L6 Poultry endoparasites
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Histomonas meleagridis
Histomonosis, Blackhead disease
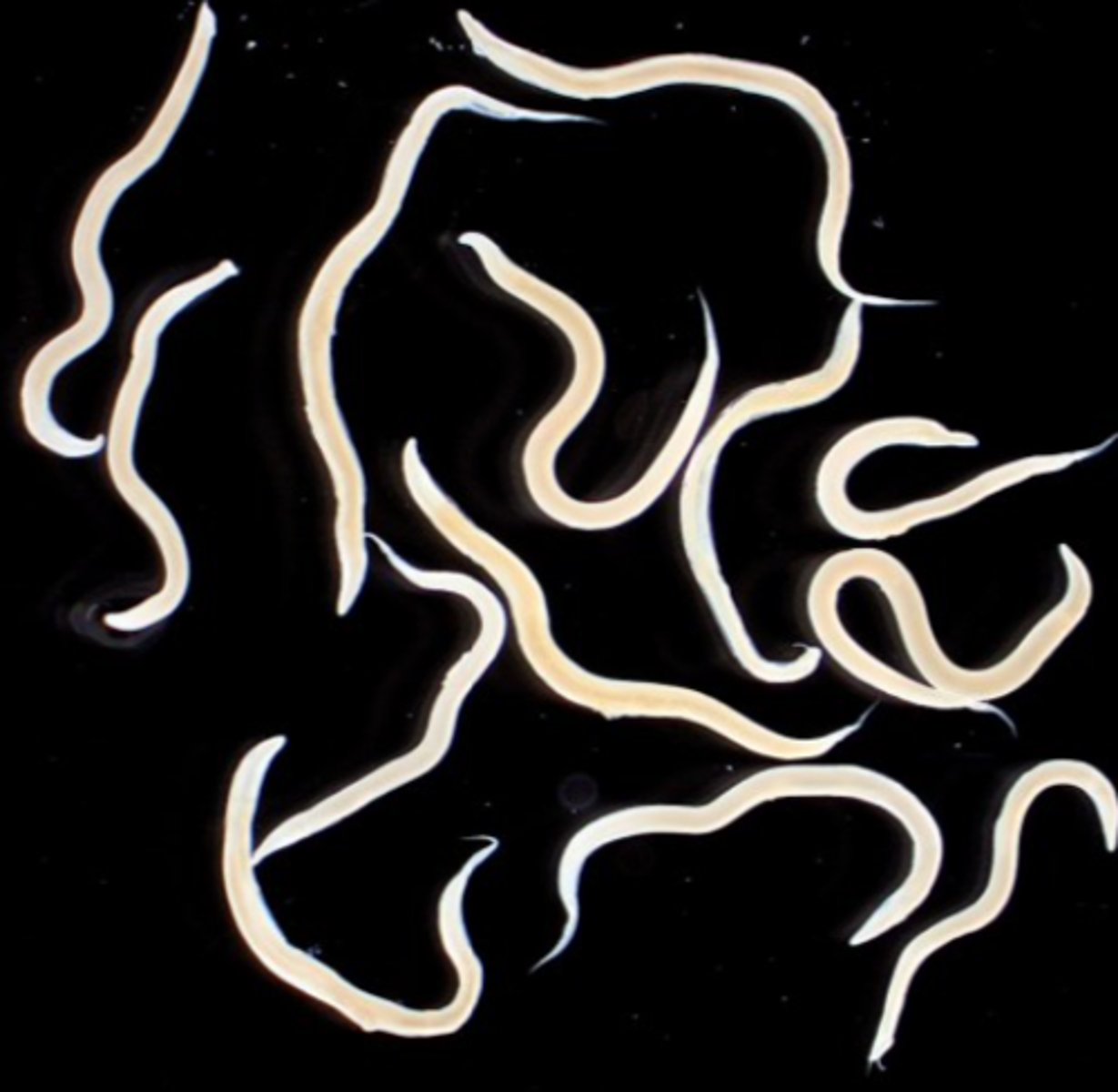
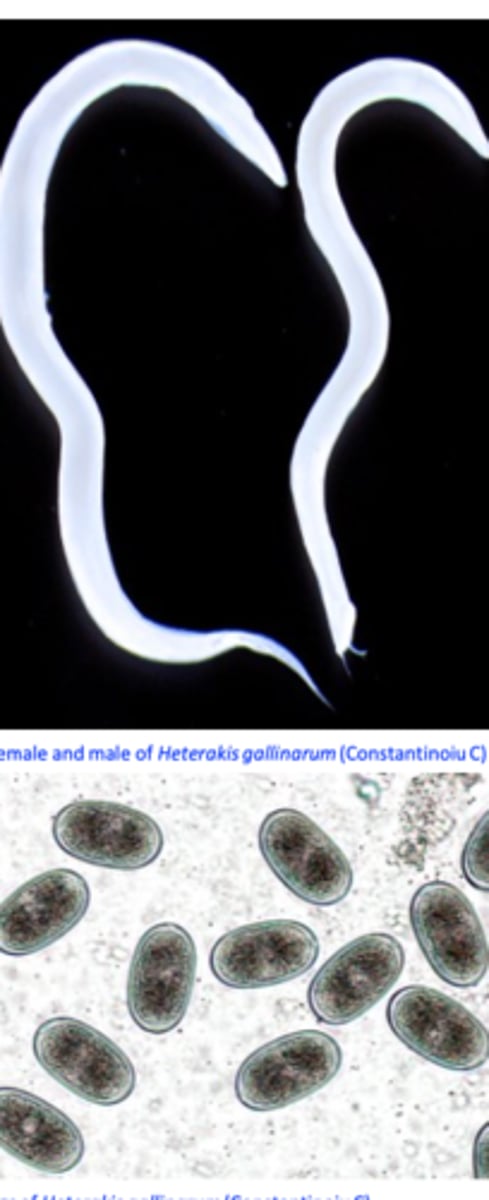
Heterakis gallinarum
• Hosts: chickens, turkeys, geese, ducks, pheasants, grouse, partridge, quail etc.
• Location: caeca;
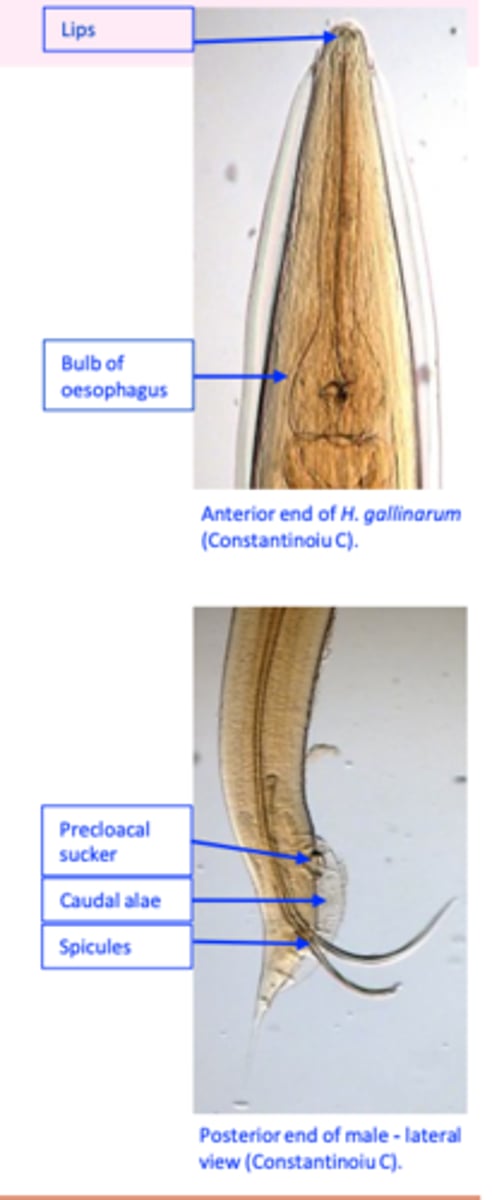
Heterakis gallinarum
Morphology/life cycle
Anterior end
Mouth provided with three lips;
Oesophagus ends in a well-developed bulb;
Posterior end
• Male
- precloacal sucker
• Female
- Long, narrow and pointed.
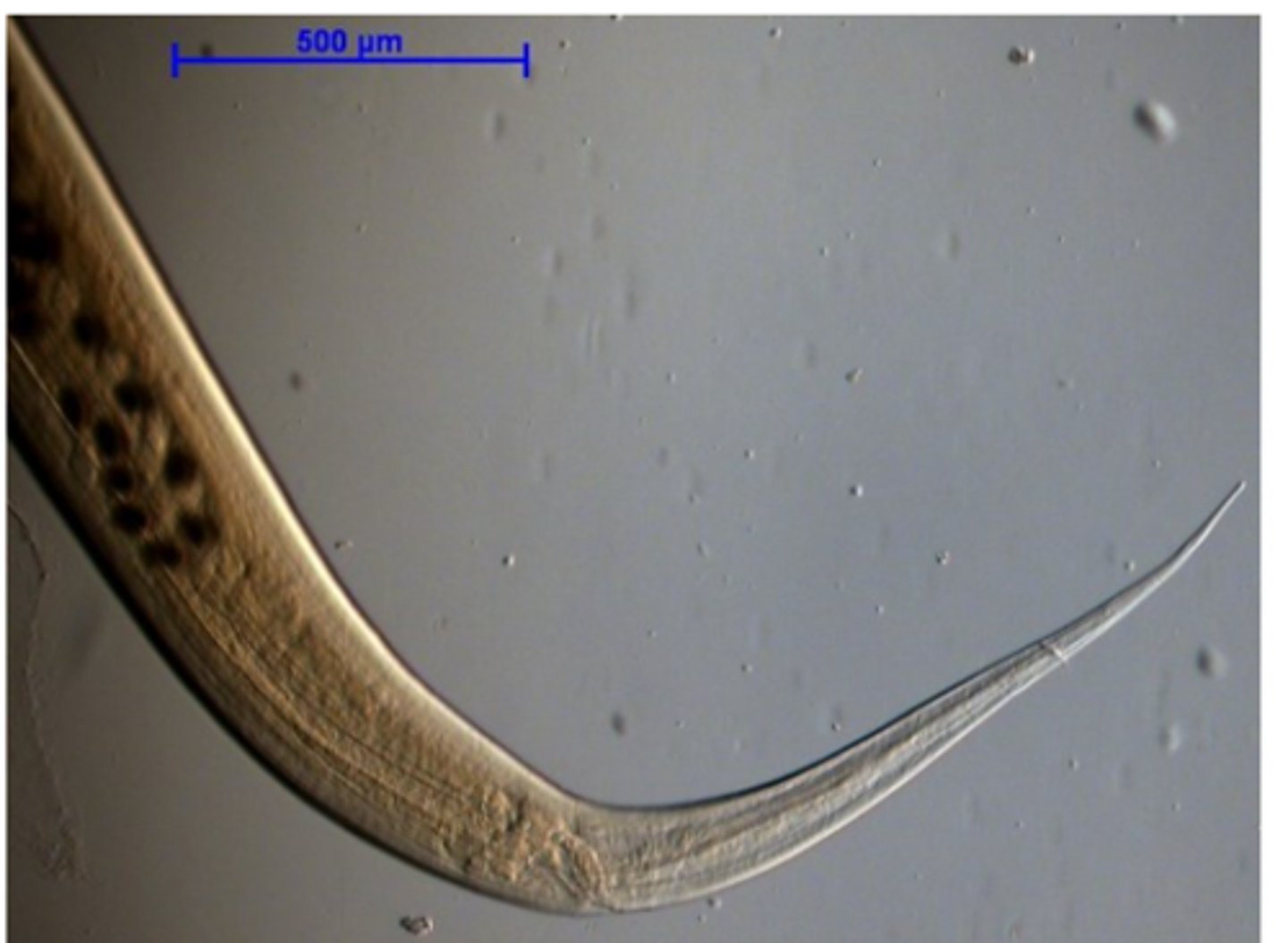
Heterakis gallinarum
Posterior end FEMALE
Heterakis gallinarum
eggs
Eggs (resemble Ascaridia eggs)
Shape: elliptical, lateral sides almost parallel;
Brown, thick and smooth shell, one cell inside.
