+AP US History 1st Quarter Mid-Term Study Set
1/172
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Original quizlet study set by Mark_VanOver9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
Federalist Party
First American political party formed led by Alexander Hamilton. They were in support of the Constitution, as it gave the government more power. They believed in national banks, tariffs, an elite ruling class, and good relations with Britain. They had major influences and impacts on out national government and its debt.

Anti-Federalists
A group of members that opposed the creation of a stronger US federal government and the Constitution. They were led by Patrick Henry and Thomas Jefferson. They believed in a weak central government and strong state governments. They supported small farmers and landowners. They helped in preventing the Federalists from creating a political system like that of the British.

Democratic Party
A political party that favors greater government action than its conservative opposition does, to direct and promote the welfare of the people in the republic it often governs. Formed by supporters of Andrew Jackson

Republican Party
A political party that believed in equality among all men during the Civil War. They strongly opposed slavery. They favored national government. They were a voice against slavery.

Whig Party
were conservatives who supported government programs, reforms, and public schools. They called for internal improvements like canals, railroads, and telegraph lines.

1796 Election
Thomas Jefferson vs. John Adams. John Adams becomes President, Thomas Jefferson becomes vice-president

1800 Election
Election for presidency between Thomas Jefferson and John Adams, with Jefferson pulling the win. Federalist John Adams was removed from office, so it is considered a Revolution, a great advantage for the Republicans. It ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican rule and the eventual demise of the Federalist Party.

Marbury v Madison 1803
William Marbury had not had his commission delivered by Adams. Even though this was illegal on Adams part, Congress could not force Marbury to bring the documents. The court was able to form a basis for exercise of judicial review. It defined the boundary between the constitutionally separate executive and judicial branches. (date)

McCulloch v Maryland 1819
Maryland attempted to impede operation of a branch of the second bank of the US by imposing a tax on all notes of banks not chartered in Maryland. It established that Congress could implement the Constitution's powers, and state action couldn't impede valid constitutional exercises of power by the government. (date)

Gibbons v Ogden 1824
This case involved New York trying to grant a monopoly on waterborne trade between New York and New Jersey. Judge Marshal, of the Supreme Court, sternly reminded the state of New York that the Constitution gives Congress alone the control of interstate commerce. Marshal's decision was a major blow on states' rights. (date)

Amistad
Spanish slave ship dramatically seized off the coast of Cuba by the enslaved Africans aboard; the ship was driven ashore in Long Island and the slaves were put on trial; former president John Quincy Adams argued their case before the Supreme Court, securing their eventual release

Dred Scott v Sanford 1857
A slave went to court to try and get his citizenship and become free. The Court at first supported him, but then the Court decided they could not do anything because the slave was property. It showed that even though slaves had more rights now, they were still owned. (date)

Plessy v Fergusson
case ruled that "separate but equal" public facilities were legal. reversed in Brown v Board of Ed. Racial segregation

Appalachians to the Mississippi
Area of expansion in the eighteenth and early nineteenth century.
Louisiana Purchase 1803
The acquisition by the USA of France's claim to the territory of Louisiana. They paid $15 million. It doubled the size of the US, removed France's presence in the region, and it protected US trade access and free passage. (date)

Florida
a state in southeastern United States between the Atlantic and the Gulf of Mexico, Owned by Spain, sold to US in pieces. The last and largest piece is Florida's peninsula sold in 1819

Mississippi River
Louisiana Purchase made America gain control of this. It provided means to get their goods to coastal markets.

36 30 line
As a part of the Missouri Compromise, this line was drawn in the Louisiana Territory, which divided the North and South
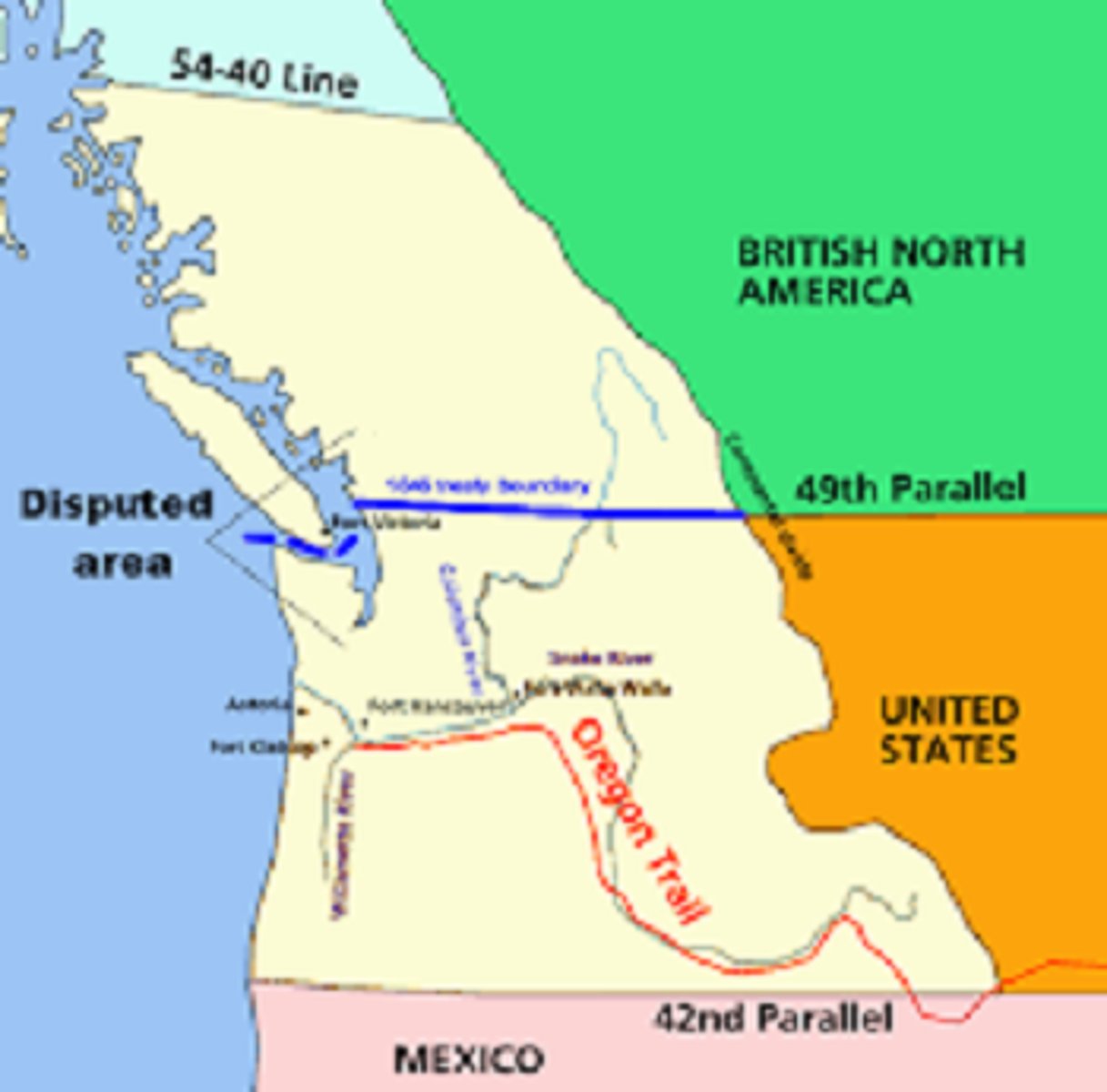
54 40 or fight
Slogan used by Polk during the presidential elections of 1844 pronouncing his support for a US-owned Oregon with a border at 54' 40. Settled for 49' in 1846
Erie Canal
A canal in New York running from Albany to Buffalo. It created a navigable water route from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes which gave the western states direct access tot he ocean without shipping goods downstream on Mississippi River.
Rio Grande River
Mexico refused to sell California to US thinking that Texas' southern border was on the Nueces River; Polk and special envoy to Mexico City John Slidell, asserted that the border of TX is to the south.
Anne Hutchinson
Puritan spiritual adviser involved in Antinomian Controversy. She suggested that she experienced divine inspiration independently of the Bible or the clergy. She claimed to have received revelation. Antinomianism.

XYZ Affair 1797
An American diplomatic commission was sent to France to negotiate problems that were threatening to break out into war, approached by agents who demanded bribes and a loan before formal negotiations could begin. It led to an undeclared war called the Quasi-War. (date)

Boston Massacre 1770
The killing of five colonists by British regulars. It was the culmination of the tensions in the American colonies. It made many colonists rally together to counter the evil British. Changed people's mind about the British. (date)

Seneca Falls Convention 1848
The first women's rights convention that advertised itself as a convention to discuss the social, civil, and religious condition and rights of women. It was seen as a continuing effort by women to gain for themselves a greater proportion of social, civil, and moral rights. (date)

Panic of 1837
A financial crisis in the US that touched off a major recession. Profits, prices, and wages went down while unemployment went up. Americans had to withdraw specie from domestic banks to pay commercial debts. Banks stopped trading specie and curtailed debts.

