Microscopes
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Resolution
The smallest distance that 2 objects can be apart while still appearing as 2 objects
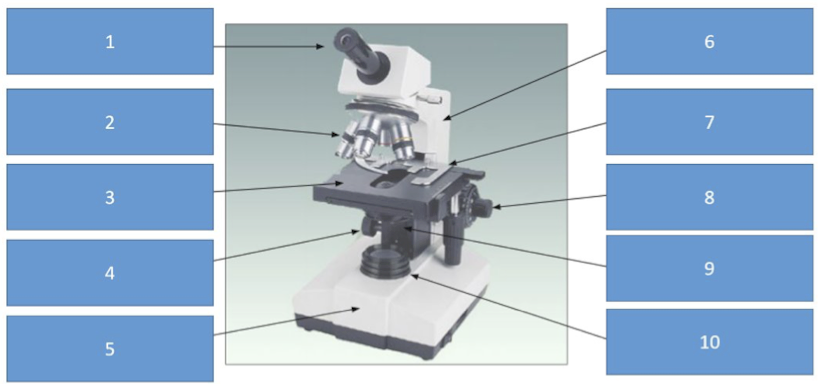
Label the parts of the microscope

Optical vs Electron Microscope
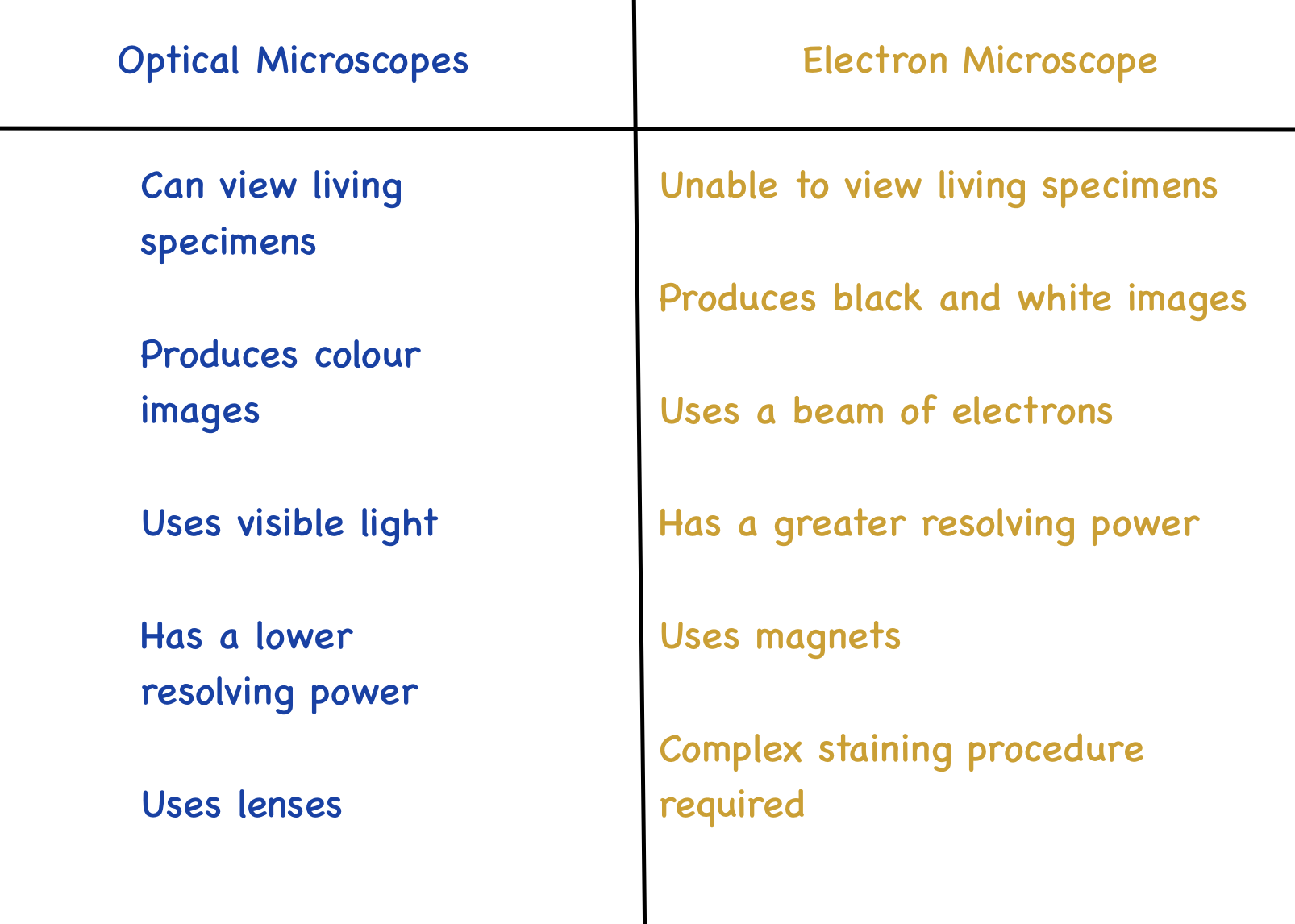
Electron Microscope
Uses magnets to focus a beam of electrons to either pass through or bounce off the surface of a specimen
Have a high resolving power because the wavelength of an electron beam is shorter than that of light
Transmission electron microscopes: the electrons pass through the specimen
Scanning electron microscope: the electrons bounce off the surface of the specimen
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
