1.3 Carbon & the Chemistry of Life
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Carbon
4 valence electrons
tetravalence - 4 covalent bonds
carbon can make many complex things
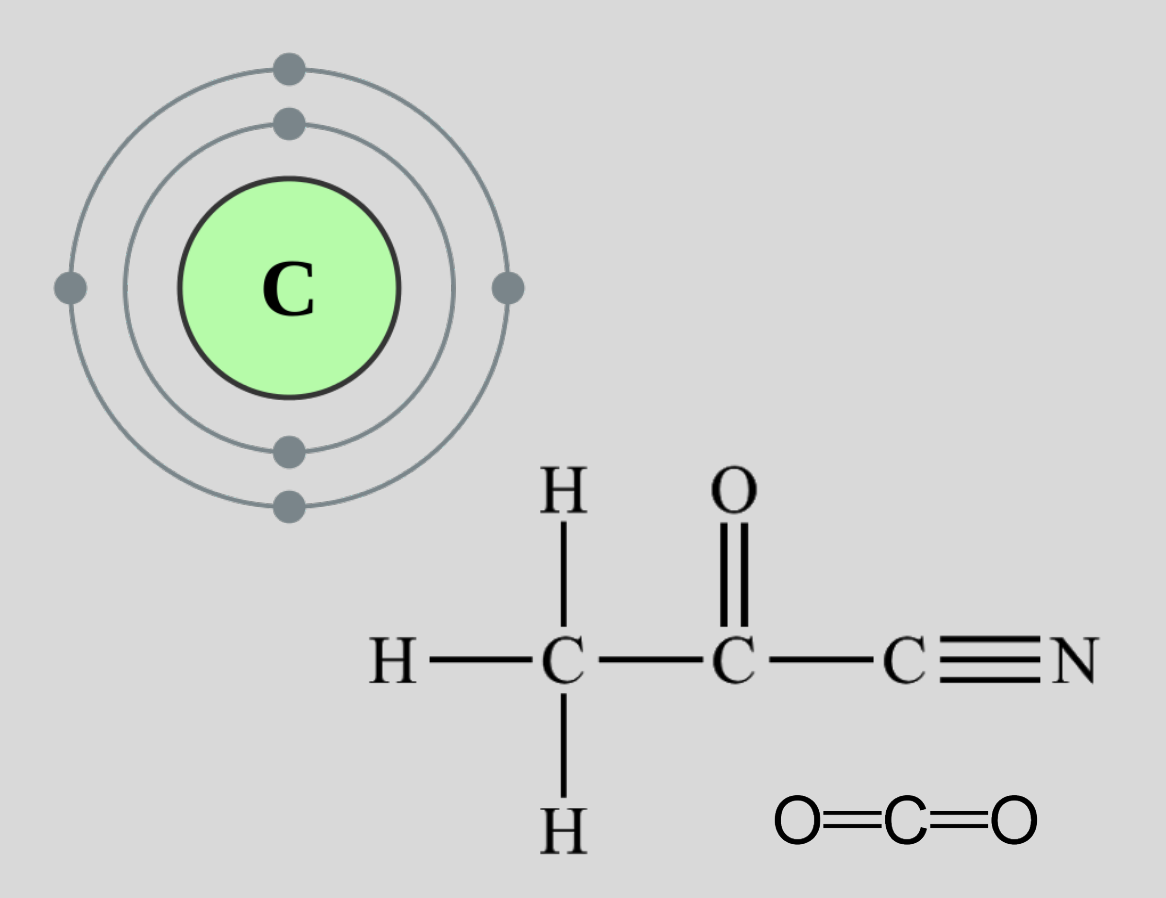
Carbon Stability
NOT electronegative → can make non-polar mlc.(have balanced charge throughout molecule)
Hydrocarbons - compounds made entirely of carbon & hydrogen
hydrophobic
carbon-carbon bonds are very strong
Chemistry of life (what chemicals make up life)
CHONP(S)
Functional Groups
Hydroxyl
Sulfhydryl
Methyl
Carbonyl
Carboxyl
Amino
Phosphate
Hydroxyl
polar
hydrophilic (bc oxygen’s electronegativity)
req.