Great Awakening
Religious Revival and evangelical religious movements in the 18th and 19th centuries. Spiritual renewal that swept the American colonies. It prepared America for its War of Independence and it taught people to be bold when confronting religious authority.

Sons of Liberty
Successful colonial american group formed to protect the rights of the colonists and to take to the streets against the abuses of the British government. They undertook the Boston Tea Party. They played a key role in uniting the colonies in the struggle for independence.

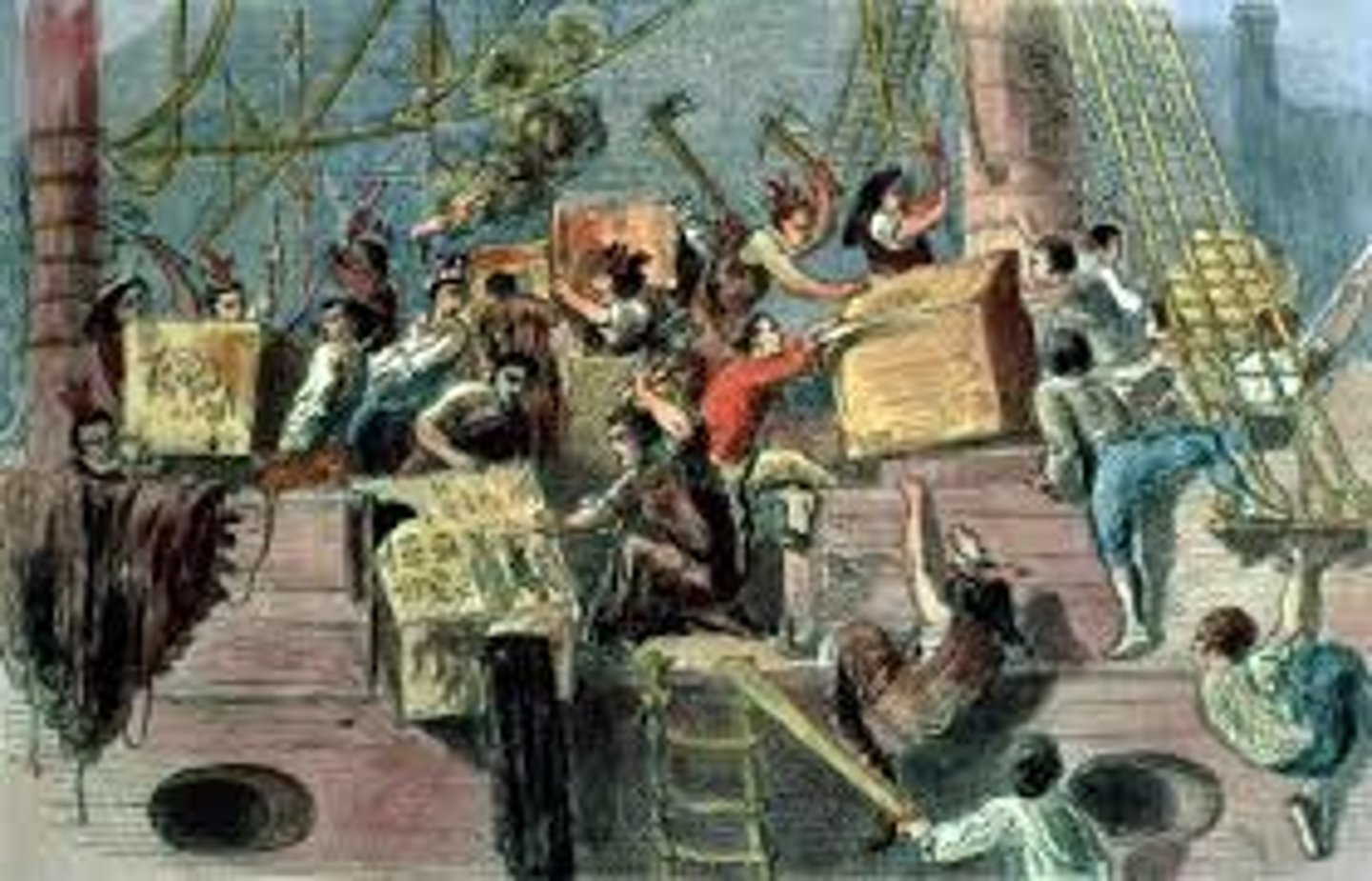
Boston Tea Party 1773
Political protest by the Sons of Liberty. They destroyed an entire shipment of tea sent by the East India company in defiance of the Tea Act by throwing the chests into the sea. It showed that the American colonies had grown tired of arbitrary taxation by the British. (date)

Popular Sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people. The people are able to vote for if they want slavery or not.

Second Great Awakening
A Protestant revival movement as a reaction against skepticism, deism, and rationalism. It enrolled new members in existing denominations and led to the formation of new denominations. It revived the emotional side of religion, weakened church authority, and played a role in social reform.

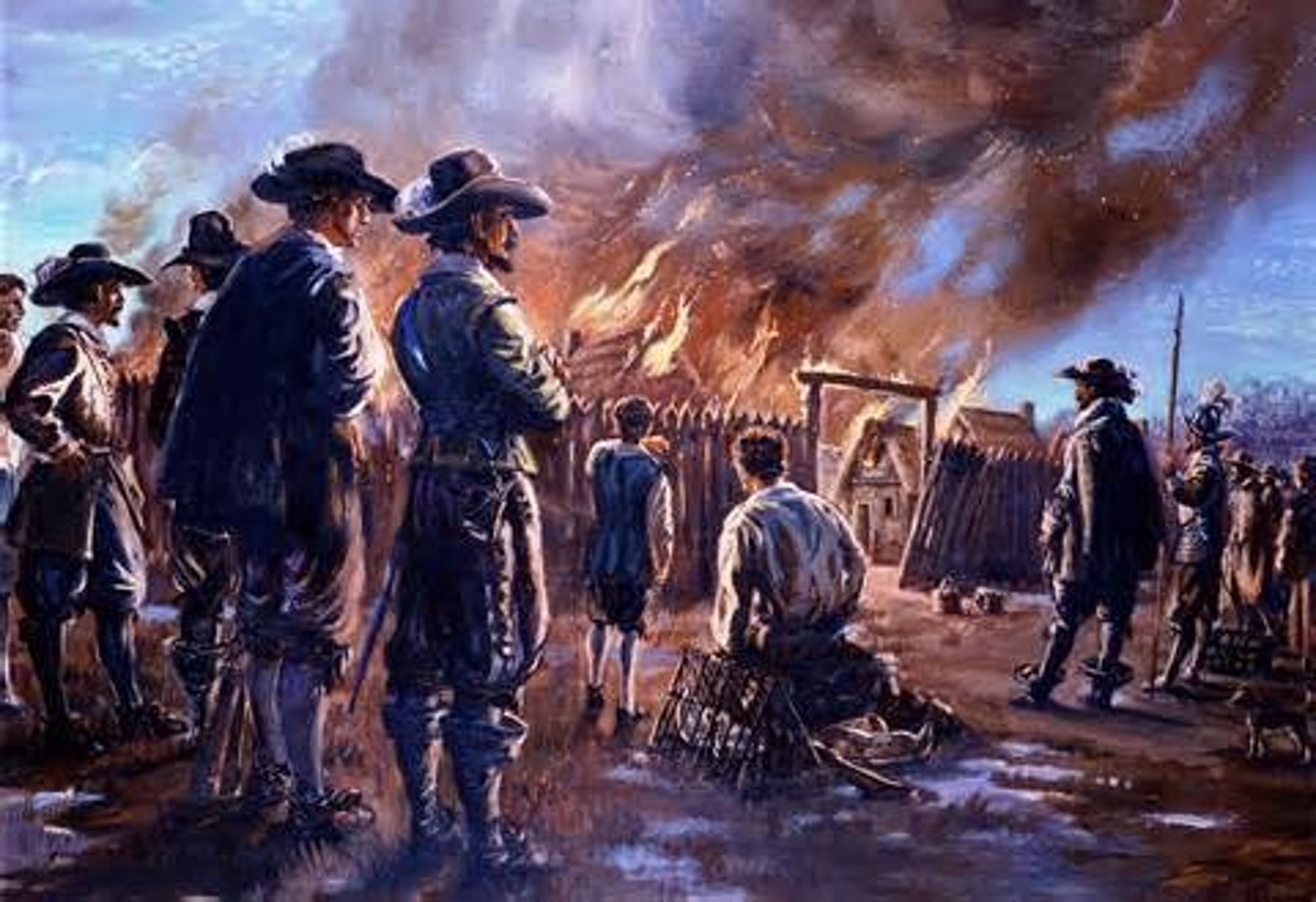
Bacon's Rebellion 1676
A rebellion led by Nathaniel Bacon against the rule of governor, William Berkeley. Bacon was upset about him not being involved in fur trade, and other followers. (Date)