2D images formed
Detailed organelles are visible
Beam of electrons is passed through a very thin specimen
Electrons pass easily through less dense areas and appear dark whilst electrons pass less easily through more dense areas and appear white
Resolving power of around 0.1nm
Magnification of x500,000
Takes place in a vacuum
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
A beam of electrons are bounced off the surface of the specimen
3D image is formed
Allows us to see the shape of whole cells
Has a slightly lower resolution than TEM of around 20nm
Lower magnification of x100,000
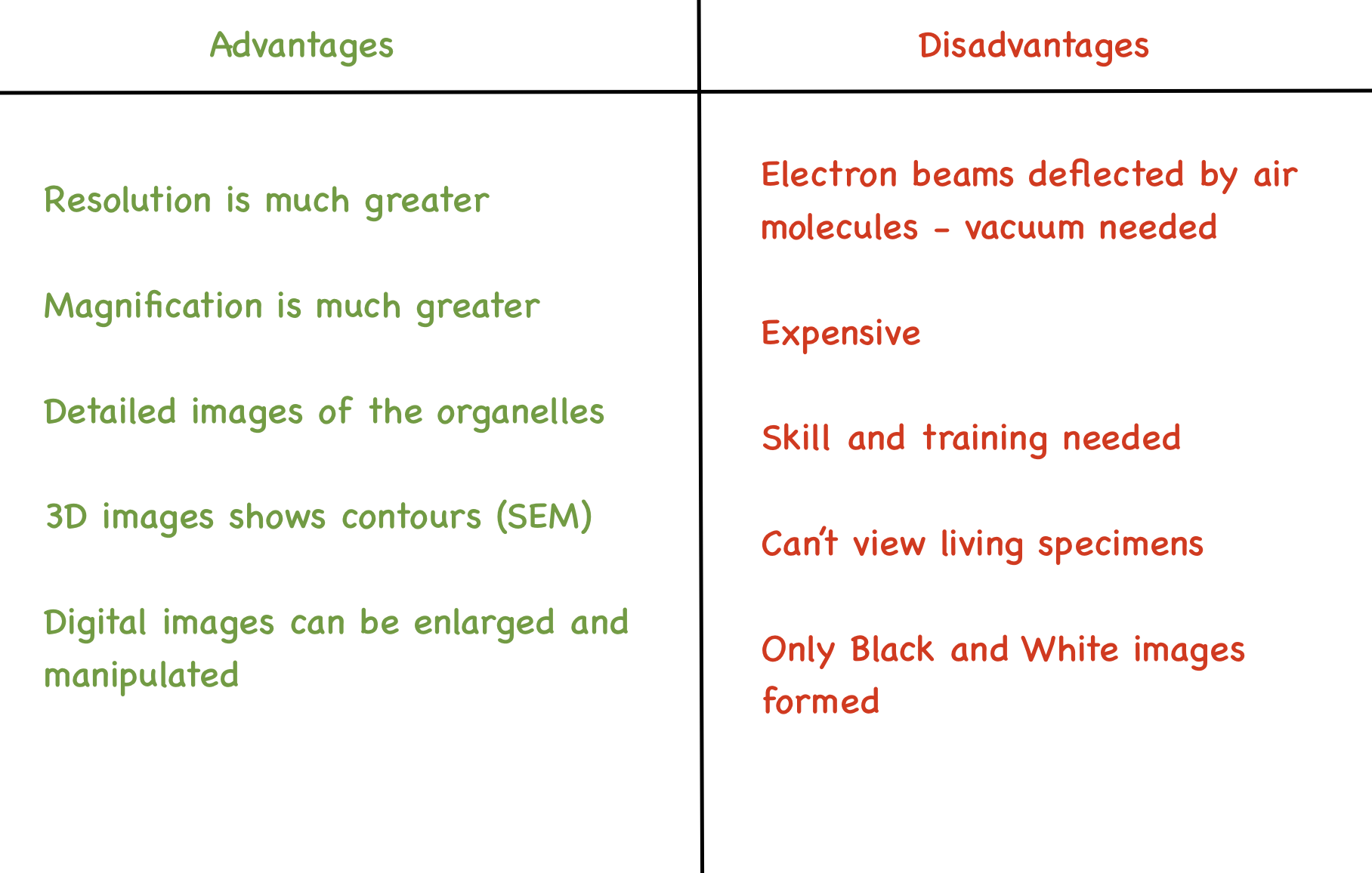
Electron Microscope: advantages and disadvantages
Eyepiece graticule equation

Magnification Equation