Eggs may survive for long time in the environment
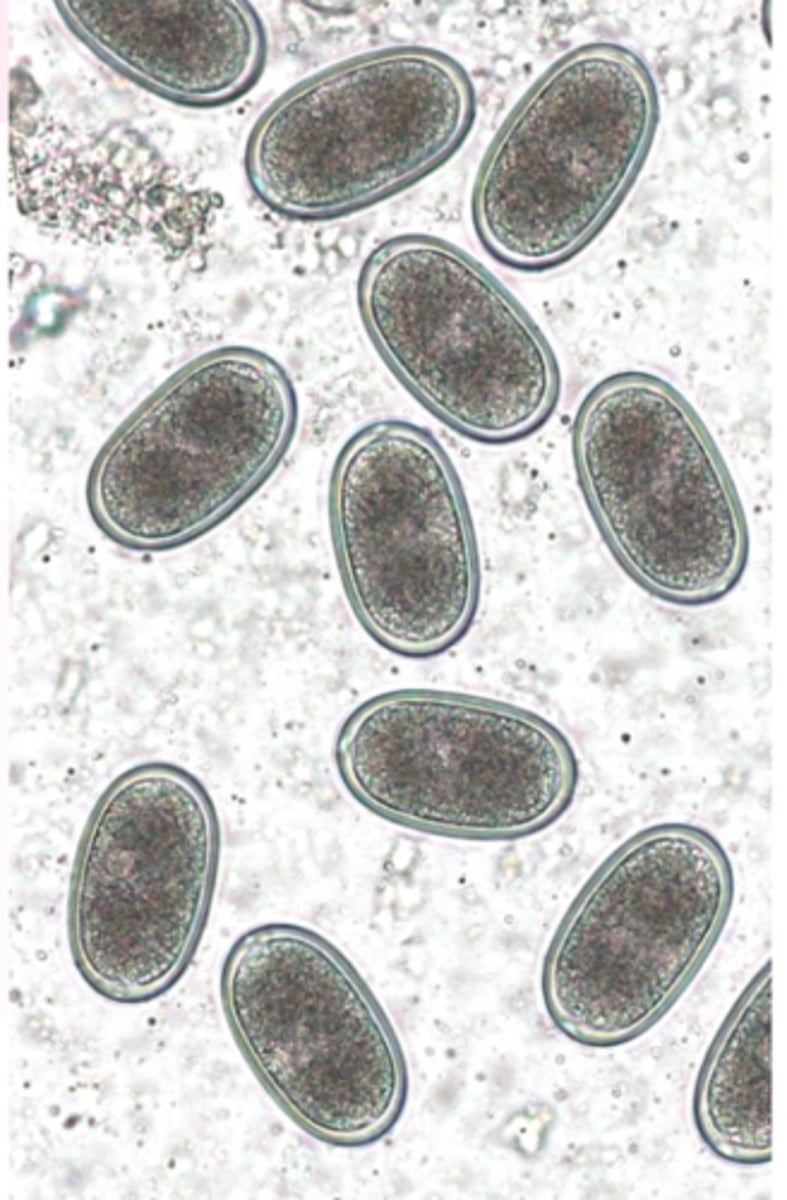
Heterakis gallinarum
Life cycle
• Infected birds shed in the environment eggs;
• In the environment eggs get embrionated in 2-3 weeks
Infection of the birds:• Ingestion of embrionated eggs;
• Ingestion of earthworms
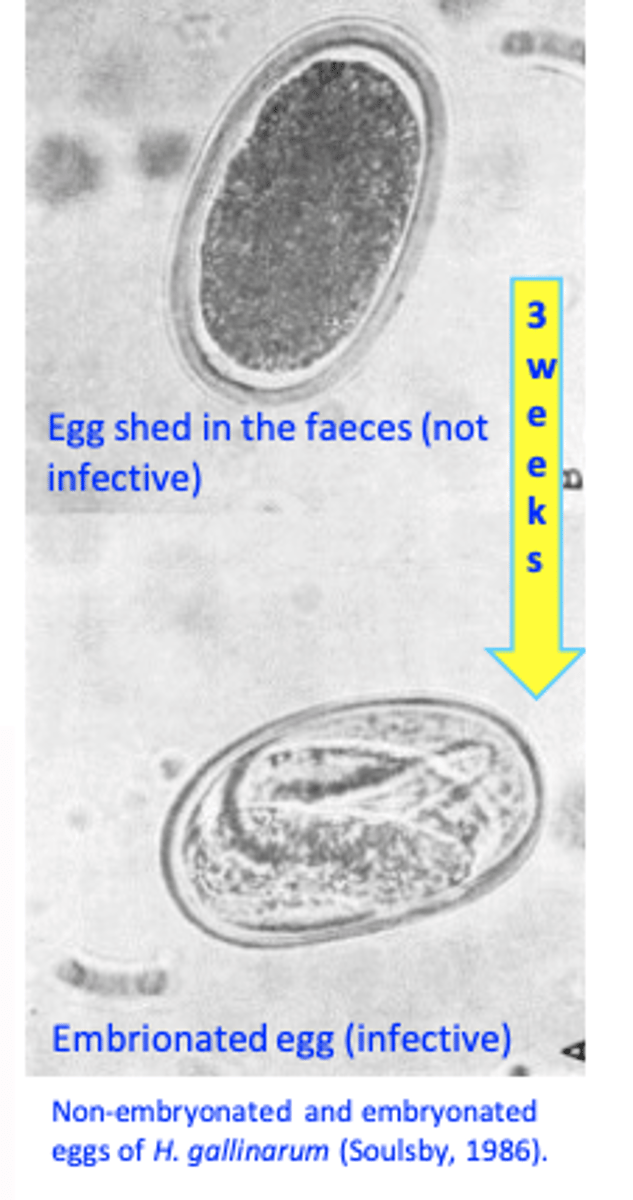
Heterakis gallinarum
Epidemiology
• Worldwide distribution;
• Present in outdoor and indoor systems
• Eggs may survive for long time in the environment
• Earthworms (paratenic hosts) may survive for several years in the environment;
Heterakis gallinarum
PATH
• Non-pathogenic/low pathogenicity: inflammation and thickening of the wall of caeca, nodules in the mucosa;
• Important because it is a vector for Histomonas meleagridis.
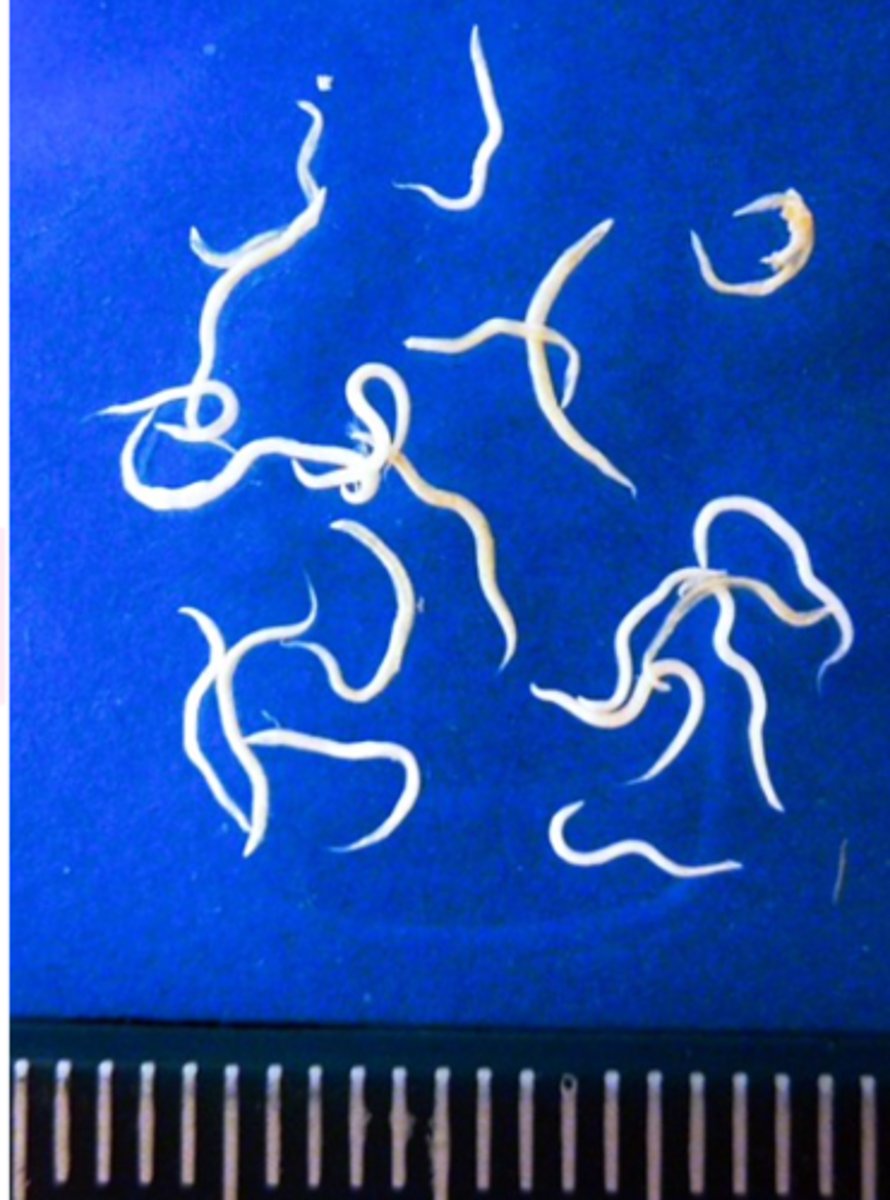
Heterakis gallinarum
Diagnosis
• Finding eggs in the faeces (floatation methods);
• Eggs look like eggs of Ascaridia galli!!• Postmortem examination of caeca
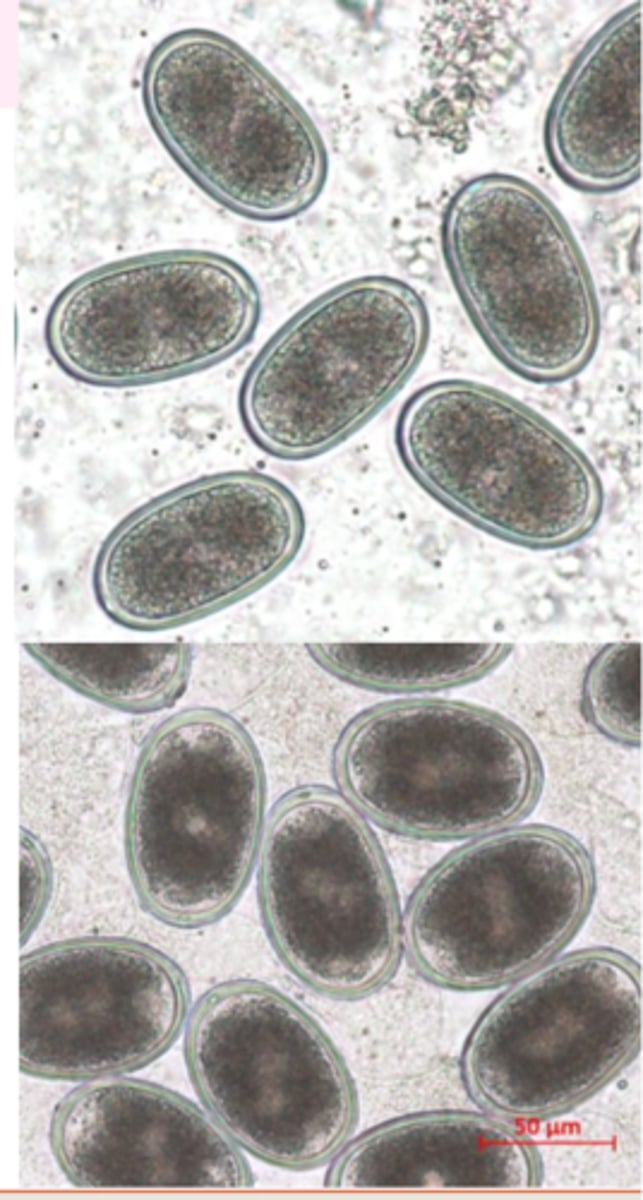
Heterakis gallinarum
Treatment
• Imidazothiazoles
• Levamisole :water
• Benzimidazoles
• Flubendazole: food
Heterakis gallinarum
Control
• In the outdoor systems: difficult because of the resistance of the eggs and presence of earthworms;
• Control required when histomonosis is a problem in turkeys;
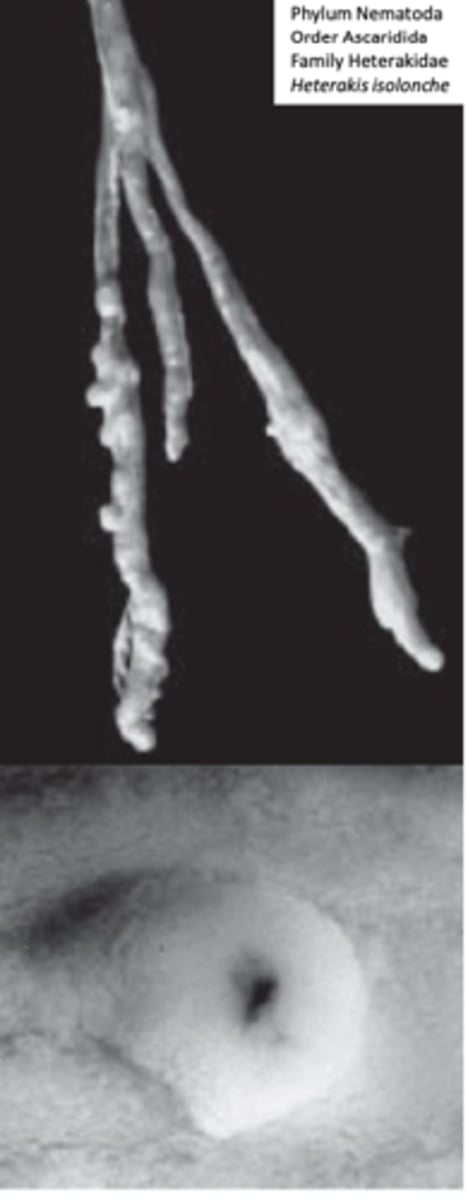
Heterakis isolonche
• Location: caeca of pheasants
• Larval stages invade the mucosa of the caeca where they develop
to adults in nodules;
• Diarrhoea, weight depression, death (sometimes >50%).