French and Indian War 1754-1763
Fought between the colonies of British America and New France, supported by military units from their parent countries. Hostilities intensified between the two as they both attempted to colonize land in the Ohio Valley. It marked the beginning of conflicts between Great Britain and the American colonists. (Dates)
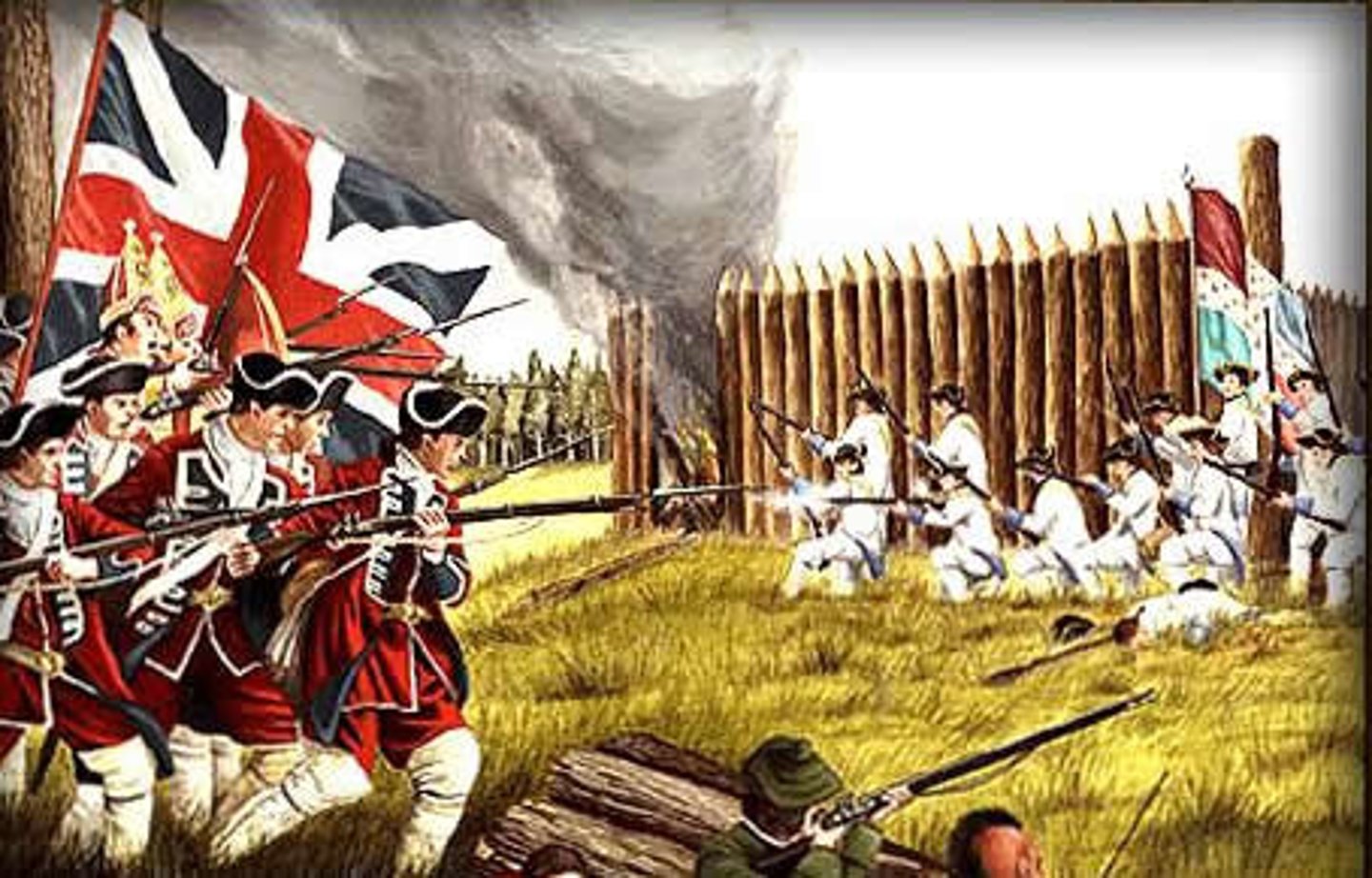

Revolutionary War 1775-1783
War fought between the American colonies and England. American colonies won war and gained independence and British land in North America. (date)
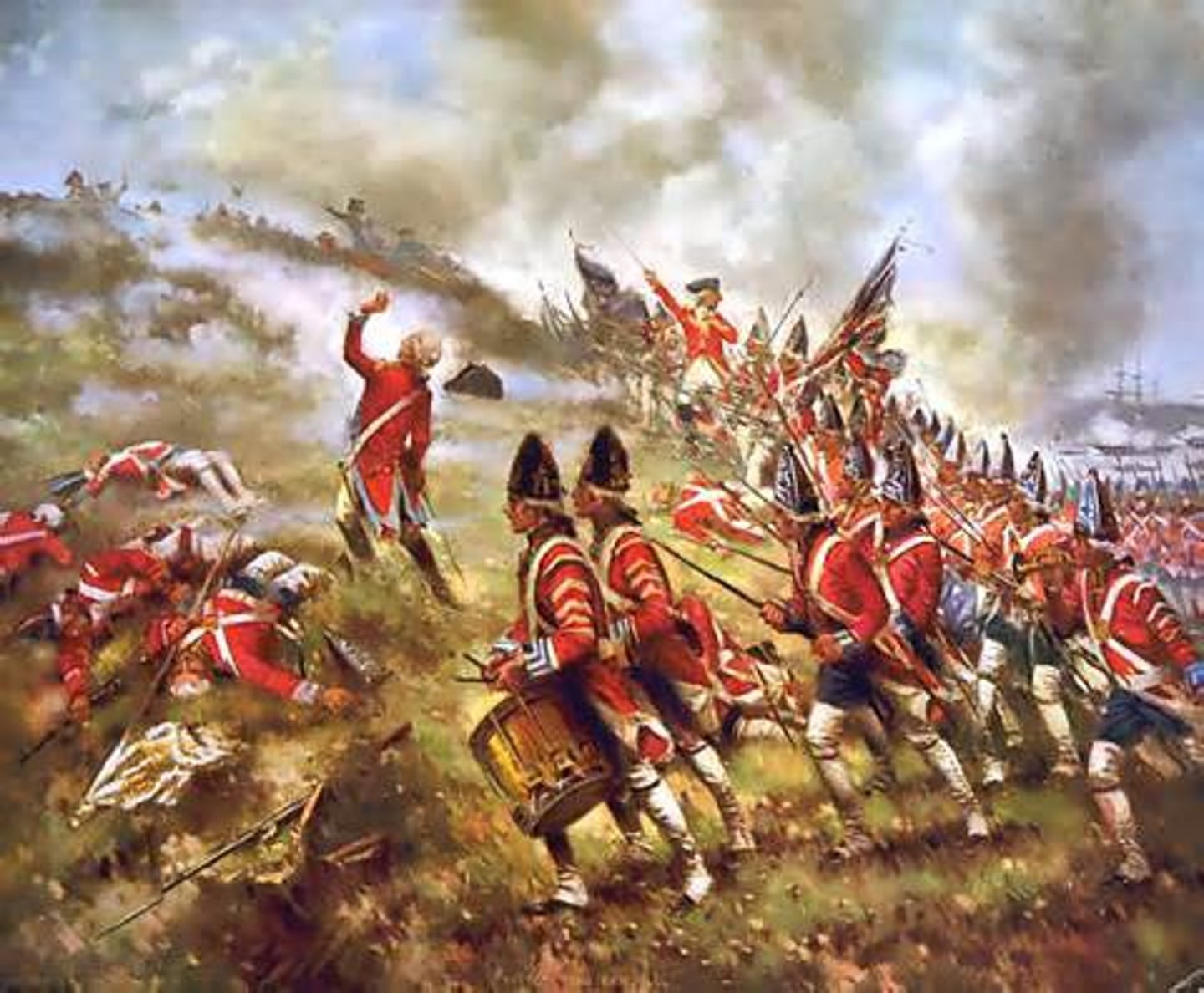

Shay's Rebellion 1787
A rebellion in which ex-Revolutionary War soldiers attempted to prevent foreclosures of farms as a result of high interest rates and taxes. (date)