has OH
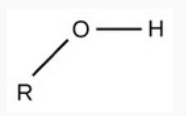
Sulfhydryl
polar
hydrophilic (Sulfur is electronegative)
req.
has S & H
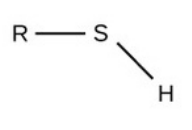
Methyl [group]
non-polar
hydrophobic (no electroneg. elements)
req.
has H & C
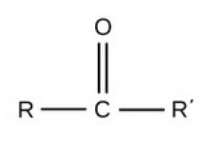
Carbonyl
polar
hydrophilic (bc oxygen electroneg.)
req.
central C & O
bound to 2 organic side grps
double bond to O increases polarity
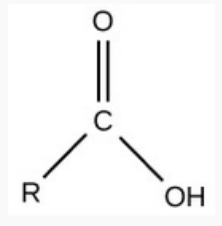
Carboxyl
like a carbonyl + hydroxyl = carboxyl
charged, ionized to release H+ → acidic
req.
O & OH bound to same central C
note
hydrogen may be missing (released) and OH → O-
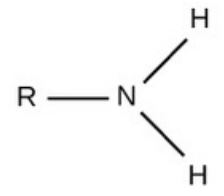
Amino
charged, accepts H+ to form NH3+
basic
req.
anything with an N w/ only single bonds
note
an amino may have an N+ (single) bonded to 3 R groups and 1 H
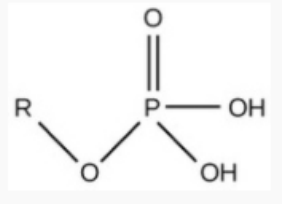
Phosphate
acidic; releases H+ and is charged
req.
has a P
note
H may be missing (released) so OH → O-
BPQ
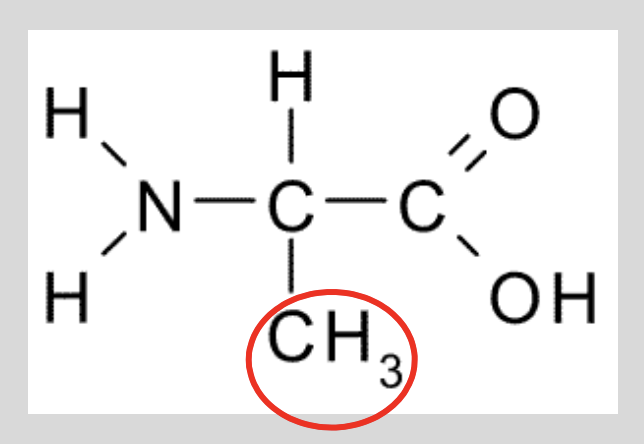
The properties of an amino acid is determined by its R group. The R group for the amino acid alanine is a methyl group. Where are you likely to find this amino acid?
Methyl is non-polar, so alanine will be found somewhere without water b/c it’s hydrophobic!
Macromolecules
large mlc. composed mostly of covalently bonded atoms
4 Types
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Polymers
a mlc. consisting of repeating subunits (monomers)
Hydrolysis
process of breaking polymers into monomers by adding water
hydro = water
lysis = break down
Dehydration Synthesis (Condensation)
process of removing water (dehydration) from monomers to create a polymer
dehydration = remove water
synthesis = creation
Carbohydrates
Monomer: monosaccharides
Polymer: polysaccharides
Bond Name: glycosidic bond
Elements: CHO
Proteins
Monomer: Amino Acids
Polymer: polypeptide
Bond Name: peptide bond
Elements: CHON(S)
Nucleic Acid
Monomer: nucleotide
Polymer: DNA, RNA
Bond Name: phosphodiester bond
Elements: CHONP
Lipids
Monomer: n/a
Polymer: n/a
Bond Name: n/a
Elements: CHO(P)
lipids don’t really make big polymers