Histomonas meleagridis
Histomonosis (Blackhead disease, Entero-hepatitis)
Hosts: many galliform birds
Severely affected: turkeys chickens
• Location: commonly in caeca and liver
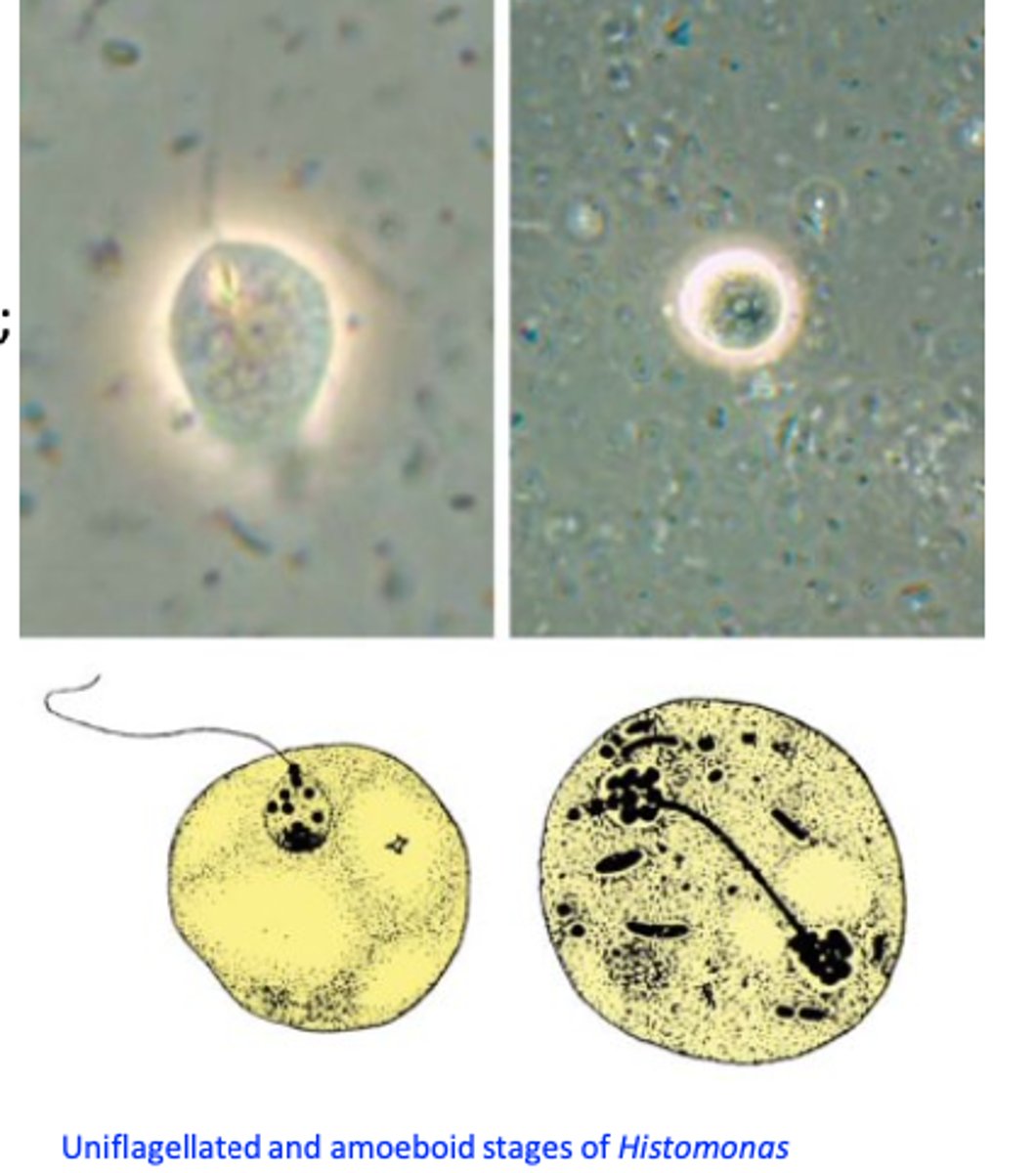
Histomonas meleagridis: Morphology
Pleomorphic: its appearance depends on location;
• Caecal lumen form
• Tissue form (wall of caeca/liver)
• A cyst-like form has been described recently in cultures;
• A 3 μm form exists in the eggs of H. gallinarum;
Histomonas meleagridis: Life cycle 1
I) Transmission via Heterakis gallinarum
Enables transmission from one farm to another farm!
• Heterakis gallinarum acts as a vector for H. meleagridis;
In the caeca of the bird host Histomonas meleagridis infects Heterakis gallinarum => ovaries of the female => become incorporated in the eggs;
Within the eggs the histomonads may survive for up to 2-3 years;
Histomonas meleagridis: Life cycle 2
Infection of the birds:
a) Ingestion of embrionated eggs of Heterakis gallinarum that contain Histomonas meleagridis;
b) Ingestion of earthworms that contain larvae of Heterakis gallinarum infected with Histomonas meleagridis;
In the caeca of the host the histomonads multiply (binary fission) and in 2-3 days enter the bloodstream and reach the liver;
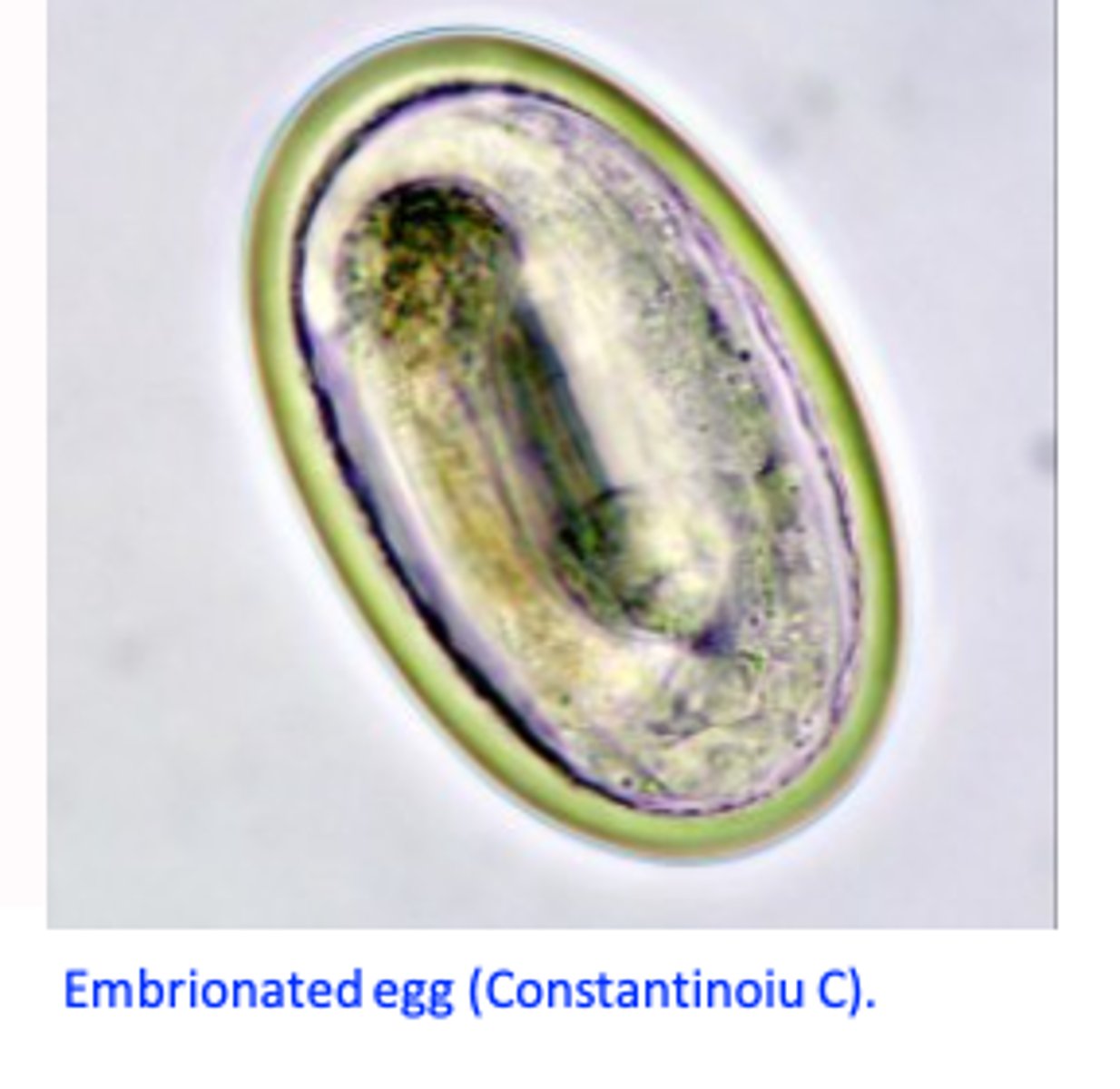
Histomonas meleagridis: Life cycle 3
II) Transmission by direct contact
Enables transmission from one bird to another bird
Via cloacal drinking;
After ingestion of the histomonads from environment:
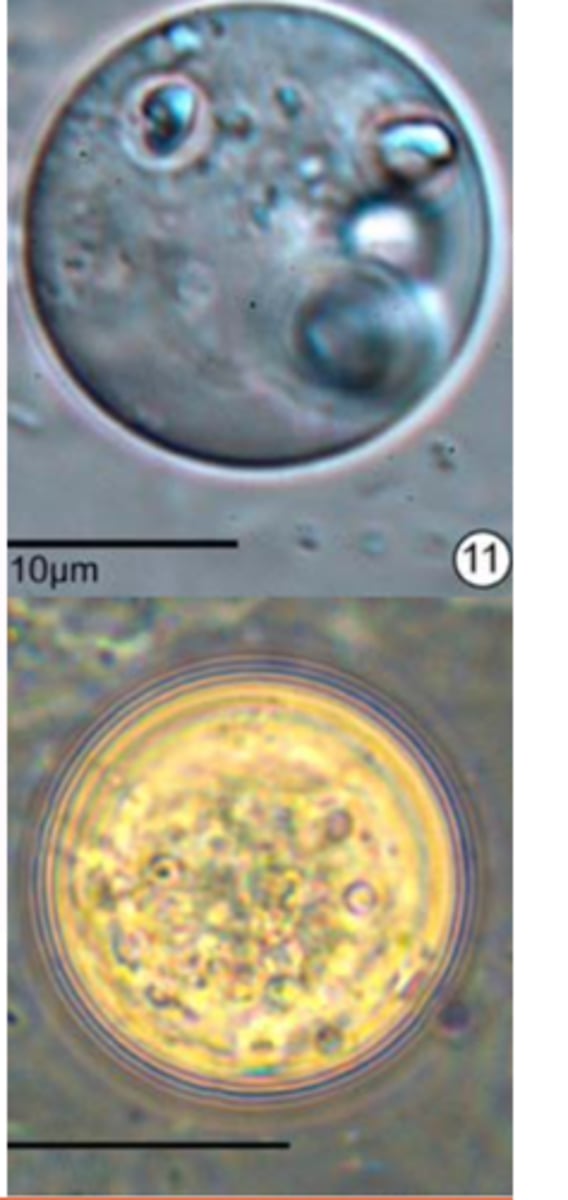
Histomonas meleagridis: HOSTS
Hosts: galliform birds
Severe disease: turkey
Mild disease: chicken
• Age affected: chickens 4-6 weeks of age are most susceptible while turkeys of any age are susceptible;

Histomonas meleagridis: Epidemiology
Chickens often remain carriers => source of infection for turkeys => do not rear chickens with turkeys;
• The role of Heterakis gallinarum and earthworms as vectors explain the long period the disease might persist in affected farms;