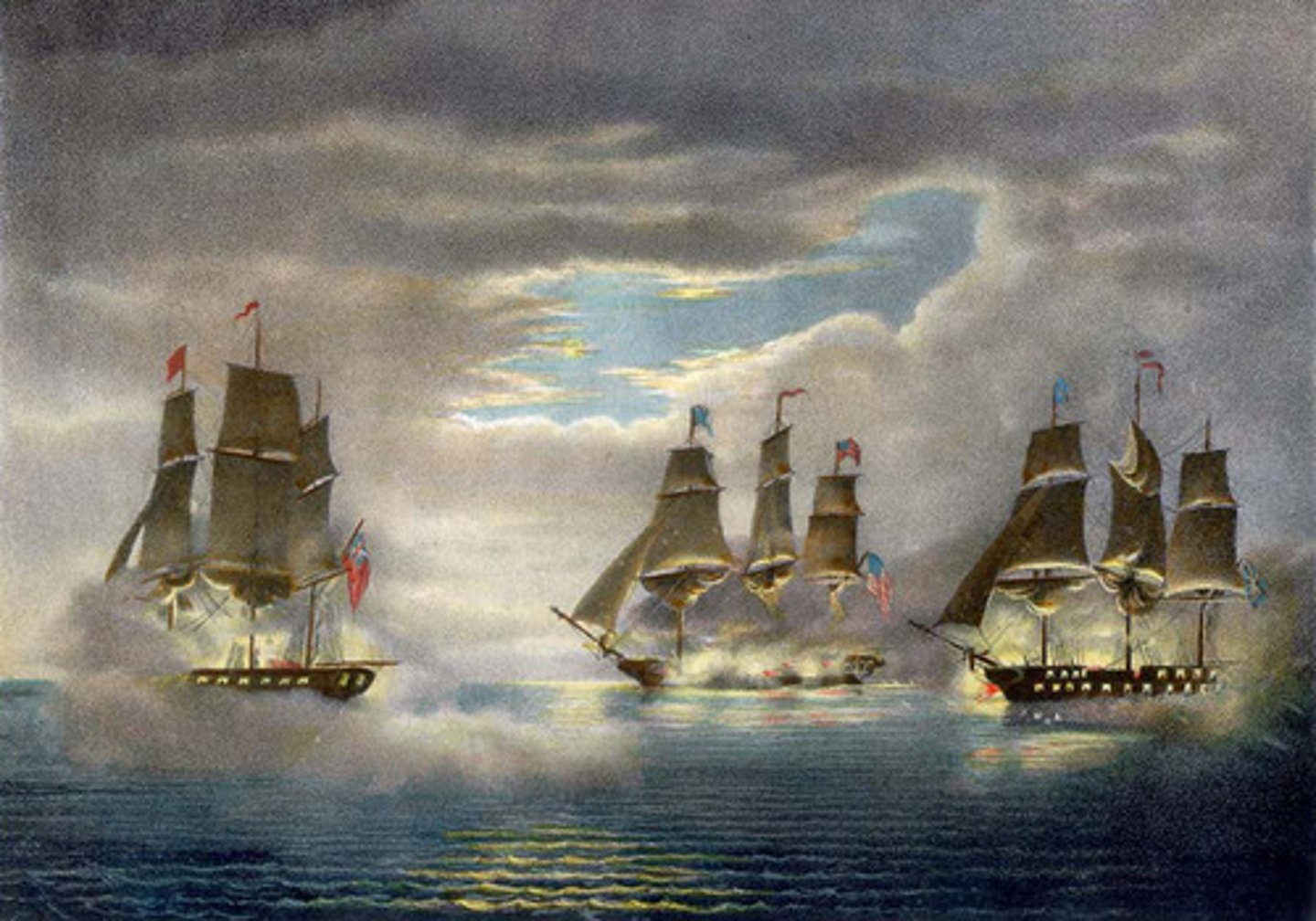
War of 1812
A military conflict between US and Britain brought about by trade restrictions, presentiment of sailors, British support of Indians, and interest in annexing territory. It resolved many issues which remain from the Revolution. Us proved that it had a right to be its own country.

Nullification Crisis
A sectional crisis with an ordinance declared by the power of the state that the Tariffs of 1828 and 1832 were unconstitutional and therefore void in South Carolina. It showed that the economic and political interests of the North and South were drifting, as they had opposing ideas.

Lexington and Concord Battle
"The Shot Heard Round the World"- The first battle of the Revolution in which British general Thomas Gage went after the stockpiled weapons of the colonists in Concord, Massachusetts.

Mexican-American War 1846
An armed conflict between the US and Mexico that started with the US annexation of Texas and was the result of a disagreement over where the Mexican-American border should be. the US received Mexican territory and it raised the question of slavery in the new territory. (date)

Saratoga Battle
A battle that took place in New York where the Continental Army defeated the British. It proved to be the turning point of the war. This battle ultimately had France to openly support the colonies with military forces in addition to the supplies and money already being sent.

Yorktown Battle
A win of the americans when the Americans set a trap for the British and General Cornwallis surrenders.
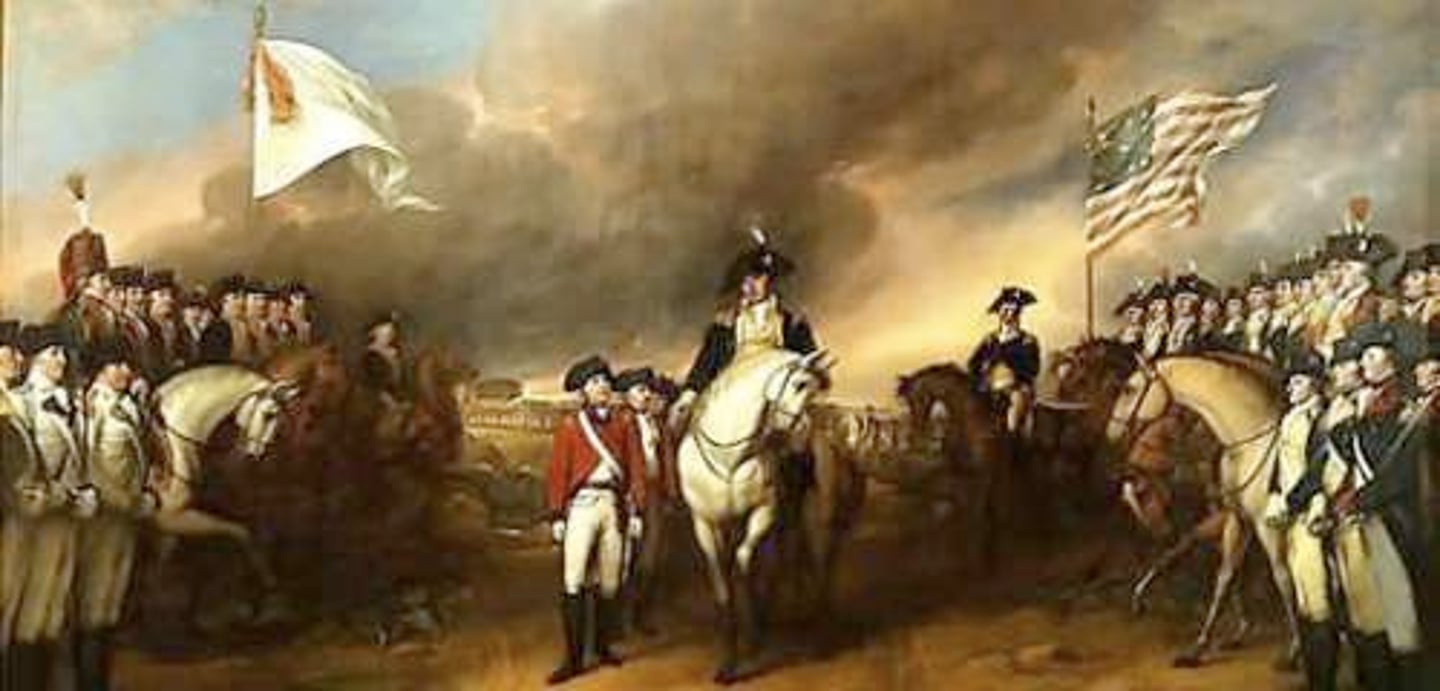

