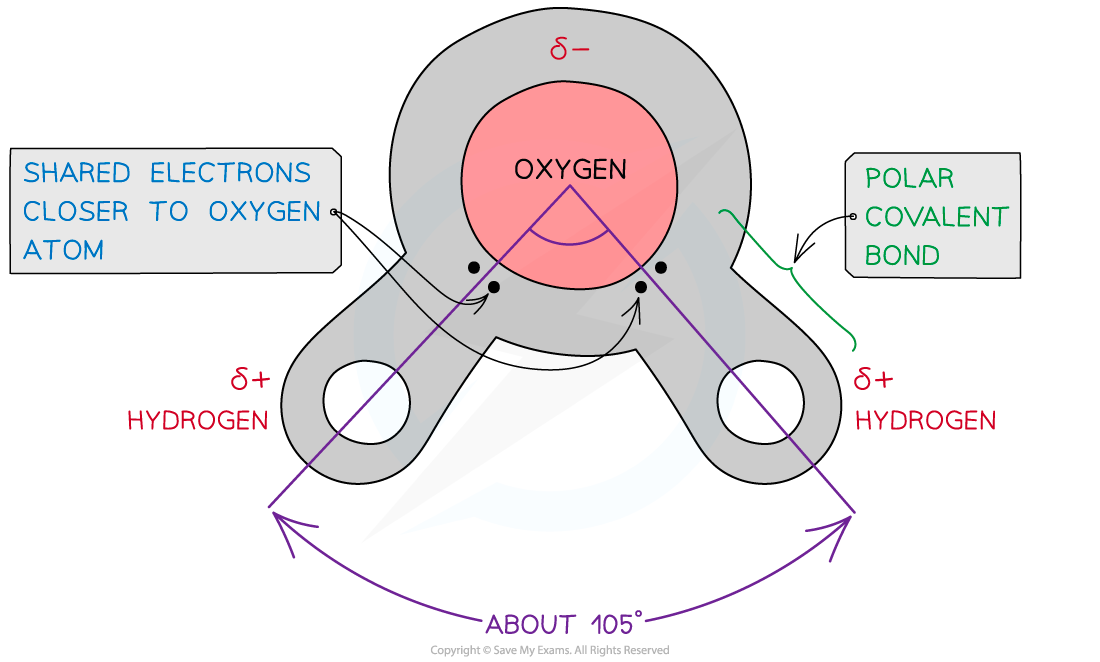
Hydrogen bonding
as a result of the polarity of water:
hydrogen bonds form between the positive and negatively charged regions of adjacent water molecules
Hydrogen bonds are weak, when there are few, so they are constantly breaking and reforming. However when there are large numbers present they form a strong structure

dashed lines between o and h

water as a solvent
As water is a polar molecule many ions (e.g. sodium chloride) and covalently bonded polar substances (e.g. glucose) will dissolve in it
because the slightly positive end of water will be attracted to the negative ion (chloride) and the negative end to the positive sodium ion - getting totally surrounded by water molecules
This allows chemical reactions to occur within cells
(as the dissolved solutes are more chemically reactive when they are free to move about)
Metabolites can be transported efficiently (except non-polar molecules which are hydrophobic)
This process allows prokaryotic cells to exchange substances,
such as nutrients and waste products, with their surroundings
via the process of diffusion
specific heat capacity
The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of thermal energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of that substance by 1°C
Water’s specific heat capacity is 4200 J/kg°C meaning a relatively large amount of energy is required to raise its temperature
this is due to the many hydrogen bonds present in water. It takes a lot of thermal energy to break these bonds and a lot of energy to build them, thus the temperature of water does not fluctuate greatly
advantages of specific heat capacity
Provides suitable stable habitats in aquatic environments such as in lakes and the ocean
Is able to maintain a constant temperature
which is vital in maintaining temperatures that are optimal for enzyme activity in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Water in blood plasma is also vital in transferring heat around the body, helping to maintain a fairly constant temperature
As blood passes through more active (‘warmer’) regions of the body, heat energy is absorbed but the temperature remains fairly constant
Water in tissue fluid also plays an important regulatory role in maintaining a constant body temperature
high latent heat of vaporisation
In order to change state (from liquid to gas) a large amount of thermal energy must be absorbed by water to break the hydrogen bonds and evaporate
This is an advantage for living organisms as only a little water is required to evaporate for the organism to lose a great amount of heat
This provides a cooling effect for living organisms
for example the transpiration from leaves or evaporation of water in sweat on the skin
cohesion and adhesion
Hydrogen bonds between water molecules allows for strong cohesion between water molecules
This allows columns of water to move through the xylem of plants and through blood vessels in animals
This also enables surface tension where a body of water meets the air, these hydrogen bonds occur between the top layer of water molecules to create a sort of film on the body of water (this is what allows insects such as pond skaters to float)
Water is also able to hydrogen bond to other molecules, such as cellulose, which is known as adhesion
This also enables water to move up the xylem due to transpiration
Lower density when solid
when water becomes ice,
water molecules are held further apart because each water molecule forms 4 fixed hydrogen bonds to other water molecules making a lattice shape.
this makes ice less dense then liquid water, which is why ice floats
this is useful for living organisms because in cold temperatures ice forms an insulating layer on top of water
allowing the organsism below to move around and not freeze