Turkey farms are not contaminated with Heterakis gallinarum => outbreaks occur after introduction of the eggs of the caecal worm H. gallinarum from chickens farms;
• Once the infection is established in a flock it spreads rapidly without the need of vectors: cloacal drinking and ingestion of histomonads;
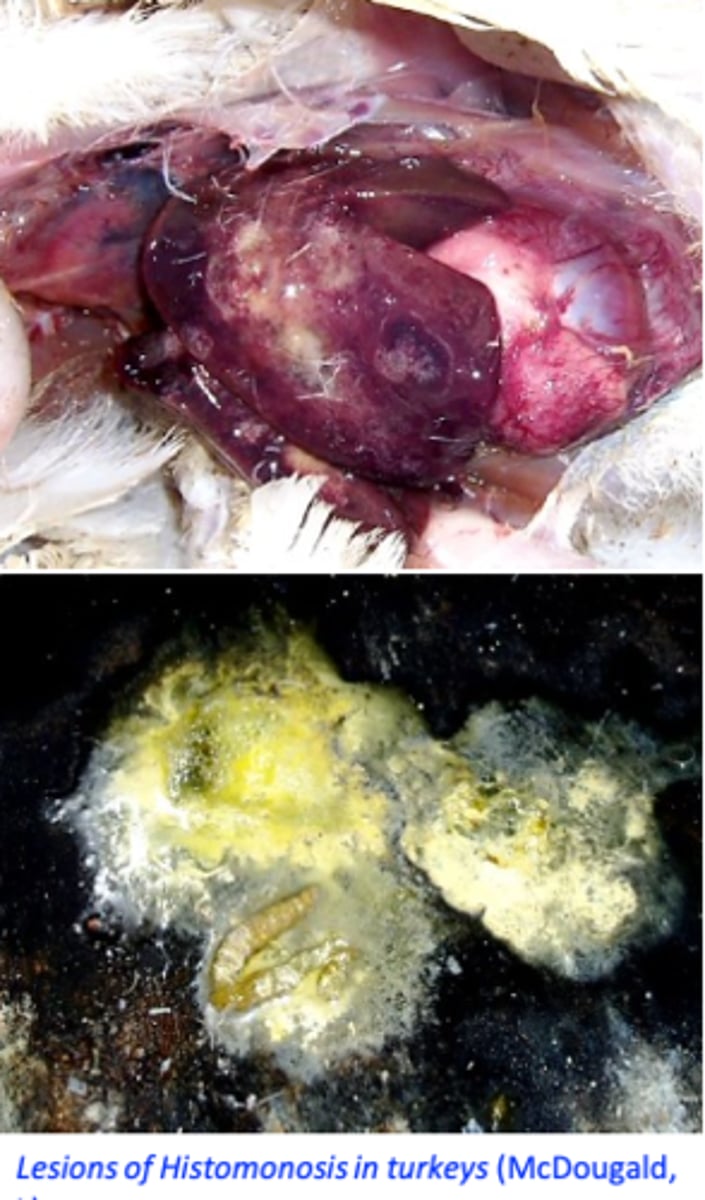
HIstomonas meleagridis: Pathogensis/Pathology
• Host species: turkey,
• Intestinal flora: lesions can not be produced in germ-free turkey
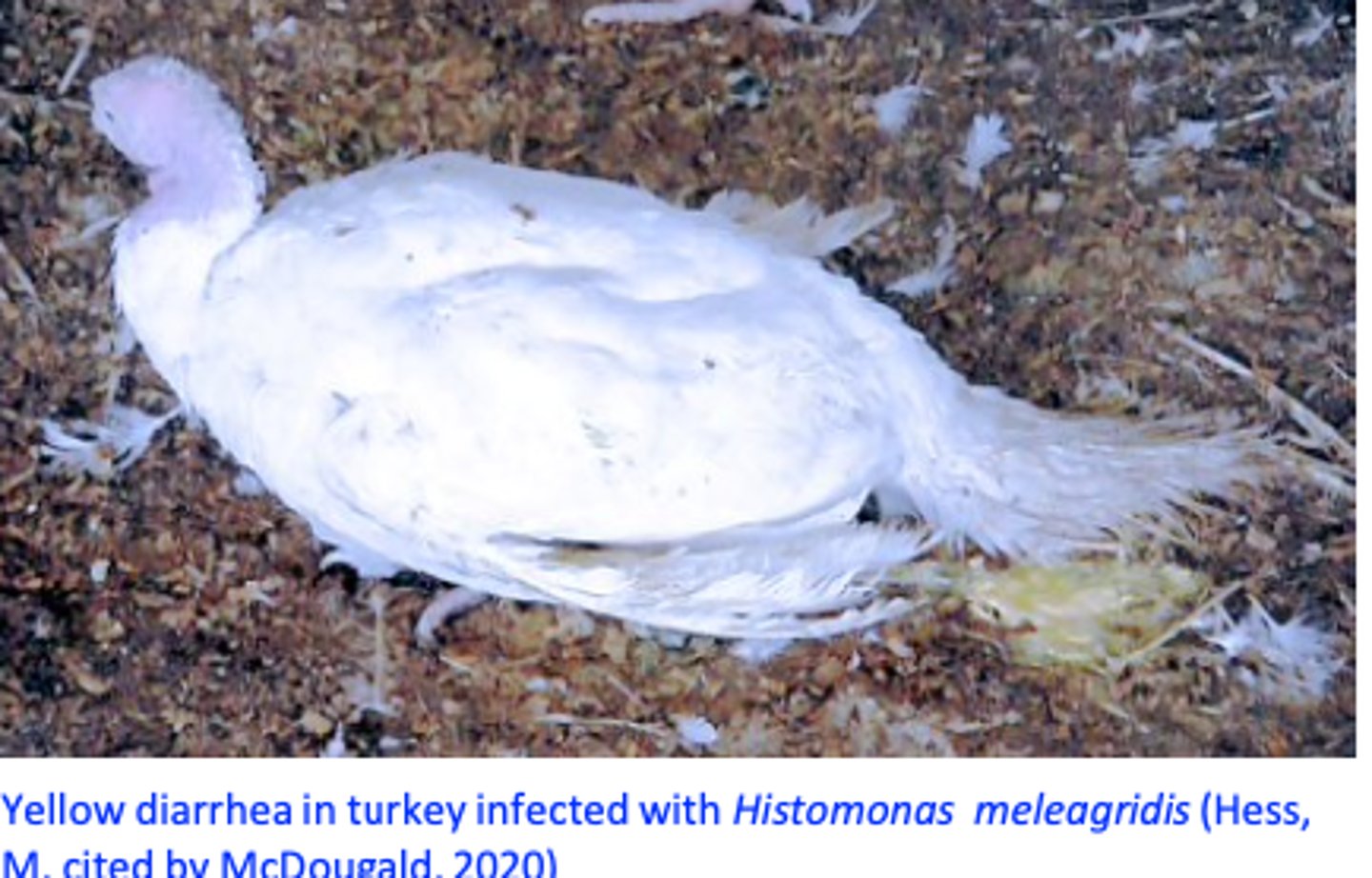
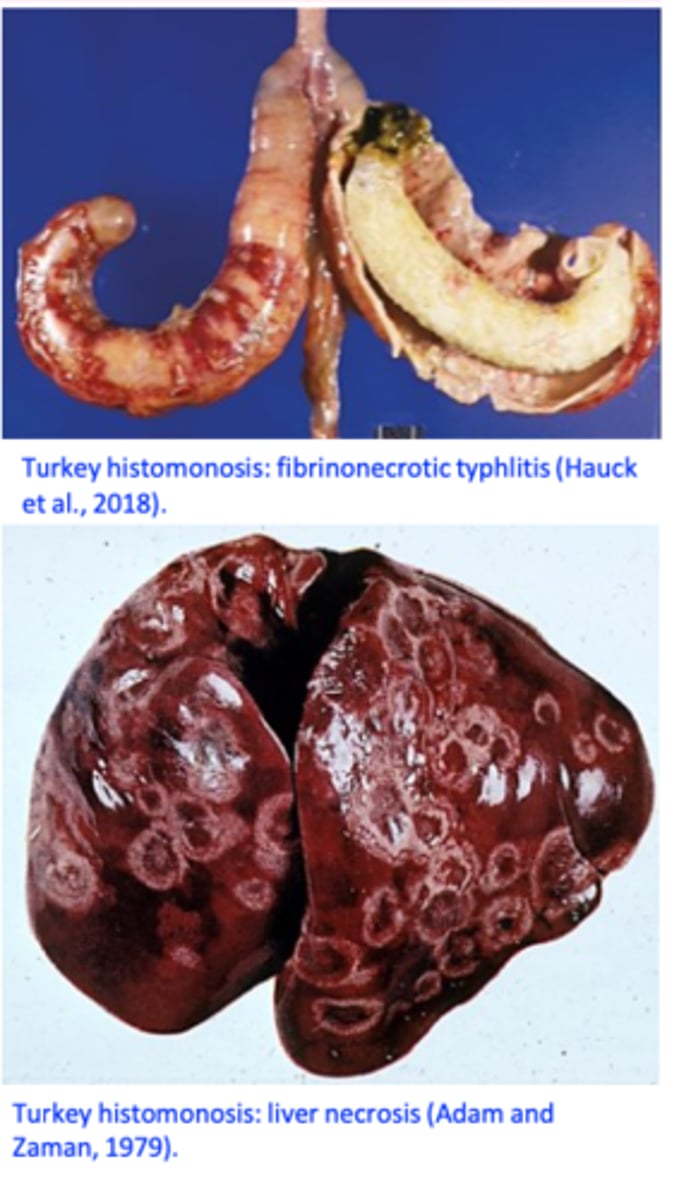
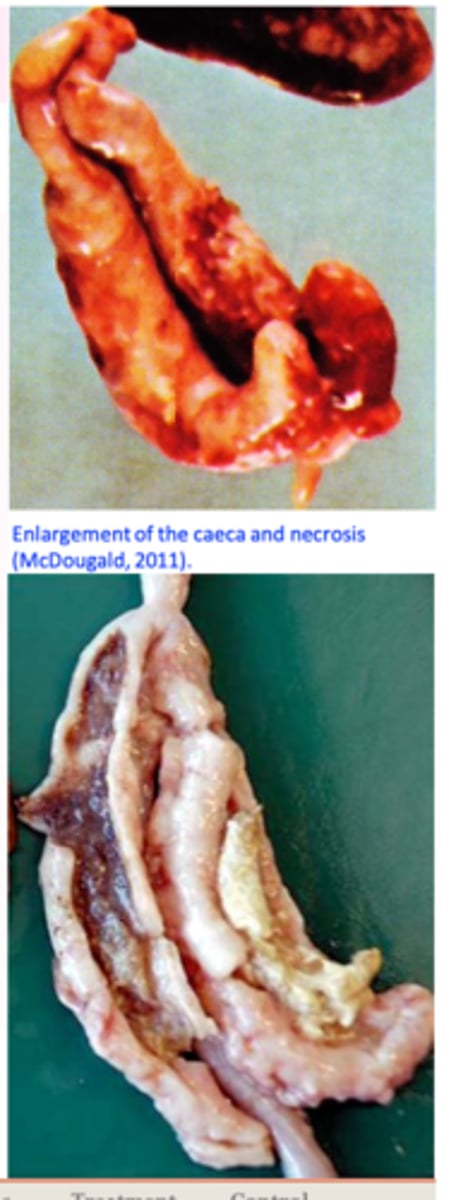
H. meleagridis: Pathogensis CAECA PATH
Multiplication of the histomonads in the caecal wall and the
liver => necrosis;
After tissue invasion => caecal walls become thickened and
hyperemic => necrosis develops;
Caeca become distended with a caseous/cheesy core made up of concentric layers;
Ulcers=>perforation of the caeca=> generalized peritonitis;
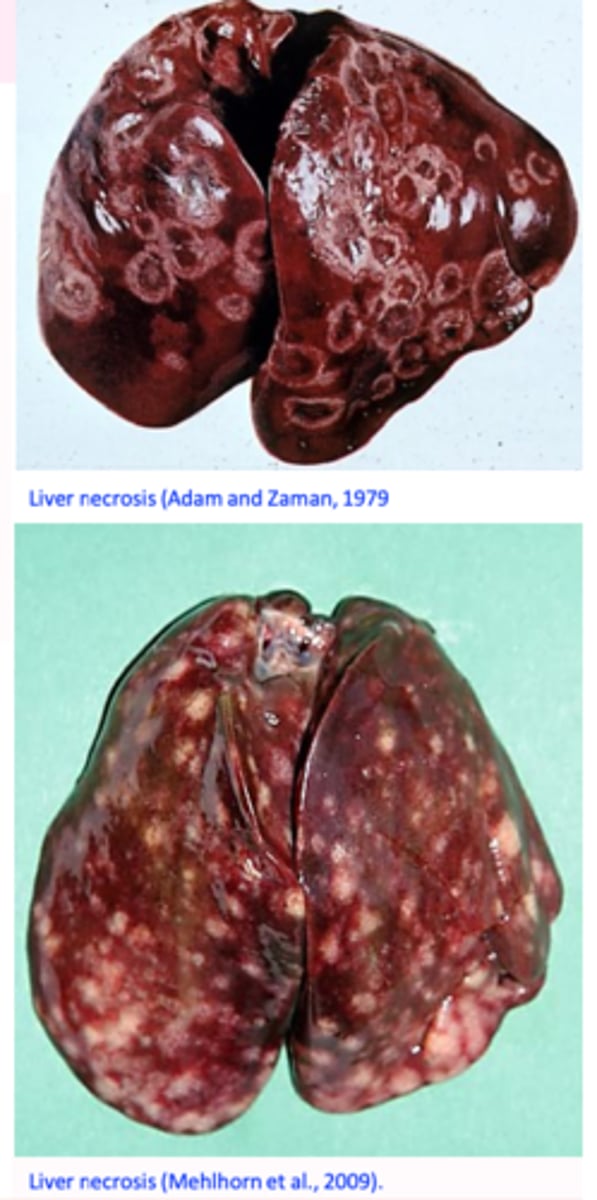
LIVER PATHOLOGY
Areas of depressed necrosis that grow up to 1 cm in diameter and are surrounded by a raised ring;
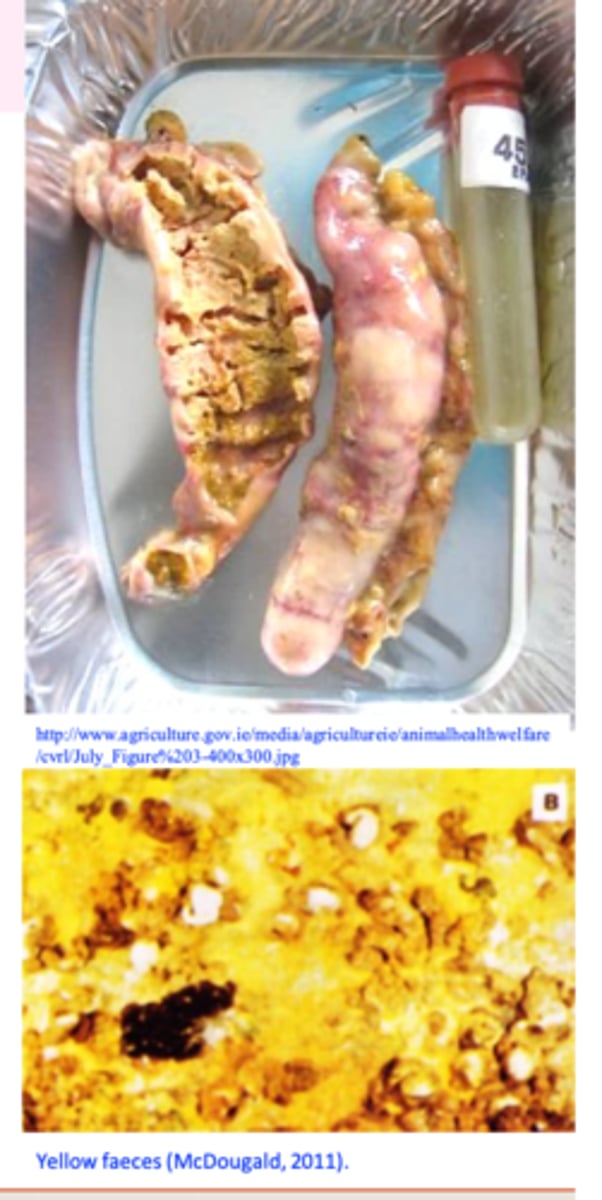
H. meleagridis: Clinical signs TURKEYS
Yellow faeces, drowsiness, dropping of the wings, closed eyes, head down close to the body or tucked under a wing, anorexia
Emaciation and death in high percentage
H. meleagridis: Clinical signs CHICKENS
Rarely yellow faeeces (the liver is not affected) but the chickens may shed bloody faeces and caseous caecal cores (pathology resembles caecal coccidiosis);
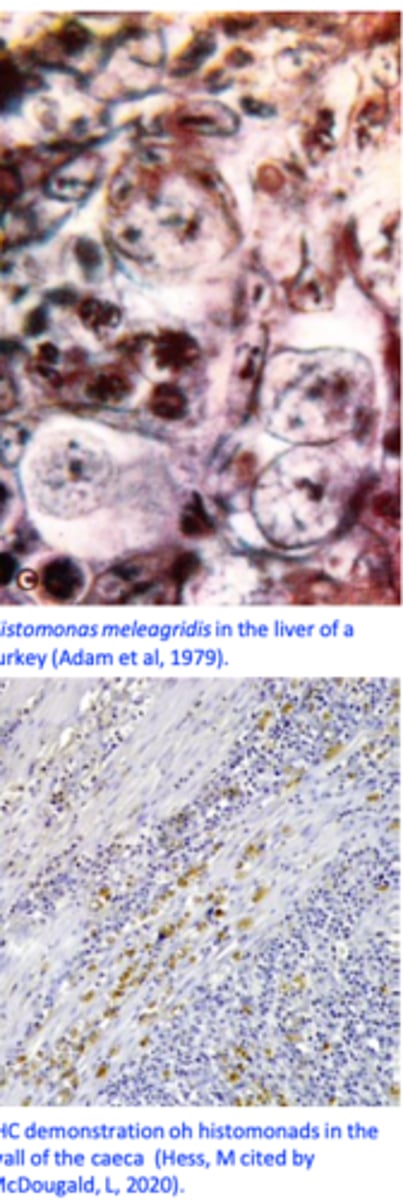
Histomonas meleagridis: Diagnosis
I. Clinical signs & history/Gross appearance of the lesions
II. Confirmation
- Identification of the histomonads in the caecal fluids or
mucosal scrapings
- Cultivation
- Histopathology, inc
- PCR
Histomomas meleagridis: Treatment
5-Nitroimidazoles
For use only in breeder game birds!!