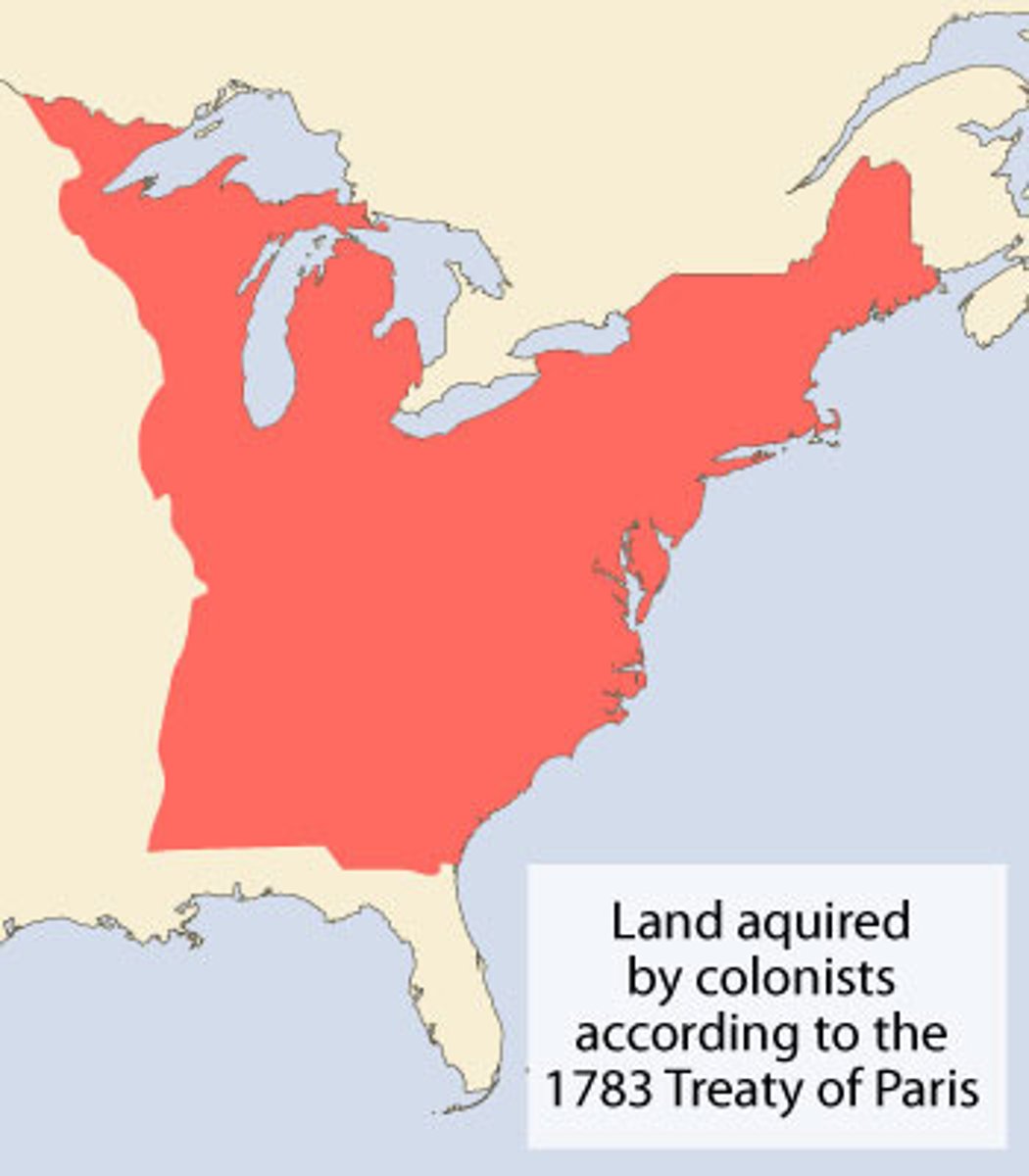
Treaty of Paris 1783
It ended the American Revolution between Great Britain and the USA. It allowed enlarged boundaries for the USA. This was important because it ended the war, and began independence for the US. (date)
Washington's Farewell Address
A letter written by George Washington. It is a statement of republicanism, warning Americans of the political dangers they must avoid if they are to remain true to their values.

Jay's Treaty 1794
A treaty between the US and Britain to avert war, resolve issues remaining with the Treaty of Paris, and facilitate 10 years of peaceful trade between the two countries. It created a tremendous uproar, as it failed to settle the issue of the British presentment of American merchant sailors. (date)

Embargo Act 1807
It made illegal any exports from the US. It was sponsored by Jefferson. The goal was to force Britain and France to respect American rights during the Napoleonic Wars. It increased capital and labor in the New England textile and other manufacturing industries, lessening America's reliance on England. (date)

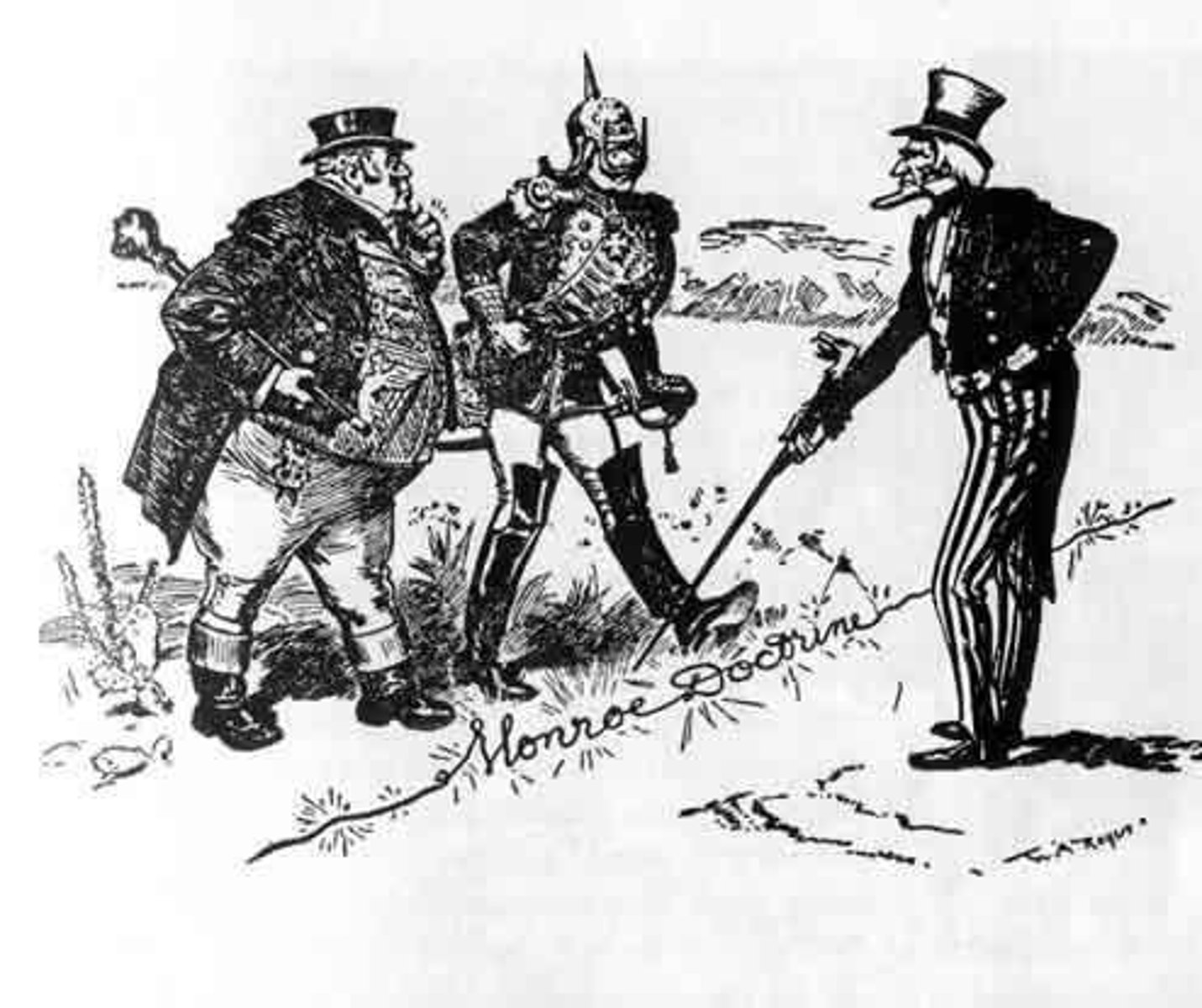
Monroe Doctrine 1823
A US foreign policy regarding Latin American countries. It stated that further efforts by European nations to colonize land or interfere with states in North or South American would be viewed as acts of aggression. It directed a clear warning towards all foreign countries telling them to leave the US alone and to stop settling within the country's borders. (date)

Articles of Confederation 1781
Document signed among the 13 colonies to establish the USA as a confederation of sovereign states and serve as the first constitution. It provided direction for the Revolution, the ability to conduct diplomacy with Europe, and deal with territorial issues and Native American relations. (date)
Constitutional Convention 1787
A meeting in Philadelphia that produced a new constitution (date)

Bill of Rights
The first ten amendments to the Constitution. They guarantee a number of personal freedoms, limits the government's power in judicial and other proceedings, and reserve some powers to the states and the public.

