Total Body Irradiation
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Diseases where BMT used
Leukemia, aplastic Anemia, Fanconi’s Anemia, Epidermolysis bulosa, osetpetrosis, leukencephalopathy, Hurlers syndrome, sickle cell anemia
Allogeneic
from donor
healthy donor marrow regenerates in place of eradicated marrow
donor lymphocytes show a anti-tumor effect
Autologous
from patient
infused marrow from patient
may have residual malignant cells
can try to purge
no lymphocyte anti-tumor effect
Steps
Eradicate native bone marrow
immunosuppression to avoid rejection
minimal toxicity to healthy tissues
*conditioning determined by disease, type of donor, etc.
Common dose scheules
200 cGy 1 fraction
1320 cGy 8 fractions
300 cGy in 1 fraction
400 cGy in 2 fractions
Common complications
intersitial pneumonitis
dose rate dependent
up to 20% of patient develop
infection
infertility
endocrine anomalies
nausea
muted growth
Dosimetric goal
within 10% of prescribed dose to whole body
Most common techniques
Bilateral reclining and Anterior-Posterior standing
may use lung compensations
both use a beam spoiler
beam spoiler
to increase dose at superficial depth
Bilateral reclining
patient is semi-recombent, at extended distance
TBI copensators for head/neck, legs, and lungs
Anterior- Posterior standing
patient on TBI stand at extended distance
most important factor in devliery
beam energy
higher energy = more uniform dose
distance dependence
greater distance = more uniform dose
Simulation
NOT CT based
Calipers and meterstick measurements used
need position of hte stsrt of the leg compensator
also need a chest x-ray or chest CT -to determine if a lung compensator is needed
Reclining TBI Measurements
thickness: head, neck, shoulder, mid mediastinum, umbilicus, pelvis, knees and ankle
length: shoulder-to-top of had, iliac crest-to-knee, ilic crest-to-heel, and foot
Calculations needed
monitor units
dose rate
compensator thickness
head/neck and legs based on caliper measurements
lun compensator based on chest x-ray or chest CT
compensator length
Monitor Unit Calculation
TMR calculation with extended distance
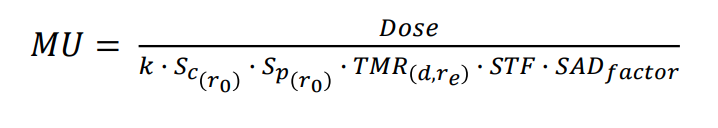
SAD factor
corrects fro inverse square effect
must be verified during commissioning
room geometry may cause it to be invalid
floors, walls, etc. can cause extra scatter
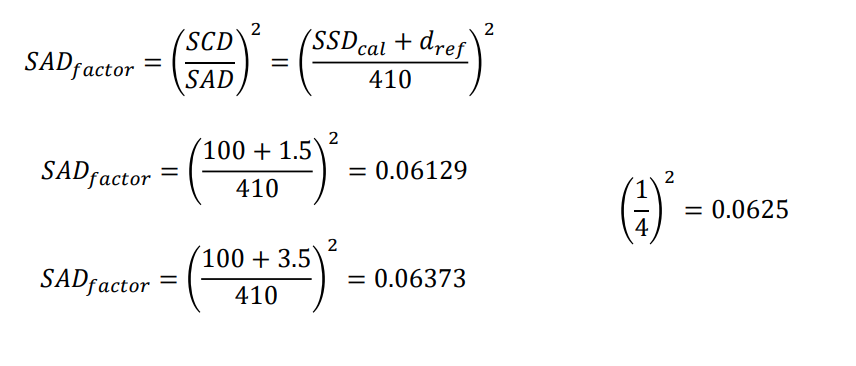
STF
spoiler-tray factor
Sc
Collimator scatter factor
use 40×40 cm factor
Sp
Phantom Scatter factor
assume 30×30 cm for whole body
k
calibration factor = 1 cGy/MU
Tissue Deficit (TD)
how mush tissue to missing for given
TD = Lref - L
Lref = thickness at prescription point
L = thickness at given site
TD for lung
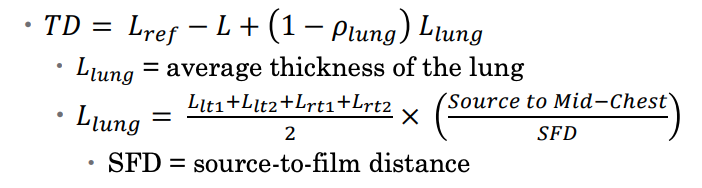
Aluminum compensator thickness
density of Al is 2.7 g/cm3
higher density limits physical dimensions
Compensator thickenss formula
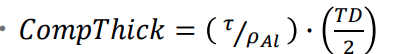
Thickness ratio
t = 0.7
accounts for loss of beam intesnity due to out of field scatter from TBI compensators
large magnification factor
compensators on tray near source (72 cm)
patient at extended distance (410 cm)
M = 0.182
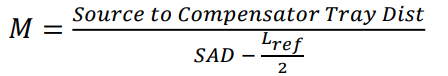
Energy
bilateral: high energy usually used
AP: low energy (6 MV)
Comepensators
Bilateral: head/ neck, legs, cometimes lungs
AP: always lungs
AP vs. Bilateral
AP
comps close to patient
measure lung on sagittal
Bilateral
comps far from patient
measure lng on coronal
Beam blocking
sometime block sensitive organs
like lungs, kidneys, ovaries, testes, thymus
lung blocking requires electron boost beams to chest wall under block
ovary blocking
5 HVL block in front of one
surgeon moves ovary and marks location
Thymus blocking
blocked with 5 HVL for Fanconi’s anemia
accelerate immune system recovery
contour on contrast enhanced CT
generate a block with 1 cm expension
Pediatric Patients
standing not possible for sedated
bilateral still possible
move monitor and pumps out of beam
AP - performed laying on floor
Verification
in-vivo measurements to verify dose
Commissioning TBI
verify TMR ratios at TBI distance in solid water
inverse square at TBI distance
STF at TBI distance
Verify in a RANDO phantom
Total Marrow irradiation
improved therapeutic ratio - higher bone marrow dose, lower normal tissue
patient position more complex
over 1 hour per treatment
high expense of resources
field matching in 1 or more locations
TBI with VMAT
takes longer to plan since have more beam matching
but will limit lung dose to < 8 to 10 GY to reduce idiopathic pneumonitis syndrome (IPS)
dose rate
-dependence on dose rate with toxicity
proven for kidneys, working on thyroid