Do not use in birds intended for human consumption!!
Do not medicate birds laying eggs for human consumption!!
Nitroimidazole products have been prohibited for use in food animals in EU, USA and Australia.
Histomonas meleagridis: Prevention
Do not grow chickens and turkeys together
Do not use chickens sheds for turkeys
House flocks in concrete or wire floored pens;
Hygiene, cleaning and disinfection of the floors, feeders,
drinkers etc before restocking, quarantine new birds;
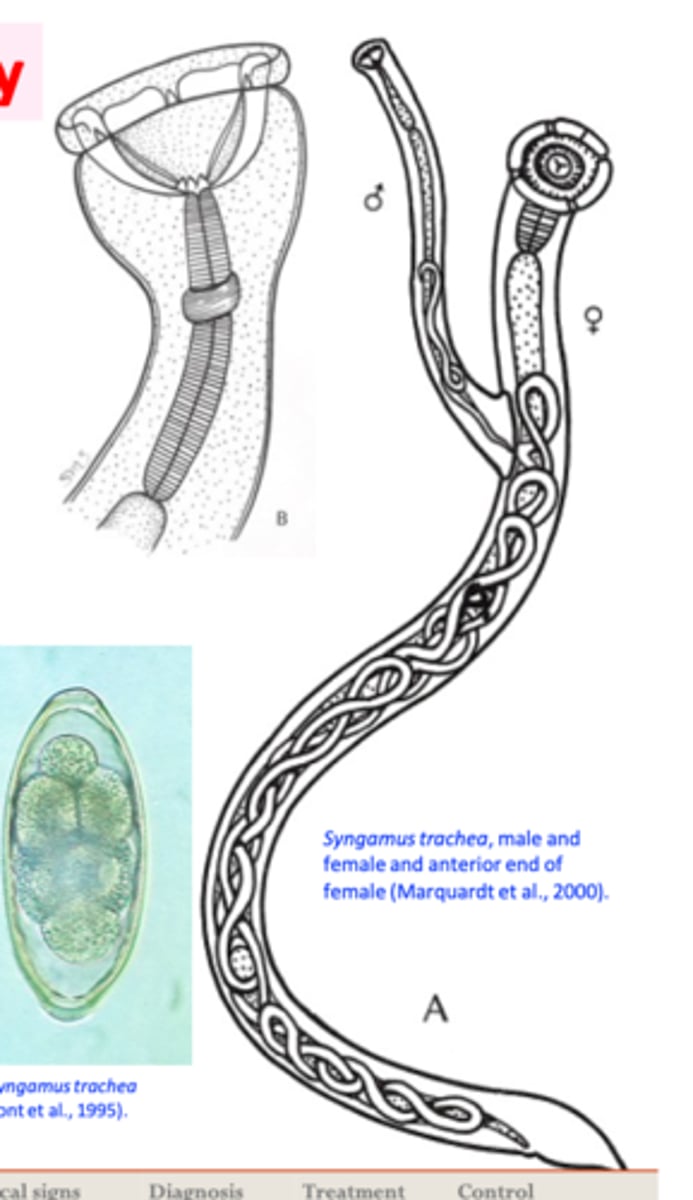
Syngamus trachea
Location: tracheaHosts: turkey, fowl, pheasants etc
Adult worms
Female worm and male always coupled => couple has the shape of letter ‘Y’;
Red colour (when fresh); feed on blood (Buccal capsule is cup shaped, no leaf- crowns)
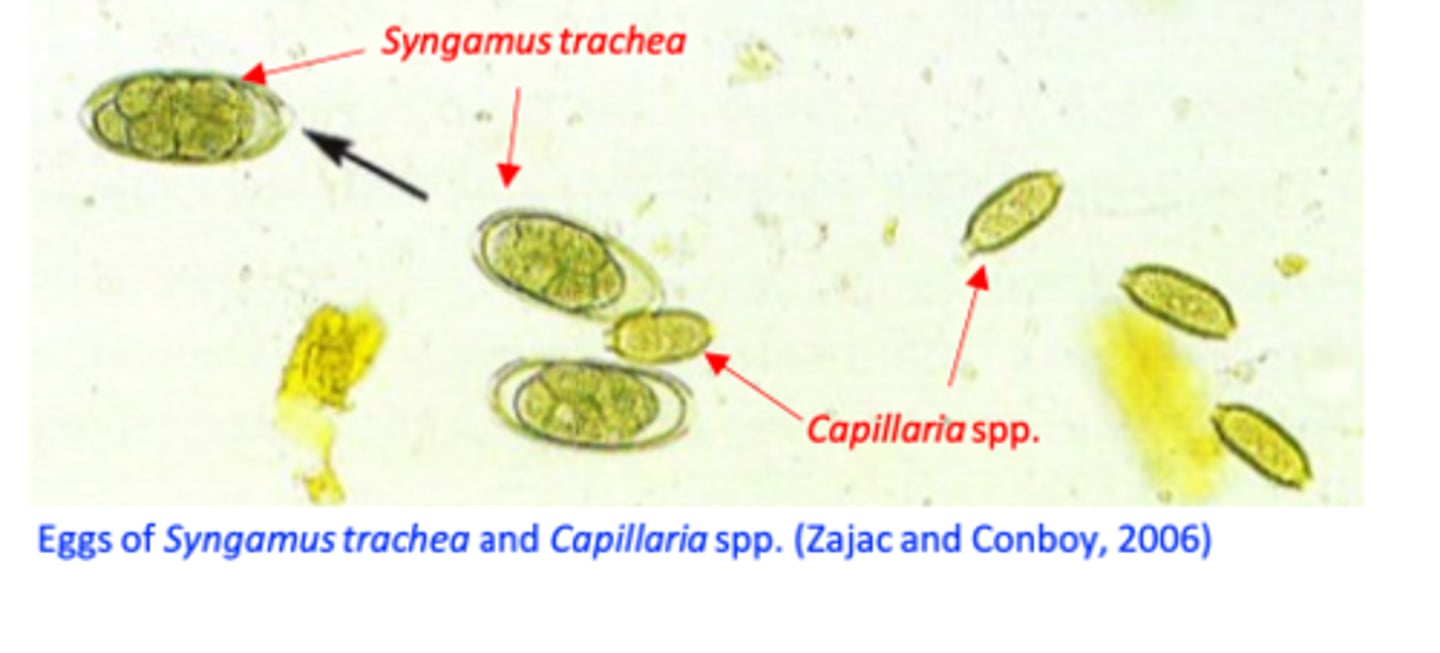
Eggs
ellipsoidal shape;
• An operculum at each pole;
• Relatively thick shell;•
Morula stage;
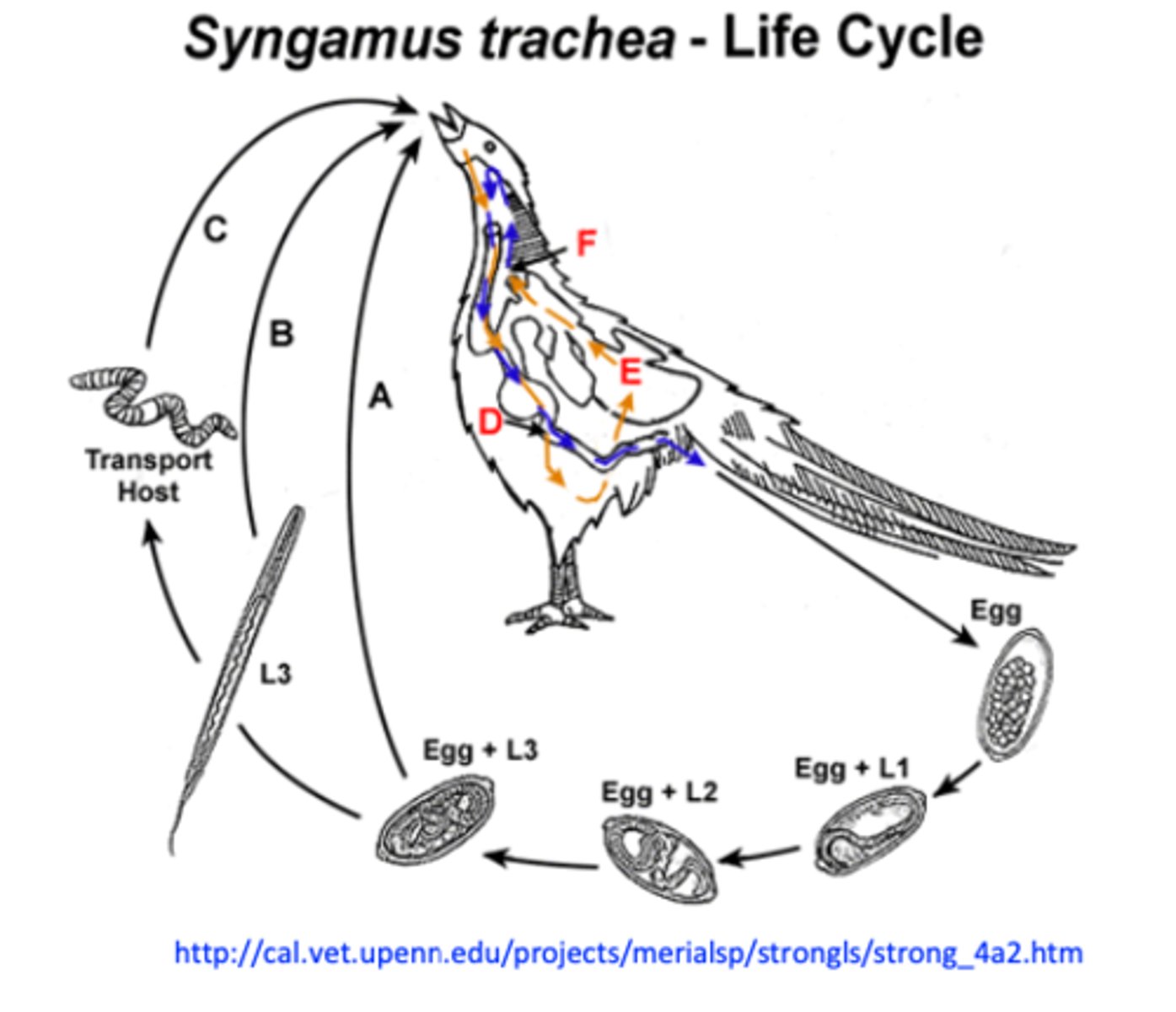
Syngamus trachea: Life cycle
• Eggs coughed up, swallowed => in the environment
with faeces;
• L1-L3 within egg =>some L3s might hatch;
• Infection of the host by ingestion of:
- Eggs with L3
- Free L3
- Paratenic host containing L3
Syngamus trachea: Epidemiology
• Hosts: turkey, chicken, pheasant, goose, guinea fowl, peafowl, emu, quail etc;
• Birds of all ages are susceptible to infection but generally young birds suffer severe disease, especially turkey poults, baby chicks and pheasant chicks;
• Common in outdoor systems;
• Infections occur seasonally
Syngamus trachea Sources of infection
Young birds and adult birds with inapparent infections;
Earthworms: larvae may persists for 4 years => the ground remains