New Jersey Plan
A constitutional proposal that would have given each state one vote in a new congress

3/5 Compromise
3 out of every 5 slaves will be counted as one citizen in order to determine representation in House of Representatives

The Great Compromise
A state's representation in the House of Representation would be based on population; Two senators for each state; all bills would originate in the house; direct taxes on states were to be assessed according to population

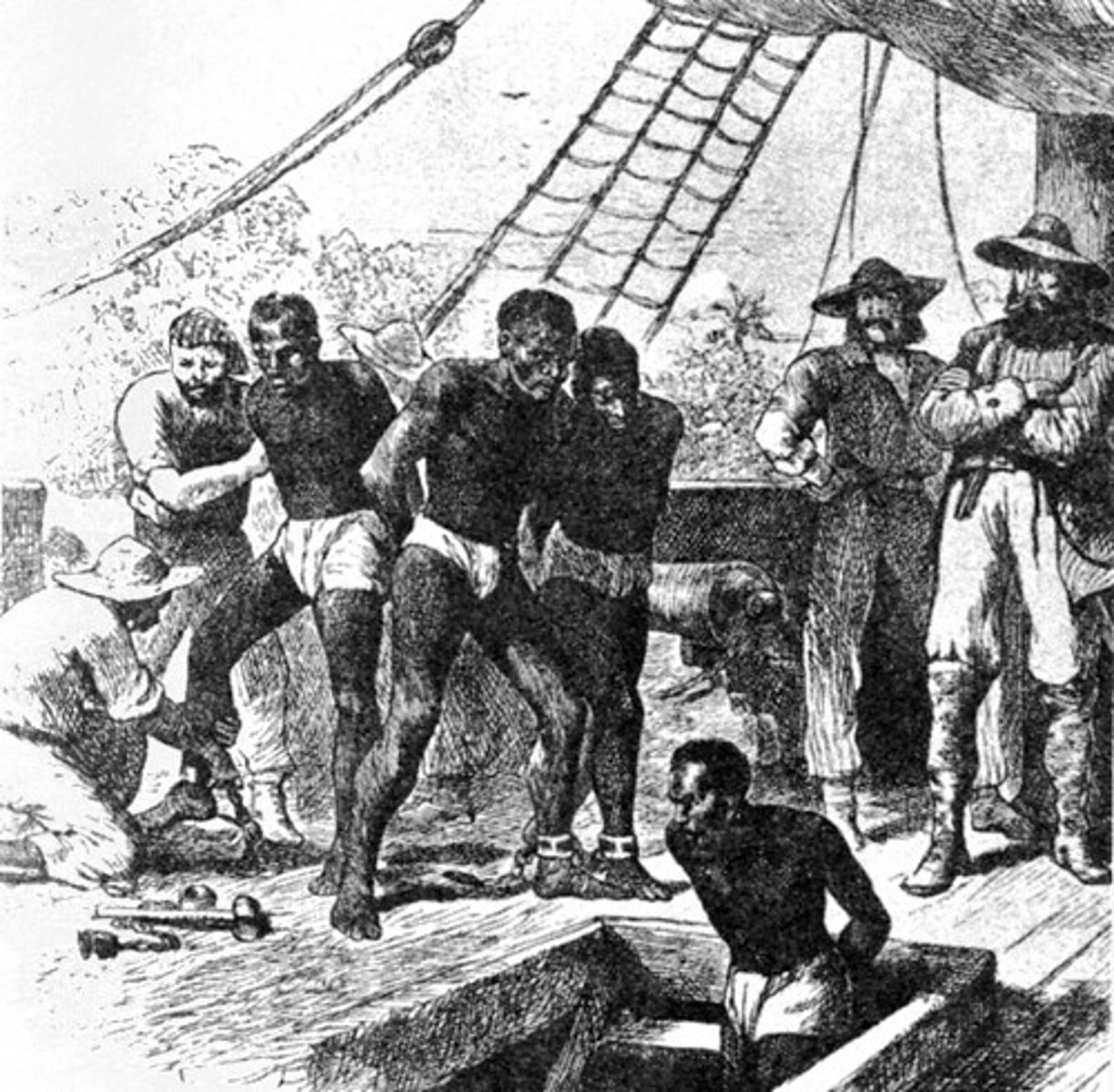
Slave Trade
European trade agreement with Africa dealing with slaves brought from Africa. Integral part of Triangle Trade between the Americas, Africa, and Europe.

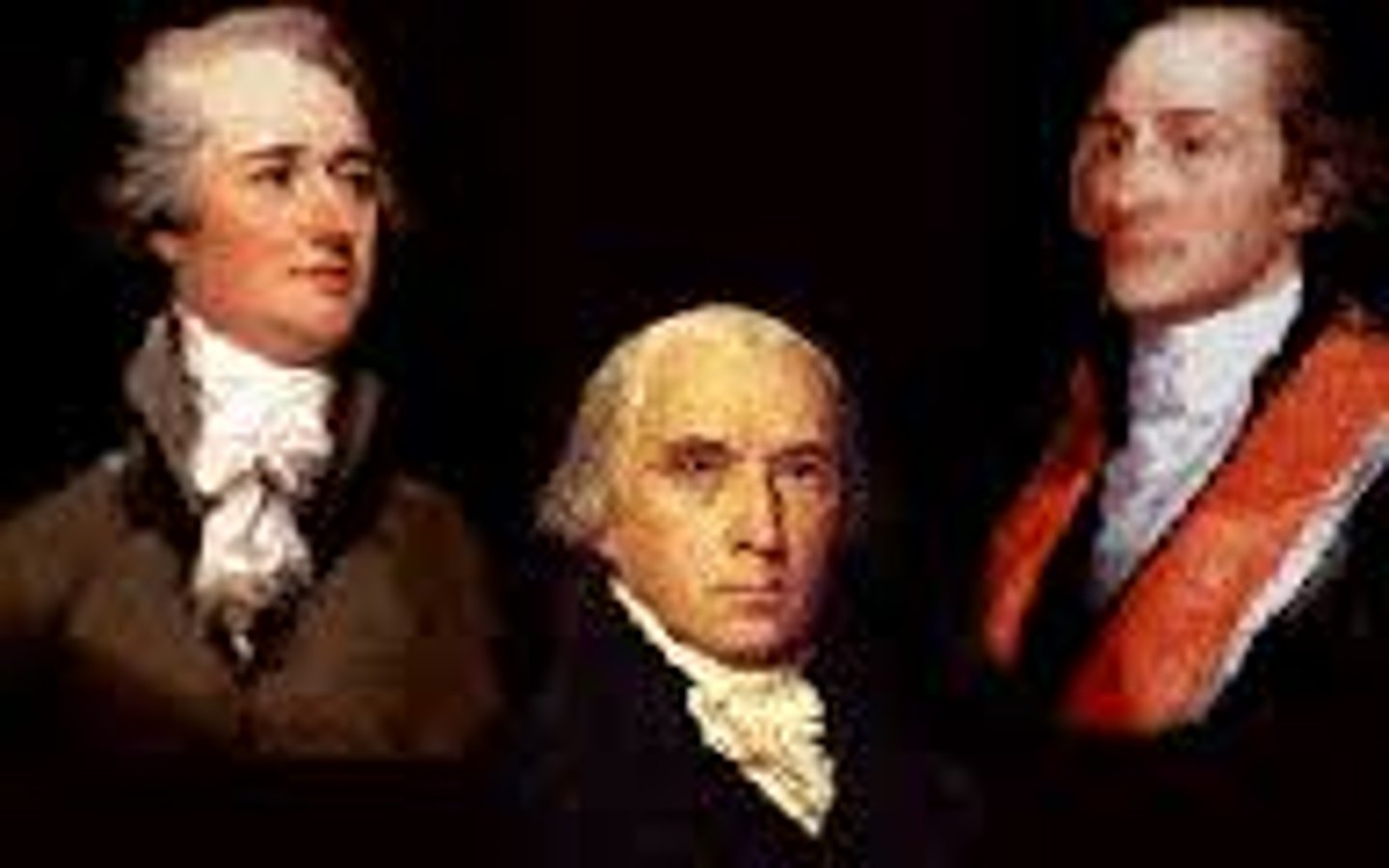
Federalist Papers
A collection of articles and essays written by Hamilton, Madison, and Jay promoting the ratification of the Constitution. They outlined the form of government preferred by the Federalists and persuaded other states to ratify the Constitution.

Amendment 12 1804
Changes in manner of electing president and vice president; procedure when no presidential candidate receives electoral majority (date)

Ratification
An official approval.

Checks and Balances
A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power.

Executive Branch
Branch of government that enforces the laws

Legislative Branch
Branch of Gov't charged with creation of new laws.

Judicial Branch
Government department that interprets laws

English Bill of Rights 1689
King William and Queen Mary accepted this document. It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently. By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people. (date)

John Locke
English philosopher and physician regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers. He affected the development of epistemology and political philosophy. He contributed to the Enlightenment.

Navigation Acts
Laws that governed trade between England and its colonies. Colonists were required to ship certain products exclusively to England. These acts made colonists very angry because they were forbidden from trading with other countries.