contaminated for long time
Wild birds
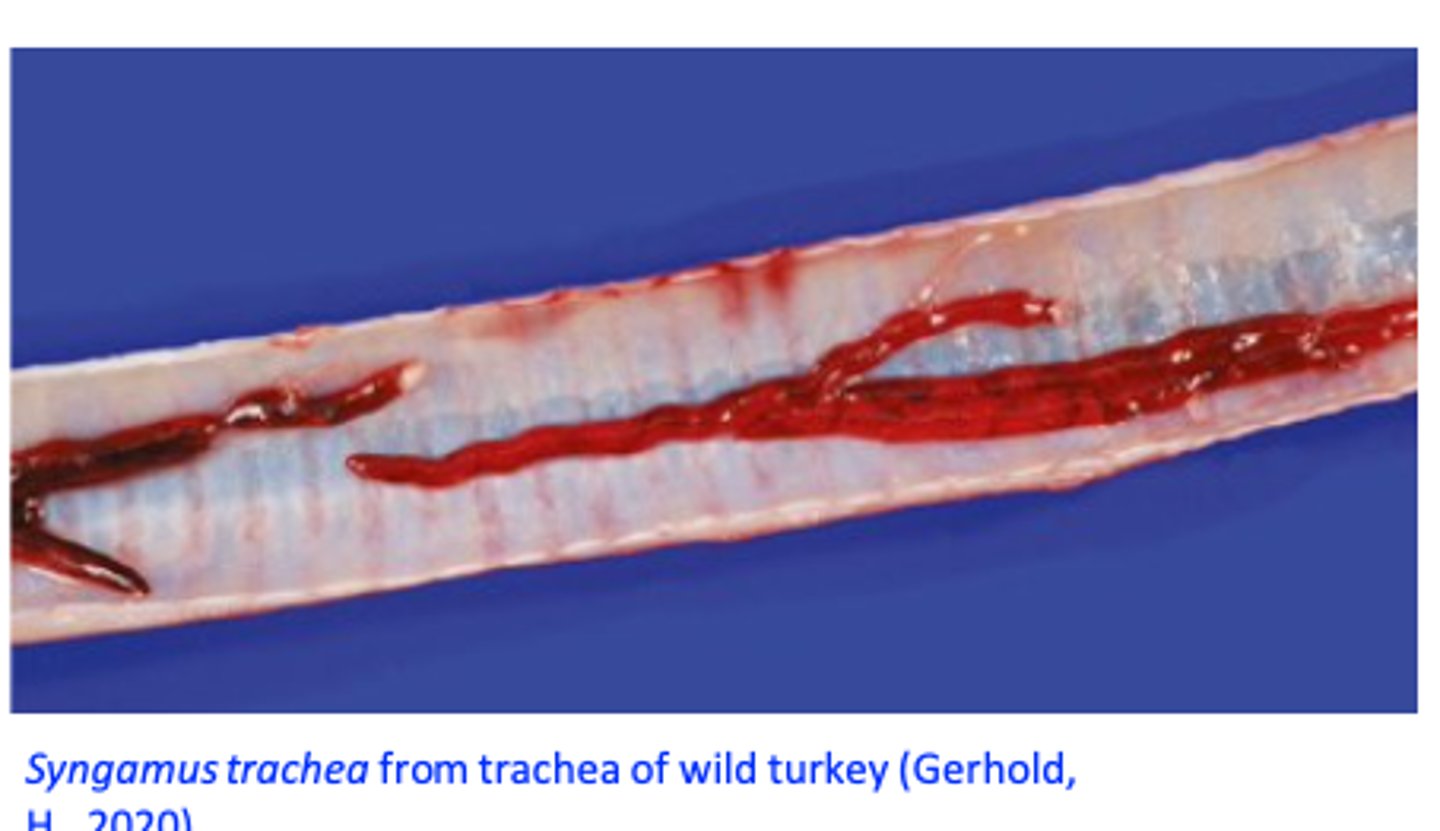
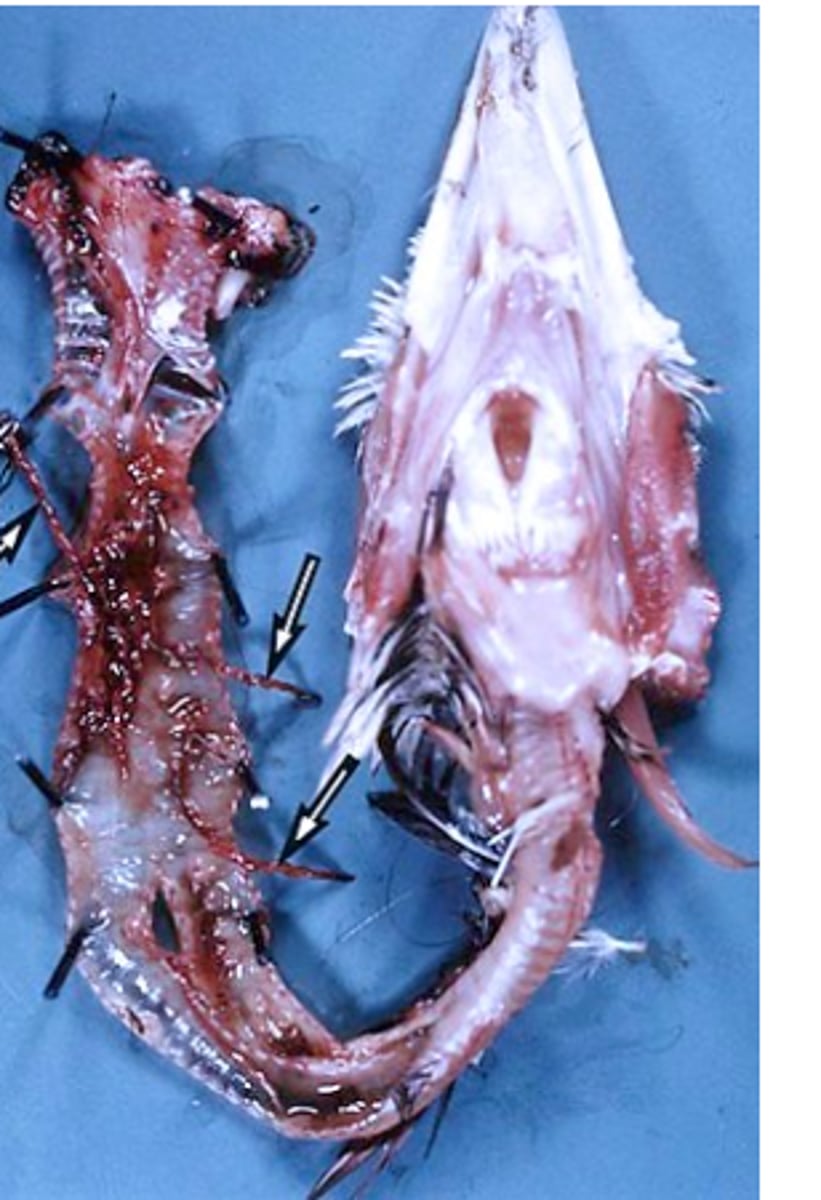
Syngamus trachea: Pathogensis/pathology
• Caused by larvae while migrating in the lungs and adults in the trachea;
II. Adult worms:
Feed on blood (males) and tissue (females)
Grow rapidly
Cause
- Haemorrhagic inflammation and excess mucus
- Males are deeply embedded into the wall of trachea => nodules;
Block the lumen of the trachea => suffocation => death
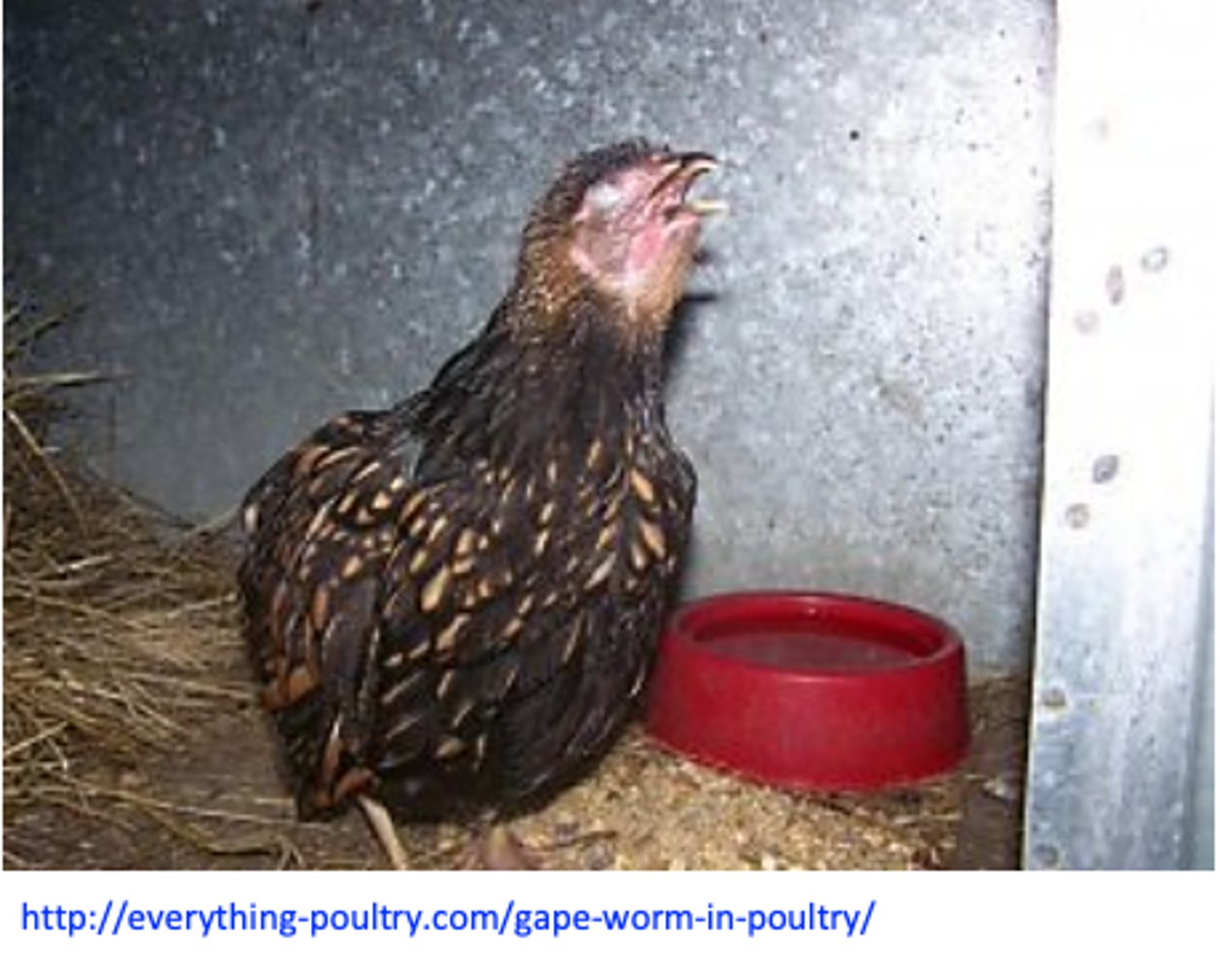
Syngamus trachea: Clinical signs
• Suffocation => birds gasp for air and stand “gaping”;
Coughing, dispnoea, shaking of the head, extending of the neck etc;
Death in 2-3 days;

Syngamus trachea: Diagnosis Live birds
Clinical signs;
History
Detection of the eggs in the faeces and worms in the trachea on necropsy;
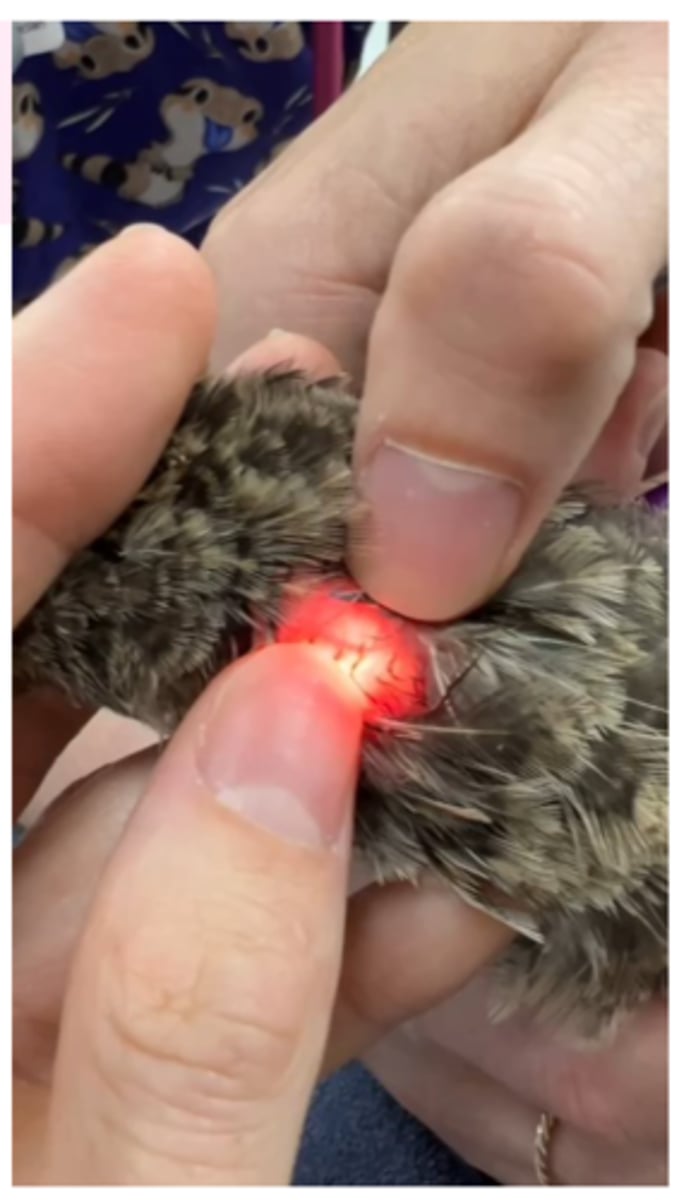
Live birds other diagnosis
• Transillumination;
Syngamus trachea: Treatment
Imidazothiazoles
Levamisole
Benzimidazoles
Flubendazole
Syngamus trachea: CONTROL
Indoor systems;
Separate young from old birds, do not grow mixed species;
Prevent contact with wild birds;
Treat prophylactically before/in the periods the outbreaks occur;
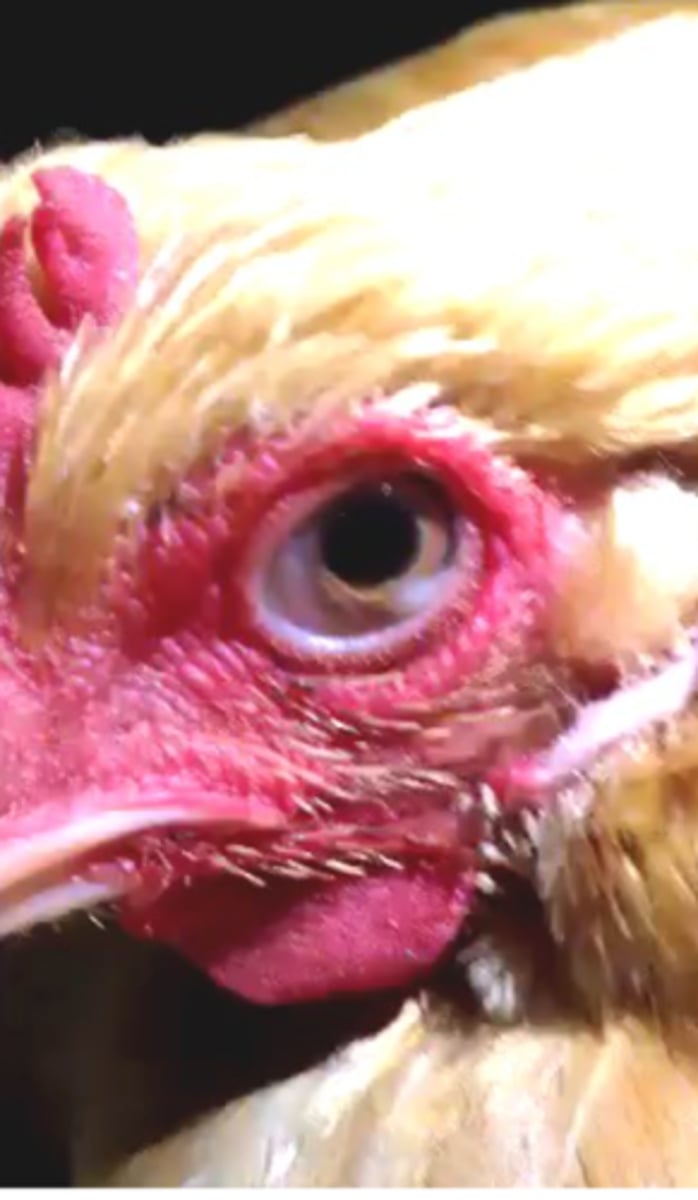
Oxyspirura mansoni
Host: chickens, turkey, ducks;
Location: inner corner of the orbit, under the nictitating membrane => causes blindness;

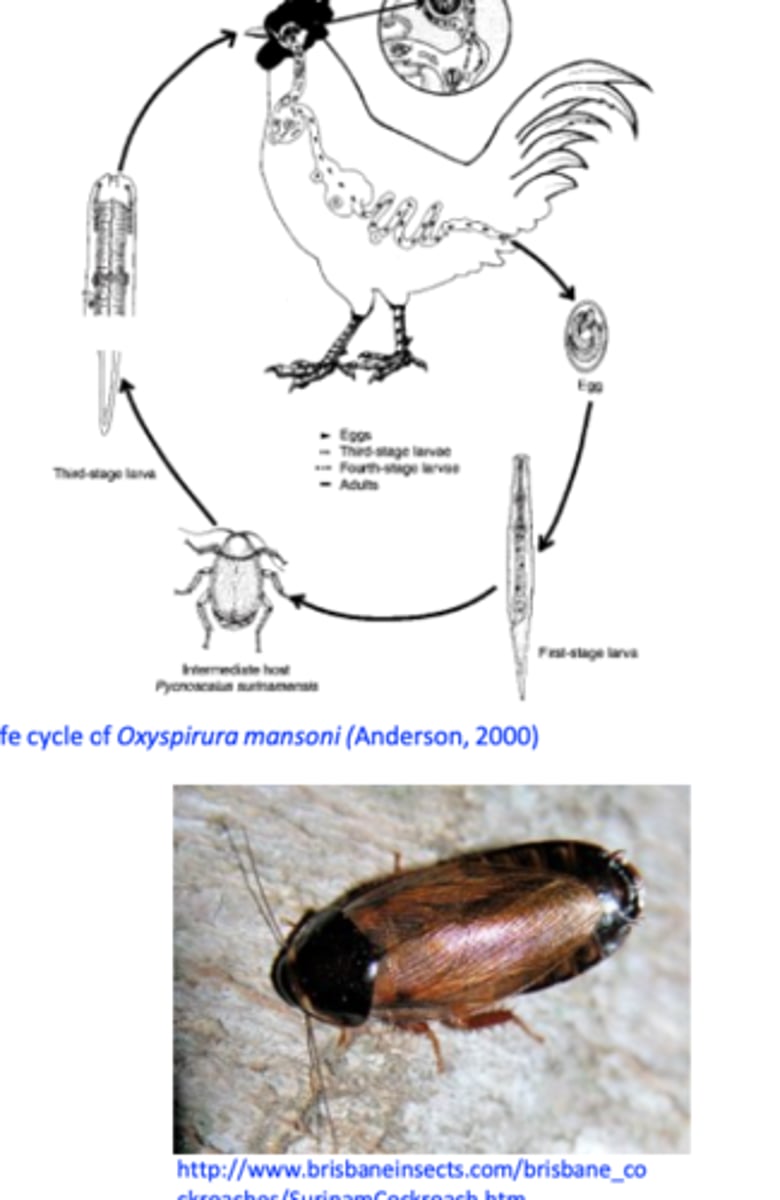
Oxyspirura mansoni LIFECYCLE
Intermediate host: cockroaches
Eggs are deposited in the eye => secretions => lachrymal ducts => mouth => swallowed => passed in the faeces;