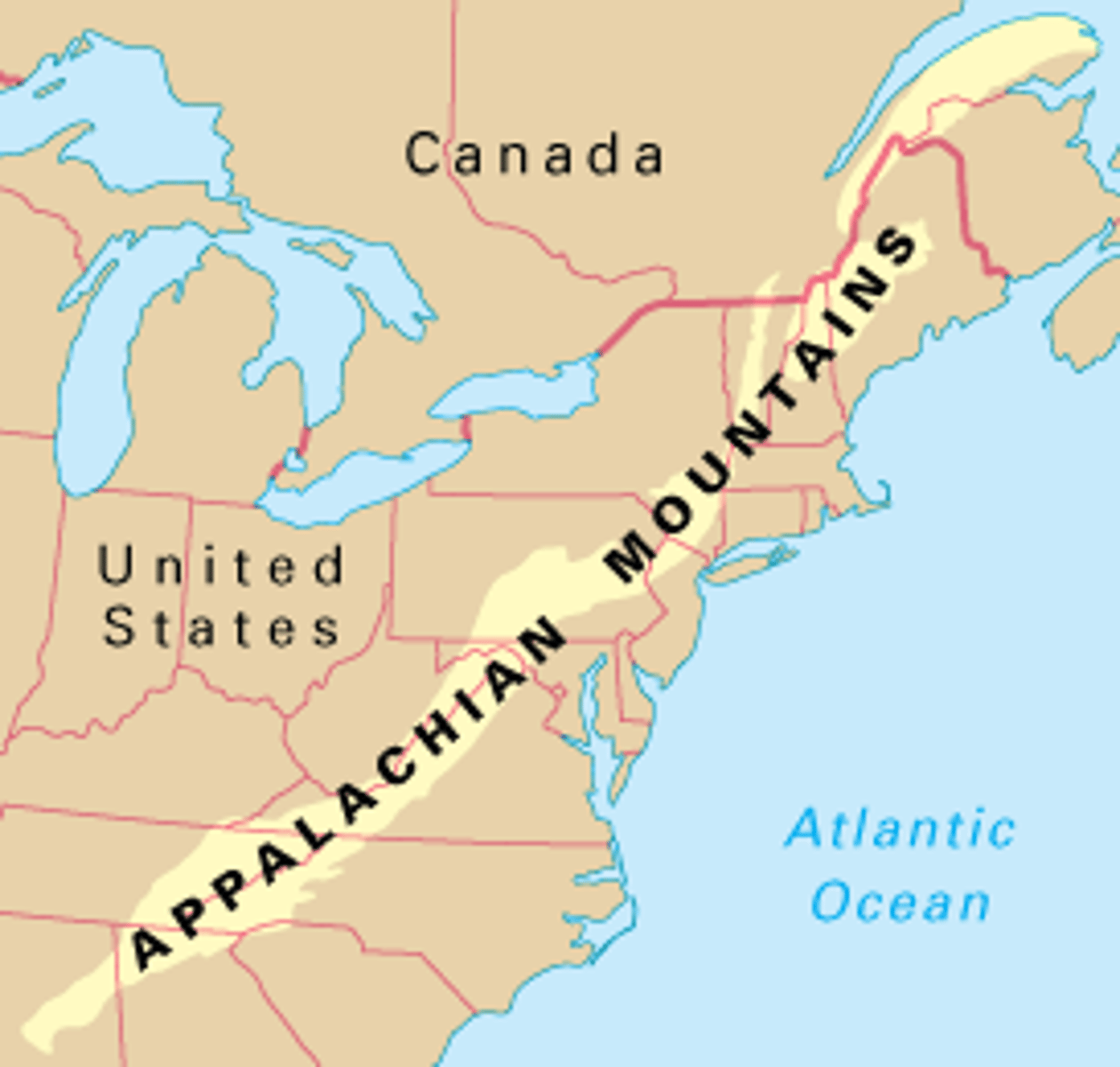
Proclamation Act 1763
Issued by King George III following Great Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America. It forbade settlers from settling past a line drawn along the Appalachian Mountains. It organized Britain's empire and stabilized relations with Native Americans through trade, settlement, and land purchases. (date)
Sugar Act 1764
It reduced the tax to three pence (previously six pence). The tax was more enforced and it occurred on other goods like wine, coffee, and calico. It raised revenue for Britain through American colonists, not Europeans. (date)

Stamp Act 1765
An act of the Parliament of Great Britain that required the colonies have printed materials be produced on stamp paper. These were legal documents. It helped British troops who were stationed in North America, as the taxes went to their benefit. This angered the colonists. It was considered the last straw, leading to the Revolution. (date)

Decarlatory Act
Repealed Stamp act due to massive boycotts on all trade. Said that congress has the same power in Britain as they do in America

Judiciary Act 1789
A law that established the federal court system and the number of Supreme Court justices and that provided for the appeal of certain state court decisions to the federal courts

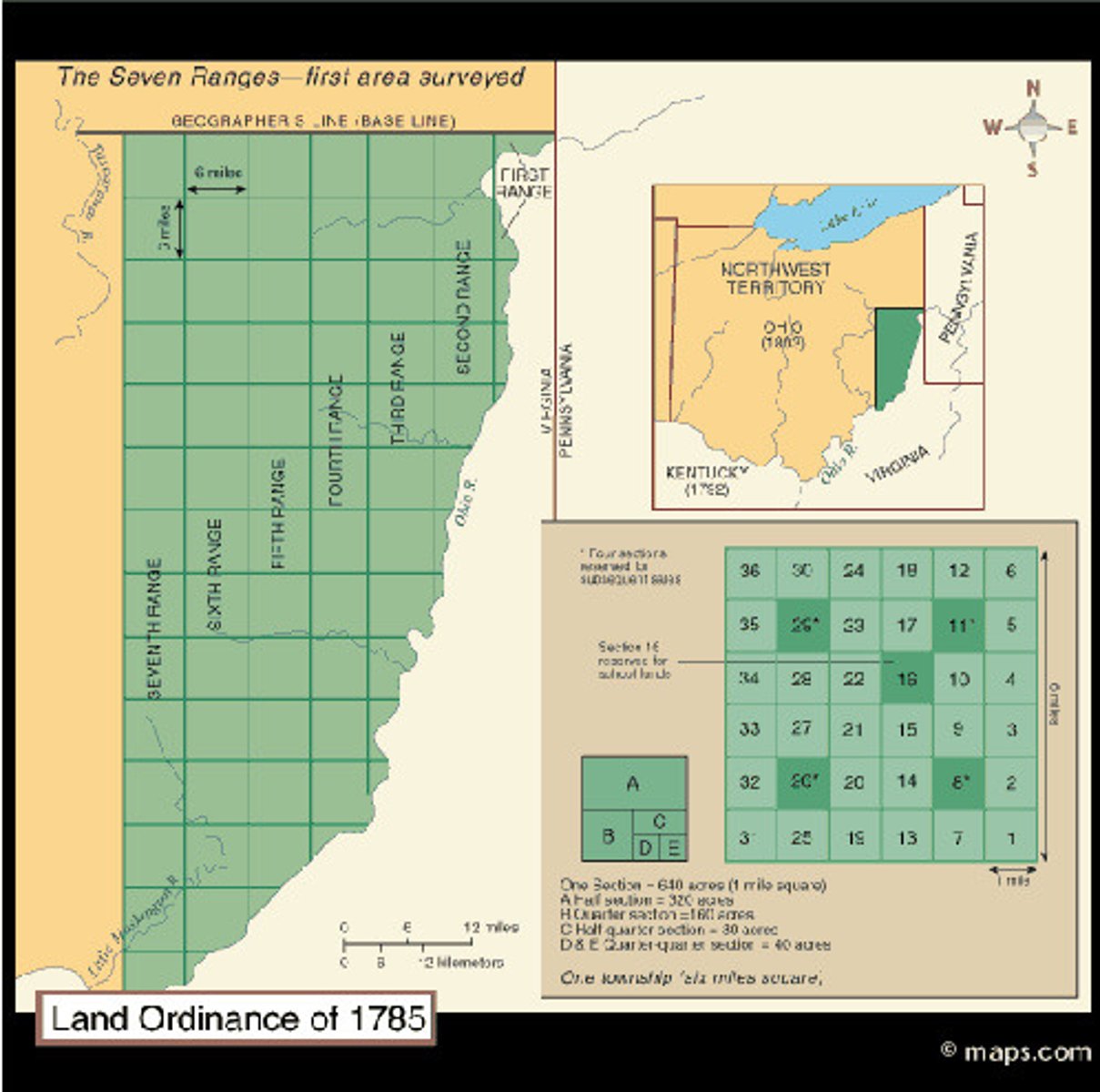
Land Ordinance 1785
The goal was to raise money through the sale of land in the territory west of the states. It was important because it established the precedent by which the US would expand westward across North America by the admission of new states. (date)
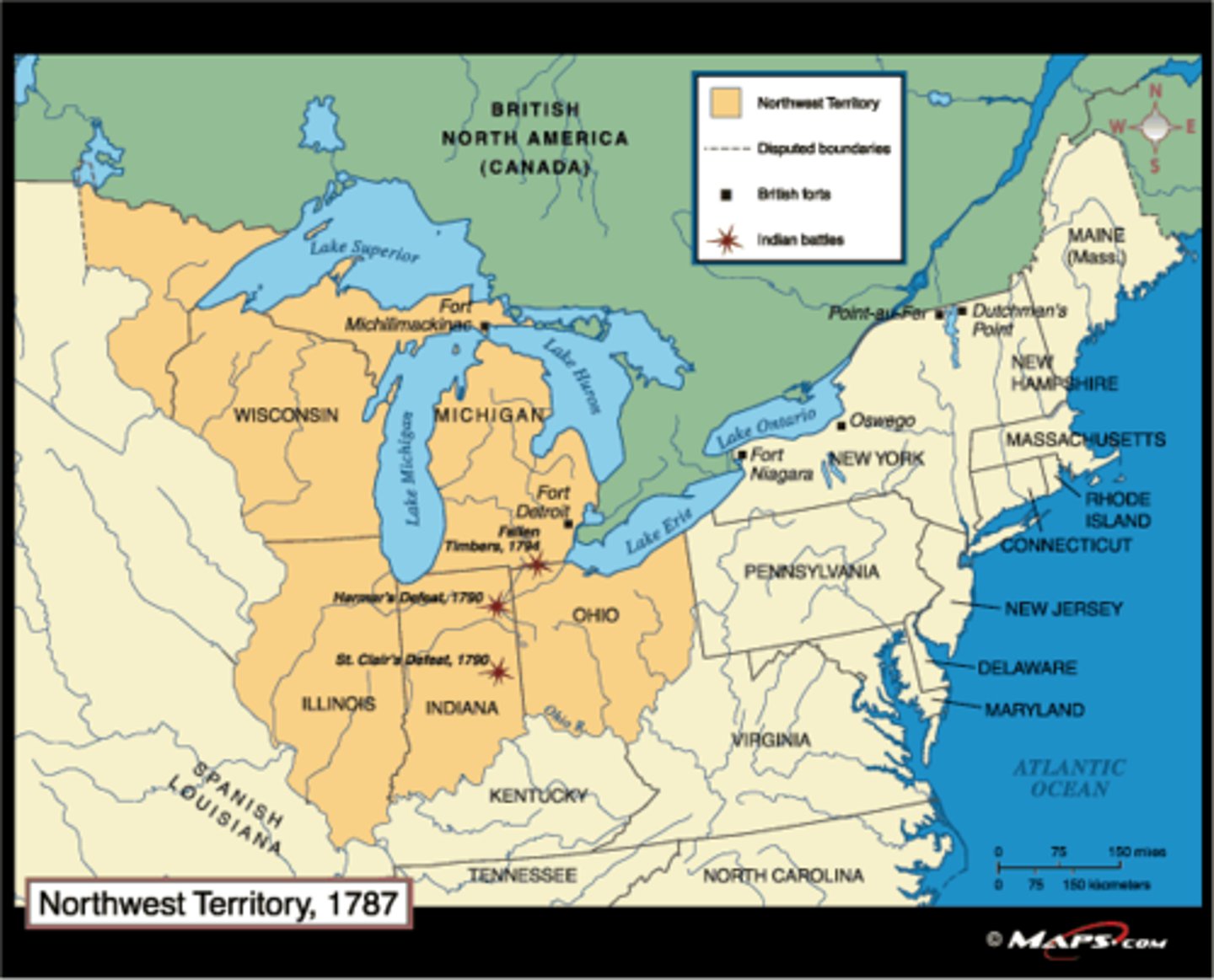
Northwest Ordinance 1787
It created the Northwest territory from lands beyond the Appalachian Mountains, between Canada and the Great Lakes. Rather than the expansion of existing states and their established sovereignty, it establish admission for new states. (date)
Bank of the United States
The central bank of the nation designed to facilitate the issuance of a stable national currency and to provide a convenient means of exchange for the people. The bank was responsible for providing the nation economic stability.

Compromise of 1850
This admitted California as a free state while it also created fugitive slave laws to capture escaped slaves. It created a way for slaves to not be able to go to the North and be free. The North had to help the South.

Intolerable Acts 1774
A series of laws passed by the British Parliament after the Boston Tea Party intending to punish the Massachusetts colonists for their defiance. It was a wake up call for the colonies. The Boston harbor closed. England took over all governmental activities. (date)
Virginia Resolution 1798
Interposition to express the idea that the states have a right to interpose to prevent harm caused by unconstitutional laws. It let states decide the constitutionality of passed laws and it favored states' rights. (date)
Missouri Compromise 1820
It involved primarily the regulation of slavery in the western territories. It prohibited slavery in the Louisiana Territory north of the southern Missouri border. It became precedent for settling subsequent North and South disagreements over slavery and duty issues. (date)
John Smith
English explorer who helped found the colony at Jamestown, Virginia
John Rolfe
He was one of the English settlers at Jamestown (and he married Pocahontas). He discovered how to successfully grow tobacco in Virginia and cure it for export, which made Virginia an economically successful colony.
Pocahontas
A Powhatan woman (the daughter of Powhatan) who befriended the English at Jamestown and is said to have saved Captain John Smith's life (1595-1617)
Powhatan
An Indian chieftain who dominated the peoples in the James River area. All the tribes loosely under his control came to be called Powhatan's confederacy. The colonists inaccurately called all of the Indians Powhatan.
William Bradford
A Pilgrim, the second governor of the Plymouth colony, 1621-1657. He developed private land ownership and helped colonists get out of debt. He helped the colony survive droughts, crop failures, and Indian attacks.
Squanto
Native American who helped the English colonists in Massachusetts develop agricultural techniques and served as an interpreter between the colonists and the Wampanoag.
William Penn
An English real estate entrepreneur, philosopher, and early Quaker. This man was significant because he fought religious oppression and founded the colony of Pennsylvania (1681).
William Berkeley
A Governor of Virginia, appointed by King Charles I, of whom he was a favorite. He was governor from 1641-1652 and 1660-1677. Berkeley enacted friendly policies towards the Indians that led to Bacon's Rebellion in 1676.
John Winthrop
A wealthy English Puritan lawyer. He was one of the leading figures in the founding of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, and the first governor of that region.
Pontiac
an Ottawa chief who opposed British expansion into the western Ohio Valley and began destroying British forts in a rebellion.
Patrick Henry
American attorney, planter, and politician, who became known as an orator during the movement for independence in Virginia in the 1770s. He led the opposition to the Stamp Act. Give me liberty or give me death.
Thomas Jefferson
..., Virginian, architect, author, governor, and president. Lived at Monticello. Wrote the Declaration of Independence. Second governor of Virgina. Third president of the United States. Designed the buildings of the University of Virginia.
George Washington
1st President of the United States; commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution (1732-1799)
Benjamin Franklin
A delegate from Pennsylvania and proposed the "Albany Plan of the Union" as a way to strengthen colonies.
John Adams
America's first Vice-President and second President. Sponsor of the American Revolution in Massachusetts, and wrote the Massachusetts guarantee that freedom of press "ought not to be restrained."
Abigail Adams
She is important because of the many letters she wrote to her husband discussing government and politics. She is known for reminding her husband to "remember the ladies."
Samuel Adams
American statesmen, political philosopher, and Founding Father of the US. He was a leader in the American Revolution, and he was one of the architects of the principles of American republicanism that shaped the political culture of the US
Thomas Gage
British General who controlled Boston following the Boston Tea Party.
John Burgoyne
.British general in the American Revolution who captured Fort Ticonderoga but lost the battle of Saratoga in 1777 (1722-1792)
Charles Cornwallis
A British general, he lost to Nathaniel Green in one campaign. He was humiliated by his defeat in the colonies. He finally lost at the Battle of Yorktown, commonly known as the end of the war, in 1781.
Thomas Paine
American Revolutionary leader and pamphleteer (born in England) who supported the American colonist's fight for independence and supported the French Revolution (1737-1809)
Alexander Hamilton
1789-1795; First Secretary of the Treasury. He advocated creation of a national bank, assumption of state debts by the federal government, and a tariff system to pay off the national debt.
James Madison
1808 and 1812; Democratic-Republican; notable events include the War of 1812, let the charter of the First Bank of the United States expire, but realized it was difficult to finance a war without the bank, so he chartered the 2nd Bank of the United States
John Jay
1st Chief Justice of the Supreme Court; made the british give up their claim to the forts in the northwest, promised to reimburse them for the seized cargo); an author of the Federalist Papers
Sacajawea
A Shoshone Indian woman whose language skills and knowledge of geography helped Lewis and Clark on their expedition.