Eggs are ingested by the cockroaches => in about 50 days the larvae reach the infective stage;
Cockroaches are ingested by the birds => larvae leave the cockroaches in the crop => up to the esophagus => mouth => lachrymal ducts => eye.
Oxyspirura mansoni DETAILS
Distribution: tropical and subtropical areas;
Pathogenesis/pathology: inflammation of the eye, oedema, watery eyes, blindness;
scratching of the eye;
Diagnosis
Clinical signs;
Visualization of the parasites;
Treatment
• MLs: Ivermectin and Moxidectin, oral
Prevention
• Reduce the number of cockroaches;
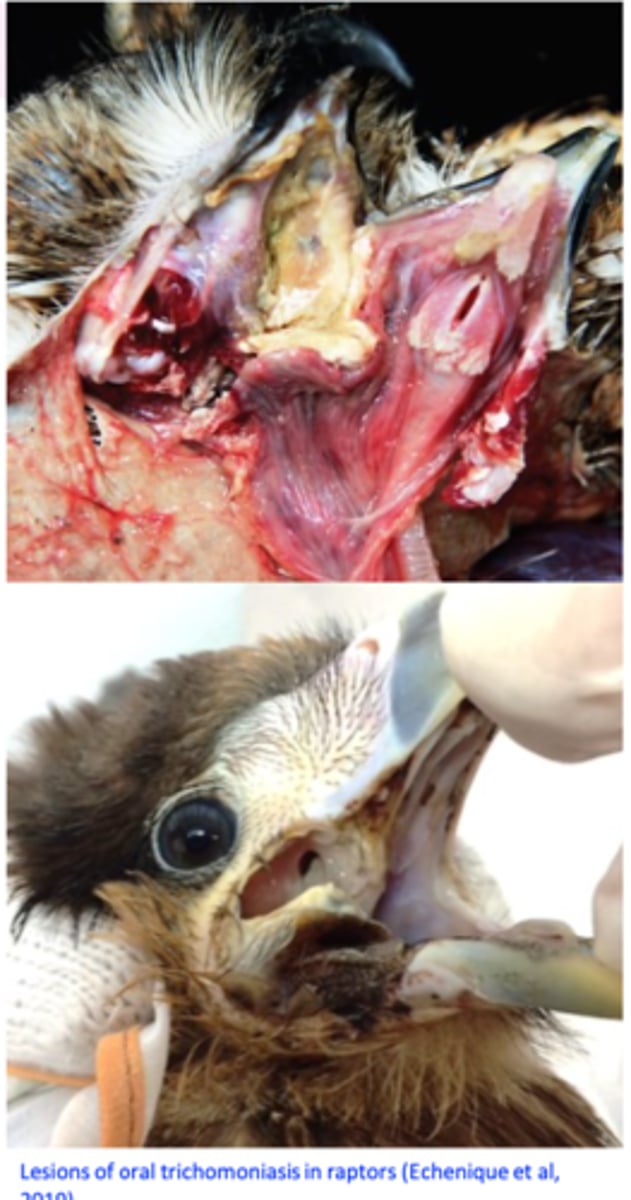
Trichomonas gallinae
Trichomonosis (canker)
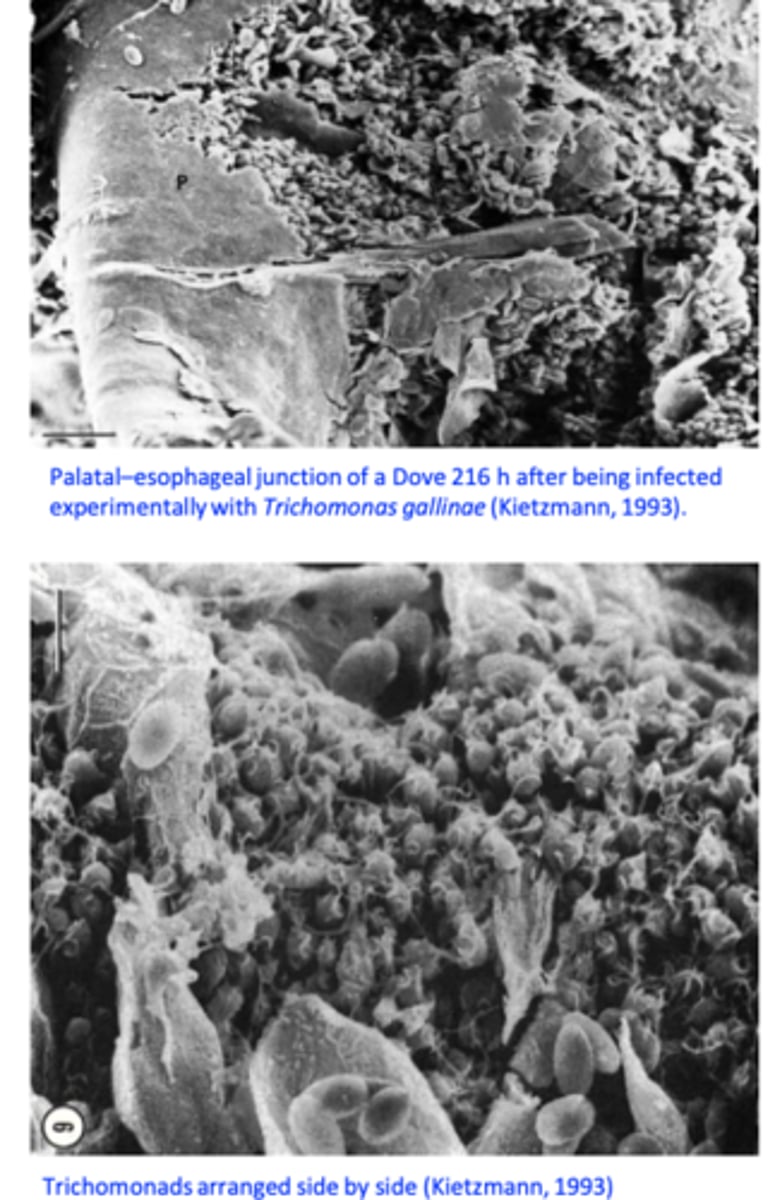
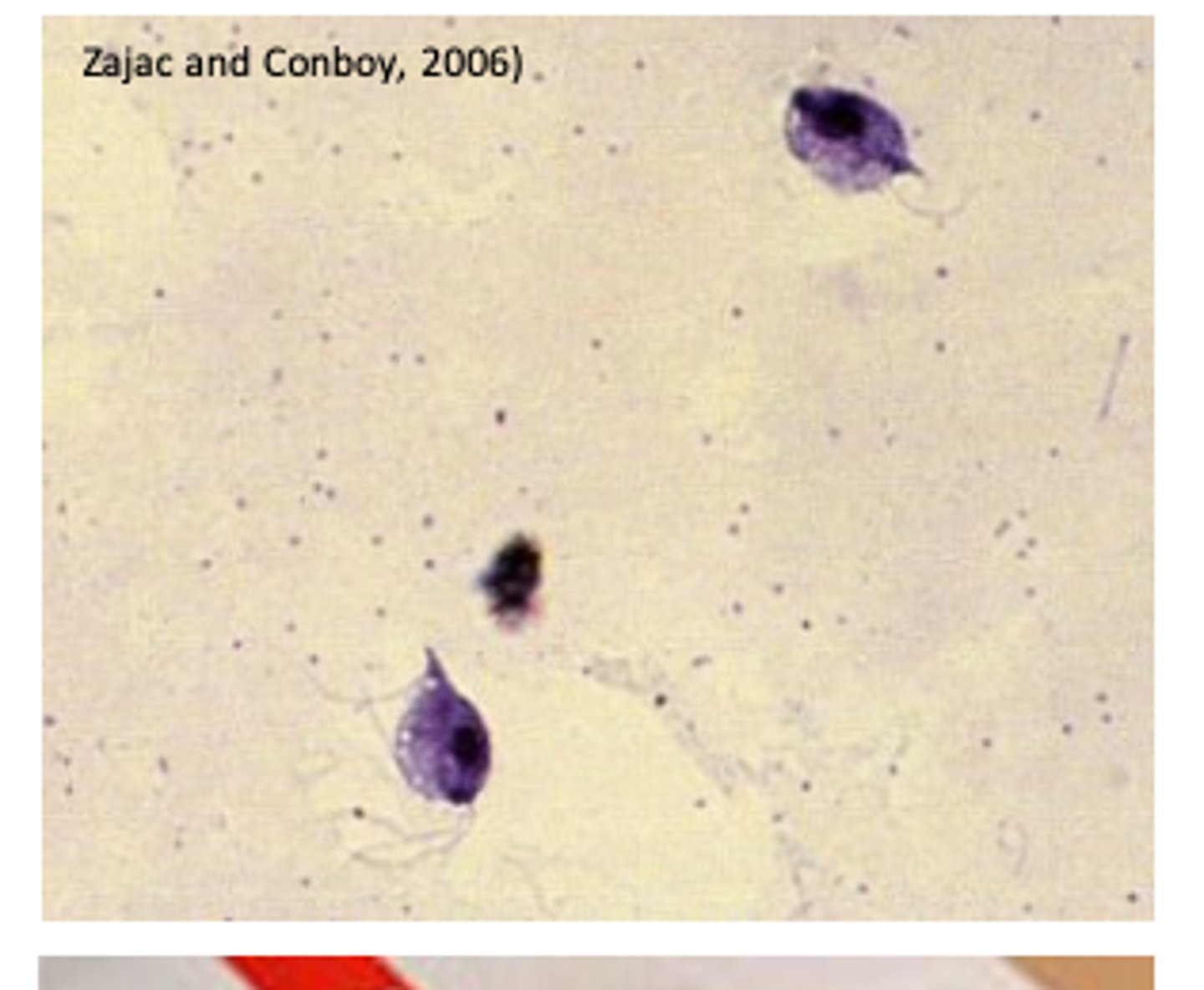
Trichomonas gallinae is a flagellate protozoan that occurs primarily in the upper digestive tract of columbiforms (pigeons, doves etc) but it can infect a wide range of species of birds;
Four anterior flagella and no free posterior flagellum;
Undulating membrane does not reach the posterior end of the body;
Trichomonas gallinae: Epidemiology
• Distribution: worldwide
• Hosts
•Birds, especially from the order Columbiformes (pigeons& doves) but also budgies, finches, sparrows, hawks, eagles, turkeys, chickens etc;
Location
Upper digestive tracts: mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, crop;
Trichomonas gallinae SOURCES OF INF.
• Pigeons: adults - up to 80-90% are asymptomatic carriers
=> clinical signs usually in birds younger than 1 month;
Trichomonas gallinae TRANSMISSION
Columbiforms
• Pigeon‘milk’
Galliforms: feeding/watering in/from places/containers infected by columbiforms or other wild birds
T. gallinae: Pathogenesis/Pathology
Depends on the strain and immune status of the birds
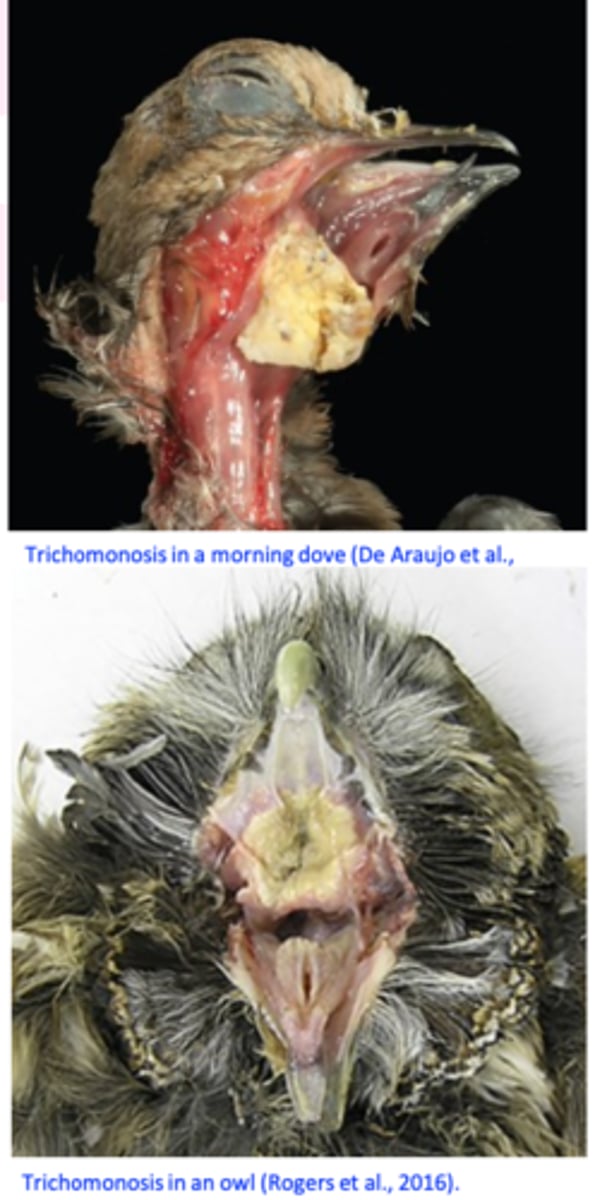
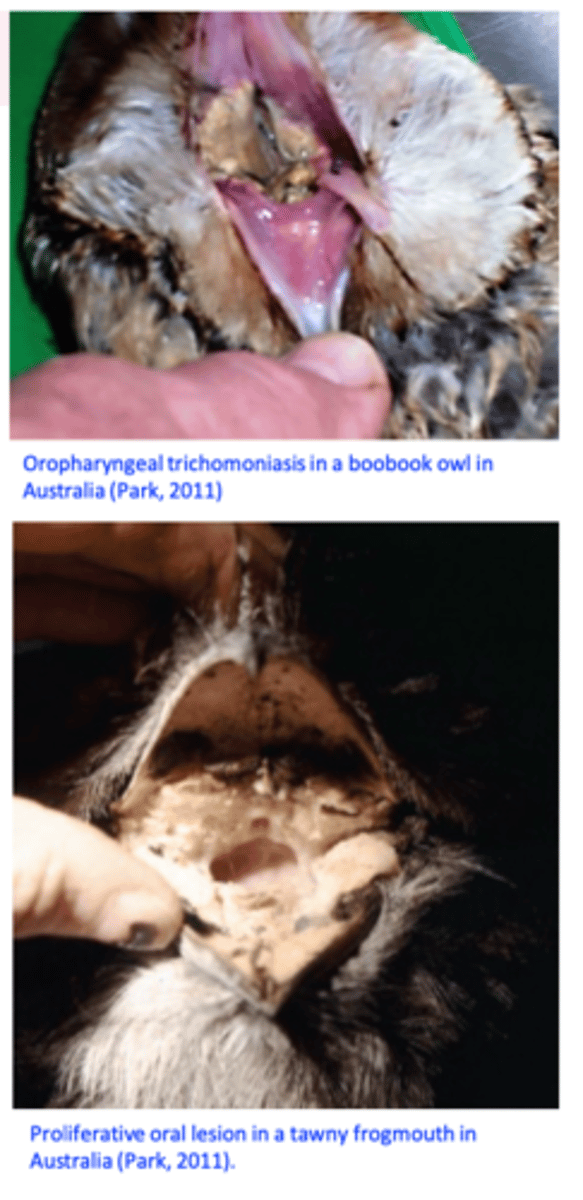
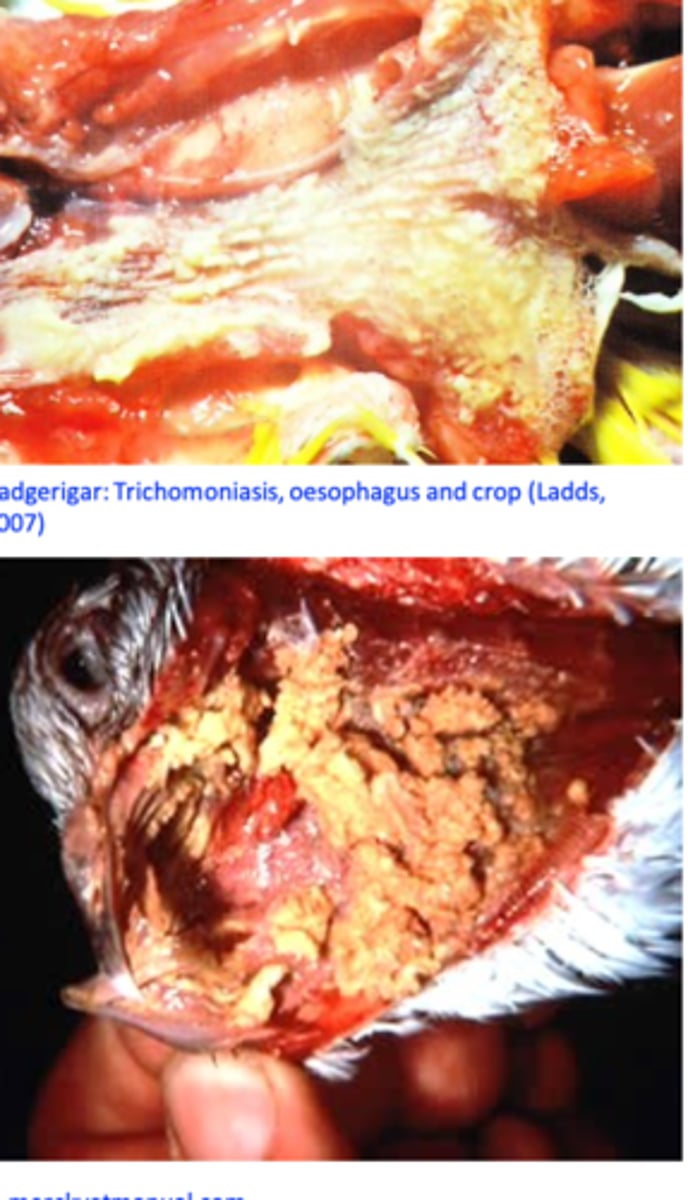
Ulcers covered by yellow membranes => caseous necrosis => build up of the caseous material that may invade the roof of the mouth and the sinuses and block the pharynx/oesophagus;
In the esophagus and crop: yellow caseous nodules that grow ‘yellow buttons’;
In the livers: abscesses, necrosis;
Trichomonas gallinae: Clinical signs
Excess of watery saliva and foul cheese-like smell;
Yellowish caseous lesions around the beak or eyes;
Yellow masses located on the floor/roof of the mouth/pharyngeal region => block the passage of the food/trachea => death from starvation or respiratory failure
Weight loss, ruffled feathers, listlessness
Trichomonas gallinae: Diagnosis
• Clinical signs
• Identification of the trichomonads
- In wet smears
- Cultures = higher sensitivity
Differential diagnosis
Vitamin A deficiency;
Infections with Candida spp, Aspergillus spp, poxvirus, Capillaria
spp.
Trichomonas gallinae: Treatment
5-Nitroimidazoles
Dimetridazole (Emtryl)
Metronidazole (Metrin)
Ronidazole
Nitroimidazole products have been prohibited for use in food animals in EU, USA and Australia
Not for use in food animals!!!
Trichomonas gallinae: Prevention
Pigeons
Prophylactic treatments of healthy adults
Treat the parents during incubation of the eggs
• Poultry
Prevent the flocks of doves/pigeons coming to feed
from feedlots of livestock;
Keep feeders and drinkers clean;
Food & water should be changed regularly;